FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
RYTARY is indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, post-encephalitic parkinsonism, and parkinsonism that may follow carbon monoxide intoxication or manganese intoxication.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage in Patients Naïve to Levodopa Therapy
The recommended starting dosage of RYTARY in levodopa-naïve patients is 23.75 mg / 95 mg taken orally three times a day for the first 3 days. On the fourth day of treatment, the dosage of RYTARY may be increased to 36.25 mg / 145 mg taken three times a day.
Based upon individual patient clinical response and tolerability, the RYTARY dose may be increased up to a maximum recommended dose of 97.5 mg / 390 mg taken three times a day. The dosing frequency may be changed from three times a day to a maximum of five times a day if more frequent dosing is needed and if tolerated.
Maintain patients on the lowest dosage required to achieve symptomatic control and to minimize adverse reactions such as dyskinesia and nausea. The maximum recommended daily dose of RYTARY is 612.5 mg / 2450 mg.
2.2 Converting from Immediate-Release Carbidopa-Levodopa to RYTARY
The dosages of other carbidopa and levodopa products are not interchangeable on a 1:1 basis with the dosages of RYTARY.
To convert patients from immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa to RYTARY, first calculate the patient’s current total daily dose of levodopa. The starting total daily dose of RYTARY is as recommended in Table 1.
After conversion, any combination of the four RYTARY dosage strengths can be used to achieve an optimal dosing. Adjust the dose and dosing frequency as necessary to maintain patient tolerance and sufficient symptomatic control. Administration of concomitant Parkinson’s disease medications should remain stable while adjusting the RYTARY dose. In clinical trials, RYTARY was administered in divided doses of three to five times a day. The maximum recommended total daily dose of RYTARY is 612.5 mg / 2,450 mg.
For patients currently treated with carbidopa and levodopa plus a catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) inhibitor (such as entacapone), the initial total daily dose of levodopa in RYTARY described in Table 1 may need to be increased.
Use of RYTARY in combination with other levodopa products has not been studied.
Table 1: Conversion from Immediate-Release Carbidopa-Levodopa to RYTARY
|
Total Daily Dose of Levodopa in Immediate-Release Carbidopa-Levodopa |
Recommended Starting Dosage of RYTARY |
|
|
Total Daily Dose of Levodopa in RYTARY |
RYTARY Dosing Regimen |
|
|
400 mg to 549 mg |
855 mg |
3 capsules RYTARY 23.75 mg / 95 mg taken TIDa |
|
550 mg to 749 mg |
1,140 mg |
4 capsules RYTARY 23.75 mg / 95 mg taken TID |
|
750 mg to 949 mg |
1,305 mg |
3 capsules RYTARY 36.25 mg / 145 mg taken TID |
|
950 mg to 1,249 mg |
1,755 mg |
3 capsules RYTARY 48.75 mg / 195 mg taken TID |
|
Equal to or greater than 1,250 mg |
2,340 mg or |
4 capsules RYTARY 48.75 mg / 195 mg taken TID or |
|
2,205 mg |
3 capsules RYTARY 61.25 mg / 245 mg taken TID |
|
a TID: three times a day
2.3 Discontinuation of RYTARY
Avoid sudden discontinuation or rapid dose reduction of RYTARY. The daily dose of RYTARY should be tapered at the time of treatment discontinuation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.4 Administration Information
Swallow RYTARY whole with or without food. A high-fat, high-calorie meal may delay the absorption of levodopa by about 2 hours [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Do not chew, divide or crush RYTARY capsules. For patients who have difficulty swallowing intact capsules, administer RYTARY by carefully twisting apart both halves of the capsule. Sprinkle the entire contents of both halves of the capsule on a small amount of applesauce (1 to 2 tablespoons) and consume the mixture immediately. Do not store the drug/food mixture for future use.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Extended-release capsules:
- 23.75 mg carbidopa and 95 mg levodopa: blue and white capsule imprinted with IPX066 on the capsule cap and 95 on the capsule body
- 36.25 mg carbidopa and 145 mg levodopa: blue and light blue capsule imprinted with IPX066 on the capsule cap and 145 on the capsule body
- 48.75 mg carbidopa and 195 mg levodopa: blue and yellow capsule imprinted with IPX066 on the capsule cap and 195 on the capsule body
- 61.25 mg carbidopa and 245 mg levodopa: blue capsule imprinted with IPX066 on the capsule cap and 245 on the capsule body
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
RYTARY is contraindicated in patients:
- Currently taking a nonselective monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor (e.g., phenelzine and tranylcypromine) or have recently (within 2 weeks) taken a nonselective MAO inhibitor. Hypertension can occur if these drugs are used concurrently [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence
Patients treated with levodopa, a component of RYTARY, have reported falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living, including the operation of motor vehicles, which sometimes resulted in accidents. Although many of these patients reported somnolence while on levodopa, some perceived that they had no warning signs (sleep attack), such as excessive drowsiness, and believed that they were alert immediately prior to the event. Some of these events have been reported more than 1 year after initiation of treatment.
