FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Pediatric Patients
Norditropin [somatropin (rDNA origin) injection] is indicated for the treatment of children with growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone (GH).
Norditropin [somatropin (rDNA origin) injection] is indicated for the treatment of children with short stature associated with Noonan syndrome.
Norditropin [somatropin (rDNA origin) injection] is indicated for the treatment of children with short stature associated with Turner syndrome.
Norditropin [somatropin (rDNA origin) injection] is indicated for the treatment of children with short stature born small for gestational age (SGA) with no catch-up growth by age 2-4 years.
1.2 Adult Patients
Norditropin [somatropin (rDNA origin) injection] is indicated for the replacement of endogenous GH in adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD) who meet either of the following two criteria:
- Adult Onset (AO): Patients who have GHD, either alone or associated with multiple hormone deficiencies (hypopituitarism), as a result of pituitary disease, hypothalamic disease, surgery, radiation therapy, or trauma; or
- Childhood Onset (CO): Patients who were GH deficient during childhood as a result of congenital, genetic, acquired, or idiopathic causes.
Patients who were treated with somatropin for GHD in childhood and whose epiphyses are closed should be reevaluated before continuation of somatropin therapy at the reduced dose level recommended for GHD adults. According to current standards, confirmation of the diagnosis of adult GHD in both groups involves an appropriate growth hormone provocative test with two exceptions: (1) patients with multiple other pituitary hormone deficiencies due to organic disease; and (2) patients with congenital/genetic growth hormone deficiency.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For subcutaneous injection.
Therapy with Norditropin should be supervised by a physician who is experienced in the diagnosis and management of pediatric patients with short stature associated with GHD, Noonan syndrome, Turner syndrome or SGA, and adult patients with either childhood onset or adult onset GHD.
2.1 Dosing of Pediatric Patients
General Pediatric Dosing Information
The Norditropin dosage and administration schedule should be individualized based on the growth response of each patient. Serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) levels may be useful during dose titration.
Response to somatropin therapy in pediatric patients tends to decrease with time. However, in pediatric patients, the failure to increase growth rate, particularly during the first year of therapy, indicates the need for close assessment of compliance and evaluation for other causes of growth failure, such as hypothyroidism, undernutrition, advanced bone age and antibodies to recombinant human GH (rhGH).
Treatment with Norditropin for short stature should be discontinued when the epiphyses are fused.
Pediatric Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD)
A dosage of 0.024 - 0.034 mg/kg/day, 6-7 times a week, is recommended.
Pediatric Patients with Short Stature Associated with Noonan Syndrome
Not all patients with Noonan syndrome have short stature; some will achieve a normal adult height without treatment. Therefore, prior to initiating Norditropin for a patient with Noonan syndrome, establish that the patient does have short stature.
A dosage of up to 0.066 mg/kg/day is recommended.
Pediatric Patients with Short Stature Associated with Turner Syndrome
A dosage of up to 0.067 mg/kg/day is recommended.
Pediatric Patients with Short Stature Born Small for Gestational Age (SGA) with No Catch-up Growth by Age 2-4 Years
A dosage of up to 0.067 mg/kg/day is recommended.
Recent literature has recommended initial treatment with larger doses of somatropin (e.g., 0.067 mg/kg/day), especially in very short children (i.e., HSDS < -3), and/or older/pubertal children, and that a reduction in dosage (e.g., gradually towards 0.033 mg/kg/day) should be considered if substantial catch-up growth is observed during the first few years of therapy. On the other hand, in younger SGA children (e.g., approximately < 4 years) (who respond the best in general) with less severe short stature (i.e., baseline HSDS values between -2 and -3), consideration should be given to initiating treatment at a lower dose (e.g., 0.033 mg/kg/day), and titrating the dose as needed over time. In all children, clinicians should carefully monitor the growth response, and adjust the rhGH dose as necessary.
2.2 Dosing of Adult Patients
Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD)
Either of two approaches to Norditropin dosing may be followed: a non-weight-based regimen or a weight-based regimen.
Non-weight based — based on published consensus guidelines, a starting dose of approximately 0.2 mg/day (range, 0.15-0.30 mg/day) may be used without consideration of body weight. This dose can be increased gradually every 1-2 months by increments of approximately 0.1-0.2 mg/day, according to individual patient requirements based on the clinical response and serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) concentrations. The dose should be decreased as necessary on the basis of adverse events and/or serum IGF-I concentrations above the age- and gender-specific normal range. Maintenance dosages vary considerably from person to person, and between male and female patients.
Weight-based — based on the dosing regimen used in the original adult GHD registration trials, the recommended dosage at the start of treatment is not more than 0.004 mg/kg/day. The dose may be increased to not more than 0.016 mg/kg/day after approximately 6 weeks according to individual patient requirements. Clinical response, side effects, and determination of age- and gender-adjusted serum IGF-I concentrations should be used as guidance in dose titration.
A lower starting dose and smaller dose increments should be considered for older patients, who are more prone to the adverse effects of somatropin than younger individuals. In addition, obese individuals are more likely to manifest adverse effects when treated with a weight-based regimen. In order to reach the defined treatment goal, estrogen-replete women may need higher doses than men. Oral estrogen administration may increase the dose requirements in women.
2.3 Preparation and Administration
Norditropin® FlexPro® 5 mg/ 1.5 mL, 10 mg/1.5 mL and 15 mg/1.5 mL:
Instructions for delivering the dosage are provided in the PATIENT INFORMATION and INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE leaflets enclosed with the Norditropin FlexPro prefilled pen.
Norditropin NordiFlex® 5 mg/1.5 mL, 10 mg/1.5 mL, 15 mg/1.5 mL and 30 mg/3 mL:
Instructions for delivering the dosage are provided in the PATIENT INFORMATION and INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE leaflets enclosed with the Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pen.
Norditropin Cartridges must be administered using the NordiPen delivery systems. Each cartridge size has a corresponding, color-coded pen which is graduated to deliver the appropriate dose based on the concentration of Norditropin in the cartridge.
Norditropin® Cartridges 5 mg/1.5 mL and 15 mg/1.5 mL:
Each cartridge of Norditropin must be inserted into its corresponding NordiPen delivery system. Instructions for delivering the dosage are provided in the NordiPen INSTRUCTION booklet.
Parenteral drug products should always be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Norditropin MUST NOT BE INJECTED if the solution is cloudy or contains particulate matter. Use it only if it is clear and colorless.
Injection sites should always be rotated to avoid lipoatrophy.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Norditropin is available preloaded in the Norditropin FlexPro or Norditropin NordiFlex pens or in cartridges for use with the corresponding NordiPens:
- 5 mg/1.5 mL (orange): Norditropin FlexPro and Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pens, and cartridges
- 10 mg/1.5 mL (blue): Norditropin FlexPro and Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pens
- 15 mg/1.5 mL (green): Norditropin FlexPro and Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pens, and cartridges
- 30 mg/3 mL (purple): Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pen only
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Acute Critical Illness
Treatment with pharmacologic amounts of somatropin is contraindicated in patients with acute critical illness due to complications following open heart surgery, abdominal surgery or multiple accidental trauma, or those with acute respiratory failure. Two placebo-controlled clinical trials in non-growth hormone deficient adult patients (n=522) with these conditions in intensive care units revealed a significant increase in mortality (41.9% vs. 19.3%) among somatropin-treated patients (doses 5.3-8 mg/day) compared to those receiving placebo [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
4.2 Prader-Willi Syndrome in Children
Somatropin is contraindicated in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese, have a history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or have severe respiratory impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. There have been reports of sudden death when somatropin was used in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Norditropin is not indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients who have growth failure due to genetically confirmed Prader-Willi syndrome.
4.3 Active Malignancy
In general, somatropin is contraindicated in the presence of active malignancy. Any preexisting malignancy should be inactive and its treatment complete prior to instituting therapy with somatropin. Somatropin should be discontinued if there is evidence of recurrent activity. Since GHD may be an early sign of the presence of a pituitary tumor (or, rarely, other brain tumors), the presence of such tumors should be ruled out prior to initiation of treatment. Somatropin should not be used in patients with any evidence of progression or recurrence of an underlying intracranial tumor.
4.4 Diabetic Retinopathy
Somatropin is contraindicated in patients with active proliferative or severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Acute Critical Illness
Increased mortality in patients with acute critical illness due to complications following open heart surgery, abdominal surgery or multiple accidental trauma, or those with acute respiratory failure has been reported after treatment with pharmacologic amounts of somatropin [see Contraindications (4.1)]. The safety of continuing somatropin treatment in patients receiving replacement doses for approved indications who concurrently develop these illnesses has not been established. Therefore, the potential benefit of treatment continuation with somatropin in patients experiencing acute critical illnesses should be weighed against the potential risk.
5.2 Prader-Willi Syndrome in Children
There have been reports of fatalities after initiating therapy with somatropin in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who had one or more of the following risk factors: severe obesity, history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or unidentified respiratory infection. Male patients with one or more of these factors may be at greater risk than females. Patients with Prader-Willi syndrome should be evaluated for signs of upper airway obstruction and sleep apnea before initiation of treatment with somatropin. If, during treatment with somatropin, patients show signs of upper airway obstruction (including onset of or increased snoring) and/or new onset sleep apnea, treatment should be interrupted. All patients with Prader-Willi syndrome treated with somatropin should also have effective weight control and be monitored for signs of respiratory infection, which should be diagnosed as early as possible and treated aggressively [see Contraindications (4.2)]. Norditropin is not indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients who have growth failure due to genetically confirmed Prader-Willi syndrome.
5.3 Neoplasms
Patients with preexisting tumors or GHD secondary to an intracranial lesion should be monitored routinely for progression or recurrence of the underlying disease process. In pediatric patients, clinical literature has revealed no relationship between somatropin replacement therapy and central nervous system (CNS) tumor recurrence or new extracranial tumors. However, in childhood cancer survivors, an increased risk of a second neoplasm has been reported in patients treated with somatropin after their first neoplasm. Intracranial tumors, in particular meningiomas, in patients treated with radiation to the head for their first neoplasm, were the most common of these second neoplasms. In adults, it is unknown whether there is any relationship between somatropin replacement therapy and CNS tumor recurrence.
Patients should be monitored carefully for potential malignant transformation of skin lesions, i.e. increased growth of preexisting nevi.
5.4 Glucose Intolerance
Treatment with somatropin may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses in susceptible patients. As a result, previously undiagnosed impaired glucose tolerance and overt diabetes mellitus may be unmasked during somatropin treatment. Therefore, glucose levels should be monitored periodically in all patients treated with somatropin, especially in those with risk factors for diabetes mellitus, such as obesity, Turner syndrome, or a family history of diabetes mellitus. Patients with preexisting type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance should be monitored closely during somatropin therapy. The doses of antihyperglycemic drugs (i.e., insulin or oral agents) may require adjustment when somatropin therapy is instituted in these patients.
5.5 Intracranial Hypertension
Intracranial hypertension (IH) with papilledema, visual changes, headache, nausea, and/or vomiting has been reported in a small number of patients treated with somatropin products. Symptoms usually occurred within the first eight (8) weeks after the initiation of somatropin therapy. In all reported cases, IH-associated signs and symptoms rapidly resolved after cessation of therapy or a reduction of the somatropin dose.
Funduscopic examination should be performed routinely before initiating treatment with somatropin to exclude preexisting papilledema, and periodically during the course of somatropin therapy. If papilledema is observed by funduscopy during somatropin treatment, treatment should be stopped. If somatropin-induced IH is diagnosed, treatment with somatropin can be restarted at a lower dose after IH-associated signs and symptoms have resolved. Patients with Turner syndrome may be at increased risk for the development of IH.
5.6 Fluid Retention
Fluid retention during somatropin replacement therapy in adults may frequently occur. Clinical manifestations of fluid retention are usually transient and dose dependent.
5.7 Hypothyroidism
Undiagnosed/untreated hypothyroidism may prevent an optimal response to somatropin, in particular, the growth response in children. Patients with Turner syndrome have an inherently increased risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease and primary hypothyroidism. In patients with GHD, central (secondary) hypothyroidism may first become evident or worsen during somatropin treatment. Therefore, patients treated with somatropin should have periodic thyroid function tests and thyroid hormone replacement therapy should be initiated or appropriately adjusted when indicated.
In patients with hypopituitarism (multiple hormone deficiencies), standard hormonal replacement therapy should be monitored closely when somatropin therapy is administered.
5.8 Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis in Pediatric Patients
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may occur more frequently in patients with endocrine disorders (including GHD and Turner syndrome) or in patients undergoing rapid growth. Any pediatric patient with the onset of a limp or complaints of hip or knee pain during somatropin therapy should be carefully evaluated.
5.9 Progression of Preexisting Scoliosis in Pediatric Patients
Progression of scoliosis can occur in patients who experience rapid growth. Because somatropin increases growth rate, patients with a history of scoliosis who are treated with somatropin should be monitored for progression of scoliosis. However, somatropin has not been shown to increase the occurrence of scoliosis. Skeletal abnormalities including scoliosis are commonly seen in untreated patients with Turner syndrome and Noonan syndrome. Scoliosis is also commonly seen in untreated patients with Prader-Willi syndrome. Physicians should be alert to these abnormalities, which may manifest during somatropin therapy.
5.10 Otitis Media and Cardiovascular Disorders in Turner Syndrome
Patients with Turner syndrome should be evaluated carefully for otitis media and other ear disorders since these patients have an increased risk of ear and hearing disorders. Somatropin treatment may increase the occurrence of otitis media in patients with Turner syndrome. In addition, patients with Turner syndrome should be monitored closely for cardiovascular disorders (e.g., stroke, aortic aneurysm/dissection, hypertension) as these patients are also at risk for these conditions.
5.11 Confirmation of Childhood Onset Adult GHD
Patients with epiphyseal closure who were treated with somatropin replacement therapy in childhood should be reevaluated according to the criteria in Indications and Usage (1.2) before continuation of somatropin therapy at the reduced dose level recommended for GH deficient adults.
