FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
2 DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution should be taken as a split-dose oral regimen.
The dose for colon cleansing requires administration of two bottles of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution. Each bottle is administered as 16 ounces of diluted Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution with an additional 1 quart of water taken orally. The total volume of liquid required for colon cleansing (using two bottles) is 3 quarts (approximately 2.8 L) taken orally prior to the colonoscopy in the following way:
Split-Dose (Two-Day) Regimen
Day prior to colonoscopy:
- A light breakfast may be consumed, or have only clear liquids on the day before colonoscopy. Avoid red and purple liquids, milk, and alcoholic beverages.
- Early in the evening prior to colonoscopy: pour the contents of one bottle of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution into the mixing container provided. Fill the container with water to the 16 ounce fill line, and drink the entire amount.
- Drink two additional containers filled to the 16 ounce line with water over the next hour.
- Have only clear liquids until after the colonoscopy. Avoid red and purple liquids, milk, and alcoholic beverages.
- The morning of colonoscopy (10 to 12 hours after the evening dose): pour the contents of the second bottle of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution into the mixing container provided. Fill the container with water to the 16 ounce fill line, and drink the entire amount.
- Drink two additional containers filled to the 16 ounce line with water over the next hour.
- Complete all Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution and required water at least two hours prior to colonoscopy or as directed by physician.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Gastrointestinal obstruction
- Bowel perforation
- Gastric retention
- Ileus
- Toxic colitis or toxic megacolon
- Known allergies to components of the kit [see Description (11)]
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Fluid and Serum Chemistry Abnormalities
Advise all patients to hydrate adequately before, during, and after the use of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution. If a patient develops significant vomiting or signs of dehydration after taking Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution, consider performing post-colonoscopy lab tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN). Fluid and electrolyte disturbances can lead to serious adverse events including cardiac arrhythmias, seizures and renal impairment.
Patients with electrolyte abnormalities should have them corrected before treatment with Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution. In addition, use caution when prescribing Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution for patients with conditions, or who are using medications, that increase the risk for fluid and electrolyte disturbances or may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmias, and renal impairment. [See Drug Interactions (7.1)]
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution can cause temporary elevations in uric acid. [See Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Uric acid fluctuations in patients with gout may precipitate an acute flare. The potential for uric acid elevation should be considered before administering Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution to patients with gout or other disorders of uric acid metabolism.
5.2 Cardiac Arrhythmias
There have been rare reports of serious arrhythmias associated with the use of ionic osmotic laxative products for bowel preparation. Use caution when prescribing Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution for patients at increased risk of arrhythmias (e.g., patients with a history of prolonged QT, uncontrolled arrhythmias, recent myocardial infarction, unstable angina, congestive heart failure, or cardiomyopathy). Pre-dose and post-colonoscopy ECGs should be considered in patients at increased risk of serious cardiac arrhythmias.
5.3 Seizures
There have been reports of generalized tonic-clonic seizures and/or loss of consciousness associated with use of bowel preparation products in patients with no prior history of seizures. The seizure cases were associated with electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia) and low serum osmolality. The neurologic abnormalities resolved with correction of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities.
Use caution when prescribing Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution for patients with a history of seizures and in patients at increased risk of seizure, such as patients taking medications that lower the seizure threshold (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants), patients withdrawing from alcohol or benzodiazepines, or patients with known or suspected hyponatremia.
5.4 Renal Impairment
Use caution when prescribing Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution for patients with impaired renal function or patients taking concomitant medications that may affect renal function (such as diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Advise these patients of the importance of adequate hydration, and consider performing baseline and post-colonoscopy laboratory tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN) in these patients.
5.5 Colonic Mucosal Ulcerations and Ischemic Colitis
Administration of osmotic laxative products may produce colonic mucosal aphthous ulcerations, and there have been reports of more serious cases of ischemic colitis requiring hospitalization. Concurrent use of stimulant laxatives and Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution may increase these risks. The potential for mucosal ulcerations resulting from the bowel preparation should be considered when interpreting colonoscopy findings in patients with known or suspect inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
5.6 Use in Patients with Significant Gastrointestinal Disease
If gastrointestinal obstruction or perforation is suspected, perform appropriate diagnostic studies to rule out these conditions before administering Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution.
