FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Malignant Diseases
Cyclophosphamide Injection is indicated for the treatment of:
- malignant lymphomas (Stages III and IV of the Ann Arbor staging system), Hodgkin's disease, lymphocytic lymphoma (nodular or diffuse), mixed-cell type lymphoma, histiocytic lymphoma, Burkitt's lymphoma
- multiple myeloma
- leukemias: chronic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic granulocytic leukemia (it is usually ineffective in acute blastic crisis), acute myelogenous and monocytic leukemia, acute lymphoblastic (stem-cell) leukemia (cyclophosphamide given during remission is effective in prolonging its duration)
- mycosis fungoides (advanced disease)
- neuroblastoma (disseminated disease)
- adenocarcinoma of the ovary
- retinoblastoma
- carcinoma of the breast
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Malignant Diseases
Adults and Pediatric Patients
Pre- and Peri-Treatment Hydration
During or immediately after the administration, adequate amounts of fluid should be ingested or infused to force diuresis in order to reduce the risk of urinary tract toxicity. Therefore, Cyclophosphamide Injection should be administered in the morning.
Recommended Dosage
When used as the only oncolytic drug therapy, the initial course of Cyclophosphamide Injection for patients with no hematologic deficiency usually consists of 40 mg per kg to 50 mg per kg given intravenously in divided doses over a period of 2 to 5 days.
Other intravenous regimens include 10 mg per kg to 15 mg per kg given every 7 to 10 days or 3 mg per kg to 5 mg per kg twice weekly.
When cyclophosphamide is included in combined cytotoxic regimens, it may be necessary to reduce the dose of Cyclophosphamide Injection as well as that of the other drugs.
2.2 Preparation, Handling and Administration
Cyclophosphamide Injection is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures. 1Caution should be exercised when handling and preparing Cyclophosphamide Injection. To minimize the risk of dermal exposure, always wear gloves when handling vials containing Cyclophosphamide Injection.
Cyclophosphamide Injection requires two-step dilution prior to administration.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use cyclophosphamide vials if there are visible particulate matter or discoloration of the solution.
Initial Dilution of Cyclophosphamide Injection
Dilute Cyclophosphamide Injection using Sterile Water for Injection, USP with the volume of diluent listed below in Table 1. Add the diluent to the vial and gently swirl to mix.
| * Volume of diluent has been adjusted for vial overfill | ||
| Cyclophosphamide Injection
| Volume of Diluent*
| Initial Dilution Cyclophosphamide Concentration
|
| 500 mg/2.5 mL | 25 mL | 20 mg/mL |
| 1 g/5 mL | 50 mL |
|
Final Dilution of Cyclophosphamide Injection
Calculate and withdraw the volume needed for the prescribed dose.
Further dilute the initial diluted Cyclophosphamide Injection solution to a concentration of 2 mg per mL with any of the following diluents:
- 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
To reduce the likelihood of adverse reactions that appear to be administration rate-dependent (e.g., facial swelling, headache, nasal congestion, scalp burning), Cyclophosphamide Injection should be injected or infused very slowly. Duration of the infusion also should be appropriate for the volume and type of final diluted solution to be infused.
Storage of Initial and Final Diluted Cyclophosphamide Injection Solutions
If not used immediately, for microbiological integrity, Cyclophosphamide Injection solutions should be stored as described in Table 2:
| 1 Storage time is the total time Cyclophosphamide Injection is in the diluted solutions including the time it is diluted in Sterile Water for Injection, USP. | ||
| Diluent
| Storage
|
|
| Room Temperature
| Refrigerated
|
|
| Initial Diluted Solution
|
||
| Sterile Water for Injection, USP | up to 24 hrs | up to 24 hrs |
| Final Diluted Solution for Intravenous Infusion1
|
||
| 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP | up to 24 hrs | up to 6 days |
| 5% Dextrose Injection, USP | up to 24 hrs | up to 36 hrs |
| 5% Dextrose and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP | up to 24 hrs | up to 36 hrs |
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Cyclophosphamide Injection is a sterile, colorless to slightly yellow clear solution in single-dose vials containing:
- 500 mg/2.5 mL (200 mg/mL)
- 1 g/5 mL (200 mg/mL)
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Hypersensitivity
Cyclophosphamide Injection is contraindicated in patients who have a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to it, any of its metabolites, or to other components of the product. Anaphylactic reactions including death have been reported with cyclophosphamide. Possible cross-sensitivity with other alkylating agents can occur.
