FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from combination oral contraceptive (COC) use. This risk increases with age, particularly in women over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, COCs are contraindicated in women who are over 35 years of age and smoke [see Contraindications (4)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Nexesta Fe is indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 How to Start Nexesta Fe
Nexesta Fe is dispensed in a blister pack [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]. Nexesta Fe may be started using either a Day 1 start or a Sunday start (see Table 1). For the first cycle of a Sunday Start regimen, an additional method of contraception should be used until after the first 7 consecutive days of administration.
2.2 How to Take Nexesta Fe
Nexesta Fe (white to off-white active tablets and brown placebo tablets) may be swallowed whole or chewed and swallowed. If the tablet is chewed, the patient should drink a full glass (8 ounces) of liquid immediately after swallowing.
| Table 1: Instructions for Administration of Nexesta Fe
|
|
| Starting CHCs in women not currently using hormonal contraception (Day 1 Start or Sunday Start)
Important: Consider the possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of this product. Tablet Color: • Nexesta Fe active tablets are white to off-white (Day 1 to Day 21). • Nexesta Fe placebo tablets are brown (Day 22 to Day 28). | Day 1 Start:
• Take first white to off-white active tablet on the first day of menses. • Take subsequent white to off-white active tablets once daily at the same time each day for a total of 21 days. • Take one brown placebo tablet daily for 7 days and at the same time of day that active tablets were taken. • Begin each subsequent pack on the same day of the week as the first cycle pack (i.e., on the day after taking the last inactive tablet). Sunday Start: • Take first active tablet on the first Sunday after the onset of menses. Due to the potential risk of becoming pregnant, use additional non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) for the first seven days of the patient’s first cycle pack of Nexesta Fe. • Take subsequent white to off-white active tablets once daily at the same time each day for a total of 21 days. • Take one brown placebo tablet daily for the following 7 days and at the same time of day that active tablets were taken. • Begin each subsequent pack on the same day of the week as the first cycle pack (i.e., on the Sunday after taking the last inactive tablet) and additional non-hormonal contraceptive is not needed. |
| Switching to Nexesta Fe from another hormonal contraceptive
| Start on the same day that a new pack of the previous hormonal contraceptive would have started. |
| Switching from another contraceptive method to Nexesta Fe
| Start Nexesta Fe:
|
| • Transdermal patch
| • On the day when next application would have been scheduled |
| • Vaginal ring
| • On the day when next insertion would have been scheduled |
| • Injection
| • On the day when next injection would have been scheduled |
| • Intrauterine contraceptive
| • On the day of removal • If the IUD is not removed on first day of the patient’s menstrual cycle, additional non-hormonal contraceptive (such as condoms and spermicide) is needed for the first seven days of the first cycle pack. |
| • Implant
| • On the day of removal |
| Complete instructions to facilitate patient counseling on proper tablet usage are located in the FDA-Approved Patient Labeling.
|
|
Starting Nexesta Fe after Abortion or Miscarriage
First-trimester
- After a first-trimester abortion or miscarriage, Nexesta Fe may be started immediately. An additional method of contraception is not needed if Nexesta Fe is started within 5 days after termination of the pregnancy.
- If Nexesta Fe is not started within 5 days after termination of the pregnancy, the patient should use additional non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) for the first seven days of her first cycle pack of Nexesta Fe.
Second-trimester
- Do not start until 4 weeks after a second-trimester abortion or miscarriage, due to the increased risk of thromboembolic disease. Start Nexesta Fe, following the instructions in Table 1 for Day 1 or Sunday start, as desired. If using Sunday start, use additional non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) for the first seven days of the patient’s first cycle pack of Nexesta Fe. [See Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and FDA-Approved Patient Labeling.]
Starting Nexesta Fe after Childbirth
- Do not start until 4 weeks after delivery, due to the increased risk of thromboembolic disease. Start contraceptive therapy with Nexesta Fe following the instructions in Table 1 for women not currently using hormonal contraception.
- If the woman has not yet had a period postpartum, consider the possibility of ovulation and conception occurring prior to use of Nexesta Fe. [See Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.1 and 8.3), and FDA-Approved Patient Labeling].
2.3 Missed Tablets
| Table 2: Instructions for Missed Nexesta Fe Tablets
|
|
| Take the tablet as soon as possible. Continue taking one tablet a day until the pack is finished. |
| Take the two missed tablets as soon as possible and the next two active tablets the next day. Continue taking one tablet a day until the pack is finished. Additional non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) should be used as back-up if the patient has sex within 7 days after missing tablets. |
| Day 1 start: Throw out the rest of the pack and start a new pack that same day. Sunday start: Continue taking one tablet a day until Sunday, then throw out the rest of the pack and start a new pack that same day. Additional non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) should be used as back-up if the patient has sex within 7 days after missing tablets. |
2.4 Advice in Case of Gastrointestinal Disturbances
In case of severe vomiting or diarrhea, absorption may not be complete and additional contraceptive measures should be taken. If vomiting or diarrhea occurs within 3 to 4 hours after taking an active tablet, handle this as a missed tablet [see FDA-Approved Patient Labeling].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Nexesta Fe (norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP (chewable) and ferrous fumarate tablets (chewable)) is available in blister packs.
Each blister pack contains 28 tablets in the following order:
- 21 round, flat faced, beveled edge, white to off-white (active) tablets debossed with ‘S’ on one side and ‘47’ on other side and each containing 0.4 mg norethindrone USP and 0.035 mg ethinyl estradiol USP.
- 7 round, mottled, flat-faced, beveled-edge, brown (non-hormonal placebo) tablets debossed with ‘S’ on one side and ‘57’ on other side each containing 75 mg ferrous fumarate USP. The ferrous fumarate tablets do not serve any therapeutic purpose.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Nexesta Fe is contraindicated in females who are known to have or develop the following conditions:
• A high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic diseases. Examples include women who are known to:
o Smoke, if over age 35 [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
o Have deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, now or in the past [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
o Have inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
o Have cerebrovascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
o Have coronary artery disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
o Have thrombogenic valvular or thrombogenic rhythm diseases of the heart (for example, subacute bacterial endocarditis with valvular disease, or atrial fibrillation) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
o Have uncontrolled hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
o Have diabetes mellitus with vascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
o Have headaches with focal neurological symptoms or have migraine headaches with aura [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
• Women over age 35 with any migraine headaches [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
• Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
• Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
• Pregnancy, because there is no reason to use COCs during pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
• Current diagnosis of, or history of, breast cancer, which may be hormone-sensitive [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
• Hypersensitivity to any of the components.