Use with caution in patients with severe active ulcerative colitis.
5.7 Aspiration
Use with caution in patients with impaired gag reflex and patients prone to regurgitation or aspiration. Such patients should be observed during administration of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution.
5.8 Not for Direct Ingestion
Each bottle must be diluted with water to a final volume of 16 ounces and ingestion of additional water as recommended is important to patient tolerance. Direct ingestion of the undiluted solution may increase the risk of nausea, vomiting, dehydration, and electrolyte disturbances.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In a multicenter, controlled clinical trial comparing Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution with a bowel prep containing polyethylene glycol and electrolytes (PEG + E) that were administered in a split-dose (2-day) regimen, the most common adverse reactions after administration of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution were overall discomfort, abdominal distention, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and headache; see Table 1, below. Less common Adverse Reactions occurring were AV Block (1 case) and CK increase. In this study, patients receiving Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium
Sulfate Oral Solution were limited to a light breakfast followed by clear liquids; patients receiving the PEG + E bowel prep were allowed to have a normal breakfast and a light lunch, followed by clear liquids.
| Table 1: Treatment-Emergent Adverse Reactions Observed in at Least 2% of Patients on the Split-Dose (2-Day) Regimen
|
||
| Symptom
| Split-Dose (2-Day) Regimen
|
|
| Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution N=190 | PEG + E Product N=189 |
|
| Overall Discomfort | 54% | 67% |
| Abdominal Distension | 40% | 52% |
| Abdominal Pain | 36% | 43% |
| Nausea | 36% | 33% |
| Vomiting | 8% | 4% |
| Headache | 1.1% | 0.5% |
Table 2 shows the percentages of patients who developed new abnormalities of important electrolytes and uric acid after completing the bowel preparation with either Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution or PEG+E administered as a split-dose (2-day) regimen.
| Table 2: Patients with Normal Baseline Serum Chemistry with A Shift to an Abnormal Value While on the Split-Dose (2-Day) Regimen
|
|||
| Day of
Colonoscopy n (%)* | Day 30n
(%)* |
||
| Anion gap (high) † | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 14 (8.9) | 3 (1.9) |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 12 (7.6) | 2 (1.4) |
|
| Bicarbonate (low) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 20 (12.7) | 7 (4.4) |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 24 (15.2) | 4 (2.7) |
|
| Bilirubin, total (high) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 14 (8.5) | 0 (0) |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 20 (11.7) | 3 (1.9) |
|
| BUN (high) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 2 (1.6) | 14 (11.2) |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 4 (2.9) | 19 (14.5) |
|
| Calcium (high) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 16 (10.4) | 8 (5.2) |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 6 (3.7) | 6 (3.9) |
|
| Chloride (high) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 4 (2.4) | 6 (3.7) |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 20 (12.2) | 6 (3.8) |
|
| Creatinine (high) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 3 (1.9) | 5 (3.2) |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 2 (1.2) | 8 (5.2) |
|
| Osmolality (high) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 8 (5.8) | NA |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 19 (12.9) | NA |
|
| Osmolality (low) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 3 (2.2) | NA |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 2 (1.4) | NA |
|
| Potassium (high) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 3 (1.8) | 6 (3.7) |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 5 (2.9) | 8 (4.9) |
|
| Sodium (low) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 5 (3.1) | 1 (0.6) |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 4 (2.3) | 2 (1.2) |
|
| Uric acid (high) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution | 27 (23.5) | 13 (11.5) |
| PEG + Electrolytes | 12 (9.5) | 20 (16.7) |
|
There were also 408 patients who participated in a study in which either Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution or PEG+E were administered in an evening-only (1-day) regimen. Higher rates of overall discomfort, abdominal distention, and nausea were observed with the evening-only (1-day) regimen compared to the split-dose (2-day) regimen for both preparations. Patients treated with Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution had increased rates of vomiting with the evening-only (1-day) regimen. An evening-only (1-day) dosing regimen was associated with higher rates of abnormal values for some electrolytes when compared to the split-dose (2-day) regimen for both preparations. For Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution, the evening-only (1-day) regimen was associated with higher rates of total bilirubin (high), BUN (high), creatinine (high), osmolality (high), potassium (high) and uric acid (high) than the Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution split dose (2-day) regimen. Administration of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution in an evening-only (1-day) dosing regimen is not recommended.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs That May Increase Risks Due to Fluid and Electrolyte Abnormalities
Use caution when prescribing Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution for patients with conditions, or who are using medications, that increase the risk for fluid and electrolyte disturbances or may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmias, and prolonged QT in the setting of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities. Consider additional patient evaluations as appropriate [see Warnings (5)] in patients taking these concomitant medications.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects: Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution. It is also not known whether Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution is administered to a nursing woman.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 375 patients who received Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution in clinical trials, 94 (25%) were 65 years of age or older, and 25 (7%) were 75 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution administered as a split-dose (2-day) regimen were observed between geriatric patients and younger patients. Geriatric patients reported more vomiting when Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution was given as a one-day preparation.
