FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Radiation Safety – Drug Handling
Technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin is a radioactive drug and should be handled with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure during administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Use waterproof gloves and effective shielding, including syringe shields, when preparing and administering technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin injection.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
- The recommended dose range for MYOVIEW is 185 to 1,221 megabecquerels (MBq) (5 to 33 millicuries (mCi) by intravenous administration for rest and stress imaging.
- When rest and stress intravenous injections are administered on the same day, the first dose should be 185 to 444 MBq (5 to 12 mCi) and followed by the second dose of 555 to 1,221 MBq (15 to 33 mCi) given approximately 1 to 4 hours later.
- The recommended dose range for MYOVIEW is 185 to 1,221 MBq (5 to 33 millicuries (mCi) by intravenous administration as an intravenous injection for ventricular function assessment.
2.3 Administration Instructions
- Use aseptic technique for all drug preparation and handling.
- Measure the dose in a suitable radioactivity calibration system immediately prior to intravenous administration.
- Visually inspect the drug for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use or administer the drug if there is evidence of particulate matter or discoloration.
- Instruct patients to remain hydrated and void frequently following administration to decrease radiation exposure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.4 Instructions for Preparation
The following steps as detailed are critical and should be followed to ensure adequate preparation of the product.
- The technetium Tc99m labeling reaction involved in the preparation of MYOVIEW Injection depends on maintaining tin in the divalent (reduced) state. Any oxidant present in the sodium pertechnetate Tc99m used may adversely affect the quality of the preparation. Sodium pertechnetate Tc99m containing oxidants should not be used for the preparation of the labeled product.
- Elute the technetium generator with sodium chloride injection, USP.
- Insert a venting needle (standard 18 to 26 gauge needle, not provided) through the rubber septum of the shielded vial containing the lyophilized powder.
- Inject no more than 8.8 GBq (240 mCi) of technetium Tc99m generator eluate into the shielded vial.
- Use sodium chloride injection, USP as a diluent. Inject 4 to 8 mL to achieve a radioactive concentration no greater than 1.1 GBq/mL (30 mCi/mL) in the vial.
- Before removing the syringe from the vial, withdraw 2 mL of gas from above the solution.
- Remove the venting needle.
- Mix gently for 10 seconds to ensure complete dissolution of the powder.
- Incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes.
- Assay the total activity using a suitably calibrated instrument; complete the user radiation label and attach it to the vial.
- Measure the pH of the prepared injection and verify it is between 7.5 to 9.0.
- Store the radiolabeled MYOVIEW vial at 2° to 25°C (36° to 77°F) and use radiolabeled injection within 12 hours of preparation.
2.5 Determination of Radiochemical Purity
Obtain the following materials:
- SA TLC strip (2 cm × 20 cm), do not heat activate
- Ascending chromatography tank and cover
- Mixture of acetone and dichloromethane (65:35% v/v), prepare freshly
- Syringe (1 mL) with needle (22 to 25 gauge)
- Suitable counting equipment
Perform the following:
- Pour the 65:35% v/v acetone:dichloromethane mixture into the chromatography tank to a depth of 1 cm and cover the tank to allow the solvent vapor to equilibrate.
- Mark SA TLC strip with a pencil line at 3 cm from the bottom and, using an ink marker pen, at 15 cm from the pencil line. The pencil line indicates the origin where the sample is to be applied and movement of color from the ink line will indicate the position of the solvent front when upward elution should be stopped.
- Mark cutting positions at 3.75 cm and 12 cm above the origin [retention value (Rf) 0.25 and 0.8 respectively] in pencil.
- Using a 1 mL syringe and needle, apply a 10 microliter sample of the prepared injection at the origin of the strip. Do not allow the spot to dry. Place the strip in the chromatography tank immediately and replace the cover. Ensure that the strip is not adhering to the walls of the tank.
Note: A 10 microliter sample will produce a spot with a diameter of approximately 10 mm. Different sample volumes have been shown to give unreliable radiochemical purity values. - When the solvent reaches the ink line, remove the strip from the tank and allow it to dry.
- Cut the strip into 3 pieces at the marked cutting positions and measure the activity on each using suitable counting equipment. Ensure similar counting geometry for each piece and minimize equipment dead time losses. Note: Free Tc99m pertechnetate runs to the top piece of the strip. MYOVIEW runs to the center piece of the strip. Reduced hydrolyzed Tc99m and any hydrophilic complex impurities remain at the origin in the bottom piece of the strip.