• Use of Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for ALT elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thrombotic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems
• Stop Nexesta Fe if an arterial thrombotic event or venous thromboembolic (VTE) event occurs.
• Stop Nexesta Fe if there is unexplained loss of vision, proptosis, diplopia, papilledema, or retinal vascular lesions. Evaluate for retinal vein thrombosis immediately.
• If feasible, stop Nexesta Fe at least 4 weeks before and through 2 weeks after major surgery or other surgeries known to have an elevated risk of VTE as well as during the following prolonged immobilization.
• Start Nexesta Fe no earlier than 4 weeks after delivery, in women who are not breastfeeding. The risk of postpartum VTE decreases after the third postpartum week, whereas the risk of ovulation increases after the third postpartum week.
• The use of COCs increases the risk of VTE. However, pregnancy increases the risk of VTE as much or more than the use of COCs. The risk of VTE in women using COCs is 3 to 9 per 10,000 woman-years. The risk of VTE is highest during the first year of use of COCs and when restarting hormonal contraception after a break of 4 weeks or longer. The risk of thromboembolic disease due to COCs gradually disappears after use is discontinued.
Use of COCs also increases the risk of arterial thromboses such as strokes and myocardial infarctions, especially in women with other risk factors for these events. COCs have been shown to increase both the relative and attributable risks of cerebrovascular events (thrombotic and hemorrhagic strokes). The risk increases with age, particularly in women over 35 years of age who smoke.
• Use COCs with caution in women with cardiovascular disease risk factors.
5.2 Liver Disease
Impaired Liver Function
Do not use Nexesta Fe in women with liver disease, such as acute viral hepatitis or severe (decompensated) cirrhosis of liver [see Contraindications (4)]. Acute or chronic disturbances of liver function may necessitate the discontinuation of COC use until markers of liver function return to normal and COC causation has been excluded. Discontinue Nexesta Fe if jaundice develops.
Liver Tumors
Nexesta Fe is contraindicated in women with benign and malignant liver tumors [see Contraindications (4)]. Hepatic adenomas are associated with COC use. An estimate of the attributable risk is 3.3 cases/100,000 COC users. Rupture of hepatic adenomas may cause death through intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
Studies have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in long-term (>8 years) COC users. However, the risk of liver cancers in COC users is less than one case per million users.
5.3 Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment
During clinical trials with the Hepatitis C combination drug regimen that contains ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, ALT elevations greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), including some cases greater than 20 times the ULN, were significantly more frequent in women using ethinyl estradiol-containing medications, such as COCs. Discontinue Nexesta Fe prior to starting therapy with the combination drug regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir [see Contraindications (4)]. Nexesta Fe can be restarted approximately 2 weeks following completion of treatment with the Hepatitis C combination drug regimen.
5.4 High Blood Pressure
Nexesta Fe is contraindicated in women with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease [see Contraindications (4)]. For women with well-controlled hypertension, monitor blood pressure and stop Nexesta Fe if blood pressure rises significantly.
An increase in blood pressure has been reported in women taking COCs, and this increase is more likely in older women with extended duration of use. The incidence of hypertension increases with increasing concentrations of progestin.
5.5 Gallbladder Disease
Studies suggest a small increased relative risk of developing gallbladder disease among COC users. Use of COCs may worsen existing gallbladder disease. A past history of COC-related cholestasis predicts an increased risk with subsequent COC use. Women with a history of pregnancy-related cholestasis may be at an increased risk for COC related cholestasis.
5.6 Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolic Effects
Carefully monitor prediabetic and diabetic women who take Nexesta Fe. COCs may decrease glucose tolerance.
Consider alternative contraception for women with uncontrolled dyslipidemia. A small proportion of women will have adverse lipid changes while on COCs.
Women with hypertriglyceridemia, or a family history thereof, may be at an increased risk of pancreatitis when using COCs.
5.7 Headache
If a woman taking Nexesta Fe develops new headaches that are recurrent, persistent, or severe, evaluate the cause and discontinue Nexesta Fe if indicated.
Consider discontinuation of Nexesta Fe in the case of increased frequency or severity of migraine during COC use (which may be prodromal of a cerebrovascular event).
5.8 Bleeding Irregularities and Amenorrhea
Unscheduled Bleeding and Spotting
Unscheduled (breakthrough or intracyclic) bleeding and spotting sometimes occur in patients on COCs, especially during the first three months of use. If bleeding persists or occurs after previously regular cycles, check for causes such as pregnancy or malignancy. If pathology and pregnancy are excluded, bleeding irregularities may resolve over time or with a change to a different contraceptive product.
Amenorrhea and Oligomenorrhea
Women who use Nexesta Fe may experience amenorrhea. Some women may experience amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea after discontinuation of COCs, especially when such a condition was preexistent.
If scheduled (withdrawal) bleeding does not occur, consider the possibility of pregnancy. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed dosing schedule (missed one or more active tablets or started taking them on a day later than she should have), consider the possibility of pregnancy at the time of the first missed period and take appropriate diagnostic measures. If the patient has adhered to the prescribed regimen and misses two consecutive periods, rule out pregnancy.
5.9 COC Use Before or During Early Pregnancy
Extensive epidemiologic studies have revealed no increased risk of birth defects in women who have used oral contraceptives prior to pregnancy. Studies also do not suggest a teratogenic effect, particularly in so far as cardiac anomalies and limb reduction defects are concerned, when oral contraceptives are taken inadvertently during early pregnancy. Discontinue Nexesta Fe use if pregnancy is confirmed.
Administration of COCs to induce withdrawal bleeding should not be used as a test for pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.10 Depression
Carefully observe women with a history of depression and discontinue Nexesta Fe if depression recurs to a serious degree.
5.11 Malignant Neoplasms
Breast Cancer
Nexesta Fe is contraindicated in females who currently have or have had breast cancer because breast cancer may be hormonally sensitive [see Contraindications (4)].
