LEVOLEUCOVORIN- levoleucovorin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
Actavis Pharma, Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LEVOLEUCOVORIN FOR INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LEVOLEUCOVORIN FOR INJECTION.
LEVOLEUCOVORIN for injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 1952 INDICATIONS AND USAGELevoleucovorin for injection is a folate analog indicated for:
Limitation of Use Levoleucovorin for injection is not indicated for the treatment of pernicious anemia or megaloblastic anemia secondary to lack of vitamin B12, because of the risk of progression of neurologic manifestations despite hematologic remission. (1.1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Rescue After High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy
Methotrexate Overdosage or Impaired Methotrexate Elimination DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSFor Injection: 175 mg, lyophilized powder in single-dose vial for reconstitution. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSPatients who have had severe hypersensitivity reactions to leucovorin products, folic acid, or folinic acid. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSHypercalcemia: Limit rate of infusion due to calcium content. (2.1, 2.4, 5.1) Increased gastrointestinal toxicities with fluorouracil (5.2, 7) Drug interaction with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole: Increased rates of treatment failure with concomitant use of d,l-leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in patients with HIV. (5.3) ADVERSE REACTIONSThe most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in patients receiving high-dose methotrexate therapy with levoleucovorin rescue were stomatitis and vomiting. (6.1)
Revised: 3/2017 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Levoleucovorin for injection is indicated for:
- rescue after high-dose methotrexate therapy in patients with osteosarcoma [see Clinical Studies (14)].
- diminishing the toxicity associated with overdosage of folic acid antagonists or impaired methotrexate elimination.
Limitation of Use
Levoleucovorin for injection is not indicated for the treatment of pernicious anemia or megaloblastic anemia secondary to lack of vitamin B12,because of the risk of progression of neurologic manifestations despite hematologic remission.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Use Information
- Levoleucovorin for injection is indicated for intravenous administration only. Do not administer intrathecally.
- Administer intravenously at a rate less than 16 mL (160 mg of levoleucovorin) per minute [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Recommended Dosing for Rescue After High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy
The recommendations for Levoleucovorin for injection rescue are based on a methotrexate dose of 12 grams/m2 administered by intravenous infusion over 4 hours (refer to methotrexate prescribing information that includes high-dose methotrexate regimens) in adult and pediatric patients. Twenty-four hours after starting the methotrexate infusion, initiate Levoleucovorin for injection rescue at a dose of 7.5 mg (approximately 5 mg/m2) every 6 hours.
Monitor serum creatinine and methotrexate levels at least once daily. Continue Levoleucovorin for injection administration, hydration, and urinary alkalinization (pH 7.0 or greater) until the methotrexate level is below 5 x 10-8 M (0.05 micromolar). Adjust dosage or extend duration based on the guidelines in Table 1.
| Clinical Situation | Laboratory Findings | Recommendation |
| Normal methotrexate elimination | Serum methotrexate level approximately 10 micromolar at 24 hours after administration, 1 micromolar at 48 hours, and less than 0.2 micromolar at 72 hours. | Administer 7.5 mg by intravenous infusion every 6 hours for 60 hours (10 doses starting 24 hours after start of methotrexate infusion). |
| Delayed late methotrexate elimination | Serum methotrexate level remaining above 0.2 micromolar at 72 hours, and more than 0.05 micromolar at 96 hours after administration. | Continue 7.5 mg by intravenous infusion every 6 hours, until methotrexate level is less than 0.05 micromolar. |
| Delayed early methotrexate elimination and/or evidence of acute renal injury* |
| Administer 75 mg by intravenous infusion every 3 hours until methotrexate level is less than 1 micromolar; then 7.5 mg by intravenous infusion every 3 hours until methotrexate level is less than 0.05 micromolar. |
| * These patients are likely to develop reversible renal failure. In addition to appropriate levoleucovorin for injection therapy, continue hydration and urinary alkalinization, and monitoring of fluid and electrolyte status, until the serum methotrexate level has fallen to below 0.05 micromolar and the renal failure has resolved. | ||
Impaired Methotrexate Elimination or Renal Impairment
Decreased methotrexate elimination or renal impairment which are clinically important but less severe than abnormalities described in Table 1 can occur following methotrexate administration. If toxicity is observed, extend Levoleucovorin for injection rescue for an additional 24 hours (total of 14 doses over 84 hours) in subsequent courses.
