FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Glycopyrrolate tablets are indicated in adults to reduce symptoms of a peptic ulcer as an adjunct to treatment of peptic ulcer.
Limitations of Use
Glycopyrrolate tablets are not indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of peptic ulcer because effectiveness in peptic ulcer healing has not been established.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosing Information
- Glycopyrrolate tablets 2 mg are not recommended for patients in whom a lower dosage strength of oral glycopyrrolate (e.g., glycopyrrolate tablets 1 mg or another 1 mg tablet strength) is appropriate for initial or maintenance treatment because the dosage strength of glycopyrrolate tablets may exceed the recommended initial and maintenance dosage of oral glycopyrrolate tablets.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
- The recommended initial dosage of glycopyrrolate tablets 1 mg for adults is 1 mg three times daily (in the morning, early afternoon, and at bedtime). Some patients may require 2 mg at bedtime to assure overnight control of symptoms. For maintenance, a dosage of 1 mg twice a day is frequently adequate.
- The recommended dosage of glycopyrrolate tablets 2 mg for adults is 2 mg two or three times daily at equally spaced intervals.
- The maximum recommended daily dosage of glycopyrrolate is 8 mg.
- Use the lowest effective dosage of glycopyrrolate to control symptoms. If patients can be titrated to a lower dose, switch from glycopyrrolate tablets 2 mg to glycopyrrolate tablets 1 mg or another 1 mg oral tablet of glycopyrrolate.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets:
- 1 mg, white to off-white, round, beveled edge uncoated tablets, debossed with ‘Y’ and break line on one side and ‘08’ on the other side.
- 2 mg, white to off-white, round, beveled edge uncoated tablets, debossed with ‘Y’ and break line on one side and ‘51’ on the other side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Glycopyrrolate tablets are contraindicated in:
- Patients at risk for anticholinergic toxicity due to an underlying medical condition, including:
- Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Obstructive uropathies, including prostatic hypertrophy
- Mechanical obstructive diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., pyloroduodenal stenosis, strictures) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Gastrointestinal motility disorders (e.g., achalasia, paralytic ileus, intestinal atony) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Bleeding gastrointestinal ulcer
- Active inflammatory or infectious colitis which can lead to toxic megacolon
- History of or current toxic megacolon o Myasthenia gravis
- Patients with a hypersensitivity to glycopyrrolate or any of the inactive ingredients in glycopyrrolate tablets [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Description (11)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Precipitation of Acute Glaucoma
Glycopyrrolate may cause increased intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma and reduce the effects of antiglaucoma agents. Instruct patients to discontinue glycopyrrolate and promptly seek medical care if they experience symptoms of acute angle-closure glaucoma (pain and reddening of the eyes accompanied by dilated pupils) [see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Partial or Complete Mechanical Intestinal Obstruction
Glycopyrrolate may worsen intestinal mechanical obstruction, and diarrhea may be an early symptom of incomplete intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. If partial or complete intestinal obstruction is suspected, discontinue the use of glycopyrrolate and evaluate for potential intestinal obstruction [see Contraindications (4)].
5.3 Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions Due to Decreased Gastrointestinal Motility
Glycopyrrolate reduces gastrointestinal motility and may result in delayed gastric emptying, constipation, and intestinal pseudo-obstruction and may precipitate or aggravate paralytic ileus and toxic megacolon [see Contraindications (4)]. The risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions is further increased with the use of other anticholinergics and other medications that decrease gastrointestinal peristalsis.
Monitor patients for symptoms of decreased gastrointestinal motility. Concomitant use of glycopyrrolate and other anticholinergics or other medications that decrease GI peristalsis is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.4 Cognitive and Visual Adverse Reactions
Glycopyrrolate may produce drowsiness and blurred vision and impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of hazardous tasks such as driving a motor vehicle, operating machinery, or performing other hazardous work [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Concomitant use of other drugs that have anticholinergic properties may increase these effects [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Inform patients not to operate motor vehicles or other dangerous machinery or perform other hazardoustasks until they are reasonably certain that glycopyrrolate does not affect them adversely.
Discontinue glycopyrrolate if signs or symptoms of cognitive or visual impairment develop.
