DESCRIPTION:
Brimonidine Tartrate Ophthalmic Solution 0.2% is a relatively selective alpha-2 adrenergic agonist for ophthalmic use. In solution, brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% has a clear, greenish-yellow color. It has an osmolality of 280-330 mOsml/kg and a pH of 5.6-6.6 The structural formula is
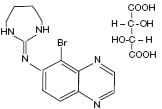
C11H10BrN5 • C4H6O6
Mol. Wt. 442.24 (as the tartrate salt)
Chemical Name: 5-bromo-6-(2-imidazolidinylideneamino) quinoxaline L-tartrate.
CAS Number 59803-98-4
Each mL Contains:
ACTIVE: Brimonidine tartrate: 0.2% (2 mg/mL).
INACTIVES: Citric Acid, Polyvinyl Alcohol, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Citrate, Purified Water. Hydrochloric Acid and/or Sodium Hydroxide may be added to adjust pH.
PRESERVATIVE ADDED: Benzalkonium Chloride (0.05 mg).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Mechanism of Action:
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% is an alpha adrenergic receptor agonist. It has a peak ocular hypotensive effect occurring at two hours post-dosing. Fluorophotometric studies in animals and humans suggest that brimonidine tartrate has a dual mechanism of action by reducing aqueous humor production and increasing uveoscleral outflow.
Pharmacokinetics:
After ocular administration of a 0.2% solution, plasma concentrations peaked within 1 to 4 hours and declined with a systemic half-life of approximately 3 hours. In humans, systemic metabolism of brimonidine is extensive. It is metabolized primarily by the liver. Urinary excretion is the major route of elimination of the drug and its metabolites. Approximately 87% of an orally administered radioactive dose was eliminated within 120 hours, with 74% found in the urine.
Clinical Evaluations:
Elevated IOP presents a major risk factor in glaucomatous field loss. The higher the level of lOP, the greater the likelihood of optic nerve damage and visual field loss. Brimonidine tartrate has the action of lowering intraocular pressure with minimal effect on cardiovascular and pulmonary parameters.
In comparative clinical studies with timolol 0.5%, lasting up to one year, the lOP lowering effect of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% was approximately 4-6 mmHg compared with approximately 6 mmHg for timolol. In these studies, both patient groups were dosed BID; however, due to the duration of action of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2%, it is recommended that brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% be dosed TID. Eight percent of subjects were discontinued from studies due to inadequately controlled intraocular pressure, which in 30% of these patients occurred during the first month of therapy. Approximately 20% were discontinued due to adverse experiences.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% is indicated for lowering intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. The lOP lowering efficacy of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% diminishes over time in some patients. This loss of effect appears with a variable time of onset in each patient and should be closely monitored.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to brimonidine tartrate or any component of this medication. It is also contraindicated in patients receiving monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor therapy.
PRECAUTIONS:
General:
Although brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% had minimal effect on blood pressure of patients in clinical studies, caution should be exercised in treating patients with severe cardiovascular disease.
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% has not been studied in patients with hepatic or renal impairment; caution should be used in treating such patients.
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% should be used with caution in patients with depression, cerebral or coronary insufficiency, Raynaud’s phenomenon, orthostatic hypotension or thromboangiitis obliterans.
During the studies there was a loss of effect in some patients. The IOP-lowering efficacy observed with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% during the first month of therapy may not always reflect the long-term level of IOP reduction. Patients prescribed IOP-lowering medication should be routinely monitored for IOP.
Information for Patients:
The preservative in brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2%, benzalkonium chloride, may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Patients wearing soft contact lenses should be instructed to wait at least 15 minutes after instilling brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% to insert soft contact lenses.
As with other drugs in this class, brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% may cause fatigue and/or drowsiness in some patients. Patients who engage in hazardous activities should be cautioned of the potential for a decrease in mental alertness.
Drug Interactions:
Although specific drug interaction studies have not been conducted with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2%, the possibility of an additive or potentiating effect with CNS depressants (alcohol, barbiturates, opiates, sedatives, or anesthetics) should be considered. Alpha-agonists, as a class, may reduce pulse and blood pressure. Caution in using concomitant drugs such as beta-blockers (ophthalmic and systemic), antihypertensives and/or cardiac glycosides is advised.
