FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Palonosetron injection is indicated in adults for prevention of:
- acute and delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of moderately emetogenic cancer chemotherapy (MEC).
- acute nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy (HEC).
- postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) for up to 24 hours following surgery. Efficacy beyond 24 hours has not been demonstrated.
As with other antiemetics, routine prophylaxis is not recommended in patients in whom there is little expectation that nausea and/or vomiting will occur postoperatively. In patients where nausea and vomiting must be avoided during the postoperative period, palonosetron is recommended even where the incidence of postoperative nausea and/or vomiting is low.
Palonosetron HCl injection is indicated in pediatric patients 1 month to less than 17 years of age for prevention of:
• acute nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of emetogenic cancer chemotherapy, including highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
The recommended dosage of palonosetron HCl injection for prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with HEC and MEC in adults and associated with emetogenic chemotherapy, including HEC in pediatric patients 1 month to less than 17 years of age is shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage of Palonosetron HCl Injection for the Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with Chemotherapy in Adults and Pediatric Patients 1 Month to Less than 17 Years
|
||
|
Age |
Dose * |
Infusion Time |
|
Adults |
0.25 mg as a single-dose |
Infuse over 30 seconds beginning approximately 30 minutes before the start of chemotherapy |
|
Pediatrics (1 month to less than 17 years) |
20 micrograms per kilogram (max 1.5 mg) as a single-dose |
Infuse over 15 minutes beginning approximately 30 minutes before the start of chemotherapy |
Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
The recommended dosage of palonosetron HCl injection in adults for PONV is 0.075 mg administered as a single intravenous dose over 10 seconds immediately before the induction of anesthesia.
2.2 Instructions for Intravenous Administration
- Palonosetron HCl injection is supplied ready for intravenous administration at a concentration of 0.05 mg/mL (50 mcg/mL).
- Do not mix palonosetron HCl injection with other drugs.
- Flush the infusion line with normal saline before and after administration of palonosetron HCl injection.
- Inspect palonosetron HCl injection visually for particulate matter and discoloration before administration.
- Discard unused portion.
3 DOSAGE FORM AND STRENGTHS
Palonosetron HCl injection is sterile, clear, colorless solution in glass vials that provide:
- 0.25 mg palonosetron in 5 mL (0.05 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Palonosetron HCl injection is contraindicated in patients known to have hypersensitivity to palonosetron [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock, have been reported with administration of palonosetron HCl injection [ see Adverse Reactions ( 6.2) ]. These reactions occurred in patients with or without known hypersensitivity to other 5-HT 3 receptor antagonists. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue palonosetron HCl injection and initiate appropriate medical treatment. Do not reinitiate palonosetron HCl injection in patients who have previously experienced symptoms of hypersensitivity [ see Contraindications ( 4) ].
5.2 Serotonin Syndrome
The development of serotonin syndrome has been reported with 5-HT 3 receptor antagonists. Most reports have been associated with concomitant use of serotonergic drugs (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors, mirtazapine, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, and intravenous methylene blue). Some of the reported cases were fatal. Serotonin syndrome occurring with overdose of another 5-HT 3 receptor antagonist alone has also been reported. The majority of reports of serotonin syndrome related to 5-HT 3 receptor antagonist use occurred in a post-anesthesia care unit or an infusion center.
Symptoms associated with serotonin syndrome may include the following combination of signs and symptoms: mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, with or without gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for the emergence of serotonin syndrome, especially with concomitant use of palonosetron HCl injection and other serotonergic drugs. If symptoms of serotonin syndrome occur, discontinue palonosetron HCl injection and initiate supportive treatment. Patients should be informed of the increased risk of serotonin syndrome, especially if palonosetron HCl injection is used concomitantly with other serotonergic drugs [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious or otherwise clinically significant adverse reactions reported in other sections of labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1) ]
- Serotonin Syndrome [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) ]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
Adults
In double-blind randomized clinical trials for the prevention of nausea and vomiting induced by MEC or HEC, 1374 adult patients received a single dose of palonosetron HCl injection, ondansetron (Studies 1 and 3) or dolasetron (Study 2) administered 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy [see Clinical Studies ( 14.1)]. Adverse reactions were similar in frequency and severity in all 3 treatment groups. Common adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of patients in these trials are shown in Table 2.
|
Adverse Reaction | Palonosetron HCl injection
0.25 mg intravenously (N=633) | Ondansetron
32 mg intravenously (N=410) | Dolasetron
100 mg intravenously (N=194) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Headache |
9% |
8% |
16% |
|
Constipation |
5% |
2% |
6% |
|
Diarrhea |
1% |
2% |
2% |
|
Dizziness |
1% |
2% |
2% |
|
Fatigue |
<1% |
1% |
2% |
|
Abdominal Pain |
<1% |
<1% |
2% |
|
Insomnia |
<1% |
1% |
2% |
* Reported in at least 2% of patients in any treatment group
Less common adverse reactions, reported in 1% or less of patients, in Studies 1, 2 and 3 were:
- Cardiovascular: non-sustained tachycardia, bradycardia, hypotension, hypertension, myocardial ischemia, extrasystoles, sinus tachycardia, sinus arrhythmia, supraventricular extrasystoles and QT prolongation.
