INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1.1 Partial Onset Seizures
Levetiracetam tablets USP are indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures in adults and children 4 years of age and older with epilepsy.
Information describing the use of levetiracetam in pediatric patients less than 4 years of age as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures is approved for UCB, Inc.'s levetiracetam tablets. However, due to UCB, Inc.'s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
1.2 Myoclonic Seizures in Patients with Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy
Levetiracetam tablets USP are indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy.
1.3 Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Levetiracetam tablets USP are indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in adults and children 6 years of age and older with idiopathic generalized epilepsy.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
- 2.1 Important Administration Instructions
Levetiracetam tablets are given orally with or without food. The levetiracetam dosing regimen depends on the indication, age group, dosage form (tablets or oral solution), and renal function.
Prescribe the oral solution for pediatric patients with body weight ≤ 20 kg. Prescribe the oral solution or tablets for pediatric patients with body weight above 20 kg.
Levetiracetam tablets should be swallowed whole. Levetiracetam tablets should not be chewed or crushed.
2.2 Partial Onset SeizuresAdults 16 Years and Older
In clinical trials, daily doses of 1000 mg, 2000 mg, and 3000 mg, given as twice-daily dosing were shown to be effective. Although in some studies there was a tendency toward greater response with higher dose [see CLINICAL STUDIES ( 14.1)], a consistent increase in response with increased dose has not been shown.
Treatment should be initiated with a daily dose of 1000 mg/day, given as twice-daily dosing (500 mg twice daily). Additional dosing increments may be given (1000 mg/day additional every 2 weeks) to a maximum recommended daily dose of 3000 mg. Doses greater than 3000 mg/day have been used in open-label studies for periods of 6 months and longer. There is no evidence that doses greater than 3000 mg/day confer additional benefit.
Pediatric Patients
Dosing information in pediatric patients less than 4 years of age as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures is approved for UCB, Inc.'s levetiracetam tablets. However, due to UCB, Inc.'s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
4 Years to < 16 Years:
Treatment should be initiated with a daily dose of 20 mg/kg in 2 divided doses (10 mg/kg twice daily). The daily dose should be increased every 2 weeks by increments of 20 mg/kg to the recommended daily dose of 60 mg/kg (30 mg/kg twice daily). If a patient cannot tolerate a daily dose of 60 mg/kg, the daily dose may be reduced. In the clinical efficacy trial, the mean daily dose was 44 mg/kg. The maximum daily dose was 3000 mg/day.
For levetiracetam tablet dosing in pediatric patients weighing 20 to 40 kg, treatment should be initiated with a daily dose of 500 mg given as twice daily dosing (250 mg twice daily). The daily dose should be increased every 2 weeks by increments of 500 mg to a maximum recommended daily dose of 1500 mg (750 mg twice daily).
For levetiracetam tablet dosing in pediatric patients weighing more than 40 kg, treatment should be initiated with a daily dose of 1000 mg/day given as twice daily dosing (500 mg twice daily). The daily dose should be increased every 2 weeks by increments of 1000 mg/day to a maximum recommended daily dose of 3000 mg (1500 mg twice daily).
Levetiracetam Oral Solution Weight-Based Dosing Calculation For Pediatric Patients
The following calculation should be used to determine the appropriate daily dose of oral solution for pediatric patients:
2.3 Myoclonic Seizures in Patients 12 Years of Age and Older with Juvenile Myoclonic EpilepsyTreatment should be initiated with a dose of 1000 mg/day, given as twice-daily dosing (500 mg twice daily). Dosage should be increased by 1000 mg/day every 2 weeks to the recommended daily dose of 3000 mg. The effectiveness of doses lower than 3000 mg/day has not been studied.
2.4 Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic SeizuresAdults 16 Years and Older
Treatment should be initiated with a dose of 1000 mg/day, given as twice-daily dosing (500 mg twice daily). Dosage should be increased by 1000 mg/day every 2 weeks to the recommended daily dose of 3000 mg. The effectiveness of doses lower than 3000 mg/day has not been adequately studied.
Pediatric Patients Ages 6 to <16 Years
Treatment should be initiated with a daily dose of 20 mg/kg in 2 divided doses (10 mg/kg twice daily). The daily dose should be increased every 2 weeks by increments of 20 mg/kg to the recommended daily dose of 60 mg/kg (30 mg/kg twice daily). The effectiveness of doses lower than 60 mg/kg/day has not been adequately studied. Patients with body weight ≤ 20 kg should be dosed with oral solution. Patients with body weight above 20 kg can be dosed with either tablets or oral solution [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ( 2.1)]. Only whole tablets should be administered.
2.5 Adult Patients with Impaired Renal FunctionLevetiracetam tablets dosing must be individualized according to the patient's renal function status. Recommended doses and adjustment for dose for adults are shown in Table 1. In order to calculate the dose recommended for patients with renal impairment, creatinine clearance adjusted for body surface area must be calculated. To do this an estimate of the patient's creatinine clearance (CLcr) in mL/min must first be calculated using the following formula:
CloseTable 1: Dosing Adjustment Regimen for Adult Patients with Impaired Renal Function Group Creatinine Clearance
(mL/min/1.73 m2)Dosage (mg) Frequency *Following dialysis, a 250 to 500 mg supplemental dose is recommended. Normal >80 500 to 1,500 Every 12 hours Mild 50 to 80 500 to 1,000 Every 12 hours Moderate 30 to 50 250 to 750 Every 12 hours Severe <30 250 to 500 Every 12 hours ESRD patients using dialysis ----- 500 to 1000 * Every 24 hours *
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
Levetiracetam tablets, 250 mg are blue coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X01" on the other side.
Levetiracetam tablets, 500 mg are yellow coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X02" on the other side.
Levetiracetam tablets, 750 mg are orange coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X03" on the other side.
Levetiracetam tablets, 1000 mg are white to off-white coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X04" on the other side.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
- 5.1 Psychiatric Reactions
In some patients levetiracetam causes behavioral abnormalities. The incidences of behavioral abnormalities in the myoclonic and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizure studies were comparable to those of the adult and pediatric partial onset seizure studies.
A total of 13.3% of adult levetiracetam-treated patients and 37.6% of pediatric levetiracetam -treated patients (4 to 16 years of age) compared to 6.2% and 18.6% of adult and pediatric placebo patients respectively, experienced non-psychotic behavioral symptoms (reported as aggression, agitation, anger, anxiety, apathy, depersonalization, depression, emotional lability, hostility, hyperkinesias, irritability, nervousness, neurosis, and personality disorder). A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study was performed to assess the neurocognitive and behavioral effects of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy in pediatric patients (4 to 16 years of age). The results from an exploratory analysis indicated a worsening in levetiracetam-treated patients on aggressive behavior (one of eight behavior dimensions) as measured in a standardized and systematic way using a validated instrument, the Achenbach Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL/6 to 18).
In pediatric patients 1 month to < 4 years of age, irritability was reported in 11.7% of the levetiracetam -treated patients compared to 0% of placebo patients.
A total of 1.7% of adult levetiracetam-treated patients discontinued treatment due to behavioral adverse events, compared to 0.2% of placebo patients. The treatment dose was reduced in 0.8% of adult levetiracetam-treated patients and in 0.5% of placebo patients. Overall, 10.9% of levetiracetam-treated pediatric patients experienced behavioral symptoms associated with discontinuation or dose reduction, compared to 6.2% of placebo patients.
One percent of adult levetiracetam-treated patients, 2% of children 4 to 16 years of age, and 17% of children 1 month to <4 years of age experienced psychotic symptoms, compared to 0.2%, 2%, and 5% respectively, in the placebo patients. In the controlled study that assessed the neurocognitive and behavioral effects of levetiracetam in pediatric patients 4 to 16 years of age, 1 (1.6%) levetiracetam-treated patient experienced paranoia compared to no placebo patients. There were 2 (3.1%) levetiracetam-treated patients that experienced confusional state compared to no placebo patients [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS ( 8.4)].
