FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Tranexamic Acid Tablets are indicated for the treatment of cyclic heavy menstrual bleeding in females of reproductive potential [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Testing Prior to Tranexamic Acid Tablets Administration
Prior to prescribing tranexamic acid tablets, exclude endometrial pathology that can be associated with heavy menstrual bleeding.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of tranexamic acid tablets for patients with normal renal function is 1300 mg orally three times daily (3900 mg/day) for a maximum of 5 days during monthly menstruation. Tranexamic acid tablets may be administered with or without food. Swallow tablets whole; do not chew or break apart.
2.3 Dosage Recommendations in Patients with Renal Impairment
The recommended dosage (for a maximum of 5 days during monthly menstruation) in patients with renal impairment with serum creatinine concentration higher than 1.4 mg/dL is described in Table 1.
Table 1. Recommended Dosage of Tranexamic Acid Tablets in Patients with Renal Impairment
|
Serum Creatinine (mg/dL) |
Recommended Dosage |
Total Daily Dose |
|
Above 1.4 and ≤ 2.8 |
1300 mg two times a day |
2600 mg |
|
Above 2.8 and ≤ 5.7 |
1300 mg once a day |
1300 mg |
|
Above 5.7 |
650 mg once a day |
650 mg |
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 650 mg white to off-white, oval, unscored tablets debossed with “AMG229” on one side with the other side blank.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Thromboembolic Risk
Tranexamic acid tablets are contraindicated in females of reproductive potential who are [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]:
- •
- Using combined hormonal contraception
- •
- Known to have any of the following conditions:
- o
- Active thromboembolic disease (e.g., deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or cerebral thrombosis)
- o
- A history of thrombosis or thromboembolism, including retinal vein or artery occlusion
- o
- An intrinsic risk of thrombosis or thromboembolism (e.g., thrombogenic valvular disease, thrombogenic cardiac rhythm disease, or hypercoagulopathy)
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thromboembolic Risk
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism, as well as cases of retinal artery and retinal vein occlusions, have been reported with tranexamic acid.
Retinal venous and arterial occlusion have been reported in patients using tranexamic acid. Patients should be instructed to report visual and ocular symptoms promptly. In the event of such symptoms, patients should be instructed to discontinue tranexamic acid tablets immediately and should be referred to an ophthalmologist for a complete ophthalmic evaluation, including dilated retinal examination, to exclude the possibility of retinal venous or arterial occlusion.
Concomitant Use of Hormonal Contraceptives
Combined hormonal contraceptives are known to increase the risk of venous thromboembolism, as well as arterial thromboses such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Because tranexamic acid is antifibrinolytic, the risk of venous thromboembolism, as well as arterial thromboses such as stroke, may increase further when combined hormonal contraceptives are administered with tranexamic acid tablets. This is of particular concern in women who are obese or smoke cigarettes, especially smokers over 35 years of age.
Women using combined hormonal contraception were excluded from the clinical trials supporting the safety and efficacy of tranexamic acid, and there are no clinical trial data on the risk of thrombotic events with the concomitant use of tranexamic acid tablets with combined hormonal contraceptives. However, there have been US postmarketing reports of venous and arterial thrombotic events in women who have used tranexamic acid tablets concomitantly with combined hormonal contraceptives. For this reason, concomitant use of tranexamic acid tablets with combined hormonal contraceptives is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4.1) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Concomitant Use with Factor IX Complex Concentrates or Anti-Inhibitor Coagulant Concentrates
Tranexamic acid tablets are not recommended in patients taking either Factor IX complex concentrates or anti-inhibitor coagulant concentrates because the risk of thrombosis may be increased [see Drug Interactions (7.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Patients with Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Taking Concomitant All-Trans Retinoic Acid (Oral Tretinoin)
Tranexamic acid tablets are not recommended in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia taking all-trans retinoic acid for remission induction because of possible exacerbation of the procoagulant effect of all-trans retinoic acid [see Drug Interactions (7.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.2 Severe Allergic Reactions
A case of severe allergic reaction to tranexamic acid was reported in the clinical trials, involving a subject who experienced dyspnea, tightening of her throat, and facial flushing that required emergency medical treatment. A case of anaphylactic shock has also been reported in the literature, involving a patient who received an intravenous bolus of tranexamic acid. Tranexamic acid tablets are contraindicated in females of reproductive potential with known hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Adverse Reactions in Short-term Studies
The safety of tranexamic acid in the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding in females of reproductive potential was studied in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies [see Clinical Studies (14)].
- •
- Study 1 compared the effects of two doses of tranexamic acid tablets (1950 mg and 3900 mg per day for up to 5 days during each menstrual period) versus placebo over a 3-cycle treatment duration. A total of 304 women were randomized to this study, with 115 receiving at least one dose of 3900 mg/day of tranexamic acid tablets.
