BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies. These studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressant use in patients over age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressant use in patients aged 65 and older [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
In patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy monitor closely for clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. Advise families and caregivers of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
- 1.1 Major Depressive Disorder
Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, USP are indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Efficacy was established in three short-term (4, 8, and 12 weeks) and two long-term, maintenance trials.
1.3 Social Anxiety DisorderVenlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, USP are indicated for the treatment of Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia. Efficacy was established in four 12-week and one 26-week, placebo-controlled trials.
1.4 Panic DisorderVenlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, USP are indicated for the treatment of Panic Disorder (PD), with or without agoraphobia. Efficacy was established in two 12-week placebo-controlled trials.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules should be administered in a single dose with food, either in the morning or in the evening at approximately the same time each day [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Each capsule should be swallowed whole with fluid and not divided, crushed, chewed, or placed in water or it may be administered by carefully opening the capsule and sprinkling the entire contents on a spoonful of applesauce. This drug/food mixture should be swallowed immediately without chewing and followed with a glass of water to ensure complete swallowing of the pellets (spheroids).
2.1 Major Depressive Disorder
For most patients, the recommended starting dose for venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules are 75 mg per day, administered in a single dose. For some patients, it may be desirable to start at 37.5 mg per day for 4 to 7 days to allow new patients to adjust to the medication before increasing to 75 mg per day. Patients not responding to the initial 75 mg per day dose may benefit from dose increases to a maximum of 225 mg per day. Dose increases should be in increments of up to 75 mg per day, as needed, and should be made at intervals of not less than 4 days, since steady-state plasma levels of venlafaxine and its major metabolites are achieved in most patients by day 4 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In the clinical studies establishing efficacy, upward titration was permitted at intervals of 2 weeks or more.
It should be noted that, while the maximum recommended dose for moderately depressed outpatients is also 225 mg per day for venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets, more severely depressed inpatients in one study of the development program for that product responded to a mean dose of 350 mg per day (range of 150 to 375 mg per day). Whether or not higher doses of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules are needed for more severely depressed patients is unknown; however, the experience with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules doses higher than 225 mg per day is very limited.
2.3 Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia)
The recommended dose is 75 mg per day, administered in a single dose. There was no evidence that higher doses confer any additional benefit.
2.4 Panic Disorder
The recommended starting dose is 37.5 mg per day of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules for 7 days. Patients not responding to 75 mg per day may benefit from dose increases to a maximum of approximately 225 mg per day. Dose increases should be in increments of up to 75 mg per day, as needed, and should be made at intervals of not less than 7 days.
2.5 Switching Patients from Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Tablets
Depressed patients who are currently being treated at a therapeutic dose with venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets may be switched to venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules at the nearest equivalent dose (mg per day), e.g., 37.5 mg venlafaxine twice a day to 75 mg venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules once daily. However, individual dosage adjustments may be necessary.
2.6 Specific Populations
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The total daily dose should be reduced by 50% in patients with mild (Child-Pugh=5 to 6) to moderate (Child-Pugh=7 to 9) hepatic impairment. In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh=10 to 15) or hepatic cirrhosis, it may be necessary to reduce the dose by 50% or more [See Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Patients with Renal Impairment
The total daily dose should be reduced by 25% to 50% in patients with mild
(CLcr= 60 to 89 mL/min) or moderate (CLcr= 30 to 59 mL/min) renal impairment. In patients undergoing hemodialysis or with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min), the total daily dose should be reduced by 50% or more. Because there was much individual variability in clearance between patients with renal impairment, individualization of dosage may be desirable in some patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
2.7 Maintenance Treatment
There is no body of evidence available from controlled studies to indicate how long patients with MDD, SAD, or PD should be treated with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules.
It is generally agreed that acute episodes of MDD require several months or longer of sustained pharmacological therapy beyond response to the acute episode. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules/venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets have demonstrated continuation of response in clinical studies up to 52 weeks, at the same dose at which patients responded during the initial treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. It is not known whether or not the dose of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules needed for maintenance treatment is identical to the dose needed to achieve an initial response. Patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the need for maintenance treatment and the appropriate dose for such treatment.
In patients with SAD, venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules have been shown to be effective in 6-month clinical studies. The need for continuing medication in patients with SAD who improve with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treatment should be periodically reassessed.
In a clinical study for PD, patients continuing venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules at the same dose at which they responded during the initial 12 weeks of treatment experienced a statistically significantly longer time to relapse than patients randomized to placebo [see Clinical Studies (14.4)]. The need for continuing medication in patients with PD who improve with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treatment should be periodically reassessed.
2.8 Discontinuing Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules
A gradual reduction in the dose, rather than abrupt cessation, is recommended whenever possible. In clinical studies with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, tapering was achieved by reducing the daily dose by 75 mg at one-week intervals. Individualization of tapering may be necessary [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
2.9 Switching Patients to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) Intended to Treat Psychiatric Disorders
At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI (intended to treat psychiatric disorders) and initiation of therapy with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules. In addition, at least 7 days should be allowed after stopping venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules before starting an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders [see Contraindications (4.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Use of Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules with other MAOIs such as Linezolid or Intravenous Methylene Blue
Do not start venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, because there is an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. In a patient who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition, other interventions, including hospitalization should be considered [see Contraindications 4.2)].
In some cases, a patient already receiving venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules therapy may require urgent treatment with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. If acceptable alternatives to linezolid or intravenous methylene blue are not available and the potential benefits of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are judged to outweigh the risks of serotonin syndrome in a particular patient, venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules should be stopped promptly, and linezolid or intravenous methylene blue can be administered. Monitor the patient for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for 7 days or until 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, whichever comes first. Therapy with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules can be resumed 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
The risk of administering methylene blue by non-intravenous routes (such as oral tablets or by local injection) or in intravenous doses much lower than 1 mg/kg concomitantly with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules are unclear. The clinician should, nevertheless, be aware of the possibility of emergent symptoms of serotonin syndrome with such use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
-
Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules, USP are available in the following strengths:
- Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules USP, 37.5 mg are white to off-white free flowing pellets filled in size '3' hard gelatin capsules with grey colored cap printed with "ZA-35" in black ink & white body printed with "37.5 mg" in black ink.
- Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules USP, 75 mg are white to off-white free flowing pellets filled in size '1' hard gelatin capsules with peach colored cap printed with "ZA-36" in black ink & white body printed with "75 mg" in black ink.
- Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules USP, 150 mg are white to off-white free flowing pellets filled in size '0' hard gelatin capsules with dark orange colored cap printed with "ZA-37" in black ink & white body printed with "150 mg" in black ink.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4.1 Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity to venlafaxine hydrochloride, desvenlafaxine succinate or to any excipients in the formulation
4.2 Concomitant Use with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
The use of MAOIs (intended to treat psychiatric disorders) concomitantly with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules or within 7 days of discontinuing treatment with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules are contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. The use of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules within 14 days of discontinuing treatment with an MAOI (intended to treat psychiatric disorders) is also contraindicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.9), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Starting venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules in a patient who is being treated with an MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated, because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome [see Dosage and Administration (2.9), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and Drug Interactions (7.3)].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
- 5.1 Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults
Patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), both adult and pediatric, may experience worsening of their depression and/or the emergence of suicidal ideation and behavior (suicidality) or unusual changes in behavior, whether or not they are taking antidepressant medications, and this risk may persist until significant remission occurs. Suicide is a known risk of depression and certain other psychiatric disorders, and these disorders themselves are the strongest predictors of suicide. There has been a long-standing concern, however, that antidepressants may have a role in inducing worsening of depression and the emergence of suicidality in certain patients during the early phases of treatment. Pooled analyses of short-term placebo-controlled studies of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and others) showed that these drugs increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults (ages 18 to 24) with MDD and other psychiatric disorders. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older.
The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled studies in children and adolescents with MDD, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 24 short-term studies of 9 antidepressant drugs in over 4,400 patients. The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled studies in adults with MDD or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 295 short-term studies (median duration of 2 months) of 11 antidepressant drugs in over 77,000 patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidality among drugs, but a tendency toward an increase in the younger patients for almost all drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidality across the different indications, with the highest incidence in MDD. The risk differences (drug versus placebo), however, were relatively stable within age strata and across indications. These risk differences (drug-placebo difference in the number of cases of suicidality per 1,000 patients treated) are provided in Table 1.