It has been reported that falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living usually occurs in a setting of pre-existing somnolence, although patients may not give such a history. For this reason, prescribers should reassess patients for drowsiness or sleepiness in RYTARY-treated patients, especially since some of the events occur well after the start of treatment. Prescribers should also be aware that patients may not acknowledge drowsiness or sleepiness until directly questioned about drowsiness or sleepiness during specific activities.
Before initiating treatment with RYTARY, advise patients of the potential to develop drowsiness and specifically ask about factors that may increase the risk for somnolence with RYTARY such as concomitant sedating medications or the presence of a sleep disorder. Consider discontinuing RYTARY in patients who report significant daytime sleepiness or episodes of falling asleep during activities that require active participation (e.g., conversations, eating, etc.).
If a decision is made to continue RYTARY, patients should be advised not to drive and to avoid other potentially dangerous activities that might result in harm if the patients become somnolent. There is insufficient information to establish that dose reduction will eliminate episodes of falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living.
5.2 Withdrawal-Emergent Hyperpyrexia and Confusion
A symptom complex that resembles neuroleptic malignant syndrome (characterized by elevated temperature, muscular rigidity, altered consciousness, and autonomic instability), with no other obvious etiology, has been reported in association with rapid dose reduction, withdrawal of, or changes in dopaminergic therapy. Avoid sudden discontinuation or rapid dose reduction in patients taking RYTARY. If the decision is made to discontinue RYTARY, the dose should be tapered to reduce the risk of hyperpyrexia and confusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Cardiovascular Ischemic Events
Cardiovascular ischemic events have occurred in patients taking RYTARY. In a placebo controlled clinical study in patients with early Parkinson's disease, 7/289 (2.4%) of RYTARY-treated patients experienced cardiovascular ischemic adverse reactions compared to 1/92 (1.1%) of placebo-treated patients. In an active-controlled clinical study in patients with advanced Parkinson's disease, 3/450 (0.7%) of RYTARY-treated patients experienced cardiovascular ischemic adverse reactions compared to 0/471 oral immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa-treated patients. These patients all had a previous history of ischemic heart disease or risk factors for ischemic heart disease.
In patients with a history of myocardial infarction who have residual atrial, nodal, or ventricular arrhythmias, cardiac function should be monitored in an intensive cardiac care facility during the period of initial dosage adjustment.
5.4 Hallucinations/Psychosis
There is an increased risk for hallucinations and psychosis in patients taking RYTARY. In a controlled clinical trial in patients with advanced Parkinson's disease, 9/201 (4%) of RYTARY-treated patients reported hallucinations or psychosis compared to 2/192 (1%) of oral immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa-treated patients.
Hallucinations present shortly after the initiation of therapy and may be responsive to dose reduction in levodopa. Hallucinations may be accompanied by confusion, insomnia, and excessive dreaming. Abnormal thinking and behavior may present with one or more symptoms, including paranoid ideation, delusions, hallucinations, confusion, psychotic-like behavior, disorientation, aggressive behavior, agitation, and delirium.
Because of the risk of exacerbating psychosis, patients with a major psychotic disorder should not be treated with RYTARY. In addition, medications that antagonize the effects of dopamine used to treat psychosis may exacerbate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease and may decrease the effectiveness of RYTARY [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.5 Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors
Case reports suggest that patients can experience intense urges to gamble, increased sexual urges, intense urges to spend money, binge eating, and/or other intense urges, and the inability to control these urges while taking one or more of the medications, including RYTARY, that increase central dopaminergic tone and that are generally used for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. In some cases, although not all, these urges were reported to have stopped when the dose was reduced or the medication was discontinued.
