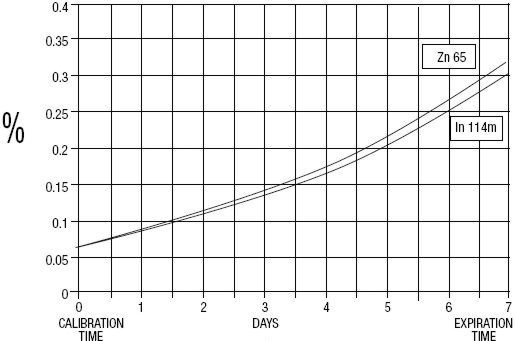
DESCRIPTION
GE Healthcare (Medi-Physics, Inc.) Indium DTPA In 111 is a diagnostic drug for intrathecal use. It is available as a sterile, pyrogen-free, isotonic, aqueous solution, buffered to pH 7 to 8. At calibration time, each milliliter contains 37 MBq, 1 mCi of Pentetate Indium Disodium In 111 (no-carrier-added), 20 to 50 µg of pentetic acid, and sodium bicarbonate for pH adjustment. The drug is to be discarded after single use. Radionuclidic purity at calibration time is at least 99.88% with less than 0.06% Indium In 114m and 0.06% Zinc Zn 65. The concentration of each radionuclidic contaminant changes with time. Graph 1 shows maximum concentration of each radionuclidic impurity as a function of time.
Graph 1 - Radionuclidic Impurities
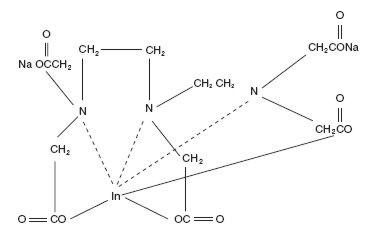
The chemical names are 1. Indate(2-)-111In-[N,N-bis[2-[bis-(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl]glycinato(5-)]-disodium; and 2. Disodium [N,N-bis[2-(carboxymethyl)amino]glycinato(5-)]-indate (2-)111In.
Molecular formula: C14H18O10N3 111In Na2
Molecular weight: 545.29
Structural formula:
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Indium 111 decays by electron capture with a physical half-life of 67.9 hours.* The energies of the photons that are useful for detection and imaging studies are listed in Table 1.
| Radiation | Mean %/Disintegration | Mean Energy (keV) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Gamma-2 | 90.2 | 171.3 |
| Gamma-3 | 94.0 | 245.4 |
EXTERNAL RADIATION
The specific gamma ray constant for Indium In 111 is 3.3 R/hr-mCi at 1 cm. The half-value thickness of lead (Pb) for Indium In 111 is 0.021 cm. To facilitate control of the radiation exposure from millicurie amounts of this radionuclide, a range of values for the relative attenuation of the radiation emitted by this radionuclide that results from interposition of various thicknesses of Pb is shown in Table 2. For example, the use of a 0.8 cm thickness of Pb will attenuate the radiation emitted by a factor of about 1,000.
| Shield Thickness (Pb) cm | Coefficient of Attenuation |
|---|---|
| To correct for physical decay of this radionuclide, the fractions that remain at selected time intervals after the time of calibration are shown in Table 3. | |
| 0.021 | 0.5 |
| 0.19 | 10-1 |
| 0.49 | 10-2 |
| 0.80 | 10-3 |
| 1.1 | 10-4 |
| Hours | Fraction Remaining | Hours | Fraction Remaining |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| 0* | 1.000 | 84 | 0.424 |
| 12 | 0.885 | 96 | 0.375 |
| 24 | 0.783 | 108 | 0.332 |
| 36 | 0.693 | 120 | 0.294 |
| 48 | 0.613 | 132 | 0.260 |
| 60 | 0.542 | 144 | 0.230 |
| 72 | 0.480 | 168 | 0.180 |
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
After intrathecal administration, the radiopharmaceutical is absorbed from the subarachnoid space as described below, and the remainder flows superiorly to the basal cisterns within 2 to 4 hours and subsequently will be apparent in the Sylvian cisterns, the interhemispheric cisterns, and over the cerebral convexities. In normal individuals, the radiopharmaceutical will have ascended to the parasagittal region within 24 hours with simultaneous partial or complete clearance of activity from the basal cisterns and Sylvian regions. In contrast to air, the radiopharmaceutical does not normally enter the cerebral ventricles.
Although the primary absorption of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) into the blood stream occurs at the arachnoid villi, there is some evidence that a significant fraction of CSF is also absorbed across both the cerebral and spinal leptomeninges. Lesser quantities may also be absorbed across the ventricular ependyma. It is also generally held that these alternate routes of CSF absorption may assume primary importance when the major routes of the flow are pathologically obstructed. Approximately 65% of the administered dose is excreted by the kidneys within 24 hours and this increases to 85% in 72 hours.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Pentetate Indium Disodium In 111 is recommended for use in radionuclide cisternography.
WARNINGS
The contents of the vial are radioactive. Adequate shielding of the preparation must be maintained at all times.
Since the drug is excreted by the kidneys, caution should be exercised in patients with severely impaired renal function.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Pentetate Indium Disodium In 111, as well as other radioactive drugs, must be handled with care and appropriate safety measures should be used to minimize external radiation exposure to clinical personnel, and to minimize radiation exposure to patients consistent with proper patient management.
