Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for REGIOCIT (Sodium Chloride and Sodium Citrate Renal Replacement and Regional Anticoagulant Solution)
FACT SHEET FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
REGIOCIT
(Sodium Chloride and Sodium Citrate Renal Replacement and Regional Anticoagulant solution) For continuous renal replacement therapy
For extracorporeal use only
Emergency Use Authorization for the United States
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to permit the emergency use of the unapproved product, REGIOCIT: a replacement solution that contains citrate for Regional Citrate Anticoagulation (RCA) of the extracorporeal circuit. REGIOCIT has been authorized for emergency use as a replacement solution in adult patients treated with Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT), and for whom RCA is appropriate, during the COVID-19 pandemic. REGIOCIT is intended for use in a critical care setting. REGIOCIT is intended to be used in continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVH) and continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration (CVVHDF) modalities. Use of REGIOCIT is limited to healthcare providers and/or institutions that Baxter has qualified to administer REGIOCIT for these emergency uses.
REGIOCIT has been authorized by FDA for emergency use. REGIOCIT is not FDA-approved.
REGIOCIT is authorized only for the duration of the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of the emergency use of REGIOCIT under section 564(b)(1) of the Act, 21 U.S.C. § 360bbb-3(b)(1), unless the authorization is terminated or revoked sooner.
The scope of the EUA is as follows:
- •
- REGIOCIT will be used as a replacement solution only in adult patients being treated with CRRT and for whom RCA is appropriate.
- •
- REGIOCIT will be administered only by a licensed healthcare provider in a critical care setting.
- •
- REGIOCIT will available for use only in facilities that Baxter Healthcare Corporation has qualified and provided appropriate training on the use of REGIOCIT.
Product Description
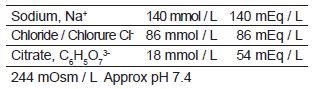
REGIOCIT is a sterile, replacement solution intended for use in adult patients being treated with CRRT and for whom RCA is appropriate. REGIOCIT, contains physiological concentrations of sodium (140 mmol/l), chloride (86 mmol/l), and a low concentration of citrate (18 mmol/L).
• A separate systemic infusion of calcium must be administered during use of REGIOCIT to prevent or treat hypocalcemia. Blood calcium concentrations (ionized and total) must be monitored throughout CRRT. • REGIOCIT solution must be used in pre-dilution mode only, with appropriate extracorporeal renal replacement equipment intended for CRRT, using an integrated pre-blood pump for RCA and in combination with other replacement and/or dialysate solution to provide the recommended dose of CRRT. • REGIOCIT may only be administered by health care providers/institutions that have been qualified by Baxter to administer the product. |
Instructions for Use
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
1.1 Administration Instructions
Renal Replacement Solution: Not for direct intravenous infusion.
The recommended effluent volume for patients receiving CRRT for acute kidney injury (AKI) is 20 to 25 mL/kg/h. This usually requires a higher prescription of effluent volume. The prescription of REGIOCIT solution must consider the flow rates of the effluent and other therapeutic fluids, the patient’s fluid removal requirements, additional fluid inputs and outputs, and the desired acid-base and electrolyte balance.
The mode of therapy, solute formulations, flow rates and length of therapy should be selected by the physician responsible for managing treatment depending on the clinical condition of the patient as well as the patient’s fluid, electrolyte, acid base and glucose balance.
Dialysate and replacement fluid formulations and flow rates are prescribed in accordance with the patient’s clinical needs. The use of a calcium-containing dialysate or replacement fluid is not recommended, since the calcium provided by these solutions may counteract the anticoagulant effect of citrate in the circuit.
1.2 Suggested Dosing
The rate at which REGIOCIT solution is administered depends on the targeted citrate dose and the prescribed blood flow rate. The pre-filter infusion rate of REGIOCIT solution is indexed to the blood flow rate to achieve a target blood citrate concentration of 3 mmol/L of blood (See Table 1). Flow rate for anticoagulation of the extracorporeal circuit should be titrated to achieve a post-filter concentration of ionized calcium in the range of 0.25 to 0.35 mmol/L.
Table 1: REGIOCIT Solution Flow Rates to Achieve Citrate Dose of 3 mmol/L of Blood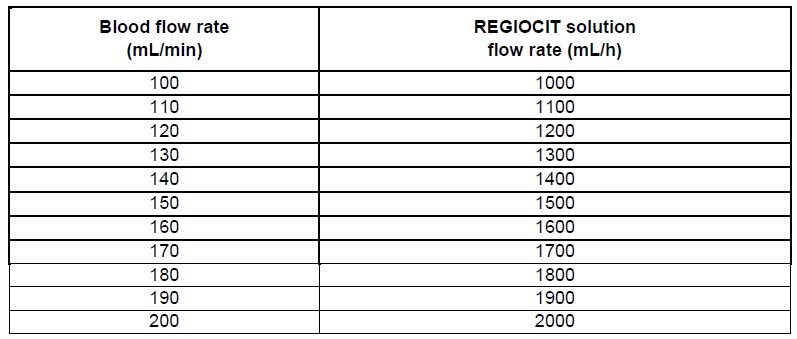
Prior to initiating therapy, the patient’s systemic ionized calcium concentration should be within the normal physiologic range (1.0 to 1.2 mmol/L) by adjustment of calcium supplementation. A separate infusion of calcium is always required during use of REGIOCIT, due to loss in the effluent. Calcium solution infusion is commenced at the rate of 4 mmol/h, when commencing therapy (see Table 4). Adjust or stop calcium infusion according to physician’s prescription when REGIOCIT is stopped.
Citrate also acts as a buffer source (due to conversion to bicarbonate); the infusion rate of REGIOCIT solution must be considered in relation to the rate at which buffer administration occurs from other sources (e.g., dialysate and/or replacement fluid). REGIOCIT solution must be used together with a dialysis solution/replacement solution with appropriate bicarbonate concentration.
1.3 Laboratory Monitoring
Monitoring of the post-filter blood ionized calcium (iCa), systemic blood iCa, and total blood calcium levels in conjunction with other laboratory and clinical parameters such as acid-base balance and serum electrolytes are essential to guide appropriate REGIOCIT solution dosage based on the desired level of anticoagulation. Levels should be taken at baseline, 1 hour after initiation (or adjustment), and every 6 hours (See Table 2). Rapidly decreasing systemic ionized calcium levels are an early indicator of citrate accumulation.
