Prescribing Information
SPECIAL NOTE
Gallbladder stone dissolution with ursodiol treatment requires months of therapy. Complete dissolution does not occur in all patients and recurrence of stones within 5 years has been observed in up to 50% of patients who do dissolve their stones on bile acid therapy. Patients should be carefully selected for therapy with ursodiol, and alternative therapies should be considered.
DESCRIPTION
Ursodiol is a bile acid available as 300 mg capsules suitable for oral administration.
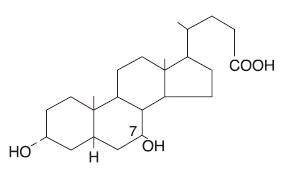
Ursodiol, USP (ursodeoxycholic acid), is a naturally occurring bile acid found in small quantities in normal human bile and in the biles of certain other mammals. It is a bitter-tasting, white powder freely soluble in ethanol, methanol, and glacial acetic acid; sparingly soluble in chloroform; slightly soluble in ether; and insoluble in water. The chemical name for ursodiol is 3α, 7β-Dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid (C24H40O4). Ursodiol, USP has a molecular weight of 392.57. Its structure is shown below:
Inactive Ingredients: Corn starch, magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide and the capsule shell contain the following ingredients, gelatin, titanium dioxide, D&C Red # 28, FD&C Blue # 1 and FD&C Red # 40.
The imprinting ink contains the following: black iron oxide, D&C Yellow # 10 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue # 1 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue # 2 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Red # 40 Aluminum Lake, propylene glycol and shellac glaze.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
About 90% of a therapeutic dose of ursodiol is absorbed in the small bowel after oral administration. After absorption, ursodiol enters the portal vein and undergoes efficient extraction from portal blood by the liver (i.e., there is a large “first-pass” effect) where it is conjugated with either glycine or taurine and is then secreted into the hepatic bile ducts. Ursodiol in bile is concentrated in the gallbladder and expelled into the duodenum in gallbladder bile via the cystic and common ducts by gallbladder contractions provoked by physiologic responses to eating. Only small quantities of ursodiol appear in the systemic circulation and very small amounts are excreted into urine. The sites of the drug’s therapeutic actions are in the liver, bile, and gut lumen.
Beyond conjugation, ursodiol is not altered or catabolized appreciably by the liver or intestinal mucosa. A small proportion of orally administered drug undergoes bacterial degradation with each cycle of enterohepatic circulation. Ursodiol can be both oxidized and reduced at the 7-carbon, yielding either 7-keto-lithocholic acid or lithocholic acid, respectively. Further, there is some bacterially catalyzed deconjugation of glyco- and tauro-ursodeoxycholic acid in the small bowel. Free ursodiol, 7-keto-lithocholic acid, and lithocholic acid are relatively insoluble in aqueous media and larger proportions of these compounds are lost from the distal gut into the feces. Reabsorbed free ursodiol is reconjugated by the liver. Eighty percent of lithocholic acid formed in the small bowel is excreted in the feces, but the 20% that is absorbed is sulfated at the 3-hydroxyl group in the liver to relatively insoluble lithocholyl conjugates which are excreted into bile and lost in feces. Absorbed 7-keto-lithocholic acid is stereospecifically reduced in the liver to chenodiol.
Lithocholic acid causes cholestatic liver injury and can cause death from liver failure in certain species unable to form sulfate conjugates. Lithocholic acid is formed by 7-dehydroxylation of the dihydroxy bile acids (ursodiol and chenodiol) in the gut lumen. The 7-dehydroxylation reaction appears to be alpha-specific, i.e., chenodiol is more efficiently 7-dehydroxylated than ursodiol and, for equimolar doses of ursodiol and chenodiol, levels of lithocholic acid appearing in bile are lower with the former. Man has the capacity to sulfate lithocholic acid. Although liver injury has not been associated with ursodiol therapy, a reduced capacity to sulfate may exist in some individuals, but such a deficiency has not yet been clearly demonstrated.
Pharmacodynamics
Ursodiol suppresses hepatic synthesis and secretion of cholesterol, and also inhibits intestinal absorption of cholesterol. It appears to have little inhibitory effect on synthesis and secretion into bile of endogenous bile acids, and does not appear to affect secretion of phospholipids into bile.