• Urinary Outflow Obstruction
Cyclophosphamide Injection is contraindicated in patients with urinary outflow obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myelosuppression, Immunosuppression, Bone Marrow Failure and Infections
Cyclophosphamide Injection can cause myelosuppression (leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia and anemia), bone marrow failure, and severe immunosuppression which may lead to serious and sometimes fatal infections, including sepsis and septic shock. Latent infections can be reactivated [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Antimicrobial prophylaxis may be indicated in certain cases of neutropenia at the discretion of the managing healthcare provider. In case of neutropenic fever, antibiotic therapy is indicated. Antimycotics and/or antivirals may also be indicated.
Monitoring of complete blood counts is essential during Cyclophosphamide Injection treatment so that the dose can be adjusted, if needed. Cyclophosphamide Injection should not be administered to patients with neutrophils ≤1,500/mm3 and platelets < 50,000/mm3. Cyclophosphamide Injection treatment may not be indicated, or should be interrupted, or the dose reduced, in patients who have or who develop a serious infection. G-CSF may be administered to reduce the risks of neutropenia complications associated with Cyclophosphamide Injection use. Primary and secondary prophylaxis with G-CSF should be considered in all patients considered to be at increased risk for neutropenia complications. The nadirs of the reduction in leukocyte count and thrombocyte count are usually reached in weeks 1 and 2 of treatment. Peripheral blood cell counts are expected to normalize after approximately 20 days. Bone marrow failure has been reported. Severe myelosuppression may be expected particularly in patients pretreated with and/or receiving concomitant chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
5.2 Urinary Tract and Renal Toxicity
Hemorrhagic cystitis, pyelitis, ureteritis, and hematuria have been reported with cyclophosphamide. Medical and/or surgical supportive treatment may be required to treat protracted cases of severe hemorrhagic cystitis. Discontinue Cyclophosphamide Injection therapy in case of severe hemorrhagic cystitis. Urotoxicity (bladder ulceration, necrosis, fibrosis, contracture and secondary cancer) may require interruption of Cyclophosphamide Injection treatment or cystectomy. Urotoxicity can be fatal. Urotoxicity can occur with short-term or long-term use of Cyclophosphamide Injection.
Before starting treatment, exclude or correct any urinary tract obstructions [see Contraindications (4)]. Urinary sediment should be checked regularly for the presence of erythrocytes and other signs of urotoxicity and/or nephrotoxicity. Cyclophosphamide Injection should be used with caution, if at all, in patients with active urinary tract infections. Aggressive hydration with forced diuresis and frequent bladder emptying can reduce the frequency and severity of bladder toxicity. Mesna has been used to prevent severe bladder toxicity.
5.3 Cardiotoxicity
Myocarditis, myopericarditis, pericardial effusion including cardiac tamponade, and congestive heart failure, which may be fatal, have been reported with cyclophosphamide therapy
Supraventricular arrhythmias (including atrial fibrillation and flutter) and ventricular arrhythmias (including severe QT prolongation associated with ventricular tachyarrhythmia) have been reported after treatment with regimens that included cyclophosphamide.
The risk of cardiotoxicity may be increased with high doses of Cyclophosphamide Injection, in patients with advanced age, and in patients with previous radiation treatment to the cardiac region and/or previous or concomitant treatment with other cardiotoxic agents.
Particular caution is necessary in patients with risk factors for cardiotoxicity and in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease.
Monitor patients with risk factors for cardiotoxicity and with pre-existing cardiac disease.