5.12 Local and Systemic Reactions
When somatropin is administered subcutaneously at the same site over a long period of time, tissue atrophy may result. This can be avoided by rotating the injection site [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
As with any protein, local or systemic allergic reactions may occur. Parents/Patients should be informed that such reactions are possible and that prompt medical attention should be sought if allergic reactions occur.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Most Serious and/or Most Frequently Observed Adverse Reactions
This list presents the most seriousb and/or most frequently observeda adverse reactions during treatment with somatropin:
- bSudden death in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome with risk factors including severe obesity, history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea and unidentified respiratory infection [see Contraindications (4.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- bIntracranial tumors, in particular meningiomas, in teenagers/young adults treated with radiation to the head as children for a first neoplasm and somatropin [see Contraindications (4.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- a,bGlucose intolerance including impaired glucose tolerance/impaired fasting glucose as well as overt diabetes mellitus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- bIntracranial hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- bSignificant diabetic retinopathy [see Contraindications (4.4)]
- bSlipped capital femoral epiphysis in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- bProgression of preexisting scoliosis in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- aFluid retention manifested by edema, arthralgia, myalgia, nerve compression syndromes including carpal tunnel syndrome/paraesthesias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- aUnmasking of latent central hypothyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- aInjection site reactions/rashes and lipoatrophy (as well as rare generalized hypersensitivity reactions) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed during the clinical trials performed with one somatropin formulation cannot always be directly compared to the rates observed during the clinical trials performed with a second somatropin formulation, and may not reflect the adverse reaction rates observed in practice.
Clinical Trials in Pediatric GHD Patients
As with all protein drugs, a small percentage of patients may develop antibodies to the protein. GH antibodies with binding capacities lower than 2 mg/L have not been associated with growth attenuation. In a very small number of patients, when binding capacity was greater than 2 mg/L, interference with the growth response was observed. In clinical trials, patients receiving Norditropin for up to 12 months were tested for induction of antibodies, and 0/358 patients developed antibodies with binding capacities above 2 mg/L. Amongst these patients, 165 had previously been treated with other somatropin formulations, and 193 were previously untreated naive patients.
Clinical Trials in Children with Noonan Syndrome
Norditropin was studied in a two-year prospective, randomized, parallel dose group trial in 21 children, 3-14 years old, with Noonan syndrome. Doses were 0.033 and 0.066 mg/kg/day. After the initial two-year randomized trial, children continued Norditropin treatment until final height was achieved; randomized dose groups were not maintained. Final height and adverse event data were later collected retrospectively from 18 children; total follow-up was 11 years. An additional 6 children were not randomized, but followed the protocol and are included in this assessment of adverse events.
Based on the mean dose per treatment group, no significant difference in the incidence of adverse events was seen between the two groups. The most frequent adverse events were the common infections of childhood, including upper respiratory infection, gastroenteritis, ear infection, and influenza. Cardiac disorders was the system organ class with the second most adverse events reported. However, congenital heart disease is an inherent component of Noonan syndrome, and there was no evidence of somatropin-induced ventricular hypertrophy or exacerbation of preexisting ventricular hypertrophy (as judged by echocardiography) during this study. Children who had baseline cardiac disease judged to be significant enough to potentially affect growth were excluded from the study; therefore the safety of Norditropin in children with Noonan syndrome and significant cardiac disease is not known. Among children who received 0.033 mg/kg/day, there was one adverse event of scoliosis; among children who received 0.066 mg/kg/day, there were four adverse events of scoliosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]. Mean serum IGF-I standard deviation score (SDS) levels did not exceed +1 in response to somatropin treatment. The mean serum IGF-I level was low at baseline and normalized during treatment.
Clinical Trials in Children with Turner Syndrome
In two clinical studies wherein children with Turner syndrome were treated until final height with various doses of Norditropin as described in Clinical Studies (14.2), the most frequently reported adverse events were common childhood diseases including influenza-like illness, otitis media, upper respiratory tract infection, otitis externa, gastroenteritis and eczema. Otitis media adverse events in Study 1 were most frequent in the highest dose groups (86.4% in the 0.045-0.067-0.089 mg/kg/day group vs. 78.3% in the 0.045-0.067 mg/kg/day group vs. 69.6% in the 0.045 mg/kg/day group) suggesting a possible dose-response relationship. Of note, approximately 40-50% of these otitis media adverse events were designated as “serious” [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. No patients in either study developed clearcut overt diabetes mellitus; however, in Study 1, impaired fasting glucose at Month 48 was more frequent in patients in the 0.045-0.067 mg/kg/day group (n=4/18) compared with the 0.045 mg/kg/day group (n=1/20). Transient episodes of fasting blood sugars between 100 and 126 mg/dL, and, on occasion, exceeding 126 mg/dL also occurred more often with larger doses of Norditropin in both studies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Three patients withdrew from the 2 high dose groups in Study 1 because of concern about excessive growth of hands or feet. In addition, in Study 1, exacerbation of preexisting scoliosis was designated a serious adverse reaction in two patients in the 0.045 mg/kg/day group [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Clinical Trials in Children Born Small for Gestational Age (SGA) with No Catch-up Growth by Age 2-4 Years
Study 1 (Long-Term)
In a multi-center, randomized, double-blind study, 53 non-GHD children with short stature born SGA with failure to catch-up were treated with 2 doses of Norditropin (0.033 or 0.067 mg/kg/day) to final height for up to 13 years (mean duration of treatment 7.9 and 9.5 years for girls and boys, respectively). The most frequently reported adverse events were common childhood diseases including influenza-like illness, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, gastroenteritis, abdominal pain, otitis media, pharyngitis, arthralgia, and headache. Adverse events possibly/probably related to Norditropin were otitis media, arthralgia, headaches (no confirmed diagnoses of benign intracranial hypertension), gynecomastia, and increased sweating. One child treated with 0.067 mg/kg/day for 4 years was reported with disproportionate growth of the lower jaw, and another child treated with 0.067 mg/kg/day developed a melanocytic nevus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. There were no clear cut reports of exacerbation of preexisting scoliosis or slipped capital femoral epiphysis. No apparent differences between the treatment groups were observed. In addition, the timing of puberty was age-appropriate in boys and girls in both treatment groups. Therefore, it can be concluded that no novel adverse events potentially related to treatment with Norditropin were reported in long-term Study 1.
Study 2 (Short-Term)
In a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study, 98 Japanese non-GHD children with short stature born SGA with failure to catch-up were treated with 2 doses of Norditropin (0.033 or 0.067 mg/kg/day) for 2 years or were untreated for 1 year. The most frequently reported adverse events were common childhood diseases almost identical to those reported above for Study 1. Adverse events possibly/probably related to Norditropin were otitis media, arthralgia and impaired glucose tolerance. No apparent differences between the treatment groups were observed. However, arthralgia and transiently impaired glucose tolerance were only reported in the 0.067 mg/kg/day treatment group. Therefore, it can also be concluded that no novel adverse events potentially related to treatment with rhGH were reported in short-term Study 2.
As with all protein drugs, some patients may develop antibodies to the protein. Eighteen of the 76 children (~24%) treated with Norditropin developed anti-rhGH antibodies. However, these antibodies did not appear to be neutralizing in that the change from baseline in height SDS at Year 2 was similar in antibody positive and antibody negative children by treatment group.
In both Study 1 and Study 2, there were no clear cut cases of new onset diabetes mellitus, no children treated for hyperglycemia, and no adverse event withdrawals due to abnormalities in glucose tolerance. In Study 2, after treatment with either dose of Norditropin for 2 years, there were no children with consecutive fasting blood glucose levels between 100 and 126 mg/dL, or with fasting blood glucose levels > 126 mg/dL. Furthermore, mean hemoglobin A1c levels tended to decrease during long-term treatment in Study 1, and remained normal in Study 2. However, in Study 1, 4 children treated with 0.067 mg/kg/day of Norditropin and 2 children treated with 0.033 mg/kg/day of Norditropin shifted from normal fasting blood glucose levels at baseline to increased levels after 1 year of treatment (100 to 126 mg/dL or > 126 mg/dL). In addition, small increases in mean fasting blood glucose and insulin levels (within the normal reference range) after 1 and 2 years of Norditropin treatment appeared to be dose-dependent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In both Study 1 and Study 2, there was no acceleration of bone maturation. A dose-dependent increase in mean serum IGF-I SDS levels within the reference range (but including a substantial number of children with serum IGF-1 SDS > +2) was observed after both long-term (Study 1) and short-term (Study 2) Norditropin treatment.
Clinical Trials in Adult GHD Patients
Adverse events with an incidence of ≥5% occurring in patients with AO GHD during the 6 month placebo-controlled portion of the largest of the six adult GHD Norditropin trials are presented in Table 1. Peripheral edema, other types of edema, arthralgia, myalgia, and paraesthesia were common in the Norditropin-treated patients, and reported much more frequently than in the placebo group. These types of adverse events are thought to be related to the fluid accumulating effects of somatropin. In general, these adverse events were mild and transient in nature. During the placebo-controlled portion of this study, approximately 5% of patients without preexisting diabetes mellitus treated with Norditropin were diagnosed with overt type 2 diabetes mellitus compared with none in the placebo group [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Anti-GH antibodies were not detected.
Of note, the doses of Norditropin employed during this study (completed in the mid 1990s) were substantially larger than those currently recommended by the Growth Hormone Research Society, and, more than likely, resulted in a greater than expected incidence of fluid retention- and glucose intolerance-related adverse events. A similar incidence and pattern of adverse events were observed during the other three placebo-controlled AO GHD trials and during the two placebo-controlled CO GHD trials.
|
Norditropin (N=53) |
Placebo (N=52) |
|||
| Adverse Reactions | n |
% | n | % |
| Peripheral Edema | 22 | 42 | 4 | 8 |
| Edema | 13 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Arthralgia | 10 | 19 | 8 | 15 |
| Leg Edema | 8 | 15 | 2 | 4 |
| Myalgia | 8 | 15 | 4 | 8 |
| Infection (non-viral) | 7 | 13 | 4 | 8 |
| Paraesthesia | 6 | 11 | 3 | 6 |
| Skeletal Pain | 6 | 11 | 1 | 2 |
| Headache | 5 | 9 | 3 | 6 |
| Bronchitis | 5 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Flu-like symptoms | 4 | 8 | 2 | 4 |
| Hypertension | 4 | 8 | 1 | 2 |
| Gastroenteritis | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 |
| Other Non-Classifiable Disorders (excludes accidental injury) | 4 | 8 | 3 | 6 |
| Increased sweating | 4 | 8 | 1 | 2 |
| Glucose tolerance abnormal | 3 | 6 | 1 | 2 |
| Laryngitis | 3 | 6 | 3 | 6 |
The adverse event pattern observed during the open label phase of the study was similar to the one presented above.
6.3 Post-Marketing Surveillance
Because these adverse events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The adverse events reported during post-marketing surveillance do not differ from those listed/discussed above in Sections 6.1 and 6.2 in children and adults.
Leukemia has been reported in a small number of GH deficient children treated with somatropin, somatrem (methionylated rhGH) and GH of pituitary origin. It is uncertain whether these cases of leukemia are related to GH therapy, the pathology of GHD itself, or other associated treatments such as radiation therapy. On the basis of current evidence, experts have not been able to conclude that GH therapy per se was responsible for these cases of leukemia. The risk for children with GHD, if any, remains to be established [see Contraindications (4.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
The following additional adverse reactions have been observed during the appropriate use of somatropin: headaches (children and adults), gynecomastia (children), and pancreatitis (children).
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Inhibition of 11ß-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 (11ßHSD-1)
The microsomal enzyme 11ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11βHSD-1) is required for conversion of cortisone to its active metabolite, cortisol, in hepatic and adipose tissue. GH and somatropin inhibit 11βHSD-1. Consequently, individuals with untreated GHD have relative increases in 11βHSD-1 and serum cortisol. Introduction of somatropin treatment may result in inhibition of 11βHSD-1 and reduced serum cortisol concentrations. As a consequence, previously undiagnosed central (secondary) hypoadrenalism may be unmasked and glucocorticoid replacement may be required in patients treated with somatropin. In addition, patients treated with glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of somatropin treatment; this may be especially true for patients treated with cortisone acetate and prednisone since conversion of these drugs to their biologically active metabolites is dependent on the activity of 11ßHSD-1.
7.2 Physiologic Glucocorticoid Replacement and Pharmacologic Glucocorticoid Therapy
Pharmacologic glucocorticoid therapy and supraphysiologic glucocorticoid treatment may attenuate the growth promoting effects of somatropin in children. Therefore, glucocorticoid replacement dosing should be carefully adjusted in children receiving concomitant somatropin and glucocorticoid treatments to avoid both hypoadrenalism and an inhibitory effect on growth.
7.3 Cytochrome P450-Metabolized Drugs
Limited published data indicate that somatropin treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)- mediated antipyrine clearance in man. These data suggest that somatropin administration may alter the clearance of compounds known to be metabolized by CYP450 liver enzymes (e.g., corticosteroids, sex steroids, anticonvulsants, cyclosporine). Careful monitoring is advisable when somatropin is administered in combination with other drugs known to be metabolized by CYP450 liver enzymes. However, formal drug interaction studies have not been conducted.
7.4 Oral Estrogen
In adult women on oral estrogen replacement, a larger dose of somatropin may be required to achieve the defined treatment goal [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
7.5 Insulin and/or Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
In patients with diabetes mellitus requiring drug therapy, the dose of insulin and/or oral agent may require adjustment when somatropin therapy is initiated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Norditropin. It is not known whether Norditropin can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Norditropin should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether Norditropin is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Norditropin is administered to a nursing woman.
8.5 Geriatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Norditropin in patients aged 65 and over has not been evaluated in clinical studies. Elderly patients may be more sensitive to the action of somatropin, and therefore may be more prone to develop adverse reactions. A lower starting dose and smaller dose increments should be considered for older patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Short-Term
Short-term overdosage could lead initially to hypoglycemia and subsequently to hyperglycemia. Furthermore, overdose with somatropin is likely to cause fluid retention.
Long-Term
Long-term overdosage could result in signs and symptoms of gigantism and/or acromegaly consistent with the known effects of excess growth hormone [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
11 DESCRIPTION
Norditropin is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk Health Care AG for somatropin, a polypeptide hormone of recombinant DNA origin. The hormone is synthesized by a special strain of E. coli bacteria that has been modified by the addition of a plasmid which carries the gene for human growth hormone. Norditropin contains the identical sequence of 191 amino acids constituting the naturally occurring pituitary human growth hormone with a molecular weight of about 22,000 Daltons.
Norditropin cartridges are supplied as sterile solutions for subcutaneous injection in ready-to-administer cartridges or prefilled pens with a volume of 1.5 mL or 3 mL.