Two (0.3%) adult levetiracetam-treated patients were hospitalized and their treatment was discontinued due to psychosis. Both events, reported as psychosis, developed within the first week of treatment and resolved within 1 to 2 weeks following treatment discontinuation. There was no difference between drug and placebo-treated patients in the incidence of the pediatric patients who discontinued treatment due to psychotic and non-psychotic adverse reactions.
The above psychiatric signs and symptoms should be monitored.
5.2 Suicidal Behavior and IdeationAntiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including levetiracetam, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Patients treated with any AED for any indication should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI:1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in drug-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo-treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as one week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5 to 100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed. Table 2 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
Table 2 Risk by Indication for Antiepileptic Drugs in the Pooled Analysis
IndicationPlacebo Patients with
Events Per
1000
PatientsDrug Patients with Events Per
1000
PatientsRelative Risk:
Incidence of Events
in Drug
Patients/Incidence in
Placebo PatientsRisk Difference:
Additional Drug Patients
with Events Per 1000
PatientsEpilepsy 1.0 3.4 3.5 2.4 Psychiatric 5.7 8.5 1.5 2.9 Other 1.0 1.8 1.9 0.9 Total 2.4 4.3 1.8 1.9 The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
Anyone considering prescribing levetiracetam or any other AED must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors with the risk of untreated illness. Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which AEDs are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
Patients, their caregivers, and families should be informed that AEDs increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and should be advised of the need to be alert for the emergence or worsening of the signs and symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm. Behaviors of concern should be reported immediately to healthcare providers.
5.3 Somnolence and FatigueIn some patients, levetiracetam causes somnolence and fatigue. The incidences of somnolence and fatigue provided below are from controlled adult partial onset seizure studies. In general, the incidences of somnolence and fatigue in the pediatric partial onset seizure studies, and in pediatric and adult myoclonic and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizure studies were comparable to those of the adult partial onset seizure studies.
In controlled trials of adult patients with epilepsy experiencing partial onset seizures, 14.8% of levetiracetam-treated patients reported somnolence, compared to 8.4% of placebo patients. There was no clear dose response up to 3000 mg/day. In a study where there was no titration, about 45% of patients receiving 4000 mg/day reported somnolence. The somnolence was considered serious in 0.3% of the treated patients, compared to 0% in the placebo group. About 3% of levetiracetam-treated patients discontinued treatment due to somnolence, compared to 0.7% of placebo patients. In 1.4% of treated patients and in 0.9% of placebo patients the dose was reduced, while 0.3% of the treated patients were hospitalized due to somnolence.
In controlled trials of adult patients with epilepsy experiencing partial onset seizures, 14.7% of levetiracetam-treated patients reported asthenia, compared to 9.1% of placebo patients. Treatment was discontinued due to asthenia in 0.8% of treated patients as compared to 0.5% of placebo patients. In 0.5% of treated patients and in 0.2% of placebo patients the dose was reduced due to asthenia.
Somnolence and asthenia occurred most frequently within the first 4 weeks of treatment.
Patients should be monitored for these signs symptoms and advised not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on levetiracetam to gauge whether it adversely affects their ability to drive or operate machinery.
5.4 Serious Dermatological ReactionsSerious dermatological reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), have been reported in both children and adults treated with levetiracetam. The median time of onset is reported to be 14 to 17 days, but cases have been reported at least four months after initiation of treatment. Recurrence of the serious skin reactions following rechallenge with levetiracetam has also been reported. Levetiracetam should be discontinued at the first sign of a rash, unless the rash is clearly not drug-related. If signs or symptoms suggest SJS/TEN, use of this drug should not be resumed and alternative therapy should be considered.
5.5 Coordination DifficultiesCoordination difficulties were only observed in the adult partial onset seizure studies. A total of 3.4% of adult levetiracetam-treated patients experienced coordination difficulties, (reported as either ataxia, abnormal gait, or incoordination) compared to 1.6% of placebo patients. A total of 0.4% of patients in controlled trials discontinued levetiracetam treatment due to ataxia, compared to 0% of placebo patients. In 0.7% of treated patients and in 0.2% of placebo patients the dose was reduced due to coordination difficulties, while one of the treated patients was hospitalized due to worsening of pre-existing ataxia.
These events occurred most frequently within the first 4 weeks of treatment.
Patients should be monitored for these signs and symptoms and advised not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on levetiracetam to gauge whether it could adversely affect their ability to drive or operate machinery.
5.6 Withdrawal SeizuresAntiepileptic drugs, including levetiracetam, should be withdrawn gradually to minimize the potential of increased seizure frequency.
5.7 Hematologic AbnormalitiesPartial Onset Seizures
Adults:
Minor, but statistically significant, decreases compared to placebo in total mean RBC count (0.03 x 106/mm3), mean hemoglobin (0.09 g/dL), and mean hematocrit (0.38%), were seen in levetiracetam-treated patients in controlled trials.
A total of 3.2% of treated and 1.8% of placebo patients had at least one possibly significant (≤2.8 x 109/L) decreased WBC, and 2.4% of treated and 1.4% of placebo patients had at least one possibly significant (≤1.0 x 109/L) decreased neutrophil count. Of the treated patients with a low neutrophil count, all but one rose towards or to baseline with continued treatment. No patient was discontinued secondary to low neutrophil counts.
Pediatric Patients 4 Years to < 16 Years:
Statistically significant decreases in WBC and neutrophil counts were seen in levetiracetam-treated patients as compared to placebo. The mean decreases from baseline in the levetiracetam-treated group were -0.4 x 109/L and - 0.3 x 109/L, respectively, whereas there were small increases in the placebo group. Mean relative lymphocyte counts increased by 1.7% in levetiracetam-treated patients, compared to a decrease of 4% in placebo patients (statistically significant).
In the controlled trial, more levetiracetam-treated patients had a possibly clinically significant abnormally low WBC value (3.0% levetiracetam-treated versus 0% placebo), however, there was no apparent difference between treatment groups with respect to neutrophil count (5.0% levetiracetam-treated versus 4.2% placebo). No patient was discontinued secondary to low WBC or neutrophil counts.
In the controlled cognitive and neuropsychological safety study, two subjects (6.1%) in the placebo group and 5 subjects (8.6%) in the levetiracetam-treated group had high eosinophil count values that were possibly clinically significant (≥10% or≥0.7X109/L).
Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy:
Although there were no obvious hematologic abnormalities observed in patients with JME, the limited number of patients makes any conclusion tentative. The data from the partial seizure patients should be considered to be relevant for JME patients.
5.8 Blood Pressure IncreasesIn a randomized, placebo-controlled study in patients aged 1 month to <4 years of age, a significantly higher risk of at least one measured increase in diastolic blood pressure was observed in the levetiracetam-treated patients (17%) compared to the placebo-treated patients (2%). There was no overall difference in mean diastolic blood pressure between the treatment groups. This disparity between the levetiracetam and placebo treatment groups was not observed in the studies of older children or in adults.
5.9 Seizure Control During PregnancyPhysiological changes may gradually decrease plasma levels of levetiracetam throughout pregnancy. This decrease is more pronounced during the third trimester. It is recommended that patients be monitored carefully during pregnancy. Close monitoring should continue through the postpartum period especially if the dose was changed during pregnancy.