- Dermatological: allergic dermatitis, rash
- Hearing and Vision: motion sickness, tinnitus, eye irritation and amblyopia
- Gastrointestinal System: diarrhea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, dry mouth, hiccups and flatulence
- General: weakness, fatigue, fever, hot flash, flu-like syndrome
- Liver: transient, asymptomatic increases in AST and/or ALT and bilirubin. These changes occurred predominantly in patients receiving highly emetogenic chemotherapy
- Metabolic: hyperkalemia, electrolyte fluctuations, hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, glycosuria, appetite decrease, anorexia
- Musculoskeletal: arthralgia
- Nervous System: dizziness, somnolence, insomnia, hypersomnia, paresthesia
- Psychiatric: anxiety, euphoric mood
- Urinary System: urinary retention
- Vascular: vein discoloration, vein distention
In other studies, 2 subjects experienced severe constipation following a single palonosetron HCl injection dose of approximately 0.75 mg (three times the recommended dose).
Pediatrics Aged 2 Months to 17 Years
In a pediatric clinical trial, 163 pediatric cancer patients with a mean age of 8 years received a single 20 mcg/kg (maximum 1.5 mg) intravenous infusion of palonosetron HCl injection 30 minutes before beginning the first cycle of emetogenic chemotherapy [ see Clinical Studies ( 14.2) ]. Adverse reactions were evaluated in pediatric patients receiving palonosetron HCl injection for up to 4 chemotherapy cycles. The following adverse reactions were reported in less than 1% of patients:
- Nervous System: headache, dizziness, dyskinesia.
- General: infusion site pain.
- Dermatological: allergic dermatitis, skin disorder.
Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
The most common adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of adults receiving palonosetron HCl injection 0.075 mg intravenously immediately before induction of anesthesia in 3 randomized placebo-controlled trials [ see Clinical Studies ( 14.3) ] are shown in Table 3. Rates of adverse reactions between palonosetron HCl injection and placebo groups were similar. Some events are known to be associated with, or may be exacerbated by, concomitant perioperative and intraoperative medications administered in this surgical population. A thorough QT/QTc study demonstrated palonosetron HCl injection does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent [ see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.2) ].
Table 3: Common Adverse Reactions* in Trials of Adults with Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
| Adverse Reaction | Palonosetron HCl injection
0.075 mg intravenously (N=336) |
Placebo (N=369) |
|---|---|---|
|
Electrocardiogram QT prolongation |
5% |
3% |
|
Bradycardia |
4% |
4% |
|
Headache |
3% |
4% |
|
Constipation |
2% |
3% |
*Reported in at least 2% of patients in any treatment group
Less common adverse reactions, reported in 1% of less of patients, in these PONV clinical trials were:
- Cardiovascular: QTc prolongation, sinus bradycardia, tachycardia, blood pressure decreased, hypotension, hypertension, arrhythmia, ventricular extrasystoles, generalized edema, ECG T wave amplitude decreased, platelet count decreased. The frequency of these adverse effects did not appear to be different from placebo.
- Dermatological: pruritus
- Gastrointestinal System: flatulence, dry mouth, upper abdominal pain, salivary hypersecretion, dyspepsia, diarrhea, intestinal hypomotility, anorexia
- General: chills
- Liver: increases in AST and/or ALT, hepatic enzyme increased
- Metabolic: hypokalemia, anorexia
- Nervous System: dizziness
- Respiratory: hypoventilation, laryngospasm
- Urinary System: urinary retention
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of palonosetron HCl. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Hypersensitivity reactions: including dyspnea, bronchospasm, swelling/edema, erythema, pruritus, rash, urticaria, anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1) ]
- Injection site reactions: including burning, induration, discomfort and pain
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Serotonergic Drugs
Serotonin syndrome (including altered mental status, autonomic instability, and neuromuscular symptoms) has been described following the concomitant use of 5-HT 3 receptor antagonists and other serotonergic drugs, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). Monitor for the emergence of serotonin syndrome. If symptoms occur, discontinue palonosetron and initiate supportive treatment [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) ].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on palonosetron HCl use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk.