Each Norditropin Cartridge contains the following (see Table 2):
| Component | 5 mg/1.5 mL | 10 mg/1.5 mL | 15 mg/1.5 mL | 30 mg/3 mL |
| Somatropin | 5 mg | 10 mg | 15 mg | 30 mg |
| Histidine | 1 mg | 1 mg | 1.7 mg | 3.3 mg |
| Poloxamer 188 | 4.5 mg | 4.5 mg | 4.5 mg | 9.0 mg |
| Phenol | 4.5 mg | 4.5 mg | 4.5 mg | 9.0 mg |
| Mannitol | 60 mg | 60 mg | 58 mg | 117 mg |
| HCl/NaOH | as needed | as needed | as needed | as needed |
| Water for Injection | up to 1.5 mL | up to 1.5 mL | up to 1.5 mL | up to 3.0 mL |
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Somatropin (as well as endogenous GH) binds to a dimeric GH receptor in the cell membrane of target cells resulting in intracellular signal transduction and a host of pharmacodynamic effects. Some of these pharmacodynamic effects are primarily mediated by IGF-I produced in the liver and also locally (e.g., skeletal growth, protein synthesis), while others are primarily a consequence of the direct effects of somatropin (e.g., lipolysis) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Tissue Growth
The primary and most intensively studied action of somatropin is the stimulation of linear growth. This effect is demonstrated in children with GHD.
Skeletal Growth
The measurable increase in bone length after administration of somatropin results from its effect on the cartilaginous growth areas of long bones. Studies in vitro have shown that the incorporation of sulfate into proteoglycans is not due to a direct effect of somatropin, but rather is mediated by the somatomedins or insulin-like growth factors (IGFs). The somatomedins, among them IGF-I, are polypeptide hormones which are synthesized in the liver, kidney, and various other tissues. IGF-I levels are low in the serum of hypopituitary dwarfs and hypophysectomized humans or animals, and increase after treatment with somatropin.
Cell Growth
It has been shown that the total number of skeletal muscle cells is markedly decreased in children with short stature lacking endogenous GH compared with normal children, and that treatment with somatropin results in an increase in both the number and size of muscle cells.
Organ Growth
Somatropin influences the size of internal organs, and it also increases red cell mass.
Protein Metabolism
Linear growth is facilitated in part by increased cellular protein synthesis. This synthesis and growth are reflected by nitrogen retention which can be quantitated by observing the decline in urinary nitrogen excretion and blood urea nitrogen following the initiation of somatropin therapy.
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Hypopituitary children sometimes experience fasting hypoglycemia that may be improved by treatment with somatropin. In healthy subjects, large doses of somatropin may impair glucose tolerance. Although the precise mechanism of the diabetogenic effect of somatropin is not known, it is attributed to blocking the action of insulin rather than blocking insulin secretion. Insulin levels in serum actually increase as somatropin levels increase. Administration of human growth hormone to normal adults and patients with growth hormone deficiency results in increases in mean serum fasting and postprandial insulin levels, although mean values remain in the normal range. In addition, mean fasting and postprandial glucose and hemoglobin A1C levels remain in the normal range.
Lipid Metabolism
Somatropin stimulates intracellular lipolysis, and administration of somatropin leads to an increase in plasma free fatty acids and triglycerides. Untreated GHD is associated with increased body fat stores, including increased abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue. Treatment of growth hormone deficient patients with somatropin results in a general reduction of fat stores, and decreased serum levels of low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol.
Mineral Metabolism
Administration of somatropin results in an increase in total body potassium and phosphorus and to a lesser extent sodium. This retention is thought to be the result of cell growth. Serum levels of phosphate increase in children with GHD after somatropin therapy due to metabolic activity associated with bone growth. Serum calcium levels are not altered. Although calcium excretion in the urine is increased, there is a simultaneous increase in calcium absorption from the intestine. Negative calcium balance, however, may occasionally occur during somatropin treatment.
Connective Tissue Metabolism
Somatropin stimulates the synthesis of chondroitin sulfate and collagen, and increases the urinary excretion of hydroxyproline.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
A 180-min IV infusion of Norditropin (33 ng/kg/min) was administered to 9 GHD patients. A mean (±SD) hGH steady state serum level of approximately 23.1 (±15.0) ng/mL was reached at 150 min and a mean clearance rate of approximately 2.3 (±1.8) mL/min/kg or 139 (±105) mL/min for hGH was observed. Following infusion, serum hGH levels had a biexponential decay with a terminal elimination half-life (T1/2) of approximately 21.1 (±5.1) min.
In a study conducted in 18 GHD adult patients, where a SC dose of 0.024 mg/kg or 3 IU/m2 was given in the thigh, mean (±SD) Cmax values of 13.8 (±5.8) and 17.1 (±10.0) ng/mL were observed for the 4 and 8 mg Norditropin vials, respectively, at approximately 4 to 5 hr. post dose. The mean apparent terminal T1/2 values were estimated to be approximately 7 to 10 hr. However, the absolute bioavailability for Norditropin after the SC route of administration is currently not known.
The aqueous Norditropin cartridge formulation is bioequivalent to the lyophilized Norditropin vial formulation.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Short Stature in Children with Noonan Syndrome
A prospective, open label, randomized, parallel group trial with 21 children was conducted for 2 years to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Norditropin treatment for short stature in children with Noonan syndrome. An additional 6 children were not randomized, but did follow the protocol. After the initial two-year trial, children continued on Norditropin until final height. Retrospective final height and adverse event data were collected from 18 of the 21 subjects who were originally enrolled in the trial and the 6 who had followed the protocol without randomization. Historical reference materials of height velocity and adult height analyses of Noonan patients served as the controls.
The twenty-four (24) (12 female, 12 male) children 3 – 14 years of age received either 0.033 mg/kg/day or 0.066 mg/kg/day of Norditropin subcutaneously which, after the first 2 years, was adjusted based on growth response.
In addition to a diagnosis of Noonan syndrome, key inclusion criteria included bone age determination showing no significant acceleration, prepubertal status, height SDS <-2, and HV SDS <1 during the 12 months pre-treatment. Exclusion criteria were previous or ongoing treatment with growth hormone, anabolic steroids or corticosteroids, congenital heart disease or other serious disease perceived to possibly have major impact on growth, FPG >6.7 mmol/L (>120 mg/dL), or growth hormone deficiency (peak GH levels <10 ng/mL).
Patients obtained a final height (FH) gain from baseline of 1.5 and 1.6 SDS estimated according to the national and the Noonan reference, respectively. A height gain of 1.5 SDS (national) corresponds to a mean height gain of 9.9 cm in boys and 9.1 cm in girls at 18 years of age, while a height gain of 1.6 SDS (Noonan) corresponds to a mean height gain of 11.5 cm in boys and 11.0 cm in girls at 18 years of age.
A comparison of HV between the two treatment groups during the first two years of treatment for the randomized subjects was 10.1 and 7.6 cm/year with 0.066 mg/kg/day versus 8.55 and 6.7 cm/year with 0.033 mg/kg/day, for Year 1 and Year 2, respectively.
Age at start of treatment was a factor for change in height SDS (national reference). The younger the age at start of treatment, the larger the change in height SDS.
Examination of gender subgroups did not identify differences in response to Norditropin.
Not all patients with Noonan syndrome have short stature; some will achieve a normal adult height without treatment. Therefore, prior to initiating Norditropin for a patient with Noonan syndrome, establish that the patient does have short stature.
14.2 Short Stature in Children with Turner Syndrome
Two randomized, parallel group, open label, multicenter studies were conducted in the Netherlands to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Norditropin for the treatment of children with short stature associated with Turner syndrome. Patients were treated to final height in both studies [height velocity (HV) < 2 cm/year]. Changes in height were expressed as standard deviation scores (SDS) utilizing reference data for untreated Turner syndrome patients as well as the national Dutch population.
In Study 1 (the primary study), 68 euthyroid Caucasian patients stratified based on age and baseline height SDS were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to three different Norditropin treatment regimens: 0.045 mg/kg/day (Dose A) for the entire study; 0.045 mg/kg/day for the first year and 0.067 mg/kg/day thereafter (Dose B); or 0.045 mg/kg/day for the first year, 0.067 for the second year, and 0.089 mg/kg/day thereafter (Dose C). Overall, at baseline, mean age was 6.5 years, mean height SDS (National standard) was -2.7, and mean HV during the previous year was 6.5 cm/year. Patients also received estrogen therapy after age 12 and following four years of Norditropin treatment if they did not have spontaneous puberty.
Patients were treated for a mean of 8.4 years. As seen in Table 3, overall mean final height was 161 cm in the 46 children who attained final height. Seventy percent of these children reached a final height within the normal range (height SDS > -2 using the National standard). A greater percentage of children in the two escalated dose groups reached normal final height. The mean changes from baseline to final height in height SDS after treatment with Dose B and Dose C were significantly greater than the mean changes observed after treatment with Dose A (utilizing both the National and Turner standards). The mean changes from baseline to final height in height SDS (Turner standard) in Table 3 correspond to mean height gains of 9.4, 14.1 and 14.4 cm after treatment with Doses A, B and C, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to final height in height SDS (National standard) in Table 3 correspond to mean height gains of 4.5, 9.1 and 9.4 cm after treatment with Doses A, B and C, respectively. In each treatment group, peak HV was observed during treatment Year 1, and then gradually decreased each year; during Year 4, HV was less than the pre-treatment HV. However, between Year 2 and Year 6, a greater HV was observed in the two dose escalation groups compared to the 0.045 mg/kg/day group.
|
||||
|
Dose A 0.045 mg/kg/day (n=19) |
Dose B up to 0.067 mg/kg/day (n=15) |
Dose C up to 0.089 mg/kg/day (n=12) |
Total (n=46) |
|
| Baseline height (cm)* | 105 (12) | 108 (12.7) | 107 (11.7) | 106 (11.9) |
| Final height (cm)* | 157 (6.7) | 163 (6.0) | 163 (4.9) | 161 (6.5) |
| Number (%) of patients reaching normal height (height SDS >-2 using National standard) | 10 (53%) | 12 (80%) | 10 (83%) | 32 (70%) |
| Height SDS (Turner standard)† | ||||
| Final [95% CI] | 1.7 [1.4, 2.0] | 2.5 [2.1, 2.8]‡ | 2.5 [2.1, 2.9]§ | NA |
| Change from baseline [95% CI] | 1.5 [1.2, 1.8] | 2.2 [1.9, 2.5]‡ | 2.2 [1.9, 2.6]§ | NA |
| Height SDS (National standard)† | ||||
| Final [95% CI] | -1.9 [-2.2, -1.6] | -1.2 [-1.5, -0.9]§ | -1.2 [-1.6, -0.8]¶ | NA |
| Change from baseline [95% CI] | 0.7 [0.4, 1.0] | 1.4 [1.1, 1.7]§ | 1.4 [1.1, 1.8]¶ | NA |
| Values are expressed as mean (SD) unless otherwise indicated. SDS: Standard deviation score. | ||||
In Study 2 (a supportive study), 19 euthyroid Caucasian patients (with bone age ≤13.9 years) were randomized to treatment with 0.067 mg/kg/day of Norditropin as a single subcutaneous dose in the evening, or divided into two doses (1/3 morning and 2/3 evening). All subjects were treated with concomitant ethinyl estradiol. Overall, at baseline, mean age was 13.6 years, mean height SDS (National standard) was -3.5 and mean HV during the previous year was 4.3 cm/year. Patients were treated for a mean of 3.6 years. In that there were no significant differences between the two treatment groups for any linear growth variables, the data from all patients were pooled. Overall mean final height was 155 cm in the 17 children who attained final height. Height SDS changed significantly from -3.5 at baseline to -2.4 at final height (National standard), and from 0.7 to 1.3 at final height (Turner standard).
14.3 Short Stature in Children Born Small for Gestational Age (SGA) with No Catch-up Growth by Age 2-4 Years
A multi-center, randomized, double-blind, two-arm study to final height (Study 1) and a 2-year, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study (Study 2) were conducted to assess the efficacy and safety of Norditropin in children with short stature born SGA with no catch-up growth. Changes in height and height velocity were compared to a national reference population in both studies.
Study 1
The pivotal study included 53 (38 male, 15 female) non-GHD, Dutch children 3-11 years of age with short stature born SGA with no catch-up growth. Catch-up growth was defined as obtaining a height of ≥ 3rd percentile within the first 2 years of life or at a later stage. These prepubertal children needed to meet the following additional inclusion criteria: birth length < 3rd percentile for gestational age, and height velocity (cm/year) for chronological age < 50th percentile. Exclusion criteria included chromosomal abnormalities, signs of a syndrome (except for Silver-Russell syndrome), serious/chronic co-morbid disease, malignancy, and previous rhGH therapy. Norditropin was administered subcutaneously daily at bedtime at a dose of approximately 0.033 (Dose A) or 0.067 mg/kg/day (Dose B) for the entire treatment period. Final height was defined as a height velocity below 2 cm/year. Treatment with Norditropin was continued to final height for up to 13 years. Mean duration of treatment was 9.5 years (boys) and 7.9 years (girls).
38 out of 53 children (72%) reached final height. Sixty-three percent (24 out of 38) of the children who reached final height were within the normal range of their healthy peers (Dutch national reference). For both doses combined, actual mean final height was 171 (SD 6.1) cm in boys and 159 (SD 4.3) cm in girls.
As seen in Table 4, for boys and girls combined, both mean final height SDS (Dose A, -1.8 vs. Dose B, -1.3), and increase in height SDS from baseline to final height (Dose A, 1.4 vs. Dose B, 1.8), were significantly greater after treatment with Dose B (0.067 mg/kg/day). A similar dose response was observed for the increase in height SDS from baseline to Year 2 (Table 4).
Overall mean height velocity at baseline was 5.4 cm/y (SD 1.2; n=29). Height velocity was greatest during the first year of Norditropin treatment and was significantly greater after treatment with Dose B (mean 11.1 cm/y [SD 1.9; n=19]) compared with Dose A (mean 9.7 cm/y [SD 1.3; n=10]).
|
|||
| Raw Mean + SD (N) | |||
|
Dose A 0.033 mg/kg/day |
Dose B 0.067 mg/kg/day |
Total |
|
| Baseline Height SDS | -3.2 + 0.7 (26) | -3.2 + 0.7 (27) | -3.2 + 0.7 (53) |
| Adjusted least-squares mean + standard error (N) and [95% confidence intervals] | |||
| Height SDS: Change from Baseline at Year 2 |
1.4 + 0.1 (26) [1.1, 1.6] |
1.8 + 0.1 (26) [1.5, 2.0] |
Treatment Diff = 0.4 [0.2, 0.7] p-value = 0.002 |
| Height SDS: Change from Baseline at Final Height* |
1.4 + 0.2 (19) [0.9, 1.8] |
1.8 + 0.2 (19) [1.4, 2.2] |
Treatment Diff = 0.5 [0.0, 0.9] p-value = 0.045 |
| Final Height SDS* |
-1.8 + 0.2 (19) [-2.2, -1.4] |
-1.3 + 0.2 (19) [-1.7, -0.9] |
|
| Final Height SDS > -2 | 13/19 (68%) | 11/19 (58%) | 24/38 (63%) |
| SDS: Standard deviation score. | |||
Study 2
In this study, 84 randomized, prepubertal, non-GHD, Japanese children (age 3-8) with short stature born SGA with no catch-up growth were treated for 2 years with 0.033 or 0.067 mg/kg/day of Norditropin subcutaneously daily at bedtime or received no treatment for 1 year. Additional inclusion criteria included birth length or weight SDS ≤ -2 or < 10th percentile for gestational age, height SDS for chronological age ≤ -2, and height velocity SDS for chronological age < 0 within one year prior to Visit 1. Exclusion criteria included diabetes mellitus, history or presence of active malignancy, and serious co-morbid conditions.