With repeated dosing, bile ursodeoxycholic acid concentrations reach a steady state in about 3 weeks. Although insoluble in aqueous media, cholesterol can be solubilized in at least two different ways in the presence of dihydroxy bile acids. In addition to solubilizing cholesterol in micelles, ursodiol acts by an apparently unique mechanism to cause dispersion of cholesterol as liquid crystals in aqueous media. Thus, even though administration of high doses (e.g., 15 - 18 mg/kg/day) does not result in a concentration of ursodiol higher than 60% of the total bile acid pool, ursodiol-rich bile effectively solubilizes cholesterol. The overall effect of ursodiol is to increase the concentration level at which saturation of cholesterol occurs.
The various actions of ursodiol combine to change the bile of patients with gallstones from cholesterol-precipitating to cholesterolsolubilizing, thus resulting in bile conducive to cholesterol stone dissolution.
After ursodiol dosing is stopped, the concentration of the bile acid in bile falls exponentially, declining to about 5% - 10% of its steady state level in about 1 week.
Clinical Results
Gallstone Dissolution
On the basis of clinical trial results in a total of 868 patients with radiolucent gallstones treated in 8 studies (three in the U.S. involving 282 patients, one in the U.K. involving 130 patients, and four in Italy involving 456 patients) for periods ranging from 6 - 78 months with ursodiol doses ranging from about 5 - 20 mg/kg/day, an ursodiol dose of about 8 - 10 mg/kg/day appeared to be the best dose.
With an ursodiol dose of about 10 mg/kg/day, complete stone dissolution can be anticipated in about 30% of unselected patients with uncalcified gallstones < 20 mm in maximal diameter treated for up to 2 years. Patients with calcified gallstones prior to treatment, or patients who develop stone calcification or gallbladder nonvisualization on treatment, and patients with stones > 20 mm in maximal diameter rarely dissolve their stones. The chance of gallstone dissolution is increased up to 50% in patients with floating or floatable stones (i.e., those with high cholesterol content), and is inversely related to stone size for those < 20 mm in maximal diameter.
Complete dissolution was observed in 81% of patients with stones up to 5 mm in diameter. Age, sex, weight, degree of obesity, and serum cholesterol level are not related to the chance of stone dissolution with ursodiol.
A nonvisualizing gallbladder by oral cholecystogram prior to the initiation of therapy is not a contraindication to ursodiol therapy (the group of patients with nonvisualizing gallbladders in the ursodiol studies had complete stone dissolution rates similar to the group of patients with visualizing gallbladders). However, gallbladder nonvisualization developing during ursodiol treatment predicts failure of complete stone dissolution and in such cases therapy should be discontinued. Partial stone dissolution occurring within 6 months of beginning therapy with ursodiol appears to be associated with a > 70% chance of eventual complete stone dissolution with further treatment; partial dissolution observed within 1 year of starting therapy indicates a 40% probability of complete dissolution. Stone recurrence after dissolution with ursodiol therapy was seen within 2 years in 8/27 (30%) of patients in the U.K. studies. Of 16 patients in the U.K. study whose stones had previously dissolved on chenodiol but later recurred, 11 had complete dissolution on ursodiol. Stone recurrence has been observed in up to 50% of patients within 5 years of complete stone dissolution on ursodiol therapy. Serial ultrasonographic examinations should be obtained to monitor for recurrence of stones, bearing in mind that radiolucency of the stones should be established before another course of ursodiol is instituted. A prophylactic dose of ursodiol has not been established.
Gallstone Prevention
Two placebo-controlled, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, parallel group trials in a total of 1,316 obese patients were undertaken to evaluate ursodiol in the prevention of gallstone formation in obese patients undergoing rapid weight loss. The first trial consisted of 1,004 obese patients with a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 38 who underwent weight loss induced by means of a very low calorie diet for a period of 16 weeks. An intent-to-treat analysis of this trial showed that gallstone formation occurred in 23% of the placebo group, while those patients on 300, 600, or 1200 mg/day of ursodiol experienced a 6%, 3%, and 2% incidence of gallstone formation, respectively. The mean weight loss for this 16-week trial was 47 lb for the placebo group, and 47, 48, and 50 lb for the 300, 600, and 1200 mg/day ursodiol groups, respectively.
The second trial consisted of 312 obese patients (BMI ≥ 40) who underwent rapid weight loss through gastric bypass surgery. The trial drug treatment period was for 6 months following this surgery. Results of this trial showed that gallstone formation occurred in 23% of the placebo group, while those patients on 300, 600, or 1200 mg/day of Ursodiol experienced a 9%, 1%, and 5% incidence of gallstone formation, respectively. The mean weight loss for this 6-month trial was 64 lb for the placebo group, and 67, 74, and 72 lb for the 300, 600, and 1200 mg/day ursodiol groups, respectively.