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more details in other sections of labeling:
Behavior Abnormalities and Psychotic Symptoms [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
Suicidal Behavior and Ideation [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)]
Somnolence and Fatigue [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.3)]
Anaphylaxis and Angioedema[see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.4)]
Serious Dermatological Reactions [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.5)]
Coordination Difficulties [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.6)]
Hematologic Abnormalities [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.8)]
Increase in Blood Pressure [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.9)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Partial - Onset Seizures
Adults:
In controlled clinical studies in adults with partial - onset seizures-, [see CLINICAL STUDIES (14.1)], the most common adverse reactions in patients receiving levetiracetam in combination with other AEDs, for events with rates greater than placebo, were somnolence, asthenia, infection, and dizziness. Of the most common adverse reactions in adults experiencing partial - onset seizures, asthenia, somnolence, and dizziness occurred predominantly during the first 4 weeks of treatment with levetiracetam.
Table 3 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 1% of adult epilepsy patients receiving levetiracetam in placebo-controlled studies and were numerically more common than in patients treated with placebo. In these studies, either levetiracetam or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy.
Levetiracetam
(N = 769)
%
Placebo
(N=439)
%
Asthenia
15
9
Somnolence
15
8
Headache
14
13
Infection
13
8
Dizziness
9
4
Pain
7
6
Pharyngitis
6
4
Depression
4
2
Nervousness
4
2
Rhinitis
4
3
Anorexia
3
2
Ataxia
3
1
Vertigo
3
1
Amnesia
2
1
Anxiety
2
1
Cough Increased
2
1
Diplopia
2
1
Emotional Lability
2
0
Hostility
2
1
Paresthesia
2
1
Sinusitis
2
1
In controlled adult clinical studies, 15% of patients receiving levetiracetam and 12% receiving placebo either discontinued or had a dose reduction as a result of an adverse reaction. Table 4 lists the most common (>1%) adverse reactions that resulted in discontinuation or dose reduction and that occurred more frequently in levetiracetam-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients.
Adverse Reaction
Levetiracetam
(N=769)
%
Placebo
(N=439)
%
Somnolence
4
2
Dizziness
1
0
Pediatric Patients 4 Years to <16 Years:
The adverse reaction data presented below was obtained from a pooled analysis of two controlled pediatric clinical studies in pediatric patients 4 to 16 years of age with partial onset seizures. The most common adverse reactions in pediatric patients receiving levetiracetam in combination with other AEDs, for events with rates greater than placebo, were fatigue, aggression, nasal congestion, decreased appetite, and irritability.
Table 5 lists adverse reactions from the pooled pediatric controlled studies (4 to 16 years of age) that occurred in at least 2% of pediatric levetiracetam-treated patients and were numerically more common than in pediatric patients treated with placebo. In these studies, either levetiracetam or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy.
Levetiracetam
(N=165) %
Placebo (N=131)
%
Headache
19
15
Nasopharyngitis
15
12
Vomiting
15
12
Somnolence
13
9
Fatigue
11
5
Aggression
10
5
Cough
9
5
Nasal Congestion
9
2
Upper Abdominal Pain
9
8
Decreased Appetite
8
2
Abnormal Behavior
7
4
Dizziness
7
5
Irritability
7
1
Pharyngolaryngeal Pain
7
4
Diarrhea
6
2
Lethargy
6
5
Insomnia
5
3
Agitation
4
1
Anorexia
4
3
Head Injury
4
0
Altered Mood
3
1
Constipation
3
1
Contusion
3
1
Depression
3
1
Fall
3
2
Influenza
3
1
Affect Lability
2
1
Anxiety
2
1
Arthralgia
2
0
Confusional State
2
0
Conjunctivitis
2
0
Ear Pain
2
1
Gastroenteritis
2
0
Joint Sprain
2
1
Mood Swings
2
1
Neck Pain
2
1
Rhinitis
2
0
Sedation
2
1
In the controlled pooled pediatric clinical studies in patients 4 to 16 years of age, 7% of patients receiving levetiracetam and 9% receiving placebo discontinued as a result of an adverse reaction.
Pediatric Patients 1 Month to < 4 Years:
In the 7-day, controlled pediatric clinical study in children 1 month to less than 4 years of age with partial - onset seizures, the most common adverse reactions in patients receiving levetiracetam in combination with other AEDs, for events with rates greater than placebo, were somnolence and irritability. Because of the shorter exposure period, incidences of adverse reactions are expected to be lower than in other pediatric studies in older patients. Therefore, other controlled pediatric data, presented above, should also be considered to apply to this age group.
Table 6 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of pediatric epilepsy patients (ages 1 month to < 4 years) treated with levetiracetam in the placebo-controlled study and were numerically more common than in patients treated with placebo. In this study, either levetiracetam or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy.
Levetiracetam
(N=60)
%
Placebo
(N=56)
%
Somnolence
13
2
Irritability
12
0
In the 7-day controlled pediatric clinical study in patients 1 month to < 4 years of age, 3% of patients receiving levetiracetam and 2% receiving placebo either discontinued or had a dose reduction as a result of an adverse reaction.
There was no adverse reaction that resulted in discontinuation for more than one patient.
Myoclonic Seizures
Although the pattern of adverse reactions in this study seems somewhat different from that seen in patients with partial-onset seizures, this is likely due to the much smaller number of patients in this study compared to partial seizure studies. The adverse reaction pattern for patients with JME is expected to be essentially the same as for patients with partial seizures.
In the controlled clinical study in patients 12 years of age and older with myoclonic seizures, [see CLINICAL STUDIES (14.2)], the most common adverse reactions in patients receiving levetiracetam in combination with other AEDs, for events with rates greater than placebo, were somnolence, neck pain, and pharyngitis.
Table 7 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy patients experiencing myoclonic seizures treated with levetiracetam and were numerically more common than in patients treated with placebo. In this study, either levetiracetam or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy.
Levetiracetam
(N=60)
%
Placebo
(N=60)
%
Somnolence
12
2
Neck Pain
8
2
Pharyngitis
7
0
Depression
5
2
Influenza
5
2
Vertigo
5
3
In the placebo-controlled study, 8% of patients receiving levetiracetam and 2% receiving placebo either discontinued or had a dose reduction as a result of an adverse reaction. The adverse reactions that led to discontinuation or dose reduction and that occurred more frequently in levetiracetam-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients are presented in Table 8.
Adverse Reaction
Levetiracetam
(N=60)
%
Placebo
(N=60)
%
Anxiety
3
2
Depressed mood
2
0
Depression
2
0
Diplopia
2
0
Hypersomnia
2
0
Insomnia
2
0
Irritability
2
0
Nervousness
2
0
Somnolence
2
0
Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
Although the pattern of adverse reactions in this study seems somewhat different from that seen in patients with partial-onset seizures, this is likely due to the much smaller number of patients in this study compared to partial seizure studies. The adverse reaction pattern for patients with primary generalized tonic-clonic (PGTC) seizures is expected to be essentially the same as for patients with partial seizures.
In the controlled clinical study that included patients 4 years of age and older with PGTC seizures, [see CLINICAL STUDIES (14.3)], the most common adverse reaction in patients receiving levetiracetam in combination with other AEDs, for events with rates greater than placebo, was nasopharyngitis.
Table 9 lists adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of idiopathic generalized epilepsy patients experiencing PGTC seizures treated with levetiracetam and were numerically more common than in patients treated with placebo. In this study, either levetiracetam or placebo was added to concurrent AED therapy.
Levetiracetam
(N=79)
%
Placebo
(N=84)
%
Nasopharyngitis
14
5
Fatigue
10
8
Diarrhea
8
7
Irritability
6
2
Mood swings
5
1
In the placebo-controlled study, 5% of patients receiving levetiracetam and 8% receiving placebo either discontinued or had a dose reduction during the treatment period as a result of an adverse reaction.
This study was too small to adequately characterize the adverse reactions that could be expected to result in discontinuation of treatment in this population. It is expected that the adverse reactions that would lead to discontinuation in this population would be similar to those resulting in discontinuation in other epilepsy trials (see Tables 4 and 8).