In animal reproduction studies, no effects on embryo-fetal development were observed with the administration of oral palonosetron HCl during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 1,894 and 3,789 times the recommended human intravenous dose in rats and rabbits, respectively ( see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In animal reproduction studies, no effects on embryo-fetal development were observed in pregnant rats given oral palonosetron HCl at doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (1,894 times the recommended human intravenous dose based on body surface area) or pregnant rabbits given oral doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (3,789 times the recommended human intravenous dose based on body surface area) during the period of organogenesis.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of palonosetron in human milk, the effects of palonosetron on the breastfed infant, or the effects of palonosetron on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for palonosetron and any potential adverse effect on the breastfed infant from palonosetron or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
Safety and effectiveness of palonosetron HCl injection have been established in pediatric patients aged 1 month to less than 17 years for the prevention of acute nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of emetogenic cancer chemotherapy, including HEC. Use is supported by a clinical trial where 165 pediatric patients aged 2 months to less than 17 years were randomized to receive a single dose of palonosetron HCl injection 20 mcg/kg (maximum 1.5 mg) administered as an intravenous infusion 30 minutes prior to the start of emetogenic chemotherapy [ see Clinical Studies (14.2)] . While this study demonstrated that pediatric patients require a higher palonosetron dose than adults to prevent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, the safety profile is consistent with the established profile in adults [ see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
Safety and effectiveness of palonosetron HCl injection in neonates (less than 1 month of age) have not been established.
Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting Studies
Safety and effectiveness have not been established in pediatric patients for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Two pediatric trials were performed.
Pediatric Study 1, a dose finding study was conducted to compare two doses of palonosetron, 1 mcg/kg (maximum 0.075 mg) versus 3 mcg/kg (maximum 0.25 mg). A total of 150 pediatric surgical patients participated, age range 1 month to less than 17 years. No dose response was observed.
Pediatric Study 2, a multicenter, double-blind, double-dummy, randomized, parallel group, active control, single-dose non-inferiority study, compared intravenous palonosetron HCl (1 mcg/kg, maximum 0.075 mg) versus intravenous ondansetron. A total of 670 pediatric surgical patients participated, age 30 days to less than 17 years. The primary efficacy endpoint, Complete Response (CR: no vomiting, no retching, and no antiemetic rescue medication) during the first 24 hours postoperatively was achieved in 78.2% of patients in the palonosetron group and 82.7% in the ondansetron group. Given the pre-specified non-inferiority margin of -10%, the stratum adjusted Mantel-Haenszel statistical non-inferiority confidence interval for the difference in the primary endpoint, complete response (CR), was [-10.5, 1.7%], therefore non-inferiority was not demonstrated. Adverse reactions to palonosetron were similar to those reported in adults.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 1374 adult cancer patients in clinical studies of intravenously administered palonosetron HCl, 316 (23%) were 65 years and over, while 71 (5%) were at least 75 years and over. Of the 1520 adult patients in clinical studies of intravenously administered palonosetron HCl, 73 (5%) were at least 65 years old [ see Clinical Studies ( 14.1, 14.3) ]. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, but greater sensitivity in some older individuals cannot be ruled out. Population pharmacokinetics analysis did not reveal any differences in palonosetron pharmacokinetics between cancer patients 65 years of age and older compared to younger patients [ see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3) ]. No dose adjustment is required for geriatric patients.
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no known antidote to palonosetron. Overdose should be managed with supportive care.
Dialysis studies have not been performed, however, due to the large volume of distribution, dialysis is unlikely to be an effective treatment for palonosetron overdose. A single intravenous dose of palonosetron HCl at 30 mg/kg (947 and 474 times the human dose for rats and mice, respectively, based on body surface area) was lethal to rats and mice. The major signs of toxicity were convulsions, gasping, pallor, cyanosis and collapse.
11 DESCRIPTION
Palonosetron hydrochloride is an antiemetic and antinauseant agent. It is a serotonin-3 (5-HT 3) receptor antagonist with a strong binding affinity for this receptor. Chemically, palonosetron hydrochloride is: (3a S)-2-[( S)-1-Azabicyclo [2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-2,3,3a,4,5,6-hexahydro-1-oxo-1 Hbenz[ de]isoquinoline hydrochloride. The molecular formula is C 19H 24N 2O.HCl, with a molecular weight of 332.87. Palonosetron hydrochloride exists as a single isomer and has the following structural formula:
Palonosetron hydrochloride is a white to off-white crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water, soluble in propylene glycol, and slightly soluble in ethanol and 2-propanol.
Palonosetron HCl injection is a sterile, clear, colorless, non-pyrogenic, isotonic, buffered solution for intravenous administration. Palonosetron HCl injection is available as a 5 mL single-dose vial. Each 5 mL vial contains: 0.25 mg palonosetron equivalent to 0.28 mg palonosetron hydrochloride, 207.5 mg mannitol, disodium edetate and citrate buffer in water for intravenous administration. Hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide may have been added to adjust pH.
The pH of the solution in the 5 mL vial is 4.5 to 5.5.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Palonosetron is a 5-HT 3 receptor antagonist with a strong binding affinity for this receptor and little or no affinity for other receptors.
Cancer chemotherapy may be associated with a high incidence of nausea and vomiting, particularly when certain agents, such as cisplatin, are used. 5-HT 3 receptors are located on the nerve terminals of the vagus in the periphery and centrally in the chemoreceptor trigger zone of the area postrema. It is thought that chemotherapeutic agents produce nausea and vomiting by releasing serotonin from the enterochromaffin cells of the small intestine and that the released serotonin then activates 5-HT 3 receptors located on vagal afferents to initiate the vomiting reflex.