ALTERNATIVE THERAPIES
Watchful Waiting
Watchful waiting has the advantage that no therapy may ever be required. For patients with silent or minimally symptomatic stones, the rate of development of moderate-to-severe symptoms or gallstone complications is estimated to be between 2% and 6% per year, leading to a cumulative rate of 7% - 27% in 5 years. Presumably the rate is higher for patients already having symptoms.
Cholecystectomy
For patients with symptomatic gallstones, surgery offers the advantage of immediate and permanent stone removal, but carries a high risk in some patients. About 5% of cholecystectomized patients have residual symptoms or retained common duct stones. The spectrum of surgical risk varies as a function of age and the presence of disease other than cholelithiasis.
Mortality Rates for Cholecystectomy in the U.S.
(National Halothane Study, JAMA 1966; 197:775-8)
27,600 Cholecystectomies
(Smoothed Rates)
Deaths/1000 Operations***
| Mortality Rates for Cholecystectomy in the US | |||
|
Low Risk Patients* |
Age (yrs) |
Cholecystectomy |
Cholecystectomy Common Duct Exploration |
|
Women |
0-49 |
.54 |
2.13 |
|
50-69 |
2.80 |
10.10 |
|
|
Men |
0-49 |
1.04 |
4.12 |
|
50-69 |
5.41 |
19.23 |
|
|
High Risk Patients** | |||
|
Women |
0-49 |
12.66 |
47.62 |
|
50-69 |
17.24 |
58.82 |
|
|
Men |
0-49 |
24.39 |
90.91 |
|
50-69 |
33.33 |
111.11 |
|
* In good health or with moderate systemic disease.
** With severe or extreme systemic disease.
*** Includes both elective and emergency surgery.
Women in good health or who have only moderate systemic disease and are under 49 years of age have the lowest surgical mortality rate (0.054); men in all categories have a surgical mortality rate twice that of women. Common duct exploration quadruples the rates in all categories. The rates rise with each decade of life and increase tenfold or more in all categories with severe or extreme systemic disease.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 1.
- Ursodiol is indicated for patients with radiolucent, noncalcified gallbladder stones < 20 mm in greatest diameter in whom elective cholecystectomy would be undertaken except for the presence of increased surgical risk due to systemic disease, advanced age, idiosyncratic reaction to general anesthesia, or for those patients who refuse surgery. Safety of use of ursodiol beyond 24 months is not established.
- 2.
- Ursodiol is indicated for the prevention of gallstone formation in obese patients experiencing rapid weight loss.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 1.
- Ursodiol will not dissolve calcified cholesterol stones, radiopaque stones, or radiolucent bile pigment stones. Hence, patients with such stones are not candidates for ursodiol therapy.
- 2.
- Patients with compelling reasons for cholecystectomy including unremitting acute cholecystitis, cholangitis, biliary obstruction, gallstone pancreatitis, or biliary-gastrointestinal fistula are not candidates for ursodiol therapy.
- 3.
- Allergy to bile acids.
PRECAUTIONS
Liver Tests
Ursodiol therapy has not been associated with liver damage. Lithocholic acid, a naturally occurring bile acid, is known to be a liver-toxic metabolite. This bile acid is formed in the gut from ursodiol less efficiently and in smaller amounts than that seen from chenodiol. Lithocholic acid is detoxified in the liver by sulfation and, although man appears to be an efficient sulfater, it is possible that some patients may have a congenital or acquired deficiency in sulfation, thereby predisposing them to lithocholate-induced liver damage.
Abnormalities in liver enzymes have not been associated with ursodiol therapy and, in fact, ursodiol has been shown to decrease liver enzyme levels in liver disease. However, patients given ursodiol should have SGOT (AST) and SGPT (ALT) measured at the initiation of therapy and thereafter as indicated by the particular clinical circumstances.