- •
- Study 2 compared the effects of tranexamic acid tablets (3900 mg/day) versus placebo over a 6-cycle treatment duration. A total of 196 women were randomized to this study, with 117 receiving at least one dose of tranexamic acid tablets.
Across the studies, the combined exposure to 3900 mg/day tranexamic acid tablets was 947 cycles and the average duration of use was 3.4 days per cycle. In both studies, subjects were generally healthy women who had menstrual blood loss of ≥ 80 mL. In these studies, subjects were 18 to 49 years of age with a mean age of approximately 40 years, had cyclic menses every 21-35 days, and a body mass index (BMI) of approximately 32 kg/m2. On average, subjects had a history of heavy menstrual bleeding for approximately 10 years and 40% had fibroids as determined by transvaginal ultrasound. Approximately 70% were Caucasian, 25% were Black, and 5% were Asian, Native American, Pacific Islander, or Other. Seven percent (7%) of all subjects were of Hispanic origin. Women using hormonal contraception were excluded from the trials.
A list of adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 5% of subjects and more frequently in tranexamic acid-treated subjects receiving 3900 mg/day compared to placebo-treated subjects is provided in Table 2.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions* Reported in Women with Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Studies 1 and 2)
|
Tranexamic Acid Tablets |
Placebo |
|
|
Number of Subjects with at Least One Adverse Reaction |
208 (89.7%) |
122 (87.8%) |
|
Headache a |
117 (50.4%) |
65 (46.8%) |
|
Nasal & sinus symptoms b |
59 (25.4%) |
24 (17.3%) |
|
Back pain |
48 (20.7%) |
21 (15.1%) |
|
Abdominal pain c |
46 (19.8%) |
25 (18.0%) |
|
Musculoskeletal pain d |
26 (11.2%) |
4 (2.9%) |
|
Arthralgia e |
16 (6.9%) |
7 (5.0%) |
|
Muscle cramps & spasms |
15 (6.5%) |
8 (5.8%) |
|
Migraine |
14 (6.0%) |
8 (5.8%) |
|
Anemia |
13 (5.6%) |
5 (3.6%) |
|
Fatigue |
12 (5.2%) |
6 (4.3%) |
- * Adverse reactions that were reported by ≥ 5% of tranexamic acid-treated subjects and more frequently in tranexamic acid-treated subjects compared to placebo-treated subjects
a Includes headache and tension headache
b Nasal and sinus symptoms include nasal, respiratory tract and sinus congestion, sinusitis, acute sinusitis, sinus headache, allergic sinusitis and sinus pain, and multiple allergies and seasonal allergies
c Abdominal pain includes abdominal tenderness and discomfort
d Musculoskeletal pain includes musculoskeletal discomfort and myalgia
e Arthralgia includes joint stiffness and swelling
Adverse Reactions in Long-term Studies
Long-term safety of tranexamic acid was studied in two open-label studies. In one study, subjects with physician-diagnosed heavy menstrual bleeding (not using the alkaline hematin methodology) were treated with 3900 mg/day for up to 5 days during each menstrual period for up to 27 menstrual cycles. A total of 781 subjects were enrolled and 239 completed the study through 27 menstrual cycles. A total of 12.4% of the subjects withdrew due to adverse reactions. Women using hormonal contraception were excluded from the study. The total exposure in this study to 3900 mg/day tranexamic acid tablets was 10,213 cycles. The average duration of tranexamic acid tablet use was 2.9 days per cycle.
A long-term open-label extension study of subjects from the two short-term efficacy studies was also conducted in which subjects were treated with 3900 mg/day for up to 5 days during each menstrual period for up to 9 menstrual cycles. A total of 288 subjects were enrolled and 196 subjects completed the study through 9 menstrual cycles. A total of 2.1% of the subjects withdrew due to adverse reactions. The total exposure to 3900 mg/day tranexamic acid tablets in this study was 1,956 cycles. The average duration of tranexamic acid tablet use was 3.5 days per cycle.
The types and severity of adverse reactions in these two long-term open-label trials were similar to those observed in the double-blind, placebo-controlled studies although the percentage of subjects reporting them was greater in the 27-month study, most likely because of the longer study duration.
A case of severe allergic reaction to tranexamic acid was reported in the extension trial, involving a subject on her fourth cycle of treatment, who experienced dyspnea, tightening of her throat, and facial flushing that required emergency medical treatment.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified from postmarketing experience with tranexamic acid tablets. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- •
- Eye disorders: Impaired color vision and other visual disturbances
- •
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- •
- Immune system disorders: Anaphylactic shock and anaphylactoid reactions
- •
- Nervous system disorders: Dizziness
- •
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Allergic skin reactions
- •
- Vascular disorders: Thromboembolic events (e.g., deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, cerebral thrombosis, acute renal cortical necrosis, and central retinal artery and vein obstruction); cases have been
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with tranexamic acid tablets.