Postoperative nausea and vomiting is influenced by multiple patient, surgical and anesthesia related factors and is triggered by release of 5-HT in a cascade of neuronal events involving both the central nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract. The 5-HT 3 receptor has been demonstrated to selectively participate in the emetic response.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of intravenous palonosetron on blood pressure, heart rate, and ECG parameters including QTc were comparable to intravenous ondansetron and dolasetron in CINV clinical trials. In PONV clinical trials the effect of palonosetron on the QTc interval was no different from placebo. In non-clinical studies palonosetron possesses the ability to block ion channels involved in ventricular de- and re-polarization and to prolong action potential duration.
At a dose of 9 times the maximum recommended adult dose, palonosetron HCl injection does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
After intravenous dosing of palonosetron HCl in healthy subjects and cancer patients, an initial decline in palonosetron plasma concentrations is followed by a slow elimination from the body. Mean maximum plasma concentration (C max) and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC 0-∞) are generally dose-proportional over the dose range of 0.3 to 90 mcg/kg in healthy subjects and in cancer patients. Following a single intravenous dose of palonosetron HCl at 3 mcg/kg (or 0.21 mg/70 kg) to six cancer patients, mean (± SD) maximum plasma concentration was estimated to be 5630 ± 5480 ng/L and mean AUC was 35.8 ± 20.9 h•mcg/L.
Following intravenous administration of palonosetron HCl injection 0.25 mg once every other day for 3 doses in 11 cancer patients, the mean increase in plasma palonosetron concentration from Day 1 to Day 5 was 42 ± 34%. Following intravenous administration of palonosetron HCl injection 0.25 mg once daily for 3 days in 12 healthy subjects, the mean (± SD) increase in plasma palonosetron concentration from Day 1 to Day 3 was 110 ± 45%.
After intravenous dosing of palonosetron HCl injection in patients undergoing surgery (abdominal surgery or vaginal hysterectomy), the pharmacokinetic characteristics of palonosetron were similar to those observed in cancer patients.
Distribution
Palonosetron has a volume of distribution of approximately 8.3 ± 2.5 L/kg. Approximately 62% of palonosetron is bound to plasma proteins.
Elimination
After a single intravenous dose of 10 mcg/kg [ 14C]-palonosetron, approximately 80% of the dose was recovered within 144 hours in the urine with palonosetron representing approximately 40% of the administered dose. In healthy subjects, the total body clearance of palonosetron was 0.160 ± 0.035 L/h/kg and renal clearance was 0.067± 0.018 L/h/kg. Mean terminal elimination half-life is approximately 40 hours.
Metabolism
Palonosetron is eliminated by multiple routes with approximately 50% metabolized to form two primary metabolites: N-oxide-palonosetron and 6-S-hydroxy-palonosetron. These metabolites each have less than 1% of the 5-HT 3 receptor antagonist activity of palonosetron. In vitro metabolism studies have suggested that CYP2D6 and to a lesser extent, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 are involved in the metabolism of palonosetron. However, clinical pharmacokinetic parameters are not significantly different between poor and extensive metabolizers of CYP2D6 substrates.
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients
Pharmacokinetic data was obtained from a subset of pediatric cancer patients that received 10 mcg/kg or 20 mcg/kg as a single intravenous dose of palonosetron HCl injection. When the dose was increased from 10 mcg/kg to 20 mcg/kg a dose-proportional increase in mean AUC was observed. Peak plasma concentrations (CT) reported at the end of the 15-minute infusion of 20 mcg/kg were highly variable in all age groups and tended to be lower in patients less than 6 years than in older patients as shown in Table 4. The median half-life was 30 hours in overall age groups and ranged from about 20 to 30 hours across age groups after administration of 20 mcg/kg.
The total body clearance (L/h/kg) in patients 12 to 17 years old was similar to that in healthy adults. There are no apparent differences in volume of distribution when expressed as L/kg.