Drug Interactions
Bile acid sequestering agents such as cholestyramine and colestipol may interfere with the action of ursodiol by reducing its absorption. Aluminum-based antacids have been shown to absorb bile acids in vitro and may be expected to interfere with ursodiol in the same manner as the bile acid sequestering agents. Estrogens, oral contraceptives, and clofibrate (and perhaps other lipid-lowering drugs) increase hepatic cholesterol secretion, and encourage cholesterol gallstone formation and hence may counteract the effectiveness of ursodiol.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Ursodeoxycholic acid was tested in 2-year oral carcinogenicity studies in CD-1 mice and Sprague-Dawley rats at daily doses of 50, 250, and 1000 mg/kg/day. It was not tumorigenic in mice. In the rat study, it produced statistically significant dose-related increased incidences of pheochromocytomas of adrenal medulla in males (p=0.014, Peto trend test) and females (p=0.004, Peto trend test). A 78-week rat study employing intrarectal instillation of lithocholic acid and tauro-deoxycholic acid, metabolites of ursodiol and chenodiol, has been conducted. These bile acids alone did not produce any tumors. A tumor-promoting effect of both metabolites was observed when they were co-administered with a carcinogenic agent. Results of epidemiologic studies suggest that bile acids might be involved in the pathogenesis of human colon cancer in patients who had undergone a cholecystectomy, but direct evidence is lacking. Ursodiol is not mutagenic in the Ames test. Dietary administration of lithocholic acid to chickens is reported to cause hepatic adenomatous hyperplasia.
Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits with ursodiol doses up to 200-fold the therapeutic dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus at doses of 20- to 100-fold the human dose in rats and at 5-fold the human dose (highest dose tested) in rabbits. Studies employing 100- to 200-fold the human dose in rats have shown some reduction in fertility rate and litter size. There have been no adequate and well-controlled studies of the use of ursodiol in pregnant women, but inadvertent exposure of 4 women to therapeutic doses of the drug in the first trimester of pregnancy during the ursodiol trials led to no evidence of effects on the fetus or newborn baby. Although it seems unlikely, the possibility that ursodiol can cause fetal harm cannot be ruled out; hence, the drug is not recommended for use during pregnancy.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether ursodiol is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ursodiol is administered to a nursing mother.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ursodiol in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
In worldwide clinical studies of ursodiol, approximately 14% of subjects were over 65 years of age (approximately 3% were over 75 years old). In a subgroup analysis of existing clinical trials, patients greater than 56 years of age did not exhibit statistically significantly different complete dissolution rates from the younger population. No age-related differences in safety and effectiveness were found. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in response in elderly and younger patients. However, small differences in efficacy and greater sensitivity of some elderly individuals taking ursodiol cannot be ruled out. Therefore, it is recommended that dosing proceed with caution in this population.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The nature and frequency of adverse experiences were similar across all groups.
The following tables provide comprehensive listings of the adverse experiences reported that occurred with a 5% incidence level:
| Gallstone Dissolution In Ursodiol and Placebo Patients | ||||
|
GALLSTONE DISSOLUTION |
||||
|
Ursodiol 8 - 10 mg/kg/day (N=155) |
Placebo (N=159) |
|||
|
N |
(%) |
N |
(%) |
|
|
Body as a Whole | ||||
|
Allergy |
8 |
(5.2) |
7 |
(4.4) |
|
Chest Pain |
5 |
(3.2) |
10 |
(6.3) |
|
Fatigue |
7 |
(4.5) |
8 |
(5.0) |
|
Infection Viral |
30 |
(19.4) |
41 |
(25.8) |
|
Digestive System | ||||
|
Abdominal Pain |
67 |
(43.2) |
70 |
(44.0) |