TLC strip diagram
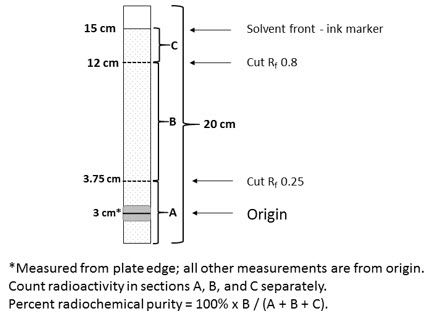
- Calculate the radiochemical purity from:
% Tc99m tetrofosmin = Activity of Center Piece (B) × 100 Total Activity of Three Pieces (A+B+C) - Do not use material if the radiochemical purity is less than 90%.
2.6 Imaging Instructions
- Imaging may begin 15 minutes after injection.
- The recommended imaging duration of the scan may vary depending on dose, imaging acquisition, and reconstruction parameters.
2.7 Radiation Dosimetry
Radiation absorbed dose per unit activity of the agent injected intravenously in an adult of average weight (74 kg) is estimated in Table 1 for exercise and resting conditions. The values listed correspond to a 3.5-hour voiding period for excretion from the urinary bladder.
| Radiation absorbed dose per unit activity injected intravenously | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise | Rest | |||
| Target organ | rad/mCi | microGy/MBq | rad/mCi | microGy/MBq |
| Gall bladder wall | 0.10 | 27 | 0.13 | 36 |
| Upper large intestine | 0.074 | 20 | 0.10 | 27 |
| Lower large intestine | 0.055 | 15 | 0.074 | 20 |
| Bladder wall | 0.052 | 14 | 0.063 | 17 |
| Small intestine | 0.041 | 11 | 0.056 | 15 |
| Kidney | 0.037 | 10 | 0.048 | 13 |
| Salivary glands | 0.030 | 8.0 | 0.043 | 12 |
| Ovaries | 0.029 | 7.7 | 0.033 | 8.8 |
| Uterus | 0.026 | 7.0 | 0.029 | 7.8 |
| Bone surface | 0.023 | 6.3 | 0.021 | 5.8 |
| Thyroid | 0.017 | 4.7 | 0.020 | 5.5 |
| Pancreas | 0.019 | 5.0 | 0.018 | 4.9 |
| Heart wall | 0.019 | 5.2 | 0.017 | 4.7 |
| Stomach | 0.017 | 4.6 | 0.017 | 4.5 |
| Adrenals | 0.016 | 4.4 | 0.016 | 4.2 |
| Liver | 0.012 | 3.3 | 0.015 | 4.0 |
| Spleen | 0.015 | 4.1 | 0.014 | 3.9 |
| Red marrow | 0.014 | 3.9 | 0.014 | 3.8 |
| Muscle | 0.013 | 3.5 | 0.012 | 3.3 |
| Testes | 0.013 | 3.4 | 0.011 | 3.1 |
| Thymus | 0.012 | 3.3 | 0.010 | 2.8 |
| Esophagus | 0.012 | 3.3 | 0.010 | 2.8 |
| Lungs | 0.012 | 3.2 | 0.010 | 2.8 |
| Brain | 0.010 | 2.7 | 0.0085 | 2.3 |
| Skin | 0.0081 | 2.2 | 0.0074 | 2.0 |
| Breasts | 0.0085 | 2.3 | 0.0074 | 2.0 |
| Remaining organs | 0.014 | 3.8 | 0.014 | 3.8 |
| Effective dose per unit activity | 0.026 rem/mCi | 6.9 microSv/MBq | 0.030 rem/mCi | 8.0 microSv/MBq |
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Kit for the preparation of technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin injection: 10 mL multiple-dose, clear, glass vial with a white sterile, non-pyrogenic, lyophilized powder of 0.23 mg tetrofosmin, 0.03 mg stannous chloride dihydrate, 0.32 disodium sulphosalicylate, 1 mg sodium D-gluconate and 1.8 mg sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Following radiolabeling with the Tc99m eluate, MYOVIEW is a clear solution not exceeding 1,110 MBq/mL (30 mCi/mL) of Tc99m.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risks Associated with Exercise or Pharmacologic Stress
Patients evaluated with exercise or pharmacologic stress may experience serious adverse reactions such as myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, hypotension, bronchoconstriction, and cerebrovascular reactions such as headache, paraesthesias, convulsions, somnolence and cerebrovascular accident, including hemorrhage. Perform stress testing in the setting where cardiac resuscitation equipment and trained staff are readily available. When pharmacologic stress is selected as an alternative to exercise, perform the procedure in accordance with the pharmacologic stress agent's prescribing information.