Third-Space Fluid Collection and Other Causes of Delayed Methotrexate Elimination
Accumulation in a third-space fluid collection (i.e., ascites, pleural effusion), renal insufficiency, or inadequate hydration can cause delayed methotrexate elimination. Under such circumstances, higher doses of Levoleucovorin for injection or prolonged administration may be indicated.
2.3 Recommended Dosing for Treatment of Methotrexate Overdosage or Impaired Methotrexate Elimination
Start Levoleucovorin for injection rescue in adult and pediatric patients as soon as possible after an overdosage of methotrexate or within 24 hours of methotrexate administration when there is impaired methotrexate elimination. As the time interval between methotrexate administration and Levoleucovorin for injection rescue increases, effectiveness of Levoleucovorin for injection in diminishing toxicity may decrease. Administer Levoleucovorin for injection 7.5 mg (approximately 5 mg/m2) intravenously every 6 hours until the serum methotrexate level is less than 10-8 M (0.05 micromolar).
Monitor serum creatinine and methotrexate levels at least every 24 hours. If 24-hour serum creatinine has increased 50% over baseline or if the 24-hour methotrexate level is greater than 5 x 10-6 M or 48-hour level is greater than 9 x 10-7 M, increase the dose of Levoleucovorin for injection to 50 mg/m2 intravenously every 3 hours until the methotrexate level is less than 10-8 M. Continue concomitant hydration (3 L per day) and urinary alkalinization with sodium bicarbonate. Adjust the bicarbonate dose to maintain urine pH at 7.0 or greater.
2.4 Preparation and Administration
Preparation
- Reconstitute vial contents with 17.7 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, to obtain a clear, colorless to yellowish solution (resultant concentration 10 mg/mL levoleucovorin). Reconstitution with a sodium chloride solution with preservatives (e.g. benzyl alcohol) has not been studied.
- Discard vial if particulate matter or discoloration is observed.
- Dilute reconstituted solution immediately, to concentrations of 0.5 mg/mL to 5 mg/mL in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP.
Storage
- If necessary, store reconstituted solution for not more than 24 hours at room temperature.
- Do not store reconstituted solution diluted with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, for more than 24 hours at room temperature.
- Do not store reconstituted solution diluted with 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, for more than 4 hours at room temperature.
Administration
- Inspect reconstituted solution in the vial for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.
- Do not co-administer with other agents in the same admixture, due to risk of precipitation.
- Administer intravenously at a rate less than 16 mL (160 mg of levoleucovorin) per minute [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For injection: 175 mg sterile, off-white to yellowish lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Levoleucovorin is contraindicated in patients who have had severe hypersensitivity to leucovorin products, folic acid, or folinic acid [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypercalcemia
Due to the calcium content of the levoleucovorin solution, inject no more than 16 mL (160 mg of levoleucovorin) intravenously per minute [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 and 2.4)].
5.2 Increased Gastrointestinal Toxicities with Fluorouracil
Leucovorin products increase the toxicities of fluorouracil [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Gastrointestinal toxicities, (particularly stomatitis and diarrhea) occur more commonly, and may be of greater severity and prolonged duration. Deaths from severe enterocolitis, diarrhea, and dehydration have been reported in elderly patients receiving weekly d,l-leucovorin and fluorouracil.
5.3 Drug-Interaction with Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole
Concomitant use of d,l-leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the acute treatment of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in patients with HIV infection was associated with increased rates of treatment failure and morbidity in a placebo-controlled study.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypercalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Increased gastrointestinal toxicities with fluorouracil [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Drug-interaction with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Table 2 presents the frequency of adverse reactions which occurred during the administration of 58 courses of high-dose methotrexate 12 grams/m2 followed by levoleucovorin rescue, for osteosarcoma, in 16 patients, ages 6-21 years. Most patients received levoleucovorin 7.5 mg every 6 hours for 60 hours or longer, beginning 24 hours after completion of methotrexate administration.