Measurement of total calcium and assessment of total-to-ionized calcium ratio is necessary. Citrate accumulation causes systemic ionized calcium levels to drop and the ratio of total-to-ionized calcium increases (total-to-ionized calcium ratio > 2.5). In the presence of impaired citrate metabolism, a progressively higher calcium infusion rate is required to maintain the systemic ionized calcium concentration within the intended target. When a total-to-ionized-calcium ratio > 2.5 is recorded, any one of the following abnormalities reported concurrently increases the likelihood of citrate accumulation:
- o
- A rapid decline in systemic iCa concentration despite adequate calcium compensation
- o
- A rapid decrease in pH or a decrease in base excess
- o
- A rapid increase in anion gap
In order to avoid metabolic alkalosis, acid-base balance and systemic ionized calcium can be measured using blood gas analysis. If metabolic alkalosis or citrate accumulation is suspected, decrease the citrate dose while tolerating a post-filter ionized calcium of < 0.5 mmol/L. This can be achieved by either decreasing the blood flow rate to decrease the overall citrate load, increasing the dialysate/replacement flow rate (when applicable) to increase the citrate removal, or decreasing the citrate flow to decrease the citrate dose. Dialysate solutions contain bicarbonate below or above physiological range of 22 to 26 mmol/L, and increasing or decreasing the flow rates of the dialysate solutions can impact the acid-base status of the patient.
Plasma levels of sodium, magnesium, potassium, and glucose, and phosphate should be monitored regularly and should be supplemented as needed.
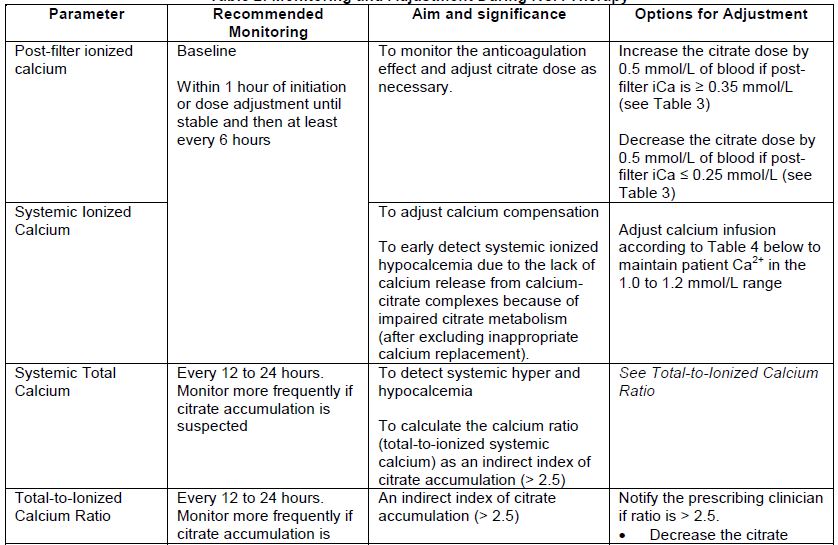
Table 2 provides a summary of the most important parameters to be monitored during RCA therapy, as well as options for adjustment.
Table 2: Monitoring and Adjustment During RCA Therapy
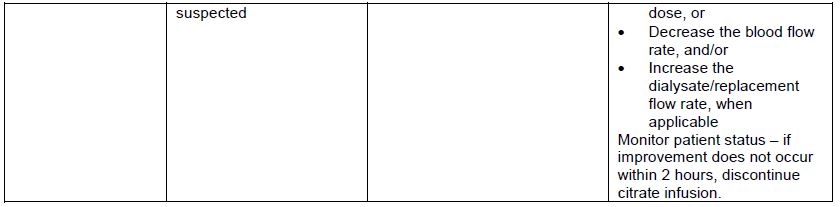
Table 3 provides the REGIOCIT solution flow rate adjustment based on a citrate dose adjustment of 0.5 mmol/L.
Table 3: REGIOCIT Solution Flowrate Adjustment Based on a Citrate Dose Adjustment of 0.5 mmol/L
Table 4 provides recommendations to maintain a systemic ionized calcium level between 1.0 mmol/L and 1.2 mmol/L.
Table 4: Sliding Scale of Calcium Infusion
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
2.1 Hypocalcemia
REGIOCIT solution contains no calcium, and may lead to systemic ionized hypocalcemia due to loss of calcium bound to citrate in the effluent and/or in the case of systemic citrate accumulation. Calcium
reinfusion is required during use of REGIOCIT and blood calcium concentrations (ionized and total) must be monitored.
2.3 Hypomagnesemia
REGIOCIT solution contains no magnesium. Use of the REGIOCIT solution may result in hypomagnesemia due to CRRT effluent losses. Magnesium levels must be monitored as infusion of magnesium may be necessary.
2.4 Hypoglycemia
REGIOCIT solution contains no dextrose. Administration of REGIOCIT solution may lead to hypoglycemia. Blood glucose levels must be monitored regularly.
2.5 Hypokalemia
REGIOCIT solution contains no potassium. The serum potassium concentration must be monitored before and during CRRT.
2.6 Metabolic Alkalosis
REGIOCIT solution contains citrate, which contributes to the overall buffer load. Metabolization of 1 mol of citrate generates 3 mol of bicarbonate. Additional sodium bicarbonate (or buffer source) contained in the CRRT fluids or in other fluids administered during therapy may increase the risk of metabolic alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis may occur if the net citrate administration rate exceeds that which is necessary to maintain acid–base balance. If metabolic alkalosis occurs, decrease the citrate dose, and/or increase the dialysate/replacement flow rate (when applicable) or change the composition of the CRRT solution.
2.7 Metabolic Acidosis
Metabolic acidosis may occur if metabolic clearance of citrate by the liver or skeletal muscle is impaired. If citrate accumulation develops and/or metabolic acidosis develops or worsens during therapy with REGIOCIT solution, the infusion rate may need to be decreased or its administration stopped.