In addition, the following adverse reactions were seen in other controlled adult studies of levetiracetam: balance disorder, disturbance in attention, eczema, memory impairment, myalgia, and blurred vision.
Comparison of Gender, Age and Race
The overall adverse reaction profile of levetiracetam was similar between females and males. There are insufficient data to support a statement regarding the distribution of adverse reactions by age and race.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of levetiracetam. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following adverse reactions have been reported in patients receiving marketed levetiracetam worldwide. The listing is alphabetized: abnormal liver function test, acute kidney injury, anaphylaxis, angioedema, agranulocytosis, choreoathetosis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), dyskinesia, erythema multiforme, hepatic failure, hepatitis, hyponatremia, muscular weakness, pancreatitis, pancytopenia (with bone marrow suppression identified in some of these cases), panic attack, thrombocytopenia, weight loss and worsening of seizures. Alopecia has been reported with levetiracetam use; recovery was observed in majority of cases where levetiracetam was discontinued.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
No significant pharmacokinetic interactions were observed between levetiracetam or its major metabolite and concomitant medications via human liver cytochrome P450 isoforms, epoxide hydrolase, UDP-glucuronidation enzymes, P-glycoprotein, or renal tubular secretion [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.3)].
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
- 8.1 Pregnancy
Levetiracetam levels may decrease during pregnancy [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.9)].
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. In animal studies, levetiracetam produced evidence of developmental toxicity, including teratogenic effects, at doses similar to or greater than human therapeutic doses. Levetiracetam should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Oral administration of levetiracetam to female rats throughout pregnancy and lactation led to increased incidences of minor fetal skeletal abnormalities and retarded offspring growth pre- and/or postnatally at doses ≥350 mg/kg/day (equivalent to the maximum recommended human dose of 3000 mg [MRHD] on a mg/m2 basis) and with increased pup mortality and offspring behavioral alterations at a dose of 1800 mg/kg/day (6 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). The developmental no effect dose was 70 mg/kg/day (0.2 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). There was no overt maternal toxicity at the doses used in this study.
Oral administration of levetiracetam to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in increased embryofetal mortality and increased incidences of minor fetal skeletal abnormalities at doses ≥600 mg/kg/day (4 times MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) and in decreased fetal weights and increased incidences of fetal malformations at a dose of 1800 mg/kg/day (12 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). The developmental no effect dose was 200 mg/kg/day (equivalent to the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). Maternal toxicity was also observed at 1800 mg/kg/day.
When levetiracetam was administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis, fetal weights were decreased and the incidence of fetal skeletal variations was increased at a dose of 3600 mg/kg/day (12 times the MRHD). 1200 mg/kg/day (4 times the MRHD) was a developmental no effect dose. There was no evidence of maternal toxicity in this study.
Treatment of rats with levetiracetam during the last third of gestation and throughout lactation produced no adverse developmental or maternal effects at doses of up to 1800 mg/kg/day (6 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis).
Pregnancy Registries
To provide information regarding the effects of in utero exposure to levetiracetam, physicians are advised to recommend that pregnant patients taking levetiracetam enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) pregnancy registry. This can be done by calling the toll free number 1-888-233-2334, and must be done by the patients themselves. Information on the registry can also be found at the website http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/.
8.2 Labor And DeliveryThe effect of levetiracetam on labor and delivery in humans is unknown.
8.3 Nursing MothersLevetiracetam is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from levetiracetam, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric UseThe safety and effectiveness of levetiracetam in the adjunctive treatment of partial onset seizures in pediatric patients age 4 years to 16 years old with epilepsy have been established [see CLINICAL STUDIES ( 14.1)]. The dosing recommendation in these pediatric patients varies according to age group and is weight-based [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ( 2.2)].
Pediatric use information in pediatric patients less than 4 years of age as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures is approved for UCB, Inc.'s levetiracetam tablets. However, due to UCB, Inc.'s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
The safety and effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive treatment of myoclonic seizures in adolescents 12 years of age and older with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy have been established [see CLINICAL STUDIES ( 14.2)].
The safety and effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of primary generalized tonic- clonic seizures in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with idiopathic generalized epilepsy have been established [see CLINICAL STUDIES ( 14.3)].
A 3-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was performed to assess the neurocognitive and behavioral effects of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy in 98 (levetiracetam N=64, placebo N=34) pediatric patients, ages 4 to 16 years old, with partial seizures that were inadequately controlled. The target dose was 60 mg/kg/day. Neurocognitive effects were measured by the Leiter-R Attention and Memory (AM) Battery, which measures various aspects of a child's memory and attention. Although no substantive differences were observed between the placebo and drug treated groups in the median change from baseline in this battery, the study was not adequate to assess formal statistical non-inferiority of the drug and placebo. The Achenbach Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL/6 to 18), a standardized validated tool used to assess a child's competencies and behavioral/emotional problems, was also assessed in this study. An analysis of the CBCL/6 to 18 indicated on average a worsening in levetiracetam treated patients in aggressive behavior, one of the eight syndrome scores. [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.1)]
Studies of levetiracetam in juvenile rats (dosing from day 4 through day 52 of age) and dogs (dosing from week3 through week 7 of age) at doses of up to 1800 mg/kg/day (approximately 7 and 24 times, respectively, the maximum recommended pediatric dose of 60 mg/kg/day on a mg/m2 basis) did not indicate a potential for age-specific toxicity.
8.5 Geriatric UseThere were 347 subjects in clinical studies of levetiracetam that were 65 and over. No overall differences in safety were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. There were insufficient numbers of elderly subjects in controlled trials of epilepsy to adequately assess the effectiveness of levetiracetam in these patients.
Levetiracetam is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ( 12.3)].
8.6 Use in Patients with Impaired Renal FunctionClearance of levetiracetam is decreased in patients with renal impairment and is correlated with creatinine clearance [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY ( 12.3)]. Dose adjustment is recommended for patients with impaired renal function and supplemental doses should be given to patients after dialysis [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ( 2.5)].
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10.1 Signs, Symptoms and Laboratory Findings of Acute Overdosage in Humans
The highest known dose of levetiracetam received in the clinical development program was 6000 mg/day. Other than drowsiness, there were no adverse events in the few known cases of overdose in clinical trials. Cases of somnolence, agitation, aggression, depressed level of consciousness, respiratory depression and coma were observed with levetiracetam overdoses in postmarketing use.
10.2 Management of Overdose
There is no specific antidote for overdose with levetiracetam. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed drug should be attempted by emesis or gastric lavage; usual precautions should be observed to maintain airway. General supportive care of the patient is indicated including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the patient's clinical status. A Certified Poison Control Center should be contacted for up to date information on the management of overdose with levetiracetam.
10.3 Hemodialysis
Standard hemodialysis procedures result in significant clearance of levetiracetam (approximately 50% in 4 hours) and should be considered in cases of overdose. Although hemodialysis has not been performed in the few known cases of overdose, it may be indicated by the patient's clinical state or in patients with significant renal impairment.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
Levetiracetam USP is an antiepileptic drug available as 250 mg (blue), 500 mg (yellow), 750 mg (orange), and 1000 mg (white) tablets for oral administration.
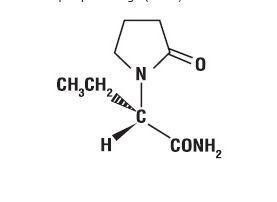
The chemical name of levetiracetam, a single enantiomer, is (-)-(S)-α-ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide, its molecular formula is C8H14N2O2 and its molecular weight is 170.21. Levetiracetam is chemically unrelated to existing antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). It has the following structural formula:
Levetiracetam USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a faint odor and a bitter taste. It is very soluble in water (104.0 g/100 mL). It is freely soluble in chloroform (65.3 g/100 mL) and in methanol (53.6 g/100 mL), soluble in ethanol (16.5 g/100 mL), sparingly soluble in acetonitrile (5.7 g/100 mL) and practically insoluble in n-hexane. (Solubility limits are expressed as g/100 mL solvent).