| Body System/Adverse Reaction | Number (%) of Patients | |
| (N = 16) | ||
| All Grades | ≥ Grade 3 | |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Stomatitis | 6 (37.5) | 1 (6.3) |
| Vomiting | 6 (37.5) | 0 |
| Nausea | 3 (18.8) | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 1 (6.3) | 0 |
| Dyspepsia | 1 (6.3) | 0 |
| Typhlitis | 1 (6.3) | 1 (6.3) |
| Respiratory | ||
| Dyspnea | 1 (6.3) | 0 |
| Skin and Appendages | ||
| Dermatitis | 1 (6.3) | 0 |
| Other | ||
| Confusion | 1 (6.3) | 0 |
| Neuropathy | 1 (6.3) | 0 |
| Renal function abnormal | 1 (6.3) | 0 |
| Taste perversion | 1 (6.3) | 0 |
| Total number of patients |
9 (56.3) |
|
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions were identified during postapproval use of levoleucovorin, administered in combination with a methotrexate or other regimen. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate reliably their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The following have been reported:
-
Respiratory: dyspnea
-
Dermatologic: pruritus, rash
- Other Clinical Events: temperature change, rigors, allergic reactions
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effect of leucovorin products on fluorouracil: Leucovorin products increase the toxicity of fluorouracil [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are limited data with levoleucovorin use in pregnant women. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with levoleucovorin.
Levoleucovorin is administered in combination with methotrexate, which can cause embryo-fetal harm. Refer to methotrexate prescribing information for additional information.
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of levoleucovorin in human milk or its effects on the breastfed infant or on milk production.
Levoleucovorin is administered in combination with methotrexate. Refer to methotrexate prescribing information for additional information.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of levoleucovorin have been established in pediatric patients. Use of levoleucovorin in pediatric patients is supported by open-label clinical trial data in 16 pediatric patients, 6 years of age and older and with additional supporting evidence from literature [see Clinical Studies (14)].
11 DESCRIPTION
The active pharmaceutical ingredient in Levoleucovorin for injection is the calcium salt in a pentahydrate form of levoleucovorin. Levoleucovorin is a folate analog and the pharmacologically active levo-isomer of d,l-leucovorin. The chemical name of the salt is calcium (6S)-N-{4-[[(2-amino-5-formyl-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-4-oxo-6-pteridinyl)methyl] amino]benzoyl}-L-glutamate pentahydrate. The molecular formula is C20H21CaN7O7 • 5 H2O with molecular weight 601.6 amu. The molecular structure is:
![The molecular structure for Levoleucovorin for injection is the calcium salt in a pentahydrate form of levoleucovorin. Levoleucovorin is a folate analog and the pharmacologically active levo-isomer of d,l-leucovorin. The chemical name of the salt is calcium (6S)-N-{4-[[(2-amino-5-formyl-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-4-oxo-6-pteridinyl)methyl] amino]benzoyl}-L-glutamate pentahydrate. The molecular formula is C20H21CaN7O7 • 5 H2O with molecular weight 601.6 amu.](/dailymed/image.cfm?name=image-1.jpg&archiveid=392678)
Levoleucovorin for injection is a sterile lyophilized powder consisting of 175 mg levoleucovorin (equivalent to 222 mg levoleucovorin calcium pentahydrate) and 175 mg mannitol per vial. Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid are used to adjust pH during manufacturing. It is an intravenous infusion, after reconstitution with 17.7 mL of sterile 0.9% sodium chloride injection, USP [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Levoleucovorin is the pharmacologically active isomer of 5-formyl tetrahydrofolic acid (THF). Levoleucovorin does not require reduction by dihydrofolate reductase to participate in reactions utilizing folates as a source of “one-carbon” moieties. Administration of levoleucovorin counteracts the therapeutic and toxic effects of folic acid antagonists such as methotrexate, which act by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In a crossover-design pharmacokinetic comparability study, healthy subjects received a single 2-hour infusion of either levoleucovorin (200 mg/m2) or racemic d,l-leucovorin (400 mg/m2). The 90% confidence intervals for the geometric mean ratios for both AUC0-inf and Cmax were within the standard limit of 80-125% for both l-leucovorin and l-5-methyl-THF. The exposure to l-leucovorin and 5-methyl-THF was comparable whether it was administered as levoleucovorin or as d,l-leucovorin as shown in Table 3:
| Parameter | l-leucovorin | d,l-leucovorin | 5-methyl-THF-l-
leucovorin | 5-methyl-THF- d,l-leucovorin |
| AUC0-inf (ng.h/mL) | 30719 | 31296 | 52105 | 50137 |
| Cmax (ng.h/mL) | 10895 | 11301 | 4930 | 4658 |
Distribution
The pharmacokinetics of levoleucovorin after intravenous administration of a 15 mg dose was studied in healthy male volunteers. After rapid intravenous administration, serum total tetrahydrofolate (total-THF) concentrations reached a mean peak of 1722 ng/mL. Serum (6S)-5-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate concentrations reached a mean peak of 275 ng/mL and the mean time to peak was 0.9 hours.