2.8 Use in Patients with Mild to Moderate Hepatic Impairment
Metabolism of citrate (to bicarbonate) may be impaired in patients with hepatic impairment, resulting in accumulation of citrate. If REGIOCIT solution is administered to patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, frequent monitoring of pH, electrolytes, total-to-ionized calcium ratio, and systemic ionized calcium is important to avoid electrolyte and/or acid–base imbalance.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Contraindications for the use of REGIOCIT include:
- •
- Severe liver failure
- •
- Shock with muscle hypoperfusion
- •
- Known hypersensitivity to any component of REGIOCIT
Adverse Event Reporting
Report adverse events or quality problems experienced with the use of this product.
Healthcare facilities and prescribing health care providers or their designee receiving REGIOCIT will track all medication errors associated with the use of and all serious adverse events that are considered to be potentially attributable to REGIOCIT use and must report these to FDA using one of the following methods:
- •
- Complete and submit a MedWatch form online (www.fda.gov/medwatch/report.htm)
- •
- Complete and submit FDA Form 3500 (health professional) by fax (1-800-FDA-0178) (this form can be found via link above).
Call 1-800-FDA-1088 for questions. Submitted reports should state, “use of REGIOCIT was under an EUA” at the beginning of the question “Describe Event” for further analysis.
Contact Baxter Healthcare Corporation at 1-866-888-2472 or global_pharmacovigilance_deerfield@baxter.com
What is an EUA?
The United States FDA has made REGIOCIT available to treat patients in an ICU during the COVID-19 pandemic under an emergency access mechanism called an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA). The EUA is supported by a Secretary of Health and Human Service (HHS) declaration that circumstances exist to justify the emergency use of drugs and biological products during the COVID-19 pandemic.
REGIOCIT made available under an EUA have not undergone the same type of review as an FDA-approved product. FDA may issue an EUA when certain criteria are met, which includes that there are no adequate, approved, available alternatives. In addition, the FDA decision is based on the totality of scientific evidence available showing that it is reasonable to believe that REGIOCIT may be effective for use as a replacement solution in adult patients treated with Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) and requiring regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) of the extracorporeal circuit in an ICU setting during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, and that the known and potential benefits of REGIOCIT for such use outweigh the known and potential risks of REGIOCIT.
This EUA for REGIOCIT is in effect for the duration of the COVID-19 declaration justifying emergency use of the products, unless terminated or revoked (after which the products may no longer be needed). The EUA will end when the declaration is terminated or revoked or when there is a change in the approval status of the product such that an EUA is no longer needed.
This communication and product information is available on Baxter Healthcare’s website:
To access COVID-19 Resources, product details, product use information, and the comprehensive Prismaflex Control Unit Operator’s Manual and PrisMax Control Unit Operator’s Manual please visit the Baxter Healthcare Acute Therapies website at http://www.renalacute.com
FDA’s webpage also includes links to patient fact sheet and manufacturer’s instructions https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/mcm-legal-regulatory-and-policy-framework/emergency-use-authorization#covidtherapeutics.
Fact Sheet For Patients And Parent/Caregivers Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for REGIOCIT (Sodium Chloride and Sodium Citrate Renal Replacement and Regional Anticoagulant Solution)
You are being given REGIOCIT: a replacement solution for Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) that also reduces the risk of filter clotting. This fact sheet contains information to help you understand the risks and benefits of taking the REGIOCIT you have received or may receive.
There is currently a shortage of U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved replacement solutions that may be used to provide CRRT. REGIOCIT is not an FDA-approved medicine in the United States. REGIOCIT is currently approved in Europe and other countries. Read this Fact Sheet for information about REGIOCIT. Talk to your health care provider if you have questions. It is your choice to receive REGIOCIT or stop it at any time.
What is COVID-19?
COVID-19 is caused by a virus called a coronavirus. This type of coronavirus has not been seen before. This new virus was first found in people in December 2019. You can get COVID-19 through contact with another person who has the virus.
COVID-19 illnesses have ranged from very mild (including some with no reported symptoms) to severe, including illness resulting in death. While information so far suggests that most COVID-19 illness is mild, serious illness can happen and may cause some of your other medical conditions to become worse. Older people and people of all ages with severe, long lasting (chronic) medical conditions like heart disease, lung disease and diabetes, for example seem to be at higher risk of being hospitalized for COVID-19.
What are the symptoms of COVID-19?
The symptoms of COVID-19 are fever, cough, and shortness of breath, which may appear 2-14 days after exposure. Serious illness, including breathing problems, can occur and may cause your other medical conditions to become worse.
What is REGIOCIT?
Regiocit is a replacement solution for CRRT, which is a form of “dialysis” treatment, that also reduces the risk of filter clotting. Replacement solutions are used during CRRT to help correct acid-base abnormalities and electrolyte abnormalities, remove “uremic” and other toxins and facilitate the use of CRRT to control fluid overload.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before I receive REGIOCIT?
Tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- •
- Have any allergies
- •
- Have liver disease
- •
- Are pregnant or plan to become pregnant
- •
- Are breast-feeding or plan to breastfeed
- •
- Are taking any medicines (prescription, over-the-counter, vitamins, or herbal products)
Who should not receive REGIOCIT?
Do not take Regiocit if you:
- •
- Have severe liver failure
- •
- Have shock with decreased blood flow to the muscles (muscle hypoperfusion)
- •
- Are allergic to any of the ingredients in REGIOCIT
What are the important possible side effects for REGIOCIT?
Possible side effects of REGIOCIT include:
- •
- Low levels of calcium in your blood
- •
- Low levels of magnesium, potassium, or phosphate in your blood, or changes in the glucose level in your blood
- •
- Too much acid or base in your blood (acid-base status)
What other treatment choices are there?
Your healthcare provider may use a different replacement solution for CRRT or a type of “dialysis” that does not require a replacement solution.
How do I report side effects with REGIOCIT?
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any side effects that bother you or do not go away. Report side effects to FDA MedWatch at www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088 or contact Baxter Healthcare Corporation at 1-866-888-2472 or global_pharmacovigilance_deerfield@baxter.com.
How can I learn more?
- •
- Ask your healthcare provider
- •
- Visit www.cdc.gov/COVID19
- •
- Contact your local or state public health department
- •
- Visit www.baxter.com
What is an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA)?
The United States FDA has made REGIOCIT available under an emergency access mechanism called an EUA. The EUA is supported by a Secretary of Health and Human Service (HHS) declaration that circumstances exist to justify the emergency use of drugs and biological products during the COVID-19 pandemic.
