DESCRIPTION
Terconazole Vaginal Cream 0.8% is a white to off-white, water washable cream for intravaginal administration containing 0.8% of the antifungal agent terconazole, cis-1-[p-[[2-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-4-isopropylpiperazine, compounded in a cream base consisting of butylated hydroxyanisole, cetyl alcohol, isopropyl myristate, polysorbate 60, polysorbate 80, propylene glycol, stearyl alcohol, and purified water.
The structural formula of terconazole is as follows:
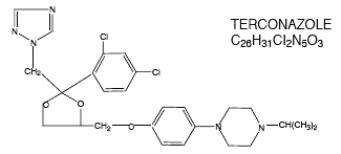
Terconazole, a triazole derivative, is a white to almost white powder with a molecular weight of 532.47. It is insoluble in water; sparingly soluble in ethanol; and soluble in butanol.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Following intravaginal administration of terconazole in humans, absorption ranged from 5-8% in three hysterectomized subjects and 12-16% in two non-hysterectomized subjects with tubal ligations.
Following daily intravaginal administration of 0.8% terconazole 40 mg (0.8% cream × 5 g) for seven days to normal humans, plasma concentrations were low and gradually rose to a daily peak (mean of 5.9 ng/mL or 0.006 mcg/mL) at 6.6 hours.
Results from similar studies in patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis indicate that the slow rate of absorption, the lack of accumulation, and the mean peak plasma concentrations of terconazole was not different from that observed in healthy women. The absorption characteristics of terconazole 0.8% in pregnant or non-pregnant patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis were also similar to those found in normal volunteers.
Following oral (30 mg) administration of 14C-labelled terconazole, the harmonic half-life of elimination from the blood for the parent terconazole was 6.9 hours (range 4.0-11.3). Terconazole is extensively metabolized; the plasma AUC for terconazole compared to the AUC for total radioactivity was 0.6%. Total radioactivity was eliminated from the blood with a harmonic half-life of 52.2 hours (range 44-60). Excretion of radioactivity was both by renal (32-56%) and fecal (47-52%) routes.
In vitro, terconazole is highly protein bound (94.9%) and the degree of binding is independent of drug concentration.
Photosensitivity reactions were observed in some normal volunteers following repeated dermal application of terconazole 2.0% and 0.8% creams under conditions of filtered artificial ultraviolet light.
Photosensitivity reactions have not been observed in U.S. and foreign clinical trials in patients who were treated with terconazole vaginal cream, 0.8%.
MicrobiologyTerconazole exhibits fungicidal activity in vitro against Candida albicans. Antifungal activity also has been demonstrated against other fungi. The MIC values of terconazole against most Lactobacillus spp. typically found in the human vagina were ≥ 128 mcg/mL, therefore these beneficial bacteria are not affected by drug treatment.
The exact pharmacologic mode of action of terconazole is uncertain; however, it may exert its antifungal activity by the disruption of normal fungal cell membrane permeability. No resistance to terconazole has developed during successive passages of C. albicans.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Terconazole Vaginal Cream is indicated for the local treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis (moniliasis). As Terconazole Vaginal Cream is effective only for vulvovaginitis caused by the genus Candida, the diagnosis should be confirmed by KOH smears and/or cultures.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Patients known to be hypersensitive to terconazole or to any of the components of the cream.
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralDiscontinue use and do not retreat with terconazole if sensitization, irritation, fever, chills or flu-like symptoms are reported during use.
Laboratory TestsIf there is lack of response to Terconazole Vaginal Cream, appropriate microbiologic studies (standard KOH smear and/or cultures) should be repeated to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other pathogens.
Drug InteractionsThe levels of estradiol (E2) and progesterone did not differ significantly when 0.8% terconazole vaginal cream was administered to healthy female volunteers established on a low dose oral contraceptive.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of FertilityCarcinogenesisStudies to determine the carcinogenic potential of terconazole have not been performed.
MutagenicityTerconazole was not mutagenic when tested in vitro for induction of microbial point mutations (Ames test), or for inducing cellular transformation, or in vivo for chromosome breaks (micronucleus test) or dominant lethal mutations in mouse germ cells.