Elimination
The mean terminal half-life for total-THF and (6S)-5-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate was 5.1 and 6.8 hours, respectively.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Rescue after High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy in Patients with Osteosarcoma
The safety and efficacy of levoleucovorin rescue following high-dose methotrexate were evaluated in 16 patients, ages 6-21 years, who received 58 courses of chemotherapy for osteogenic sarcoma. High-dose methotrexate was one component of several different combination chemotherapy regimens evaluated across several trials. Methotrexate 12 g/m2 IV over 4 hours was administered to 13 patients, who received levoleucovorin 7.5 mg every 6 hours for 60 hours or longer beginning 24 hours after completion of methotrexate. Three patients received methotrexate 12.5 g/m2 IV over 6 hours, followed by levoleucovorin 7.5 mg every 3 hours for 18 doses beginning 12 hours after completion of methotrexate. The mean number of levoleucovorin doses per course was 18.2 and the mean total dose per course was 350 mg. The efficacy of levoleucovorin rescue following high-dose methotrexate was based on adverse reaction profile [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
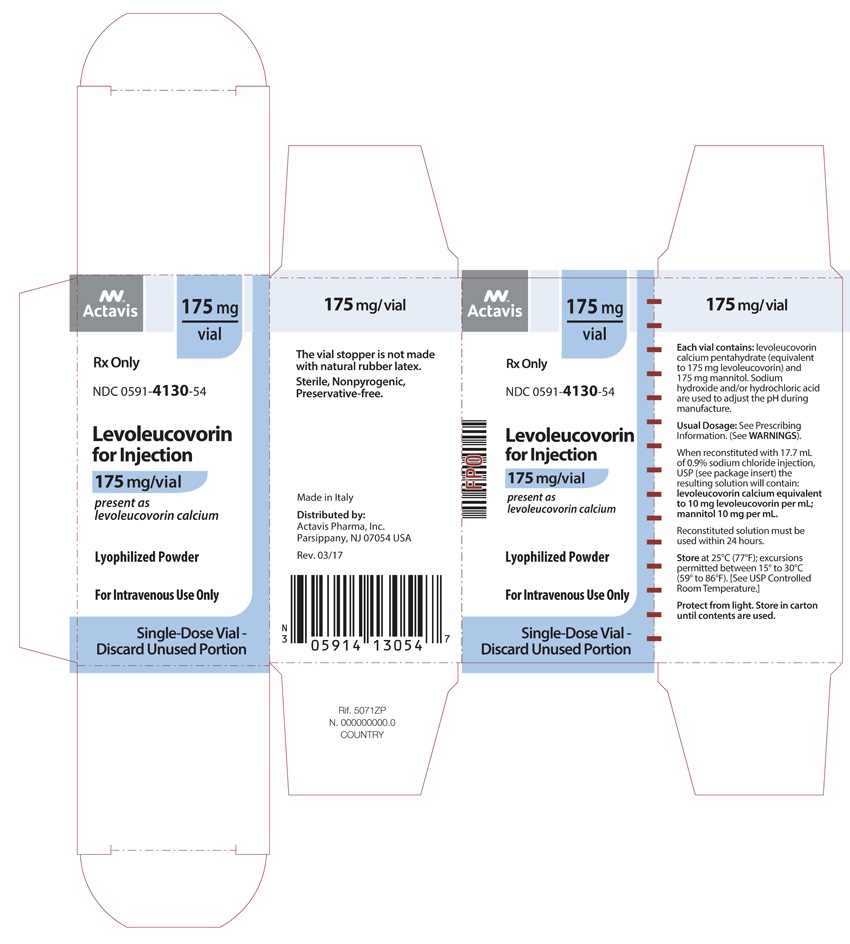
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Single-dose vial containing 175 mg of levoleucovorin formulated as a sterile, preservative-free, off-white to yellowish lyophilized powder. The vial stopper is not made with natural rubber latex.
NDC 0591-4130-54
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted from 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light.
Made in Italy
Distributed by:
Actavis Pharma, Inc.
Parsippany, NJ 07054 USA
Revised – March 2017
| LEVOLEUCOVORIN
levoleucovorin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Actavis Pharma, Inc. (119723554) |