Because patients may not recognize these behaviors as abnormal, it is important for prescribers to specifically ask patients or their caregivers about the development of new or increased gambling urges, sexual urges, uncontrolled spending or other urges while being treated with RYTARY. Consider a dose reduction or stopping the medication if a patient develops such urges while taking RYTARY.
5.6 Dyskinesia
RYTARY can cause dyskinesias that may require a dosage reduction of RYTARY or other medications used for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Withdrawal-Emergent Hyperpyrexia and Confusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cardiovascular Ischemic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hallucinations/Psychosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Peptic Ulcer Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety population consisted of a total of 978 Parkinson’s disease patients who received at least one dose of RYTARY, and had an average duration of exposure of 40 weeks.
Adverse Reactions in Early Parkinson’s Disease
In a placebo-controlled clinical study in patients with early Parkinson’s disease (Study 1), the most common adverse reactions with RYTARY (in at least 5% of patients and more frequently than in placebo) were nausea, dizziness, headache, insomnia, abnormal dreams, dry mouth, dyskinesia, anxiety, constipation, vomiting, and orthostatic hypotension.
Table 2 lists adverse reactions occurring in at least 5% of RYTARY-treated patients and at a higher rate than placebo in Study 1.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions in Study 1 in Patients with Early Stage Parkinson’s Disease
| Placebo | RYTARY 36.25 mg Carbidopa 145 mg Levodopa TID | RYTARY 61.25 mg Carbidopa 245 mg Levodopa TID | RYTARY 97.5 mg Carbidopa 390 mg Levodopa TID | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N=92) % | (N=87) % | (N=104) % | (N=98) % | |
|
Nausea |
9 |
14 |
19 |
20 |
|
Dizziness |
5 |
9 |
19 |
12 |
|
Headache |
11 |
7 |
13 |
17 |
|
Insomnia |
3 |
2 |
9 |
6 |
|
Abnormal Dreams |
0 |
2 |
6 |
5 |
|
Dry Mouth |
1 |
3 |
2 |
7 |
|
Dyskinesia |
0 |
2 |
4 |
5 |
|
Anxiety |
0 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
|
Constipation |
1 |
2 |
6 |
2 |
|
Vomiting |
3 |
2 |
2 |
5 |
|
Orthostatic Hypotension |
1 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation in Study 1
In Study 1, 12% of patients discontinued RYTARY early due to adverse reactions; a higher proportion of patients in the 61.25 mg / 245 mg RYTARY-treated group (14%) and in the 97.5 mg / 390 mg RYTARY-treated group (15%) experienced adverse reactions leading to early discontinuation compared to (4%) in the placebo group. The most common adverse reactions resulting in early discontinuation were nausea, dizziness, and vomiting.
Adverse Reactions in Advanced Parkinson’s Disease
In an active-controlled clinical study in patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease (Study 2), the most common adverse reactions with RYTARY that occurred during dose conversion or maintenance (in at least 5% of patients and more frequently than on oral immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa) were nausea and headache.
Table 3 lists adverse reactions occurring in at least 5% of RYTARY-treated patients and at a higher rate than oral immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa in Study 2.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions in Study 2 in Patients with Advanced Parkinson’s Disease
| RYTARY (N=201) | Immediate-Release Carbidopa-Levodopa (N=192) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | Dose Conversiona % | Maintenance % | Dose Conversiona % | Maintenance % |
|
Nausea |
4 |
3 |
6 |
2 |
|
Headache |
5 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
a All patients were converted to RYTARY in the open-label Dose Conversion period and then received randomized treatment during maintenance.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation in Study 2
In Study 2, 5% of patients discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions during conversion to RYTARY. The common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation during dose conversion were dyskinesia, anxiety, dizziness, and on and off phenomenon.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of RYTARY. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish causal relationship to RYTARY exposure.
Psychiatric: Suicide attempt, suicidal ideation.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors
The use of nonselective MAO inhibitors with RYTARY is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. Discontinue use of any nonselective MAO inhibitors at least two weeks prior to initiating RYTARY.
The use of selective MAO-B inhibitors (e.g., rasagiline and selegiline) with RYTARY may be associated with orthostatic hypotension. Monitor patients who are taking these drugs concurrently.
7.2 Dopamine D2 Receptor Antagonists and Isoniazid
Dopamine D2 receptor antagonists (e.g., phenothiazines, butyrophenones, risperidone, metoclopramide) and isoniazid may reduce the effectiveness of levodopa. Monitor patients for worsening Parkinson's symptoms.