Table 1Difference in the Number of Cases of Suicidality per 1,000 Patients Treated versus Placebo Age Range Increases Compared to Placebo < 18 14 additional cases 18 to 24 5 additional cases Decreases Compared to Placebo 25 to 64 1 fewer case ≥ 65 6 fewer cases No suicides occurred in any of the pediatric studies. There were suicides in the adult studies, but the number was not sufficient to reach any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
It is unknown whether the suicidality risk extends to longer term use, i.e., beyond several months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance studies in adults with depression that the use of antidepressants can delay the recurrence of depression.
All patients being treated with antidepressants for any indication should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, and unusual changes in behavior, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases.
The following symptoms, anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, and mania, have been reported in adult and pediatric patients being treated with antidepressants for MDD, as well as for other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric. Although a causal link between the emergence of such symptoms and either the worsening of depression and/or the emergence of suicidal impulses has not been established, there is concern that such symptoms may represent precursors to emerging suicidality.
Consideration should be given to changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing the medication, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidality or symptoms that might be precursors to worsening depression or suicidality, especially if these symptoms are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms.
If the decision has been made to discontinue treatment, medication should be tapered, as rapidly as is feasible, but with recognition that abrupt discontinuation can be associated with certain symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7) and Dosage and Administration ( 2.8)].
Families and caregivers of patients being treated with antidepressants for MDD or other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric, should be alerted about the need to monitor patients for the emergence of agitation, irritability, unusual changes in behavior, and the other symptoms described above, as well as the emergence of suicidality, and to report such symptoms immediately to healthcare providers. Such monitoring should include daily observation by families and caregivers. Prescriptions for venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules should be written for the smallest quantity of capsules consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder
A major depressive episode may be the initial presentation of bipolar disorder. It is generally believed (though not established in controlled studies) that treating such an episode with an antidepressant alone may increase the likelihood of precipitation of a mixed/manic episode in patients at risk for bipolar disorder. Whether any of the symptoms described above represent such a conversion is unknown. However, prior to initiating treatment with an antidepressant, patients with depressive symptoms should be adequately screened to determine if they are at risk for bipolar disorder; such screening should include a detailed psychiatric history, including a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression. It should be noted that venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules are not approved for use in treating bipolar depression.
5.2 Serotonin SyndromeThe development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with SNRIs and SSRIs, including venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules alone, but particularly with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, and St. John's wort) and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin in particular, MAOIs, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and others, such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue). Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, coma) autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, flushing, and dizziness), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination); seizures and gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for the emergence of serotonin syndrome.
The concomitant use of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules with MAOIs (intended to treat psychiatric disorders) is contraindicated. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules should also not be started in a patient who is being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. All reports with methylene blue that provided information on the route of administration involved intravenous administration in the dose range of 1 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg. No reports involved the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection) or at lower doses. There may be circumstances when it is necessary to initiate treatment with a MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules should be discontinued before initiating treatment with the MAOI [see Contraindications ( 4.2), Dosage and Administration ( 2.6), and Drug Interactions ( 7.3)].
If concomitant use of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules with other serotonergic drugs (e.g., triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, mirtazapine, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, buspirone, tryptophan, or St. John's wort) is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases [see Drug Interactions ( 7.3)]. Patients should be made aware of the potential risk of serotonin syndrome. Treatment with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules and any concomitant serotonergic agents should be discontinued immediately if the above events occur, and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
5.3 Elevations in Blood PressureIn controlled trials, there were dose-related increases in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, as well as cases of sustained hypertension [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.2)].
Monitor blood pressure before initiating treatment with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules and regularly during treatment. Control preexisting hypertension before initiating treatment with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules. Use caution in treating patients with preexisting hypertension or cardiovascular or cerebrovascular conditions that might be compromised by increases in blood pressure. Sustained blood pressure elevation can lead to adverse outcomes. Cases of elevated blood pressure requiring immediate treatment have been reported with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules. Consider dose reduction or discontinuation of treatment for patients who experience a sustained increase in blood pressure.
Across all clinical studies with venlafaxine hydrochloride, 1.4% of patients in the venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treated groups experienced a ≥15 mm Hg increase in supine diastolic blood pressure (SDBP) ≥ 105 mm Hg, compared to 0.9% of patients in the placebo groups. Similarly, 1% of patients in the venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treated groups experienced a ≥ 20 mm Hg increase in supine systolic blood pressure (SSBP) with blood pressure ≥ 180 mm Hg, compared to 0.3% of patients in the placebo groups [see Table 10 in Adverse Reactions ( 6.2)]. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treatment was associated with sustained hypertension (defined as treatment-emergent SDBP ≥ 90 mm Hg and ≥ 10 mm Hg above baseline for three consecutive on-therapy visits [see Table 11 in Adverse Reactions ( 6.2)]. An insufficient number of patients received mean doses of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules over 300 mg per day in clinical studies to fully evaluate the incidence of sustained increases in blood pressure at these higher doses.
5.4 Abnormal BleedingSSRIs and SNRIs, including venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, may increase the risk of bleeding events, ranging from ecchymoses, hematomas, epistaxis, petechiae, and gastrointestinal hemorrhage to life-threatening hemorrhage. Concomitant use of aspirin, Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), warfarin, and other anti-coagulants or other drugs known to affect platelet function may add to this risk. Case reports and epidemiological studies (case-control and cohort design) have demonstrated an association between use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding. Caution patients about the risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation.
5.5 Angle-Closure GlaucomaThe pupillary dilation that occurs following use of many antidepressant drugs including venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules may trigger an angle closure attack in a patient with anatomically narrow angles who does not have a patent iridectomy.
5.6 Activation of Mania/HypomaniaMania or hypomania was reported in venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treated patients in the premarketing studies in MDD, SAD, and PD (see Table 2). Mania/hypomania has also been reported in a small proportion of patients with mood disorders who were treated with other marketed drugs to treat MDD. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules should be used cautiously in patients with a history of mania or hypomania.
5.7 Discontinuation SyndromeTable 2Incidence (%) of Mania or Hypomania Reported in Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Treated Patients in the Premarketing Studies Indication Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Placebo MDD 0.3 0 SAD 0.2 0 PD 0.1 0 Discontinuation symptoms have been systematically evaluated in patients taking venlafaxine, including retrospective surveys of studies in MDD and SAD. Abrupt discontinuation or dose reduction of venlafaxine at various doses has been found to be associated with the appearance of new symptoms, the frequency of which increased with increased dose level and with longer duration of treatment. Reported symptoms include agitation, anorexia, anxiety, confusion, impaired coordination and balance, diarrhea, dizziness, dry mouth, dysphoric mood, fasciculation, fatigue, flu-like symptoms, headaches, hypomania, insomnia, nausea, nervousness, nightmares, sensory disturbances (including shock-like electrical sensations), somnolence, sweating, tremor, vertigo, and vomiting.
During marketing of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, other SNRIs, and SSRIs, there have been spontaneous reports of adverse events occurring upon discontinuation of these drugs, particularly when abrupt, including the following: dysphoric mood, irritability, agitation, dizziness, sensory disturbances (e.g., paresthesia, such as electric shock sensations), anxiety, confusion, headache, lethargy, emotional lability, insomnia, hypomania, tinnitus, and seizures. While these events are generally self-limiting, there have been reports of serious discontinuation symptoms.
Patients should be monitored for these symptoms when discontinuing treatment with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules. A gradual reduction in the dose, rather than abrupt cessation, is recommended whenever possible. If intolerable symptoms occur following a decrease in the dose or upon discontinuation of treatment, then resuming the previously prescribed dose may be considered. Subsequently, the physician may continue decreasing the dose, but at a more gradual rate [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.8)].
5.8 SeizuresSeizures have occurred with venlafaxine therapy. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, like many antidepressants, should be used cautiously in patients with a history of seizures and should be discontinued in any patient who develops seizures. [Must mitigate the risk: Risk factors, concomitant meds that lower the seizure threshold.]