11 DESCRIPTION
Each Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution contains two 6 ounce bottles of solution. Each 6 ounce bottle contains: sodium sulfate 17.5 grams, potassium sulfate 3.13 grams, magnesium sulfate 1.6 grams. Inactive ingredients include: sodium benzoate, sucralose, malic acid, citric acid, lemon flavor, purified water. The solution is a clear to slightly hazy liquid. The solution is clear and colorless when diluted to a final volume of 16 ounces with water.
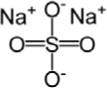
Sodium Sulfate, USP
The chemical name is Na2SO4. The average Molecular Weight is 142.04. The structural formula is:
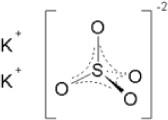
Potassium Sulfate, FCC, Granular
The chemical name is K2SO4. The average Molecular Weight is 174.26. The structural formula is:
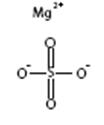
The chemical name is MgSO4. The average Molecular Weight: 120.37. The structural formula is:
Each Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution package also contains a polypropylene mixing container.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sulfate salts provide sulfate anions, which are poorly absorbed. The osmotic effect of unabsorbed sulfate anions and the associated cations causes water to be retained within the gastrointestinal tract.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The osmotic effect of the unabsorbed ions, when ingested with a large volume of water, produces a copious watery diarrhea.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Fecal excretion was the primary route of sulfate elimination. After administration of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution in six healthy volunteers, the time at which serum sulfate reached its highest point (Tmax) was approximately 17 hours after the first half dose or approximately 5 hours after the second dose, and then declined with a half-life of 8.5 hours.
The disposition of sulfate after Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution was also studied in patients (N=6) with mild-moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh grades A and B) and in patients (N=6) with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 30 to 49 mL/min). The renal impairment group had the highest serum sulfate AUC and Cmax, followed by the hepatic impairment group, and then by healthy subjects. Systemic exposure of serum sulfate (AUC and Cmax) was similar between healthy subjects and hepatic impairment patients. Renal impairment resulted in 54% higher mean AUC and 44% higher mean Cmax than healthy subjects. The mean sulfate levels of all three groups returned to their respective baseline levels by Day 6 after dose initiation. Urinary excretion of sulfate over 30 hours, starting after the first half dose, was similar between hepatic patients and normal volunteers, but was approximately 16% lower in moderate renal impairment patients than in healthy volunteers.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution. Studies to evaluate the possible impairment of fertility or mutagenic potential of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution have not been performed.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
The sulfate salts of sodium, potassium, and magnesium contained in Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution were administered orally (gavage) to rats and dogs up to 28 days up to a maximum daily dose of 5 grams/kg/day (approximately 0.9 and 3 times for rats and dogs, respectively, the recommended human dose of 44 grams/day or 0.89 grams/kg based on the body surface area). In rats, the sulfate salts caused diarrhea and electrolyte and metabolic changes, including hypochloremia, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, lower serum osmolality, and high serum bicarbonate. Significant renal changes included increased fractional sodium excretion, increased urinary sodium and potassium excretion, and alkaline urine in both males and females. In addition, creatinine clearance was significantly decreased in females at the highest dose. No microscopic renal changes were seen. In dogs, the sulfate salts caused emesis, excessive salivation, excessive drinking of water, and abnormal excreta (soft and/or mucoid feces and/or diarrhea) and increased urine pH and sodium excretion.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The colon cleansing efficacy of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution was evaluated in a randomized, single-blind, active-controlled, multicenter study. In this study, 363 adult patients were included in the efficacy analysis. Patients ranged in age from 20 to 84 years (mean age 55 years) and 54% were female. Race distribution was 86% Caucasian, 9% African-American, and 5% other.