Table 4: Pharmacokinetics Parameters in Pediatric Cancer Patients following Intravenous Infusion of 20 mcg/kg Palonosetron HCl Injection over 15 minutes
|
PK Parameter* |
Pediatric Age Group |
|||
|
Less than 2 years |
2 years to less than 6 years |
6 years to less than 12 years |
12 years to less than 17 years |
|
|
N=12 |
N=42 |
N=38 |
N=44 |
|
|
C T†, ng/L |
9025 (197) |
9414 (252) |
16275 (203) |
11831 (176) |
|
N=5 |
N=7 |
N=10 |
||
|
AUC 0-∞, h·mcg/L |
103.5 (40.4) |
98.7 (47.7) |
124.5 (19.1) |
|
|
N=6 |
N=14 |
N=13 |
N=19 |
|
|
Clearance ‡, L/h/kg |
0.31 (34.7) |
0.23 (51.3) |
0.19 (46.8) |
0.16 (27.8) |
|
Vss ‡, L/kg |
6.08 (36.5) |
5.29 (57.8) |
6.26 (40) |
6.20 (29) |
Racial or Ethnic Groups
The pharmacokinetics of palonosetron were characterized in 24 healthy Japanese subjects over an intravenous dose range of 3 to 90 mcg/kg. Total body clearance was 25% higher in Japanese subjects compared to Whites, however, this increase is not considered to be clinically meaningful.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Mild to moderate renal impairment does not significantly affect palonosetron pharmacokinetic parameters. Total systemic exposure increased by approximately 28% in patients with severe renal impairment relative to healthy subjects. This increase is not considered clinically meaningful.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Hepatic impairment does not significantly affect total body clearance of palonosetron compared to the healthy subjects.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro studies indicated that palonosetron is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4/5 (CYP2C19 was not investigated) nor does it induce the activity of CYP1A2, CYP2D6, or CYP3A4/5. Therefore, the potential for clinically significant drug interactions with palonosetron appears to be low.
Dexamethasone
Co-administration of 0.25 mg palonosetron HCl injection and 20 mg dexamethasone administered intravenously in healthy subjects revealed no pharmacokinetic drug-interactions between palonosetron and dexamethasone.
Oral Aprepitant
In an interaction study in healthy subjects where a single 0.25 mg intravenous dose of palonosetron HCl injection was administered on day 1 and oral aprepitant for 3 days (125 mg/80 mg/80 mg), the pharmacokinetics of palonosetron were not significantly altered (AUC: no change, C max: 15% increase).
Metoclopramide
A study in healthy subjects involving a single 0.75 mg intravenous dose of palonosetron HCl injection and steady state oral metoclopramide (10 mg four times daily) demonstrated no significant pharmacokinetic interaction.
Corticosteroids, Analgesics, Antiemetics/Antinauseants, Antispasmodics and Anticholinergic Agents
In controlled clinical trials, palonosetron HCl injection has been safely administered with corticosteroids, analgesics, antiemetics/antinauseants, antispasmodics and anticholinergic agents.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 104-week carcinogenicity study in CD-1 mice, animals were treated with oral doses of palonosetron HCl at 10, 30 and 60 mg/kg/day. Treatment with palonosetron was not tumorigenic. The highest tested dose produced a systemic exposure to palonosetron (Plasma AUC) of about 150 to 289 times the human exposure (AUC=29.8 h•mcg/L) at the recommended intravenous dose of 0.25 mg. In a 104-week carcinogenicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats, male and female rats were treated with oral doses of 15, 30 and 60 mg/kg/day and 15, 45 and 90 mg/kg/day, respectively. The highest doses produced a systemic exposure to palonosetron (Plasma AUC) of 137 and 308 times the human exposure at the recommended dose. Treatment with palonosetron produced increased incidences of adrenal benign pheochromocytoma and combined benign and malignant pheochromocytoma, increased incidences of pancreatic Islet cell adenoma and combined adenoma and carcinoma and pituitary adenoma in male rats. In female rats, it produced hepatocellular adenoma and carcinoma and increased the incidences of thyroid C-cell adenoma and combined adenoma and carcinoma.
Palonosetron was not genotoxic in the Ames test, the Chinese hamster ovarian cell (CHO/HGPRT) forward mutation test, the ex vivo hepatocyte unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) test or the mouse micronucleus test. It was, however, positive for clastogenic effects in the Chinese hamster ovarian (CHO) cell chromosomal aberration test.
Palonosetron HCl at oral doses up to 60 mg/kg/day (about 1894 times the recommended human intravenous dose based on body surface area) was found to have no effect on fertility and reproductive performance of male and female rats.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with MEC and HEC in Adults
Efficacy of a single intravenous dose of palonosetron HCl injection in preventing acute and delayed nausea and vomiting associated with MEC or HEC were studied in 4 trials. In these double-blind studies, complete response rates (no emetic episodes and no rescue medication) and other efficacy parameters were assessed through at least 120 hours after administration of chemotherapy. The safety and efficacy of palonosetron HCl injection in repeated courses of chemotherapy was also assessed.
Moderately Emetogenic Chemotherapy
Two double-blind trials (Study 1 and Study 2) involving 1132 patients compared a single dose of palonosetron HCl injection with either a single-dose of ondansetron (Study 1) or dolasetron (Study 2) given 30 minutes prior to MEC, including carboplatin, cisplatin ≤ 50 mg/m², cyclophosphamide < 1500 mg/m², doxorubicin > 25 mg/m², epirubicin, irinotecan, and methotrexate > 250 mg/m². Concomitant corticosteroids were not administered prophylactically in Study 1 and were only used by 4 to 6% of patients in Study 2. The majority of patients in these studies were women (77%), White (65%) and naïve to previous chemotherapy (54%). The mean age was 55 years.