REGIOCIT has not undergone the same type of review as an FDA-approved or cleared product. FDA may issue an EUA when certain criteria are met, which includes that there are no adequate, approved, available alternatives. In addition, the FDA decision is based on the totality of scientific evidence available showing that it is reasonable to believe that the product may be effective in treatment of patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. All of these criteria must be met to allow for the product to be used in the treatment of patients during the COVID-19 pandemic, and that the known and potential benefits outweigh the known and potential risks for such use.
The EUA for REGIOCIT is in effect for the duration of the COVID-19 declaration justifying emergency use of these products, unless terminated or revoked (after which the products may no longer be used).
REGIOCIT Package Insert for Emergency Use Authorization
REGIOCIT has been authorized by FDA for emergency use.
REGIOCIT is not FDA-approved.
REGIOCIT is authorized only for the duration of the declaration that
circumstances exist justifying the authorization of the emergency use of
REGIOCIT under section 564(b)(1) of the Act, 21 U.S.C. § 360bbb-3(b)(1),
unless the authorization is terminated or revoked sooner.
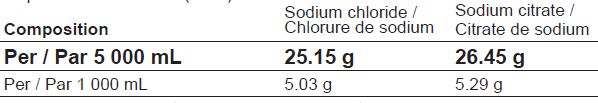
Sodium chloride and sodium citrate solution
for hemofiltration and regional citrate anticoagulation during Continuous Renal
Replacement Therapy (CRRT)
Sodium chloride 5.03 g/L, sodium citrate 5.29 g/L
Solution for Extracorporeal use only. Not for direct intravenous infusion
EN Package insert............................................................................2
REGIOCIT
Sodium chloride and sodium citrate solution
for hemofiltration and regional citrate anticoagulation
during Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT)
sodium chloride 5.03 g/L, sodium citrate 5.29 g/L
Solution for Extracorporeal use only, Not for direct intravenous infusion
INDICATIONS
REGIOCIT (sodium chloride and sodium citrate) solution is indicated for use as
replacement solution for regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) of the extracorporeal
circuit in patients treated with continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT),
particularly when systemic anticoagulation with heparin is contraindicated, e.g., in
patients with increased bleeding risks.
REGIOCIT should be administered only under the supervision of a physician
experienced in the use of CRRT.
Pediatrics
Pediatrics (<18 years of age): No data are available to Health Canada; therefore,
Health Canada has not authorized an indication for pediatric use.
Geriatrics
Geriatrics (> 65 years of age): Evidence from clinical studies and experience
suggests that use in the geriatric population is not associated with differences in
safety or effectiveness.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
REGIOCIT solution is contraindicated in:
- •
- patients who are hypersensitive to this drug or to any ingredient in the formulation, including any non-medicinal ingredient, or component of the container. For a complete listing, see Dosage Forms, Strengths, Composition and Packaging.
- •
- severe liver failure
- •
- shock with muscle hypoperfusion
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For Extracorporeal use only. Not for direct intravenous infusion.
REGIOCIT solution is used as a renal replacement solution. The product has an
osmolarity of 244 mOsm/L and a pH of approximately 7.4.
Dosing Considerations
Dosing considerations of the drug:
- •
- REGIOCIT solution should not be used for direct intravenous infusion. The product must be used in pre-dilution mode only, with appropriate extracorporeal renal replacement equipment intended for CRRT, using an integrated pre-blood pump for RCA.
- •
- In addition to providing anticoagulation to the extracorporeal circuit and hemofilters, citrate also acts as a buffer source due to its metabolic conversion to bicarbonate systemically. Thus, the infusion rate of REGIOCIT solution to be administered should take into account the rate at which buffer administration occurs from other sources, e.g., dialysate and/or replacement fluid. The product must be used together with a dialysis/replacement solution at an appropriate bicarbonate concentration.
- •
- Dose reduction may be needed in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. In these patients, more frequent monitoring of citrate accumulation is advised. REGIOCIT solution should not be administered to patients with reduced liver and muscle perfusion, e.g., during conditions such as septic shock and lactic acidosis, or in patients with severe hepatic impairment, due to limited citrate metabolism (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
- •
- A separate systemic infusion of calcium is always required to prevent or treat hypocalcemia. Adjust calcium infusion depending on measured serum total-to-ionized calcium ratio and ionized calcium levels, to maintain values in the physiologic range. Adjust or stop calcium infusion according to the direction of the attending physician when REGIOCIT solution has been stopped.
- •
- Magnesium may need to be supplemented intravenously, based on systemic serum magnesium levels.
Recommended Dose and Dosage Adjustment
The rate at which REGIOCIT solution is administered depends on the targeted citrate dose and the prescribed blood flow rate (BFR). The prescription of the product must consider the flow rates of the effluent and other therapeutic fluids, the patient’s fluid removal requirements, additional fluid inputs and outputs, and the desired acid-base and electrolyte balance.
REGIOCIT solution should be prescribed and its administration (dose, infusion rate, and cumulative volume) established only by critical care or nephrology physicians experienced in administration of CRRT.
The pre-filter infusion rate of REGIOCIT solution (based on its concentration) is indexed to the blood flow rate to achieve a target blood citrate concentration of 3 to 4 mmol/L in the blood. Flow rate for anticoagulation of the extracorporeal circuit should be titrated to achieve a post-filter concentration of ionized calcium in the range 0.25 to 0.35 mmol/L. The patient’s systemic ionized calcium concentration should be maintained in the normal physiologic range by adjustment of calcium supplementation.
Administration
Monitoring of the post-filter blood ionized calcium (iCa), systemic blood iCa, and total blood calcium levels in conjunction with other laboratory and clinical parameters is essential to guide appropriate REGIOCIT solution dosage based on the desired level of anticoagulation (see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS). Plasma levels of sodium, magnesium, potassium, and phosphate should also be monitored regularly and these electrolytes supplemented as needed.
REGIOCIT solution may be warmed to 37°C to enhance patient comfort. Warming of the product prior to use should be done with dry heat only. Solution should not be heated in water or in a microwave oven due to the potential for patient injury or discomfort.
REGIOCIT solution should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not administer unless the solution is clear and the seal is intact.
OVERDOSAGE
Electrolyte imbalance and acid–base balance abnormalities, e.g., hypocalcemia, metabolic alkalosis, etc. may occur in the event of an overdose. Stop administration promptly (see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS).