7.1 Combined Hormonal Contraceptives
Because tranexamic acid is antifibrinolytic, concomitant use of combined hormonal contraception and tranexamic acid may increase the thrombotic risk associated with combined hormonal contraceptives. For this reason, concomitant use of tranexamic acid tablets with combined hormonal contraceptives is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.2 Tissue Plasminogen Activators
Concomitant therapy with tissue plasminogen activators may decrease the efficacy of both tranexamic acid and tissue plasminogen activators. Discontinue tranexamic acid tablets if a patient requires tissue plasminogen activators.
7.3 Factor IX Complex Concentrates or Anti-Inhibitor Coagulant Concentrates
Tranexamic acid tablets are not recommended in patients taking either Factor IX complex concentrates or anti-inhibitor coagulant concentrates because the risk of thrombosis may be increased [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.4 All-Trans Retinoic Acid (Oral Tretinoin)
Tranexamic acid tablets are not recommended in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia taking all-trans retinoic acid for remission induction because of possible exacerbation of the procoagulant effect of all-trans retinoic acid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Tranexamic acid tablets are not indicated for use in pregnant women. There are no available data on tranexamic acid use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Tranexamic acid crosses the placenta. Animal reproduction studies have not identified adverse developmental outcomes with oral administration of tranexamic acid to pregnant rats at doses up to 4 times the recommended human dose (see Data).
In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a rat embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study, tranexamic acid had no adverse effects on embryo- fetal development when administered during the period of organogenesis (from gestation days 6 through
17) at twice daily doses of 0, 150, 375, and 750 mg/kg (1, 2 and 4 times the recommended human oral dosage of 3900 mg/day based on body surface area (mg/m2)).
In a perinatal-postnatal developmental toxicity study in rats administered tranexamic acid from gestation day 6 through postnatal day 20 at twice daily doses of 0, 150, 375, and 750 mg/kg, no significant adverse effects on maternal behavior or body weight were observed, and no significant effects on pup viability, body weight, developmental milestones or adult fertility were observed. It was concluded that the no-observed-effect-level (NOEL) for this study was 1500 mg/kg/day in both F0 and F1 generations, which is equivalent to 4 times the recommended human oral dose of 3900 mg/day based on body surface area (mg/m2).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Tranexamic acid is present in the mother’s milk at a concentration of about one hundredth of the corresponding serum concentration (see Data). The amount of tranexamic acid a nursing infant would absorb is unknown. There are no adequate data on the effects of tranexamic acid on the breastfed infant or the effects of tranexamic acid on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for tranexamic acid tablets and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from tranexamic acid tablets or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Human Data
One hour after the last dose following a 2-day treatment course in lactating women, the milk concentration of the tranexamic acid was 1% of the peak serum concentration.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of tranexamic acid tablets have been established in females of reproductive potential. Efficacy is expected to be the same for post-menarchal females under the age of 17 as for those 17 years and older. Tranexamic acid tablets are not indicated before menarche.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Tranexamic acid tablets are indicated for females of reproductive potential and are not intended for use by postmenopausal women.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of tranexamic acid has not been studied. Because tranexamic acid is primarily eliminated via the kidneys by glomerular filtration with more than 95% excreted as unchanged in urine, the recommended dosage in patient with renal impairment is lower than the recommended dosage in patients with normal renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of tranexamic acid has not been studied. Because only a small fraction of the drug is metabolized, the recommended dosage in patients with hepatic impairment is the same as in patients with normal hepatic function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
There are no known cases of intentional overdose with tranexamic acid tablets and no subjects in the clinical program took more than 2 times the prescribed amount of tranexamic acid tablets in a 24-hour period (>7800 mg/day). However, cases of overdose of tranexamic acid have been reported. Based on these reports, symptoms of overdose may include gastrointestinal (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea); hypotensive (e.g., orthostatic symptoms); thromboembolic (arterial, venous, embolic); visual impairment; mental status changes; myoclonus; or rash. No specific information is available on the treatment of overdose with tranexamic acid. In the event of overdose, employ the usual supportive measures (e.g., clinical monitoring and supportive therapy) as dictated by the patient's clinical status.
11 DESCRIPTION
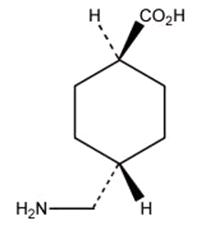
Tranexamic Acid Tablets USP are an antifibrinolytic drug administered orally. The chemical name is trans-4-aminomethyl‑cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. The structural formula is:
Tranexamic acid USP is a white crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water and in glacial acetic acid and is very slightly soluble in ethanol and practically insoluble in ether. The molecular formula is C8H15NO2 and the molecular weight is 157.2.