5.9 HyponatremiaHyponatremia can occur as a result of treatment with SSRIs and SNRIs, including venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules. In many cases, the hyponatremia appears to be the result of the Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH) secretion. Cases with serum sodium lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported. Elderly patients may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia with SSRIs and SNRIs [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5)]. Also, patients taking diuretics, or those who are otherwise volume-depleted, may be at greater risk. Consider discontinuation of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia, and institute appropriate medical intervention.
Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls. Signs and symptoms associated with more severe and/or acute cases have included hallucination, syncope, seizure, coma, respiratory arrest, and death.
5.10 Weight and Height Changes in Pediatric PatientsWeight Changes
The average change in body weight and incidence of weight loss (percentage of patients who lost 3.5% or more) in the placebo-controlled pediatric studies in MDD, and SAD are shown in Tables 3 and 4.
Table 3Average Change in Body Weight (kg) From Beginning of Treatment in Pediatric Patients in Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Studies of Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Indication (Duration) Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Placebo MDD
(4 pooled studies, 8 weeks)-0.45 (n = 333) +0.77 (n = 333) SAD
(16 weeks)-0.75 (n = 137) +0.76 (n = 148) Table 4Incidence (%) of Pediatric Patients Experiencing Weight Loss (3.5% or more) in Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Studies of Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules ap < 0.001 versus placebo
Indication (Duration) Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Placebo MDD
(4 pooled studies, 8 weeks)18a (n = 333)
3.6 (n = 333) SAD
(16 weeks)47a (n = 137)
14 (n = 148) Weight loss was not limited to patients with treatment-emergent anorexia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.11)].
The risks associated with longer term venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules use were assessed in an open-label MDD study of children and adolescents who received venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules for up to six months. The children and adolescents in the study had increases in weight that were less than expected, based on data from age- and sex-matched peers. The difference between observed weight gain and expected weight gain was larger for children (< 12 years old) than for adolescents (≥ 12 years old).
Height Changes
Table 5 shows the average height increase in pediatric patients in the short-term, placebo-controlled MDD, and SAD studies. The differences in height increases in MDD studies were most notable in patients younger than twelve.
Table 5Average Height Increases (cm) in Pediatric Patients in Placebo-controlled Studies of Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules ap = 0.041
Indication (Duration) Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Placebo MDD
(8 weeks)0.8 (n = 146) 0.7 (n = 147) SAD
(16 weeks)1 (n = 109) 1 (n = 112) In the six-month, open-label MDD study, children and adolescents had height increases that were less than expected, based on data from age- and sex-matched peers. The difference between observed and expected growth rates was larger for children (< 12 years old) than for adolescents (≥ 12 years old).
5.11 Appetite Changes in Pediatric PatientsDecreased appetite (reported as treatment-emergent anorexia) was more commonly observed in venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treated patients versus placebo-treated patients in the premarketing evaluation of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules for MDD, and SAD (see Table 6).
5.12 Interstitial Lung Disease and Eosinophilic PneumoniaTable 6Incidence (%) of Decreased Appetite and Associated Discontinuation Ratesa(%) in Pediatric Patients in Placebo-controlled Studies of Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules aThe discontinuation rates for weight loss were 0.7% for patients receiving either venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules or placebo.
Indication
(Duration)Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules
IncidenceDiscontinuation Placebo
IncidenceDiscontinuation MDD
(pooled, 8 weeks)
10
0
3
–SAD
(16 weeks)
22
0.7
3
0Interstitial lung disease and eosinophilic pneumonia associated with venlafaxine therapy have been rarely reported. The possibility of these adverse events should be considered in venlafaxine-treated patients who present with progressive dyspnea, cough or chest discomfort. Such patients should undergo a prompt medical evaluation, and discontinuation of venlafaxine therapy should be considered.
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
-
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Hypersensitivity [see Contraindications ( 4.1) ]
- Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Children, Adolescents, and Adults [see Warnings andPrecautions ( 5.1) ]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) ]
- Elevations in Blood Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3) ]
- Abnormal Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4) ]
- Angle Closure Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5) ]
- Activation of Mania/Hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6) ]
- Discontinuation Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7) ]
- Renal Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions ( 2.6) ]
- Hepatic Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions ( 2.6) ]
- Seizure [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.8) ]
- Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9) ]
- Weight and Height changes in Pediatric Patients [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.10) ]
- Appetite Changes in Pediatric Patients [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.11) ]
- Interstitial Lung Disease and Eosinophilic Pneumonia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.12)]
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Most Common Adverse Reactions
The most commonly observed adverse reactions in the clinical study database in venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treated patients in MDD, SAD, and PD (incidence ≥ 5% and at least twice the rate of placebo) were: nausea (30%), somnolence (15.3%), dry mouth (14.8%), sweating (11.4%), abnormal ejaculation (9.9%), anorexia (9.8%), constipation (9.3%), impotence (5.3%) and decreased libido (5.1%).
Adverse Reactions Reported as Reasons for Discontinuation of Treatment
Combined across short-term, placebo-controlled premarketing studies for all indications, 12% of the 3,558 patients who received venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules (37.5 to 225 mg) discontinued treatment due to an adverse experience, compared with 4% of the 2,197 placebo-treated patients in those studies.
The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation in ≥ 1% of the venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treated patients in the short-term studies (up to 12 weeks) across indications are shown in Table 7.
Table 7Incidence (%) of Patients Reporting Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation in Placebo-controlled Clinical Studies (up to 12 Weeks Duration) Body System
Adverse ReactionVenlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules
n = 3,558Placebo
n = 2,197Body as a whole Asthenia 1.7 0.5 Headache 1.5 0.8 Digestive system Nausea 4.3 0.4 Nervous system Dizziness 2.2 0.8 Insomnia 2.1 0.6 Somnolence 1.7 0.3 Skin and appendages 1.5 0.6 Sweating 1 0.2 Common Adverse Reactions in Placebo-controlled Studies
The number of patients receiving multiple doses of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules during the premarketing assessment for each approved indication is shown in Table 8. The conditions and duration of exposure to venlafaxine in all development programs varied greatly, and included (in overlapping categories) open and double-blind studies, uncontrolled and controlled studies, inpatient (venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets only) and outpatient studies, fixed-dose, and titration studies.
Table 8Patients Receiving Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules in Premarketing Clinical Studies aIn addition, in the premarketing assessment of venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets, multiple doses were administered to 2,897 patients in studies for MDD.
Indication Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules MDD 705a SAD 819 PD 1,314 The incidences of common adverse reactions (those that occurred in ≥ 2% of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treated patients [357 MDD patients, 819 SAD patients, and 1,001 PD patients] and more frequently than placebo) in venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treated patients in short-term, placebo-controlled, fixed- and flexible-dose clinical studies (doses 37.5 to 225 mg per day) are shown in Table 9.
The adverse reaction profile did not differ substantially between the different patient populations.