5.4 Pulmonary Toxicity
Pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary veno-occlusive disease and other forms of pulmonary toxicity leading to respiratory failure have been reported during and following treatment with cyclophosphamide. Late onset pneumonitis (greater than 6 months after start of cyclophosphamide) appears to be associated with increased mortality. Pneumonitis may develop years after treatment with Cyclophosphamide Injection.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of pulmonary toxicity.
5.5 Secondary Malignancies
Cyclophosphamide Injection is genotoxic [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Secondary malignancies (urinary tract cancer, myelodysplasia, acute leukemias, lymphomas, thyroid cancer, and sarcomas) have been reported in patients treated with cyclophosphamide-containing regimens.
The risk of bladder cancer may be reduced by prevention of hemorrhagic cystitis.
5.6 Veno-Occlusive Liver Disease
Veno-occlusive liver disease (VOD) including fatal outcome has been reported in patients receiving cyclophosphamide-containing regimens. A cytoreductive regimen in preparation for bone marrow transplantation that consists of cyclophosphamide in combination with whole-body irradiation, busulfan, or other agents has been identified as a major risk factor. VOD has also been reported to develop gradually in patients receiving long-term low-dose immunosuppressive doses of cyclophosphamide. Other risk factors predisposing to the development of VOD include preexisting disturbances of hepatic function, previous radiation therapy of the abdomen, and a low performance status.
5.7 Alcohol Content
The alcohol content in a dose of Cyclophosphamide Injection may affect the central nervous system and should be taken into account for patients in whom alcohol intake should be avoided or minimized. Consideration should be given to the alcohol content in Cyclophosphamide Injection on the ability to drive or use machines immediately after the infusion. Each administration of Cyclophosphamide Injection at 50 mg per kg deliver 0.17 g/kg of ethanol. For a 75 kg patient this would deliver 12.7 grams of ethanol [see Description (11)].
Other cyclophosphamide products may have a different amount of alcohol or no alcohol.
5.8 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action and published reports of effects in pregnant patients or animals, Cyclophosphamide Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.1), and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Exposure to cyclophosphamide during pregnancy may cause birth defects, miscarriage, fetal growth retardation, and fetotoxic effects in the newborn. Cyclophosphamide is teratogenic and embryo-fetal toxic in mice, rats, rabbits and monkeys.
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiation of Cyclophosphamide Injection. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Cyclophosphamide Injection and for up to 1 year after completion of therapy. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Cyclophosphamide Injection and for 4 months after completion of therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
5.9 Infertility
Male and female reproductive function and fertility may be impaired in patients being treated with Cyclophosphamide Injection. Cyclophosphamide interferes with oogenesis and spermatogenesis. It may cause sterility in both sexes. Development of sterility appears to depend on the dose of cyclophosphamide, duration of therapy, and the state of gonadal function at the time of treatment. Cyclophosphamide-induced sterility may be irreversible in some patients. Advise patients on the potential risks for infertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3, 8.4)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling.
- Hypersensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]
- Myelosuppression, Immunosuppression, Bone Marrow Failure, and Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Urinary Tract and Renal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cardiotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Pulmonary Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Secondary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Veno-Occlusive Liver Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Alcohol Content [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Infertility [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3 and 8.4)]
- Impaired Wound Healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
6.1 Common Adverse Reactions
Hematopoietic system:
Neutropenia occurs in patients treated with cyclophosphamide. The degree of neutropenia is particularly important because it correlates with a reduction in resistance to infections. Fever without documented infection has been reported in neutropenic patients.
Gastrointestinal system:
Nausea and vomiting occur with cyclophosphamide therapy. Anorexia and, less frequently, abdominal discomfort or pain and diarrhea may occur. There are isolated reports of hemorrhagic colitis, oral mucosal ulceration and jaundice occurring during therapy.
Skin and its structures:
Alopecia occurs in patients treated with cyclophosphamide. Skin rash occurs occasionally in patients receiving the drug. Pigmentation of the skin and changes in nails can occur.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified from clinical trials or post-marketing surveillance. Because they are reported from a population from unknown size, precise estimates of frequency cannot be made.