Tranexamic Acid Tablets USP are provided as white to off-white, oval, unscored tablets debossed with “AMG229” on one side with the other side blank. The active ingredient in each tablet is 650 mg tranexamic acid USP. The inactive ingredients contained in each tablet are: hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, colloidal silicon dioxide, stearic acid, and magnesium stearate.
The USP dissolution test is pending.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Tranexamic acid is a synthetic lysine amino acid derivative, which diminishes the dissolution of hemostatic fibrin by plasmin. In the presence of tranexamic acid, the lysine receptor binding sites of plasmin for fibrin are occupied, preventing binding to fibrin monomers, thus preserving and stabilizing fibrin’s matrix structure.
The antifibrinolytic effects of tranexamic acid are mediated by reversible interactions at multiple binding sites within plasminogen. Native human plasminogen contains 4 to 5 lysine binding sites with low affinity for tranexamic acid (Kd = 750 µmol/L) and 1 with high affinity (Kd = 1.1 µmol/L). The high affinity lysine site of plasminogen is involved in its binding to fibrin. Saturation of the high affinity binding site with tranexamic acid displaces plasminogen from the surface of fibrin. Although plasmin may be formed by conformational changes in plasminogen, binding to and dissolution of the fibrin matrix is inhibited.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Tranexamic acid, at in vitro concentrations of 25 - 100 µM, reduces by 20 - 60% the maximal rate of plasmin lysis of fibrin catalyzed by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA).
Elevated concentrations of endometrial, uterine, and menstrual blood tPA are observed in women with heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) compared to women with normal menstrual blood loss. The effect of tranexamic acid on lowering endometrial tPA activity and menstrual fluid fibrinolysis is observed in women with HMB receiving tranexamic acid total oral doses of 2-3 g/day for 5 days.
In healthy subjects, tranexamic acid at blood concentrations less than 10 mg/mL has no effect on the platelet count, the coagulation time or various coagulation factors in whole blood or citrated blood. Tranexamic acid, however, at blood concentrations of 1 and 10 mg/mL prolongs the thrombin time.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of tranexamic acid on QT interval was evaluated in a randomized, single-dose, 4-way crossover study in 48 healthy females aged 18 to 49 years. Subjects received (1) tranexamic acid tablets 1300 mg, (2) tranexamic acid tablets 3900 mg (three times the maximum recommended single dose), (3) moxifloxacin 400 mg, and (4) placebo. There was no significant increase in the corrected QT interval at any time up to 24 hours after the administration of either dose of tranexamic acid tablets. Moxifloxacin, the active control, was associated with a maximum 14.1 msec mean increase in corrected QT interval (moxifloxacin – placebo) at 3 hours after administration.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After a single oral administration of 1300 mg of tranexamic acid tablets, the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) occurred at approximately 3 hours (Tmax). The absolute bioavailability of tranexamic acid in women aged 18‑49 is approximately 45%. Following multiple oral doses (1300 mg tablets three times daily) administration of tranexamic acid tablets for 5 days, the mean Cmax increased by approximately 19% and the mean area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) remained unchanged, compared to a single oral dose administration (1300 mg). Plasma concentrations reached steady state at the 5th dose of tranexamic acid tablets on Day 2.
The mean plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of tranexamic acid determined in 19 healthy women following a single (1300 mg) and multiple (1300 mg tablets three times daily for 5 days) oral dose of tranexamic acid tablets are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Mean (CV%) Pharmacokinetic Parameters Following a Single (1300 mg) and Multiple Dose (1300 mg three times daily for 5 days) Oral Administration of Tranexamic Acid Tablets in 19 Healthy Women under Fasting Conditions
|
Parameter |
Arithmetic Mean (CV%) |
|
|
Single dose |
Multiple dose |
|
|
Cmax (mcg/mL) |
13.83 (32.14) |
16.41 (26.19) |
|
AUCtldc (mcg∙h/mL) |
77.96 (31.14) |
77.67a (29.39) |
|
AUCinf (mcg∙h/mL) |
80.19 (30.43) |
- |
|
Tmax (h)b |
2.5 (1 – 5) |
2.5 (2 – 3.5) |
|
t1/2 (h) |
11.08 (16.94) |
- |
Cmax = maximum concentration
AUCtldc = area under the drug concentration curve from time 0 to time of last determinable concentration
AUCinf = area under the drug concentration curve from time 0 to infinity
Tmax = time to maximum concentration
t1/2 = terminal elimination half-life
aAUC0-tau (mcg·h/mL) = area under the drug concentration curve from time 0 to 8 hours
bData presented as median (range)
Effect of food: Tranexamic acid tablets may be administered with or without food. A single dose administration (1300 mg) of tranexamic acid tablets with food increased both Cmax and AUC by 7% and 16%, respectively.
Distribution
Tranexamic acid is 3% bound to plasma proteins with no apparent binding to albumin. Tranexamic acid is distributed with an initial volume of distribution of 0.18 L/kg and steady-state apparent volume of distribution of 0.39 L/kg.