5.2 Radiation Risks
Technetium Tc99m contributes to a patient's overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure. Long-term cumulative radiation exposure is associated with an increased risk of cancer. Ensure safe handling and preparation radiolabeling procedures to protect patients and health care workers from unintentional radiation exposure. Encourage adequate hydration; instruct patients to void when the examination is completed and as often thereafter as possible [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and (2.3)].
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, dyspnea, bronchospasm, throat tightness, coughing, tachycardia, chest pain, hypotension, abdominal pain, and cutaneous reactions (rash, urticaria, pruritus, erythema, and swelling or angioedema) have been observed after the administration of MYOVIEW. Always have cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment and personnel available and monitor all patients for hypersensitivity reactions.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of MYOVIEW cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse reactions were evaluated in clinical studies (using an exercise/rest protocol) of 764 adults (511 men and 253 women) with a mean age of 58.7 years (range 29 to 94 years). The subjects received a mean dose of 285 MBq (7.7 mCi) on the first injection and 829 MBq (22.4 mCi) on the second injection of MYOVIEW.
After MYOVIEW injection, angina occurred in 4 subjects, ventricular tachycardia in 1 subject, and respiratory arrest in 1 subject.
The following reactions were noted in less than 1% of subjects:
Cardiovascular: angina, hypertension, torsades de pointes.
Gastrointestinal: vomiting, abdominal discomfort.
Hypersensitivity: cutaneous allergy, hypotension, dyspnea.
Special Senses: metallic taste, burning of the mouth, smell alteration.
In four studies, 438 adults (232 men and 205 women: gender was not recorded for one subject) with a mean age of 65 years (range 27 to 97 years) received a single pharmacologic stress agent. The subjects received a mean dose of 7 to 8 mCi on the rest/first injection and 22 to 34 mCi on the stress/second injection. Among the 438 subjects, 319 subjects (73%) experienced an adverse reaction. Reactions occurring in ≥1% of the subjects included angina (39%), flushing (36%), dyspnea (28%), headache (14%), abdominal pain (11%), dizziness (7%), palpitations (2%), nausea (2%), hypotension (1%) and pain (1%). Events occurring in <1% include cough, arrhythmia, bronchospasm, ECG abnormalities, hypertension, vomiting and asthenia.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of MYOVIEW. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The most common adverse reactions reported included: rash, urticaria, abnormal vision, hypersensitivity reactions, and fever.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no data with technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin use in pregnant women to inform any drug associated risks. Animal reproduction studies with technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin have not been conducted. However, all radiopharmaceuticals have the potential to cause fetal harm depending on the fetal stage of development and the magnitude of the radiation dose. If considering technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin administration to a pregnant woman advise the pregnant woman of risk to the fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin is present in human milk in small amounts (<1% of maternal dose). There are no data available regarding the effects of technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin on the breastfed infant or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for MYOVIEW and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from MYOVIEW or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of 2,300 subjects in clinical studies of MYOVIEW, 1,053 (46%) were 65 or older and 270 (12%) were 75 or older. No overall differences in safety were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 Chemical Characteristics
MYOVIEW is a kit for the preparation of technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin injection for intravenous use. Technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin is a radioactive diagnostic agent. Each multiple-dose 10 mL glass vial contains a sterile, non-pyrogenic, lyophilized powder of 0.23 mg tetrofosmin [6,9-bis(2-ethoxyethyl)-3,12-dioxa-6,9-diphosphatetradecane], 0.03 mg stannous chloride dihydrate, (minimum stannous tin 0.015 mg; total stannous and stannic tin 0.0522 mg) 0.32 mg disodium sulphosalicylate, 1 mg sodium D-gluconate, and 1.8 mg sodium hydrogen carbonate. The lyophilized powder is sealed under a nitrogen atmosphere with a rubber closure. The product contains no antimicrobial preservative. The chemical formula of tetrofosmin is C18H40O4P2 with the following structural formula:
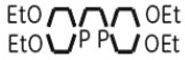
C18H40O4P2
When sterile, pyrogen-free sodium pertechnetate Tc99m in isotonic saline is added to the vial, a Tc99m complex of tetrofosmin is formed. The radiolabeled product is a clear solution and the pH is in the range of 7.5 to 9.0.