In patients with impaired citrate metabolism, e.g., liver failure, circulatory shock etc, overdosage with REGIOCIT solution may be manifested as citrate accumulation, metabolic acidosis, systemic total hypercalcemia and ionized hypocalcemia along with increased total calcium/ionized calcium ratio (see CONTRAINDICATIONS, and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS).
Careful calcium supplementation can reverse the effects of an overdose. The risk can be minimized by close monitoring during treatment.
DOSAGE FORMS, STRENGTHS, COMPOSITION AND PACKAGING
Table 1 – Dosage Forms, Strengths, Composition and Packaging
Table 2 – Electrolyte Concentrations from the Medicinal Ingredients
REGIOCIT (sodium chloride and sodium citrate) solution is available in a 5 000 mL bag, with a luer connector valve and a spike connector. The bag is made of a multilayer film containing polyolefins and elastomers.
This product is not made with natural rubber latex.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
There have been reports of system failure due to apparent operator error during administration of CRRT with REGIOCIT solution, leading to serious adverse events, including life-threatening hypocalcemia. Plasma electrolyte and acid-base parameters should be closely monitored during CRRT, and appropriate action taken if imbalances of electrolytes or acid-base balance are detected. Instructions for use of REGIOCIT and CRRT must be strictly followed.
Cautionary statements are provided in WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS, Endocrine and Metabolism, Hematologic, Hepatic / Biliary / Pancreatic, and Monitoring and Laboratory Tests, and in DRUG INTERACTIONS to avoid the following when performing the CRRT procedure:
- - Hypercalcemia
- - Hyponatremia
- - Fluid retention, dehydration
- - Nausea, vomiting
- - Muscle spasms
Citrate Accumulation
Special attention is required in patients with liver failure, including hepatic cirrhosis or acute hepatic failure, or in shock, since metabolism of citrate may be markedly reduced and patients may be thus exposed to citrate accumulation. In these circumstances, more frequent monitoring of citrate accumulation should be undertaken. With systemic citrate accumulation, metabolic acidosis and ionized hypocalcemia may ensue, and the ratio of total to ionized calcium in the blood rises. If total/ionized calcium ratio rises above 2.3, REGIOCIT infusion should be reduced or stopped. CRRT may then be continued without anticoagulation, or by using other means of anticoagulation.
REGIOCIT is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment or in circulatory shock with muscle hypoperfusion (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Excessive infusion of citrate can lead to acute hypocalcemia and metabolic alkalosis, with neurologic and cardiac complications. Treatment consists of discontinuation of the citrate infusion and infusion of calcium.
Endocrine and Metabolism
Hypocalcemia
REGIOCIT solution contains no calcium, and may lead to systemic ionized hypocalcemia, due to loss of calcium bound to citrate in the effluent and/or in the case of systemic citrate accumulation (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Administration).
Electrolyte and Acid–Base Balance
REGIOCIT solution contains citrate, which can influence the patient’s electrolyte and acid–base balance. Plasma electrolyte and acid–base parameters should be closely monitored during CRRT. Closely monitor sodium, magnesium, potassium, phosphate, and calcium. Infusion of electrolytes may be needed to supplement any loss.
Hypercalcemia
Medicinal products containing calcium used for maintenance of calcium homeostasis in CRRT patients can increase the risk of hypercalcemia, and can result in a reduced anticoagulation effect. Care should be taken to avoid excessive titration in administering calcium as this can lead to hypercalcemia. Frequent monitoring of pH, electrolytes, total-to-ionized calcium ratio, and systemic ionized calcium is important to avoid electrolyte and/or acid-base imbalance.
Hypomagnesemia
REGIOCIT solution contains no magnesium. Use of the REGIOCIT solution may result in hypomagnesemia due to CRRT effluent losses (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Administration).
Hypoglycemia
REGIOCIT solution contains no dextrose. Administration of REGIOCIT solution may lead to hypoglycemia. Blood glucose levels should be monitored regularly.
Hypokalemia
REGIOCIT solution contains no potassium. The serum potassium concentration must be monitored before and during CRRT.
Metabolic Alkalosis
REGIOCIT solution contains citrate, which contributes to the overall buffer load. Additional sodium bicarbonate (or buffer source) contained in the CRRT fluids or in other fluids administered during therapy may increase the risk of metabolic alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis may occur if the net citrate administration rate exceeds that which is necessary to maintain acid–base balance.
If metabolic alkalosis occurs, decrease the citrate dose, and/or increase the dialysate flow rate or change the composition of the CRRT solution.
Blood calcium levels, pH and bicarbonate should be monitored regularly in patients with metabolic alkalosis since this condition may potentiate hypocalcemia.
Metabolic Acidosis
Metabolic acidosis may occur if metabolic clearance of citrate by the liver or skeletal muscle is impaired (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
If citrate accumulation develops and/or metabolic acidosis develops or worsens during therapy with REGIOCIT, the infusion rate may need to be decreased or its administration stopped.
Hypo-osmolarity/Hypotonicity
REGIOCIT solution is hypo-osmolar/hypotonic relative to standard CRRT replacement fluids and should be used with caution in patients with traumatic brain injury, cerebral edema, or increased intracranial pressure.
Instructions for use of REGIOCIT must be strictly followed. Incorrect use of the access ports or other restrictions to fluid flow may lead to incorrect patient weight loss and may result in machine alarms being set off. Continuing treatment without resolving the originating cause may lead to patient injury or death.
Careful ongoing assessment is required of all solutions infused during REGIOCIT administration, whether related to CRRT dialysis fluids or to other solutions infused systemically.
REGIOCIT has a physiological sodium level of 140 mmol/L. However, sodium losses occurring during CRRT must be balanced as part of overall fluid and electrolyte management to avoid a drop in blood sodium level leading to systemic hyponatremia.
Hematologic
Hemodynamic Status and Fluid Balance
The patient’s hematocrit, hemodynamic status and fluid balance should be monitored throughout the procedure.
- - In case of hypervolemia, the net ultrafiltration rate prescribed for the CRRT device can be increased, and/or the rate of administration of solutions other than replacement fluid and/or dialysate can be reduced.
- - In case of hypovolemia, the net ultrafiltration rate prescribed for the CRRT device can be reduced, and/or the rate of administration of solutions other than replacement fluid and/or dialysate can be increased.
