DESCRIPTION
FOSTEUM® consists of a specially formulated proprietary blend of high purity genistein aglycone from a natural source, citrated zinc bisglycinate and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3). Genistein aglycone reduces osteoclast activity and stimulates osteoblast activity. Citrated zinc bisglycinate works synergistically with genistein aglycone, while both citrated zinc bisglycinate and vitamin D3 also work independently to promote mineralization activity in bone. Vitamin D3 also facilitates calcium absorption from the intestine.Genistein aglycone
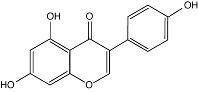
Each FOSTEUM capsule contains 27 mg of genistein aglycone (genistein), derived from a natural source, for a total daily intake of 54 mg. In clinical trials, this level of intake has been shown to increase bone mineral density (BMD). Genistein is chemically described as 4',5,7-trihydroxyisoflavone or 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one. It is the aglycone form of the glucoside isoflavone molecule genistin. The empirical formula of genistein is C15H10O5; its molecular weight is 270.2. The structural formula is:
Citrated Zinc Bisglycinate
Each FOSTEUM capsule contains 20 mg citrated zinc bisglycinate, a glycine amino acid chelate of zinc formed in the presence of citric acid that provides approximately 4 mg of elemental zinc per capsule. Zinc is an essential mineral co-factor required by enzymes involved in bone metabolism and has important physiological functions in other tissues throughout the body. Elemental zinc has also been shown to have synergistic effects with genistein on bone formation. This zinc bisglycinate, formed in the presence of citric acid, has been shown to have improved absorption over inorganic zinc salts, such as zinc sulfate. Zinc bisglycinate, a chelate of zinc, is complex with an empirical formula of C4H8O4Zn; its molecular weight is 215.5. Its structural formula is:
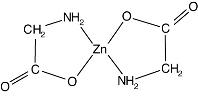
When generated in the presence of citric acid, citrate and additional glycinate ions (not shown) also participate in this structure, forming citrated zinc bisglycinate, contributing to the complexity of the molecule.
Cholecalciferol
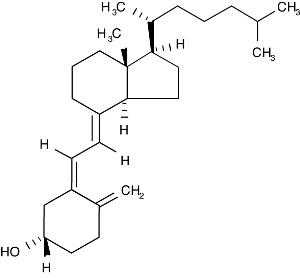
Each FOSTEUM capsule contains cholecalciferol equivalent to 200 IU vitamin D3. Vitamin D3 is the natural form of vitamin D produced when skin is exposed to the sun. Vitamin D is necessary for proper absorption of calcium from the intestine and the use of absorbed calcium in the mineralization of bone. Cholecalciferol is the natural precursor of calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxy-cholecalciferol), the physiologically active form of vitamin D in bone. It is described as (3ßμ,5Z,7E)-9,10-secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-triene-3-ol. The empirical formula is C27H44O; its molecular weight is 384.6. The structural formula is:
Other Ingredients
FOSTEUM contains the following other ingredients as excipients: dicalcium malate, magnesium oxide, micro-crystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate and silicon dioxide in a capsule made from plant sources. FD&C Blue #2 is used for the imprint on the capsule. FOSTEUM does not contain fructose, glucose, sucrose, lactose, gluten, maltodextrin, tree nuts, peanuts, flavors or products of animal or seafood origin. FOSTEUM is suitable for vegans.Medical Food
Medical Food products are used under a physician's supervision for the dietary management of diseases in patients with particular medical or metabolic needs due to their disease or condition. The U.S. Congress defined "medical food" in the Orphan Drug Act and Amendments of 1988 as "a food which is formulated to be consumed or administered enterally under the supervision of a physician, and which is intended for the specific dietary management of a disease or condition for which distinctive nutritional requirements, based on recognized scientific principles, are established by medical evaluation." FOSTEUM has been developed, manufactured and labeled in accordance with both the statutory and the FDA regulatory definition of a medical food. FOSTEUM is to be used only under a physician's supervision.Generally Recognized As Safe
