FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Metronidazole Gel USP, 1% is indicated for the topical treatment of inflammatory lesions of rosacea.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For topical use only, not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
Cleanse treated areas before the application of metronidazole gel.
Apply and rub in a thin film of metronidazole gel once daily to affected area(s).
Cosmetics may be applied after the application of metronidazole gel.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Gel, 1%. Metronidazole is a colorless to slightly yellow gel. Each gram of metronidazole gel contains 10 mg (1%) of metronidazole.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Metronidazole gel is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to metronidazole or to any other ingredient in the formulation.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Neurologic Disease
Peripheral neuropathy, characterized by numbness or paresthesia of an extremity, has been reported in patients treated with systemic metronidazole. Peripheral neuropathy has been reported with the post approval use of topical metronidazole. The appearance of abnormal neurologic signs should prompt immediate reevaluation of metronidazole therapy. Metronidazole should be administered with caution to patients with central nervous system diseases.
5.2 Blood Dyscrasias
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole; use with care in patients with evidence of, or history of, blood dyscrasia.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In a controlled clinical trial, 557 subjects used metronidazole gel and 189 subjects used the gel vehicle once daily for up to 10 weeks. The following table summarizes selected adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of ≥1%:
| System Organ Class/Preferred Term | Metronidazole Gel | Vehicle |
|---|---|---|
| N=557 | N=189 | |
|
Patients with at least one AE
|
186 (33.4) |
51 (27.0) |
|
Infections and infestations |
76 (13.6) |
28 (14.8) |
|
Bronchitis |
6 (1.1) |
3 (1.6) |
|
Influenza |
8 (1.4) |
1 (0.5) |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
17 (3.1) |
8 (4.2) |
|
Sinusitis |
8 (1.4) |
3 (1.6) |
|
Upper respiratory tract infection |
14 (2.5) |
4 (2.1) |
|
Urinary tract infection |
6 (1.1) |
1 (0.5) |
|
Vaginal mycosis |
1 (0.2) |
2 (1.1) |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders |
19 (3.4) |
5 (2.6) |
|
Back pain |
3 (0.5) |
2 (1.1) |
|
Neoplasms |
4 (0.7) |
2 (1.1) |
|
Basal cell carcinoma |
1 (0.2) |
2 (1.1) |
|
Nervous system disorders |
18 (3.2) |
3 (1.6) |
|
Headache |
12 (2.2) |
1 (0.5) |
|
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders |
22 (3.9) |
5 (2.6) |
|
Nasal congestion |
6 (1.1) |
3 (1.6) |
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders |
36 (6.5) |
12 (6.3) |
|
Contact dermatitis |
7 (1.3) |
1 (0.5) |
|
Dry skin |
6 (1.1) |
3 (1.6) |
|
Vascular disorders |
8 (1.4) |
1 (0.5) |
|
Hypertension |
6 (1.1) |
1 (0.5) |
| Metronidazole Gel | Vehicle | |
|---|---|---|
| Sign/Symptom | N=544 | N=184 |
|
Dryness |
138 (25.4) |
63 (34.2) |
|
Mild |
93 (17.1) |
41 (22.3) |
|
Moderate |
42 (7.7) |
20 (10.9) |
|
Severe |
3 (0.6) |
2 (1.1) |
|
Scaling |
134 (24.6) |
60 (32.6) |
|
Mild |
88 (16.2) |
32 (17.4) |
|
Moderate |
43 (7.9) |
27 (14.7) |
|
Severe |
3 (0.6) |
1 (0.5) |
|
Pruritus |
86 (15.8) |
35 (19.0) |
|
Mild |
53 (9.7) |
21 (11.4) |
|
Moderate |
27 (5.0) |
13 (7.1) |
|
Severe |
6 (1.1) |
1 (0.5) |
|
Stinging/burning |
56 (10.3) |
28 (15.2) |
|
Mild |
39 (7.2) |
18 (9.8) |
|
Moderate |
7 (1.3) |
9 (4.9) |
|
Severe |
10 (1.8) |
1 (0.5) |
The following additional adverse experiences have been reported with the topical use of metronidazole: transient redness, metallic taste, tingling or numbness of extremities, and nausea.