Radiopharmaceuticals should be used only by physicians who are qualified by training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate government agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides.
Do not use after the expiration time and date (7 days after calibration time and date stated on the label).
Discard vial after a single use. Do not use if contents are turbid.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term animal studies have been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential, or whether Pentetate lndium Disodium In 111 affects fertility in males or females.
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with GE Healthcare (Medi-Physics, Inc.) Indium DTPA In 111. Also, it is not known whether Pentetate Indium Disodium In 111 can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Pentetate Indium Disodium In 111 should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Ideally, examinations using radiopharmaceuticals, especially those elective in nature, of a woman of childbearing capability should be performed during the first few (approximately 10) days following the onset of menses.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, formula feedings should be substituted for breast feedings when Pentetate Indium Disodium In 111 is administered to a nursing mother.
Geriatric use
Clinical studies of Indium DTPA In 111 did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
The drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Aseptic meningitis and pyrogenic reactions have been rarely (less than 0.4%) observed following cisternography with Pentetate lndium Disodium In 111.
One death has been reported to have occurred within 20 minutes following the administration of Pentetate Indium Disodium In 111 and appears to be drug related. In addition, two cases of septic meningitis have also been reported. There have also been reports of skin reactions and vomiting following administration of Pentetate lndium Disodium In 111. Relationship of the drug to these latter occurrences has not been established.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Extreme care must be exercised to assure aseptic conditions in intrathecal injections.
The maximum recommended intrathecal dose in the average patient (70 kg) is 18.5 MBq, 500 µCi. The patient dose should be measured by a suitable radioactivity calibration system immediately prior to administration.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
RADIATION DOSIMETRY
The estimated absorbed radiation doses* to selected organs of an average (70 kg) patient from intrathecal administration of a maximum dose of 18.5 MBq, 500 µCi of Pentetate Indium Disodium In 111 are shown in Table 4.
| Organ | mGy/18.5 MBq | rads/500 µCi |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Total Body | 0.41 | 0.041 |
| Kidneys | 2.2 | 0.22 |
| Spinal Cord | ||
| Surface | 50.0 | 5.0 |
| Average | 15.0 | 1.5 |
| Brain | ||
| Surface | 41.0 | 4.1 |
| Average | 4.0 | 0.4 |
| Bladder | ||
| 2-hour void | 2.1 | 0.21 |
| 4.8-hour void | 5.0 | 0.5 |
| Testes | ||
| 2-hour void | 0.4 | 0.04 |
| 4.8-hour void | 0.5 | 0.05 |
| Ovaries | ||
| 2-hour void | 0.6 | 0.06 |
| 4.8-hour void | 0.6 | 0.06 |
HOW SUPPLIED
Pentetate Indium Disodium In 111 (no-carrier-added) is supplied in single-dose glass vials, each containing 1.5 mL of solution with a concentration of 37 MBq, 1 mCi per mL and a total activity of 55.5 MBq, 1.5 mCi per vial at calibration time. Vials are packaged in individual lead shields with plastic outer containers.
NDC 17156-251-08
Disposal
The residual materials may be discarded in ordinary trash provided the vials and syringes read no greater than background with an appropriate low-range survey meter. All identifying labels should be destroyed before discarding.
This radiopharmaceutical is licensed by Illinois Emergency Management Agency for distribution to persons licensed pursuant to 32 III. Adm. Code 330.260(a) and Part 335, Subpart E, 335.4010, or under equivalent licenses of an Agreement State or a Licensing State.
Product Number: 2051
GE Healthcare
Medi-Physics, Inc.
3350 North Ridge Avenue
Arlington Heights, IL 60004
GE and the GE Monogram are trademarks of General Electric Company.
43-2051G
Revised February 2020
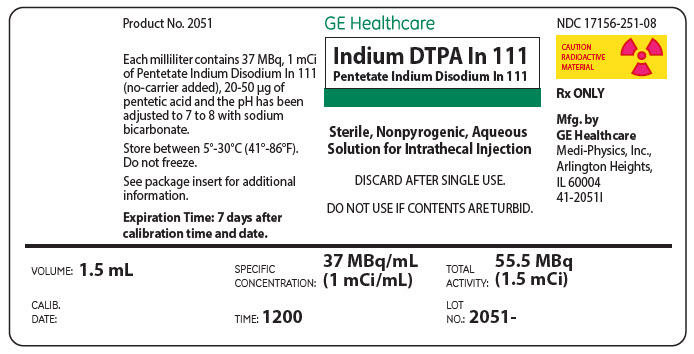
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1.5 mL Vial Label
GE Healthcare
Indium DTPA In 111
Pentetate Indium Disodium In 111
Sterile, Nonpyrogenic, Aqueous
Solution for Intrathecal Injection
DISCARD AFTER SINGLE USE.
DO NOT USE IF CONTENTS ARE TURBID.
VOLUME: 1.5 mL
SPECIFIC
CONCENTRATION:
37 MBq/mL
(1 mCi/mL)
TOTAL
ACTIVITY:
55.5 MBq
(1.5 mCi)
CALIB.
DATE:
TIME: 1200
LOT
NO.:
2051 –