The ingredients in FOSTEUM are Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS). This is the statutory safety standard that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires of all ingredients added to food products. The standard for an ingredient to achieve GRAS status requires technical demonstration of non-toxicity and safety, general recognition of safety through widespread usage and agreement of that safety by experts in the field.LOW BONE MASS AND OSTEOPOROSIS
Low bone mass (osteopenia) and osteoporosis are gradations of bone loss. Low bone mass may progress to osteoporosis. Low bone mass and osteoporosis occur when the homeostasis of the metabolic processes of normal bone turnover is unbalanced in favor of resorption activity. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines low bone mass as a T-score between -1.0 and -2.5. Osteoporosis is defined at a T-score lower than -2.5.DIETARY NEED
The highly concentrated, pure form of genistein plus citrated zinc bisglycinate and vitamin D3 in FOSTEUM is specially formulated for the dietary management of the metabolic processes of osteopenia and osteoporosis that cannot be achieved by a change in the normal diet. FOSTEUM provides the distinctive nutrients needed by osteopenic and osteoporotic patients. It restores the metabolic balance of bone turnover toward normal levels.
Epidemiological studies have shown that the risk of osteopenia and osteoporosis in Asian populations is generally 20-30% lower than in Western populations. This lowered risk has been associated with diet, specifically with intake of isoflavones, including genistein, of more than 20 mg per day, and protein from certain legumes of more than 5 g per day. At first glance, it is paradoxical that Asian countries with some of the lowest calcium intakes worldwide have a relatively low rate of osteoporotic hip fractures. Other dietary components, such as isoflavones, may affect the maintenance of bone density in these populations. Isoflavones are found in a variety of natural products. Data exist that support the reduction in bone loss when individuals adopt a diet rich in isoflavones. Moreover, the absence of high isoflavone intake when individuals transition to a more Western style diet results in increased bone loss. Clinical evidence has shown that pure genistein increases bone density in women who have been diagnosed with osteopenia or osteoporosis. Genistein exists in very low concentrations in natural products (generally less than 1%). This amount is not adequate to meet the dietary need of patients with osteopenia or osteoporosis. Concentrating and specially formulating the genistein in FOSTEUM allows the dietary need to be met in a convenient capsule form.
Daily Reference Intake for elemental zinc is 8 mg/day for women and 11 mg/day for men, as established by the Institute of Medicine of the National Academies as published by the National Academy of Sciences (IOM) in 2004. Supplementation with zinc and other minerals has been shown to improve spinal bone mineral density in post-menopausal women. Zinc is an essential co-factor for enzymes involved in the synthesis of bone matrix constituents. As people age, the level of zinc intake generally drops, potentially leading to zinc deficiency and reduced bone quality. Zinc has been shown to act synergistically with the genistein in FOSTEUM to favorably influence bone metabolism.
Vitamin D3 is synthesized in the skin after exposure to UV radiation. A large segment of the American population is vitamin D deficient due to lack of sun exposure or skin aging, especially in northern latitudes and among the elderly who do not produce enough vitamin D3. In the absence of sufficient vitamin D3 production by the body, the vitamin must be obtained from the diet. Many Americans have inadequate dietary vitamin D intake. Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, is required for absorption of calcium from the intestine, regulation of serum calcium, bone formation and bone resorption among other activities.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
FOSTEUM acts by restoring and maintaining the balance of bone turnover toward normal levels in osteopenia and osteoporosis. Clinical and preclinical data suggest that the genistein in FOSTEUM both reduces osteoclast-mediated bone resorption and stimulates the bone forming activity of osteoblasts. The zinc in FOSTEUM acts synergistically with the genistein, and the cholecalciferol improves the absorption of calcium and its deposition into the mineral matrix of bone.