Table 9Common Adverse Reactions: Percentage of Patients Reporting Adverse Reactions(≥ 2% and > placebo) in Placebo-controlled Studies (up to 12 Weeks Duration) across All Indications a Percentages based on the number of men (venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, n = 1,440; placebo, n = 923)
b Percentages based on the number of women (venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, n = 2,118; placebo, n = 1,274)
Body System
Adverse ReactionVenlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules
n = 3,558Placebo
n = 2,197Body as a whole Asthenia 12.6 7.8 Cardiovascular system Hypertension 3.4 2.6 Palpitation 2.2 2 Vasodilatation 3.7 1.9 Digestive system Anorexia 9.8 2.6 Constipation 9.3 3.4 Diarrhea 7.7 7.2 Dry mouth 14.8 5.3 Nausea 30 11.8 Vomiting 4.3 2.7 Nervous system Abnormal dreams 2.9 1.4 Dizziness 15.8 9.5 Insomnia 17.8 9.5 Libido decreased 5.1 1.6 Nervousness 7.1 5 Paresthesia 2.4 1.4 Somnolence 15.3 7.5 Tremor 4.7 1.6 Respiratory system Yawn 3.7 0.2 Skin and appendages Sweating (including night sweats) 11.4 2.9 Special senses Abnormal vision 4.2 1.6 Urogenital system Abnormal ejaculation/orgasm (men)a 9.9 0.5 Anorgasmia (men)a 3.6 0.1 Anorgasmia (women)b 2 0.2 Impotence (men)a 5.3 1 Other Adverse Reactions Observed in Clinical Studies
Body as a whole
Photosensitivity reaction
Cardiovascular system
Postural hypotension, syncope, hypotension, tachycardia
Digestive system
Gastrointestinal hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4)], bruxism
Hemic/Lymphatic system
Ecchymosis [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4)]
Metabolic/Nutritional
Hypercholesterolemia, weight gain [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.10)], weight loss [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.10)]
Nervous system
Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.8)], manic reaction [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6)], agitation, confusion, akathisia, hallucinations, hypertonia, myoclonus, depersonalization, apathy
Skin and appendages
Urticaria, pruritus, rash, alopecia
Special senses
Mydriasis, abnormality of accommodation, tinnitus, taste perversion
Urogenital system
Urinary retention, urination impaired, urinary incontinence, urinary frequency increased, menstrual disorders associated with increased bleeding or increased irregular bleeding (e.g., menorrhagia, metrorrhagia)
6.2 Vital Sign ChangesIn placebo-controlled premarketing studies, there were increases in mean blood pressure (see Table 10). Across most indications, a dose-related increase in mean supine systolic and diastolic blood pressure was evident in patients treated with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules. Across all clinical studies in MDD, SAD and PD, 1.4% of patients in the venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules groups experienced an increase in SDBP of ≥15 mm Hg along with a blood pressure ≥ 105 mm Hg, compared to 0.9% of patients in the placebo groups. Similarly, 1% of patients in the venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules groups experienced an increase in SSBP of ≥ 20 mm Hg with a blood pressure ≥ 180 mm Hg, compared to 0.3% of patients in the placebo groups.
Table 10Final On-therapy Mean Changes From Baseline in Supine Systolic (SSBP) and Diastolic (SDBP) Blood Pressure (mm Hg) in Placebo-controlled Studies Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Placebo Indication
≤ 75 mg per day > 75 mg per day (Duration) SSBP SDBP SSBP SDBP SSBP SDBP MDD (8 to 12 weeks) -0.28 0.37 2.93 3.56 -1.08 -0.10 SAD (12 weeks) -0.29 -1.26 1.18 1.34 -1.96 -1.22 (6 months) -0.98 -0.49 2.51 1.96 -1.84 -0.65 PD (10 to 12 weeks) -1.15 0.97 -0.36 0.16 -1.29 -0.99 Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treatment was associated with sustained hypertension (defined as treatment-emergent Supine Diastolic Blood Pressure [SDBP] ≥ 90 mm Hg and ≥ 10 mm Hg above baseline for three consecutive on- therapy visits (see Table 11). An insufficient number of patients received mean doses of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules over 300 mg per day in clinical studies to fully evaluate the incidence of sustained increases in blood pressure at these higher doses.
Table 11Sustained Elevations in SDBP in Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Premarketing Studies Indication Dose Range (mg per day) Incidence (%) MDD 75 to 375 19/705 (3) SAD 75 to 225 5/771 (0.6) PD 75 to 225 9/973 (0.9) Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsule was associated with mean increases in pulse rate compared with placebo in premarketing placebo-controlled studies (see Table 12) [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3, 5.4)].
6.3 Laboratory ChangesTable 12Approximate Mean Final On-therapy Increase in Pulse Rate (beats/min) in Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Premarketing Placebo-controlled Studies (up to 12 Weeks Duration) Indication
(Duration)Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Placebo MDD (12 weeks) 2 1 SAD (12 weeks) 3 1 PD (12 weeks) 1 <1 Serum Cholesterol
Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsule was associated with mean final increases in serum cholesterol concentrations compared with mean final decreases for placebo in premarketing MDD, SAD and PD clinical studies (Table 13).
Table 13Mean Final On-therapy Changes in Cholesterol Concentrations (mg/dL) in Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Premarketing Studies Indication
(Duration)Venlafaxine Hydrochloride
Extended-release CapsulesPlacebo MDD (12 weeks) +1.5 -7.4 SAD (12 weeks) +7.9 -2.9 (6 months) +5.6 -4.2 PD (12 weeks) 5.8 -3.7 Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treatment for up to 12 weeks in premarketing placebo-controlled trials for major depressive disorder was associated with a mean final on- therapy increase in serum cholesterol concentration of approximately 1.5 mg/dL compared with a mean final decrease of 7.4 mg/dL for placebo. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treatment for up to 12 weeks and up to 6 months in premarketing placebo-controlled Social Anxiety Disorder trials was associated with mean final on-therapy increases in serum cholesterol concentration of approximately 7.9 mg/dL and 5.6 mg/dL, respectively, compared with mean final decreases of 2.9 and 4.2 mg/dL, respectively, for placebo. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treatment for up to 12 weeks in premarketing placebo- controlled panic disorder trials was associated with mean final on-therapy increases in serum cholesterol concentration of approximately 5.8 mg/dL compared with a mean final decrease of 3.7 mg/dL for placebo.
Patients treated with venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets for at least 3 months in placebo-controlled 12-month extension trials had a mean final on-therapy increase in total cholesterol of 9.1 mg/dL compared with a decrease of 7.1 mg/dL among placebo-treated patients. This increase was duration dependent over the study period and tended to be greater with higher doses. Clinically relevant increases in serum cholesterol, defined as 1) a final on-therapy increase in serum cholesterol ≥50 mg/dL from baseline and to a value ≥261 mg/dL, or 2) an average on-therapy increase in serum cholesterol ≥50 mg/dL from baseline and to a value ≥261 mg/dL, were recorded in 5.3% of venlafaxine-treated patients and 0% of placebo- treated patients.
Serum Triglycerides
Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules was associated with mean final on-therapy increases in fasting serum triglycerides compared with placebo in premarketing clinical studies of SAD and PD up to 12 weeks (pooled data) and 6 months duration (Table 14).
6.4 Pediatric PatientsTable 14Mean Final On-therapy Increases in Triglyceride Concentrations (mg/dL) in Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules Premarketing Studies Indication
(Duration)Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules Placebo SAD (12 weeks) 8.2 0.4 SAD (6 months) 11.8 1.8 PD (12 weeks) 5.9 0.9 PD (6 months) 9.3 0.3 In general, the adverse reaction profile of venlafaxine (in placebo-controlled clinical studies) in children and adolescents (ages 6 to 17) was similar to that seen for adults. As with adults, decreased appetite, weight loss, increased blood pressure, and increased serum cholesterol were observed [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3, 5.10, 5.11) and Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4)].
In pediatric clinical studies, the adverse reaction, suicidal ideation, was observed.
Particularly, the following adverse reactions were observed in pediatric patients: abdominal pain, agitation, dyspepsia, ecchymosis, epistaxis, and myalgia.
6.5 Adverse Reactions Identified During Postapproval UseThe following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
Body as a whole
Anaphylaxis, angioedema
Cardiovascular system
QT prolongation, ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia (including torsade de pointes)
Digestive system
Pancreatitis
Hemic/Lymphatic system
Mucous membrane bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4)], blood dyscrasias (including agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, neutropenia and pancytopenia), prolonged bleeding time, thrombocytopenia
Metabolic/Nutritional
Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9)], Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH) secretion [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9)], abnormal liver function tests, hepatitis, prolactin increased
Musculoskeletal
Rhabdomyolysis
Nervous system
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)], serotonergic syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)], delirium, extrapyramidal reactions (including dystonia and dyskinesia), impaired coordination and balance, tardive dyskinesia
Respiratory system
Pulmonary eosinophilia
Skin and appendages
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme
Special senses
Angle-closure glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5)]
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7.1 Central Nervous System (CNS)-Active Drugs
The risk of using venlafaxine in combination with other CNS-active drugs has not been systematically evaluated. Consequently, caution is advised when venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules are taken in combination with other CNS- active drugs.