Epidemiology studies have not found a consistent association between use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and breast cancer risk. Studies do not show an association between ever (current or past) use of COCs and risk of breast cancer. However, some studies report a small increase in the risk of breast cancer among current or recent users (<6 months since last use) and current users with longer duration of COC use [see Postmarketing Experience (6)].
Cervical Cancer
A causal relationship between the use of CHCs and the development of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia has not been clearly established. In observational studies, some studies suggest that COC use has been associated with an increase in the risk of cervical cancer or intraepithelial neoplasia. However, there continues to be controversy about the extent to which such findings may be due to differences in sexual behavior and other factors.
5.12 Effect on Binding Globulins
The estrogen component of COCs may raise the serum concentrations of thyroxine-binding globulin, sec hormone-binding globulin, and cortisol-binding globulin. The dose of replacement thyroid hormone or cortisol therapy may need to be increased.
5.13 Monitoring
A woman who is taking COCs should have a yearly visit with her healthcare provider for a blood pressure check and for other indicated healthcare.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions with the use of COCs are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious cardiovascular events and stroke [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Vascular events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
The following adverse reactions are commonly reported by COC users. Because these reactions are voluntarily reported by from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
- Irregular uterine bleeding
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Headache
Postmarketing Experience
Five studies that compared breast cancer risk between ever-users (current or past use) of COCs and never-users of COCs reported no association between ever use of COCs and breast cancer risk, with effect estimates ranging from 0.90 to 1.12 (Figure 1).
Three studies compared breast cancer risk between current or recent COC users (<6 months since last use) and never users of COCs (Figure 1). One of these studies reported no association between breast cancer risk and COC use. The other two studies found an increased relative risk of 1.19 to 1.33 with current or recent use. Both of these studies found an increased risk of breast cancer with current use of longer duration, with relative risks ranging from 1.03 with less than one year of COC use to approximately 1.4 with more than 8 to 10 years of COC use.
Figure 1: Risk of Breast Cancer with Combined Oral Contraceptive Use
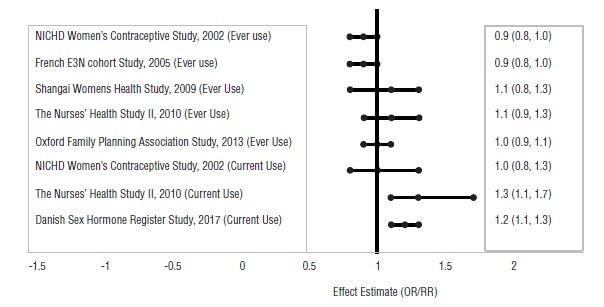
RR = relative risk; OR = odds ratio; HR = hazard ratio. “ever COC” are females with current or past COC use; “never COC use” are females that never used COCs.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Consult the labeling of concurrently used drugs to obtain further information about interactions with hormonal contraceptives or the potential for enzyme alterations.
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on Combined Oral Contraceptives
Substances decreasing the plasma concentrations of COCs and potentially diminishing the efficacy of COCs:
Drugs or herbal products that induce certain enzymes, including cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), may decrease the plasma concentrations of COCs and potentially diminish the effectiveness of COCs or increase breakthrough bleeding. Some drugs or herbal products that may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives include phenytoin, barbiturates, carbamazepine, bosentan, felbamate, griseofulvin, oxcarbazepine, rifampicin, topiramate, rifabutin, rufinamide, aprepitant, and products containing St. John’s wort. Interactions between hormonal contraceptives and other drugs may lead to breakthrough bleeding and/or contraceptive failure. Counsel women to use an alternative method of contraception or a back-up method when enzyme inducers are used with COCs, and to continue back-up contraception for 28 days after discontinuing the enzyme inducer to ensure contraceptive reliability.
Colesevelam: Colesevelam, a bile acid sequestrant, given together with a COC, has been shown to significantly decrease the AUC of EE. The drug interaction between the contraceptive and colesevelam was decreased when the two drug products were given 4 hours apart.
Substances increasing the plasma concentrations of COCs:
Co-administration of atorvastatin or rosuvastatin and certain COCs containing EE increase AUC values for EE by approximately 20 to 25%. Ascorbic acid and acetaminophen may increase plasma EE concentrations, possibly by inhibition of conjugation. CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as itraconazole, fluconazole, grapefruit juice, or ketoconazole may increase plasma hormone concentrations.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/Hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors:
Significant changes (increase or decrease) in the plasma concentrations of estrogen and/or progestin have been noted in some cases of co-administration with HIV protease inhibitors (decrease [e.g., nelfinavir, ritonavir, darunavir/ritonavir, (fos)amprenavir/ritonavir, lopinavir/ritonavir, and tipranavir/ritonavir] or increase [e.g., indinavir and atazanavir/ritonavir])/HCV protease inhibitors (decrease [e.g., nevirapine] or increase [e.g., etravirine]).
7.2 Effects of Combined Oral Contraceptives on Other Drugs
COCs containing EE may inhibit the metabolism of other compounds (e.g., cyclosporine prednisolone, theophylline, tizanidine, and voriconazole) and increase their plasma concentrations. COCs have been shown to decrease plasma concentrations of acetaminophen, clofibric acid, morphine, salicylic acid, temazepam and lamotrigine. Significant decrease in plasma concentration of lamotrigine has been shown, likely due to induction of lamotrigine glucuronidation. This may reduce seizure control; therefore, dosage adjustments of lamotrigine may be necessary.
Women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy may need increased doses of thyroid hormone because the serum concentration of thyroid-binding globulin increases with use of COCs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
7.3 Concomitant Use with HCV Combination Therapy – Liver Enzyme Elevation
Do not co-administer Nexesta Fe with HCV drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to potential for ALT elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
There is little or no increased risk of birth defects in women who inadvertently use COCs during early pregnancy. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or non-genital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb reduction defects) following exposure to low dose COCs prior to conception or during early pregnancy.