Osteopenia and osteoporosis generally occur because of hormonal changes associated with the aging process or the use of certain classes of drugs. Bone loss associated with these conditions is primarily due to the metabolic imbalance that occurs when osteoclast activity is greater than osteoblast activity. The imbalance of bone resorption in excess of bone formation is progressive and often leads to fractures. These minimal trauma fractures may lead to significant morbidity and mortality. Successful dietary management of the metabolic processes underlying osteopenia and osteoporosis helps to restore the balance of bone resorption versus bone formation and consequently increases bone density over time.
Genistein aglycone
The genistein in FOSTEUM reduces the activity of osteoclasts and promotes the formation of osteoblasts from progenitor stem cells to increase their number and activity in bone. The net effect is an enhancement of bone formation which restores bone remodeling toward normal levels and results in an increase in bone mineral density (BMD) over time. Through these clinical dietary modifications, FOSTEUM manages the metabolic processes of osteopenia and osteoporosis.
More specifically, preclinical studies suggest the following mechanisms of action: Genistein acts to reverse the effects of estrogen loss by decreasing cytokine production and increasing transforming growth factor ß (TGFß) levels. The net effect is a decrease in receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANK-L) production, an increase in osteoprotegerin (OPG) levels, and a consequent decrease in overall osteoclast activity. Genistein also increases insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) leading to an increased number of proto-osteoblasts developed from mesenchymal stem cells. Genistein restores endothelial cell signals resulting in increased recruitment of these precursor cells to form osteoblasts. Genistein also reverses early apoptosis of osteoblasts. These actions likely produce a net increase in osteoblast activity and concomitant decrease in osteoclast activity.
In clinical trials, the genistein in FOSTEUM decreased urinary levels of the bone resorption markers deoxypyridinoline (DPYR) and pyridinoline (PYR), and increased serum levels of the bone formation markers bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BAP), osteocalcin (OC), and IGF-1. These data suggest that genistein increases BMD over time by decreasing bone resorption and increasing bone formation.
Zinc (Elemental)
Studies have shown that zinc has a positive effect on bone formation. The zinc in FOSTEUM is the citrated bisglycinate form, which has been shown to have improved absorption from the intestine compared to inorganic zinc salts.
Cell cultures of rat femoral-metaphyseal tissue treated with zinc and genistein produced a greater increase in BAP, DNA and bone calcium content compared with either agent alone. Other studies have demonstrated that genistein and zinc produce synergistic effects on osteoclast apoptosis and bone mineralization. Animal studies support these findings by showing that the combination of zinc and genistein increases mineralization in bone over genistein alone. In both men and women, zinc was shown to potentiate the effect of high genistein-containing fermented food on bone markers by further increasing the levels of BAP and OC. Based on these data, genistein and zinc increase osteoblast activity while decreasing osteoclast activity to a greater extent than either genistein or zinc alone.
Cholecalciferol
The physiologically active form of vitamin D, calcitriol, regulates calcium and phosphate absorption and modulates serum calcium, renal calcium and phosphate excretion, bone formation and bone resorption. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with a negative calcium balance, increased parathyroid hormone levels, bone loss and increased risk of skeletal fracture. Severe deficiency results in hyperparathyroidism, hypophosphatemia, bone loss, proximal muscle weakness and osteomalacia.
METABOLISM
Genistein
The genistein in FOSTEUM is freely absorbed in the gut, where it is at least partly converted to one metabolite, 7-O-beta-glucuronide, before it crosses the mucosa from the intestinal lumen. In hepatic first pass metabolism, genistein is converted via a two-stage process involving initial CYP450-mediated hydroxylation, followed by glucuronidation and sulfonation to the principal conjugated circulating metabolites. Genistein metabolites are converted back into the aglycone form in a variety of tissues. The aglycone is believed to be the principal active form, but conjugates have shown some activity in estrogen-receptor binding assays. Genistein and its conjugates are excreted via urine and bile.