Tranexamic acid crosses the placenta. The concentration in cord blood after an intravenous injection of 10 mg/kg to pregnant women is about 30 mg/L, as high as in the maternal blood.
Tranexamic acid concentration in cerebrospinal fluid is about one tenth of the plasma concentration.
The drug passes into the aqueous humor of the eye achieving a concentration of approximately one tenth of plasma concentrations.
Elimination
Most elimination post intravenous administration occurred during the first 10 hours, giving an apparent elimination half-life of approximately 2 hours. The mean terminal half-life of tranexamic acid is approximately 11 hours. Plasma clearance of tranexamic acid is 110-116 mL/min.
-
Metabolism
A small fraction of the tranexamic acid is metabolized.
-
Excretion
Tranexamic acid is eliminated by urinary excretion primarily via glomerular filtration with more than 95% of the dose excreted unchanged. Excretion of tranexamic acid is about 90% at 24 hours after intravenous administration of 10 mg/kg.
Specific Populations
-
Pediatric Patients
Tranexamic acid tablets are indicated for females of reproductive age (not approved for use in premenarcheal girls). In a randomized, single dose, two-way crossover study of two dose levels (650 mg and 1,300 mg), pharmacokinetics of tranexamic acid was evaluated in 20 female adolescents (12 to 16 years of age) with heavy menstrual bleeding. The Cmax and AUC values after a single oral dose of 650 mg in the adolescent females were 32 – 36% less than those after a single oral dose of 1,300 mg in the adolescent females. The Cmax and AUC values after a single oral dose of 1300 mg in the adolescent females were 20 – 25% less than those in the adult females given the same dose in a separate study. [See Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]
-
Patients with Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the disposition of tranexamic acid has not been evaluated. Urinary excretion following a single intravenous injection of tranexamic acid declines as renal function decreases. Following a single 10 mg/kg intravenous injection of tranexamic acid in 28 patients, the 24-hour urinary fractions of tranexamic acid with serum creatinine concentrations 1.4 – 2.8, 2.8 – 5.7, and greater than 5.7 mg/dL were 51, 39, and 19%, respectively. The 24-hour tranexamic acid plasma concentrations for these patients demonstrated a direct relationship to the degree of renal impairment. Therefore, a lower dosage is needed in patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
-
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the disposition of tranexamic acid has not been evaluated. One percent and 0.5 percent of an oral dose are excreted as a dicarboxylic acid and acetylated metabolite, respectively. Because only a small fraction of the drug is metabolized, the recommended dosage in patients with hepatic impairment is the same as in patients with normal hepatic impairment.
Drug Interactions Studies
No drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with tranexamic acid.
-
All-Trans Retinoic Acid (Oral Tretinoin)
In a study involving 28 patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia who were given either orally administered (1) all-trans retinoic acid plus intravenously administered tranexamic acid, (2) all-trans retinoic acid plus chemotherapy, or (3) all-trans retinoic acid plus tranexamic acid plus chemotherapy, all 4 patients who were given all-trans retinoic acid plus tranexamic acid died, with 3 of the 4 deaths due to thrombotic complications. The procoagulant effect of all-trans retinoic acid may have been exacerbated by concomitant use of tranexamic acid. Therefore, tranexamic acid tablets are not recommended in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia taking all-trans retinoic acid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.4)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies with tranexamic acid in male mice at doses as high as 6 times the recommended human dose of 3900 mg/day showed an increased incidence of leukemia which may have been related to treatment. Female mice were not included in this experiment.
The dose multiple referenced above is based on body surface area (mg/m2). Actual daily dose in mice was up to 5000 mg/kg/day in food.
Hyperplasia of the biliary tract and cholangioma and adenocarcinoma of the intrahepatic biliary system have been reported in one strain of rats after dietary administration of doses exceeding the maximum tolerated dose for 22 months. Hyperplastic, but not neoplastic, lesions were reported at lower doses.
Subsequent long-term dietary administration studies in a different strain of rat, each with an exposure level equal to the maximum level employed in the earlier experiment, have failed to show such hyperplastic/neoplastic changes in the liver.
Mutagenesis
Tranexamic acid was neither mutagenic nor clastogenic in the in vitro Bacterial Reverse Mutation Assay (Ames test), in vitro chromosome aberration test in Chinese hamster cells, and in in vivo chromosome aberration tests in mice and rats.
Impairment of Fertility
Reproductive studies performed in mice, rats and rabbits have not revealed any evidence of impaired fertility or adverse effects on the fetus due to tranexamic acid.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Ocular Effects
In a 9-month toxicology study, dogs were administered tranexamic acid in food at doses of 0, 200, 600, or 1200 mg/kg/day. These doses are approximately 2, 5, and 6 times, respectively, the recommended human oral dose of 3900 mg/day based on AUC. At 6 times the human dose, some dogs developed reversible reddening and gelatinous discharge from the eyes. Ophthalmologic examination revealed reversible changes in the nictitating membrane/conjunctiva. In some female dogs, the presence of inflammatory exudate over the bulbar conjunctival mucosa was observed. Histopathological examinations did not reveal any retinal alteration. No adverse effects were observed at 5 times the human dose.