Highly Emetogenic Chemotherapy
A double-blind, dose-ranging trial evaluated the efficacy of a single intravenous dose of palonosetron HCl injection from 0.3 to 90 mcg/kg (equivalent to < 0.1 mg to 6 mg fixed dose) in 161 chemotherapy-naïve adult cancer patients receiving HEC, either cisplatin ≥ 70 mg/m² or cyclophosphamide > 1100 mg/m². Concomitant corticosteroids were not administered prophylactically. Analysis of data from this trial indicates that 0.25 mg is the lowest effective dose in preventing acute nausea and vomiting associated with HEC.
A double-blind trial involving 667 patients compared a single intravenous dose of palonosetron HCl injection with a single intravenous dose of ondansetron (Study 3) given 30 minutes prior to HEC, including cisplatin ≥ 60 mg/m², cyclophosphamide > 1500 mg/m², and dacarbazine. Corticosteroids were co-administered prophylactically before chemotherapy in 67% of patients. Of the 667 patients, 51% were women, 60% White, and 59% naïve to previous chemotherapy. The mean age was 52 years.
Efficacy Results
Studies 1, 2 and 3 show that palonosetron HCl injection was effective in the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of MEC and HEC in the acute phase (0 to 24 hours) [ Table 5]. Clinical superiority over other 5-HT 3 receptor antagonists has not been adequately demonstrated in the acute phase. In Study 3, efficacy was greater when prophylactic corticosteroids were administered concomitantly.
Studies 1 and 2 show that palonosetron HCl injection was effective in the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat course of MEC in the delayed phase (24 to 120 hours) [Table 6] and overall phase (0 to 120 hours) [ Table 7].
Table 5: Prevention of Acute Nausea and Vomiting (0 to 24 Hours) in Adults with Nausea and Vomiting Associated with MEC or HEC in Studies 1, 2 and 3: Complete Response Rates
|
Chemotherapy |
Study |
Treatment Group |
N * |
% with Complete Response |
p-value † | 97.5% Confidence Interval
Palonosetron HCl injection minus Comparator ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Moderately
|
1 |
Palonosetron HCl Injection
|
189 |
81 |
0.009 | 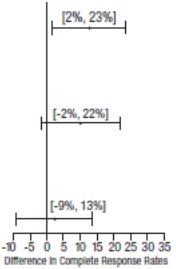 |
|
Ondansetron
|
185 |
69 |
||||
|
2 |
Palonosetron HCl Injection
|
189 |
63 |
NS |
||
|
Dolasetron 100 mg intravenously |
191 |
53 |
||||
|
Highly
|
3 |
Palonosetron HCl injection
|
223 |
59 |
NS |
|
|
Ondansetron 32 mg intravenously |
221 |
57 |
||||
Table 6: Prevention of Delayed Nausea and Vomiting (24 to 120 Hours) Associated with MEC in Adults in Studies 1 and 2: Complete Response Rates
|
Chemotherapy |
Study |
Treatment Group |
N * |
% with Complete Response |
p-value † | 97.5% Confidence Interval
Palonosetron HCl injection minus Comparator 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
|
Moderately
|
1 |
Palonosetron HCl injection
|
189 |
74 |
<0.001 | 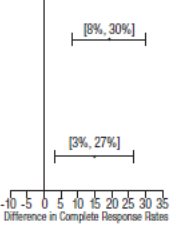 |
|
Ondansetron 32 mg intravenously ‡ |
185 |
55 |
||||
|
2 |
Palonosetron HCl injection 0.25 mg intravenously |
189 |
54 |
0.004 |
||
|
Dolasetron 100 mg intravenously |
191 |
39 |
||||
Table 7: Prevention of Overall Nausea and Vomiting (0 to 120 Hours) Associated with MEC in Adults in Studies 1 and 2: Complete Response Rates
| Chemotherapy | Study | Treatment
Group | N* | % with
Complete Response | p-value† | 97.5% Confidence Interval
Palonosetron HCl injection minus Comparator 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
|
Moderately Emetogenic |
1 |
Palonosetron HCl injection 0.25 mg intravenously |
189 |
69 |
<0.001 | 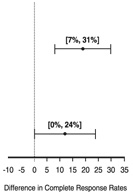 |
|
Ondansetron 32 mg intravenously ‡ |
185 |
50 |
||||
|
2 |
Palonosetron HCl injection 0.25 mg intravenously |
189 |
46 |
0.021 |
||
|
Dolasetron 100 mg intravenously |
191 |
34 |
||||
14.2 Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with Emetogenic Chemotherapy, Including HEC in Pediatric Patients
One double-blind, active-controlled clinical trial was conducted in pediatric cancer patients. The total population (N=327) had a mean age of 8.3 years (range 2 months to 16.9 years) and were 53% male; and 96% white. Patients were randomized and received a 20 mcg/kg (maximum 1.5 mg) intravenous infusion of palonosetron HCl injection 30 minutes prior to the start of emetogenic chemotherapy (followed by placebo infusions 4 and 8 hours after the dose of palonosetron HCl injection) or 0.15 mg/kg of intravenous ondansetron 30 minutes prior to the start of emetogenic chemotherapy (followed by ondansetron 0.15 mg/kg infusions 4 and 8 hours after the first dose of ondansetron, with a maximum total dose of 32 mg). Emetogenic chemotherapies administered included doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide (<1500 mg/m 2), ifosfamide, cisplatin, dactinomycin, carboplatin, and daunorubicin. Adjuvant corticosteroids, including dexamethasone, were administered with chemotherapy in 55% of patients.