Citrated zinc bisglycinate
Citrated zinc bisglycinate consists of zinc chelated by glycine in the presence of citric acid. Once absorbed, the zinc is released from the chelate. Subsequently, glycine is utilized in normal protein metabolism and zinc is bound to albumin as well as blood cells and distributed throughout the body. The citrate is absorbed and utilized in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (Krebs cycle). The majority of zinc in the human body is found in muscle and bone. Excretion occurs predominantly via the feces.Cholecalciferol
Ultraviolet light acts on 7-dehydrocholesterol (provitamin D3) in skin, where it is converted to 9,10-secosterol (previtamin D3). Previtamin D3 is converted into 25-hydroxycholecalciferol in the liver by the P450 enzyme CYP27. This molecule is further converted in the kidney by the P450 enzyme CYP27B1 to the active hormone 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol).CLINICAL EXPERIENCE
Hepatic and Renal Effects
In clinical studies, the effects of genistein in FOSTEUM on blood chemical, hepatic and renal functional measures were compared in post-menopausal subjects receiving genistein plus calcium carbonate (calcium) and vitamin D3 with post-menopausal, age-matched subjects receiving only calcium and vitamin D3. No changes were noted over a three year period in either group and all measures remained within normal limits.
Since the precursor form of vitamin D3 is transformed to the active form in the liver and then kidney, it is expected that patients with severe liver or kidney impairment may not transform the vitamin adequately.
Effects on Reproductive Tissues
Effects of the genistein in FOSTEUM on breast density, vaginal cytology and endometrial thickness were tested in double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials. One trial with 30 post-menopausal subjects in each arm found that genistein did not affect endometrial thickness over a one year period compared to placebo. In other controlled trials, daily administration of 54 mg of genistein over one, two and three year periods produced no increases in endometrial thickness or breast density in post-menopausal women. Furthermore, a subset of 113 post-menopausal women showed no change in vaginal cytology following one year of daily genistein therapy. These data suggest that the genistein in FOSTEUM does not produce adverse estrogenic effects in reproductive tissues.
Cardiovascular Safety
In a study of 60 post-menopausal subjects comparing the cardiovascular markers of those receiving the genistein in FOSTEUM to a matched group receiving placebo, homocysteine and C-reactive protein (CRP) were assessed at baseline and again at 6 months. No statistically significant differences were seen between groups. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (iCAM), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (vCAM), fibrinogen and F2-isoprostane levels were assessed at baseline and again at 12 and 24 months in 389 post-menopausal subjects randomized to receive either genistein, calcium and vitamin D3 or calcium and vitamin D3 only (placebo). At both 12 and 24 months, the levels of all four cardiovascular markers were reduced in the genistein group compared to both baseline and placebo at all time points. No significant changes in lipid profile were observed in either the genistein or placebo group over the course of the study. These data indicate that genistein does not adversely affect markers of cardiovascular risk. An additional study of 53 post-menopausal women measured changes in flow-mediated vasodilation and plasma nitric oxide status. The genistein in FOSTEUM significantly increased plasma nitrite/nitrate levels and reduced levels of endothelin-1 compared to placebo. After 12 months of use, forearm blood flow increased significantly during reactive hyperemia in the genistein group compared to placebo. Flow-mediated dilation in the proximal and distal brachial arteries both increased significantly after genistein administration. The purified genistein in FOSTEUM improved endothelial function in a cohort of post-menopausal women.