In other studies, focal areas of retinal degeneration were observed in cats, dogs and rats following oral or intravenous tranexamic acid doses at 6-40 times the recommended usual human dose based on mg/m2 (actual animal doses between 250-1600 mg/kg/day).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Overview of the Clinical Studies
The efficacy of tranexamic acid in the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) in women of reproductive potential was demonstrated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies: one 3-cycle treatment study (Study 1) and one 6-cycle treatment study (Study 2) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In these studies, HMB was defined as an average menstrual blood loss of ≥ 80 mL as assessed by alkaline hematin analysis of collected sanitary products over two baseline menstrual cycles. Subjects were 18 to 49 years of age with a mean age of approximately 40 years, had cyclic menses every 21-35 days, and a BMI of approximately 32 kg/m2. On average, subjects had an HMB history of approximately 10 years and 40% had fibroids as determined by transvaginal ultrasound. Approximately 70% were Caucasian, 25% were Black, and 5% were Asian, Native American, Pacific Islander, or Other. Seven percent (7%) of all subjects were of Hispanic origin.
In these studies, the primary outcome measure was menstrual blood loss (MBL), measured using the alkaline hematin method. The endpoint was change from baseline in MBL, calculated by subtracting the mean MBL during treatment from the mean pretreatment MBL. The key secondary outcome measures were based on specific questions concerning limitations in social or leisure activities (LSLA) and limitations in physical activities (LPA). Large stains (soiling beyond the undergarment) were also included as a key secondary outcome measure.
14.2 Heavy Menstrual Bleeding in the Three-Cycle Treatment Study
Study 1 compared the effects of two doses of tranexamic acid tablets (1950 mg and 3900 mg per day for up to 5 days during each menstrual period) versus placebo on MBL over a 3-cycle treatment duration. Of the 294 evaluable subjects, 115 subjects received tranexamic acid tablets 1950 mg/day, 112 subjects received tranexamic acid tablets 3900 mg/day and 67 subjects received placebo (subjects took at least one dose of study drug and had post-treatment data available).
Results are shown in Table 4. Menstrual blood loss (MBL) was statistically significantly reduced in patients treated with 3900 mg/day tranexamic acid tablets compared to placebo. Study success also required achieving a reduction in MBL that was determined to be clinically meaningful to the subjects. The 1950 mg/day tranexamic acid tablets dose did not meet the criteria for success.
Table 4. Mean Reduction from Baseline in Menstrual Blood Loss in Women with Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Study 1)
|
Treatment Arm |
N |
Baseline Mean MBL (mL) |
Least Squares Mean Reduction in MBL (mL) |
Percent Reduction in MBL |
|
Tranexamic acid tablets 3900 mg/day |
112 |
169 |
65* |
39% |
|
Tranexamic acid tablets 1950 mg/day |
115 |
178 |
44 |
25% |
|
Placebo |
67 |
154 |
7 |
5% |
* p<0.001 versus placebo
Tranexamic acid tablets also statistically significantly reduced limitations on social, leisure, and physical activities in the 3900 mg/day dose group compared to the placebo group (see Table 5). No statistically significant treatment difference was observed in response rates on the number of large stains.
Table 5: Secondary Outcomes in 3-Cycle Study in Women with Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Study 1)
|
Outcome Measure |
N |
Baseline Mean a |
Least Squares Mean Reduction b |
|
Social and Leisure Activities
Physical Activities |
|
|
|
|
N |
Responders d |
||
|
Reduction in Large Stains |
|
|
a Response categories: 1=not at all limited; 2=slightly limited; 3=moderately limited; 4=quite a bit limited; 5=extremely limited
b Positive means reflect an improvement from baseline.
c p-value <0.05 versus placebo
d Responders are defined as subjects who experienced a reduction from baseline in frequency of large stains.
e Non-significant difference versus placebo
14.3 Heavy Menstrual Bleeding in the Six-Cycle Treatment Study
Study 2 compared the effects of tranexamic acid tablets 3900 mg/day given daily for up to 5 days during each menstrual period versus placebo on menstrual blood loss (MBL) over a 6-cycle treatment duration. Of the 187 evaluable subjects, 115 subjects received tranexamic acid tablets and 72 subjects received placebo (subjects took at least one dose of study drug and had post-treatment data available).
Results are shown in Table 6. MBL was statistically significantly reduced in patients treated with 3900 mg/day tranexamic acid tablets compared to placebo. Study success also required achieving a reduction in MBL that was determined to be clinically meaningful to the subjects.
