DESCRIPTION
Lactulose solution, USP is a synthetic disaccharide in solution form for oral administration. Each 15 mL of lactulose solution contains: 10 g lactulose (and less than 1.6 g galactose, less than 1.2 g lactose, and 1.2 g or less of other sugars). Also contains FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Yellow No. 6, flavoring and purified water. A minimal quantity of sodium hydroxide is used to adjust pH, when necessary. The pH range is 2.5 to 6.5.
Lactulose solution is a colonic acidifier which promotes laxation.
The chemical name for lactulose is 4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-fructofuranose. It has the following structural formula:
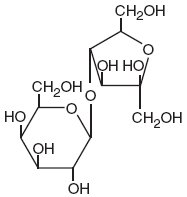
It has the molecular formula of C12H22O11 and the molecular weight is 342.30. It is freely soluble in water.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Lactulose solution is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and no enzyme capable of hydrolysis of this disaccharide is present in human gastrointestinal tissue. As a result, oral doses of lactulose solution reach the colon virtually unchanged. In the colon, lactulose solution is broken down primarily to lactic acid, and also to small amounts of formic and acetic acids, by the action of colonic bacteria, which results in an increase in osmotic pressure and slight acidification of the colonic contents. This in turn causes an increase in stool water content and softens the stool.
Since lactulose solution does not exert its effect until it reaches the colon, and since transit time through the colon may be slow, 24 to 48 hours may be required to produce the desired bowel movement.
Lactulose given orally to man and experimental animals resulted in only small amounts reaching the blood. Urinary excretion has been determined to be 3% or less and is essentially complete within 24 hours.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
For the treatment of constipation. In patients with a history of chronic constipation, lactulose solution therapy increases the number of bowel movements per day and the number of days on which bowel movements occur.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Since lactulose solution contains galactose (less than 1.6 g/15 mL), it is contraindicated in patients who require a low galactose diet.
WARNINGS
A theoretical hazard may exist for patients being treated with lactulose solution who may be required to undergo electrocautery procedures during proctoscopy or colonoscopy. Accumulation of H2 gas in significant concentration in the presence of an electrical spark may result in an explosive reaction. Although this complication has not been reported with lactulose, patients on lactulose therapy undergoing such procedures should have a thorough bowel cleansing with a non-fermentable solution. Insufflation of CO2 as an additional safeguard may be pursued but is considered to be a redundant measure.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Since lactulose solution contains galactose (less than 1.6 g/15 mL) and lactose (less than 1.2 g/15 mL), it should be used with caution in diabetics.
Information for Patients
In the event that an unusual diarrheal condition occurs, contact your physician.
Laboratory Tests
Elderly, debilitated patients who receive lactulose solution for more than six months should have serum electrolytes (potassium, chloride, carbon dioxide) measured periodically.
Drug Interaction
Results of preliminary studies in humans and rats suggest that nonabsorbable antacids given concurrently with lactulose may inhibit the desired lactulose-induced drop in colonic pH. Therefore, a possible lack of desired effect of treatment should be taken into consideration before such drugs are given concomitantly with lactulose solution.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
There are no known human data on long-term potential for carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or impairment of fertility.
There are no known animal data on long-term potential for mutagenicity.
Administration of lactulose solution in the diet of mice for 18 months in concentrations of 3 and 10 percent (V/W) did not produce any evidence of carcinogenicity.
In studies in mice, rats, and rabbits, doses of lactulose solution up to 6 or 12 mL/kg/day produced no deleterious effects in breeding, conception, or parturition.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies have been performed in mice, rats, and rabbits at doses up to 3 or 6 times the usual human oral dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to lactulose solution. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Precise frequency data are not available.
Initial dosing may produce flatulence and intestinal cramps, which are usually transient. Excessive dosage can lead to diarrhea with potential complications such as loss of fluids, hypokalemia, and hypernatremia.
Nausea and vomiting have been reported.
OVERDOSAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The usual dose is 1 to 2 tablespoonfuls (15 to 30 mL, containing 10 g to 20 g of lactulose) daily. The dose may be increased to 60 mL daily if necessary. Twenty-four to 48 hours may be required to produce a normal bowel movement.
Note: Some patients have found that lactulose solution may be more acceptable when mixed with fruit juice, water or milk.