|
Cholecystitis |
8 |
(5.2) |
7 |
(4.4) |
|
Constipation |
15 |
(9.7) |
14 |
(8.8) |
|
Diarrhea |
42 |
(27.1) |
34 |
(21.4) |
|
Dyspepsia |
26 |
(16.8) |
18 |
(11.3) |
|
Flatulence |
12 |
(7.7) |
12 |
(7.5) |
|
Gastrointestinal Disorder |
6 |
(3.9) |
8 |
(5.0) |
|
Nausea |
22 |
(14.2) |
27 |
(17.0) |
|
Vomiting |
15 |
(9.7) |
11 |
(6.9) |
|
Musculoskeletal System | ||||
|
Arthralgia |
12 |
(7.7) |
24 |
(15.1) |
|
Arthritis |
9 |
(5.8) |
4 |
(2.5) |
|
Back Pain |
11 |
(7.1) |
18 |
(11.3) |
|
Myalgia |
9 |
(5.8) |
9 |
(5.7) |
|
Nervous System | ||||
|
Headache |
28 |
(18.1) |
34 |
(21.4) |
|
Insomnia |
3 |
(1.9) |
8 |
(5.0) |
|
Respiratory System | ||||
|
Bronchitis |
10 |
(6.5) |
6 |
(3.8) |
|
Coughing |
11 |
(7.1) |
7 |
(4.4) |
|
Pharyngitis |
13 |
(8.4) |
5 |
(3.1) |
|
Rhinitis |
8 |
(5.2) |
11 |
(6.9) |
|
Sinusitis |
17 |
(11.0) |
18 |
(11.3) |
|
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection |
24 |
(15.5) |
21 |
(13.2) |
|
Urogenital System | ||||
|
Urinary Tract Infection |
10 |
(6.5) |
7 |
(4.4) |
| Gallstone Prevention in Ursodiol and Placebo-Treated Patients | |||||||||
|
GALLSTONE PREVENTION |
|||||||||
|
Ursodiol 600 mg (N=322) |
Placebo (N=325) |
||||||||
|
N |
(%) |
N |
(%) |
||||||
|
Body as a Whole | |||||||||
|
Fatigue |
25 |
(7.8) |
33 |
(10.2) |
|||||
|
Infection Viral |
29 |
(9.0) |
29 |
(8.9) |
|||||
|
Influenza-like Symptoms |
21 |
(6.5) |
19 |
(5.8) |
|||||
|
Digestive System | |||||||||
|
Abdominal Pain |
20 |
(6.2) |
39 |
(12.0) |
|||||
|
Constipation |
85 |
(26.4) |
72 |
(22.2) |
|||||
|
Diarrhea |
81 |
(25.2) |
68 |
(20.9) |
|||||
|
Flatulence |
15 |
(4.7) |
24 |
(7.4) |
|||||
|
Nausea |
56 |
(17.4) |
43 |
(13.2) |
|||||
|
Vomiting |
44 |
(13.7) |
44 |
(13.5) |
|||||
|
Musculoskeletal System | |||||||||
|
Back Pain |
38 |
(11.8) |
21 |
(6.5) |
|||||
|
Musculoskeletal Pain |
19 |
(5.9) |
15 |
(4.6) |
|||||
|
Nervous System | |||||||||
|
Dizziness |
53 |
(16.5) |
42 |
(12.9) |
|||||
|
Headache |
80 |
(24.8) |
78 |
(24.0) |
|||||
|
Respiratory System | |||||||||
|
Pharyngitis |
10 |
(3.1) |
19 |
(5.8) |
|||||
|
Sinusitis |
17 |
(5.3) |
18 |
(5.5) |
|||||
|
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection |
40 |
(12.4) |
35 |
(10.8) |
|||||
|
Skin and Appendages | |||||||||
|
Alopecia |
17 |
(5.3) |
8 |
(2.5) |
|||||
|
Urogenital System | |||||||||
|
Dysmenorrhea |
18 |
(5.6) |
19 |
(5.8) |
|||||
OVERDOSAGE
Neither accidental nor intentional overdosing with ursodiol has been reported. Doses of ursodiol in the range of 16 - 20 mg/kg/day have been tolerated for 6 - 37 months without symptoms by 7 patients. The LD50 for ursodiol in rats is over 5000 mg/kg given over 7 - 10 days and over 7500 mg/kg for mice. The most likely manifestation of severe overdose with ursodiol would probably be diarrhea, which should be treated symptomatically.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Gallstone Dissolution
The recommended dose for ursodiol treatment of radiolucent gallbladder stones is 8 - 10 mg/kg/day given in 2 or 3 divided doses. Ultrasound images of the gallbladder should be obtained at 6-month intervals for the first year of ursodiol therapy to monitor gallstone response. If gallstones appear to have dissolved, ursodiol therapy should be continued and dissolution confirmed on a repeat ultrasound examination within 1 to 3 months. Most patients who eventually achieve complete stone dissolution will show partial or complete dissolution at the first on-treatment reevaluation. If partial stone dissolution is not seen by 12 months of ursodiol therapy, the likelihood of success is greatly reduced.
HOW SUPPLIED
Ursodiol Capsules USP, 300 mg are #0 capsules with a pink opaque cap, white opaque body, imprinted “Є503” in black ink on cap and body, filled with white powder.
They are supplied:
NDC 24658-780-01 Bottles of 100 Capsules.
NDC 24658-999-10 Bottles of 1000 Capsules.
Store at 20° - 25°C (68° - 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense contents in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Keep out of reach of children.
Distributed by:
PuraCap Laboratories, LLC
DBA Blu Pharmaceuticals
Franklin, KY 42134 USA
1-877-264-0258
Manufactured in USA
Issued September 2016
MF503ISS09/16
OE2631
