FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended starting dose of darifenacin extended-release tablet is 7.5 mg orally once daily. Based upon individual response, the dose may be increased to 15 mg once daily, as early as two weeks after starting therapy.
Darifenacin extended-release tablets should be taken orally once daily with water. Darifenacin extended-release tablets may be taken with or without food, and should be swallowed whole and not chewed, divided or crushed.
For patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) or when co-administered with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (for example, ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir, nelfinavir, clarithromycin and nefazadone), the daily dose of darifenacin extended-release tablets should not exceed 7.5 mg. Darifenacin extended-release tablets are not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see Warnings & Precautions (5.6), Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Darifenacin extended-release tablets 7.5 mg are white to off white colored circular biconvex film coated tablet debossed with "C" on one side and "431" on the other side.
Darifenacin extended-release tablets 15 mg are light peach colored circular biconvex film coated tablet debossed with "C" on one side and "432" on the other side.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Urinary Retention
Darifenacin extended-release tablets should be administered with caution to patients with clinically significant bladder outflow obstruction because of the risk of urinary retention.
5.2 Decreased Gastrointestinal Motility
Darifenacin extended-release tablets should be administered with caution to patients with gastrointestinal obstructive disorders because of the risk of gastric retention. Darifenacin extended-release tablets, like other anticholinergic drugs, may decrease gastrointestinal motility and should be used with caution in patients with conditions such as severe constipation, ulcerative colitis, and myasthenia gravis.
5.3 Controlled Narrow-Angle Glaucoma
Darifenacin extended-release tablets should be used with caution in patients being treated for narrow-angle glaucoma and only where the potential benefits outweigh the risks.
5.4 Angioedema
Angioedema of the face, lips, tongue, and/or larynx have been reported with darifenacin. In some cases angioedema occurred after the first dose. Angioedema associated with upper airway swelling may be life threatening. If involvement of the tongue, hypopharynx, or larynx occurs, darifenacin should be promptly discontinued and appropriate therapy and/or measures necessary to ensure a patent airway should be promptly provided.
5.5 Central Nervous System Effects
Darifenacin extended-release tablets are associated with anticholinergic central nervous system (CNS) effects [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. A variety of CNS anticholinergic effects have been reported, including headache, confusion, hallucinations and somnolence. Patients should be monitored for signs of anticholinergic CNS effects, particularly after beginning treatment or increasing the dose. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until they know how darifenacin extended-release tablets affects them. If a patient experiences anticholinergic CNS effects, dose reduction or drug discontinuation should be considered.
5.6 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The daily dose of darifenacin extended-release tablet should not exceed 7.5 mg for patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B). Darifenacin extended-release tablet has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) and therefore is not recommended for use in this patient population [see Dosage and Administration (2) Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of darifenacin extended-release tablet was evaluated in controlled clinical trials in a total of 8,830 patients, 6,001 of whom were treated with darifenacin extended-release tablet. Of this total, 1,069 patients participated in three, 12-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose efficacy and safety studies (Studies 1, 2 and 3). Of this total, 337 and 334 patients received darifenacin extended-release tablets 7.5 mg daily and 15 mg daily, respectively. In all long-term trials combined, 1,216 and 672 patients received treatment with darifenacin extended-release tablets for at least 24 and 52 weeks, respectively.
In Studies 1, 2 and 3 combined, the serious adverse reactions to darifenacin extended-release tablets were urinary retention and constipation.
In Studies 1, 2 and 3 combined, dry mouth leading to study discontinuation occurred in 0 %, 0.9 %, and 0 % of patients treated with darifenacin extended-release tablets 7.5 mg daily, darifenacin extended-release tablets 15 mg daily and placebo, respectively. Constipation leading to study discontinuation occurred in 0.6 %, 1.2 %, and 0.3 % of patients treated with darifenacin extended-release tablets 7.5 mg daily, darifenacin extended-release tablets 15 mg daily and placebo, respectively.
Table 1 lists the rates of identified adverse reactions, derived from all reported adverse events in 2 % or more of patients treated with 7.5 mg or 15 mg darifenacin extended-release tablets, and greater than placebo in Studies 1, 2 and 3. In these studies, the most frequently reported adverse reactions were dry mouth and constipation. The majority of the adverse reactions were mild or moderate in severity and most occurred during the first two weeks of treatment.
| Body System
| Adverse Reaction
| % of Subjects
|
||
|
|
| Darifenacin extended-release tablet
7.5 mg N=337 | Darifenacin extended-
release tablet 15 mg N=334 | Placebo
N=338 |
| Digestive | Dry Mouth | 20.2 | 35.3 | 8.2 |
| Constipation | 14.8 | 21.3 | 6.2 |
|
| Dyspepsia | 2.7 | 8.4 | 2.6 |
|
| Abdominal Pain | 2.4 | 3.9 | 0.5 |
|
| Nausea | 2.7 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
|
| Diarrhea | 2.1 | 0.9 | 1.8 |
|
| Urogenital | Urinary Tract Infection | 4.7 | 4.5 | 2.6 |
| Nervous | Dizziness | 0.9 | 2.1 | 1.3 |
| Body as whole | Asthenia | 1.5 | 2.7 | 1.3 |
| Eye | Dry Eyes | 1.5 | 2.1 | 0.5 |
Other adverse reactions reported by 1% to 2 % of darifenacin extended-release tablets -treated patients include: abnormal vision, accidental injury, back pain, dry skin, flu syndrome, hypertension, vomiting, peripheral edema, weight gain, arthralgia, bronchitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, rash, pruritus, urinary tract disorder and vaginitis.