Hepatic/Biliary/Pancreatic
Use in Patients with Mild to Moderate Hepatic Impairment
Systemic metabolism of citrate to bicarbonate may be impaired in patients with hepatic impairment, resulting in accumulation of citrate. If REGIOCIT solution is administered to patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, frequent monitoring of pH, electrolytes, total-to-ionized calcium ratio, and systemic ionized calcium is important to avoid electrolyte and/or acid–base imbalance (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Monitoring and Laboratory Tests
Plasma electrolyte and acid–base parameters should be closely monitored during CRRT. Closely monitor sodium, magnesium, potassium, phosphate, calcium, blood glucose levels, hematocrit, hemodynamic status and fluid balance, pH, bicarbonate, total-to-ionized calcium ratio, and systemic ionized calcium. Infusion of electrolytes may be needed to supplement any loss.
Special Populations
Pregnant Women
There are no adequate data from the use of REGIOCIT solution in pregnant women.
Physicians should carefully consider the potential risks and benefits for each specific patient before administering REGIOCIT solution.
Breast-feeding
There are no adequate data from the use of REGIOCIT solution in lactating women.
Physicians should carefully consider the potential risks and benefits for each specific patient before administering REGIOCIT solution.
It is unknown if the drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised.
Pediatrics
Pediatrics (< 18 years of age): No data are available to Health Canada; therefore, Health Canada has not authorized an indication for pediatric use.
Geriatrics
Geriatrics (> 65 years of age): Evidence from clinical studies and experience suggests that use in the geriatric population is not associated with differences in safety or effectiveness.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse Reaction Overview
The following adverse reactions represent those adverse reactions that are thought to have an association with the use of REGIOCIT solution or that may occur in conjunction with performing the CRRT procedure:
Adverse reactions reported with other CRRT products include:
- - Hypotension
- - Hypocalcemia (due to excessive and uncorrected effect of citrate in the body)
- - Other electrolyte imbalances (hypomagnesemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia)
- - Acid–base balance disorders (including metabolic alkalosis, metabolic acidosis)
- - Hypoglycemia
- - Fluid imbalance
Clinical Trial Adverse Reactions
Because clinical trials are conducted under very specific conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials may not reflect the rates observed in practice and should not be compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug. Adverse reaction information from clinical trials is useful for identifying drug-related adverse events and for approximating rates.
In an open-label randomised study, 54 patients were administered RCA with an equimolar solution of citrate, sodium and chloride, as contained in REGIOCIT solution, and 49 received systemic anticoagulation with unfractionated heparin (UFH) while undergoing CRRT using continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration. Adverse events related to metabolic disorders occurred in 26% of patients in the RCA-treated group, compared to 28% of patients in the UFH-treated group. These adverse events were generally transient and reversible. Metabolic alkalosis was seen in 6% of patients treated with RCA, compared to none treated with UFH, and metabolic acidosis was reported in 6% and 2% of patients in the RCA and UFH groups, respectively. Six patients treated with RCA experienced severe hypocalcemia, compared to one patient treated with UFH.
In a second hemodiafiltration trial which evaluated 19 patients randomised to an equimolar solution of citrate, sodium and chloride, as contained in REGIOCIT solution, and 11 patients randomised to UFH anticoagulation, Hypocalcemia requiring intervention was reported in 3 patients treated with RCA, with 2 of these patients requiring treatment interruption of RCA.
Post-Market Adverse Reactions
To date, adverse events reported in the post-marketing setting for REGIOCIT appear to be consistent with those listed above in Adverse Reaction Overview.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Overview
The blood concentration of filterable/dialyzable drugs may be reduced during treatment due to their removal by the extracorporeal filter. Corresponding corrective therapy should be instituted if necessary to establish the desired blood concentrations for drugs removed during treatment. Patient monitoring at an appropriate frequency is required.
When prescribing REGIOCIT, the physician needs to consider the use of other anticoagulants along with other buffer-containing and electrolyte solutions (including CRRT replacement fluid and dialysate).
Drug-Drug Interactions
The drugs listed in this table are based on either drug interaction case studies or clinical trials, or potential interactions due to the expected magnitude and seriousness of the interaction (i.e., those identified as contraindicated).
Table 3 - Established or Potential Drug-Drug Interactions
ACTION AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Citrate provides regional anticoagulation of blood in the continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) extracorporeal circuit by binding calcium and rendering calcium unavailable to the clotting cascade. Several steps of the clotting cascade are dependent on calcium and the absence of calcium prevents clotting in the circuit.
During CRRT, pre-dilution infusion of citrate into the access line of the extracorporeal circuit provides only regional extracorporeal anticoagulation (and thus avoids systemic anticoagulation of the patient) for two reasons. First, once blood from the extracorporeal circuit is returned to the patient, it mixes with the central venous blood which contains calcium. The second way in which a systemic anticoagulant effect is avoided is by infusion of calcium in the post-filter (return) bloodline of the extracorporeal circuit.
This procedure not only helps neutralize citrate’s anticoagulant effect in the patient’s blood, but also prevents any depletion of the patient’s calcium stores which may result from the loss of calcium (bound to citrate) in the CRRT effluent fluid.
Pharmacodynamics
Citrate provides anticoagulation by its ability to form complexes with ionized calcium, making it unavailable to the clotting cascade. In REGIOCIT, sodium concentration has been set to 140 mmol/l as critically ill patients may develop severe hyponatremia. Chloride is set to the level required to balance cations as the solution is hydrogen carbonate free. Sodium and chloride are normal constituents of the human body and are considered to be pharmacologically inactive. Citrate is a normal metabolite in the human body that acts as a first intermediate substance in the Krebs cycle. REGIOCIT does not contain potassium or glucose.
Two studies provide information on the dose/response relationship between citrate concentration and anticoagulation. In one study, ex-vivo anticoagulation with anticoagulant citrate dextrose formula A (ACD-A) in blood collected from six healthy volunteers was studied. The study concluded that the clinically relevant effects of citrate anticoagulation rely solely on the disturbed formation of the calcium-dependent coagulation factors complexes. In this study, the anticoagulation effects of citrate were monitored either by methods that quantify clot formation (i.e., activated clotting time) or by direct assessment of ionized calcium levels.
The correlation between concentrations of ionized calcium and clotting times revealed almost no anticoagulant effect when ionized calcium levels were up to or above 0.50 mmol/L, while clotting times showed a steep increase when calcium levels were decreased below 0.50 mmol/L. With respect to maximum effect, 5.65 mmol/L citrate induced clotting times of infinity in all samples.
