DESCRIPTION
Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution contains clindamycin phosphate, USP, at a concentration equivalent to 10 mg clindamycin per milliliter.
Clindamycin phosphate is a water-soluble ester of the semi-synthetic antibiotic produced by a 7(S) - chloro-substitution of the 7(R)-hydroxyl group of the parent antibiotic lincomycin. The solution contains isopropyl alcohol 50% v/v, propylene glycol, sodium hydroxide, and water. The structural formula is represented below:
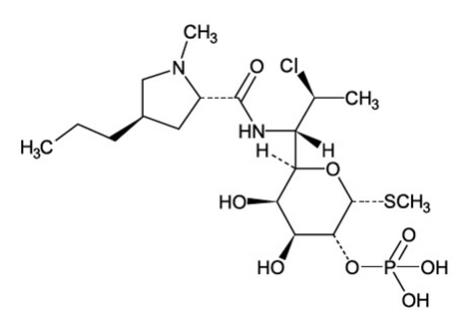
The chemical name for clindamycin phosphate is Methyl-7-chloro-6,7,8-trideoxy-6-(1-methyl- trans-4- propyl-L-2-pyrrolidinecarboxamido)-1-thio-L- threo-α-D- galacto-octopyranoside 2-(dihydrogen phosphate).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of clindamycin in treating acne vulgaris is unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
Following multiple topical applications of clindamycin phosphate at a concentration equivalent to 10 mg clindamycin per mL in an isopropyl alcohol and water solution, very low levels of clindamycin are present in the serum (0–3 ng/mL) and less than 0.2% of the dose is recovered in urine as clindamycin.
Although clindamycin phosphate is inactive in vitro, rapid in vivo hydrolysis converts this compound to the antibacterially active clindamycin.
Microbiology
Clindamycin inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 23S RNA of the 50S subunit of the ribosome. Clindamycin is bacteriostatic.
Antimicrobial Activity
Clindamycin is active in vitro against most isolates of Propionibacterium acnes; however, the clinical significance is unknown.
Resistance
Resistance to clindamycin is most often caused by modification of specific bases of the 23S ribosomal RNA. Cross-resistance between clindamycin and lincomycin is complete. Because the binding sites for these antibacterial drugs overlap, cross-resistance is sometimes observed among lincosamides, macrolides and streptogramin B. Macrolide inducible resistance to clindamycin occurs in some isolates of macrolide-resistant bacteria.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution USP, 1% is indicated in the treatment of acne vulgaris. In view of the potential for diarrhea, bloody diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis, the physician should consider whether other agents are more appropriate. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution USP, 1% is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to preparations containing clindamycin or lincomycin, a history of regional enteritis or ulcerative colitis, or a history of antibiotic-associated colitis.
WARNINGS
Orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been associated with severe colitis which may result in patient death. Use of the topical formulation of clindamycin results in absorption of the antibiotic from the skin surface. Diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported with the use of topical and systemic clindamycin.
Studies indicate a toxin(s) produced by clostridia is one primary cause of antibiotic-associated colitis. The colitis is usually characterized by severe persistent diarrhea and severe abdominal cramps and may be associated with the passage of blood and mucus. Endoscopic examination may reveal pseudomembranous colitis. Stool culture for Clostridium difficile and s tool assay for C. difficile toxin may be helpful diagnostically.
When significant diarrhea occurs, the drug should be discontinued. Large bowel endoscopy should be considered to establish a definitive diagnosis in cases of severe diarrhea.
Antiperistaltic agents such as opiates and diphenoxylate with atropine may prolong and/or worsen the condition. Vancomycin has been found to be effective in the treatment of antibiotic- associated pseudomembranous colitis produced by Clostridium difficile. The usual adult dosage is 500 milligrams to 2 grams of vancomycin orally per day in three to four divided doses administered for 7 to 10 days. Choles tyramine or coles tipol res ins bind vancomycin in vitro. If both a resin and vancomycin are to be administered concurrently, it may be advisable to separate the time of administration of each drug.
Diarrhea, colitis, and pseudomembranous colitis have been observed to begin up to several weeks following cessation of oral and parenteral therapy with clindamycin.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution USP, 1% contains an alcohol base which will cause burning and irritation of the eye. In the event of accidental contact with sensitive surfaces (eye, abraded skin, mucous membranes), bathe with copious amounts of cool tap water. The solution has an unpleasant taste and caution should be exercised when applying medication around the mouth.
Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution USP, 1% should be prescribed with caution in atopic individuals.
Drug Interactions
Clindamycin has been shown to have neuromuscular blocking properties that may enhance the action of other neuromuscular blocking agents. Therefore it should be used with caution in patients receiving such agents.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects
In clinical trials with pregnant women, the systemic administration of clindamycin during the second and third trimesters has not been associated with an increased frequency of congenital abnormalities. There are no adequate studies in pregnant women during the first trimester of pregnancy. Clindamycin should be used during the first trimester of pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether clindamycin is excreted in human breast milk following use of Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution. Clindamycin has been reported to appear in human breast milk in ranges from <0.5 to 3.8 µg/mL following systemic use. Clindamycin has the potential to cause adverse effects on the breastfed infant's gastrointestinal flora. If oral or intravenous clindamycin is required by a nursing mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding, but an alternate drug may be preferred. Monitor the infant for possible adverse effects on the gastrointestinal flora, such as diarrhea, candidiasis (thrush, diaper rash) or rarely, blood in the stool indicating possible antibiotic-associated colitis.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for clindamycin and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from clindamycin or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under the age of 12 have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies for Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution did not include sufficient number of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in response between the elderly and younger patients.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In 18 clinical studies of various formulations of Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution using placebo vehicle and/or active comparator drugs as controls, patients experienced a number of treatment emergent adverse dermatologic events [see table below].
Number of Patients Reporting Event
| Treatment Emergent Adverse Event | Solution n=553(%) |
| Burning | 62 (11) |
| Itching | 36 (7) |
| Burning/Itching | 60 (11) |
| Dryness | 105 (19) |
| Erythema | 86 (16) |
| Oiliness/Oily Skin | 8 (1) |
| Peeling | 61 (11) |
Orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been associated with severe colitis which may end fatally.
Cases of diarrhea, bloody diarrhea and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported as adverse reactions in patients treated with oral and parenteral formulations of clindamycin and rarely with topical clindamycin (see WARNINGS).
Abdominal pain, gastrointestinal disturbances, gram-negative folliculitis, eye pain and contact dermatitis have also been reported in association with the use of topical formulations of clindamycin.
OVERDOSAGE
Topically applied Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution can be absorbed in sufficient amounts to produce systemic effects (see WARNINGS).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply a thin film of Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution USP, 1% twice daily to affected area. Keep all liquid dosage forms in containers tightly closed.
HOW SUPPLIED
Clindamycin Phosphate Topical Solution USP, 1% containing clindamycin phosphate equivalent to 10 mg clindamycin per milliliter is available in the following size:
60 mL applicator bottle – NDC – 10135-0691-61
Store at controlled room temperature 20 to 25 °C (68 to 77 °F) [see USP]. Protect from freezing.
Rx only
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or
www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Manufactured for & Distributed by:
Marlex Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
New Castle, DE 19720
Rev. 02/20 GH