Do not use COCs to induce withdrawal bleeding as a test for pregnancy. Do not use COCs during pregnancy to treat threatened or habitual abortion.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Advise the nursing mother to use other forms of contraception, when possible, until she has weaned her child. COCs can reduce milk production in breastfeeding mothers. This is less likely to occur once breastfeeding is well-established; however, it can occur at any time in some women. Small amounts of oral contraceptive steroids and/or metabolites are present in breast milk.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of Nexesta Fe have been established in women of reproductive age. Efficacy is expected to be the same in post-pubertal adolescents under the age of 18 years as for users 18 years and older. Use of this product before menarche is not indicated.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Nexesta Fe has not been studied in postmenopausal women and is not indicated in this population.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of Nexesta Fe has not been studied in women with hepatic impairment. However, steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in patients with hepatic impairment. Acute or chronic disturbances of liver function may necessitate the discontinuation of COC use until markers of liver function return to normal and COC causation has been excluded [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
There have been no reports of serious ill effects from overdosage of oral contraceptives, including ingestion by children. Overdosage may cause withdrawal bleeding in females and nausea.
11 DESCRIPTION
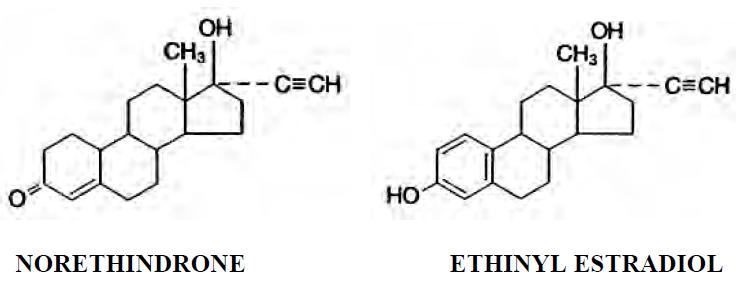
Nexesta Fe is a combinational contraceptive containing the progestational compound norethindrone and the estrogenic compound ethinyl estradiol. The packaging includes 21 white to off-white tablets composed of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol followed by 7 brown ferrous fumarate (placebo) tablets. The chemical name for norethindrone is 17-hydroxy-19-nor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one and for ethinyl estradiol the chemical name is 19-nor-17α-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yne-3,17-diol. The structural formulas are:
The active white to off-white Nexesta Fe (norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP (chewable) 0.4 mg/0.035 mg and ferrous fumarate tablets (chewable)) tablets contain 0.4 mg norethindrone USP and 0.035 mg ethinyl estradiol USP and the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide, dibasic calcium phosphate, dihydrate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, nat spearmint, povidone, sodium starch glycolate, and sucralose.
The brown tablets contain croscarmellose sodium, ferrous fumarate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, nat spearmint, povidone, and sucralose. The ferrous fumarate tablets do not serve any therapeutic purpose.
USP dissolution test is pending.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
COCs lower the risk of becoming pregnant primarily by suppressing ovulation. Other possible mechanisms may include cervical mucus changes that inhibit sperm penetration and endometrial changes that reduce the likelihood of implantation.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone are rapidly absorbed with maximum plasma concentrations occurring within 2 hours after Nexesta Fe administration (see Table 1). Norethindrone appears to be completely absorbed following oral administration; however, it is subject to first-pass metabolism resulting in an absolute bioavailability of approximately 65 percent. Large intersubject variability is reflected in a 3- to 5-fold variation in norethindrone bioavailability. Ethinyl estradiol bioavailability is approximately 43 percent due to small-intestinal and hepatic first-pass metabolism.
|
an = 26 bn = 25 Cmax= maximum plasma concentration; tmax= time to reach Cmax; AUC = area under the curve; t1/2= elimination half-life. |
||||
| Norethindrone/Ethinyl Estradiol | tmax (h) | Cmax (pg/mL) | AUC0-∞ (pg•h/mL) | t1/2 (h) |
| Norethindrone 0.4 mg | 1.24 ± 0.40a
| 4210.6 ± 1628.8a
| 18034.9 ± 7852.9b
| 8.6 ± 3.7b
|
| Ethinyl Estradiol 0.035 mg | 1.44 ± 0.33b
| 131.4 ± 34.2b
| 1065.8 ± 276.2b
| 17.1 ± 4.4b
|
Food Effect:
Single-dose administration of Nexesta Fe tablets with food decreased the maximum norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol concentration by 53 percent and 47 percent, respectively; the extent of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol absorption (AUC values) was not affected by food administration.
Distribution
Norethindrone is 36 percent bound to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and 61 percent bound to albumin. Ethinyl estradiol is not bound to SHBG but is highly (98.5 percent) bound to albumin. Volume of distribution of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol ranges from 2 to 4 L/kg.
Metabolism
Norethindrone undergoes extensive biotransformation, primarily via reduction, followed by sulfate and glucuronide conjugation; less than 5 percent of a norethindrone dose is excreted unchanged; greater than 50 percent and 20 to 40 percent of a dose is excreted in urine and feces, respectively. The majority of metabolites in the circulation are sulfates, with glucuronides accounting for most of the urinary metabolites.
Ethinyl estradiol is also extensively metabolized, both by oxidation and by conjugation with sulfate and glucuronide. Sulfates are the major circulating conjugates of ethinyl estradiol, and glucuronides predominate in urine. The primary oxidative metabolite is 2-hydroxy-ethinyl estradiol, which is formed by the CYP3A4 isoform of cytochrome P450.
Excretion
Plasma clearance values for norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol are similar (approximately 0.4 L/hr/kg). Ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone are excreted in both urine and feces, primarily as metabolites. Ethinyl estradiol is excreted in urine and feces as glucuronides and sulfates, and about 28 to 43 percent undergoes enterohepatic circulation. The mean terminal elimination half-lives of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol following single dose administration of Nexesta Fe are approximately 9 hours and 17 hours, respectively.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
[See Warnings and Precautions (5.11) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1).]
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The data presented in Section 14 are from a clinical trial conducted with norethindrone 0.4 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.035 mg tablets. Nexesta Fe is bioequivalent to these norethindrone acetate/ethinyl estradiol tablets.
In a multicenter open-label clinical trial, 1,970 women, 98% of whom were 16 to 39 years of age, were studied for up to 31 cycles (28 days per cycle) to assess the efficacy of norethindrone/ethinyl estradiol tablets, completing the equivalent of 20,230 cycles of exposure. The racial demographic of all enrolled women was: Caucasian (56%), African-American (14%), and Other (30%) (Hispanic, Native American, etc.). Of treated women, 10% were lost to follow-up, 11% discontinued related to cycle control and 7% discontinued due to other adverse events.