7.2 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Adverse reactions, some of which were serious, have been reported in patients who have recently been discontinued from an MAOI and started on antidepressants with pharmacological properties similar to venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules (SNRIs or SSRIs), or who have recently had SNRI or SSRI therapy discontinued prior to initiation of an MAOI [see Dosage and Administration (2.9), Contraindications (4.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.3 Serotonergic Drugs
Based on the mechanism of action of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules and the potential for serotonin syndrome, caution is advised when venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules are coadministered with other drugs that may affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter systems, such as triptans, SSRIs, other SNRIs, linezolid (an antibiotic which is a reversible non-selective MAOI), lithium, tramadol, or St. John's wort. If concomitant treatment with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules and these drugs is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases. The concomitant use of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules with tryptophan supplements is not recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.9), Contraindications (4.2), and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.4 Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g., NSAIDs, Aspirin, and Warfarin)
Serotonin release by platelets plays an important role in hemostasis. The use of psychotropic drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake is associated with the occurrence of upper gastrointestinal bleeding and concurrent use of an NSAID or aspirin may potentiate this risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Altered anticoagulant effects, including increased bleeding, have been reported when SSRIs and SNRIs are coadministered with warfarin. Patients receiving warfarin therapy should be carefully monitored when venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules are initiated or discontinued.
7.5 Weight Loss Agents
The safety and efficacy of venlafaxine therapy in combination with weight loss agents, including phentermine, have not been established. Coadministration of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules and weight loss agents is not recommended. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules are not indicated for weight loss alone or in combination with other products.
7.6 Effects of Other Drugs on Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules
Figure 1: Effect of interacting drugs on the pharmacokinetics of venlafaxine and active metabolite
Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, USP
Abbreviations: ODV, O-desmethylvenlafaxine; AUC, area under the curve; Cmax, peak plasma concentrations; EM's, extensive metabolizers; PM's, poor metabolizers
* No dose adjustment on coadministration with CYP2D6 inhibitors (Fig 3 and Metabolism Section 12.3)
7.7 Effects of Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules on Other Drugs
Figure 2: Effect of venlafaxine on the pharmacokinetics interacting drugs and their active metabolites.
Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, USP
Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; Cmax, peak plasma concentrations; OH, hydroxyl
* Data for 2-OH desipramine were not plotted to enhance clarity; the fold change and 90% CI for Cmax and AUC of 2-OH desipramine were 6.6 (5.5, 7.9) and 4.4 (3.8, 5), respectively.
Note:
*: Administration of venlafaxine in a stable regimen did not exaggerate the psychomotor and psychometric effects induced by ethanol in these same subjects when they were not receiving venlafaxine.
7.8 Drug-Laboratory Test Interactions
False-positive urine immunoassay screening tests for phencyclidine (PCP) and amphetamine have been reported in patients taking venlafaxine. This is due to lack of specificity of the screening tests. False positive test results may be expected for several days following discontinuation of venlafaxine therapy. Confirmatory tests, such as gas chromatography/mass spectrometry, will distinguish venlafaxine from PCP and amphetamine.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
- 8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects – Pregnancy Category C
Venlafaxine did not cause malformations in offspring of rats or rabbits given doses up to 2.5 times (rat) or 4 times (rabbit) the maximum recommended human daily dose on a mg/m2 basis. However, in rats, there was a decrease in pup weight, an increase in stillborn pups, and an increase in pup deaths during the first 5 days of lactation, when dosing began during pregnancy and continued until weaning. The cause of these deaths is not known. These effects occurred at 2.5 times (mg/m2) the maximum human daily dose. The no effect dose for rat pup mortality was 0.25 times the human dose on a mg/m2 basis. In reproductive developmental studies in rats and rabbits with O-desmethylvenlafaxine (ODV), the major human metabolite of venlafaxine, evidence of teratogenicity was not observed at exposure margins of 13 in rats and 0.3 in rabbits. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Non-teratogenic Effects
Neonates exposed to venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, other SNRIs, or SSRIs, late in the third trimester have developed complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding. Such complications can arise immediately upon delivery. Reported clinical findings have included respiratory distress, cyanosis, apnea, seizures, temperature instability, feeding difficulty, vomiting, hypoglycemia, hypotonia, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, tremor, jitteriness, irritability, and constant crying. These features are consistent with either a direct toxic effect of SSRIs and SNRIs, or possibly a drug discontinuation syndrome. It should be noted, that in some cases the clinical picture is consistent with serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) and Drug Interactions ( 7.3)]. When treating a pregnant woman with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules during the third trimester, the physician should carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of treatment.
8.2 Labor and DeliveryThe effect of venlafaxine on labor and delivery in humans is unknown.
8.3 Nursing MothersVenlafaxine and ODV have been reported to be excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric UseTwo placebo-controlled trials in 766 pediatric patients with MDD have been conducted with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, and the data were not sufficient to support a claim for use in pediatric patients.
Anyone considering the use of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules in a child or adolescent must balance the potential risks with the clinical need [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1, 5.10, 5.11) and Adverse Reactions ( 6.4)].
Although no studies have been designed to primarily assess venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsule's impact on the growth, development, and maturation of children and adolescents, the studies that have been done suggest that venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules may adversely affect weight and height (see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.10)). Should the decision be made to treat a pediatric patient with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, regular monitoring of weight and height is recommended during treatment, particularly if treatment is to be continued long-term [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.10, 5.11)]. The safety of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treatment for pediatric patients has not been systematically assessed for chronic treatment longer than six months in duration. In the studies conducted in pediatric patients (ages 6 to 17), the occurrence of blood pressure and cholesterol increases considered to be clinically relevant in pediatric patients was similar to that observed in adult patients. Consequently, the precautions for adults apply to pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3, 6.3)].
8.5 Geriatric UseThe percentage of patients in clinical studies for venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules for MDD, SAD, and PD who were 65 years of age or older are shown in Table 15.
Table 15Percentage (and Number of Patients Studied) of Patients 65 Years of Age and Older by Indicationa aIn addition, in the premarketing assessment of venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets, 12% (357/2,897) of patients were ≥ 65 years of age.
Indication Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules MDD 4 (14/357) SAD 1 (10/819) PD 2 (16/1,001) No overall differences in effectiveness or safety were observed between geriatric patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience generally has not identified differences in response between the elderly and younger patients. However, greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. SSRIs and SNRIs, including venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, have been associated with cases of clinically significant hyponatremia in elderly patients, who may be at greater risk for this adverse event [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9)].
The pharmacokinetics of venlafaxine and ODV are not substantially altered in the elderly [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3) and (see Figure 3)]. No dose adjustment is recommended for the elderly on the basis of age alone, although other clinical circumstances, some of which may be more common in the elderly, such as renal or hepatic impairment, may warrant a dose reduction [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.6)].
8.6 Age and GenderA population pharmacokinetic analysis of 404 venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets-treated patients from two studies involving both twice daily and three times daily regimens showed that dose-normalized trough plasma levels of either venlafaxine or ODV were unaltered by age or gender differences. Dosage adjustment based on the age or gender of a patient is generally not necessary [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.6)] (see Table 15).
8.7 Use in Patient SubgroupsFigure 3: Pharmacokinetics of venlafaxine and its metabolite O-desmethylvenlafaxine (ODV) in special populations.
Abbreviations: ODV, O-desmethylvenlafaxine; AUC, area under the curve; Cmax, peak plasma concentrations;
*Similar effect is expected with strong CYP2D6 inhibitors
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE SECTION
- 9.1 Controlled Substance
Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsule is not a controlled substance.
9.2 AbuseWhile venlafaxine has not been systematically studied in clinical studies for its potential for abuse, there was no indication of drug-seeking behavior in the clinical studies. However, it is not possible to predict on the basis of premarketing experience the extent to which a CNS-active drug will be misused, diverted, and/or abused once marketed. Consequently, physicians should carefully evaluate patients for history of drug abuse and follow such patients closely, observing them for signs of misuse or abuse of venlafaxine (e.g., development of tolerance, incrementation of dose, drug-seeking behavior).
9.3 DependenceIn vitro studies revealed that venlafaxine has virtually no affinity for opiate, benzodiazepine, phencyclidine (PCP), or N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptors.
Venlafaxine was not found to have any significant CNS stimulant activity in rodents. In primate drug discrimination studies, venlafaxine showed no significant stimulant or depressant abuse liability. Discontinuation effects have been reported in patients receiving venlafaxine [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.8)].