5.5 Heat Prostration at High Environmental Temperatures
In the presence of a high environmental temperature, heat prostration resulting in fever and heatstroke can occur with the use of glycopyrrolate due to decreased sweating, particularly in geriatric patients [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Advise patients to avoid exposure to hot or very warm environmental temperatures when taking glycopyrrolate. Glycopyrrolate is not recommended in geriatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
5.6 Other Conditions Exacerbated by Anticholinergic Adverse Reactions
Glycopyrrolate is not recommended in patients with other conditions exacerbated by anticholinergic adverse reactions (e.g., autonomic neuropathy, hyperthyroidism, cardiac disease, and hiatal hernia associated with reflux esophagitis) and in patients taking other anticholinergic medications [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.7 Increased Risk of Anticholinergic Adverse Reactions in Geriatric Patients
Geriatric patients 65 years of age and older are at increased risk of anticholinergic adverse reactions that may lead to complications of urinary retention, bowel obstruction, heat prostration, arrhythmias, delirium, and falls or fractures. Glycopyrrolate is not recommended in geriatric patients and may be contraindicated in some geriatric patients with underlying medical conditions [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.5), Adverse Reactions (6) and Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious or otherwise important adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Precipitation of Acute Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Partial or Complete Mechanical Intestinal Obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions due to Decreased Gastrointestinal Motility [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Cognitive and Visual Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Heat Prostration at High Environmental Temperatures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Other Conditions Exacerbated by Anticholinergic Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Increased Risk of Anticholinergic Adverse Reactions in Geriatric Patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of glycopyrrolate, or other anticholinergic drugs, were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiac Disorders: chest, pain, hypertension, tachycardia
Endocrine Disorders: decreased sweating
Eye Disorders: blurred vision, cycloplegia, dilatation of the pupil, increased ocular tension
Gastrointestinal Disorders: bloated feeling, constipation, dry mouth, dysgeusia, nausea, vomiting
Immune System Disorders: anaphylaxis [see Contraindications (4)]
Nervous System Disorders: agitation, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, mental confusion, nervousness, weakness
Respiratory Disorders: respiratory depression, throat irritation
Renal and Urinary Disorders: urinary hesitancy, urinary retention
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: impotence, suppression of lactation
Vascular Disorders: flushing
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Other Anticholinergic Drugs
There is potential for an additive interaction between glycopyrrolate and concomitantly used anticholinergic drugs (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants, anti-epileptics, class I antiarrhythmics, anti-spasmodics, amantadine) resulting in increased anticholinergic adverse reactions. Coadministration of antipsychotics with glycopyrrolate may lead to worsening of tardive dyskinesia. Glycopyrrolate is not recommended in patients taking other anticholinergic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4, 5.6)].
7.2 Drugs with Altered Absorption due to Decreased Gastrointestinal Motility and Increased Transit Time
Decreased gastrointestinal motility by glycopyrrolate may impact absorption of other drugs leading toincreased or decreased drug exposure. Glycopyrrolate is not recommended in patients taking other drugs that are affected by altered gastrointestinal motility [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
7.3 Gastrointestinal Toxicity with Solid Dosage Forms of Potassium Chloride
Oral glycopyrrolate may worsen gastrointestinal mucosal injury reported with solid oral dosage forms of potassium chloride due to decreased gastric motility and increased transit time, leading to prolonged contact with the gastrointestinal mucosa. Glycopyrrolate is not recommended in patients taking solid oral dosage forms of potassium chloride.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Over decades of use, there is an absence of published data on orally administered glycopyrrolate in pregnant women, including an absence of any reports of a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal studies, at non-maternally toxic doses of oral glycopyrrolate, there were no adverse developmental effects in rats or rabbits. A pre- and post-natal development study of oral glycopyrrolate in rats showed a decrease in pup mean bodyweight that recovered post nursing, with no other developmental effects observed (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
At non-maternally toxic doses of oral glycopyrrolate, there were no effects on embryo-fetal development or toxicity in rats or rabbits. A pre- and post-natal development study of oral glycopyrrolate in rats showed a decrease in pup mean bodyweight that recovered post nursing, with no other developmental effects observed.
In a published reproductive and developmental study, male and female rats were administered glycopyrrolate in the diet at 0 mg/kg/day, 32.5 mg/kg/day, 63 mg/kg/day, and 130 mg/kg/day for 3 weeks to 5 weeks and through up to three consecutive litters. There was no indication of abnormalities in the pups of treated dams. There was a decreased rate of conception and in survival rate at weaning for all treated animals in a dose-related manner. Diminished rates of conception may be due to diminished seminal secretion [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of glycopyrrolate in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. As with other anticholinergic drugs, glycopyrrolate may cause suppression of lactation. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for glycopyrrolate and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from glycopyrrolate.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Geriatric patients 65 years of age and older may be more sensitive to the anticholinergic adverse reactions of glycopyrrolate leading to complications of urinary retention, bowel obstruction, heat prostration, arrhythmias, delirium, and falls or fractures; therefore, glycopyrrolate is not recommended in geriatric patients and may be contraindicated in some geriatric patients with underlying medical conditions [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Glycopyrrolate is substantially excreted by the kidney [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Monitor patients with renal impairment for anticholinergic adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. If anticholinergic adverse reactions occur, discontinue glycopyrrolate.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Signs and symptoms of glycopyrrolate overdosage are related to excessive anti-muscarinic anticholinergic activity and are generally peripheral (e.g., flushing, hyperthermia, tachycardia, ileus, urinary retention, loss of ocular accommodation, and light sensitivity due to mydriasis), but central nervous system toxicity (agitation, seizures, hyperthermia) may also occur.