Levetiracetam tablets USP contain the labeled amount of levetiracetam.
For 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg strengths:
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, crospovidone, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide, and additional agents listed below:
250 mg tablets: FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake
500 mg tablets: Yellow Iron Oxide
750 mg tablets: FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake, FD&C yellow No.6 Aluminum Lake, iron oxide red
For 1000 mg strength:
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, crospovidone, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
- 12.1 Mechanism of Action
The precise mechanism(s) by which levetiracetam exerts its antiepileptic effect is unknown. The antiepileptic activity of levetiracetam was assessed in a number of animal models of epileptic seizures. Levetiracetam did not inhibit single seizures induced by maximal stimulation with electrical current or different chemoconvulsants and showed only minimal activity in submaximal stimulation and in threshold tests. Protection was observed, however, against secondarily generalized activity from focal seizures induced by pilocarpine and kainic acid, two chemoconvulsants that induce seizures that mimic some features of human complex partial seizures with secondary generalization. Levetiracetam also displayed inhibitory properties in the kindling model in rats, another model of human complex partial seizures, both during kindling development and in the fully kindled state. The predictive value of these animal models for specific types of human epilepsy is uncertain.
In vitro and in vivo recordings of epileptiform activity from the hippocampus have shown that levetiracetam inhibits burst firing without affecting normal neuronal excitability, suggesting that levetiracetam may selectively prevent hypersynchronization of epileptiform burst firing and propagation of seizure activity.
Levetiracetam at concentrations of up to 10 µM did not demonstrate binding affinity for a variety of known receptors, such as those associated with benzodiazepines, GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), glycine, NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate), re-uptake sites, and second messenger systems. Furthermore, in vitro studies have failed to find an effect of levetiracetam on neuronal voltage-gated sodium or T-type calcium currents and levetiracetam does not appear to directly facilitate GABAergic neurotransmission. However, in vitro studies have demonstrated that levetiracetam opposes the activity of negative modulators of GABA- and glycine-gated currents and partially inhibits N-type calcium currents in neuronal cells.
A saturable and stereoselective neuronal binding site in rat brain tissue has been described for levetiracetam. Experimental data indicate that this binding site is the synaptic vesicle protein SV2A, thought to be involved in the regulation of vesicle exocytosis. Although the molecular significance of levetiracetam binding to SV2A is not understood, levetiracetam and related analogs showed a rank order of affinity for SV2A which correlated with the potency of their antiseizure activity in audiogenic seizure-prone mice. These findings suggest that the interaction of levetiracetam with the SV2A protein may contribute to the antiepileptic mechanism of action of the drug.
12.2 PharmacodynamicsEffects on QTc Interval
The effect of levetiracetam on QTc prolongation was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, positive-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) and placebo-controlled crossover study of levetiracetam (1000 mg or 5000 mg) in 52 healthy subjects. The upper bound of the 90% confidence interval for the largest placebo-adjusted, baseline-corrected QTc was below 10 milliseconds. Therefore, there was no evidence of significant QTc prolongation in this study.
12.3 PharmacokineticsAbsorption and Distribution
Absorption of levetiracetam is rapid, with peak plasma concentrations occurring in about an hour following oral administration in fasted subjects. The oral bioavailability of levetiracetam tablets is 100% and the tablets and oral solution are bioequivalent in rate and extent of absorption. Food does not affect the extent of absorption of levetiracetam but it decreases Cmax by 20% and delays Tmax by 1.5 hours. The pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam are linear over the dose range of 500 to 5000 mg. Steady state is achieved after 2 days of multiple twice-daily dosing. Levetiracetam and its major metabolite are less than 10% bound to plasma proteins; clinically significant interactions with other drugs through competition for protein binding sites are therefore unlikely.
Metabolism
Levetiracetam is not extensively metabolized in humans. The major metabolic pathway is the enzymatic hydrolysis of the acetamide group, which produces the carboxylic acid metabolite, ucb L057 (24% of dose) and is not dependent on any liver cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. The major metabolite is inactive in animal seizure models. Two minor metabolites were identified as the product of hydroxylation of the 2-oxo-pyrrolidine ring (2% of dose) and opening of the 2-oxo-pyrrolidine ring in position 5 (1% of dose). There is no enantiomeric interconversion of levetiracetam or its major metabolite.
Elimination
Levetiracetam plasma half-life in adults is 7 ± 1 hour and is unaffected by either dose or repeated administration. Levetiracetam is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug which represents 66% of administered dose. The total body clearance is 0.96 mL/min/kg and the renal clearance is 0.6 mL/min/kg. The mechanism of excretion is glomerular filtration with subsequent partial tubular reabsorption. The metabolite ucb L057 is excreted by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion with a renal clearance of 4 mL/min/kg. Levetiracetam elimination is correlated to creatinine clearance. Levetiracetam clearance is reduced in patients with impaired renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Specific Populations
Elderly:
Pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam were evaluated in 16 elderly subjects (age 61 to 88 years) with creatinine clearance ranging from 30 to 74 mL/min. Following oral administration of twice-daily dosing for 10 days, total body clearance decreased by 38% and the half-life was 2.5 hours longer in the elderly compared to healthy adults. This is most likely due to the decrease in renal function in these subjects.
Pediatric Patients:
Pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam were evaluated in 24 pediatric patients (age 6 to 12 years) after single dose (20 mg/kg). The body weight adjusted apparent clearance of levetiracetam was approximately 40% higher than in adults.
A repeat dose pharmacokinetic study was conducted in pediatric patients (age 4 to 12 years) at doses of 20 mg/kg/day, 40 mg/kg/day, and 60 mg/kg/day. The evaluation of the pharmacokinetic profile of levetiracetam and its metabolite (ucb L057) in 14 pediatric patients demonstrated rapid absorption of levetiracetam at all doses with a Tmax of about 1 hour and a t1/2 of 5 hours across the three dosing levels. The pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam in children was linear between 20 to 60 mg/kg/day. The potential interaction of levetiracetam with other AEDs was also evaluated in these patients. Levetiracetam had no significant effect on the plasma concentrations of carbamazepine, valproic acid, topiramate or lamotrigine. However, there was about a 22% increase of apparent clearance of levetiracetam when it was co-administered with an enzyme-inducing AED (e.g. carbamazepine).
Pharmacokinetics information in pediatric patients less than 4 years of age is approved for UCB, Inc.'s levetiracetam tablets. However, due to UCB, Inc.'s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that body weight was significantly correlated to the clearance of levetiracetam in pediatric patients; clearance increased with an increase in body weight.
Pregnancy:
Levetiracetam levels may decrease during pregnancy.
Gender:
Levetiracetam Cmax and AUC were 20% higher in women (N=11) compared to men (N=12). However, clearances adjusted for body weight were comparable.
Race:
Formal pharmacokinetic studies of the effects of race have not been conducted. Cross study comparisons involving Caucasians (N=12) and Asians (N=12), however, show that pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam were comparable between the two races. Because levetiracetam is primarily renally excreted and there are no important racial differences in creatinine clearance, pharmacokinetic differences due to race are not expected.
Renal Impairment:
The disposition of levetiracetam was studied in adult subjects with varying degrees of renal function. Total body clearance of levetiracetam is reduced in patients with impaired renal function by 40% in the mild group (CLcr = 50 to 80 mL/min), 50% in the moderate group (CLcr = 30 to 50 mL/min) and 60% in the severe renal impairment group (CLcr <30 mL/min). Clearance of levetiracetam is correlated with creatinine clearance.