Study 4 was a randomized, 12-week, placebo-controlled, dose-titration regimen study in which darifenacin extended-release tablet was administered in accordance with dosing recommendations [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. All patients initially received placebo or darifenacin extended-release tablets 7.5 mg daily, and after two weeks, patients and physicians were allowed to adjust upward to darifenacin extended-release tablet 15 mg if needed. In this study, the most commonly reported adverse reactions were also constipation and dry mouth. Table 2 lists the identified adverse reactions, derived from all adverse events reported in greater than 3% of patients treated with darifenacin extended-release tablets and greater than placebo.
| Adverse Reaction
| Darifenacin extended-release
tablet 7.5mg/15 mg N=268 | Placebo
N=127 |
| Constipation | 56 (20.9%) | 10 (7.9% ) |
| Dry Mouth | 50 (18.7%) | 11 (8.7%) |
| Headache | 18 (6.7%) | 7 (5.5% ) |
| Dyspepsia | 12 (4.5%) | 2 (1.6%) |
| Nausea | 11 (4.1%) | 2 (1.6%) |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 10 (3.7%) | 4 (3.1% ) |
| Accidental Injury | 8 (3.0%) | 3 (2.4% ) |
| Flu Syndrome | 8 (3.0% ) | 3 (2.4 %) |
6.2 Post Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of darifenacin extended-release tablets (darifenacin). Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Dermatologic: erythema multiforme, interstitial granuloma annulare
General: hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema with airway obstruction and anaphylactic reaction
Central Nervous: confusion, hallucinations and somnolence
Cardiovascular: palpitations and syncope
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP3A4 Inhibitors
The systemic exposure of darifenacin from darifenacin extended-release tablets is increased in the presence of CYP3A4 inhibitors. The daily dose of darifenacin extended-release tablet should not exceed 7.5 mg when co-administered with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (for example, ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir, nelfinavir, clarithromycin and nefazadone). No dosing adjustments are recommended in the presence of moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (for example, erythromycin, fluconazole, diltiazem and verapamil) [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 CYP2D6 Inhibitors
No dosing adjustments are recommended in the presence of CYP2D6 inhibitors (for example, paroxetine, fluoxetine, quinidine and duloxetine) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 CYP2D6 Substrates
Caution should be taken when darifenacin extended-release tablet is used concomitantly with medications that are predominantly metabolized by CYP2D6 and which have a narrow therapeutic window (for example, flecainide, thioridazine and tricyclic antidepressants) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.4 CYP3A4 Substrates
Darifenacin (30 mg daily) did not have a significant impact on midazolam (7.5 mg) pharmacokinetics [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.5 Combination oral contraceptives
Darifenacin (10 mg three times daily) had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of the combination oral contraceptives containing levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.6 Warfarin
Darifenacin had no significant effect on prothrombin time when a single dose of warfarin 30 mg was co-administered with darifenacin (30 mg daily) at steady-state. Standard therapeutic prothrombin time monitoring for warfarin should be continued.
7.7 Digoxin
Darifenacin (30 mg daily) did not have a clinically relevant effect on the pharmacokinetics of digoxin (0.25 mg) at steady-state. Routine therapeutic drug monitoring for digoxin should be continued [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.8 Other Anticholinergic Agents
The concomitant use of darifenacin extended-release tablets with other anticholinergic agents may increase the frequency and/or severity of dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision and other anticholinergic pharmacological effects. Anticholinergic agents may potentially alter the absorption of some concomitantly administered drugs due to effects on gastrointestinal motility.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
There are no available data on darifenacin use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal studies, darifenacin was not teratogenic in rats and rabbits at plasma exposures of free drug (via AUC) up to 59 and 28 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 15 mg, respectively. Effects on embryofetal development were observed following administration of darifenacin during pregnancy (dilated ureter and/or kidney pelvis in rabbits at about 9 times the MRHD, post-implantation loss in rabbits at about 28 times, and delayed ossification in rats at about 59 times) and during pregnancy and lactation (developmental delays in rats at about 17 times the MRHD), which was associated with maternal toxicity (see Data). Dystocia was observed in rat dams at about 17 times the MRHD.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Embryofetal development studies were conducted with oral darifenacin in female rats (0, 3, 10, and 50 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (0, 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg/day) during the period of organogenesis (gestation days 6 to 17 in the rat and gestation days 6 to 18 in the rabbit).
Darifenacin was not teratogenic in rats and rabbits at plasma exposures of free drug (via AUC) up to 59 times and 28 times, respectively (doses up to 50 and 30 mg/kg/day, respectively) the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of 15 mg.