7.3 Iron Salts
Iron salts or multivitamins containing iron salts can form chelates with levodopa and carbidopa and can cause a reduction in the bioavailability of RYTARY. If iron salts or multivitamins containing iron salts are co-administered with RYTARY, monitor patients for worsening Parkinson's symptoms.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of RYTARY in pregnant women. In animal studies, carbidopa-levodopa has been shown to be developmentally toxic (including teratogenic effects) at clinically relevant doses (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
When administered to pregnant rabbits throughout organogenesis, carbidopa-levodopa caused both visceral and skeletal malformation in fetuses at all doses and ratios of carbidopa-levodopa tested. No teratogenic effects were observed when carbidopa-levodopa was administered to pregnant mice throughout organogenesis.
There was a decrease in the number of live pups delivered by rats receiving carbidopa-levodopa during organogenesis
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Levodopa has been detected in human milk after administration of carbidopa-levodopa. There are no data on the presence of carbidopa in human milk, the effects of levodopa or carbidopa on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, inhibition of lactation may occur because levodopa decreases secretion of prolactin in humans. Carbidopa is excreted in rat milk.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for RYTARY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from RYTARY or from the underlying maternal condition.
10 OVERDOSAGE
In the active-controlled clinical study, a patient accidentally ingested 4.68 grams of carbidopa/18.7 grams of levodopa contained in RYTARY over a 2-day period. The patient experienced acute psychosis and dyskinesias. The patient recovered and completed the study on a reduced dose of RYTARY.
Based on the limited available information, the acute symptoms of levodopa/dopa decarboxylase inhibitor overdosage can be expected to arise from dopaminergic overstimulation. Doses of a few grams may result in CNS disturbances, with an increasing likelihood of cardiovascular disturbance (e.g., hypotension, tachycardia) and more severe psychiatric problems at higher doses. An isolated report of rhabdomyolysis and another of transient renal insufficiency suggest that levodopa overdosage may give rise to systemic complications, secondary to dopaminergic overstimulation.
Monitor patients and provide supportive care. Patients should receive electrocardiographic monitoring for the development of arrhythmias; if needed, appropriate antiarrhythmic therapy should be given. The possibility that the patient may have taken other drugs, increasing the risk of drug interactions (especially catechol-structured drugs) should be taken into consideration.
11 DESCRIPTION
RYTARY is a combination of carbidopa, an inhibitor of aromatic amino acid decarboxylation, and levodopa, an aromatic amino acid, in extended-release capsules for oral use.
Carbidopa is a white, crystalline compound, slightly soluble in water, with a molecular weight of 244.3. It is designated chemically as (–)-L-α-hydrazino-α-methyl-β-(3,4-dihydroxy-benzene) propanoic acid monohydrate. Its molecular formula is C10H14N2O4∙H2O and its structural formula is:
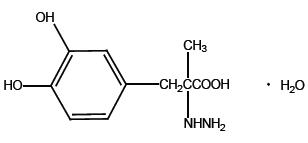
Capsule content is expressed in terms of anhydrous carbidopa, which has a molecular weight of 226.3.
Levodopa is a white, crystalline compound, slightly soluble in water, with a molecular weight of 197.2. It is designated chemically as (–)-L-α-amino-β-(3,4-dihydroxybenzene) propanoic acid. Its molecular formula is C9H11NO4 and its structural formula is:
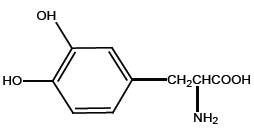
Each extended-release capsule contains 23.75 mg carbidopa and 95 mg levodopa, 36.25 mg carbidopa and 145 mg levodopa, 48.75 mg carbidopa and 195 mg levodopa, or 61.25 mg carbidopa and 245 mg levodopa. The inactive ingredients are microcrystalline cellulose, mannitol, tartaric acid, ethyl cellulose, hypromellose, sodium starch glycolate, sodium lauryl sulfate, povidone, talc, methacrylic acid copolymers, triethyl citrate, croscarmellose sodium, and magnesium stearate.