Impairment of FertilityNo impairment of fertility occurred when female rats were administered terconazole orally up to 40 mg/kg/day for a three month period.
PregnancyTeratogenic EffectsPregnancy Category CThere was no evidence of teratogenicity when terconazole was administered orally up to 40 mg/kg/day (50× the recommended intravaginal human dose of the 0.8% vaginal cream formulation) in rats, or 20 mg/kg/day in rabbits, or subcutaneously up to 20 mg/kg/day in rats.
Dosages at or below 10 mg/kg/day produced no embryotoxicity; however, there was a delay in fetal ossification at 10 mg/kg/day in rats. There was some evidence of embryotoxicity in rabbits and rats at 20-40 mg/kg. In rats, this was reflected as a decrease in litter size and number of viable young and reduced fetal weight. There was also delay in ossification and an increased incidence of skeletal variants.
The no-effect dose of 10 mg/kg/day resulted in a mean peak plasma level of terconazole in pregnant rats of 0.176 mcg/mL which exceeds by 30 times the mean peak plasma level (0.006 mcg/mL) seen in normal subjects after intravaginal administration of terconazole 0.8% vaginal cream. This safety assessment does not account for possible exposure of the fetus through direct transfer to terconazole from the irritated vagina by diffusion across amniotic membranes.
Since terconazole is absorbed from the human vagina, it should not be used in the first trimester of pregnancy unless the physician considers it essential to the welfare of the patient.
Nursing MothersIt is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Animal studies have shown that rat offspring exposed via the milk of treated (40 mg/kg/orally) dams showed decreased survival during the first few post-partum days, but overall pup weight and weight gain were comparable to or greater than controls throughout lactation. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential for adverse reaction in nursing infants from terconazole, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric UseSafety and efficacy in children have not been established.
Geriatric UseClinical studies of terconazole 0.8% vaginal cream did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
During controlled clinical studies conducted in the United States, patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis were treated with terconazole 0.8% vaginal cream for three days. Based on comparative analyses with placebo and a standard agent, the adverse experiences considered most likely related to terconazole 0.8% vaginal cream were headache (21% vs. 16% with placebo) and dysmenorrhea (6% vs. 2% with placebo). Genital complaints in general, and burning and itching in particular, occurred less frequently in the terconazole 0.8% vaginal cream 3 day regimen (5% vs. 6%-9% with placebo). Other adverse experiences reported with terconazole 0.8% vaginal cream were abdominal pain (3.4% vs. 1% with placebo) and fever (1% vs. 0.3% with placebo). The therapy-related dropout rate was 2.0% for the terconazole 0.8% vaginal cream. The adverse drug experience most frequently causing discontinuation of therapy was vulvovaginal itching 0.7% with the terconazole 0.8% vaginal cream group and 0.3% with the placebo group.
OVERDOSAGE
Overdose of terconazole in humans has not been reported to date. In the rat, the oral LD 50 values were found to be 1741 and 849 mg/kg for the male and female, respectively. The oral LD 50 values for the male and female dog were 1280 and ≥ 640 mg/kg, respectively.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
One full applicator (5 g) of Terconazole Vaginal Cream (40 mg terconazole) should be administered intravaginally once daily at bedtime for three consecutive days. Before prescribing another course of therapy, the diagnosis should be reconfirmed by smears and/or cultures and other pathogens commonly associated with vulvovaginitis ruled out. The therapeutic effect of Terconazole Vaginal Cream is not affected by menstruation.
HOW SUPPLIED
Terconazole Vaginal Cream 0.8% is available in 20 g tubes with 3 applicators. Store at controlled room temperature 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
NDC 54868-5183-0
Mfd. by: Taro Pharmaceuticals Inc., Brampton, Ontario, Canada L6T
1C1
Dist. by: Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Hawthorne, NY 10532
June 2003
Relabeling of "Additional Barcode Label" by:
Physicians Total Care, Inc.