At approximately 59 times the MRHD in pregnant rats, there was a delay in the ossification of the sacral and caudal vertebrae (associated with a decrease in maternal and pup body weight gains) which was not observed at an exposure approximately 13 times the AUC at the MRHD. At five times the AUC (3 mg/kg/day), there were no effects on dams or pups.
In pregnant rabbits, an exposure of darifenacin approximately 28 times the AUC at the MRHD of 15 mg (30 mg/kg/day) was shown to increase post-implantation loss (associated with decreased maternal body weight gain), with a no effect level at 10 mg/kg/day (9 times the AUC at the MRHD). Dilated ureter and/or kidney pelvis was also observed in offspring at this highest dose along with urinary bladder dilation consistent with the pharmacological action of darifenacin, with one case observed at the mid dose of 10 mg/kg/day (9 times the MRHD). No effect was observed at the lowest dose of 3 mg/kg/day (approximately 2.8 times the AUC at the MRHD).
A pre- and post-natal development study was conducted with oral darifenacin in female rats (0, 3, 10, and 50 mg/kg/day) throughout gestation and lactation. Decreased body weight gain and dystocia were observed in dams at 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 17 times the MRHD) and above. Slight developmental delays (surface righting reflex, incisor eruption, eyelid opening, vaginal opening, preputial separation) were observed in pups at these doses. At 5 times the AUC at the MRHD (3 mg/kg/day), there were no effects on dams or pups.
8.2 Lactation
There are no data on the presence of darifenacin in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects of darifenacin on milk production. Darifenacin is present in rat milk [see Data]. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for darifenacin and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from darifenacin or from the underlying maternal conditions.
Data
After a single oral dose of 14C radiolabeled darifenacin to lactating rats, darifenacin was detected in maternal milk.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of darifenacin extended-release tablets in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the fixed-dose, placebo-controlled, clinical studies, 30% of patients treated with darifenacin extended-release tablets were over 65 years of age. No overall differences in safety or efficacy were observed between patients over 65 years (n = 207) and younger patients less than 65 years (n = 464). No dose adjustment is recommended for elderly patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) have not been studied, therefore darifenacin extended-release tablet is not recommended for use in these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. The daily dose of darifenacin extended-release tablet should not exceed 7.5 mg once daily for patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. After adjusting for plasma protein binding, unbound darifenacin exposure was estimated to be 4.7-fold higher in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment than subjects with normal hepatic function. No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A).
8.7 Renal Impairment
A study of subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment (creatinine clearance between 10 and 136 mL/min) demonstrated no clear relationship between renal function and darifenacin clearance. No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage with antimuscarinic agents, including darifenacin extended-release tablets, can result in severe antimuscarinic effects. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. In the event of overdosage, ECG monitoring is recommended. Darifenacin extended-release tablet has been administered in clinical trials at doses up to 75 mg (five times the maximum therapeutic dose) and signs of overdose were limited to abnormal vision.
11 DESCRIPTION
Darifenacin is an extended-release tablet for oral administration which contains 7.5 mg or 15 mg darifenacin as its hydrobromide salt. The active moiety, darifenacin, is a potent muscarinic receptor antagonist.
Chemically, darifenacin hydrobromide is (S)-2-{1-[2-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)ethyl]-3-pyrrolidinyl}-2,2-diphenylacetamide hydrobromide. The empirical formula of darifenacin hydrobromide is C28H30N2O2•HBr.
The structural formula is:
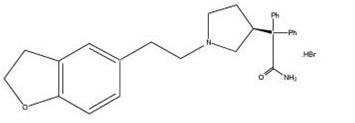
Darifenacin hydrobromide is a white to almost white, crystalline powder, with a molecular weight of 507.5.
Darifenacin is a once-a-day extended-release tablet and contains the following inactive ingredients: dibasic calcium phosphate anhydrous, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide. The 15 mg tablet also contains iron oxide red and iron oxide yellow.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Darifenacin is a competitive muscarinic receptor antagonist. Muscarinic receptors play a role in cholinergically mediated functions, including contractions of the urinary bladder smooth muscle.
In vitro studies using human recombinant muscarinic receptor subtypes show that darifenacin has greater affinity for the M3 receptor than for the other known muscarinic receptors (9- and 12-fold greater affinity for M3 compared to M1 and M5, respectively, and 59-fold greater affinity for M3 compared to both M2 and M4). M3 receptors are involved in contraction of human bladder.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In three cystometric studies performed in patients with involuntary detrusor contractions, increased bladder capacity was demonstrated by an increased volume threshold for unstable contractions and diminished frequency of unstable detrusor contractions after darifenacin extended-release tablets treatment. These findings are consistent with an antimuscarinic action on the urinary bladder.