The pregnancy rate (Pearl Index [PI]) in all 1,970 women was 1.48 pregnancies per 100 women-years of use (95% confidence interval 0.94 to 2.22), based on 23 pregnancies that occurred after the onset of treatment of norethindrone /ethinyl estradiol tablets.
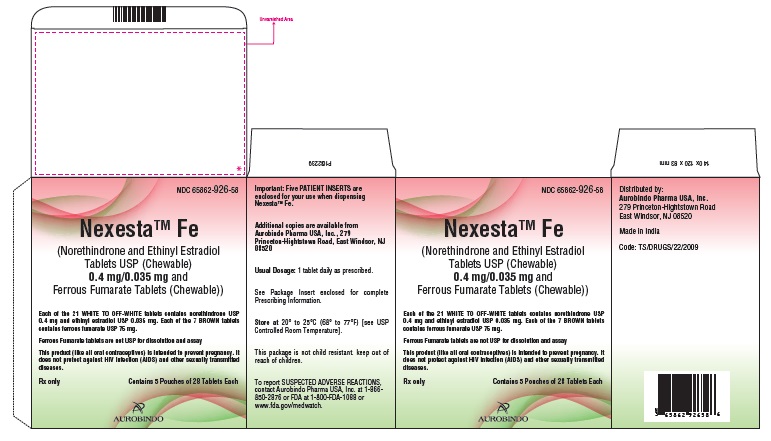
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Nexesta Fe (norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP (chewable) 0.4 mg/0.035 mg and ferrous fumarate tablets (chewable)) is available in blister packs:
The Blister Packs are packed in Pouches (NDC 65862-926-87) and the pouches are packaged in cartons
Carton of 1 Pouch NDC 65862-926-87
Carton of 3 Pouches NDC 65862-926-88
Carton of 5 Pouches NDC 65862-926-58
Carton of 72 Pouches NDC 65862-926-97
Each blister pack contains 28 tablets in the following order:
- 21 round, flat faced, beveled edge, white to off-white (active) tablets debossed with ‘S’ on one side and ‘47’ on other side and each containing 0.4 mg norethindrone USP and 0.035 mg ethinyl estradiol USP.
- 7 round, mottled, flat-faced, beveled-edge, brown (non-hormonal placebo) tablets debossed with ‘S’ on one side and ‘57’ on other side each containing 75 mg ferrous fumarate USP.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use)
Counsel patients about the following information:
- Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from COC use, and that women who are over 35 years old and smoke should not use COCs [see Boxed Warning].
- Increased risk of VTE compared to non-users of COCs is greatest after initially starting a COC or restarting (following a 4-week or greater pill-free interval) the same or a different COC [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Nexesta Fe does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases.
- Nexesta Fe is not to be used during pregnancy; if pregnancy occurs during use of Nexesta Fe, instruct the patient to stop further use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
- Take one tablet daily by mouth at the same time every day. Instruct patients what to do in the event pills are missed [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Use a back-up or alternative method of contraception when enzyme inducers are used with Nexesta Fe [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
- COCs may reduce breast milk production; this is less likely to occur if breastfeeding is well established [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- A woman who starts COCs postpartum and who has not yet had a period should use an additional method of contraception until she has taken a white to off-white tablet for 7 consecutive days [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Amenorrhea may occur. Consider pregnancy in the event of amenorrhea at the time of the first missed period. Rule out pregnancy in the event of amenorrhea in two or more consecutive cycles [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Patient Information
NexestaTM Fe (neks-ey-stuh Fe)
(norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP (chewable)
and ferrous fumarate tablets (chewable))
What is the most important information I should know about Nexesta Fe?
Do not use Nexesta Fe if you smoke cigarettes and are over 35 years old. Smoking increases your risk of serious cardiovascular side effects (heart and blood vessel problems) from birth control pills, including death from heart attack, blood clots or stroke. This risk increases with age and the number of cigarettes you smoke.
What is Nexesta Fe?
Nexesta Fe is a birth control pill (oral contraceptive) used by women to prevent pregnancy.
How does Nexesta Fe work for contraception?
Your chance of getting pregnant depends on how well you follow the directions for taking your birth control pills. The better you follow the directions, the less chance you have of getting pregnant.
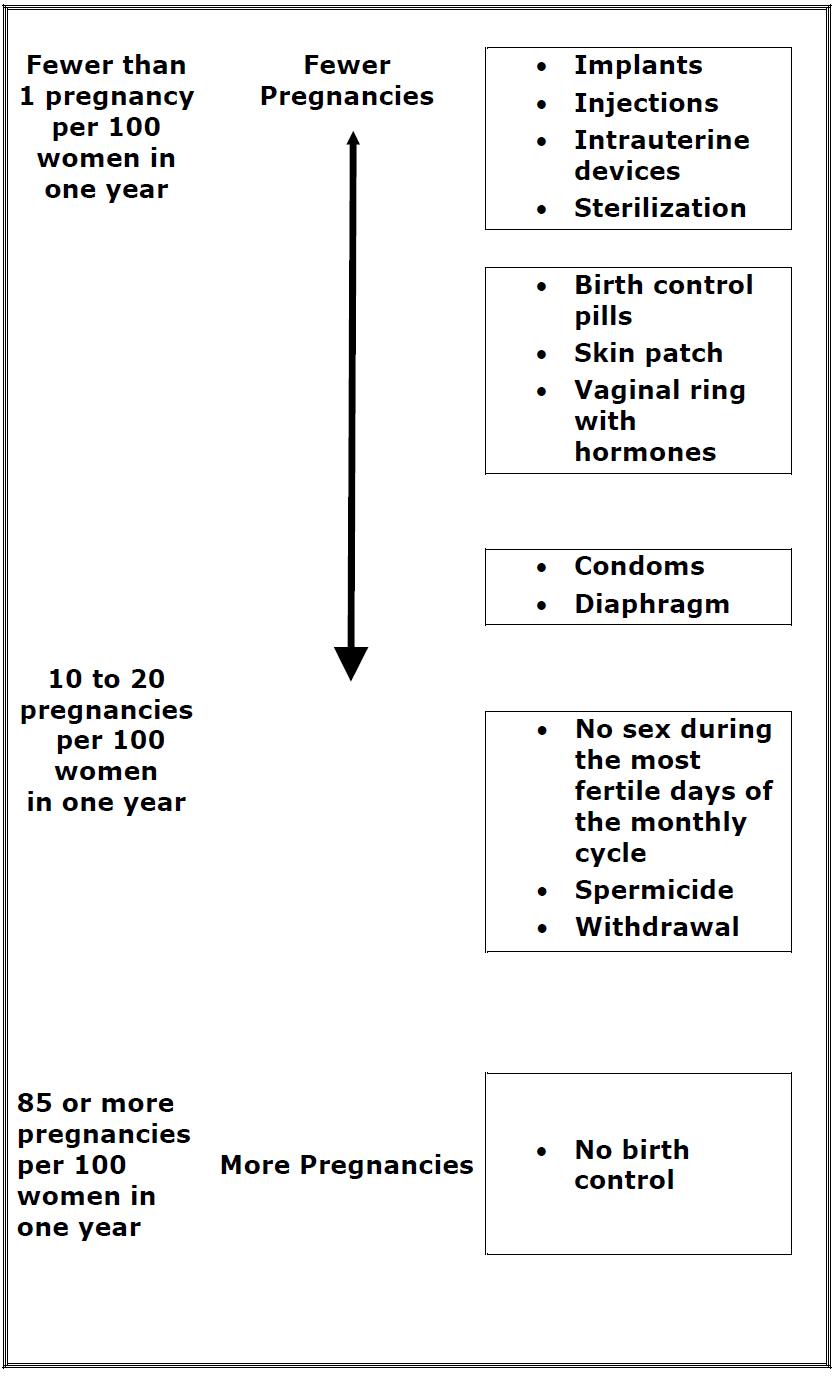
Based on the results of one clinical study of a 28-day regimen of norethindrone 0.4 mg/ethinyl estradiol 0.035 mg tablets, about 1 to 2 out of 100 women may get pregnant during the first year they use Nexesta Fe.
The following chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who use different methods of birth control. Each box on the chart contains a list of birth control methods that are similar in effectiveness. The most effective methods are at the top of the chart. The box on the bottom of the chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who do not use birth control and are trying to get pregnant.
Who should not take Nexesta Fe?
Do not take Nexesta Fe if you:
- smoke and are over 35 years of age
- had blood clots in your arms, legs, lungs, or eyes
- had a problem with your blood that makes it clot more than normal