6.2 Post Marketing Experience
The following adverse reaction has been identified during post-approval use of topical metronidazole. Because this reaction is reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate the frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Nervous System Disorders: Peripheral neuropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Oral metronidazole has been reported to potentiate the anticoagulant effect of coumarin and warfarin, resulting in a prolongation of prothrombin time. Drug interactions should be kept in mind when metronidazole is prescribed for patients who are receiving anticoagulant treatment, although they are less likely to occur with topical metronidazole administration because of low absorption.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data have not established an association with metronidazole use during pregnancy and major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. No fetotoxicity was observed after oral administration of metronidazole in pregnant rats or mice. The available data do not allow the calculation of relevant comparisons between the systemic exposures of metronidazole observed in animal studies to the systemic exposures that would be expected in humans after topical use of metronidazole.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether metronidazole is present in human milk after topical administration. Published literature reports the presence of metronidazole in human milk after oral administration. There are reports of diarrhea and candida infection in breastfed infants of mothers receiving oral treatment with metronidazole. There are no data on the effects of metronidazole on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with metronidazole gel.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Sixty-six subjects aged 65 years and older were treated with metronidazole gel in the clinical study. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
11 DESCRIPTION
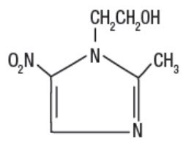
Metronidazole Gel USP, 1% contains metronidazole, USP. It is intended for topical use. Chemically, metronidazole is 2-methyl-5-nitro-1 H-imidazole-1-ethanol. The molecular formula for metronidazole is C6H9N3O3. It has the following structural formula:
Metronidazole has a molecular weight of 171.16. It is a white to pale yellow crystalline powder. It is slightly soluble in alcohol and has solubility in water of 10 mg/mL at 20°C. Metronidazole belongs to the nitroimidazole class of compounds.
Metronidazole is a colorless to slightly yellow gel; each gram contains 10 mg of metronidazole in a base of alcohol (9.3% w/w), edetate disodium, hydroxyethylcellulose, polyethylene glycol 400, propylene glycol, sorbic acid, and purified water.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of metronidazole in the treatment of rosacea is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of metronidazole in association with the treatment of rosacea are unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Topical administration of a one-gram dose of metronidazole gel to the face of 13 subjects with moderate to severe rosacea once daily for 7 days resulted in a mean ± SD Cmax of metronidazole of 32 ± 9 ng/mL. The mean ± SD AUC(0-24) was 595 ± 154 ng*hr/mL. The mean Cmax and AUC(0-24) are less than 1% of the value reported for a single 250 mg oral dose of metronidazole. The time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) was 6 to 10 hours after topical application.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Metronidazole has shown evidence of carcinogenic activity in studies involving chronic oral administration in mice and rats, but not in studies involving hamsters.
In several long-term studies in mice, oral doses of approximately 225 mg/m2/day or greater were associated with an increase in pulmonary tumors and lymphomas. Several long-term oral studies in the rat have shown statistically significant increases in mammary and hepatic tumors at doses >885 mg/m2/day.
Metronidazole has shown evidence of mutagenic activity in several in vitro bacterial assay systems. In addition, a dose-related increase in the frequency of micronuclei was observed in mice after intraperitoneal injections. An increase in chromosomal aberrations in peripheral blood lymphocytes was reported in patients with Crohn's disease who were treated with 200 to 1200 mg/day of metronidazole for 1 to 24 months. However, in another study, no increase in chromosomal aberrations in circulating lymphocytes was observed in patients with Crohn's disease treated with the drug for 8 months.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
In a randomized, vehicle-controlled trial, 746 subjects with rosacea were treated with metronidazole gel or vehicle once daily for 10 weeks. Most subjects had a disease severity score of 3 ("moderate") on the 5-point Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) scale, with 8 to 50 inflammatory lesions and no more than two nodules at baseline. The co-primary efficacy endpoints were the percent reduction in inflammatory lesion counts and percentage of subjects with success on IGA, defined as an IGA score of 0 ("clear") or 1 ("almost clear") at Week 10.
The efficacy results are shown in the following table:
| Metronidazole Gel | Vehicle | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Results N (%) | N | Results N (%) | |
|
Inflammatory lesions |
557 |
189 | ||
|
Baseline, mean count |
18.3 |
18.4 |
||
|
Week-10, mean count |
8.9 |
12.8 |
||
|
Reduction |
9.4 (50.7) |
5.6 (32.6) |
||
|
Investigator Global Assessment |
557 |
189 | ||
|
Subject clear or almost clear |
214 (38.42) |
52 (27.51) |
||
|
Subject with no change |
159 (28.5) |
77 (40.7) |
||
Subjects treated with metronidazole gel experienced a mean reduction of 9.4 inflammatory lesions in the Week-10 LOCF group, compared to a reduction of 5.6 for those treated with vehicle, or a difference in means of 3.8 lesions.
The contribution to efficacy of individual components of the vehicle has not been established.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Administration Instructions
Use as directed. Avoid contact with the eyes.
Cleanse treated areas before the application of metronidazole gel.
Advise patients to report any adverse reaction to their healthcare providers.
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with metronidazole gel [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Rx Only
Mfd. by: Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Haifa Bay, Israel 2624761
Dist. by: Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
Hawthorne, NY 10532
Revised: December 2022
5201281-1222-01
782
| PATIENT INFORMATION
Metronidazole (me troe ni⸍ da zole) Gel, 1% |
|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. |
| Revised: December 2022 |
|
Important: Metronidazole gel is for use on the skin only (topical use). Do not use metronidazole gel in your mouth, eyes, or vagina. |
|
|
|
Before using metronidazole gel, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. |
|
How should I use metronidazole gel?
|
|
What are the possible side effects of metronidazole gel?
|
|
The most common side effects of metronidazole gel include:
|
|
How should I store metronidazole gel?
|
|
Keep metronidazole gel and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
|
5201281-1222-01
782