Cardiac: cardiac arrest, ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, cardiogenic shock, pericardial effusion (progressing to cardiac tamponade), myocardial hemorrhage, myocardial infarction, cardiac failure (including fatal outcomes), cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, pericarditis, carditis, atrial fibrillation, supraventricular arrhythmia, ventricular arrhythmia, bradycardia, tachycardia, palpitations, QT prolongation.
Congenital, Familial and Genetic: intra-uterine death, fetal malformation, fetal growth retardation, fetal toxicity (including myelosuppression, gastroenteritis).
Ear and Labyrinth: deafness, hearing impaired, tinnitus.
Endocrine: water intoxication.
Eye: visual impairment, conjunctivitis, lacrimation.
Gastrointestinal: gastrointestinal hemorrhage, acute pancreatitis, colitis, enteritis, cecitis, stomatitis, constipation, parotid gland inflammation.
General Disorders and Administrative Site Conditions: multiorgan failure, general physical deterioration, influenza-like illness, injection/infusion site reactions (thrombosis, necrosis, phlebitis, inflammation, pain, swelling, erythema), pyrexia, edema, chest pain, mucosal inflammation, asthenia, pain, chills, fatigue, malaise, headache.
Hematologic: myelosuppression, bone marrow failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation and hemolytic uremic syndrome (with thrombotic microangiopathy).
Hepatic: veno-occlusive liver disease, cholestatic hepatitis, cytolytic hepatitis, hepatitis, cholestasis; hepatotoxicity with hepatic failure, hepatic encephalopathy, ascites, hepatomegaly, blood bilirubin increased, hepatic function abnormal, hepatic enzymes increased.
Immune: immunosuppression, anaphylactic shock and hypersensitivity reaction.
Infections: The following manifestations have been associated with myelosuppression and immunosuppression caused by cyclophosphamide: increased risk for and severity of pneumonias (including fatal outcomes), other bacterial, fungal, viral, protozoal and, parasitic infections; reactivation of latent infections, (including viral hepatitis, tuberculosis), Pneumocystis jiroveci, herpes zoster, Strongyloides, sepsis and septic shock.
Investigations: blood lactate dehydrogenase increased, C-reactive protein increased.
Metabolism and Nutrition: hyponatremia, fluid retention, blood glucose increased, blood glucose decreased.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue: rhabdomyolysis, scleroderma, muscle spasms, myalgia, arthralgia.
Neoplasms: acute leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, lymphoma, sarcomas, renal cell carcinoma, renal pelvis cancer, bladder cancer, ureteric cancer, thyroid cancer.
Nervous System: encephalopathy, convulsion, dizziness, neurotoxicity has been reported and manifested as reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome, myelopathy, peripheral neuropathy, polyneuropathy, neuralgia, dysesthesia, hypoesthesia, paresthesia, tremor, dysgeusia, hypogeusia, parosmia.
Pregnancy: premature labor.
Psychiatric: confusional state.
Renal and Urinary: renal failure, renal tubular disorder, renal impairment, nephropathy toxic, hemorrhagic cystitis, bladder necrosis, cystitis ulcerative, bladder contracture, hematuria, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, atypical urinary bladder epithelial cells.
Reproductive System: infertility, ovarian failure, ovarian disorder, amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, testicular atrophy, azoospermia, oligospermia.
Respiratory: pulmonary veno-occlusive disease, acute respiratory distress syndrome, interstitial lung disease as manifested by respiratory failure (including fatal outcomes), obliterative bronchiolitis, organizing pneumonia, alveolitis allergic, pneumonitis, pulmonary hemorrhage; respiratory distress, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary edema, pleural effusion, bronchospasm, dyspnea, hypoxia, cough, nasal congestion, nasal discomfort, oropharyngeal pain, rhinorrhea.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue: toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, radiation recall dermatitis, toxic skin eruption, urticaria, dermatitis, blister, pruritus, erythema, nail disorder, facial swelling, hyperhidrosis.