- have certain heart valve problems or irregular heart beat that increases your risk of having blood clots
- had a stroke
- had a heart attack
- have high blood pressure that cannot be controlled by medicine
- have diabetes with kidney, eye, nerve, or blood vessel damage
- have certain kinds of severe migraine headaches with aura, numbness, weakness or changes in vision, or any migraine headaches if you are over 35 years of age
- have liver problems, including liver tumors
- have any unexplained vaginal bleeding
- are pregnant
- had breast cancer or any cancer that is sensitive to female hormones
- Take any Hepatitis C drug combination containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir. This may increase levels of the liver enzyme “alanine aminotransferase” (ALT) in the blood
If any of these conditions happen while you are taking Nexesta Fe, stop taking Nexesta Fe right away and talk to your healthcare provider. Use non-hormonal contraception when you stop taking Nexesta Fe.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Nexesta Fe? Tell your healthcare provider if you:
- are pregnant or think you may be pregnant
- are depressed now or have been depressed in the past
- had yellowing of your skin or eyes (jaundice) caused by pregnancy (cholestasis of pregnancy)
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Nexesta Fe may decrease the amount of breast milk you make. A small amount of the hormones in Nexesta Fe may pass into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best birth control method for you while breastfeeding.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
Nexesta Fe may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how well Nexesta Fe works.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How do I take Nexesta Fe?
Read the Instructions for Use at the end of this Patient Information.
What are the possible serious side effects of Nexesta Fe?
- Like pregnancy, Nexesta Fe may cause serious side effects, including blood clots in your lungs, heart attack, or a stroke that may lead to death. Some other examples of serious blood clots include blood clots in the legs or eyes.
Serious blood clots can happen especially if you smoke, are obese, or are older than 35 years of age. Serious blood clots are more likely to happen when you:
- first start taking birth control pills
- restart the same or different birth control pills after not using them for a month or more
Call your healthcare provider or go to a hospital emergency room right away if you have:
| o leg pain that will not go away | o a sudden, severe headache unlike your usual headaches |
| o sudden severe shortness of breath | o weakness or numbness in your arm or leg |
| o sudden change in vision or blindness | o trouble speaking |
| o chest pain |
Other serious side effects include:
-
liver problems, including:
- rare liver tumors
- jaundice (cholestasis), especially if you previously had cholestasis of pregnancy. Call your healthcare provider if you have yellowing of your skin or eyes.
- high blood pressure. You should see your healthcare provider for a yearly check of your blood pressure.
- gallbladder problems
- changes in the sugar and fat (cholesterol and triglycerides) levels in your blood
- new or worsening headaches including migraine headaches
- depression
- possible cancer in your breast and cervix
- swelling of your skin especially around your mouth, eyes, and in your throat (angioedema). Call your healthcare provider if you have a swollen face, lips, mouth, tongue or throat, which may lead to difficulty swallowing or breathing. Your chance of having angioedema is higher is you have a history of angioedema.
- dark patches of skin around your forehead, nose, cheeks and around your mouth, especially during pregnancy (chloasma). Women who tend to get chloasma should avoid spending a long time in sunlight, tanning booths, and under sun lamps while taking Nexesta Fe. Use sunscreen if you have to be in the sunlight.
What are the most common side effects of Nexesta Fe?
The most common side effects of Nexesta Fe include:
- headache (including migraine)
- nausea and vomiting
- breast problems
- tenderness, pain and discomfort
- enlargement and swelling
- discharge
- nipple pain
- belly pain
- pain with your periods (menstrual cycle)
- mood changes, including depression
- acne
- vaginal infections
- bloating
- weight gain
These are not all the possible side effects of Nexesta Fe. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What else should I know about taking Nexesta Fe?
- If you are scheduled for any lab tests, tell your healthcare provider you are taking Nexesta Fe. Certain blood tests may be affected by Nexesta Fe.