In anuric (end stage renal disease) patients, the total body clearance decreased 70% compared to normal subjects (CLcr >80 mL/min). Approximately 50% of the pool of levetiracetam in the body is removed during a standard 4- hour hemodialysis procedure.
Dosage should be reduced in patients with impaired renal function receiving levetiracetam, and supplemental doses should be given to patients after dialysis [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ( 2.5)].
Hepatic Impairment:
In subjects with mild (Child-Pugh A) to moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment, the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam were unchanged. In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C), total body clearance was 50% that of normal subjects, but decreased renal clearance accounted for most of the decrease. No dose adjustment is needed for patients with hepatic impairment.
Drug Interactions
In vitro data on metabolic interactions indicate that levetiracetam is unlikely to produce, or be subject to, pharmacokinetic interactions. Levetiracetam and its major metabolite, at concentrations well above Cmax levels achieved within the therapeutic dose range, are neither inhibitors of, nor high affinity substrates for, human liver cytochrome P450 isoforms, epoxide hydrolase or UDP-glucuronidation enzymes. In addition, levetiracetam does not affect the in vitro glucuronidation of valproic acid.
Potential pharmacokinetic interactions of or with levetiracetam were assessed in clinical pharmacokinetic studies (phenytoin, valproate, warfarin, digoxin, oral contraceptive, probenecid) and through pharmacokinetic screening in the placebo-controlled clinical studies in epilepsy patients.
Phenytoin:
Levetiracetam (3000 mg daily) had no effect on the pharmacokinetic disposition of phenytoin in patients with refractory epilepsy. Pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam were also not affected by phenytoin.
Valproate:
Levetiracetam (1500 mg twice daily) did not alter the pharmacokinetics of valproate in healthy volunteers. Valproate 500 mg twice daily did not modify the rate or extent of levetiracetam absorption or its plasma clearance or urinary excretion. There also was no effect on exposure to and the excretion of the primary metabolite, ucb L057.
Other Antiepileptic Drugs:
Potential drug interactions between levetiracetam and other AEDs (carbamazepine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone and valproate) were also assessed by evaluating the serum concentrations of levetiracetam and these AEDs during placebo-controlled clinical studies. These data indicate that levetiracetam does not influence the plasma concentration of other AEDs and that these AEDs do not influence the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam.
Effect of AEDs in Pediatric Patients:
There was about a 22% increase of apparent total body clearance of levetiracetam when it was co-administered with enzyme-inducing AEDs. Dose adjustment is not recommended. Levetiracetam had no effect on plasma concentrations of carbamazepine, valproate, topiramate, or lamotrigine.
Oral Contraceptives:
Levetiracetam (500 mg twice daily) did not influence the pharmacokinetics of an oral contraceptive containing 0.03 mg ethinyl estradiol and 0.15 mg levonorgestrel, or of the luteinizing hormone and progesterone levels, indicating that impairment of contraceptive efficacy is unlikely. Coadministration of this oral contraceptive did not influence the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam.
Digoxin:
Levetiracetam (1000 mg twice daily) did not influence the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (ECG) of digoxin given as a 0.25 mg dose every day. Coadministration of digoxin did not influence the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam.
Warfarin:
Levetiracetam (1000 mg twice daily) did not influence the pharmacokinetics of R and S warfarin. Prothrombin time was not affected by levetiracetam. Coadministration of warfarin did not affect the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam.
Probenecid:
Probenecid, a renal tubular secretion blocking agent, administered at a dose of 500 mg four times a day, did not change the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam 1000 mg twice daily. Cssmax of the metabolite, ucb L057, was approximately doubled in the presence of probenecid while the fraction of drug excreted unchanged in the urine remained the same. Renal clearance of ucb L057 in the presence of probenecid decreased 60%, probably related to competitive inhibition of tubular secretion of ucb L057. The effect of levetiracetam on probenecid was not studied.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
- 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Rats were dosed with levetiracetam in the diet for 104 weeks at doses of 50, 300 and 1800 mg/kg/day. The highest dose is 6 times the maximum recommended daily human dose (MRHD) of 3000 mg on a mg/m2 basis and it also provided systemic exposure (AUC) approximately 6 times that achieved in humans receiving the MRHD. There was no evidence of carcinogenicity. In mice, oral administration of levetiracetam for 80 weeks (doses up to 960 mg/kg/day) or 2 years (doses up to 4000 mg/kg/day, lowered to 3000 mg/kg/day after 45 weeks due to intolerability) was not associated with an increase in tumors. The highest dose tested in mice for 2 years (3000 mg/kg/day) is approximately 5 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis.
Mutagenesis
Levetiracetam was not mutagenic in the Ames test or in mammalian cells in vitro in the Chinese hamster ovary/HGPRT locus assay. It was not clastogenic in an in vitro analysis of metaphase chromosomes obtained from Chinese hamster ovary cells or in an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. The hydrolysis product and major human metabolite of levetiracetam (ucb L057) was not mutagenic in the Ames test or the in vitro mouse lymphoma assay.
Impairment of Fertility
No adverse effects on male or female fertility or reproductive performance were observed in rats at oral doses up to 1800 mg/kg/day (6 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 or systemic exposure [AUC] basis).
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
-
In the following studies, statistical significance versus placebo indicates a p value <0.05.
14.1 Partial Onset SeizuresEffectiveness in Partial Onset Seizures in Adults with Epilepsy
The effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy (added to other antiepileptic drugs) in adults was established in three multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies in patients who had refractory partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalization. The tablet formulation was used in all these studies. In these studies, 904 patients were randomized to placebo, 1000 mg, 2000 mg, or 3000 mg/day. Patients enrolled in Study 1 or Study 2 had refractory partial onset seizures for at least two years and had taken two or more classical AEDs. Patients enrolled in Study 3 had refractory partial onset seizures for at least 1 year and had taken one classical AED. At the time of the study, patients were taking a stable dose regimen of at least one and could take a maximum of two AEDs. During the baseline period, patients had to have experienced at least two partial onset seizures during each 4-week period.
Study 1:
Study 1 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study conducted at 41 sites in the United States comparing levetiracetam 1000 mg/day (N=97), levetiracetam 3000 mg/day (N=101), and placebo (N=95) given in equally divided doses twice daily. After a prospective baseline period of 12 weeks, patients were randomized to one of the three treatment groups described above. The 18-week treatment period consisted of a 6-week titration period, followed by a 12-week fixed dose evaluation period, during which concomitant AED regimens were held constant. The primary measure of effectiveness was a between group comparison of the percent reduction in weekly partial seizure frequency relative to placebo over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period). Secondary outcome variables included the responder rate (incidence of patients with ≥50% reduction from baseline in partial onset seizure frequency). The results of the analysis of Study 1 are displayed in Table 10.
Table 9: Reduction in Mean Over Placebo in Weekly Frequency of Partial Onset Seizures In Study 1
Placebo
(N=95)Levetiracetam
1000 mg/day
(N=97)Levetiracetam
3000 mg/day
(N=101)*statistically significant versus placebo Percent reduction
in partial seizure
frequency over
placebo- 26.1% * 30.1% * The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in partial onset seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the three treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction From Baseline) In Study 1
*statistically significant versus placebo
Study 2:
Study 2 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study conducted at 62 centers in Europe comparing levetiracetam 1000 mg/day (N=106), levetiracetam 2000 mg/day (N=105), and placebo (N=111) given in equally divided doses twice daily.
The first period of the study (Period A) was designed to be analyzed as a parallel-group study. After a prospective baseline period of up to 12 weeks, patients were randomized to one of the three treatment groups described above. The 16-week treatment period consisted of the 4-week titration period followed by a 12-week fixed dose evaluation period, during which concomitant AED regimens were held constant. The primary measure of effectiveness was a between group comparison of the percent reduction in weekly partial seizure frequency relative to placebo over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period).