Electrophysiology
The effect of a six-day treatment of 15 mg and 75 mg darifenacin extended-release tablets on QT/QTc interval was evaluated in a multiple-dose, double-blind, randomized, placebo- and active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) parallel-arm design study in 179 healthy adults (44% male, 56% female) aged 18 to 65. Subjects included 18% poor metabolizers (PMs) and 82% extensive metabolizers (EMs). The QT interval was measured over a 24-hour period both predosing and at steady-state. The 75 mg darifenacin extended-release tablets dose was chosen because this achieves exposure similar to that observed in CYP2D6 poor metabolizers administered the highest recommended dose (15 mg) of darifenacin in the presence of a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor. At the doses studied, darifenacin extended-release tablet did not result in QT/QTc interval prolongation at any time during the steady-state, while moxifloxacin treatment resulted in a mean increase from baseline QTcF of about 7.0 msec when compared to placebo. In this study, darifenacin 15 mg and 75 mg doses demonstrated a mean heart rate change of 3.1 and 1.3 bpm, respectively, when compared to placebo. However, in the clinical efficacy and safety studies, the change in median HR following treatment with darifenacin extended-release tablet was no different from placebo.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
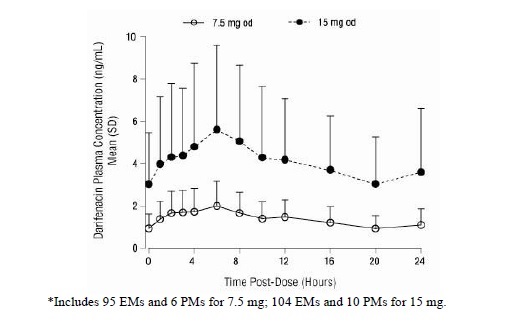
After oral administration of darifenacin extended-release tablets to healthy volunteers, peak plasma concentrations of darifenacin are reached approximately seven hours after multiple dosing and steady-state plasma concentrations are achieved by the sixth day of dosing. The mean (SD) steady-state time course of darifenacin 7.5 mg and 15 mg extended-release tablets is depicted in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Mean (SD) Steady-State Darifenacin Plasma Concentration-Time Profiles for Darifenacin Extended-Release Tablets 7.5 mg and 15 mg in Healthy Volunteers Including Both CYP2D6 EMs and PMs*
A summary of mean (standard deviation, SD) steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters of darifenacin 7.5 mg and 15 mg extended-release tablets in EMs and PMs of CYP2D6 is provided in Table 3.
| Darifenacin extended-release tablets 7.5 mg
(N = 68 EM, 5 PM) | Darifenacin extended-release tablets 15 mg
(N = 102 EM, 17 PM) |
|||||||||
| AUC24 (ng•h/mL)
| Cmax (ng/mL)
| Cavg (ng/mL)
| Tmax
(h) | t1/2
(h) | AUC24 (ng•h/mL)
| Cmax (ng/mL)
| Cavg (ng/mL)
| Tmax
(h) | t1/2
(h) |
|
| EM
| 29.24 (15.47) | 2.01 (1.04) | 1.22 (0.64) | 6.49 (4.19) | 12.43 (5.64)a
| 88.90 (67.87) | 5.76 (4.24) | 3.70 (2.83) | 7.61 (5.06) | 12.05 (12.37)b
|
| PM
| 67.56 (13.13) | 4.27 (0.98) | 2.81 (0.55) | 5.20 (1.79) | 19.95c
- | 157.71 (77.08) | 9.99 (5.09) | 6.58 (3.22) | 6.71 (3.58) | 7.40d
- |
| aN = 25; bN = 8; cN = 2; dN = 1; AUC24 = Area under the plasma concentration versus time curve for 24h; |
||||||||||
| Cmax = Maximum observed plasma concentration; Cavg = Average plasma concentration at steady-state; |
||||||||||
| Tmax = Time of occurrence of Cmax; t1/2 = Terminal elimination half-life. Regarding EM and PM [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics, Variability in Metabolism (12.3)].
|
||||||||||
The mean oral bioavailability of darifenacin extended-release tablets in EMs at steady-state is estimated to be 15% and 19% for 7.5 mg and 15 mg tablets, respectively.
Effect of Food
Following single dose administration of darifenacin extended-release tablets with food, the AUC of darifenacin was not affected, while the Cmax was increased by 22% and Tmax was shortened by 3.3 hours. There is no effect of food on multiple-dose pharmacokinetics from darifenacin extended-release tablets.
Distribution
Darifenacin is approximately 98% bound to plasma proteins (primarily to alpha-1-acid-glycoprotein). The steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) is estimated to be 163 L.
Metabolism
Darifenacin is extensively metabolized by the liver following oral dosing.
Metabolism is mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP2D6 and CYP3A4. The three main metabolic routes are as follows:
(i) monohydroxylation in the dihydrobenzofuran ring;
(ii) dihydrobenzofuran ring opening;
(iii) N-dealkylation of the pyrrolidine nitrogen.
The initial products of the hydroxylation and N-dealkylation pathways are the major circulating metabolites but they are unlikely to contribute significantly to the overall clinical effect of darifenacin.
Variability in Metabolism
A subset of individuals (approximately 7% Caucasians and 2% African Americans) are poor metabolizers (PMs) of CYP2D6 metabolized drugs. Individuals with normal CYP2D6 activity are referred to as extensive metabolizers (EMs). The metabolism of darifenacin in PMs will be principally mediated via CYP3A4. The darifenacin ratios (PM versus EM) for Cmax and AUC following darifenacin 15 mg once daily at steady-state were 1.9 and 1.7, respectively.