As seen in Table 5, for boys and girls combined, there was a dose-dependent increase in height SDS at Year 1 and Year 2. The increase in height SDS from baseline to Year 2 (0.033 mg/kg/day, 0.8 vs. 0.067 mg/kg/day, 1.4) was significantly greater after treatment with 0.067 mg/kg/day. In addition, the increase in height SDS at Year 1 was significantly greater in both active treatment groups compared to the untreated control group.
|
||||
| Raw Mean + SD (N) | ||||
|
No Treatment |
0.033 mg/kg/day |
0.067 mg/kg/day |
Total |
|
| Height SDS: Baseline | -2.9 + 0.5 (15) | -3.0 + 0.6 (35) | -2.9 + 0.7 (34) | -2.9 + 0.6 (84) |
| Height SDS: Year 1 | -2.8 + 0.5 (15) | -2.4 + 0.6 (33) | -2.0 + 0.8 (34) | -2.3 + 0.7 (82) |
| Height SDS: Year 2 | NA | -2.2 + 0.7 (33) | -1.4 + 0.7 (32) | -1.8 + 0.8 (65) |
| Adjusted least-squares mean + standard error (N) and [95% confidence intervals] | ||||
|
Height SDS: Change from Baseline at Year 1* |
0.1 + 0.1 (15) [-0.1, 0.2] |
0.6 + 0.1 (33) [0.5, 0.7] |
0.9 + 0.1 (34) [0.8, 1.0] | |
|
0.033 vs. No Treatment: Treatment Diff = 0.5, [0.3, 0.7], p < 0.0001 0.067 vs. No Treatment: Treatment Diff = 0.8, [0.6, 1.0], p < 0.0001 0.067 vs. 0.033: Treatment Diff = 0.3, [0.2, 0.5], p-value < 0.0001 |
||||
|
Height SDS: Change from Baseline at Year 2* |
NA |
0.8 + 0.1 (33) [0.7, 0.9] |
1.4 + 0.1 (32) [1.3, 1.6] | |
| 0.067 vs. 0.033: Treatment Diff = 0.6, [0.5, 0.8], p-value < 0.0001 | ||||
| SDS: Standard deviation score. | ||||
14.4 Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD)
A total of six randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies were performed. Two representative studies, one in adult onset (AO) GHD patients and a second in childhood onset (CO) GHD patients, are described below.
Study 1
A single center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, six month clinical trial was conducted in 31 adults with AO GHD comparing the effects of Norditropin [somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection] and placebo on body composition. Patients in the active treatment arm were treated with Norditropin 0.017 mg/kg/day (not to exceed 1.33 mg/day). The changes from baseline in lean body mass (LBM) and percent total body fat (TBF) were measured by total body potassium (TBP) after 6 months.
Treatment with Norditropin produced a significant (p=0.0028) increase from baseline in LBM compared to placebo (Table 6).
|
Norditropin (n=15) |
Placebo (n=16) |
|
| Baseline (mean) | 50.27 | 51.72 |
| Change from baseline at 6 months (mean) | 1.12 | -0.63 |
|
Treatment difference (mean) |
1.74 |
|
Analysis of the treatment difference on the change from baseline in percent TBF revealed a significant decrease (p=0.0004) in the Norditropin-treated group compared to the placebo group (Table 7).
|
Norditropin (n=15) |
Placebo (n=16) |
|
| Baseline (mean) | 44.74 | 42.26 |
| Change from baseline at 6 months (mean) | -2.83 | 1.92 |
|
Treatment difference (mean) |
-4.74 |
|
Fifteen (48.4%) of the 31 randomized patients were male. The adjusted mean treatment differences on the increase in LBM and decrease in percent TBF from baseline were larger in males compared to females.
Norditropin also significantly increased serum osteocalcin (a marker of osteoblastic activity).
Study 2
A single center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-finding, six month clinical trial was conducted in 49 men with CO GHD comparing the effects of Norditropin and placebo on body composition. Patients were randomized to placebo or one of three active treatment groups (0.008, 0.016, and 0.024 mg/kg/day). Thirty three percent of the total dose to which each patient was randomized was administered during weeks 1-4, 67% during weeks 5-8, and 100% for the remainder of the study. The changes from baseline in LBM and percent TBF were measured by TBP after 6 months.
Treatment with Norditropin produced a significant (p=0.0079) increase from baseline in LBM compared to placebo (pooled data) (Table 8).
|
Norditropin (n=36) |
Placebo (n=13) |
|
| Baseline (mean) | 48.18 | 48.90 |
| Change from baseline at 6 months (mean) | 2.06 | 0.70 |
|
Treatment difference (mean) |
1.40 |
|
Analysis of the treatment difference on the change from baseline in percent TBF revealed a significant decrease (p=0.0048) in the Norditropin-treated groups (pooled data) compared to the placebo group (Table 9).
|
Norditropin (n=36) |
Placebo (n=13) |
|
| Baseline (mean) | 34.55 | 34.07 |
| Change from baseline at 6 months (mean) | -6.00 | -1.78 |
|
Treatment difference (mean) |
-4.24 |
|
Norditropin also significantly reduced intraabdominal, extraperitoneal and total abdominal fat volume, waist/hip ratio and LDL cholesterol, and significantly increased serum osteocalcin.
Forty four men were enrolled in an open label follow up study and treated with Norditropin for as long as 30 additional months. During this period, the reduction in waist/hip ratio achieved during the initial six months of treatment was maintained.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pens [somatropin (rDNA origin) injection] 5 mg/1.5 mL:
Norditropin NordiFlex is individually cartoned in 5 mg/1.5 mL prefilled pens.
- Norditropin NordiFlex 5 mg/1.5 mL (orange) NDC 54868-6146-0
Unused Norditropin NordiFlex pens must be stored at 2-8°C/36-46°F (refrigerator). Do not freeze. Avoid direct light.
5 mg/1.5 mL (orange) prefilled pens:
After the initial injection, a Norditropin NordiFlex (5 mg/1.5 mL) prefilled pen may be EITHER stored in the refrigerator (2-8ºC/36-46ºF) and used within 4 weeks OR stored for up to 3 weeks at not more than 25ºC (77ºF). Discard unused portion.
| Norditropin Product Formulation | Before Use | In-use (After 1st injection) | |
| Storage requirement |
Storage Option 1 (Refrigeration) |
Storage Option 2 (Room temperature) |
|
|
5 mg |
2-8 ºC/ 36-46 ºF Until exp date |
2-8 ºC/36-46 ºF 4 weeks |
Up to 25ºC/77ºF 3 weeks |
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling
Patients being treated with Norditropin FlexPro or Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pens, or Norditropin Cartridges, (and/or their parents) should be informed about the potential risks and benefits associated with somatropin treatment [in particular, see Adverse Reactions (6.1) for a listing of the most serious and/or most frequently observed adverse reactions associated with somatropin treatment in children and adults]. This information is intended to better educate patients (and caregivers); it is not a disclosure of all possible adverse or intended effects.
Patients and caregivers who will administer Norditropin FlexPro or Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pens, or Norditropin Cartridges, should receive appropriate training and instruction on proper use from the physician or other suitably qualified health care professional. A puncture-resistant container for the disposal of used needles should be strongly recommended. Patients and/or parents should be thoroughly instructed in the importance of proper disposal, and cautioned against any reuse of needles. This information is intended to aid in the safe and effective administration of the medication.
If patients are prescribed Norditropin Cartridges (to be inserted into color-coded NordiPen delivery systems), physicians should instruct patients to read the NordiPen INSTRUCTION booklet provided with the NordiPen delivery systems.
If patients are prescribed Norditropin FlexPro or Norditropin NordiFlex, physicians should instruct patients to read the PATIENT INFORMATION and INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE leaflets provided with the Norditropin FlexPro and Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pens.
Date of Issue: March 2, 2010
Version: 12
Novo Nordisk® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S.
Norditropin®, FlexPro®, NordiPen® and Norditropin NordiFlex® are registered trademarks of Novo Nordisk Health Care AG.
© 2002-2010 Novo Nordisk Health Care AG
For information contact:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
100 College Road West
Princeton, New Jersey 08540, USA
1-888-NOVO-444 (1-888-668-6444)
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
Relabeling of "Additional Barcode label" by:
Physicians Total Care, Inc.
Tulsa, OK 74146
PATIENT INFORMATION
Norditropin® (Nor-dee-tro-pin)
(somatropin [rDNA origin]) injection
Read the Patient Information that comes with Norditropin before you start to take it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is Norditropin?
Norditropin is a prescription medicine given by injection under the skin (subcutaneous) that contains human growth hormone, identical to the growth hormone produced in the human body, used to treat:
- children who are not growing because of low or no growth hormone
- children who are short (in stature) and who have Noonan syndrome or Turner syndrome
- children who are short (in stature) because they were born small (small for gestational age-SGA) and have not caught-up in growth by age 2 to 4 years
- adults who do not make enough growth hormone
Who should not use Norditropin?
Do not use Norditropin if:
- you have a critical illness caused by certain types of heart or stomach surgery, trauma or breathing (respiratory) problems
- you are a child with Prader-Willi syndrome who is severely obese or has breathing problems including sleep apnea
- you have cancer or other tumors
- your healthcare provider tells you that you have certain types of eye problems caused by diabetes
- you are a child with closed bone growth plates (epiphyses)
- you are allergic to any of the ingredients in Norditropin. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Norditropin.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before I start Norditropin?
Before you take Norditropin, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have diabetes
- had cancer or any tumor
- have any other medical condition
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Norditropin will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. It is not known if Norditropin passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take Norditropin while you breast-feed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Norditropin may affect how other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how Norditropin works.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- glucocorticoid medication
- thyroid hormone
- insulin or other medicine for diabetes
- medicines that are metabolized by the liver
- estrogen replacement medicines
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if any of your medicines are the kind listed above. Keep a list of your medicines with you and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use Norditropin?
- Read the detailed Instructions for Use that come with Norditropin. Your healthcare provider will show you how to inject Norditropin.
- Take Norditropin exactly as prescribed.
- Norditropin FlexPro pens, NordiFlex pens and cartridges are for use by one person only.
- Novo Nordisk disposable needles are designed to be used with Norditropin for each injection.
- Always keep the pen cap closed on Norditropin when you are not using it.
- Norditropin comes in 3 dose strengths for FlexPro prefilled color coded pens, 4 dose strengths for NordiFlex prefilled color coded pens, and 2 dose strengths for color coded cartridges.
- If you inject too much Norditropin, call your healthcare provider.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses at the same time unless your healthcare provider tells you to. If you are not sure about your dosing, call your healthcare provider.
- Throw away Norditropin when the cartridge is empty.
- Refer to the Instructions for Use about what to do if you have less than a full dose left in your pen.
What are the possible side effects of Norditropin?
Norditropin can cause serious side effects, including:
- high risk of death in people who have critical illnesses because of heart or stomach surgery, trauma or serious breathing (respiratory) problems
- high risk of death in children with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese or have breathing problems, including sleep apnea
- return of tumor or cancerous growths
- high blood sugar (hyperglycemia)
- increase in pressure in the skull (intracranial hypertension). If you have headaches, eye problems, nausea or vomiting, contact your healthcare provider right away.
- swollen hands and feet due to fluid retention
- decrease in thyroid hormone levels. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your thyroid hormone levels.
- hip and knee pain or a limp in children (slipped capital femoral epiphysis)
- worsening of curvature of the spine (scoliosis)
- middle ear infection, hearing problems or ear problems in patients with Turner syndrome
- redness, itching and tissue weakness in the area you inject
- increase in phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase and parathyroid hormone levels in your blood. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check this.
The most common side effects of Norditropin include:
- headaches
- muscle pain
- joint stiffness
- high blood sugar (hyperglycemia)
- sugar in your urine (glucosuria)
- swollen hands and feet due to fluid retention
- redness and itching in the area you inject
Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Norditropin. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 (1-800-332-1088). You may also report side effects to Novo Nordisk at 1-888-NOVO-444 (1-888-668-6444).
How do I store Norditropin?
Unused Norditropin FlexPro and NordiFlex pens, and cartridges:
- Keep in a refrigerator between 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC).
- Do not freeze or expose Norditropin to heat.
- Keep Norditropin away from direct light.
- Do not use Norditropin that has been frozen or in temperatures warmer than 77ºF (25ºC).
- Do not use Norditropin after the expiration date printed on the carton and the pen or cartridge.
After the first injection
- Norditropin FlexPro, NordiFlex and cartridge 5 mg/1.5 mL (orange):
- either store in the refrigerator between 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC) and use within 4 weeks
- orkeep for up to 3 weeks at no warmer than 77ºF(25ºC).
- Throw away any unused medicine.
- Norditropin FlexPro and NordiFlex 10 mg/1.5mL (blue):
- either store in the refrigerator between 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8º C) and use within 4 weeks.
- or keep for up to 3 weeks at no warmer than 77 ºF (25ºC).
- Throw away any unused medicine.
- Norditropin FlexPro, NordiFlex and cartridge 15 mg/1.5 mL (green):
- store in the refrigerator between 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC) and use within 4 weeks
- Throw away any unused medicine after 4 weeks.
- Norditropin NordiFlex pens 30 mg/3 mL (purple):
- store in the refrigerator between 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC) and use within 4 weeks
- Throw away any unused medicine after 4 weeks
General Information about Norditropin.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in Patient Information. Do not use Norditropin for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Norditropin to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information summarizes the most important information about Norditropin. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Norditropin that is written for healthcare professionals.
What are the ingredients in Norditropin?