Tricyclic antidepressants have been reported to blunt the hypotensive effect of systemic clonidine. It is not known whether the concurrent use of these agents with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% in humans can lead to resulting interference with the IOP lowering effect. No data on the level of circulating catecholamines after brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% are available. Caution, however, is advised in patients taking tricyclic antidepressants which can affect the metabolism and uptake of circulating amines.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility:
No compound-related carcinogenic effects were observed in either mice or rats following a 21-month and 24-month study, respectively. In these studies, dietary administration of brimonidine tartrate at doses up to 2.5 mg/kg/day in mice and 1.0 mg/kg/day in rats achieved ~77 and 118 times, respectively, the plasma drug concentration estimated in humans treated with one drop brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% into both eyes 3 times per day.
Brimonidine tartrate was not mutagenic or cytogenic in a series of in vitro and in vivo studies including the Ames test, chromosomal aberation assay in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells, a host-mediated assay and cytogenic studies in mice, and dominant lethal assay.
Reproductive studies performed in rats with oral doses of 0.66 mg base/kg revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2%.
Pregnancy: Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category B.
Reproductive studies performed in rats with oral doses of 0.66 mg base/kg revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2%. Dosing at this level produced 100 times the plasma drug concentration level seen in humans following multiple ophthalmic doses.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. In animal studies, brimonidine crossed the placenta and entered into the fetal circulation to a limited extent. Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers:
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk; in animal studies brimonidine tartrate was excreted in breast milk. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use:
In a well-controlled clinical study conducted in pediatric glaucoma patients (ages 2 to 7 years) the most commonly observed adverse events with brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% dosed three times daily were somnolence (50% - 83% in patients ages 2 to 6 years) and decreased alertness. In pediatric patients 7 years of age or older (>20kg), somnolence appears to occur less frequently (25%). The most commonly observed adverse event was somnolence. Approximately 16% of patients on brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution discontinued from the study due to somnolence.
The safety and effectiveness of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% have not been studied in pediatric patients below the age of 2 years. Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% is not recommended for use in pediatric patients under the age of 2 years. (Also refer to Adverse Reactions section).
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Adverse events occurring in approximately 10-30% of the subjects, in descending order of incidence, included oral dryness, ocular hyperemia, burning and stinging, headache, blurring, foreign body sensation, fatigue/drowsiness, conjunctival follicles, ocular allergic reactions, and ocular pruritus.
Events occurring in approximately 3-9% of the subjects, in descending order included corneal staining/erosion, photophobia, eyelid erythema, ocular ache/pain, ocular dryness, tearing, upper respiratory symptoms, eyelid edema, conjunctival edema, dizziness, blepharitis, ocular irritation, gastrointestinal symptoms, asthenia, conjunctival blanching, abnormal vision and muscular pain.
The following adverse reactions were reported in less than 3% of the patients: lid crusting, conjunctival hemorrhage, abnormal taste, insomnia, conjunctival discharge, depression, hypertension, anxiety, palpitations/arrhythmias, nasal dryness and syncope.
The following events have been identified during post-marketing use of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The events, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2%, or a combination of these factors, include: bradycardia; hypotension; iritis; miosis; skin reactions (including erythema, eyelid pruritis, rash, and vasodilation); and tachycardia. Apnea, bradycardia, hypotension, hypothermia, hypotonia, and somnolence have been reported in infants receiving brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2%.
OVERDOSAGE:
No information is available on overdosage in humans. Treatment of an oral overdose includes supportive and symptomatic therapy; a patent airway should be maintained.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
The recommended dose is one drop of brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% in the affected eye(s) three times daily, approximately 8 hours apart.
Brimonidine tartrate ophthalmic solution 0.2% may be used concomitantly with other topical ophthalmic drug products to lower intraocular pressure. If more than one topical ophthalmic product is being used, the products should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
HOW SUPPLIED:
Brimonidine Tartrate Ophthalmic Solution 0.2% is supplied sterile in a plastic bottle with a controlled drop tip in the following sizes:
5 mL bottles NDC 54868-6287-0
10 mL bottles NDC 54868-6287-1
Storage: Store between 15° – 25°C (59° – 77°F).
KEEP OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
DO NOT USE IF IMPRINTED “Protective Seal” WITH YELLOW (mortar and pestle symbol) IS NOT INTACT.