Menopausal Symptoms
In two published studies with a combined enrollment of more than 300 post-menopausal women, the genistein in FOSTEUM progressively reduced the number of symptomatic vasomotor episodes by an average of more than 50% at the 12 month follow-up. In these studies, vasomotor symptoms were unchanged in the placebo groups.DRUG INTERACTIONS
Genistein
The genistein in FOSTEUM was tested in in vitro pooled human liver microsome assays for CYP1A2, 2A6, 2C8, 2C9, 2D6, and 3A4. Inhibition of the 1A2, 2A6, 2D6 and 3A4 isozymes was low, however, inhibition of CYP450 2C8 and 2C9 was observed with IC50s of 2.5 and 2.8 μM, respectively. Results from a steady-state pharmacokinetic study in post-menopausal women showed that the level of circulating genistein was in the low nanomolar range and undetectable at most time points in many subjects. These data suggest that circulating genistein does not produce any clinically significant interactions with co-administered drugs. The effects of the principal circulating metabolites of genistein on CYP450-mediated metabolism are currently unknown.TOXICITY
Genistein
Genistein showed no toxicity in rats following acute dosing up to 2000 mg/kg. Long-term toxicity studies up to 52 weeks duration using oral administration of 0-500 mg/kg/day in rats and dogs showed minimal adverse effects. Changes were primarily observed at the 500 mg/kg/day dose. From these studies, the no observed adverse effect level for genistein in rats was determined to be 50 mg/kg/day and in dogs >500 mg/kg/day. These intake levels are at least 50-fold greater than the recommended dose of the genistein in FOSTEUM on a mg/kg basis.Zinc (Elemental)
The National Academy of Sciences upper acceptable limit for self-administration is 40 mg/day of elemental zinc, the equivalent of ten FOSTEUM capsules per day. Zinc is considered acutely toxic at 200 mg elemental zinc per day, the equivalent of 50 FOSTEUM capsules per day.Cholecalciferol
Cholecalciferol may produce toxicity with long term, high-dose consumption. While medical doses of vitamin D3 up to 10,000 IU per day are sometimes administered under physician supervision, the upper acceptable limit for self-administration is 2,000 IU per day per the Daily Reference Intakes of the Institute of Medicine published by the NAS in 2004. Signs and symptoms of vitamin D toxicity include hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, polyuria, polydipsia, weakness and lethargy. Serum and urine calcium levels should be monitored in patients with suspected vitamin D toxicity. Standard therapy includes restriction of dietary calcium, hydration and systemic glucocorticoids in patients with severe hypercalcemia.SPECIAL POPULATIONS
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Indications
FOSTEUM is indicated for the clinical dietary management of the metabolic processes of osteopenia and osteoporosis.Usage
FOSTEUM should be taken with sufficient calcium and vitamin D3 as directed by a physician. In clinical trials of the genistein in FOSTEUM, patients also received 1,000 mg of calcium carbonate and 800 IU vitamin D3 per day in two divided doses. See Dosage and Administration for additional information.PRECAUTIONS AND CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity
FOSTEUM is contraindicated for anyone having a hypersensitivity to any ingredient in the product. See "Other ingredients" for a full list of ingredients.Patients with Cancer
Since no studies have been done in these populations, as a precaution, FOSTEUM is contraindicated for patients with a history of cancer of the breast or reproductive organs and should be used with caution by women who have a history of breast or reproductive cancer in first degree female relatives.Vitamin D Deficiency
FOSTEUM is not intended to treat vitamin D deficiency, generally characterized in the literature by serum levels of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol below 9 ng/mL. FOSTEUM contains 400 IU cholecalciferol in two recommended capsules per day, but the NAS recommended daily dose in patients over the age of 70 is 600 IU/day. FOSTEUM should be taken with a calcium/vitamin D3 supplement sufficient to meet the daily requirement or as recommended by a physician. Patients with gastrointestinal malabsorption or those on certain drugs (see Drug Interactions, Cholecalciferol) may require higher doses of vitamin D3 and measurement of serum levels of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol may be indicated in this population.Pregnancy
Animal studies suggest that genistein may produce developmental abnormalities of the male and female genital tracts if consumed during early stages of pregnancy. Effects in infants of nursing mothers are uncertain. Therefore, FOSTEUM is contraindicated in pregnant and lactating women. Women capable of becoming pregnant should use appropriate contraception when taking FOSTEUM. The genistein in FOSTEUM has not been tested in women capable of becoming pregnant.ADVERSE EVENTS
In a two-year clinical trial, 389 subjects were randomized to either genistein plus calcium and vitamin D3 n=198, or calcium and vitamin D3 alone n=191. A total of 52 subjects in both groups discontinued due to adverse events. Study discontinuation in these subjects was due to gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal and epigastric pain, dyspepsia, vomiting and constipation. Discontinuation was reported in both groups. The incidence of adverse events was statistically higher in the genistein group over both years of the study. The major adverse events are shown in the table below without attribution of causality.