The capsule shells all contain gelatin and titanium dioxide. All blue capsule components contain FD&C Blue #2 and yellow iron oxide. All yellow capsule components contain yellow iron oxide. All capsules with black imprinting contain iron oxide black. All capsules with blue imprinting contain FD&C Blue #2.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Carbidopa
When levodopa is administered orally, it is rapidly decarboxylated to dopamine in extracerebral tissues so that only a small portion of a given dose is transported unchanged to the central nervous system. Carbidopa inhibits the decarboxylation of peripheral levodopa, making more levodopa available for delivery to the brain.
Levodopa
Levodopa is the metabolic precursor of dopamine, does cross the blood-brain barrier, and presumably is converted to dopamine in the brain. This is thought to be the mechanism whereby levodopa relieves symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Because its decarboxylase inhibiting activity is limited to extracerebral tissues, administration of carbidopa with levodopa makes more levodopa available to the brain. The addition of carbidopa to levodopa reduces the peripheral effects (nausea, vomiting) due to decarboxylation of levodopa; however, carbidopa does not decrease the adverse reactions due to the central effects of levodopa.
Patients treated with levodopa therapy for Parkinson's disease may develop motor fluctuations characterized by end-of-dose failure, peak dose dyskinesia, 'on-off' phenomenon, and akinesia.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Carbidopa
Following oral dosing of RYTARY the maximum concentration occurred at approximately 3 hours. The bioavailability of carbidopa from RYTARY relative to immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa tablets was approximately 50%.
Levodopa
The pharmacokinetics of RYTARY were evaluated following single-doses in healthy subjects and following single- and multiple-doses in patients with Parkinson’s disease. The bioavailability of levodopa from RYTARY in patients was approximately 70% relative to immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa. For comparable doses, RYTARY results in a levodopa peak concentration (Cmax) that is 30% that of immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa. Following an initial peak at about one hour, plasma concentrations are maintained for about 4 to 5 hours before declining.
In patients with Parkinson’s disease, multiple-dose pharmacokinetics was comparable to single-dose pharmacokinetics, i.e., there was minimal accumulation of levodopa. Variation in levodopa peak to trough plasma concentrations at steady-state defined as (Cmax-Cmin)/Cavg was approximately 1.5 for RYTARY compared to approximately 3.2 for immediate-release levodopa.
Distribution
Carbidopa is approximately 36% bound to plasma proteins. Approximately 10% to 30% of levodopa is bound to plasma protein.
Metabolism and Elimination
Carbidopa
The terminal phase elimination half-life of carbidopa is approximately 2 hours.
Carbidopa is metabolized to two main metabolites: α-methyl-3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid and α-methyl-3,4-dihydroxy-phenylpropionic acid. These two metabolites are primarily eliminated in the urine unchanged or as a glucuronide. Unchanged carbidopa accounts for 30% of the total urinary excretion.
Peripheral dopa-decarboxylase may be saturated by carbidopa in other carbidopa-levodopa products at 70 mg per day to 100 mg per day, which produces equivalent exposure to 140 mg to 200 mg of carbidopa provided by RYTARY.
Levodopa
The terminal phase elimination half-life of levodopa, the active moiety of antiparkinsonian activity, is approximately 2 hours in the presence of carbidopa.
Levodopa is extensively metabolized to various metabolites. The two major metabolic pathways are decarboxylation by dopa decarboxylase (DDC) and O-methylation by catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT).
Dose Proportionality
RYTARY shows approximately dose proportional pharmacokinetics for both carbidopa and levodopa over the levodopa dosage strength range of 95 mg to 245 mg.
Effect of Food
In healthy adults, oral administration of RYTARY after a high-fat, high-calorie meal reduced Cmax approximately 21% and increased AUCinf approximately 13% for levodopa compared to administration in the fasted state. There may be a delay by 2 hours in the absorption of levodopa when RYTARY is taken with a high-fat, high-calorie meal. In addition, absorption of levodopa may be decreased by a high protein meal.
Specific Populations
Elderly
In pharmacokinetics studies following a single-dose of RYTARY, the peak concentrations of carbidopa and levodopa are generally similar between younger (45 to 60 years) and older (60 to 75 years) subjects.
Gender
In pharmacokinetics studies following a single-dose of RYTARY:
- Carbidopa
At comparable doses females are reported to have higher carbidopa peak concentrations and systemic exposure (approximately 33%) compared to males. Median time to peak concentration and terminal half-life are comparable between males and females.
- Levodopa
At comparable doses females are reported to have higher levodopa peak concentrations (approximately 23% to 33%) and systemic exposure (approximately 33% to 37%) compared to males. Median time to peak concentration and terminal half-life are comparable between males and females.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In rats, oral administration of carbidopa-levodopa for two years resulted in no evidence of carcinogenicity.