Active ingredient: somatropin (rDNA origin)
Inactive ingredients: Histidine, Poloxamer 188, Phenol, Mannitol, HCl/NaOH (as needed) and Water for Injection
Date of Issue: March 2, 2010
Version: 7
For assistance or further information, write to:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
100 College Road West
Princeton, NJ 08540, USA
1-888-NOVO-444 (1-888-668-6444)
norditropin-us.com
US Patent Nos. 6,235,004; 6,004,297; 6,582,404; 6,716,198; 6,899,699; 5,849,704; 5,691,169; 5,618,697 and other patents pending.
Norditropin®, FlexPro®, Norditropin NordiFlex® and NordiFlex PenMate® are registered trademarks of Novo Nordisk Health Care AG.
Novo Nordisk® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S.
© 2004-2010 Novo Nordisk Health Care AG
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Norditropin NordiFlex®
Somatropin (rDNA origin) injection
5 mg/1.5 mL Prefilled Pen
Using the disposable Norditropin NordiFlex® 5 mg/1.5 mL Prefilled Pen
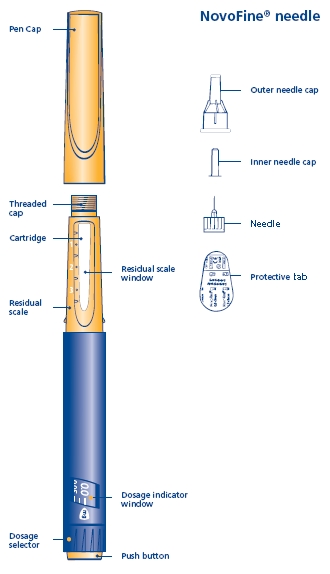
Norditropin NordiFlex 5 mg/1.5 mL is a multi-dose, disposable, prefilled pen with liquid growth hormone able to deliver doses from 0.025 to 1.5 mg. The dose can be adjusted in increments of 0.025 mg. Your doctor will determine the correct dose for you. Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pen is designed to be used with NovoFine® disposable needles (sold separately). Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pen is not recommended for people who are blind or have trouble seeing unless they have the help of a sighted individual trained to use Norditropin NordiFlex.
Please read these instructions carefully before using this pen
1 Preparing Norditropin NordiFlex 5 mg/1.5 mL for injection
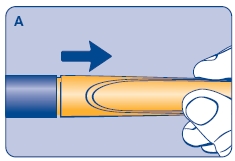
A. Pull off the pen cap and check if the growth hormone solution is clear and colorless by turning Norditropin NordiFlex upside down once or twice and view the solution through the residual scale window. DO NOT use Norditropin NordiFlex if the growth hormone solution is cloudy or contains particles. Use it only if it is clear and colorless.
Wash hands well and dry completely.
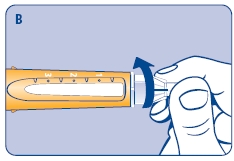
Wipe the front rubber stopper on the threaded plastic cap with an alcohol swab.
B. Place a new NovoFine disposable needle onto Norditropin NordiFlex immediately before use. Remove the protective tab from the disposable needle and screw the needle tightly onto Norditropin NordiFlex. Pull off the outer and inner needle caps. Never place a disposable needle on your Norditropin NordiFlex until you are ready to give an injection. Remove the needle immediately after use. If the needle is not removed, some growth hormone may be expelled from Norditropin NordiFlex.
2 Performing an air shot
Do an air shot before starting a new Norditropin NordiFlex as follows:
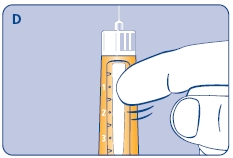
Small amounts of air may collect in the needle and cartridge. To avoid injecting air and ensure proper dosing, set the dosage selector to 0.025 mg. Each line between labeled dosages is 0.025 mg.
C. Dial 0.025 mg

D. Hold Norditropin NordiFlex with the needle pointing up, tap the cartridge gently with your finger a few times to raise any air bubbles to the top of the cartridge.
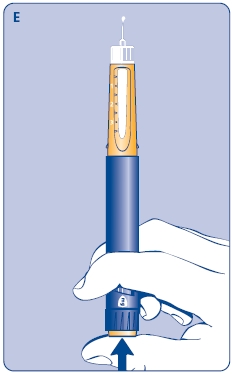
E. Still holding Norditropin NordiFlex with the needle up, press the push button all the way in. A drop of growth hormone should appear at the needle tip. If not, repeat the procedure, no more than 4 times.
If a drop of growth hormone still does not appear, call 1-888-NOVO-444 for help.
3 Setting the dose
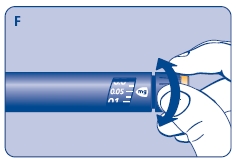
F. Check that the dose selector is set at 0.0. Dial the number of mg (milligram) that you need to inject. The dose can be changed up or down by turning the dose selector in either direction. When dialing back, be careful not to press the push button as growth hormone liquid will come out.
DO NOT use the clicking sound as a guide for selecting dose.
The numbers on the residual scale can be used to estimate the mg left in the cartridge. DO NOT use these numbers to measure the growth hormone dose.
You cannot set a dose higher than the number of mg left in the cartridge. Use a new Norditropin NordiFlex pen to inject the remaining amount of your dose. Be sure to remember the dose already received with the first dose. For example, if your dose is 0.6 mg and you can only set the dose selector to 0.4 mg, you will need to inject an additional 0.2 mg with a new Norditropin NordiFlex pen.
4 Giving the injection
Use the injection procedure recommended by your doctor or healthcare professional.
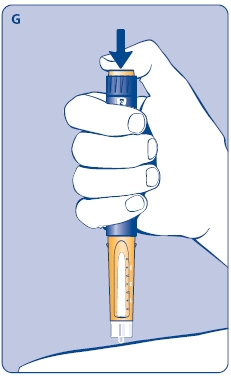
G. This product is for subcutaneous use only. Insert the needle under the skin and deliver the dose by pressing the push button all the way in. Press the push button only when injecting.
After the injection, the needle should remain under the skin for at least 6 seconds. Keep the push button fully depressed until the needle is removed from the skin. This will ensure that the full dose has been delivered. Vary the injection site using the injection procedure recommended by your doctor.
After the injection, check the dosage indicator window to make sure it shows zero (0.0).
If zero does not appear, you did not receive the full dose. Call 1-888-NOVO-444 for assistance.
5 Removing the needle
H. After the injection, remove the needle without recapping and dispose of it in a puncture-resistant container. Used needles should be placed in sharps container (such as red biohazard containers), hard plastic containers (such as detergent bottles), or metal containers (such as an empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.
It is important that you use a new needle for each injection. Healthcare professionals, relatives and other caregivers should follow general precautionary measures for removal and disposal of needles to eliminate the risk of unintended needle stick injuries.
When the cartridge is empty, throw away Norditropin NordiFlex without the needle attached.
6 Maintenance
Norditropin NordiFlex should be handled with care. Protect Norditropin NordiFlex from dust, dirt, and direct sunlight.
You can clean the outside of Norditropin NordiFlex by wiping it with a soft cloth moistened with water. Do not soak Norditropin NordiFlex in alcohol, wash, or lubricate it.
7 Important Notes
- Store unused Norditropin NordiFlex pens in a refrigerator (2ºC-8ºC/36ºF-46ºF). After the initial injection, Norditropin NordiFlex 5 mg/1.5 mL may be EITHER stored in the refrigerator (2-8ºC/36-46ºF) and used within 4 weeks OR may be stored for up to 3 weeks at not more than 25ºC (77ºF).
- Remember to perform an air shot before starting a new Norditropin NordiFlex or before the injection if you dropped or knocked the pen against a hard surface. See diagrams C, D and E.
- If you need to perform more than 4 air shots before the first use of Norditropin NordiFlex to get a droplet of growth hormone at the needle tip, DO NOT use Norditropin NordiFlex. Call 1-888-NOVO-444 for help.
- Take care not to drop Norditropin NordiFlex or knock it against a hard surface.
- DO NOT leave Norditropin NordiFlex in a car or other location where it can get too hot or too cold.
- Always have a spare Norditropin NordiFlex disposable pen in order to avoid running out of this product.
- Norditropin NordiFlex is designed to be used with NovoFine disposable needles.
- NEVER place a needle on Norditropin NordiFlex until you are ready to use it. Remove the needle right after use without recapping.
- Throw away used needles properly, so people will not be harmed.
- Throw away the used Norditropin NordiFlex, without the needle attached.
- To avoid spread of disease, do not let anyone else use your Norditropin NordiFlex, even if you attach a new needle.
- Keep Norditropin NordiFlex out of the reach of children.
- Novo Nordisk is not responsible for harm due to using Norditropin NordiFlex with products that are not recommended by Novo Nordisk.
8 Warranty
If your Norditropin NordiFlex is defective in materials or workmanship, Novo Nordisk Inc. will replace it at no charge if you mail the defective unit, postage prepaid to:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
Product Safety
100 College Road West
Princeton, NJ 08540, USA
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Norditropin NordiFlex®
Somatropin (rDNA origin) injection
10 mg/1.5 mL Prefilled Pen
Using the disposable Norditropin NordiFlex® 10 mg/1.5 mL Prefilled Pen
Norditropin NordiFlex 10 mg/1.5 mL is a multi-dose, disposable, prefilled pen with liquid growth hormone able to deliver doses from 0.05 to 3.0 mg. The dose can be adjusted in increments of 0.05 mg. Your doctor will determine the correct dose for you. Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pen is designed to be used with NovoFine® disposable needles (sold separately). Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pen is not recommended for people who are blind or have trouble seeing unless they have the help of a sighted individual trained to use Norditropin NordiFlex.
Please read these instructions carefully before using this pen
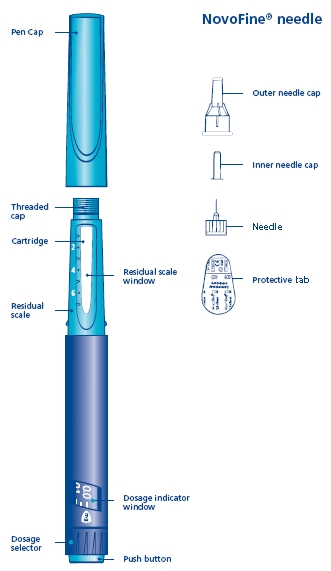
1 Preparing Norditropin NordiFlex 10 mg/1.5 mL for injection
A. Pull off the pen cap and check if the growth hormone solution is clear and colorless by turning Norditropin NordiFlex upside down once or twice and view the solution through the residual scale window. DO NOT use Norditropin NordiFlex if the growth hormone solution is cloudy or contains particles. Use it only if it is clear and colorless.
Wash hands well and dry completely.
Wipe the front rubber stopper on the threaded plastic cap with an alcohol swab.
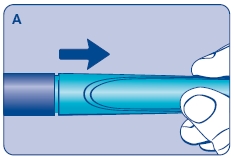
B. Place a new NovoFine disposable needle onto Norditropin NordiFlex immediately before use. Remove the protective tab from the disposable needle and screw the needle tightly onto Norditropin NordiFlex. Pull off the outer and inner needle caps. Never place a disposable needle on your Norditropin NordiFlex until you are ready to give an injection. Remove the needle immediately after use. If the needle is not removed, some growth hormone may be expelled from Norditropin NordiFlex.
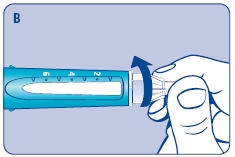
2 Performing an air shot
Do an air shot before starting a new Norditropin NordiFlex as follows:
Small amounts of air may collect in the needle and cartridge. To avoid injecting air and ensure proper dosing, set the dosage selector to 0.05 mg. Each line between labeled dosages is 0.05 mg.
C. Dial 0.05 mg

D. Hold Norditropin NordiFlex with the needle pointing up, tap the cartridge gently with your finger a few times to raise any air bubbles to the top of the cartridge.
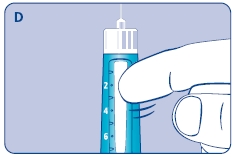
E. Still holding Norditropin NordiFlex with the needle up, press the push button all the way in. A drop of growth hormone should appear at the needle tip. If not, repeat the procedure, no more than 4 times.
If a drop of growth hormone still does not appear, call 1-888-NOVO-444 for help.
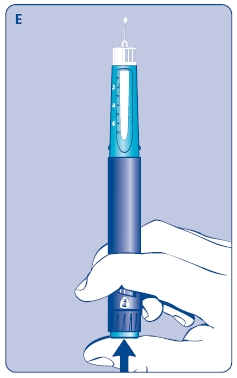
3 Setting the dose
F. Check that the dose selector is set at 0.0. Dial the number of mg (milligram) that you need to inject. The dose can be changed up or down by turning the dose selector in either direction. When dialing back, be careful not to press the push button as growth hormone liquid will come out.
DO NOT use the clicking sound as a guide for selecting dose.
The numbers on the residual scale can be used to estimate the mg left in the cartridge. DO NOT use these numbers to measure the growth hormone dose.
You cannot set a dose higher than the number of mg left in the cartridge. Use a new Norditropin NordiFlex pen to inject the remaining amount of your dose. Be sure to remember the dose already received with the first dose. For example, if your dose is 0.6 mg and you can only set the dose selector to 0.4 mg, you will need to inject an additional 0.2 mg with a new Norditropin NordiFlex pen.
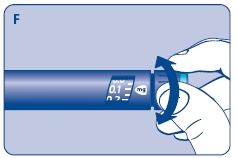
4 Giving the injection
Use the injection procedure recommended by your doctor or healthcare professional.
G. This product is for subcutaneous use only. Insert the needle under the skin and deliver the dose by pressing the push button all the way in. Press the push button only when injecting.
After the injection, the needle should remain under the skin for at least 6 seconds. Keep the push button fully depressed until the needle is removed from the skin. This will ensure that the full dose has been delivered. Vary the injection site using the injection procedure recommended by your doctor.
After the injection, check the dosage indicator window to make sure it shows zero (0.0).
If zero does not appear, you did not receive the full dose. Call 1-888-NOVO-444 for assistance.
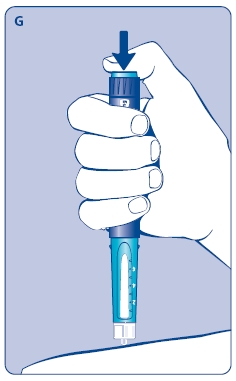
5 Removing the needle
H. After the injection, remove the needle without recapping and dispose of it in a puncture-resistant container. Used needles should be placed in sharps container (such as red biohazard containers), hard plastic containers (such as detergent bottles), or metal containers (such as an empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.