Table 6. Mean Reduction from Baseline in Menstrual Blood Loss in Women with Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Study 2)
|
Treatment Arm |
N |
Baseline Mean MBL (mL) |
Least Squares Mean Reduction in MBL (mL) |
Percent Reduction in MBL |
|
Tranexamic acid tablets 3900 mg/day |
115 |
172 |
66* |
38% |
|
Placebo |
72 |
153 |
18 |
12% |
* p<0.001 versus placebo
Limitations on social, leisure, and physical activities were also statistically significantly reduced in the tranexamic acid tablets group compared to placebo (see Table 7). No statistically significant treatment difference was observed in response rates on the number of large stains.
Table 7. Secondary Outcomes in 6-Cycle Study in Women with Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Study 2)
|
Outcome Measure |
N |
Baseline Mean a |
Least Squares Mean Reduction b |
|
Social and Leisure Activities |
|
|
|
|
N |
Responders d |
||
|
Reduction in Large Stains |
|
|
a Response categories: 1=not at all limited; 2=slightly limited; 3=moderately limited; 4=quite a bit limited; 5=extremely limited
b Positive means reflect an improvement from baseline
c p-value <0.05 versus placebo
d Responders are defined as subjects who experienced a reduction from baseline in frequency of large stains
e Non-significant difference versus placebo
14.4 Heavy Menstrual Bleeding Results over Time
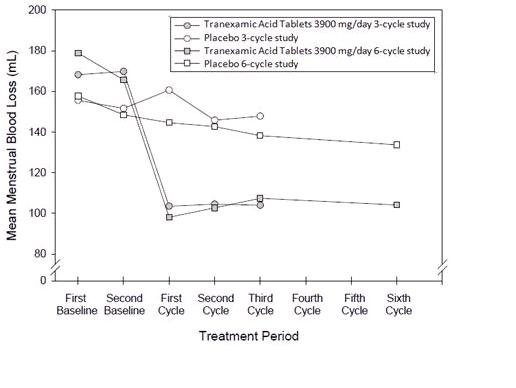
The efficacy of tranexamic acid tablets 3900 mg/day over 3 menstrual cycles and over 6 menstrual cycles was demonstrated versus placebo in Studies 1 and 2 (see Figure 1). The change in menstrual bleeding loss from baseline was similar across all post-baseline treatment cycles.
Figure 1: Menstrual Bleeding Loss Levels over Duration of Therapy in Women with Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Studies 1 and 2)
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Tranexamic Acid Tablets USP 650 mg are provided as white to off-white, oval, unscored tablets debossed with “AMG229” on one side with the other side blank.
NDC: 71335-1981-1: 8 TABLETs in a BOTTLE
NDC: 71335-1981-2: 30 TABLETs in a BOTTLE
NDC: 71335-1981-3: 4 TABLETs in a BOTTLE
Storage
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted at 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Repackaged/Relabeled by:
Bryant Ranch Prepack, Inc.
Burbank, CA 91504
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Thromboembolic Risk
Inform patients that tranexamic acid tablets may increase the risk of venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism and to contact their healthcare provider for any signs or symptoms suggestive of thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Advise patients to discontinue use of tranexamic acid tablets and promptly report visual and ocular symptoms to their health care provider as retinal venous and arterial occlusion have been reported in patients using tranexamic acid tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Severe Allergic Reactions
Inform patients that they should stop tranexamic acid tablets and seek immediate medical attention if they notice symptoms of a severe allergic reaction (e.g., shortness of breath or throat tightening) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Administration Instructions
Instruct patients to take tranexamic acid tablets only during menstruation and for a maximum of 5 days each month [see Recommended Dosage (2.1)].
Manufactured by:
Suzhou Amerigen Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
Jiangsu, China 215006
Distributed by:
ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Baudette, MN 56623
10405 Rev 01/21
PATIENT INFORMATION
Tranexamic Acid Tablets, for oral use
Read the Patient Information that comes with Tranexamic Acid Tablets before you start using the drug and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What are Tranexamic Acid Tablets?
Tranexamic Acid Tablets are a prescription medicine used to treat your heavy monthly period (menstruation) when your bleeding gets in the way of social, leisure and physical activities. Tranexamic Acid Tablets do not contain any hormones. On average, Tranexamic Acid Tablets have been shown to lower the amount of blood lost during your monthly period by about one-third, but it is not meant to stop your period.
Tranexamic Acid Tablets are taken only during your period and are not meant to treat pre-menstrual symptoms (symptoms that occur before your bleeding starts). Tranexamic Acid Tablets do not affect your fertility and cannot be used as birth control. Tranexamic Acid Tablets do not protect you against diseases that you may get if you have unprotected sex.
Tranexamic Acid Tablets have not been studied in adolescents younger than 18 years of age.