Excretion
Following administration of an oral dose of 14C-darifenacin solution to healthy volunteers, approximately 60% of the radioactivity was recovered in the urine and 40% in the feces. Only a small percentage of the excreted dose was unchanged darifenacin (3%). Estimated darifenacin clearance is 40 L/h for EMs and 32 L/h for PMs. The elimination half-life of darifenacin following chronic dosing is approximately 13 to 19 hours.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Effects of Other Drugs on Darifenacin
Darifenacin metabolism is primarily mediated by the cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP2D6 and CYP3A4. Therefore, inducers of CYP3A4 or inhibitors of either of these enzymes may alter darifenacin pharmacokinetics [see Drug Interactions (7)].
CYP3A4 Inhibitors: In a drug interaction study, when a 7.5 mg once daily dose of darifenacin extended-release tablet was given to steady-state and co-administered with the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole 400 mg, mean darifenacin Cmax increased to 11.2 ng/mL for EMs (n = 10) and 55.4 ng/mL for one PM subject (n = 1). Mean AUC increased to 143 and 939 ng•h/mL for EMs and for one PM subject, respectively. When a 15 mg daily dose of darifenacin extended-release tablet was given with ketoconazole, mean darifenacin Cmax increased to 67.6 ng/mL and 58.9 ng/mL for EMs (n = 3) and one PM subject (n = 1), respectively. Mean AUC increased to 1110 and 931 ng•h/mL for EMs and for one PM subject, respectively [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)].
The mean Cmax and AUC of darifenacin following 30 mg once daily dosing at steady-state were 128% and 95% higher, respectively, in the presence of a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor, erythromycin. Co-administration of fluconazole, a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor and darifenacin 30 mg once daily at steady-state increased darifenacin Cmax and AUC by 88% and 84%, respectively [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
The mean Cmax and AUC of darifenacin following 30 mg once daily at steady-state were 42% and 34% higher, respectively, in the presence of cimetidine, a mixed CYP P450 enzyme inhibitor.
CYP2D6 Inhibitors: Darifenacin exposure following 30 mg once daily at steady-state was 33% higher in the presence of the potent CYP2D6 inhibitor paroxetine 20 mg [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Effects of Darifenacin on Other Drugs
In Vitro Studies: Based on in vitro human microsomal studies, darifenacin extended-release tablet is not expected to inhibit CYP1A2 or CYP2C9 at clinically relevant concentrations.
In Vivo Studies: The potential for clinical doses of darifenacin extended-release tablets to act as inhibitors of CYP2D6 or CYP3A4 substrates was investigated in specific drug interaction studies.
CYP2D6 Substrates: The mean Cmax and AUC of imipramine, a CYP2D6 substrate, were increased by 57% and 70%, respectively, in the presence of steady-state darifenacin 30 mg once daily. The mean Cmax and AUC of desipramine, the active metabolite of imipramine, were increased by 260% [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
CYP3A4 Substrates: Darifenacin (30 mg daily) co-administered with a single oral dose of midazolam 7.5 mg resulted in a 17 % increase in midazolam exposure.
Combination Oral Contraceptives: Darifenacin (10 mg three times daily) had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of a combination oral contraceptive containing levonorgestrel (0.15 mg) and ethinyl estradiol (0.03 mg).
Warfarin: Darifenacin had no significant effect on prothrombin time when a single dose of warfarin 30 mg was co-administered with darifenacin (30 mg daily) at steady-state [see Drug Interactions (7.6)].
Digoxin: Darifenacin (30 mg daily) co-administered with digoxin (0.25 mg) at steady-state resulted in a 16% increase in digoxin exposure [see Drug Interactions (7.7)].
Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations
Age: A population pharmacokinetic analysis of patient data indicated a trend for clearance of darifenacin to decrease with age (6% per decade relative to a median age of 44). Following administration of darifenacin extended-release tablet 15 mg once daily, darifenacin exposure at steady-state was approximately 12% to 19% higher in volunteers between 45 and 65 years of age compared to younger volunteers aged 18 to 44 years [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Pediatric: The pharmacokinetics of darifenacin extended-release tablets has not been studied in the pediatric population [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Gender: PK parameters were calculated for 22 male and 25 female healthy volunteers. Darifenacin Cmax and AUC at steady-state were approximately 57% to 79% and 61% to 73% higher in females than in males, respectively [see Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
Renal Impairment: A study of subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment (creatinine clearance between 10 and 136 mL/min) given darifenacin extended-release tablets 15 mg once daily to steady-state demonstrated no clear relationship between renal function and darifenacin clearance [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Hepatic Impairment: Darifenacin extended-release tablets pharmacokinetics were investigated in subjects with mild (Child-Pugh A) or moderate (Child-Pugh B) impairment of hepatic function given darifenacin extended-release tablets 15 mg once daily to steady-state. Mild hepatic impairment had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of darifenacin. However, protein binding of darifenacin was affected by moderate hepatic impairment. After adjusting for plasma protein binding, unbound darifenacin exposure was estimated to be 4.7-fold higher in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment than subjects with normal hepatic function. Subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) have not been studied [see Dosage and Administration (2), Warning and Precautions (5.5) and Use in Specific Population (8.6)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with darifenacin were conducted in mice and rats. No evidence of drug-related carcinogenicity was revealed in a 24-month study in mice at dietary doses up to 100 mg/kg/day or approximately 32 times the estimated free plasma AUC reached at the maximum recommended human dose (the AUC at the MRHD) of 15 mg and in a 24-month study in rats at doses up to 15 mg/kg/day or up to approximately 12 times the AUC at the MRHD in female rats and approximately eight times the AUC at the MRHD in male rats.