It is important that you use a new needle for each injection. Healthcare professionals, relatives and other caregivers should follow general precautionary measures for removal and disposal of needles to eliminate the risk of unintended needle stick injuries.
When the cartridge is empty, throw away Norditropin NordiFlex without the needle attached.
6 Maintenance
Norditropin NordiFlex should be handled with care. Protect Norditropin NordiFlex from dust, dirt, and direct sunlight.
You can clean the outside of Norditropin NordiFlex by wiping it with a soft cloth moistened with water. Do not soak Norditropin NordiFlex in alcohol, wash, or lubricate it.
7 Important Notes
- Store unused Norditropin NordiFlex pens in a refrigerator (2ºC-8ºC/36ºF-46ºF). After the initial injection, Norditropin NordiFlex 10 mg/1.5 mL may be EITHER stored in the refrigerator (2-8ºC/36-46ºF) and used within 4 weeks OR may be stored for up to 3 weeks at not more than 25ºC (77ºF).
- Remember to perform an air shot before starting a new Norditropin NordiFlex or before the injection if you dropped or knocked the pen against a hard surface. See diagrams C, D and E.
- If you need to perform more than 4 air shots before the first use of Norditropin NordiFlex to get a droplet of growth hormone at the needle tip, DO NOT use Norditropin NordiFlex. Call 1-888-NOVO-444 for help.
- Take care not to drop Norditropin NordiFlex or knock it against a hard surface.
- DO NOT leave Norditropin NordiFlex in a car or other location where it can get too hot or too cold.
- Always have a spare Norditropin NordiFlex disposable pen in order to avoid running out of this product.
- Norditropin NordiFlex is designed to be used with NovoFine disposable needles.
- NEVER place a needle on Norditropin NordiFlex until you are ready to use it. Remove the needle right after use without recapping.
- Throw away used needles properly, so people will not be harmed.
- Throw away the used Norditropin NordiFlex, without the needle attached.
- To avoid spread of disease, do not let anyone else use your Norditropin NordiFlex, even if you attach a new needle.
- Keep Norditropin NordiFlex out of the reach of children.
- Novo Nordisk is not responsible for harm due to using Norditropin NordiFlex with products that are not recommended by Novo Nordisk.
8 Warranty
If your Norditropin NordiFlex is defective in materials or workmanship, Novo Nordisk Inc. will replace it at no charge if you mail the defective unit, postage prepaid to:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
Product Safety
100 College Road West
Princeton, NJ 08540, USA
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Norditropin NordiFlex®
Somatropin (rDNA origin) injection
15 mg/1.5 mL Prefilled Pen
Using the disposable Norditropin NordiFlex® 15 mg/1.5 mL Prefilled Pen
Norditropin NordiFlex 15 mg/1.5 mL is a multi-dose, disposable, prefilled pen with liquid growth hormone able to deliver doses from 0.075 to 4.5 mg. The dose can be adjusted in increments of 0.075 mg. Your doctor will determine the correct dose for you. Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pen is designed to be used with NovoFine® disposable needles (sold separately). Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pen is not recommended for people who are blind or have trouble seeing unless they have the help of a sighted individual trained to use Norditropin NordiFlex.
Please read these instructions carefully before using this pen
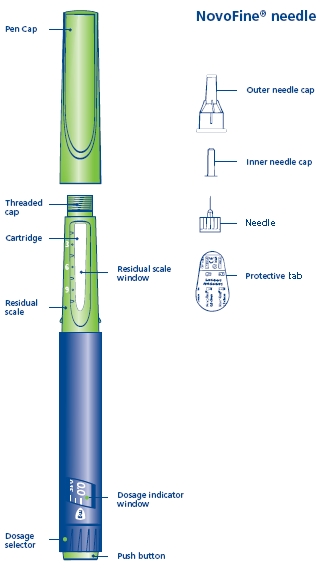
1 Preparing Norditropin NordiFlex 15 mg/1.5 mL for injection
A. Pull off the pen cap and check if the growth hormone solution is clear and colorless by turning Norditropin NordiFlex upside down once or twice and view the solution through the residual scale window. DO NOT use Norditropin NordiFlex if the growth hormone solution is cloudy or contains particles. Use it only if it is clear and colorless.
Wash hands well and dry completely.
Wipe the front rubber stopper on the threaded plastic cap with an alcohol swab.
B. Place a new NovoFine disposable needle onto Norditropin NordiFlex immediately before use. Remove the protective tab from the disposable needle and screw the needle tightly onto Norditropin NordiFlex. Pull off the outer and inner needle caps. Never place a disposable needle on your Norditropin NordiFlex until you are ready to give an injection. Remove the needle immediately after use. If the needle is not removed, some growth hormone may be expelled from Norditropin NordiFlex.
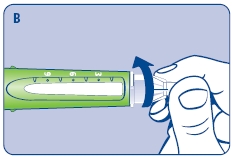
2 Performing an air shot
Do an air shot before starting a new Norditropin NordiFlex as follows:
Small amounts of air may collect in the needle and cartridge. To avoid injecting air and ensure proper dosing, set the dosage selector to 0.075 mg. Each line between labeled dosages is 0.075 mg.
C. Dial 0.075 mg
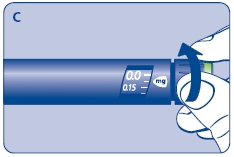
D. Hold Norditropin NordiFlex with the needle pointing up, tap the cartridge gently with your finger a few times to raise any air bubbles to the top of the cartridge.
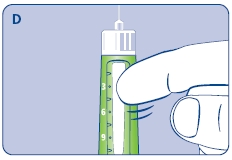
E. Still holding Norditropin NordiFlex with the needle up, press the push button all the way in. A drop of growth hormone should appear at the needle tip. If not, repeat the procedure, no more than 4 times.
If a drop of growth hormone still does not appear, call 1-888-NOVO-444 for help.
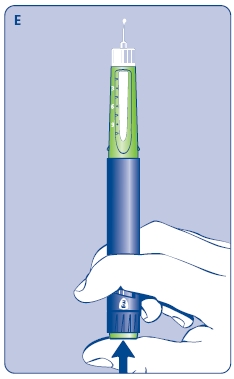
3 Setting the dose
F. Check that the dose selector is set at 0.0. Dial the number of mg (milligram) that you need to inject. The dose can be changed up or down by turning the dose selector in either direction. When dialing back, be careful not to press the push button as growth hormone liquid will come out.
DO NOT use the clicking sound as a guide for selecting dose.
The numbers on the residual scale can be used to estimate the mg left in the cartridge. DO NOT use these numbers to measure the growth hormone dose.
You cannot set a dose higher than the number of mg left in the cartridge. Use a new Norditropin NordiFlex pen to inject the remaining amount of your dose. Be sure to remember the dose already received with the first dose. For example, if your dose is 0.6 mg and you can only set the dose selector to 0.3 mg, you will need to inject an additional 0.3 mg with a new Norditropin NordiFlex pen.
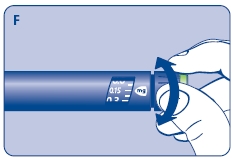
4 Giving the injection
Use the injection procedure recommended by your doctor or healthcare professional.
G. This product is for subcutaneous use only. Insert the needle under the skin and deliver the dose by pressing the push button all the way in. Press the push button only when injecting.
After the injection, the needle should remain under the skin for at least 6 seconds. Keep the push button fully depressed until the needle is removed from the skin. This will ensure that the full dose has been delivered. Vary the injection site using the injection procedure recommended by your doctor.
After the injection, check the dosage indicator window to make sure it shows zero (0.0).
If zero does not appear, you did not receive the full dose. Call 1-888-NOVO-444 for assistance.
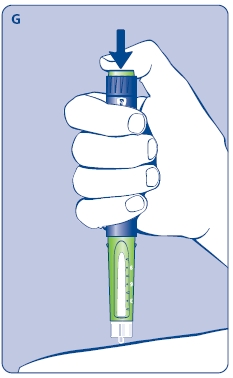
5 Removing the needle
H. After the injection, remove the needle without recapping and dispose of it in a puncture-resistant container. Used needles should be placed in sharps container (such as red biohazard containers), hard plastic containers (such as detergent bottles), or metal containers (such as an empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.
It is important that you use a new needle for each injection. Healthcare professionals, relatives and other caregivers should follow general precautionary measures for removal and disposal of needles to eliminate the risk of unintended needle stick injuries.
When the cartridge is empty, throw away Norditropin NordiFlex without the needle attached.
6 Maintenance
Norditropin NordiFlex should be handled with care. Protect Norditropin NordiFlex from dust, dirt, and direct sunlight.
You can clean the outside of Norditropin NordiFlex by wiping it with a soft cloth moistened with water. Do not soak Norditropin NordiFlex in alcohol, wash, or lubricate it.
7 Important Notes
- Store unused Norditropin NordiFlex pens in a refrigerator (2ºC-8ºC/36ºF-46ºF). After the initial injection, keep Norditropin NordiFlex 15 mg/1.5 mL refrigerated and use within 4 weeks.
- Remember to perform an air shot before starting a new Norditropin NordiFlex or before the injection if you dropped or knocked the pen against a hard surface. See diagrams C, D and E.
- If you need to perform more than 4 air shots before the first use of Norditropin NordiFlex to get a droplet of growth hormone at the needle tip, DO NOT use Norditropin NordiFlex. Call 1-888-NOVO-444 for help.
- Take care not to drop Norditropin NordiFlex or knock it against a hard surface.
- DO NOT leave Norditropin NordiFlex in a car or other location where it can get too hot or too cold.
- Always have a spare Norditropin NordiFlex disposable pen in order to avoid running out of this product.
- Norditropin NordiFlex is designed to be used with NovoFine disposable needles.
- NEVER place a needle on Norditropin NordiFlex until you are ready to use it. Remove the needle right after use without recapping.
- Throw away used needles properly, so people will not be harmed.
- Throw away the used Norditropin NordiFlex, without the needle attached.
- To avoid spread of disease, do not let anyone else use your Norditropin NordiFlex, even if you attach a new needle.
- Keep Norditropin NordiFlex out of the reach of children.
- Novo Nordisk is not responsible for harm due to using Norditropin NordiFlex with products that are not recommended by Novo Nordisk.
8 Warranty
If your Norditropin NordiFlex is defective in materials or workmanship, Novo Nordisk Inc. will replace it at no charge if you mail the defective unit, postage prepaid to:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
Product Safety
100 College Road West
Princeton, NJ 08540, USA
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Norditropin NordiFlex®
Somatropin (rDNA origin) injection
30 mg/3 mL Prefilled Pen
Using the disposable Norditropin NordiFlex® 30 mg/3 mL Prefilled Pen
Norditropin NordiFlex 30 mg/3 mL is a multi-dose, disposable, prefilled pen with liquid growth hormone able to deliver doses from 0.1 to 6.0 mg. The dose can be adjusted in increments of 0.1 mg. Your doctor will determine the correct dose for you. Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pen is designed to be used with NovoFine® disposable needles (sold separately). Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pen is not recommended for people who are blind or have trouble seeing unless they have the help of a sighted individual trained to use Norditropin NordiFlex.
Please read these instructions carefully before using this pen
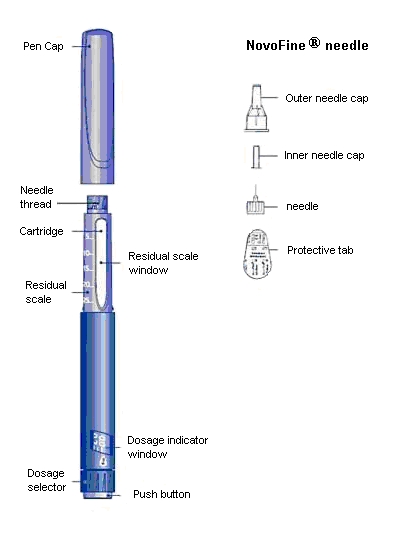
1 Preparing Norditropin NordiFlex 30 mg/3 mL for Injection
A. Pull off the pen cap and check if the growth hormone solution is clear and colorless by turning the Norditropin NordiFlex upside down once or twice and view the solution through the residual scale window. DO NOT use Norditropin NordiFlex if the growth hormone solution is cloudy or contains particles. Use it only if it is clear and colorless.
Wash hands well and dry completely.
Wipe the front rubber stopper on the needle thread with an alcohol swab.
B. Place a new NovoFine disposable needle onto Norditropin NordiFlex immediately before use. Remove the protective tab from the disposable needle and screw the needle tightly onto Norditropin NordiFlex. Pull off the outer and inner needle caps. Never place a disposable needle on your Norditropin NordiFlex until you are ready to give an injection. Remove the needle immediately after use. If the needle is not removed, some liquid may be expelled from Norditropin NordiFlex.
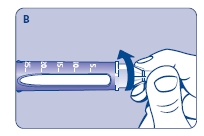
2 Performing an Air Shot
Do an air shot before starting a new Norditropin NordiFlex as follows:
Small amounts of air may collect in the needle and cartridge. To ensure proper dosing and to avoid injecting air, you must perform an air shot before administering your first injection.
C. Dial the dosage selector to 0.1 mg. Each line between labeled dosages is 0.1 mg.

D. Hold Norditropin NordiFlex with the needle pointing up, tap the cartridge gently with your finger a few times to make any air bubbles rise to the top of the cartridge.
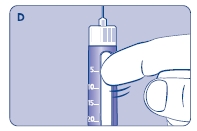
E. Still holding Norditropin NordiFlex with the needle up, press the push button all the way in. A drop of liquid should appear at the needle tip. If not, repeat the above steps, no more than 4 times.
If a drop of liquid still does not appear, call 1-888-NOVO-444 for help.
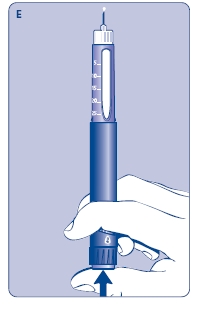
3 Setting the Dose
F. Check that the dose selector is set at 0.0. Dial the number of mg (milligram) that you need to inject. If you dial more than your dose, the dose can be changed up or down by turning the dose selector in either direction. When dialing back, be careful not to press the push button as liquid will come out.
Use dosage indicator, NOT the clicking sound, as a guide for selecting the dose.
The numbers on the residual scale can be used to estimate the mg left in the cartridge. DO NOT use these numbers to measure the dose.