Secondary outcome variables included the responder rate (incidence of patients with ≥50% reduction from baseline in partial onset seizure frequency). The results of the analysis of Period A are displayed in Table 10.
Table 10: Reduction in Mean Over Placebo in Weekly Frequency of Partial Onset Seizures In Study 2: Period A
Placebo
(N=111)Levetiracetam
1000 mg/day
(N=106)Levetiracetam
2000 mg/day
(N=105)*statistically significant versus placebo Percent reduction
in partial seizure
frequency over
placebo- 17.1% * 21.4% * The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in partial onset seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the three treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction From Baseline) In Study 2: Period A
*statistically significant versus placebo
The comparison of levetiracetam 2000 mg/day to levetiracetam 1000 mg/day for responder rate was statistically significant (P=0.02). Analysis of the trial as a cross-over yielded similar results.
Study 3:
Study 3 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study conducted at 47 centers in Europe comparing levetiracetam 3000 mg/day (N=180) and placebo (N=104) in patients with refractory partial onset seizures, with or without secondary generalization, receiving only one concomitant AED. Study drug was given in two divided doses. After a prospective baseline period of 12 weeks, patients were randomized to one of two treatment groups described above. The 16-week treatment period consisted of a 4-week titration period, followed by a 12-week fixed dose evaluation period, during which concomitant AED doses were held constant. The primary measure of effectiveness was a between group comparison of the percent reduction in weekly seizure frequency relative to placebo over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period). Secondary outcome variables included the responder rate (incidence of patients with ≥50% reduction from baseline in partial onset seizure frequency). Table 11 displays the results of the analysis of Study 3.
Table 11: Reduction in Mean Over Placebo in Weekly Frequency of Partial Onset Seizures In Study 3
Placebo
(N=104)Levetiracetam
3000 mg/day
(N=180)*statistically significant versus placebo Percent reduction in
partial seizure
frequency over placebo- 23.0% * The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in partial onset seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the two treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction From Baseline) In Study 3
*statistically significant versus placebo
Effectiveness in Partial Onset Seizures in Pediatric Patients 4 Years to 16 Years With Epilepsy
The effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy (added to other antiepileptic drugs) in pediatric patients was established in one multicenter, randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study, conducted at 60 sites in North America, in children 4 to 16 years of age with partial seizures uncontrolled by standard antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Eligible patients on a stable dose of 1 to 2 AEDs, who still experienced at least 4 partial onset seizures during the 4 weeks prior to screening, as well as at least 4 partial onset seizures in each of the two 4-week baseline periods, were randomized to receive either levetiracetam or placebo. The enrolled population included 198 patients (levetiracetam N=101, placebo N=97) with refractory partial onset seizures, whether or not secondarily generalized. The study consisted of an 8-week baseline period and 4-week titration period followed by a 10-week evaluation period. Dosing was initiated at a dose of 20 mg/kg/day in two divided doses. During the treatment period, levetiracetam doses were adjusted in 20 mg/kg/day increments, at 2-week intervals to the target dose of 60 mg/kg/day. The primary measure of effectiveness was a between group comparison of the percent reduction in weekly partial seizure frequency relative to placebo over the entire 14-week randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period). Secondary outcome variables included the responder rate (incidence of patients with ≥ 50% reduction from baseline in partial onset seizure frequency per week). Table 12 displays the results of this study.
Table 12: Reduction In Mean Over Placebo In Weekly Frequency of Partial Onset Seizures
Placebo
(N=97)Levetiracetam
(N=101)*statistically significant versus placebo Percent reduction in
partial seizure
frequency over placebo- 26.8% * The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥ 50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in partial onset seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the two treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Responder Rate (≥ 50% Reduction From Baseline)
*statistically significant versus placebo
Clinical trial information in pediatric patients less than 4 years of age as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures is approved for UCB, Inc.'s levetiracetam tablets. However, due to UCB, Inc.'s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
14.2 Myoclonic Seizures in Patients with Juvenile Myoclonic EpilepsyEffectiveness of Myoclonic Seizures in Patients ≥12 Years of Age with Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy (JME)
The effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy (added to other antiepileptic drugs) in patients 12 years of age and older with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME) experiencing myoclonic seizures was established in one multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, conducted at 37 sites in 14 countries. Of the 120 patients enrolled, 113 had a diagnosis of confirmed or suspected JME. Eligible patients on a stable dose of 1 antiepileptic drug (AED) experiencing one or more myoclonic seizures per day for at least 8 days during the prospective 8-week baseline period were randomized to either levetiracetam or placebo (levetiracetam N=60, placebo N=60). Patients were titrated over 4 weeks to a target dose of 3000 mg/day and treated at a stable dose of 3000 mg/day over 12 weeks (evaluation period). Study drug was given in 2 divided doses.
The primary measure of effectiveness was the proportion of patients with at least 50% reduction in the number of days per week with one or more myoclonic seizures during the treatment period (titration + evaluation periods) as compared to baseline. Table 13 displays the results for the 113 patients with JME in this study.
14.3 Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic SeizuresTable 13: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) In Myoclonic Seizure Days Per Week for Patients with JME
Placebo
(N=59)Levetiracetam
(N=54)*statistically significant versus placebo Percentage of responders 23.7% 60.4% * Effectiveness in Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures in Patients ≥6 Years of Age
The effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy (added to other antiepileptic drugs) in patients 6 years of age and older with idiopathic generalized epilepsy experiencing primary generalized tonic-clonic (PGTC) seizures was established in one multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, conducted at 50 sites in 8 countries. Eligible patients on a stable dose of 1 or 2 antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) experiencing at least 3 PGTC seizures during the 8-week combined baseline period (at least one PGTC seizure during the 4 weeks prior to the prospective baseline period and at least one PGTC seizure during the 4-week prospective baseline period) were randomized to either levetiracetam or placebo. The 8-week combined baseline period is referred to as "baseline" in the remainder of this section. The population included 164 patients (levetiracetam N=80, placebo N=84) with idiopathic generalized epilepsy (predominately juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, juvenile absence epilepsy, childhood absence epilepsy, or epilepsy with Grand Mal seizures on awakening) experiencing primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Each of these syndromes of idiopathic generalized epilepsy was well represented in this patient population. Patients were titrated over 4 weeks to a target dose of 3000 mg/day for adults or a pediatric target dose of 60 mg/kg/day and treated at a stable dose of 3000 mg/day (or 60 mg/kg/day for children) over 20 weeks (evaluation period). Study drug was given in 2 equally divided doses per day.
The primary measure of effectiveness was the percent reduction from baseline in weekly PGTC seizure frequency for levetiracetam and placebo treatment groups over the treatment period (titration + evaluation periods). There was a statistically significant decrease from baseline in PGTC frequency in the levetiracetam-treated patients compared to the placebo-treated patients.
Table 14: Median Percent Reduction from Baseline In PGTC Seizure Frequency Per Week
Placebo
(N=84)Levetiracetam
(N=78)*statistically significant versus placebo Percent reduction in
PGTC seizure frequency44.6% 77.6% * The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in PGTC seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the two treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction From Baseline) In PGTC Seizure Frequency Per Week
*statistically significant versus placebo
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
- 16.1 How Supplied
Levetiracetam tablets USP, 250 mg are blue coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X01" on the other side.
They are supplied as follows:
NDC 68180-112-09 Bottles of 90's
NDC 68180-112-16 Bottles of 120's
NDC 68180-112-02 Bottles of 500's
Levetiracetam tablets USP, 500 mg are yellow coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X02" on the other side.