Mutagenesis
Darifenacin was not genotoxic in the bacterial mutation assay (Ames test), the Chinese hamster ovary assay, the human lymphocyte assay, or the in vivo mouse bone marrow cytogenetics assay.
Impairment of Fertility
There was no evidence for effects on fertility in male or female rats treated at oral doses associated with up to approximately 78 times (50 mg/kg/day) the AUC at the MRHD.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Darifenacin extended-release tablets were evaluated for the treatment of patients with overactive bladder with symptoms of urgency, urge urinary incontinence, and increased urinary frequency in three randomized, fixed-dose, placebo-controlled, multicenter, double-blind, 12-week studies (Studies 1, 2 and 3) and one randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, dose-titration study (Study 4). For study eligibility in all four studies, patients with symptoms of overactive bladder for at least six months were required to demonstrate at least eight micturitions and at least one episode of urinary urgency per day, and at least five episodes of urge urinary incontinence per week. The majority of patients were white (94%) and female (84%), with a mean age of 58 years, range 19 to 93 years. Thirty-three percent of patients were greater than or equal to 65 years of age. These characteristics were well balanced across treatment groups. The study population was inclusive of both naïve patients who had not received prior pharmacotherapy for overactive bladder (60%) and those who had (40%).
Table 4 shows the efficacy data collected from 7- or 14-day voiding diaries in the three fixed-dose placebo-controlled studies of 1,059 patients treated with placebo, 7.5 mg or 15 mg once daily darifenacin extended-release tablet for 12 weeks. A significant decrease in the primary endpoint, change from baseline in average weekly urge urinary incontinence episodes was observed in all three studies. Data is also shown for two secondary endpoints, change from baseline in the average number of micturitions per day (urinary frequency) and change from baseline in the average volume voided per micturition.
|
*Indicates statistically significant difference versus placebo (p less than 0.05, Wilcoxon rank-sum test) |
||||||||
| Study 1
| Study 2
| Study 3
| ||||||
| Darifenacin extended-release tablet
7.5 mg | Darifenacin extended-release tablet
15 mg | Placebo
| Darifenacin extended-release tablet
7.5 mg | Darifenacin extended-release tablet
15 mg | Placebo
| Darifenacin extended-release tablet
15 mg | Placebo
|
|
| No. of Patients Entered
| 229 | 115 | 164 | 108 | 107 | 109 | 112 | 115 |
| Urge Incontinence Episodes per Week
|
||||||||
| Median Baseline | 16.3 | 17.0 | 16.6 | 14.0 | 17.3 | 16.1 | 16.2 | 15.5 |
| Median Change from Baseline | -9.0 | -10.4 | -7.6 | -8.1 | -10.4 | -5.9 | -11.4 | -9.0 |
| Median Difference to Placebo | -1.5* | -2.1* | - | -2.8* | -4.3* | - | -2.4* | - |
| Micturitions per Day
|
||||||||
| Median Baseline | 10.1 | 10.1 | 10.1 | 10.3 | 11.0 | 10.1 | 10.5 | 10.4 |
| Median Change from Baseline | -1.6 | -1.7 | -0.8 | -1.7 | -1.9 | -1.1 | -1.9 | -1.2 |
| Median Difference to Placebo | -0.8* | -0.9* | - | -0.5 | -0.7* | - | -0.5 | - |
| Volume of Urine Passed per Void (mL)
|
||||||||
| Median Baseline | 160.2 | 151.8 | 162.4 | 161.7 | 157.3 | 162.2 | 155.0 | 147.1 |
| Median Change from Baseline | 14.9 | 30.9 | 7.6 | 16.8 | 23.6 | 7.1 | 26.7 | 4.6 |
| Median Difference to Placebo | 9.1* | 20.7* | - | 9.2 | 16.6* | - | 20.1* | - |
Table 5 shows the efficacy data from the dose-titration study in 395 patients who initially received 7.5 mg darifenacin extended-release tablets or placebo daily with the option to increase to 15 mg darifenacin extended-release tablets or placebo daily after two weeks.