If over-exposure occurs, call the Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222 for current information on the management of glycopyrrolate poisoning and overdosage.
Management of glycopyrrolate overdosage is based upon presenting signs and symptoms, including close observation for severe or life-threatening complications which may require respiratory and cardiovascular monitoring and support. Consider administration of activated charcoal and/or use of a reversible anticholinesterase as appropriate or recommended by Poison Control.
11 DESCRIPTION
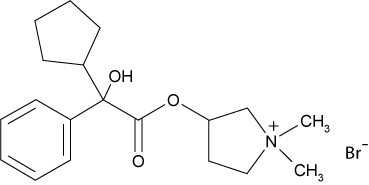
Glycopyrrolate tablets, USP contain synthetic anticholinergic glycopyrrolate. Glycopyrrolate is a quaternary ammonium compound with the following chemical name: 3-[(cyclopentyl hydroxyphenylacetyl)oxy]-1,1-dimethylpyrrolidinium bromide. The molecular formula for glycopyrrolate is C19H28BrNO3, the molecular weight is 398.3 g/mol, and the structural formula is:
Each glycopyrrolate tablets, USP contains glycopyrrolate, USP 1 mg or 2 mg, as the active ingredient. The inactive ingredients are dibasic calcium phosphate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, povidone, and sodium starch glycolate.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Glycopyrrolate, an anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) agent, inhibits the action of acetylcholine on parietal cells in the stomach and decreases the volume and acidity of gastric secretions.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Patients with Renal Impairment
In the published literature, glycopyrrolate 4 mcg/kg was administered intravenously (glycopyrrolate tablets are not recommended for intravenous use) in uremic patients undergoing renal transplantation surgery. The mean AUC (10.6 mcg·h/L) and 24-hour urinary excretion (7%) for glycopyrrolate were significantly different from normal healthy adult subjects undergoing general surgery (3.7 mcg·h/L, and 65%, respectively) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Reproduction studies in rats resulted in diminished rates of conception in a dose-related manner. Studies in dogs suggest that diminished rates of conception may be due to diminished seminal secretion, which is evident at high doses of glycopyrrolate.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Glycopyrrolate tablets USP, 1 mg are white to off-white, round, beveled edge uncoated tablets, debossed with ‘Y’ and break line on one side and ‘08’ on the other side.
Bottles of 100 NDC 13107-014-01
Glycopyrrolate tablets USP, 2 mg are white to off-white, round, beveled edge uncoated tablets, debossed with ‘Y’ and break line on one side and ‘51’ on the other side.
Bottles of 100 NDC 13107-015-01
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep this and all medication out of the reach of children.
Dispense in a tight container.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Precipitation of Acute Glaucoma
Advise patients to discontinue glycopyrrolate and promptly seek medical care if they experience symptoms of acute angle-closure glaucoma (pain and reddening of the eyes accompanied by dilated pupils) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Partial or Complete Mechanical Intestinal Obstruction
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if diarrhea occurs, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions Due to Decreased Gastrointestinal Motility
Inform patients that glycopyrrolate may cause adverse reactions related to decreased gastrointestinal motility and report to their healthcare provider if they experience symptoms such as vomiting, early satiety, abdominal distention, and constipation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Cognitive and Visual Adverse Reactions
Inform patients that glycopyrrolate may cause cognitive or visual impairment and not operate motor vehicles or other dangerous machinery or perform other hazardous tasks until they are reasonably certain that glycopyrrolate do not affect them adversely. Advise patients to discontinue glycopyrrolate immediately and contact their healthcare provider if symptoms develop (e.g., drowsiness or blurred vision) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Heat Prostration at High Environmental Temperatures
Inform patients that glycopyrrolate can reduce sweating, leading to the possibility of heat exhaustion or heat stroke. Advise patients to avoid exposure to hot or very warm environmental temperatures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Distributed by:
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
279 Princeton-Hightstown Road
East Windsor, NJ 08520
Manufactured by:
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Hyderabad-500 032, India
Revised: 05/2023