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
- 10.1 Human Experience
During the premarketing evaluations of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules (for MDD, SAD, and PD) and venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets (for MDD), there were twenty reports of acute overdosage with venlafaxine hydrochloride (6 and 14 reports in venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules and venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets patients, respectively), either alone or in combination with other drugs and/or alcohol.
Somnolence was the most commonly reported symptom. Among the other reported symptoms were paresthesia of all four limbs, moderate dizziness, nausea, numb hands and feet, and hot-cold spells 5 days after the overdose. In most cases, no signs or symptoms were associated with overdose. The majority of the reports involved ingestion in which the total dose of venlafaxine taken was estimated to be no more than several-fold higher than the usual therapeutic dose. One patient who ingested 2.75 g of venlafaxine was observed to have two generalized convulsions and a prolongation of QTc to 500 msec, compared with 405 msec at baseline. Mild sinus tachycardia was reported in two of the other patients.
Actions taken to treat the overdose included no treatment, hospitalization and symptomatic treatment, and hospitalization plus treatment with activated charcoal. All patients recovered.
In postmarketing experience, overdose with venlafaxine has occurred predominantly in combination with alcohol and/or other drugs. The most commonly reported events in overdosage include tachycardia, changes in level of consciousness (ranging from somnolence to coma), mydriasis, seizures, and vomiting. Electrocardiogram changes (e.g., prolongation of QT interval, bundle branch block, QRS prolongation), ventricular tachycardia, bradycardia, hypotension, rhabdomyolysis, vertigo, liver necrosis, serotonin syndrome, and death have been reported.
Published retrospective studies report that venlafaxine overdosage may be associated with an increased risk of fatal outcomes compared to that observed with SSRI antidepressant products, but lower than that for tricyclic antidepressants. Epidemiological studies have shown that venlafaxine-treated patients have a higher preexisting burden of suicide risk factors than SSRI-treated patients. The extent to which the finding of an increased risk of fatal outcomes can be attributed to the toxicity of venlafaxine in overdosage, as opposed to some characteristic(s) of venlafaxine-treated patients, is not clear. Prescriptions for venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules should be written for the smallest quantity of capsules consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
10.2 Management of OverdosageConsult a Certified Poison Control Center for up-to-date guidance and advice (1-800-222-1222 or www.poison.org). In case of an overdose, provide supportive care, including close medical supervision and monitoring. Treatment should consist of those general measures employed in the management of overdosage with any drug. Consider the possibility of multiple drug overdose. Ensure an adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation. Monitor cardiac rhythm and vital signs. Provide supportive and symptomatic measures.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsule, USP is an extended-release capsule for once-a-day oral administration that contains venlafaxine hydrochloride, a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI).
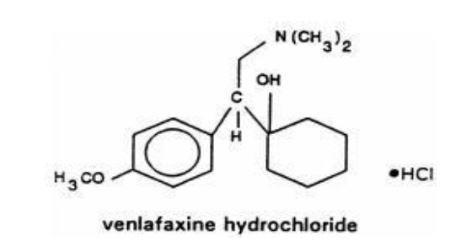
Venlafaxine is designated (R/S)-1-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl] cyclohexanol hydrochloride or (±)-1-[α- [(dimethylamino)methyl]-p-methoxybenzyl] cyclohexanol hydrochloride and has the molecular formula of C17H27NO2 HCl. Its molecular weight is 313.86. The structural formula is shown as follows:
Venlafaxine hydrochloride, USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder; soluble in methanol and in water. Its octanol:water (0.2 M sodium chloride) partition coefficient is 0.43.
Drug release is controlled by diffusion through the coating membrane on the spheroids and is not pH-dependent. Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, USP intended for oral administration contains 37.5 mg, 75 mg and 150 mg of venlafaxine. In addition, each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, cetostearyl alcohol, gelatin, hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, polyacrylate dispersion, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc and titanium dioxide. Additionally each 37.5 mg capsule shell contains black iron oxide and each 75 mg and 150 mg capsule shell contains red iron oxide. The capsule is printed with black pharmaceutical ink which contains black iron oxide as coloring agent.
The product complies with USP dissolution test 7.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The exact mechanism of the antidepressant action of venlafaxine in humans is unknown, but is thought to be related to the potentiation of serotonin and norepinephrine in the central nervous system, through inhibition of their reuptake. Non- clinical studies have demonstrated that venlafaxine and its active metabolite, ODV, are potent and selective inhibitors of neuronal serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake and weak inhibitors of dopamine reuptake.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Venlafaxine and ODV have no significant affinity for muscarinic-cholinergic, H1-histaminergic, or α1 adrenergic receptors in vitro. Pharmacologic activity at these receptors is hypothesized to be associated with the various anticholinergic, sedative, and cardiovascular effects seen with other psychotropic drugs. Venlafaxine and ODV do not possess monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitory activity.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Steady-state concentrations of venlafaxine and ODV in plasma are attained within 3 days of oral multiple- dose therapy. Venlafaxine and ODV exhibited linear kinetics over the dose range of 75 to 450 mg per day. Mean±SD steady-state plasma clearance of venlafaxine and ODV is 1.3±0.6 and 0.4±0.2 L/h/kg, respectively; apparent elimination half-life is 5±2 and 11±2 hours, respectively; and apparent (steady state) volume of distribution is 7.5±3.7 and 5.7±1.8 L/kg, respectively. Venlafaxine and ODV are minimally bound at therapeutic concentrations to plasma proteins (27% and 30%, respectively).
Absorption and Distribution
Venlafaxine is well absorbed and extensively metabolized in the liver. ODV is the major active metabolite. On the basis of mass balance studies, at least 92% of a single oral dose of venlafaxine is absorbed. The absolute bioavailability of venlafaxine is approximately 45%.
Administration of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules (150 mg once daily) generally resulted in lower Cmax and later Tmax values than for venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets administered twice daily (Table 16). When equal daily doses of venlafaxine were administered as either an immediate-release tablet or the extended-release capsule, the exposure to both venlafaxine and ODV was similar for the two treatments, and the fluctuation in plasma concentrations was slightly lower with the venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules. Therefore, venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules provide a slower rate of absorption, but the same extent of absorption compared with the immediate-release tablet.
Table 16Comparison of Cmax and Tmax Values for Venlafaxine and ODV Following OralAdministration of Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules and Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Tablets
Venlafaxine
ODV
Cmax
(ng/mL)
Tmax
(h)
Cmax
(ng/mL)
Tmax
(h)
Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (150 mg once daily)
150
5.5
260
9
Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Tablets (75 mg twice daily)
225
2
290
3
Food did not affect the bioavailability of venlafaxine or its active metabolite, ODV. Time of administration (AM versus PM) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of venlafaxine and ODV from the 75 mg venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules.
Venlafaxine is not highly bound to plasma proteins; therefore, administration of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules to a patient taking another drug that is highly protein-bound should not cause increased free concentrations of the other drug.
Metabolism and Elimination
Following absorption, venlafaxine undergoes extensive presystemic metabolism in the liver, primarily to ODV, but also to N-desmethylvenlafaxine, N,O-didesmethylvenlafaxine, and other minor metabolites. In vitro studies indicate that the formation of ODV is catalyzed by CYP2D6; this has been confirmed in a clinical study showing that patients with low CYP2D6 levels (poor metabolizers) had increased levels of venlafaxine and reduced levels of ODV compared to people with normal CYP2D6 levels (extensive metabolizers) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Approximately 87% of a venlafaxine dose is recovered in the urine within 48 hours as unchanged venlafaxine (5%), unconjugated ODV (29%), conjugated ODV (26%), or other minor inactive metabolites (27%). Renal elimination of venlafaxine and its metabolites is thus the primary route of excretion.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
- 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Tumors were not increased by venlafaxine treatment in mice or rats. Venlafaxine was given by oral gavage to mice for 18 months at doses up to 120 mg/kg per day, which was 1.7 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis. Venlafaxine was also given to rats by oral gavage for 24 months at doses up to 120 mg/kg per day. In rats receiving the 120 mg/kg dose, plasma concentrations of venlafaxine at necropsy were 1 times (male rats) and 6 times (female rats) the plasma concentrations of patients receiving the maximum recommended human dose. Plasma levels of the O-desmethyl metabolite (ODV) were lower in rats than in patients receiving the maximum recommended dose. O desmethylvenlafaxine (ODV), the major human metabolite of venlafaxine, administered by oral gavage to mice and rats for 2 years did not increase the incidence of tumors in either study. Mice received ODV at dosages up to 500/300 mg/kg/day (dosage lowered after 45 weeks of dosing). The exposure at the 300 mg/kg/day dose is 9 times that of a human dose of 225 mg/day. Rats received ODV at dosages up to 300 mg/kg/day (males) or 500 mg/kg/day (females). The exposure at the highest dose is approximately 8 (males) or 11 (females) times that of a human dose of 225 mg/day.