Tranexamic Acid Tablets are not for women who have already gone through menopause (post-menopausal).
Who should not take Tranexamic Acid Tablets?
Do not take Tranexamic Acid Tablets if you:
- •
- Are using a form of birth control that contains estrogen and a progestin (like a birth control pill, patch, or vaginal ring). Ask your healthcare provider before taking Tranexamic Acid Tablets if you are not sure if your birth control method contains estrogen and a progestin.
- •
- Currently have a blood clot
- •
- Have ever had a blood clot
- •
- Have been told that you are at risk of having a blood clot
- •
- Are allergic to tranexamic acid tablets or tranexamic acid
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Tranexamic Acid Tablets?
Before taking Tranexamic Acid Tablets, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including whether:
- •
- You have ever had a blood clot or been told that you are at risk of having a blood clot
- •
- You are using a form of birth control that contains estrogen and a progestin (like a birth control pill, patch, or vaginal ring). Using hormonal birth control along with Tranexamic Acid Tablets may increase your chance of having a serious blood clot, stroke, or heart attack. For this reason, do not use Tranexamic Acid Tablets if you use a form of birth control that contains estrogen and a progestin.
- •
- You are pregnant or think you may be pregnant
- •
- You are breastfeeding or plan to breast-feed. Tranexamic acid can pass into your milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take Tranexamic Acid Tablets.
- •
- The time between the start of your periods is less than 21 days or more than 35 days
- •
- You have any other medical conditions
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Tranexamic Acid Tablets and other medicines can affect each other, causing side effects. Tranexamic Acid Tablets can affect the way other medicines work and other medicines can affect how Tranexamic Acid Tablets work.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- •
- Birth control pills or other hormonal birth control
- •
- Medicines used to help your blood form clots
- •
- Medicines used to break up blood clots
- •
- Any medicines to treat leukemia
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if your medicine is one that is described above.
How should I take Tranexamic Acid Tablets?
- •
- Take Tranexamic Acid Tablets exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- •
- Do not take Tranexamic Acid Tablets until your period has started.
- •
- Do not take Tranexamic Acid Tablets for more than 5 days in a row.
- •
- Do not take Tranexamic Acid Tablets when you do not have your period.
- •
- Once your period has started, take 2 tablets of Tranexamic Acid Tablets three times per day (e.g., in the morning, afternoon, and evening).
- •
- Tranexamic Acid tablets should be swallowed whole and not chewed or broken apart.
- •
- Tranexamic Acid Tablets may be taken with or without food.
- •
- Do not take more than 6 tablets of Tranexamic Acid Tablets in a day. If you take more than 6 tablets, call your healthcare provider.
- •
- If you miss a dose, take it when you remember, and then take your next dose at least six hours later. Do not take more than two tablets at a time to make up for missed doses.
- •
- If Tranexamic Acid Tablets do not help to lessen bleeding with your periods after 2 cycles or seems to stop working, talk to your healthcare provider.
What are the possible side effects of Tranexamic Acid Tablets?
Tranexamic acid tablets can cause serious side effects, including:
- •
- Blood clots. You may have a higher risk of having serious blood clots if you take Tranexamic Acid Tablets with:
- o
- medicines used to help your blood form clots
- o
- some medicines used to treat leukemia
- •
- Eye changes. Stop taking Tranexamic Acid Tablets and promptly report any eye problems you have while taking Tranexamic Acid Tablets. Your doctor will refer you to an eye doctor who will examine your eyes.
- •
- Allergic reaction. If you have severe shortness of breath and your throat feels tight, stop taking Tranexamic Acid Tablets and get medical care right away.
The most common side effects of Tranexamic Acid Tablets include:
- •
- Headaches
- •
- Sinus and nasal problems
- •
- Back pain
- •
- Pain in your abdomen
- •
- Pain in your muscles or joints
- •
- Anemia
- •
- Fatigue
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of Tranexamic Acid Tablets. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
If you notice a change in your usual bleeding pattern that worries you, or your heavy bleeding continues, contact your healthcare provider right away. This may be a sign of a more serious condition.
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-308-6755.
How should I store Tranexamic Acid Tablets?
Store Tranexamic Acid Tablets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep Tranexamic Acid Tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about Tranexamic Acid Tablets
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in Patient Information Leaflets. Do not use Tranexamic Acid Tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Tranexamic Acid Tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This patient information leaflet summarizes the most important information about Tranexamic Acid Tablets. If you would like more information about Tranexamic Acid Tablets, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Tranexamic Acid Tablets that is written for healthcare professionals.
What are the ingredients of Tranexamic Acid Tablets?
Active ingredient: tranexamic acid
Inactive ingredients: hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, colloidal silicon dioxide, stearic acid, and magnesium stearate.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Suzhou Amerigen Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
Jiangsu, China 215006
Distributed by:
ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Baudette, MN 56623
10405 Rev 01/21