Pharmacokinetics
Citrate is a normal metabolite in the human body and an intermediate substance in the Krebs cycle. This physiological pathway is capable of processing high amounts of citric acid as long as it occurs at low concentrations. The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria, and all cells that contain these cellular organelles can metabolize citrate. Tissues rich in mitochondria such as liver, skeletal muscles, and kidney therefore have a higher capacity for citrate generation and elimination.
Absorption: Absorption of sodium and chloride is determined by the patient’s clinical condition, metabolic status, and residual renal function.
Distribution: Extracellular citrate can be transported from the blood across the plasma membrane by a group of proteins i.e. the plasma membrane citrate transporters (PMCTs) into the cells and then metabolized in various organs and tissues.
Metabolism: Citrate is an intermediate in the central metabolic pathway called Krebs cycle as mentioned above. Citrate is rapidly metabolized mainly in the liver, but can also be metabolized by other organs/tissues.
Elimination: Any excess of circulating citrate is normally excreted via the kidneys.
Special Populations and Conditions
Hepatic Insufficiency:
When treating decompensated cirrhosis patients, one should also consider:
- •
- Impairment of citrate metabolism due to failure of microcirculation and oxidative metabolism (lactic acidosis and/or shock),
- •
- Impaired muscular utilization of citrate (cachexia, high doses of vasopressors),
- •
- Citrate load associated with blood products.
SPECIAL HANDLING INSTRUCTIONS
Aseptic technique should be used throughout the handling and administration to the patient.
Remove the overwrap from the bag immediately before use.
Use only if the overwrap is not damaged, all seals are intact, and the solution is clear. Press bag firmly to test for any leakage. If leakage is discovered, discard the solution immediately since sterility can no longer be assured.
Follow the instructions below when connecting the solution bags for correct use of the access ports.
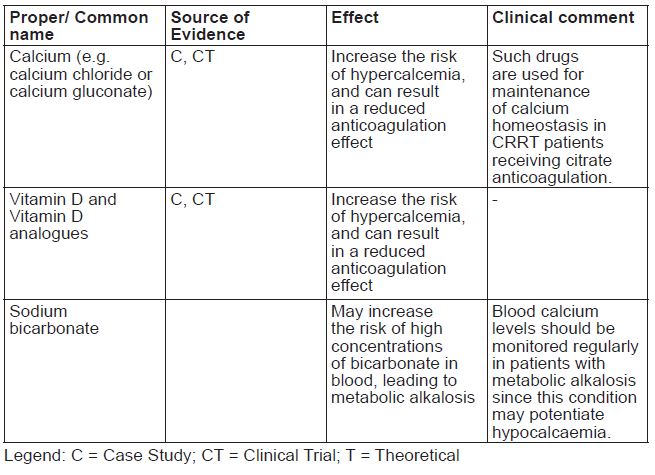
- •
- If the luer connector is used, remove the cap with a twist and pull motion. Connect the male luer lock on the pre-blood pump line to the female luer connector on the bag using a push and twist motion. Ensure that the connection is fully sealed and tighten (see Figure I). The connector is now open. Verify that the fluid is flowing freely. When the pre-blood pump line is disconnected from the luer connector, the connector will close and the flow of the solution will stop. The luer is a needle-less port.
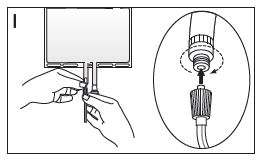
- •
- If the injection connector (or spike connector) is used, remove the snap-off cap. Introduce the spike through the rubber septum (see Figure II). Verify that the fluid is flowing freely.
- •
- Before adding a substance or medication, verify that it is soluble and stable in REGIOCIT, and that the pH range of REGIOCIT is appropriate.
- •
- Additives known or determined to be incompatible should not be added.
- •
- The instructions for use of the medication to be added and other relevant literature must be consulted.
- •
- After addition, if there is a discoloration and/or the appearance of precipitates, insoluble complexes, or crystals, do not use.
- •
- Mix the solution thoroughly when additives have been introduced. The introduction and mixing of additives must always be performed prior to connecting the solution bag to the extracorporeal circuit.
- •
- The solution is for single use only.
- •
- Discard any unused portion.
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION
REGIOCIT
Sodium chloride and sodium citrate solution
Read this carefully before you start taking REGIOCIT solution and each time you get a refill. This leaflet is a summary and will not tell you everything about this drug. Talk to your healthcare professional about your medical condition and treatment and ask if there is any new information about REGIOCIT solution.
What is REGIOCIT solution used for?
- •
- Is a solution for hemofiltration and prevents blood clotting during continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT), which is a form or dialysis treatment. This medicine is used for critically ill patients particularly when other medicine used to prevent blood clotting is not an appropriate choice.
How does REGIOCIT solution work?
This medicine is to be administered into the blood circuit outside of your body when you have CRRT. This medicine is to be used in hospitals and administered by medical professionals only.
What are the ingredients in REGIOCIT solution?
Medicinal ingredients: sodium chloride and sodium citrate
Non-medicinal ingredients: hydrochloric acid, water
REGIOCIT solution comes in the following dosage forms:
Solution with 5.03 g/L of sodium chloride and 5.29 g/L of sodium citrate
Do not use REGIOCIT solution if:
- •
- You are allergic to any ingredients (See What are the ingredients in REGIOCIT solution).
- •
- Severely impaired liver function
- •
- Severely decreased blood flow in the muscles
To help avoid side effects and ensure proper use, talk to your healthcare professional before you take REGIOCIT solution. Talk about any health conditions or problems you may have, including if you:
• have diabetes
• have been treated for chronic kidney disease
• have a history of liver disease
Tell your healthcare professional about all the medicines you take, including any drugs, vitamins, minerals, natural supplements or alternative medicines.
The following may interact with REGIOCIT solution:
• Medicinal products that contain calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or any form of vitamin D.
How to take REGIOCIT solution:
Your healthcare professional will prescribe and administer the product.
Overdose:
|
If you think you have taken too much REGIOCIT solution, contact your healthcare professional, hospital emergency department or regional poison control centre immediately, even if there are no symptoms. |
What are possible side effects from using REGIOCIT solution?
These are not all the possible side effects you may feel when taking REGIOCIT solution. If you experience any side effects, contact your healthcare professional.