Mutagenesis
Venlafaxine and the major human metabolite, ODV, were not mutagenic in the Ames reverse mutation assay in Salmonella bacteria or the Chinese hamster ovary/HGPRT mammalian cell forward gene mutation assay. Venlafaxine was also not mutagenic or clastogenic in the in vitro BALB/c-3T3 mouse cell transformation assay, the sister chromatid exchange assay in cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells, or in the in vivo chromosomal aberration assay in rat bone marrow. ODV was not clastogenic in the in vitro Chinese hamster ovary cell chromosomal aberration assay or in the in vivo chromosomal aberration assay in rats.
Impairment of Fertility
Reproduction and fertility studies of venlafaxine in rats showed no adverse effects of venlafaxine on male or female fertility at oral doses of up to 2 times the maximum recommended human dose of 225 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis. However, reduced fertility was observed in a study in which male and female rats were treated with O-desmethylvenlafaxine (ODV), the major human metabolite of venlafaxine, prior to and during mating and gestation. This occurred at an ODV exposure (AUC) approximately 2 to 3 times that associated with a human venlafaxine dose of 225 mg/day.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
- 14.1 Major Depressive Disorder
The efficacy of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules as a treatment for Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) was established in two placebo-controlled, short-term (8 weeks for study 1; 12 weeks for study 2), flexible-dose studies, with doses starting at 75 mg per day and ranging to 225 mg per day in adult outpatients meeting DSM-III-R or DSM-IV criteria for MDD. In moderately depressed outpatients, the initial dose of venlafaxine was 75 mg per day. In both studies, venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules demonstrated superiority over placebo on the primary efficacy measure defined as change from baseline in the HAM-D-21 total score to the endpoint visit, venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules also demonstrated superiority over placebo on the key secondary efficacy endpoint, the Clinical Global Impressions (CGI) Severity of Illness scale. Examination of gender subsets of the population studied did not reveal any differential responsiveness on the basis of gender.
A 4-week study of inpatients meeting DSM-III-R criteria for MDD with melancholia utilizing venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets in a range of 150 to 375 mg per day (divided in a three-times-a-day schedule) demonstrated superiority of venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets over placebo based on the HAM-D-21 total score. The mean dose in completers was 350 mg per day (study 3).
In a longer-term study, adult outpatients with MDD who had responded during an 8-week open-label study on venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules (75, 150, or 225 mg, once daily every morning) were randomized to continuation of their same venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules dose or to placebo, for up to 26 weeks of observation for relapse. Response during the open-label phase was defined as a CGI Severity of Illness item score of ≤3 and a HAM-D-21 total score of ≤10 at the day 56 evaluation. Relapse during the double-blind phase was defined as follows: (1) a reappearance of major depressive disorder as defined by DSM-IV criteria and a CGI Severity of Illness item score of ≥4 (moderately ill), (2) 2 consecutive CGI Severity of Illness item scores of ≥4, or (3) a final CGI Severity of Illness item score of ≥4 for any patient who withdrew from the study for any reason.
Patients receiving continued venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules treatment experienced statistically significantly lower relapse rates over the subsequent 26 weeks compared with those receiving placebo (study 4).
In a second longer term trial, adult outpatients with MDD, recurrent type, who had responded (HAM-D 21 total score ≤ 12 at the day 56 evaluation) and continued to be improved [defined as the following criteria being met for days 56 through 180: (1) no HAM-D-21 total score ≥ 20; (2) no more than 2 HAM D-21 total scores > 10, and (3) no single CGI Severity of Illness item score ≥ 4 (moderately ill)] during an initial 26 weeks of treatment on venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets [100 to 200 mg per day, on a twice daily schedule] were randomized to continuation of their same venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets dose or to placebo. The follow-up period to observe patients for relapse, defined as a CGI Severity of Illness item score ≥ 4, was for up to 52 weeks. Patients receiving continued venlafaxine hydrochloride tablets treatment experienced statistically significantly lower relapse rates over the subsequent 52 weeks compared with those receiving placebo (study 5).
14.3 Social Anxiety Disorder (also known as Social Phobia)Table 17Major Depressive Disorder Studies SD: standard deviation; LS Mean: least-squares mean; CI: confidence interval.
aDifference (drug minus placebo) in least-squares mean change from baseline
* Doses statistically significantly superior to placebo.
Study Number Treatment
GroupPrimary Efficacy Measure: HAM-D Score Mean Baseline Score (SD)
LS Mean Change from Baseline Placebo Subtracted Differencea (95%CI) Study 1 Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (75 to 225 mg/day)* 24.5 -11.7 -4.45(-6.66,-2.25) Placebo 23.6 -7.24 - Study 2 Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules (75 to 225 mg/day)* 24.5 -15.11 -6.40(-8.45,-4.34) Placebo 24.9 -8.71 - Study 3 Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Tablets (150 to 375 mg/day)* 28.2 (0.5) -14.9 -10.2 (-14.4,-6) Placebo 28.6 (0.6) -4.7 - The efficacy of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules as a treatment for Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) was established in four double-blind, parallel-group, 12-week, multicenter, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose studies (studies 1-4) and one double-blind, parallel-group, 6-month, placebo-controlled, fixed/flexible-dose study, which included doses in a range of 75 to 225 mg per day in adult outpatients meeting DSM-IV criteria for SAD (study 5).
In these five studies, venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsule was statistically significantly more effective than placebo on change from baseline to endpoint on the Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale (LSAS) total score. There was no evidence for any greater effectiveness of the 150 to 225 mg per day group compared to the 75 mg per day group in the 6-month study.
Examination of subsets of the population studied did not reveal any differential responsiveness on the basis of gender. There was insufficient information to determine the effect of age or race on outcome in these studies.
14.4 Panic DisorderTable 19Social Anxiety Disorder Studies SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error; LS Mean: least-squares mean; CI: confidence interval.
a Difference (drug minus placebo) in least-squares mean change from baseline
* Doses statistically significantly superior to placebo.
Study Number Treatment Group Primary Efficacy Measure: LSAS Score Mean Baseline Score
(SD)LS Mean Change from Baseline
(SE)Placebo Subtracted Differencea
(95% CI)Study 1 Ven XR (75 to 225 mg) Placebo 91.1
86.7-31(2.22)
-19.9 (2.22)11.2 (-5.3, -17.1)
-Study 2 Ven XR (75 to 225 MG) Placebo 90.8
87.4-32.8 (2.69)
-22.1 (2.66)-10.7 (-3.7,-17.6)
-Study 3 Ven XR (75 to 225 MG) Placebo 83.2
83.6-36 (2.35)
-19.1 (2.40)-16.9(-22.6, -11.2)
-12.7 (-6.5, -19)Study 4 Ven XR (75 to 225 mg) Placebo 86.2
86.1-35 (2.64)
-22.2 (2,47)-14.6 (-21.8, -7.4)
-Study 5 Ven XR 75 mg 91.8 -38.1 (3.16) -14.6 (-21.8, -7.4) Ven XR (150 to 225 mg) 86.2 -37.6 (3.05) -14.1 (-21.3, -6.9) Placebo 89.3 -23.5 (3.08) - The efficacy of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules as a treatment for Panic Disorder (PD) was established in two double-blind, 12-week, multicenter, placebo-controlled studies in adult outpatients meeting DSM-IV criteria for PD, with or without agoraphobia. Patients received fixed doses of 75 or 150 mg per day in one study (study 1) and 75 or 225 mg per day in the other study (study 2).