They are supplied as follows:
NDC 68180-113-09 Bottles of 90's
NDC 68180-113-16 Bottles of 120's
NDC 68180-113-02 Bottles of 500's
Levetiracetam tablets USP, 750 mg are orange coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X03" on the other side.
They are supplied as follows:
NDC 68180-114-09 Bottles of 90's
NDC 68180-114-16 Bottles of 120's
NDC 68180-114-02 Bottles of 500's
Levetiracetam tablets USP, 1000 mg are white to off-white coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X04" on the other side.
They are supplied as follows:
NDC 68180-115-07 Bottles of 60's
NDC 68180-115-02 Bottles of 500's
16.2 StorageStore at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15 to 30°C (59 to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Pharmacist: Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container with child-resistant closure along with medication guide provided separately.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
-
See FDA-approved Patient Labeling (Medication Guide).
Counsel patients on the benefits and risks of receiving levetiracetam. Provide the Medication Guide to patients and/or caregivers, and instruct them to read the Medication Guide prior to taking levetiracetam. Instruct patients to take levetiracetam only as prescribed.
Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Counsel patients, their caregivers, and/or families that antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including levetiracetam, may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and advise patients to be alert for the emergence or worsening of symptoms of depression; unusual changes in mood or behavior; or suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm. Advise patients, their caregivers, and/or families to immediately report behaviors of concern to a healthcare provider.
Psychiatric Reactions and Changes in Behavior
Advise patients that levetiracetam may cause changes in behavior (e.g. aggression, agitation, anger, anxiety, apathy, depression, hostility, and irritability) and in rare cases, psychotic symptoms have occurred.
Effects on Driving or Operating Machinery
Inform patients that levetiracetam may cause dizziness and somnolence. Inform patients not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on levetiracetam to gauge whether it adversely affects their ability to drive or operate machinery.
Dermatological Adverse Reactions
Advise patients that serious dermatological adverse reactions have occurred in patients treated with levetiracetam and instruct them to call their physician immediately if a rash develops.
Pregnancy
Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during levetiracetam therapy. Encourage patients to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) pregnancy registry if they become pregnant. This registry is collecting information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. To enroll, patients can call the toll free number 1-888-233-2334.
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Baltimore, Maryland 21202
United States.
MADE IN INDIA.
November 2014 ID# 2389
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
MEDICATION GUIDE
LEVETIRACETAM TABLETS USP
250 mg, 500 mg, 750 mg and 1000 mg
Rx only
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking levetiracetam tablets and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about levetiracetam tablets?
Like other antiepileptic drugs, levetiracetam tablets may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500 people taking it.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
thoughts about suicide or dying
attempts to commit suicide
new or worse depression
new or worse anxiety
feeling agitated or restless
panic attacks
trouble sleeping (insomnia)
new or worse irritability
acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
acting on dangerous impulses
an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
other unusual changes in behavior or mood
Do not stop levetiracetam tablets without first talking to a healthcare provider.
Stopping levetiracetam tablets suddenly can cause serious problems. Stopping a seizure medicine suddenly can cause seizures that will not stop (status epilepticus).
Suicidal thoughts or actions can be caused by things other than medicines. If you have suicidal thoughts or actions, your healthcare provider may check for other causes.
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
What are levetiracetam tablets?
Levetiracetam tablets are a prescription medicine taken by mouth that is used with other medicines to treat:
partial onset seizures in people 4 years of age and older with epilepsy
myoclonic seizures in people 12 years of age and older with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in people 6 years of age and older with certain types of generalized epilepsy.
It is not known if levetiracetam tablets are safe or effective in children under 1 month of age.
Before taking your medicine, make sure you have received the correct medicine. Compare the name above with the name on your bottle and the appearance of your medicine with the description of levetiracetam tablets provided below. Tell your pharmacist immediately if you think you have been given the wrong medicine.
Levetiracetam tablets USP, 250 mg are blue coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X01" on the other side.
Levetiracetam tablets USP, 500 mg are yellow coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X02" on the other side.
Levetiracetam tablets USP, 750 mg are orange coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X03" on the other side.
Levetiracetam tablets USP, 1000 mg are white to off-white coloured, oblong-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L" and "U" on either side of the breakline on one side and "X04" on the other side.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before starting levetiracetam tablets?
Before taking levetiracetam tablets, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
have or have had depression, mood problems or suicidal thoughts or behavior
have kidney problems
are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if levetiracetam tablets will harm your unborn baby. You and your healthcare provider will have to decide if you should take levetiracetam tablets while you are pregnant. If you become pregnant while taking levetiracetam tablets, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug Pregnancy Registry. You can enroll in this registry by calling 1-888-233-2334. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of levetiracetam and other antiepileptic medicine during pregnancy.
are breast feeding. Levetiracetam can pass into your milk and may harm your baby. You and your healthcare provider should discuss whether you should take levetiracetam tablets or breastfeed; you should not do both.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Do not start a new medicine without first talking with your healthcare provider.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take levetiracetam tablets?
Take levetiracetam tablets exactly as prescribed.
Your healthcare provider will tell you how much levetiracetam tablets to take and when to take it. Levetiracetam tablets are usually taken twice a day. Take levetiracetam tablets at the same times each day.
Your healthcare provider may change your dose. Do not change your dose without talking to your healthcare provider.
Take levetiracetam tablets with or without food.
Swallow the tablets whole. Do not chew or crush tablets. Ask your healthcare provider for levetiracetam oral solution if you cannot swallow tablets.
If you miss a dose of levetiracetam tablets, take it as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, just skip the missed dose. Take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take two doses at the same time.
If you take too much levetiracetam tablets, call your local Poison Control Center or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking levetiracetam tablets?
Do not drive, operate machinery or do other dangerous activities until you know how levetiracetam tablets affect you. Levetiracetam tablets may make you dizzy or sleepy.
What are the possible side effects of levetiracetam tablets?
See "What is the most important information I should know about levetiracetam tablets?"
Levetiracetam tablets can cause serious side effects.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
mood and behavior changes such as aggression, agitation, anger, anxiety, apathy, mood swings, depression, hostility, and irritability. A few people may get psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are really not there), delusions (false or strange thoughts or beliefs) and unusual behavior.
extreme sleepiness, tiredness, and weakness
problems with muscle coordination (problems walking and moving)
a skin rash. Serious skin rashes can happen after you start taking levetiracetam tablets. There is no way to tell if a mild rash will become a serious reaction.
The most common side effects seen in people who take levetiracetam tablets include:
sleepiness
weakness
infection
dizziness
The most common side effects seen in children who take levetiracetam tablets include, in addition to those listed above:
tiredness
acting aggressive
nasal congestion
decreased appetite
irritability
These side effects can happen at any time but happen more often within the first 4 weeks of treatment except for infection.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of levetiracetam tablets. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-399-2561.
How should I store levetiracetam tablets?
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15 to 30°C (59 to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep levetiracetam tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about levetiracetam tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use levetiracetam tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give levetiracetam tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about levetiracetam tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about levetiracetam tablets that is written for health professionals. You can also get information about levetiracetam tablets at www.lupinpharmaceuticals.com or call 1-800-399-2561.
What are the ingredients of levetiracetam tablets?
Levetiracetam tablets
active ingredient: levetiracetam
For 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg strengths:
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, crospovidone, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide, and additional agents listed below:
250 mg tablets: FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake
500 mg tablets: Yellow Iron Oxide
750 mg tablets: FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake, FD&C yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake, iron oxide red
For 1000 mg strength:
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, crospovidone, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc and titanium dioxide.
Levetiracetam tablets do not contain lactose or gluten.
Information on the use of levetiracetam in pediatric patients less than 4 years of age as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures is approved for UCB, Inc.'s levetiracetam tablets. However, due to UCB, Inc.'s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Baltimore, Maryland 21202
United States.
MADE IN INDIA.