|
*Indicates statistically significant difference versus placebo (p less than 0.05, Wilcoxon rank-sum test) |
||
| Darifenacin extended-release tablet
7.5 mg /15 mg | Placebo
|
|
| No. of Patients Treated
| 268 | 127 |
| Urge Incontinence Episodes per Week
|
||
| Median Baseline | 16.0 | 14.0 |
| Median Change from Baseline | -8.2 | -6.0 |
| Median Difference to Placebo | -1.4* | - |
| Micturitions per Day
|
||
| Median Baseline | 9.9 | 10.4 |
| Median Change from Baseline | -1.9 | -1.0 |
| Median Difference to Placebo | -0.8* | - |
| Volume of Urine Passed per Void (mL)
|
||
| Median Baseline | 173.7 | 177.2 |
| Median Change from Baseline | 18.8 | 6.6 |
| Median Difference to Placebo | 13.3* | - |
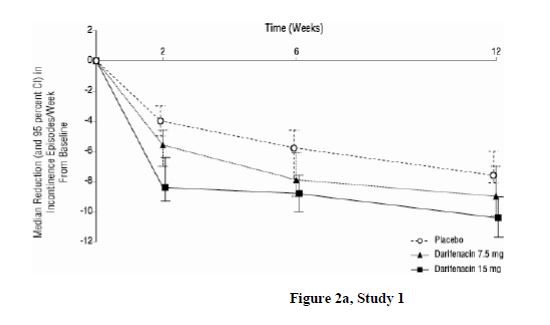
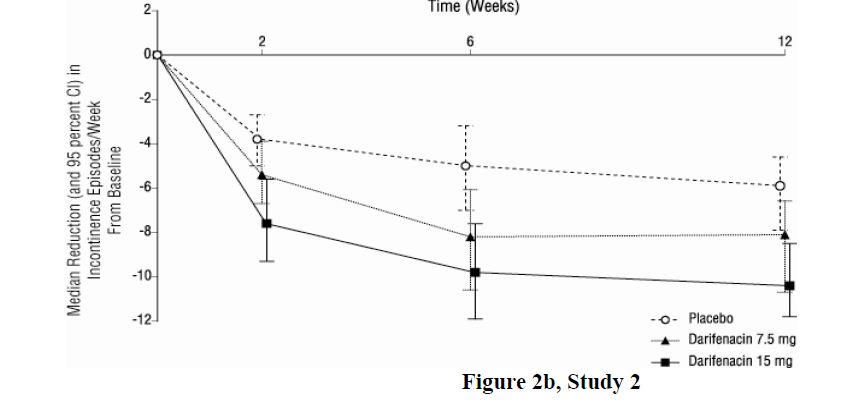
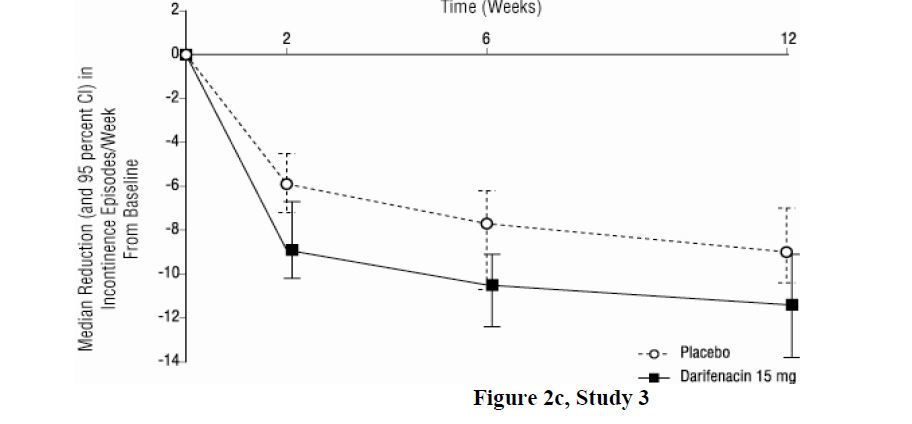
As seen in Figures 2 a, 2b and 2c, reductions in the number of urge incontinence episodes per week were observed within the first two weeks in patients treated with darifenacin extended-release tablets 7.5 mg and 15 mg once daily compared to placebo. Further, these effects were sustained throughout the 12-week treatment period.
Figures 2a, 2b, 2c. Median Change from Baseline at Weeks 2, 6, 12 for Number of Urge Incontinence Episodes per Week (Studies 1, 2 and 3)
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Darifenacin extended-release tablet 7.5 mg are white to off white colored circular biconvex film coated tablet debossed with "C" on one side and "431" on the other side.
Bottle of 30 ...............................................................................................................NDC 69097-431-02
Bottle of 90 ...............................................................................................................NDC 69097-431-05
Bottle of 1000 ...........................................................................................................NDC 69097-431-15
Darifenacin extended-release tablet 15 mg are light peach colored circular biconvex film coated tablet debossed with "C" on one side and "432" on the other side.
Bottle of 30................................................................................................................NDC 69097-432-02
Bottle of 90................................................................................................................NDC 69097-432-05
Bottle of 1000 ...........................................................................................................NDC 69097-432-15
Storage
Store at 25° C (77° F); excursions permitted between 15° C to 30° C (59° F to 86° F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light.
