DESCRIPTION
Econazole nitrate cream contains the antifungal agent, econazole nitrate USP 1%, in a water-miscible base consisting of benzoic acid, butylated hydroxytoluene, mineral oil, oleoyl polyoxylglycerides PEG-6-32 stearate/glycol stearate and purified water. The white to off-white soft cream is for topical use only.
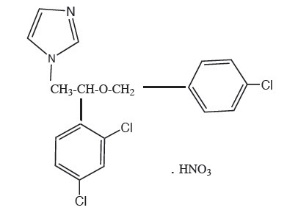
Chemically, econazole nitrate is 1-[2-{(4-chloro-phenyl) methoxy}-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-1H-imidazole mononitrate. Its structure is as follows:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
After topical application to the skin of normal subjects, systemic absorption of econazole nitrate is extremely low. Although most of the applied drug remains on the skin surface, drug concentrations were found in the stratum corneum, which, by far, exceeded the minimum inhibitory concentration for dermatophytes. Inhibitory concentrations were achieved in the epidermis and as deep as the middle region of the dermis. Less than 1% of the applied dose was recovered in the urine and feces.
Microbiology
Econazole nitrate has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section.
| Dermatophytes | Yeasts |
|---|---|
|
Epidermophyton floccosum |
Candida albicans |
|
Microsporum audouini |
Malassezia furfur |
|
Microsporum canis | |
|
Microsporum gypseum | |
|
Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |
|
Trichophyton rubrum | |
|
Trichophyton tonsurans |
Econazole nitrate exhibits broad-spectrum antifungal activity against the following organisms in vitro, but the clinical significance of these data is unknown.
| Dermatophytes | Yeasts |
|---|---|
|
Trichophyton verrucosum |
Candida guillermondii |
|
Candida parapsilosis |
|
|
Candida tropicalis |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Econazole nitrate cream is indicated for topical application in the treatment of tinea pedis, tinea cruris, and tinea corporis caused by Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton tonsurans, Microsporum canis, Microsporum audouini, Microsporum gypseum, and Epidermophyton floccosum, in the treatment of cutaneous candidiasis, and in the treatment of tinea versicolor.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Econazole nitrate cream is contraindicated in individuals who have shown hypersensitivity to any of its ingredients.
PRECAUTIONS
General
If a reaction suggesting sensitivity or chemical irritation should occur, use of the medication should be discontinued.
For external use only. Avoid introduction of econazole nitrate cream into the eyes.
Drug Interactions
Warfarin
Concomitant administration of econazole and warfarin has resulted in enhancement of anticoagulation effect. Most cases reported product application with use under occlusion, genital application, or application to large body surface area which may increase the systemic absorption of econazole nitrate. Monitoring of International Normalized Ratio (INR) and/or prothrombin time may be indicated especially for patients who apply econazole to large body surface areas, in the genital area, or under occlusion.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility
Long-term animal studies to determine carcinogenic potential have not been performed.
Oral administration of econazole nitrate in rats has been reported to produce prolonged gestation. Intravaginal administration in humans has not shown prolonged gestation or other adverse reproductive effects attributable to econazole nitrate therapy.
Pregnancy
Econazole nitrate has not been shown to be teratogenic when administered orally to mice, rabbits or rats. Fetotoxic or embryotoxic effects were observed in Segment I oral studies with rats receiving 10 to 40 times the human dermal dose. Similar effects were observed in Segment II or Segment III studies with mice, rabbits and/or rats receiving oral doses 80 or 40 times the human dermal dose.
Econazole nitrate should be used in the first trimester of pregnancy only when the physician considers it essential to the welfare of the patient. The drug should be used during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether econazole nitrate is excreted in human milk. Following oral administration of econazole nitrate to lactating rats, econazole and/or metabolites were excreted in milk and were found in nursing pups. Also, in lactating rats receiving large oral doses (40 or 80 times the human dermal dose), there was a reduction in post partum viability of pups and survival to weaning; however, at these high doses, maternal toxicity was present and may have been a contributing factor. Caution should be exercised when econazole nitrate is administered to a nursing woman.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of econazole nitrate cream did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
During clinical trials, approximately 3% of patients treated with econazole nitrate cream 1% reported side effects thought possibly to be due to the drug, consisting mainly of burning, itching, stinging and erythema. One case of pruritic rash has also been reported.
OVERDOSE
Overdosage of econazole nitrate in humans has not been reported to date. In mice, rats, guinea pigs and dogs, the oral LD 50 values were found to be 462, 668, 272, and >160 mg/kg, respectively.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Sufficient econazole nitrate cream, 1%, should be applied to cover affected areas once daily in patients with tinea pedis, tinea cruris, tinea corporis, and tinea versicolor, and twice daily (morning and evening) in patients with cutaneous candidiasis.
Early relief of symptoms is experienced by the majority of patients and clinical improvement may be seen fairly soon after treatment is begun; however, candidal infections and tinea cruris and corporis should be treated for two weeks and tinea pedis for one month in order to reduce the possibility of recurrence. If a patient shows no clinical improvement after the treatment period, the diagnosis should be redetermined. Patients with tinea versicolor usually exhibit clinical and mycological clearing after two weeks of treatment.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Taro Pharmaceuticals, Inc., at 1-866-923-4914 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch for voluntary reporting of adverse reactions.
Mfd. by: Taro Pharmaceuticals Inc., Brampton, Ontario, Canada L6T 1C1
Dist. by: Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Hawthorne, NY 10532
Revised: February, 2020
PK-3310-3 0220-3 43
Relabeled By: Preferred Pharmaceuticals Inc.