You cannot set a dose higher than the number of mg left in the cartridge. Use a new Norditropin NordiFlex pen to inject the remaining amount of your dose. Be sure to remember the dose already received with the first dose. For example, if your dose is 0.6 mg and you can only set the dose selector to 0.3 mg. You will need to inject an additional 0.3 mg with a new Norditropin NordiFlex pen.

4 Giving the Injection
Use the injection technique recommended by your healthcare professional.
G. This product is for subcutaneous use only. Insert the needle under the skin and press the push button as far as it goes to deliver the dose. To ensure that the full dose is injected keep the needle in the skin for at least 6 seconds after injection with your thumb on the push button. Keep the push button fully pushed in until after the needle has been removed from the skin.
After the injection, check the dosage indicator window to make sure it shows zero (0.0).
If zero does not appear, you did not receive the full dose. Call 1-888-NOVO-444 for assistance.
Note:
Always press the push button to inject the dose. Turning the dosage selector will not inject the dose.
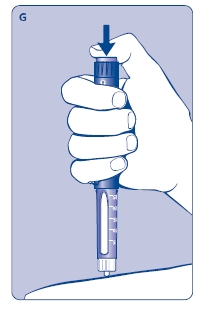
5 Removing the NovoFine Disposable Needle
H. After the injection, remove the needle without recapping and dispose of it in a puncture-resistant container. Used needles should be placed in sharps container (such as red biohazard containers), hard plastic containers (such as detergent bottles), or metal containers (such as an empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.
It is important that you use a new needle for each injection. Healthcare professionals, relatives and other caregivers should follow general precautionary measures for removal and disposal of needles to reduce the risk of unintended needle stick injuries.
When the cartridge is empty, dispose of Norditropin NordiFlex without the needle attached.
6 Maintenance
Handle Norditropin NordiFlex with care. Protect Norditropin NordiFlex from dust, dirt, and direct sunlight.
You can clean the outside of Norditropin NordiFlex by wiping it with a soft cloth moistened with water. Do not soak Norditropin NordiFlex in alcohol, wash, or lubricate it.
7 Important Things to Know
- Norditropin NordiFlex 30 mg/3 mL cannot be used with the NordiFlex PenMate® auto-insertion accessory.
- Store unused Norditropin NordiFlex pens in a refrigerator (2ºC - 8ºC/36ºF - 46ºF). After the initial injection, keep Norditropin NordiFlex 30 mg/3 mL refrigerated and use within 4 weeks.
- Remember to perform an air shot before starting a new Norditropin NordiFlex or before the injection if you dropped or knocked the pen against a hard surface. See diagrams C, D and E.
- If you need to perform more than 4 air shots before the first use of Norditropin NordiFlex to get a droplet of liquid at the needle tip, DO NOT use Norditropin NordiFlex. Call 1-888-NOVO-444 for help.
- Take care not to drop Norditropin NordiFlex or knock it against a hard surface.
- DO NOT leave Norditropin NordiFlex in a car or other location where it can get too hot or too cold.
- Always have a spare Norditropin NordiFlex disposable pen in order to avoid running out of this product.
- Norditropin NordiFlex is designed to be used with NovoFine disposable needles.
- NEVER place a needle on Norditropin NordiFlex until you are ready to use it. Remove the needle right after use without recapping.
- Dispose of used needles properly, so people will not be harmed.
- Dispose of used Norditropin NordiFlex, without the needle attached.
- To avoid spread of disease, do not let anyone else use your Norditropin NordiFlex, even if you attach a new needle.
- Keep the Norditropin NordiFlex out of the reach of children.
- Novo Nordisk is not responsible for harm due to using the Norditropin NordiFlex with products that are not recommended by Novo Nordisk.
8 Customer Satisfaction
Customer service and satisfaction are our top concerns. If you have any questions about Norditropin NordiFlex prefilled pens please call Novo Nordisk Inc. at 1-888-NOVO-444.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Norditropin® FlexPro®
(somatropin [rDNA origin] injection)
5 mg/1.5 mL (orange) Prefilled Pen
Read these instructions before using your Norditropin® FlexPro® pen.
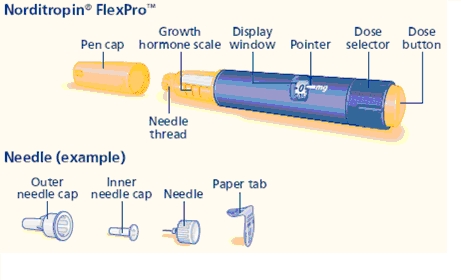
Norditropin FlexPro contains 5 mg human growth hormone solution and delivers doses from 0.025 mg to 2 mg, in increments of 0.025 mg. Norditropin FlexPro is made to be used with Novo Nordisk® disposable needles. Needles are not included with Norditropin FlexPro.
Prepare your Norditropin FlexPro pen
A.
- Pull off the pen cap.
- Check that the liquid in the pen is clear and colorless by tipping it upside down 1 or 2 times. If the liquid looks unclear or cloudy, do not use the pen.
- Wash hands well and dry them.
- Wipe the front stopper on the needle thread with an alcohol swab.
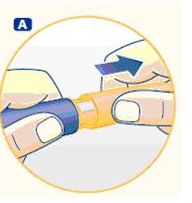
B.
- Take a new disposable needle.
- Tear the paper tab off and screw the needle straight onto the pen.
- Make sure the needle is on tight.
- Never place a disposable needle on your Norditropin FlexPro pen until you are ready to give an injection.
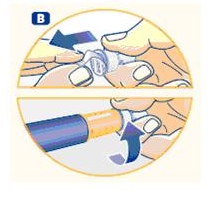
C.
- Pull off the outer needle cap and inner needle cap and throw them both away.
- If you try to put the needle caps back on, you may accidentally hurt yourself with the needle.
- A drop of liquid may appear at the needle tip. This is normal.
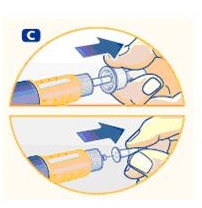
Important:
- Always use a new needle for each injection. This will help prevent contamination.
- Never bend or damage the needle.
Check the growth hormone flow (airshot)
Make sure that you receive your full dose by checking the growth hormone flow (performing an airshot) before you select and inject your first dose from a new pen.
D. Turn the dose selector to select 0.025 mg. This is the smallest amount of medicine for a dose.
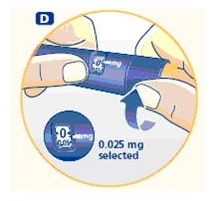
E.
- Hold the pen with the needle pointing up.
- Tap the top of the pen gently a few times to let any air bubbles rise to the top.

F.
- Press the dose button until the "0" in the display window lines up with the pointer and a drop of liquid appears at the needle tip.
- If no drop appears, repeat steps D, E and F up to 6 times.
- If no drop appears after these attempts, change the needle and repeat steps D, E and F one more time.
- If a drop of liquid still does not appear, call (1-888-668-6444) for help.
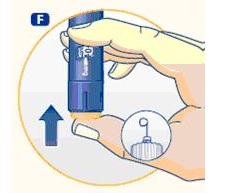
Important:
- Be careful not to drop Norditropin FlexPro pen or knock it against a hard surface. If this happens you will need to repeat the airshot.
- Always make sure that a drop appears at the needle tip after completing your airshot.
Select your dose
Use the dose selector on your Norditropin FlexPro pen to make sure you have the exact dose selected. You can select up to 2 mg per dose.
G.
- Select or adjust the dose you need by turning the dose selector forwards or backwards until the right number of mg lines up with the pointer.
- When dialing back, be careful not to press the dose button as liquid will come out.
- To guide you, the dose selector clicks differently when turned forwards, backwards or past the number of mg that is left in the pen.
- When the pen has less than 2 mg, the dose selector stops at the number of mg that is left in the pen.
How much growth hormone is left in the pen?
You can use the growth hormone scale to see how much growth hormone is left in the pen.
You can use the dose selector to see exactly how much growth hormone is left in the pen. If the pen contains less than 2 mg, turn the dose selector until it stops. The figure that lines up with the pointer shows how many mg is left in the pen.
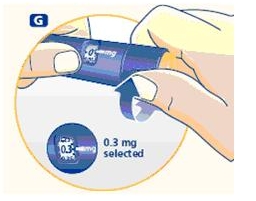
- You cannot set a dose higher than the number of mg left in the pen.
- If there is not enough Norditropin left in the pen to deliver your full dose, use a new Norditropin FlexPro pen to inject the remaining amount of your dose or contact your healthcare provider.
- Be sure to subtract the dose already received. For example, if your dose is 0.6 mg and you can only set the dose selector to 0.3 mg, you should inject another 0.3 mg with a new Norditropin FlexPro pen.
Important:
- Never use the pen clicks to count the number of mg you select. Only the display window and pointer will show the exact number.
- Never use the growth hormone scale to measure how much liquid to inject. Only the display window and pointer will show the exact number.
Inject your dose
Make sure that you receive your full dose by using the injection technique recommended by your healthcare provider. This medicine is injected under your skin (subcutaneous) only.
H.
- Insert the needle into your skin as your healthcare provider has shown you.
- Press and hold the dose button to inject until the "0" in the display window lines up with the pointer. As you do this, you may hear or feel a firm click.
- If you remove your finger from the dose button before the “0” is in the display window the full dose has not been delivered. Leave the needle in the skin and press and hold the dose button again until the “0” lines up with the pointer.
If "0" does not appear in the display window, you did not receive the full dose. Call 1(-888-668-6444 ) for assistance.
- After the “0” in the display window lines up with the pointer, leave the needle under the skin for at least 6 seconds to make sure that you get your full dose. You can let go of the dose button while you wait.
- Change the injection site using the injection procedure recommended by your healthcare provider.
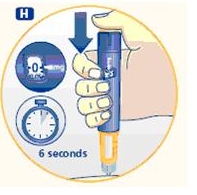
Important:
- Always press the dose button to inject the dose. Turning the dose selector will not inject the dose.
- Never touch the display window when you inject, as this can block the injection.
I.
- Remove the needle from your skin. After that, you may see a drop of liquid at the needle tip. This is normal and does not affect the dose you received.
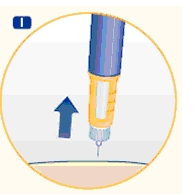
- After the injection, remove the needle right away and put the pen cap back on. If the needle is not removed, some liquid may come out of the Norditropin FlexPro.
- Unscrew the needle and throw away the needle and any empty Norditropin FlexPro pen as directed by your healthcare provider. A special “sharps” container (such as a red biohazard container), a hard plastic container (such as an empty detergent bottle), or a metal container (such as an empty coffee can) should be used. The container should be sealed and disposed of properly.
- Caregivers should be most careful when handling used needles to avoid hurting themselves.
Care for your Norditropin FlexPro pen
You must take care of your Norditropin FlexPro pen:
- Do not drop your pen or knock it against hard surfaces. If you do drop it or think that something is wrong with it, always screw on a new disposable needle and check the growth hormone flow (airshot) before you inject.
- Do not try to refill your disposable pen – it is prefilled.
- Do not try to repair your pen or pull it apart.
- Do not expose your pen to dust, dirt or any kind of liquid.
- Do not try to wash, soak or lubricate your pen. You may clean the Norditropin FlexPro pen with a mild detergent on a moistened cloth. See section “How do I store Norditropin FlexPro?” above for information about how to store your pen.
- Always keep your pen and needles out of reach of others, especially children.
- Never share your needles and pen with anyone.
Date of Issue: March 2, 2010
Version: 1
US Patent Nos. 6,235,004; 6,004,297; 6,582,404; 6,716,198; 6,899,699; 5,849,704; 5,691,169; 5,618,697 and other patents pending.
Norditropin®, FlexPro®, Norditropin NordiFlex® and NordiFlex PenMate® are registered trademarks of Novo Nordisk Health Care AG.
Novo Nordisk® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S.
© 2004-2010 Novo Nordisk Health Care AG
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Norditropin® FlexPro®
(somatropin [rDNA origin] injection)
10 mg/1.5 mL (blue) Prefilled Pen
Read these instructions before using your Norditropin® FlexPro® pen.
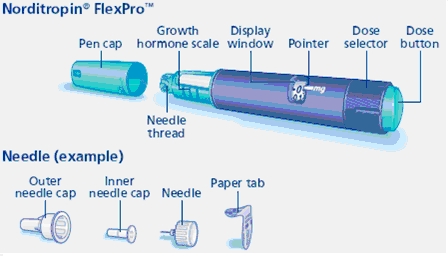
Norditropin FlexPro contains 10 mg human growth hormone solution and delivers doses from 0.05 mg to 4 mg, in increments of 0.05 mg. Norditropin FlexPro is made to be used with Novo Nordisk® disposable needles. Needles are not included with Norditropin FlexPro.
Prepare your Norditropin FlexPro pen
A.
- Pull off the pen cap.
- Check that the liquid in the pen is clear and colorless by tipping it upside down 1 or 2 times. If the liquid looks unclear or cloudy, do not use the pen.
- Wash hands well and dry them.
- Wipe the front stopper on the needle thread with an alcohol swab.
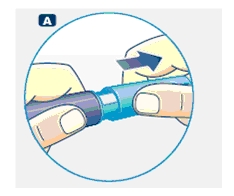
B.
- Take a new disposable needle.
- Tear the paper tab off and screw the needle straight onto the pen.
- Make sure the needle is on tight.
- Never place a disposable needle on your Norditropin FlexPro pen until you are ready to give an injection.
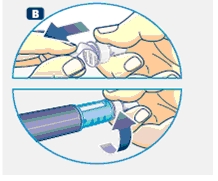
C.
- Pull off the outer needle cap and inner needle cap and throw them both away.
- If you try to put the needle caps back on, you may accidentally hurt yourself with the needle.
- A drop of liquid may appear at the needle tip. This is normal.
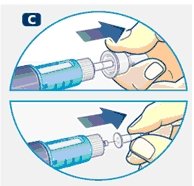
Important:
- Always use a new needle for each injection. This will help prevent contamination.
- Never bend or damage the needle.
Check the growth hormone flow (airshot)
Make sure that you receive your full dose by checking the growth hormone flow (performing an airshot) before you select and inject your first dose from a new pen.
D. Turn the dose selector to select 0.05 mg. This is the smallest amount of medicine for a dose.
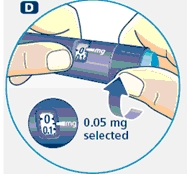
E.
- Hold the pen with the needle pointing up.