- Nexesta Fe does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections.
How should I store Nexesta Fe?
- Store Nexesta Fe at room temperature between 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Keep Nexesta Fe and all medicines out of the reach of children.
- Store away from light.
General information about the safe and effective use of Nexesta Fe.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Nexesta Fe for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Nexesta Fe to other people.
This Patient Information summarizes the most important information about Nexesta Fe. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Nexesta Fe that is written for health professionals.
For more information, call Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876
Does hormonal birth control cause cancer?
It is not known if hormonal birth control pills causes breast cancer. Some studies, but not all, suggest that there could be a slight increase in the risk of breast cancer among current users with longer duration of use.
If you have breast cancer now, or have had it in the past, do not use hormonal birth control because some breast cancers are sensitive to hormones.
Women who use birth control pills may have a slightly higher chance of getting cervical cancer. However, this may be due to other reasons such as having more sexual partners.
What if I want to become pregnant?
You may stop taking the pill whenever you wish. Consider a visit with your healthcare provider for a pre-pregnancy checkup before you stop taking the pill.
What should I know about my period when taking Nexesta Fe?
Your periods may be lighter and shorter than usual. Some women may miss a period. Irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting may happen while you are taking Nexesta Fe, especially during the first few months of use. This usually is not a serious problem. It is important to continue taking your pills on a regular schedule to prevent a pregnancy.
What are the ingredients in Nexesta Fe?
Active ingredients:
White to off-white pills: norethindrone USP and ethinyl estradiol USP
Brown pills: ferrous fumarate USP
Inactive ingredients:
White to off-white pills: anhydrous lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide, dibasic calcium phosphate, dihydrate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, nat spearmint, povidone, sodium starch glycolate, and sucralose.
Brown pills: croscarmellose sodium, ferrous fumarate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, nat spearmint, povidone, and sucralose.
Instructions For Use
NexestaTM Fe (neks-ey-stuh Fe)
(norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP (chewable)
and ferrous fumarate tablets (chewable))
Important Information about taking Nexesta Fe
- Take 1 pill every day at the same time. Take the pills in the order directed on your blister pack.
- Both the white to off-white pills and the brown pills may be swallowed whole or chewed and swallowed. If the pill is chewed, drink a full glass (8 ounces) of liquid immediately after swallowing.
- Do not skip your pills, even if you do not have sex often. If you miss pills (including starting the pack late) you could get pregnant. The more pills you miss, the more likely you are to get pregnant.
- If you have trouble remembering to take Nexesta Fe, talk to your healthcare provider. When you first start taking Nexesta Fe, spotting or light bleeding in between your periods may occur. Contact your healthcare provider if this does not go away after a few months.
- You may feel sick to your stomach (nauseous), especially during the first few months of taking Nexesta Fe. If you feel sick to your stomach, do not stop taking the pill. The problem will usually go away. If your nausea does not go away, call your healthcare provider.
- Missing pills can also cause spotting or light bleeding, even when you take the missed pills later. On the days you take 2 pills to make up for missed pills (see below), you could also feel a little sick to your stomach.
- It is not uncommon to miss a period. However, if you miss a period and have not taken Nexesta Fe according to directions, or miss 2 periods in a row, or feel like you may be pregnant, call your healthcare provider. If you have a positive pregnancy test, you should stop taking Nexesta Fe.
- If you have vomiting or diarrhea within 3 to 4 hours of taking your pill, take another pill of the same color from your extra blister pack. If you do not have an extra blister pack, take the next pill in your blister pack. Continue taking all your remaining pills in order. Start the first pill of your next blister pack the day after finishing your current blister pack. This will be 1 day earlier than originally scheduled. Continue on your new schedule.
- If you have vomiting or diarrhea for more than 1 day, your birth control pills may not work as well. Use an additional birth control method, like condoms and a spermicide, until you check with your healthcare provider.
- Stop taking Nexesta Fe at least 4 weeks before you have major surgery and do not restart after the surgery without asking your healthcare provider. Be sure to use other forms of contraception (like condoms and spermicide) during this time period.
Before you start taking Nexesta Fe:
- Decide what time of day you want to take your pill. It is important to take it at the same time every day and in the order as directed on your blister pack.
- Have backup contraception (condoms and spermicide) available and if possible, an extra full pack of pills as needed.
When should I start taking Nexesta Fe?
If you start taking Nexesta Fe and you have not used a hormonal birth control method before:
- There are 2 ways to start taking your birth control pills. You can either start on a Sunday (Sunday Start) or on the first day (Day 1) of your natural menstrual period (Day 1 Start). Your healthcare provider should tell you when to start taking your birth control pill.
- If you use the Sunday Start, use non-hormonal back-up contraception such as condoms and spermicide for the first 7 days that you take Nexesta Fe. You do not need back-up contraception if you use the Day 1 Start.
If you start taking Nexesta Fe and you are switching from another birth control pill:
- Start your new Nexesta Fe pack on the same day that you would start the next pack of your previous birth control method.
- Do not continue taking the pills from your previous birth control pack.
If you start taking Nexesta Fe and previously used a vaginal ring or transdermal patch:
- Start using Nexesta Fe on the day you would have reapplied the next ring or patch.
If you start taking Nexesta Fe and you are switching from a progestin-only method such as an implant or injection:
- Start taking Nexesta Fe on the day of removal of your implant or on the day when you would have had your next injection.
If you start taking Nexesta Fe and you are switching from an intrauterine device or system (IUD or IUS):
- Start taking Nexesta Fe on the day of removal of your IUD or IUS.
- You do not need back-up contraception if your IUD or IUS is removed on the first day (Day 1) of your period. If your IUD or IUS is removed on any other day, use non-hormonal back-up contraception such as condoms and spermicide for the first 7 days that you take Nexesta Fe.
Keep a calendar to track your period:
If this is the first time you are taking birth control pills, read, “When should I start taking Nexesta Fe?” above. Follow these instructions for either a Sunday Start or a Day 1 Start.
Sunday Start:
You will use a Sunday Start if your healthcare provider told you to take your first pill on a Sunday.
- Take pill 1 on the Sunday after your period starts.
- If your period starts on a Sunday, take pill “1” that day and refer to Day 1 Start instructions below.