11.2 Physical Characteristics
Technetium Tc99m decays by isomeric transition with a physical half-life of 6 hours. Photons that are useful for imaging studies are listed in Table 2.
| Radiation | Mean % disintegration | Mean energy (keV) |
|---|---|---|
| Gamma 2 | 88.5 | 140.5 |
11.3 External Radiation
The air-kerma-rate (exposure-rate) constant for technetium Tc99m is 5.23 m2∙pGy∙(MBq)−1∙s−1 [0.795 cm2∙R∙(mCi)−1∙h−1].
A range of values for the relative radiation attenuation by various thicknesses of Pb shielding is shown in Table 3. For example, the use of 3 mm thick Pb will decrease the external radiation exposure by a factor of approximately 1,000.
| Shield thickness (Pb) mm | Factor of attenuation |
|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 10-1 |
| 2 | 10-2 |
| 3 | 10-3 |
| 4 | 10-4 |
| 5 | 10-5 |
To correct for physical decay of this radionuclide, the fractions that remain at selected intervals relative to the time of calibration are shown in Table 4.
| Hours | Fraction Remaining | Hours | Fraction Remaining |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| 0* | 1.000 | 7 | 0.446 |
| 1 | 0.891 | 8 | 0.397 |
| 2 | 0.794 | 9 | 0.354 |
| 3 | 0.707 | 10 | 0.315 |
| 4 | 0.630 | 11 | 0.281 |
| 5 | 0.562 | 12 | 0.250 |
| 6 | 0.500 | 24 | 0.063 |
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Technetium (99mTc) tetrofosmin is a lipophilic, cationic complex which diffuses passively through the cell membrane and is locally retained actively due to the presence of intact mitochondria reflecting the presence of viable cells. After intravenous injection, it is distributed within the myocardium according to myocardial perfusion and viability.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The relationship between Tc99m tetrofosmin plasma concentrations and successful imaging has not been explored in clinical trials.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Uptake in the myocardium is dependent on coronary flow and reaches a maximum of 1.2% of the injected dose (i.d.) at 5 minutes and 1% of the i.d. at 2 hours, respectively. Background activities in the blood, liver and lung were less than 5% of the administered activity in whole blood at 10 minutes post-injection, less than 4.5% i.d., after 60 minutes, and less than 2% i.d. after 30 minutes.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies have not been conducted to evaluate carcinogenic potential or effects on fertility. Tetrofosmin sulphosalicylate was not mutagenic in vitro in the Ames test, mouse lymphoma, or human lymphocyte tests, nor was it clastogenic in vivo in the mouse micronucleus test.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Exercise/Resting Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Studies
A total of 252 subjects with ischemic heart disease or atypical chest pain were studied in two open-label, multi-center, clinical studies (study a and study b). Of these 252 subjects there were 212 (84%) males and 40 (16%) females with a mean age of 60.5 years (range 33.7 to 82.4 years).
All subjects had exercise and rest planar imaging with MYOVIEW and thallium-201; 191 (76%) subjects also had single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging. At peak exercise, maximum heart rate achieved and peak systolic blood pressure were comparable after MYOVIEW and thallium-201 exercise studies. The MYOVIEW and thallium-201 images were separated by a mean of 5.1 days (1 to 14 days before or 2 to 14 days after MYOVIEW). For MYOVIEW imaging, each subject received 185 to 296 MBq (5 to 8 mCi) Tc99m tetrofosmin at peak exercise and 555 to 888 MBq (15 to 24 mCi) Tc99m tetrofosmin at rest approximately 4 hours later. For thallium-201 imaging, subjects received thallium-201 55.5 to 74 MBq (1.5 to 2 mCi) at peak exercise.