- Tap the top of the pen gently a few times to let any air bubbles rise to the top.
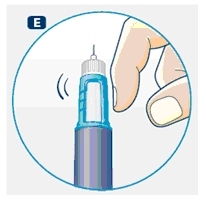
F.
- Press the dose button until the “0” in the display window lines up with the pointer and a drop of liquid appears at the needle tip.
- If no drop appears, repeat steps D, E, and F up to 6 times.
- If no drop appears after these attempts, change the needle and repeat steps D, E, and F one more time.
- If a drop of liquid still does not appear, call (1-888-668-6444) for help.
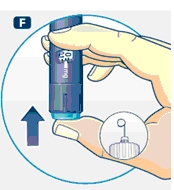
Important:
- Be careful not to drop Norditropin FlexPro pen or knock it against a hard surface. If this happens you will need to repeat the airshot.
- Always make sure that a drop appears at the needle tip after completing your airshot.
Select your dose
Use the dose selector on your Norditropin FlexPro pen to make sure you have the exact dose selected. You can select up to 4 mg per dose.
G.
- Select or adjust the dose you need by turning the dose selector forwards or backwards until the right number of mg lines up with the pointer.
- When dialing back, be careful not to press the dose button as liquid will come out.
- To guide you, the dose selector clicks differently when turned forwards, backwards or past the number of mg that is left in the pen.
- When the pen has less than 4 mg, the dose selector stops at the number of mg that is left in the pen.
How much growth hormone is left in the pen?
You can use the growth hormone scale to see how much growth hormone is left in the pen.
You can use the dose selector to see exactly how much growth hormone is left in the pen. If the pen contains less than 4 mg, turn the dose selector until it stops.
The figure that lines up with the pointer shows how many mg is left in the pen.
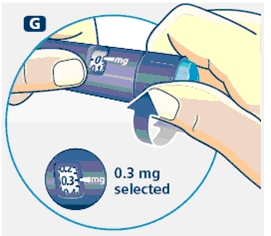
- You cannot set a dose higher than the number of mg left in the pen.
- If there is not enough Norditropin left in the pen to deliver your full dose, use a new Norditropin FlexPro pen to inject the remaining amount of your dose or contact your healthcare provider.
- Be sure to subtract the dose already received. For example, if your dose is 0.6 mg and you can only set the dose selector to 0.3 mg, you should inject another 0.3 mg with a new Norditropin FlexPro pen.
Important:
- Never use the pen clicks to count the number of mg you select. Only the display window and pointer will show the exact number.
- Never use the growth hormone scale to measure how much liquid to inject. Only the display window and pointer will show the exact number.
Inject your dose
Make sure that you receive your full dose by using the injection technique recommended by your healthcare provider. This medicine is injected under your skin (subcutaneous) only.
H.
- Insert the needle into your skin as your healthcare provider has shown you.
- Press and hold the dose button to inject until the “0” in the display window lines up with the pointer. As you do this, you may hear or feel a firm click.
- If you remove your finger from the dose button before the “0” is in the display window the full dose has not been delivered. Leave the needle in the skin and press and hold the dose button again until the “0” lines up with the pointer.
If “0” does not appear in the display window, you did not receive the full dose. Call (1-888-668-6444) for assistance.
- After the “0” in the display window lines up with the pointer, leave the needle under the skin for at least 6 seconds to make sure that you get your full dose. You can let go of the dose button while you wait.
- Change the injection site using the injection procedure recommended by your healthcare provider.
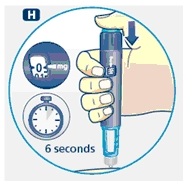
Important:
- Always press the dose button to inject the dose. Turning the dose selector will not inject the dose.
- Never touch the display window when you inject, as this can block the injection.
I.
- Remove the needle from your skin. After that, you may see a drop of liquid at the needle tip. This is normal and does not affect the dose you received.
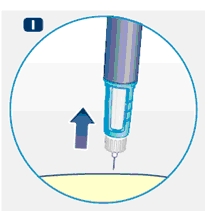
- After the injection, remove the needle right away and put the pen cap back on. If the needle is not removed, some liquid may come out of the Norditropin FlexPro.
- Unscrew the needle and throw away the needle and any empty Norditropin FlexPro pen as directed by your healthcare provider. A special “sharps” container (such as a red biohazard container), a hard plastic container (such as an empty detergent bottle), or a metal container (such as an empty coffee can) should be used. The container should be sealed and disposed of properly.
- Caregivers should be most careful when handling used needles to avoid hurting themselves.
Care for your Norditropin FlexPro pen
You must take care of your Norditropin FlexPro pen:
- Do not drop your pen or knock it against hard surfaces. If you do drop it or think that something is wrong with it, always screw on a new disposable needle and check the growth hormone flow (airshot) before you inject.
- Do not try to refill your disposable pen – it is prefilled.
- Do not try to repair your pen or pull it apart.
- Do not expose your pen to dust, dirt or any kind of liquid.
- Do not try to wash, soak or lubricate your pen. You may clean the Norditropin FlexPro pen with a mild detergent on a moistened cloth. See section “How do I store Norditropin FlexPro?” above for information about how to store your pen.
- Always keep your pen and needles out of reach of others, especially children.
- Never share your needles and pen with anyone.
Date of Issue: March 2, 2010
Version: 1
US Patent Nos. 6,235,004; 6,004,297; 6,582,404; 6,716,198; 6,899,699; 5,849,704; 5,691,169; 5,618,697 and other patents pending.
Norditropin®, FlexPro®, Norditropin NordiFlex® and NordiFlex PenMate® are registered trademarks of Novo Nordisk Health Care AG.
Novo Nordisk® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S.
© 2004-2010 Novo Nordisk Health Care AG
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Norditropin® FlexPro®
(somatropin [rDNA origin] injection)
15 mg/1.5 mL (green) Prefilled Pen
Read these instructions before using your Norditropin® FlexPro® pen.
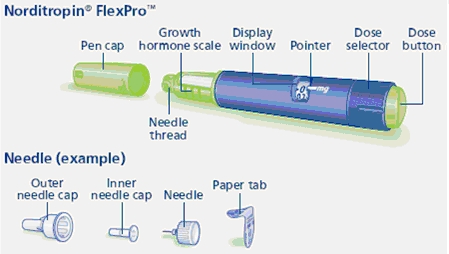
Norditropin FlexPro contains 15 mg human growth hormone solution and delivers doses from 0.1 mg to 8 mg, in increments of 0.1 mg. Norditropin FlexPro is made to be used with Novo Nordisk® disposable needles. Needles are not included with Norditropin FlexPro.
Prepare your Norditropin FlexPro pen
A.
- Pull off the pen cap.
- Check that the liquid in the pen is clear and colorless by tipping it upside down 1 or 2 times. If the liquid looks unclear or cloudy, do not use the pen.
- Wash hands well and dry them.
- Wipe the front stopper on the needle thread with an alcohol swab.
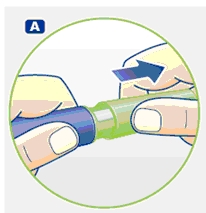
B.
- Take a new disposable needle.
- Tear the paper tab off and screw the needle straight onto the pen.
- Make sure the needle is on tight.
- Never place a disposable needle on your Norditropin FlexPro pen until you are ready to give an injection.
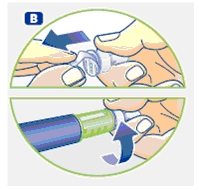
C.
- Pull off the outer needle cap and inner needle cap and throw them both away.
- If you try to put the needle caps back on, you may accidentally hurt yourself with the needle.
- A drop of liquid may appear at the needle tip. This is normal.
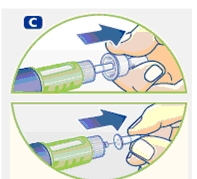
Important:
- Always use a new needle for each injection. This will help prevent contamination.
- Never bend or damage the needle.
Check the growth hormone flow (airshot)
Make sure that you receive your full dose by checking the growth hormone flow (performing an airshot) before you select and inject your first dose from a new pen.
D. Turn the dose selector to select 0.1 mg. This is the smallest amount of medicine for a dose.
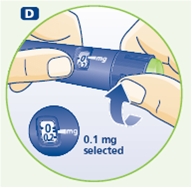
E.
- Hold the pen with the needle pointing up.
- Tap the top of the pen gently a few times to let any air bubbles rise to the top.
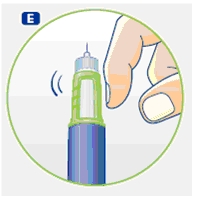
F.
- Press the dose button until the “0” in the display window lines up with the pointer and a drop of liquid appears at the needle tip.
- If no drop appears, repeat steps D, E and F up to 6 times.
- If no drop appears after these attempts, change the needle and repeat steps D, E and F one more time.
- If a drop of liquid still does not appear, call (1-888-668-6444) for help.
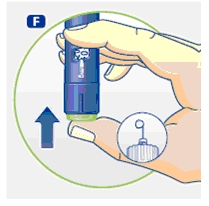
Important:
- Be careful not to drop Norditropin FlexPro pen or knock it against a hard surface. If this happens you will need to repeat the airshot.
- Always make sure that a drop appears at the needle tip after completing your airshot.
Select your dose
Use the dose selector on your Norditropin FlexPro pen to make sure you have the exact dose selected. You can select up to 8 mg per dose.
G.
- Select or adjust the dose you need by turning the dose selector forwards or backwards until the right number of mg lines up with the pointer.
- When dialing back, be careful not to press the dose button as liquid will come out.
- To guide you, the dose selector clicks differently when turned forwards, backwards or past the number of mg that is left in the pen.
- When the pen has less than 8 mg, the dose selector stops at the number of mg that is left in the pen.
How much growth hormone is left in the pen?
You can use the growth hormone scale to see how much growth hormone is left in the pen.
You can use the dose selector to see exactly how much growth hormone is left in the pen. If the pen contains less than 8 mg, turn the dose selector until it stops.
The figure that lines up with the pointer shows how many mg is left in the pen.
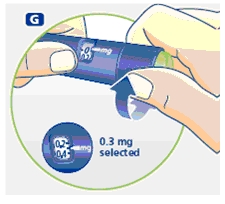
- You cannot set a dose higher than the number of mg left in the pen.
- If there is not enough Norditropin left in the pen to deliver your full dose, use a new Norditropin FlexPro pen to inject the remaining amount of your dose or contact your healthcare provider.
- Be sure to subtract the dose already received. For example, if your dose is 0.6 mg and you can only set the dose selector to 0.3 mg, you should inject another 0.3 mg with a new Norditropin FlexPro pen.
Important:
- Never use the pen clicks to count the number of mg you select. Only the display window and pointer will show the exact number.
- Never use the growth hormone scale to measure how much liquid to inject. Only the display window and pointer will show the exact number.
Inject your dose
Make sure that you receive your full dose by using the injection technique recommended by your healthcare provider. This medicine is injected under your skin (subcutaneous) only.
H.
- Insert the needle into your skin as your healthcare provider has shown you.
- Press and hold the dose button to inject until the “0” in the display window lines up with the pointer. As you do this, you may hear or feel a firm click.
- If you remove your finger from the dose button before the “0” is in the display window the full dose has not been delivered. Leave the needle in the skin and press and hold the dose button again until the “0” lines up with the pointer.
If “0” does not appear in the display window, you did not receive the full dose. Call (1-888-668-6444) for assistance.
- After the “0” in the display window lines up with the pointer, leave the needle under the skin for at least 6 seconds to make sure that you get your full dose. You can let go of the dose button while you wait.
- Change the injection site using the injection procedure recommended by your healthcare provider.
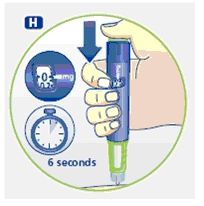
Important:
- Always press the dose button to inject the dose. Turning the dose selector will not inject the dose.
- Never touch the display window when you inject, as this can block the injection.
I.
- Remove the needle from your skin. After that, you may see a drop of liquid at the needle tip. This is normal and does not affect the dose you received.
- After the injection, remove the needle right away and put the pen cap back on. If the needle is not removed, some liquid may come out of the Norditropin FlexPro.
- Unscrew the needle and throw away the needle and any empty Norditropin FlexPro pen as directed by your healthcare provider. A special “sharps” container (such as a red biohazard container), a hard plastic container (such as an empty detergent bottle), or a metal container (such as an empty coffee can) should be used. The container should be sealed and disposed of properly.
- Caregivers should be most careful when handling used needles to avoid hurting themselves.
Care for your Norditropin FlexPro pen
You must take care of your Norditropin FlexPro pen:
- Do not drop your pen or knock it against hard surfaces. If you do drop it or think that something is wrong with it, always screw on a new disposable needle and check the growth hormone flow (airshot) before you inject.
- Do not try to refill your disposable pen – it is prefilled.
- Do not try to repair your pen or pull it apart.
- Do not expose your pen to dust, dirt or any kind of liquid.
- Do not try to wash, soak or lubricate your pen. You may clean the Norditropin FlexPro pen with a mild detergent on a moistened cloth. See section “How do I store Norditropin FlexPro?” above for information about how to store your pen.
- Always keep your pen and needles out of reach of others, especially children.
- Never share your needles and pen with anyone.
Date of Issue: March 2, 2010
Version: 1
US Patent Nos. 6,235,004; 6,004,297; 6,582,404; 6,716,198; 6,899,699; 5,849,704; 5,691,169; 5,618,697 and other patents pending.
Norditropin®, FlexPro®, Norditropin NordiFlex® and NordiFlex PenMate® are registered trademarks of Novo Nordisk Health Care AG.
Novo Nordisk® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S.
© 2004-2010 Novo Nordisk Health Care AG
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NORDITROPIN NORDIFLEX 5 MG/1.5ML
Norditropin NordiFlex®
Somatropin (rDNA origin) injection
5 mg/1.5 mL Prefilled Pen
1 x 1.5 mL prefilled disposable pen
Each 1.5 mL contains 5 mg somatropin
CONTAINS ONE
NORDITROPIN NORDIFLEX® 5 mg/1.5 mL
Rx ONLY
List: 770411
Before use MUST keep refrigerated. (2ºC-8ºC/36ºF-46ºF). Do not store with needles. After initial injection, EITHER keep refrigerated for 4 weeks OR store not above 25ºC (77ºF) for 3 weeks. Do not freeze. Discard unused portion. Avoid direct light. Keep out of the reach and sight of children. For subcutaneous administration only. Please read the enclosed leaflet before use.