- Take 1 pill every day in the order on the blister pack at the same time each day for 28 days.
- After taking the last pill on Day 28 from the blister pack, start taking the first pill from a new pack, on the same day of the week as the first pack (Sunday). Take the first pill in the new pack whether or not you are having your period.
- Use non-hormonal back-up contraception such as condoms and spermicide for the first 7 days of the first cycle that you take Nexesta Fe.
Day 1 Start:
You will use a Day 1 Start if your doctor told you to take your first pill (Day 1) on the first day of your period.
- Take 1 pill every day in the order of the blister pack, at the same time each day, for 28 days.
- After taking the last pill on Day 28 from the blister pack, start taking the first pill from a new pack, on the same day of the week as the first pack. Take the first pill in the new pack whether or not you are having your period.
Instructions for using your pill pack:
Step 1.
Look at your Nexesta Fe pill pack. See Figure A.
The Nexesta Fe pill pack has:
- 21 white to off-white (active) pills with hormone for Week 1 through Week 3.
- 7 brown (inactive) pills without hormones for Week 4.
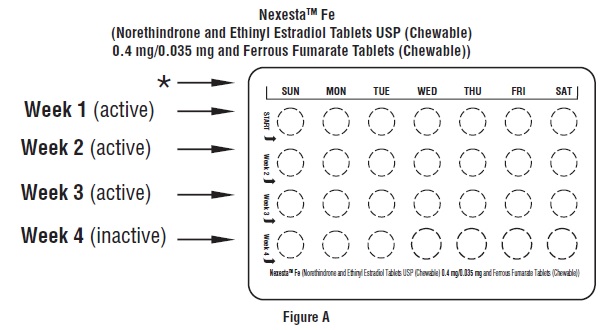
Figure A
Step 2.
Find:
- where on your pack to start taking pills
- in what order to take your pills (follow the arrows)
- the week numbers
Step 3.
Remove the white to off-white pill by pressing the pill through the foil in the bottom of the pill pack. See Figure B. Continue taking the white to off-white pills for 21 days.
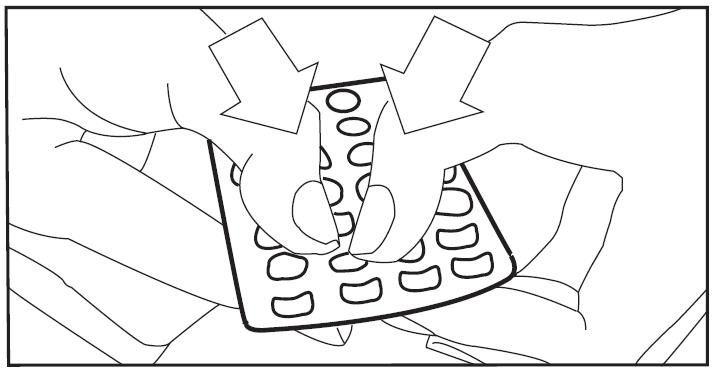
Figure B
Step 4.
On the first day of Week 4 start taking the brown pills. Take the brown pill for 7 days. Your period should start during this time.
Step 5.
When you have taken all of the brown pills in your pill pack, get a new pill pack and start taking the white to off-white pills.
- For a Day 1 start:
Begin your next pill pack on the same day of the week as your first cycle pill pack.
- For a Sunday Start:
Begin your next pill pack on Sunday.
What should I do if I miss any Nexesta Fe pills?
If you miss 1 pill in Weeks 1, 2, or 3, follow these steps:
- Take it as soon as you remember. Take the next pill at your regular time. This means you may take 2 pills in 1 day.
- Then continue taking 1 pill every day until you finish the pack.
- You do not need to use a back-up birth control method if you have sex.
If you miss 2 pills in Week 1 or Week 2 of your pack, follow these steps:
- Take the 2 missed pills as soon as possible and the next 2 pills the next day.
- Then continue to take 1 pill every day until you finish the pack.
- Use a non-hormonal birth control method (such as a condom and spermicide) as a back-up if you have sex during the first 7 days after missing your pills.
If you miss 2 pills in a row in Week 3, or you miss 3 or more pills in a row during Weeks 1, 2, or 3 of the pack, follow these steps:
- If you are a Day 1 Starter:
- Throw out the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day.
- If you are a Sunday Starter:
- Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday. On Sunday, throw out the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
- You may not have your period this month but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a row, call your healthcare provider because you might be pregnant.
- You could become pregnant if you have sex during the first 7 days after you restart your pills. You MUST use a non-hormonal birth control method (such as a condom and spermicide) as a back-up if you have sex during the first 7 days after you restart your pills.
If you have any questions or are unsure about the information in this leaflet, call your healthcare provider.
This Patient Information and Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
279 Princeton-Hightstown Road
East Windsor, NJ 08520
Manufactured by:
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Hyderabad-500 032, India
Revised: 12/2021
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.4 mg/0.035 mg 1 Pouch Label
NDC 65862-926-87
NexestaTM Fe
(Norethindrone and Ethinyl Estradiol
Tablets USP (Chewable) 0.4 mg/0.035 mg
and Ferrous Fumarate Tablets (Chewable))
Each of the 21 WHITE TO OFF-WHITE tablets contains
norethindrone USP 0.4 mg and ethinyl estradiol USP
0.035 mg. Each of the 7 BROWN tablets contains ferrous
fumarate USP 75 mg.
Ferrous Fumarate tablets are not USP for dissolution and
assay.
This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to
prevent pregnancy. It does not protect against HIV
infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases.
Rx only Contains 1 Blister of 28 Tablets Each
AUROBINDO

PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.4 mg/0.035 mg Pouch Carton
NDC 65862-926-58
NexestaTM Fe
(Norethindrone and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP (Chewable)
0.4 mg/0.035 mg
and Ferrous Fumarate Tablets (Chewable))
Each of the 21 WHITE TO OFF-WHITE tablets contains norethindrone USP
0.4 mg and ethinyl estradiol USP 0.035 mg. Each of the 7 BROWN tablets
contains ferrous fumarate USP 75 mg.
Ferrous Fumarate tablets are not USP for dissolution and assay
This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to prevent pregnancy. It does not
protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases.
Rx only Conatins 5 Pouches of 28 Tablets Each