Mutagenesis
Carbidopa was mutagenic in the in vitro Ames test and in the in vitro mouse lymphoma tk assay but was negative in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
In reproduction studies, no effects on fertility were observed in rats receiving carbidopa-levodopa.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Patients with Early Parkinson's Disease
The effectiveness of RYTARY in patients with early Parkinson’s disease was established in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose, parallel-group, 30-week clinical trial (Study 1). Patients enrolled in Study 1 (n=381) were Hoehn and Yahr Stage I–III with a median disease duration of 1 year, and had limited or no prior exposure to levodopa and dopamine agonists. Patients continued taking concomitant selective monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitors, amantadine, and anticholinergics provided the doses were stable for at least 4 weeks before screening. Eligible patients were randomized (1:1:1:1) to placebo or one of three fixed doses of RYTARY (carbidopa/levodopa doses of 36.25 mg / 145 mg, 61.25 mg / 245 mg, or 97.5 mg / 390 mg, three times a day). Patients were not allowed to receive supplemental levodopa or catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) inhibitors. Patients receiving RYTARY initiated treatment at 23.75 mg / 95 mg three times daily (TID). The dose was increased on Day 4 and the maximum study dose (97.5 mg / 390 mg TID) was achieved by Day 22.
The clinical outcome measure in Study 1 was the mean change from baseline in the sum of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) Part II (activities of daily living) score, and UPDRS Part III (motor score) for RYTARY, compared to placebo at Week 30 (or early termination). The mean score decrease (i.e., improvement) from baseline to Week 30 for each of the three RYTARY dosage groups was significantly greater than for placebo. The results of Study 1 are shown in Table 4.
Table 4: Study 1: Change from Baseline in UPDRS Part II plus Part III Score at Week 30 (or at Early Termination) in Levodopa-Naïve Patients with Early Parkinson’s Disease
|
Treatment |
Mean UPDRS (Part II and Part III) Scorea |
||
|
Baselineb |
Week 30 |
Change from Baseline |
|
|
Placebo |
36.5 |
35.9 |
−0.6 |
|
RYTARY |
36.1 |
24.4 |
−11.7d |
|
RYTARY |
38.2 |
25.3 |
−12.9d |
|
RYTARY |
36.3 |
21.4 |
−14.9d |
a For the UPDRS, higher scores indicate greater severity of impairment
b All values based on 361 patients who had valid End-of-Study values
c Negative numbers indicate improvement as compared with the baseline value
d P-value is less than 0.05
14.2 Patients with Advanced Parkinson's Disease
Study 2 was a 22-week trial consisting of a 3-week dose adjustment of current levodopa treatment prior to a 6-week conversion to RYTARY, which was followed by a 13-week, randomized, multicenter, double-blind, levodopa-containing active control, double-dummy, parallel group trial. The study enrolled 471 (393 randomized) patients (Hoehn & Yahr Stages I-IV) who had been maintained on a stable regimen of at least 400 mg per day of levodopa prior to entry into the trial. Patients were continued on concomitant dopamine agonists, selective monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitors, amantadine, and anticholinergics provided the doses were stable for at least 4 weeks prior to screening. Patients were randomized to receive either RYTARY or immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa at the dose determined during the adjustment or conversion phases. Patients were not allowed to receive supplemental carbidopa-levodopa or catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) inhibitor products during the trial.
In Study 2, approximately 60% of patients required further up titration and approximately 16% of patients required down titration compared to the recommended starting dose of RYTARY. The final total daily dose of levodopa from RYTARY was approximately double that of the final total daily dose of levodopa from immediate-release tablets. The majority (88%) of patients in Study 2 received less than 2,400 mg; the median dose was 1,365 mg.
The clinical outcome measure in Study 2 was the percentage of “off” time during waking hours at Week 22 (or at early termination), as assessed by the patient’s Parkinson’s Disease Diary. The “off” time was significantly improved in RYTARY-treated patients compared to immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa-treated patients (Table 5). The decrease in “off” time observed with RYTARY occurred with a concomitant increase in “on time” without troublesome dyskinesia.