The images were evaluated for the quality of the image (excellent, good or poor) and the diagnosis (with scores of 0 = normal, 1 = ischemia, 2 = infarct, 3 = mixed infarct and ischemia). The primary outcome variable was the percentage of correct diagnoses in comparison to the final clinical diagnosis. All planar images were blindly read; SPECT images were evaluated by the unblinded investigator. The results for each blinded reader are noted in Table 5.
| Thallium 201 | MYOVIEW | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reader 1 | Reader 2 | Reader 1 | Reader 2 | ||
| Diagnosis | Study | % (95% CI) | % (95% CI) | % (95% CI) | % (95% CI) |
| Ischemia | a | 77.7 (68.8, 85.0) | 75.0 (65.9, 82.7) | 66.3 (56.7, 75.1) | 63.6 (53.9, 72.6) |
| b | 75.6 (66.9, 83.0) | 68.9 (59.8, 77.1) | 66.4 (57.2, 74.8) | 66.4 (57.2, 74.8) | |
| Infarct | a | 75.9 (66.9, 83.5) | 75.0 (65.9, 82.7) | 74.5 (65.4, 82.4) | 75.5 (66.3, 83.2) |
| b | 70.6 (61.5, 78.6) | 69.7 (60.7, 77.8) | 73.1 (64.2, 80.8) | 68.1 (58.9, 76.3) | |
14.2 Pharmacological Stress Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Studies
MYOVIEW imaging after pharmacologic stress was evaluated in two studies in subjects with known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD). Three blinded reads were obtained for 57 subjects (45 male [79%], 12 female [21%]; mean age 60.1 years) all of whom had angiography. Subject level analyses were based on the finding of SPECT myocardial perfusion abnormalities in patients with angiographically confirmed disease. Subject level sensitivities for MYOVIEW ranged from 68 to 83% and subject level specificities ranged from 45 to 82% across readers and studies.
14.3 Ventricular Function Stress Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Studies
Two open-label, multicenter, identically designed, blinded image read studies were conducted to assess left ventricular function using MYOVIEW ECG gated SPECT (GSPECT) myocardial perfusion imaging. A total of 329 subjects (216 male [65.7%], 113 female [34.3%]); mean age of 60.4 years) with known or suspected heart disease or requiring ventricular function assessments were dosed with MYOVIEW. Of these, 297 were considered evaluable. MYOVIEW was administered at rest and at peak stress using either a one-day or a 2-day dosing protocol.
For both studies, all subjects' stress GSPECT exams were compared to the reference exam of radionuclide ventriculography with Tc99m labeled RBCs (multiple gated acquisition [MUGA]), performed 1 to 5 days after the second MYOVIEW injection. All subjects' GSPECT exams were assessed by 3 independent blinded readers per study. The MUGA exams were evaluated by an independent consensus panel composed of 3 blinded readers. Subject level assessments were based upon discrimination between normal and abnormal values for LVEF (LVEF ≥50% was considered normal) and normal and abnormal wall motion as judged visually. Sensitivity and specificity of LVEF determinations ranged from 81% to 88% and 76% to 85% respectively across studies and readers. Sensitivity and specificity of wall motion determinations ranged from 80% to 92% and 68% to 86% respectively across studies and readers.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How supplied
Five (5) multiple-dose kits, each containing a 10 mL glass vial with a sterile, non-pyrogenic, lyophilized powder containing 0.23 mg tetrofosmin, 0.03 mg stannous chloride dihydrate, 0.32 mg disodium sulphosalicylate, 1 mg sodium D-gluconate, 1.8 mg sodium hydrogen carbonate.
NDC 17156-024-05
The radionuclide is not part of the kit. Before radiolabeling with Tc99m, the contents of the kit are not radioactive.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store the kit at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F), protected from light.
Store the radiolabeled vial at 2° to 25°C (36° to 77°F), using appropriate radiation shielding. Use within 12 hours of preparation.
This reagent kit is approved for use by persons under license by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission or the relevant regulatory authority of an Agreement State; store and dispose of technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin in accordance with these regulations.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Instruct patients to remain hydrated and void frequently following administration to decrease radiation exposure.
- Advise a lactating woman to pump and discard breast milk for 60 hours (10 half-lives) after technetium Tc99m tetrofosmin administration to decrease radiation exposure to the breastfed infant.