Efficacy was assessed on the basis of outcomes in three variables: (1) percentage of patients free of full- symptom panic attacks on the Panic and Anticipatory Anxiety Scale (PAAS); (2) mean change from baseline to endpoint on the Panic Disorder Severity Scale (PDSS) total score; and (3) percentage of patients rated as responders (much improved or very much improved) on the Clinical Global Impressions (CGI) Improvement scale. In these two studies, venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsule was statistically significantly more effective than placebo (for each fixed dose) on all three endpoints, but a dose-response relationship was not clearly established.
Examination of subsets of the population studied did not reveal any differential responsiveness on the basis of gender. There was insufficient information to determine the effect of age or race on outcome in these studies.
In a longer term study (study 3), adult outpatients meeting DSM-IV criteria for PD who had responded during a 12-week open phase with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules (75 to 225 mg per day) were randomly assigned to continue the same venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules dose (75, 150, or 225 mg) or switch to placebo for observation for relapse under double-blind conditions. Response during the open phase was defined as ≤ 1 full-symptom panic attack per week during the last 2 weeks of the open phase and a CGI Improvement score of 1 (very much improved) or 2 (much improved). Relapse during the double-blind phase was defined as having 2 or more full-symptom panic attacks per week for 2 consecutive weeks or having discontinued due to loss of effectiveness as determined by the investigators during the study. Randomized patients were in response status for a mean time of 34 days prior to being randomized. In the randomized phase following the 12 week open-label period, patients receiving continued venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules experienced a statistically significantly longer time to relapse.
14.5 Pediatric PatientsTable 20Panic Disorder Studies aOdds ratio (drug to placebo) in terms of probability of free of full-symptom panic attacks based on logistic regression model.
95%CI: 95% confidence interval without adjusting for multiple dose arms.
*Doses statistically significantly superior to placebo.
Study Number Treatment
GroupPrimary Efficacy Measure: Whether Free of Full-symptom Panic Attacks Percent of patients Free of Full symptom panic attack Adjusted Odds
Ratioa
to placeboAdjusted Odds Ratioa 95% Confidence Interval Study 1 Ven XR 75 mg* Ven XR 150 mg* Placebo 54.1% (85/157)
61.4% (97/158)
34.4% (53/154)2. 268
3.035
-(1.43, 3.59)
(1.91, 4.82)
-Study 2 Ven XR 75 mg* Ven XR 225 mg* Placebo 64.1% (100/156)
70% (112/160)
46.5% (73/157)2.350
2.890
-(1.46, 3.78)
(1.80, 4.64)
-Two placebo-controlled studies in 766 pediatric patients with MDD have been conducted with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules, and the data were not sufficient to support a claim for use in pediatric patients.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules USP, 37.5 mg are white to off-white free flowing pellets filled in size '3' hard gelatin capsules with grey colored cap printed with "ZA-35" in black ink & white body printed with "37.5 mg" in black ink and are supplied as follows:
NDC 68382-034-06 in bottle of 30 capsules
NDC 68382-034-16 in bottle of 90 capsules
NDC 68382-034-01 in bottle of 100 capsules
NDC 68382-034-05 in bottle of 500 capsules
NDC 68382-034-10 in bottle of 1000 capsules
Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules USP, 75 mg are white to off-white free flowing pellets filled in size '1' hard gelatin capsules with peach colored cap printed with "ZA-36" in black ink & white body printed with "75 mg" in black ink and are supplied as follows:
NDC 68382-035-06 in bottle of 30 capsules
NDC 68382-035-16 in bottle of 90 capsules
NDC 68382-035-01 in bottle of 100 capsules
NDC 68382-035-05 in bottle of 500 capsules
NDC 68382-035-10 in bottle of 1000 capsules
Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended-release Capsules USP, 150 mg are white to off-white free flowing pellets filled in size '0' hard gelatin capsules with dark orange colored cap printed with "ZA-37" in black ink & white body printed with "150 mg" in black ink and are supplied as follows:
NDC 68382-036-06 in bottle of 30 capsules
NDC 68382-036-16 in bottle of 90 capsules
NDC 68382-036-01 in bottle of 100 capsules
NDC 68382-036-05 in bottle of 500 capsules
NDC 68382-036-10 in bottle of 1000 capsules
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight container.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
-
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Prescribers or other healthcare professionals should inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules and should counsel them in its appropriate use. A patient Medication Guide about "Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and Other Serious Mental Illnesses, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions" is available for venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules. The prescriber or healthcare professional should instruct patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide and should assist them in understanding its contents. Patients should be given the opportunity to discuss the contents of the Medication Guide and to obtain answers to any questions they may have. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of this document. Patients should be advised of the following issues and should be asked to alert their prescriber if these occur while taking venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules.
Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors
Advise patients, their families and caregivers to look for the emergence of suicidality, worsening of depression, and other psychiatric symptoms (anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia, psychomotor restlessness, hypomania, mania, other unusual changes in behavior), especially early during treatment and when the dose is adjusted up or down. Such symptoms should be reported to the patient's prescriber or health professional, especially if they are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms. Symptoms such as these may be associated with an increased risk for suicidal thinking and behavior and indicate a need for very close monitoring [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)].
Concomitant Medication
Advise patients taking venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules not to use concomitantly other products containing venlafaxine or desvenlafaxine. Healthcare professionals should instruct patients not to take venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules with an MAOI or within 14 days of stopping an MAOI and to allow 7 days after stopping venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules before starting an MAOI [see Contraindications ( 4.2)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Patients should be cautioned about the risk of serotonin syndrome, with the concomitant use of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules and triptans, tramadol, tryptophan supplements, with antipsychotics or other dopamine antagonists, or other serotonergic agents [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) and Drug Interactions ( 7.3)].
Elevated Blood Pressure
Advise patients that they should have regular monitoring of blood pressure when taking venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3)].
Abnormal Bleeding
Patients should be cautioned about the concomitant use of venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules and NSAIDs, aspirin, warfarin, or other drugs that affect coagulation since combined use of psychotropic drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and these agents has been associated with an increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4)].
Angle Closure Glaucoma
Patients should be advised that taking venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules can cause mild pupillary dilation, which in susceptible individuals, can lead to an episode of angle closure glaucoma. Preexisting glaucoma is almost always open-angle glaucoma because angle closure glaucoma, when diagnosed, can be treated definitively with iridectomy. Open-angle glaucoma is not a risk factor for angle closure glaucoma. Patients may wish to be examined to determine whether they are susceptible to angle closure, and have a prophylactic procedure (e.g., iridectomy), if they are susceptible [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5)].
Activation of Mania/Hypomania
Advise patients, their families and caregivers to observe for signs of activation of mania/hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6)].
Cardiovascular/Cerebrovascular Disease
Caution is advised in administering venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules to patients with cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, or lipid metabolism disorders [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.1)].
Serum Cholesterol and Triglyceride Elevation
Advise patients that elevations in total cholesterol, LDL and triglycerides may occur and that measurement of serum lipids may be considered [see Warnings and Precautions ( 6.3)].
Discontinuation [Symptoms]
Advise patients not to stop taking venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules without talking first with their healthcare professional. Patients should be aware that discontinuation effects may occur when stopping venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7) and Adverse Reactions ( 6.1)].
Interference with Cognitive and Motor Performance
Caution patients about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules therapy does not adversely affect their ability to engage in such activities.
Alcohol
Advise patients to avoid alcohol while taking venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsules [see Drug Interactions ( 7.6)].
Allergic Reactions
Advise patients to notify their physician if they develop allergic phenomena such as rash, hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
Pregnancy
Advise patients to notify their physician if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during therapy [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1)].
Nursing
Advise patients to notify their physician if they are breast-feeding an infant [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.3)].
Residual Spheroids
Venlafaxine hydrochloride extended-release capsule contains spheroids, which release the drug slowly into the digestive tract. The insoluble portion of these spheroids is eliminated, and patients may notice spheroids passing in the stool or via colostomy. Patients should be informed that the active medication has already been absorbed by the time the patient sees the spheroids.