Patients were randomized to one of the following two colon preparation regimens: Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution or a marketed polyethylene glycol (PEG) bowel prep. In the Study Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution was administered according to a split-dose preparation regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. The PEG bowel prep was also given as a split-dose preparation according to its labeled instructions. Patients receiving Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution were limited to a light breakfast followed by clear liquids on the day prior to the day of colonoscopy; patients receiving the PEG bowel prep were allowed to have a normal breakfast and a light lunch, followed by clear liquids.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with successful colon cleansing as assessed by the colonoscopists, who were not informed about the type of preparation received. In the study, no clinically or statistically significant differences were seen between the group treated with Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution and the group treated with the PEG bowel prep. See Table 3 below.
| Table 3: Colon Cleansing Response Rates
|
||||
| Treatment Group
| Regimen
| N
| Responders1
% (95% C. I.) | Sodium Sulfate, Potassium
Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution – PEG Difference (95% CI) |
| Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution (With light breakfast) | Split- Dose | 180 | 97% (94%, 99%) | 2%2
(-2%, 5%) |
| PEG bowel prep (with normal breakfast & light lunch) | Split- Dose | 183 | 96% (92%, 98%) |
|
| 1 Responders were patients whose colon preparations were graded excellent (no more than small bits of adherent feces/fluid) or good (small amounts of feces or fluid not interfering with the exam) by the colonoscopist. |
||||
| 2 Does not equal difference in tabled responder rates due to rounding effects. |
||||
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Each Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution contains:
• Two (2) 6 ounce bottles of oral solution.
• One (1) 19 ounce mixing container with a 16 ounce fill line.
Storage:
Store at 20º to 25°C (68º to 77°F). Excursions permitted between 15º to 30°C (59º to 86°F). See USP controlled room temperature.
Keep out of reach of children.
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution Package NDC 40032-700-83
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See Medication Guide and FDA -Approved Patient Labeling
17.1 Patient Counseling
• Ask patients to let you know if they have trouble swallowing or are prone to regurgitation or aspiration.
• Instruct patients that each bottle needs to be diluted in water before ingestion and that they need to drink additional water according to the instructions. Direct ingestion of the undiluted solution may increase the risk of nausea, vomiting, and dehydration.
• Inform patients that oral medications may not be absorbed properly if they are taken within one hour of starting each dose of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution.
• Tell patients not to take other laxatives while they are taking Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution.
Manufactured by:
Novel Laboratories, Inc.
Somerset, NJ 08873
P17000000104
Rev. 12/2014
Medication Guide
Sodium Sulfate (soe' dee um sul' fate), Potassium Sulfate (poe tas' ee um sul' fate) and Magnesium Sulfate ( mag nee' zee um sul' fate) Oral Solution
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate oral solution. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution?
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution and other osmotic bowel preparations can cause serious side effects, including:
Serious loss of body fluid (dehydration) and changes in blood salts (electrolytes) in your blood.
These changes can cause:
• abnormal heartbeats that can cause death
• seizures. This can happen even if you have never had a seizure.
• kidney problems
Your chance of having fluid loss and changes in body salts with Sodium Sulfate,
Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution is higher if you:
- have heart problems
- have kidney problems
- take water pills or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS)
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms of a loss of too much body fluid (dehydration) while taking Sodium Sulfate,
Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution:
- vomiting that prevents you from keeping down the additional prescribed amount of water listed in the Instructions for Use in the Patient Instructions for Use Booklet
- dizziness
- urinating less often than normal
- headache
See Section "What are the possible side effects of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium
Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution?" for more information about side effects.
What is Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral
Solution?
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution is a prescription medicine used by adults to clean the colon before a colonoscopy. Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution cleans your colon by causing you to have diarrhea. Cleaning your colon helps your healthcare provider see the inside of your colon more clearly during your colonoscopy.