Table 5: Study 2: Parkinson’s Disease Diary Measures in Patients with Advanced Parkinson’s Disease
|
Percentage of waking hours spent in “Off” |
Baseline |
Week 22 (or Early Termination) |
|
RYTARY |
36.9% |
23.8%a |
|
Immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa |
36.0% |
29.8% |
|
“Off” Time (hours) | ||
|
RYTARY |
6.1 hours |
3.9 hoursa |
|
Immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa |
5.9 hours |
4.9 hours |
|
“On” Time with no or non-troublesome dyskinesia (hours) | ||
|
RYTARY |
10.0 hours |
11.8 hoursa |
|
Immediate-release carbidopa-levodopa |
10.1 hours |
10.9 hours |
a P-value is less than 0.05
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
RYTARY (carbidopa and levodopa) Extended-Release Capsules are available in the following strengths:
-
23.75 mg Carbidopa and 95 mg of Levodopa: blue and white capsule imprinted with IPX066 on the capsule cap and 95 on the capsule body.
They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100: (NDC 64896-661-01)
Bottles of 240: (NDC 64896-661-43)
-
36.25 mg Carbidopa and 145 mg Levodopa: blue and light blue capsule imprinted with IPX066 on the capsule cap and 145 on the capsule body.
They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100: (NDC 64896-662-01)
Bottles of 240: (NDC 64896-662-43)
-
48.75 mg Carbidopa and 195 mg Levodopa: blue and yellow capsule imprinted with IPX066 on the capsule cap and 195 on the capsule body.
They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100: (NDC 64896-663-01)
Bottles of 240: (NDC 64896-663-43)
-
61.25 mg Carbidopa and 245 mg Levodopa: blue capsule imprinted with IPX066 on the capsule cap and 245 on the capsule body.
They are available as follows:
Bottles 100: (NDC 64896-664-01)
Bottles of 240: (NDC 64896-664-43)
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Dosing Instructions
- Advise patients to not take other carbidopa-levodopa preparations with RYTARY without consulting their healthcare provider [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Advise patients to call their healthcare provider before stopping RYTARY. Discontinue RYTARY slowly. Tell patients to call their healthcare provider if they develop withdrawal symptoms such as fever, confusion or severe muscle stiffness [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Advise patients to swallow RYTARY capsules whole, without chewing, dividing, or crushing [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
- For patients with difficulty swallowing, the entire contents of the RYTARY capsule may be sprinkled on 1 to 2 tablespoons of applesauce and should be taken immediately [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
- Inform patients that a high fat, high calorie meal may delay the absorption of levodopa and the onset of action by 2 to 3 hours. For this reason, consideration should be given to taking the first dose of the day about 1 to 2 hours before eating [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Falling Asleep
Advise patients that certain side effects such as sleepiness and dizziness that have been reported with RYTARY may affect some patients’ ability to drive and operate machinery safely [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Suicide Attempt and Suicidal Ideation
Instruct patients, family members and caregivers to notify their healthcare provider if suicide attempt and/or suicidal ideation are experienced by patients using RYTARY [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Hallucinations and Psychosis
Inform patients that hallucinations can occur with levodopa products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Impulse Control Disorder
Inform patients of the potential for experiencing intense urges to gamble, increased sexual urges, and other intense urges and the inability to control these urges while taking one or more of the medications that increase central dopaminergic tone, that are generally used for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Dyskinesia
Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if abnormal involuntary movements appear or get worse during treatment with RYTARY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Hypotension and Syncope
Advise patients that they may develop orthostatic hypotension with or without symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, syncope, and sweating [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Advise patients to rise slowly after sitting or lying down, especially if they have been doing so for a prolonged period.
Advise patients of the possible additive sedative effects when taking other CNS depressants in combination with RYTARY.
Pregnancy and Breast-feeding
Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during RYTARY therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise female patients to notify their physicians if they intend to breast-feed or are breast-feeding an infant [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Manufactured By:
Bora Pharmaceutical Laboratories Inc.
Jhunan, Taiwan
Distributed by:
Amneal Specialty, a division of Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807
Printed in USA
Copyright 2019 Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
All rights reserved
1566-05
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 23.75 mg/95 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC 64896-661-01
100 Capsules
Rytary™
(Carbidopa and Levodopa)
Extended-Release Capsules
23.75 mg / 95 mg
Rx Only

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 36.25 mg/145 mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC 64896-662-01
100 Capsules
Rytary™
(Carbidopa and Levodopa)
Extended-Release Capsules
36.25 mg / 145 mg
Rx Only