Tulsa, OK 74146
3-DAY THERAPY
Filling the applicator:
| 1. Remove the cap from the tube. |
|
|
| 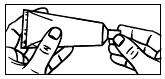 |
| 2. Use the pointed tip on the top of the cap to puncture the seal on the tube. |
|
|
|  |
| 3. Screw the applicator onto the tube. |
|
| 4. Squeeze the tube from the bottom and fill the applicator until the plunger stops. |
|
|
| 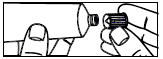 |
| 5. Unscrew the applicator from the tube. |
|
Using the applicator:
| 1. Lie on your back with your knees drawn up toward your chest. |
| 2. Holding the applicator by the barrel, insert the filled applicator into the vagina as far as it will comfortably go. |
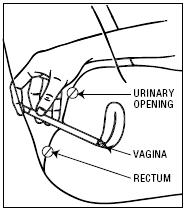 |
| 3. Slowly press the plunger of the applicator to release the cream into the vagina. |
| 4. Remove the applicator from the vagina. |
| 5. Apply one applicatorful each night for 3 nights at bedtime, as directed by your doctor. |
Discard the applicator after each use.
NOTE: Store at controlled room temperature 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). See end flap of carton or crimp of tube for lot number and expiration date.
A WORD ABOUT YEAST INFECTIONS
Why do yeast infections occur?
Yeast infections are caused by an organism called Candida (KAN di duh). It may be present in small and harmless amounts in the mouth, digestive tract, and vagina. Sometimes the natural balance of the vagina becomes upset. This may lead to rapid growth of Candida, which results in a yeast infection. Symptoms of a yeast infection include itching, burning, redness, and an abnormal discharge.
Your doctor can make the diagnosis of a yeast infection by evaluating your symptoms and looking at a sample of the discharge under the microscope.
How can I prevent yeast infections?
Certain factors may increase your chance of developing a yeast infection. These factors don't actually cause the problem, but they may create a situation that allows the yeast to grow rapidly.
- Clothing: Tight jeans, nylon underwear, pantyhose, and wet bathing suits can hold in heat and moisture (two conditions in which yeast organisms thrive). Looser pants or skirts, 100% cotton underwear, and stockings may help avoid this problem.
- Diet: Cutting down on sweets, milk products, and artificial sweeteners may reduce the risk of yeast infections.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics work by eliminating disease-causing organisms. While they are helpful in curing other problems, antibiotics may lead to an overgrowth of Candida in the vagina.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes in the body during pregnancy encourage the growth of yeast. This is a very common time for an infection to occur. Until the baby is born, it may be hard to completely eliminate yeast infections. If you believe you are pregnant, tell your doctor.
- Menstruation: Sometimes monthly changes in hormone levels may lead to yeast infections.
- Diabetes: In addition to heat and moisture, yeast thrives on sugar. Because diabetics often have sugar in their urine, their vaginas are rich in this substance. Careful control of diabetes may help prevent yeast infection.
Controlling these factors can help eliminate yeast infections and may prevent them from coming back.
Some other helpful tips:
- For best results, be sure to use the medication as prescribed by your doctor, even if you feel better very quickly.
- Avoid sexual intercourse, if your doctor advises you to do so.
- If your partner has any penile itching, redness, or discomfort, he should consult his physician and mention that you are being treated for a yeast infection.
- You can use the medication even if you are having your menstrual period. However, you should not use tampons because they may absorb the medication. Instead, use external pads or napkins until you have finished your medication. You may also wish to wear a sanitary napkin if the vaginal medication leaks.
- Dry the genital area thoroughly after showering, bathing, or swimming. Change out of a wet bathing suit or damp exercise clothes as soon as possible. A dry environment is less likely to encourage the growth of yeast.
- Wipe from front to rear (away from the vagina) after a bowel movement.
- Don't douche unless your doctor specifically tells you to do so. Douching may disturb the vaginal balance.
- Don't scratch if you can help it. Scratching can cause more irritation and spread the infection.
- Discuss with your physician any medication you are already taking. Certain types of medication can make your vagina more susceptible to infection.
- Eat nutritious meals to promote your general health.
Mfd. by:
Taro Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Brampton, Ontario, Canada L6T
1C1
Dist. by:
Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
Hawthorne, NY 10532
June 2003