It is not known if Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution is safe and effective in children
Who should not take Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution?
- Do not take Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution if your healthcare provider has told you that you have:
- a blockage in your bowel (obstruction)
- an opening in the wall of your stomach or intestine (bowel perforation)
- problems with food and fluid emptying from your stomach (gastric retention)
- a very dilated intestine (bowel)
- an allergy to any of the ingredients in Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution?
Before you take Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have heart problems
- have stomach or bowel problems
- have ulcerative colitis
- have problems with swallowing or gastric reflux
- have gout
- have a history of seizures
- are withdrawing from drinking alcohol
- have a low blood salt (sodium) level
- have kidney problems
- any other medical conditions
- are pregnant. It is not known if Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution while breastfeeding.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution may affect how other medicines work. Medicines taken by mouth may not be absorbed properly when taken within 1 hour before the start of each dose of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- medicines for blood pressure or heart problems
- medicines for kidney problems
- medicines for seizures
- water pills (diuretics)
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAID) pain medicines
- laxatives
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure if you are taking any of the medicines listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution?
See the Instructions for Use in the Patient Instructions for Use Booklet for dosing instructions. You must read, understand, and follow these instructions to take Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution the right way.
- Take Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Do not drink Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution that has not been mixed with water (diluted), it may increase your risk of nausea, vomiting and fluid loss (dehydration).
- Each bottle of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution must be mixed with water (diluted) before drinking.
- It is important for you to drink the additional prescribed amount of water listed in the Instructions for Use to prevent fluid loss (dehydration).
- Do not take other laxatives while taking sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution.
- Do not eat solid foods while taking Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution. Only clear liquids are allowed while taking Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution.
What are the possible side effects of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution?
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution can cause
serious side effects, including:
- See Section "What is the most important information I should know about Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution?"
- changes in certain blood tests. Your healthcare provider may do blood tests after you take Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution to check your blood for changes. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any symptoms of too much fluid loss, including:
- vomiting
- nausea
- bloating
- dizziness
- stomach (abdominal) cramping
- headache
- urinate less than usual
- trouble drinking clear liquid
- heart problems. Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution may cause irregular heartbeats.
- seizures
- ulcers of the bowel or bowel problems
- worsening gout
The most common side effects of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium
Sulfate Oral Solution include:
- discomfort
- bloating
- stomach (abdominal) cramping
- nausea
- vomiting
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to
FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution?
- Store Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution at room temperature, between 59ºF to 86°F (15ºC to 30°C).
Keep Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution to other people, even if they are going to have the same procedure you are. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes important information about Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information, call 1-866-403-7592
What are the ingredients in Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution?
Active ingredients: sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate
Inactive ingredients: sodium benzoate, sucralose, malic acid, citric acid, lemon flavor, purified water
Novel Laboratories, Inc.
Somerset, NJ 08873, USA
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
PI7000000104
Revised 12/2014
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 40032-700-02
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate And Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution
17.5 g/3.13 g/1.6 g per 6 ounces
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
This bottle contains 6 ounces (177 mL) of solution
Directions:
Dilute the solution concentrate prior to use. See enclosed booklet for complete dosage and administration instructions. Both 6-ounce bottles are required for a complete prep.
Keep this and other drugs out of reach of children. Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F).

NDC 40032-700-83
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate And Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution
17.5 g/3.13 g/1.6 g per 6 ounces
This carton contains:
2 6-ounce (177 mL) bottles of solution
(1 )19 ounce mixing container with a 16 ounce fill line.
Booklet includes:
1- Medication Guide3
2- Patient Instructions
3- Full Prescribing Information
Dilute the solution concentrate as directed prior to use.
Both 6-ounce bottles are required for a complete prep.
Store at 25°C (77°F): excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F).
RX only
Panel 1 and 2


NDC 40032-700-83
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate And Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution
17.5 g/3.13 g/1.6 g per 6 ounces
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
This carton contains 2 6- ounce bottles of liquid bowel prep; and
1 16- ounce mixing container.
Directions:
Dilute the solution concentrate prior to use. See enclosed booklet for complete dosage and administration instructions. Both 6-ounce bottles are required for a complete prep.
Keep this and other drugs out of reach of children. Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F).