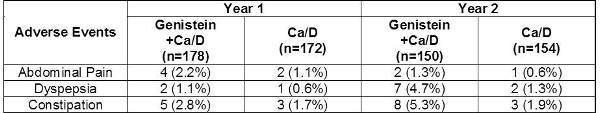
Some of these adverse event occurrences may be attributable to the intake of 1,000 mg per day of calcium carbonate by subjects in both groups. Taking FOSTEUM with food may reduce or eliminate some gastrointestinal symptoms.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Genistein
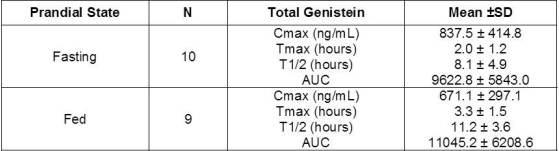
To determine the disposition of the genistein in FOSTEUM, a steady-state pharmacokinetic (PK) study was conducted in post-menopausal women aged 50-66. Ten subjects took FOSTEUM without food (fasted group) and 10 subjects took FOSTEUM with food (fed group) twice daily for seven (7) days. On the eighth day, blood was collected at 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 24, 36, 48 and 96 hours after ingesting FOSTEUM with (fed group) or without (fasted group) food. Concentrations of serum aglycone (protein bound and unbound) and total genistein (aglycone plus circulating conjugated forms) were determined at each time point for standard pharmacokinetic analyses.
Levels of free genistein aglycone were in the low nanomolar range and below the level of quantification in several subjects. Therefore, meaningful pharmaco-kinetic parameters could not be calculated from the data. Consistent with previous studies, the majority of circulating genistein existed in the conjugated form. Pharmacokinetic analyses for total genistein reported in the table below revealed no significant difference in any parameter between the fed and fasted groups, suggesting that FOSTEUM may be taken with or without food. The serum half-life (t1/2) among all subjects was 9.6 hours. Based on this profile, BID is recommended.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Dietary Management of Osteopenia and Osteoporosis
Effect on Bone Mineral Density
Efficacy of the genistein in FOSTEUM was demonstrated in a multi-center, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study of 389 randomized post-menopausal patients with osteopenia or osteoporosis (genistein n=198; placebo n=191). All subjects received calcium (1,000 mg/day) and vitamin D3 (800 IU/day) in two divided doses.
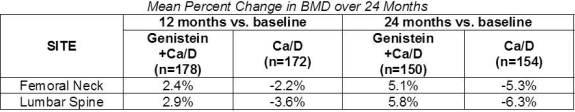
After two years, significant increases were seen in BMD at both lumbar spine and femoral neck relative to both baseline and placebo in patients who received genistein. In a third year extension, 138 patients continued on blinded study product. Patients taking the genistein in FOSTEUM showed a continued increase in BMD at both lumbar spine and femoral neck. In this cohort, 85% of the patients in the genistein arm showed increased BMD.
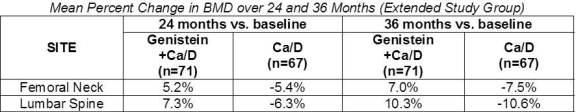
Bone markers were measured and found to support the proposed mechanism of action as levels of formation markers were increased and levels of resorption markers were reduced in the genistein group compared with baseline as shown in the table below.