Keep this and all drugs out of the reach of children.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Patients should be informed that anticholinergic agents, such as darifenacin extended-release tablets, may produce clinically significant adverse effects related to anticholinergic pharmacological activity including constipation, urinary retention and blurred vision. Heat prostration (due to decreased sweating) can occur when anticholinergics such as darifenacin extended-release tablets are used in a hot environment. Because anticholinergics, such as darifenacin extended-release tablets, may produce dizziness or blurred vision, patients should be advised to exercise caution in decisions to engage in potentially dangerous activities until the drug's effects have been determined. Patients should read the patient information leaflet before starting therapy with darifenacin extended-release tablets.
Patients should be informed that darifenacin may produce clinically significant angioedema that may result in airway obstruction. Patients should be advised to promptly discontinue darifenacin therapy and seek immediate medical attention if they experience edema of the tongue or laryngopharynx, or difficulty breathing.
Darifenacin extended-release tablets should be taken once daily with water. They may be taken with or without food, and should be swallowed whole and not chewed, divided or crushed.
Manufactured by:
Cipla Ltd.
MIDC Patalganga, India
Manufactured for:
Cipla USA, Inc.
10 Independence Boulevard, Suite 300
Warren, NJ 07059
Revised: 7/2021
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
Darifenacin Extended-Release Tablets
Read this Patient Information leaflet about darifenacin extended-release tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What are darifenacin extended-release tablets?
Darifenacin extended-release tablets are prescription medicine for adults used to treat the following symptoms due to a condition called overactive bladder:
- Urge urinary incontinence: a strong need to urinate with leaking or wetting accidents
- Urgency: a strong need to urinate right away
- Frequency: urinating often
It is unknown if darifenacin extended-release tablets are safe and effective in children.
Who should not take darifenacin extended-release tablets?
Do not take darifenacin extended-release tablets if you:
- are not able to empty your bladder ("urinary retention")
- have delayed or slow emptying of your stomach ("gastric retention")
- have an eye problem called "uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma"
What should I tell my healthcare provider before starting darifenacin extended-release tablets?
Before starting darifenacin extended-release tablets, tell your doctor if you:
- have trouble emptying your bladder or if you have a weak urine stream
- have any stomach or intestinal problems, or problems with constipation
- have liver problems
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant. It is not known if darifenacin extended-release tablets can harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if darifenacin passes into breast milk and if it can harm your baby. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take darifenacin extended-release tablets.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Darifenacin extended-release tablets and certain other medicines may affect each other, causing side effects.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take a:
- antifungal medicine ketoconazole (Nizoral®) or itraconazole (Sporanox®)
- antibiotic medicine clarithromycin (Biaxin®)
- anti-HIV medicine ritonavir (Norvir®) or nelfinavir (Viracept®)
- medicine to treat depression nefazadone (Serzone®)
- medicine to treat an abnormal heartbeat flecainide (Tambocor®)
- antipsychotic medicine thioridazine (Mellaril®)
- medicine to treat depression called a tricyclic antidepressant
Know all the medicines you take. Keep a list of them with you to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take darifenacin extended-release tablets?
- Take darifenacin extended-release tablets exactly as prescribed. Your doctor will prescribe the dose that is right for you. Take darifenacin extended-release tablets 1 time daily with water.
- Darifenacin extended-release tablets should be swallowed whole. Do not chew, cut or crush darifenacin extended-release tablets.
- Darifenacin extended-release tablets may be taken with or without food.
- If you take too much darifenacin extended-release tablets call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking darifenacin extended-release tablets?
Darifenacin extended-release tablets can cause blurred vision or dizziness. Do not drive or operate heavy machinery until you know how darifenacin extended-release tablets affects you.
What are the possible side effects of darifenacin extended-release tablets?
Darifenacin extended-release tablets may cause serious side effects including:
-
Serious allergic reaction. Stop taking darifenacin extended-release tablets and get medical help right away if you have:
- hives, skin rash or swelling
- severe itching
- swelling of your face, mouth or tongue
- trouble breathing
The most common side effects with darifenacin extended-release tablets are:
- constipation
- dry mouth
- headache
- heartburn
- nausea
- urinary tract infection
- blurred vision
- heat exhaustion or heat-stroke. This can happen when darifenacin extended-release tablet is used in hot environments.
Symptoms of heat exhaustion may include:
- decreased sweating
- dizziness
- tiredness
- nausea
- increase body temperature
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of darifenacin extended-release tablets. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How do I store darifenacin extended-release tablets?
- Store darifenacin extended-release tablet at room temperature, between 59° F to 86° F (15° C to 30° C).
- Keep darifenacin extended-release tablet out of the light.
Keep darifenacin extended-release tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about darifenacin extended-release tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use darifenacin extended-release tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give darifenacin extended-release tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about darifenacin extended-release tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about darifenacin extended-release tablets that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in darifenacin extended-release tablets?
Active ingredient: darifenacin
Inactive ingredients: dibasic calcium phosphate anhydrous, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, talc, titanium dioxide.
The 15 mg tablet also contains iron oxide red and iron oxide yellow.
The brands listed are the trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Cipla Limited.
Manufactured by:
Cipla Ltd.
MIDC Patalganga, India
Manufactured for:
Cipla USA, Inc.
10 Independence Boulevard, Suite 300
Warren, NJ 07059
Revised: 2/2020