Complete Response in the acute phase of the first cycle of chemotherapy was defined as no vomiting, no retching, and no rescue medication in the first 24 hours after starting chemotherapy. Efficacy was based on demonstrating non-inferiority of intravenous palonosetron HCl injection compared to intravenous ondansetron. Non-inferiority criteria were met if the lower bound of the 97.5% confidence interval for the difference in Complete Response rates of intravenous palonosetron HCl injection minus intravenous ondansetron was larger than -15%. The non-inferiority margin was 15%.
Efficacy Results
As shown in Table 8, intravenous palonosetron 20 mcg/kg (maximum 1.5 mg) demonstrated non-inferiority to the active comparator during the 0 to 24 hour time interval.
Table 8. Prevention of Acute Nausea and Vomiting (0 to 24 hours) Associated with Emetogenic Chemotherapy in Pediatric Patients: Complete Response Rates
|
Ondansetron 0.15 mg/kg for 3 intravenous doses (N=162) |
|
|
59.4% |
58.6% |
0.36% [-11.7%, 12.4%] |
*To adjust for multiplicity of treatment groups, a lower-bound of a 97.5% confidence interval was used to compare to -15%, the negative value of the non-inferiority margin.
In patients that received palonosetron HCl injection at a lower dose than the recommended dose of 20 mcg/kg, non-inferiority criteria were not met.
14.3 Prevention of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting in Adults
In a multicenter, randomized, stratified, double-blind, parallel-group, clinical trial, palonosetron HCl injection was compared to placebo for PONV in 546 patients undergoing abdominal and gynecological surgery. All patients received general anesthesia. The trial was conducted predominantly in the US in the out-patient setting for patients undergoing elective gynecologic or abdominal laparoscopic surgery and stratified at randomization for the following risk factors: gender, non-smoking status, history of PONV and/or motion sickness.
Patients were randomized to receive a single dose of palonosetron HCl injection 0.025 mg, 0.050 mg or 0.075 mg or placebo, each given intravenously immediately prior to induction of anesthesia. Antiemetic activity of was evaluated during the 0 to 72-hour time period after surgery.
Of the 138 patients treated with palonosetron HCl injection 0.075 mg and evaluated for efficacy, 96% were women; 66% had a history of PONV or motion sickness; 85% were non-smokers. As for race, 63% were White, 20% were Black, 15% were Hispanic, and 1% were Asian. The age of patients ranged from 21 to 74 years, with a mean age of 38 years. Three patients were greater than 65 years of age.
Co-primary efficacy measures were Complete Response (CR) defined as no emetic episode and no use of rescue medication in 0 to 24 hours and 24 to 72 hours postoperatively.
Secondary efficacy endpoints included:
- Complete Response (CR) 0 to 48 hours and 0 to 72 hours
- Complete Control (CC) defined as CR and no more than mild nausea
- Severity of nausea (none, mild, moderate, severe)
The primary hypothesis was that at least one of the three palonosetron doses were superior to placebo.
Complete Response Rates for palonosetron HCl injection 0.075 mg and placebo in this trial are described in the Table 9.
| Treatment | n/N (%) | Palonosetron HCl injection Vs Placebo | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Δ | p-value* | ||
|
Co-primary Endpoints |
|||
|
Complete Response Rate (0 to 24 hours) |
|||
|
Palonosetron HCl injection 0.075 mg intravenously |
59/138 (42.8%) |
16.8% |
0.004 |
|
Placebo |
35/135 (25.9%) | ||
|
Complete Response Rate (24 to 72 hours) |
|||
|
Palonosetron HCl injection 0.075 mg intravenously |
67/138 (48.6%) |
7.8% |
0.188 |
|
Placebo |
55/135 (40.7%) | ||
- *To reach statistical significance for each co-primary endpoint, the required significance limit for the lowest p-value was p<0.017.
- Δ Difference (%): palonosetron 0.075 mg minus placebo
Palonosetron HCl injection as a single dose of 0.075 mg reduced the severity of nausea compared to placebo. Analyses of other secondary endpoints indicate that Palonosetron HCl injection 0.075 mg was numerically better than placebo, however, statistical significance was not formally demonstrated.
A randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, dose ranging study was performed to evaluate palonosetron HCl injection for PONV following abdominal or vaginal hysterectomy. Five intravenous doses (0.1, 0.3, 1.0, 3.0 and 30 mcg/kg) were evaluated in a total of 381 intent-to-treat patients. The primary efficacy measure was the proportion of patients with CR in the first 24 hours after recovery from surgery. The lowest effective dose was palonosetron HCl injection 1 mcg/kg (approximately 0.075 mg) which had a CR rate of 44% versus 19% for placebo, p=0.004 and significantly reduced the severity of nausea versus placebo, p=0.009.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Palonosetron HCl injection is supplied as a sterile, clear and colorless solution:
NDC 0781-3312-75:
0.25 mg palonosetron in 5 mL (0.05 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial individually packaged in a carton.
Storage
- Store at controlled room temperature of 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Protect from freezing.
- Protect from light.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients that hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock, have been reported in patients with or without known hypersensitivity to other 5-HT 3 receptor antagonists. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if any signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction occur with administration of palonosetron HCl injection [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1) ].
Serotonin Syndrome
Advise patients of the possibility of serotonin syndrome, especially with concomitant use of palonosetron HCl injection and another serotonergic agent such as medications to treat depression and migraines. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if the following symptoms occur: changes in mental status, autonomic instability, neuromuscular symptoms with or without gastrointestinal symptoms [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) ].
46238557
Distributed by
Sandoz Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540
PATIENT INFORMATION
Palonosetron HCl Injection for Intravenous Use
(pal oh noe' se tron)
Read this Patient Information before you receive palonosetron HCl injection and each time you receive palonosetron HCl injection. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is palonosetron HCl injection?
Palonosetron HCl injection is a prescription medicine called an “antiemetic”.
Palonosetron HCl injection is used in adults to help prevent the nausea and vomiting that happens:
- right away or later with certain anti-cancer medicines (chemotherapy)
- up to 24 hours while recovering from anesthesia after surgery
Palonosetron HCl injection is used in children 1 month old to less than 17 years of age to help prevent the nausea and vomiting that happens right away with certain anti-cancer medicines (chemotherapy).
- It is not known if palonosetron HCl injection is safe and effective in children less than 1 month old to help prevent nausea and vomiting after chemotherapy.
- It is not known if palonosetron HCl injection is safe and effective in children for the prevention of nausea and vomiting while recovering from anesthesia after surgery.
Who should not receive palonosetron HCl injection?
Do not receive palonosetron HCl injection if you are allergic to palonosetron hydrochloride or any of the ingredients in palonosetron HCl injection. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in palonosetron HCl injection.
What should I tell my doctor before receiving palonosetron HCl injection?
Before receiving palonosetron HCl injection, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have had an allergic reaction to another medicine for nausea or vomiting.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if palonosetron HCl injection will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if palonosetron HCl injection passes into your breast milk or if it will affect your baby or your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you will receive palonosetron HCl injection.
- Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
- Palonosetron HCl injection and certain other medicines can affect each other, causing serious side effects.
How will I receive palonosetron HCl injection?
- Palonosetron HCl injection will be given to you in your vein by intravenous (I.V.) injection.
- Palonosetron HCl injection is usually given about 30 minutes before you receive your anti-cancer medicine (chemotherapy) or right before anesthesia for surgery.
What are the possible side effects of palonosetron HCl injection?
Palonosetron HCl injection may cause serious side effects, including:
- Serious allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis. Get emergency medical help right away if you get any of the following symptoms.
- hives
- swollen face
- breathing trouble
- chest pain
-
Serotonin Syndrome. A possible life threatening problem called serotonin syndrome can happen with medicines called 5-HT
3 receptor antagonists, including palonosetron HCl injection, especially when used with medicines used to treat depression and migraine headaches called serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and certain other medicines. Tell your doctor or nurse right away if you have any of the following symptoms of serotonin syndrome:
- agitation, seeing things that are not there (hallucinations), confusion, or coma
- fast heartbeat or unusual and frequent changes in your blood pressure
- dizziness, sweating, flushing, or fever
- tremors, stiff muscles, muscle twitching, overactive reflexes, or loss of coordination
- seizures
- nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
The most common side effects in adults who receive palonosetron HCl injection to help prevent nausea and vomiting that happens with certain anti-cancer medicine (chemotherapy) include: headache and constipation.
The most common side effects in adults who receive palonosetron HCl injection to help prevent nausea and vomiting that happens while recovering from anesthesia after surgery include: serious or life-threatening heart rhythm changes (QT prolongation), slow heartbeat, headache, and constipation.
These are not all the possible side effects from palonosetron HCl injection.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of palonosetron HCl injection.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet.
You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about palonosetron HCl injection that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in palonosetron HCl injection?
Active ingredient: palonosetron hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: mannitol, disodium edetate, and citrate buffer in water. Hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide may have been added to adjust pH.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: April 2020
46238557
Distributed by
Sandoz Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540