The following side effects have been associated with other CRRT products:
- •
- Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
- •
- Low blood calcium, due to excessive and uncorrected effect of citrate in the body (Hypocalcemia)
- •
- Having an imbalance in your body where you do not have enough magnesium, potassium or phosphate (Electrolyte imbalances, including hypomagnesemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia)
- •
- Disorder where the pH in your body is not balanced (Acid-base disorders, including metabolic acidosis, metabolic alkalosis)
- •
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
- •
- Having an imbalance in the fluids in your body (Fluid imbalance)
The possible side effects can be resulted from your CRRT procedure:
- •
- Having an imbalance in your body where you have too much calcium (Hypercalcemia), or do not have enough sodium (Hyponatremia)
- •
- Having too much fluids (Fluid retention) or not enough fluids in your body (Dehydration)
- •
- Nausea and vomiting
- •
- Muscle Spasms
If you have a troublesome symptom or side effect that is not listed here or becomes bad enough to interfere with your daily activities, talk to your healthcare professional.
|
Reporting Side Effects You can report any suspected side effects associated with the use of health products to Health Canada by:
NOTE: Contact your health professional if you need information about how to manage your side effects. The Canada Vigilance Program does not provide medical advice. |
Storage:
Store at 4 °C to 30 °C. Do not freeze or expose to excessive heat.
Keep out of reach and sight of children.
If you want more information about REGIOCIT solution:
- •
- Talk to your healthcare professional
- •
- Find the full product monograph that is prepared for healthcare professionals and includes this Patient Medication Information by visiting the Health Canada website (https://health-products.canada.ca/dpd-bdpp/index-eng.jsp); the manufacturer’s website (http://baxter.ca), or by calling 1-888-719-9955.
The content of this leaflet was prepared by Baxter Corporation, Mississauga, Ontario L5N 0C2, Canada.
Last Revised: August 13, 2020
Barcode
0 719002 429008
Baxter and Regiocit are trademarks of Baxter International Inc. or its subsidiaries.
Baxter logo
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
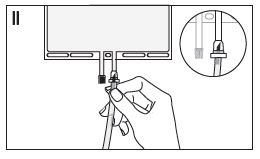
DIN 02496755
Product Code: 955791
REGIOCIT
Sodium chloride and sodium citrate solution
5.03 g / L, 5.29 g / L
Solution de chlorure de sodium et de citrate de sodium
5,03 g / L, 5,29 g / L
Sterile / Stérile
Nonpyrogenic / Apyrogène
For hemofiltration and regional citrate anticoagulation during
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) /
Pour hémofiltration et anticoagulation régionale au citrate pendant la thérapie de
remplacement rénal continue (TRRC).
Hydrochloric acid (pH adjuster) / Acide chlorhydrique (ajusteur de pH)
Water for Injection / Eau pour injection
Solution for Extracorporeal use only. Not for direct intravenous infusion. To be used in
pre-dilution only during CRRT.
For single use only. Discard any unused portion. Product Monograph available upon
request. See patient medication information. This product is not made with natural rubber
latex.
Solution pour administration extracorporelle seulement. Ne pas administrer par
perfusion intraveineuse directe. Ne doit être utilisé en mode pré-dilution que pour la
thérapie de remplacement rénal continu (TRRC).
Pour usage unique seulement. Jeter toute portion non utilisée. Monographie disponible sur
demande. Voir les renseignements pour le patient sur le médicament. Ce produit n’est pas
fabriqué avec du latex de caoutchouc naturel.
18 Citrate
mmol / L mmol / L
140 Na+
mmol / L
5 000 mL
Store at 4°C to 30 °C. Do not freeze or
expose to excessive heat.
Conserver à une température comprise
entre 4 °C et 30 °C. Ne pas congeler ni
exposer à une chaleur excessive.
Questions and Concerns /
Des questions ou problèmes
Baxter Corporation
Mississauga, ON L5N 0C2
Customer Service /
Service à la clientèle
1-888-719-9955
2 x 5 000 mL
07-05-00-0207
Baxter logo
18 Citrate
mmol / L
140 Na+
mmol / L
DIN 02496755
Product code: 955791
REGIOCIT
Sodium chloride and sodium citrate solution
5.03 g / L, 5.29 g / L
Solution de chlorure de sodium et de citrate de sodium
5,03 g / L, 5,29 g / L
Sterile / Stérile
Nonpyrogenic / Apyrogène
For hemofiltration and regional citrate anticoagulation during Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) /
Pour hémofiltration et anticoagulation régionale au citrate pendant la thérapie de remplacement rénal continue (TRRC).
244 mOsm/L
5000 mL
Approx pH 7.4
Solution for Extracorporeal use only. Not for direct intravenous infusion. To be used in pre-dilution only during Continuous
Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT).
Use only if overwrap and solution bag are not damaged and there is no leakage.
The introduction and mixing of additives must always be performed prior to connecting the solution bag to the extracorporeal circuit. Mix the solution thoroughly when additives have been introduced. Use only if solution is clear and free from visible particles.
Single use only. Discard unused portion. Product Monograph available upon request.
Dose: Read the package insert before use. This product is not made with natural rubber latex.
Store: 4°C to 30°C. Do not freeze or expose to excessive heat.
Solution pour administration extracorporelle seulement. Ne pas administrer par perfusion intraveineuse directe. Ne doit être utilisé en mode pré-dilution que pour la thérapie de remplacement rénal continu (TRRC). N’utiliser que si le suremballage et le sac de solution sont intacts et ne présentent aucune fuite. Il faut toujours injecter et mélanger les additifs avant de connecter le sac de solution au circuit extracorporel.
Bien mélanger la solution après l’injection des additifs. La solution ne doit être utilisée que si elle est limpide et ne contient aucune particule visible.
Usage unique seulement. Jeter la portion non utilisée. Monographie disponible sur demande.
Posologie : Lire la notice d'emballage avant l'utilisation. Ce produit n'est pas fabriqué avec du latex de caoutchouc naturel.
Conservation : entre 4 °C et 30 °C. Ne pas congeler ni exposer à une chaleur excessive.
Questions and Concerns / Des questions ou problèmes
Baxter Corporation
Mississauga, ON L5N 0C2
Customer Service / Service à la clientèle
1-888-719-9955
2D barcode
Baxter Logo
Barcode
00000955791
07-25-00-1832