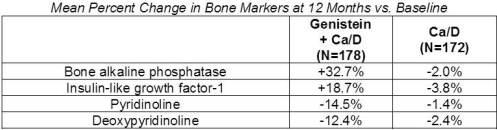
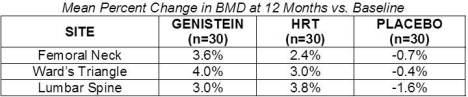
Genistein's efficacy was also shown in a one year trial of 90 osteopenic or osteoporotic, post-menopausal subjects vs. placebo and vs. HRT. Baseline values were matched for all parameters. The BMD values at 12 months are shown in the table below:
Fracture Data
The studies that have been performed on the genistein in FOSTEUM to date have not been intended to assess new incident fractures. These studies have shown reduced markers of bone resorption, increased markers of bone formation and increased BMD in clinical trials. Anecdotally, in the 389 patient clinical trial comparing genistein to placebo over a two-year period, there were three fractures of the sacrum in the placebo (Calcium and Vitamin D3) group. No fractures were observed in the genistein group over two years.OVER USAGE
Genistein
There are no known cases of over usage of the genistein in FOSTEUM. Animal studies have shown that consuming the equivalent of 75 FOSTEUM capsules at one time did not produce adverse events. However, as in most over usage situations, symptoms following an over usage of FOSTEUM could vary according to the patient. If an over usage were to occur, patients should be managed by systematic and supportive care as soon as possible following product consumption.Zinc (Elemental)
Symptoms of acute zinc toxicity occur after ingestion of 2 g or more of elemental zinc, the equivalent of 500 FOSTEUM capsules at one time. Chronic zinc toxicity, resulting from induced copper deficiency, is increasingly common as the use of large doses of zinc in supplements becomes more routine. Those on long term supplementation or high doses of zinc-containing cold medication, such as zinc lozenges, should be monitored for zinc and copper status.Cholecalciferol
There is limited information regarding acute vitamin D3 toxicity in humans. Single doses of ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) up to 600,000 IU have been given without noted toxicity. In patients suffering from diseases, such as leukemia, lymphoma or sarcoidosis, that are associated with unregulated overproduction of calcitriol, supplemental vitamin D3 may worsen hypercalcemia and/or hypercalciuria. Regular monitoring of urine and serum calcium may be indicated in this population.
Symptoms of vitamin D toxicity include hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, polyuria, polydipsia, weakness and lethargy. Serum and urine calcium levels should be monitored in patients with suspected vitamin D toxicity. Standard therapy includes restriction of dietary calcium, hydration and systemic glucocorticoids in patients with severe hypercalcemia.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
FOSTEUM should be taken twice a day, approximately 12 hours apart, and may be taken with or without food. FOSTEUM has no food limitations. There are no postural limitations. Patients taking FOSTEUM should ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, as directed by a physician.HOW SUPPLIED
FOSTEUM is an off-white capsule with "FOSTEUM" and "52003" printed in blue on the cap and body respectively. They are supplied as follows:68040-603-16 unit-of-use bottle of 60 capsules with desiccant (30-day supply)
Storage
Store at room temperature 59° – 86°F (15° – 30°C). Protect from light and moisture. Store capsules in original bottle until usage. Keep out of reach of children.Manufactured for:
Primus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Scottsdale, AZ 85251
www.primusrx.com
Manufactured by:
Cornerstone Research & Development, Inc.
Farmington, UT 84025
Avéma Pharma Solutions
Miami, FL 33172
U.S. Patent Nos. 5,935,996 and 5,516,925. Patents pending. U.S. Patent No. 5,516,925 is under license from Albion Laboratories, Inc, Clearfield, UT.
©2011 Primus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. All rights reserved. ISS. 0111 #13008