Tumor lysis syndrome: like other cytotoxic drugs, cyclophosphamide may induce tumor-lysis syndrome and hyperuricemia in patients with rapidly growing tumors.
Vascular: pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis, vasculitis, peripheral ischemia, hypertension, hypotension, flushing, hot flush.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Cyclophosphamide is a pro-drug that is activated by cytochrome P450s [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
An increase of the concentration of cytotoxic metabolites may occur with:
- Protease inhibitors: Concomitant use of protease inhibitors may increase the concentration of cytotoxic metabolites. Use of protease inhibitor-based regimens was found to be associated with a higher Incidence of infections and neutropenia in patients receiving cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and etoposide (CDE) than use of a Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor-based regimen.
Combined or sequential use of cyclophosphamide and other agents with similar toxicities can potentiate toxicities.
- Increased hematotoxicity and/or immunosuppression may result from a combined effect of cyclophosphamide and, for example:
- ACE inhibitors: ACE inhibitors can cause leukopenia.
- Natalizumab
- Paclitaxel: Increased hematotoxicity has been reported when cyclophosphamide was administered after paclitaxel infusion.
- Thiazide diuretics
- Zidovudine
- Increased cardiotoxicity may result from a combined effect of cyclophosphamide and, for example:
- Anthracyclines
- Cytarabine
- Pentostatin
- Radiation therapy of the cardiac region
- Trastuzumab
- Increased pulmonary toxicity may result from a combined effect of cyclophosphamide and, for example:
- Amiodarone
- G-CSF, GM-CSF (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte macrophage colony- stimulating factor): Reports suggest an increased risk of pulmonary toxicity in patients treated with cytotoxic chemotherapy that includes cyclophosphamide and G-CSF or GMCSF.
- Increased nephrotoxicity may result from a combined effect of cyclophosphamide and, for example:
- Amphotericin B
- Indomethacin: Acute water intoxication has been reported with concomitant use of indomethacin
- Increase in other toxicities:
- Azathioprine: Increased risk of hepatotoxicity (liver necrosis)
- Busulfan: Increased incidence of hepatic veno-occlusive disease and mucositis has been reported.
- Protease inhibitors: Increased incidence of mucositis
- Increased risk of hemorrhagic cystitis may result from a combined effect of cyclophosphamide and past or concomitant radiation treatment.
Etanercept: In patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis, the addition of etanercept to standard treatment, including cyclophosphamide, was associated with a higher incidence of non-cutaneous malignant solid tumors.
Metronidazole: Acute encephalopathy has been reported in a patient receiving cyclophosphamide and metronidazole. Causal association is unclear. In an animal study, the combination of cyclophosphamide with metronidazole was associated with increased cyclophosphamide toxicity.
Tamoxifen: Concomitant use of tamoxifen and chemotherapy may increase the risk of thromboembolic complications.
Coumarins: Both increased and decreased warfarin effect have been reported in patients receiving warfarin and cyclophosphamide.
Cyclosporine: Lower serum concentrations of cyclosporine have been observed in patients receiving a combination of cyclophosphamide and cyclosporine than in patients receiving only cyclosporine. This interaction may result in an increased incidence of graft-versus-host disease.
Depolarizing muscle relaxants: Cyclophosphamide treatment causes a marked and persistent inhibition of cholinesterase activity. Prolonged apnea may occur with concurrent depolarizing muscle relaxants (e.g., succinylcholine). If a patient has been treated with cyclophosphamide within 10 days of general anesthesia, alert the anesthesiologist.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on its mechanism of action and published reports of effects in pregnant patients or animals, Cyclophosphamide Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Exposure to cyclophosphamide during pregnancy may cause fetal malformations, miscarriage, fetal growth retardation, and toxic effects in the newborn [see Data]. Cyclophosphamide is teratogenic and embryo-fetal toxic in mice, rats, rabbits and monkeys [see Data]. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects is 2%-4% and of miscarriage is 15%-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Human Data
Malformations of the skeleton, palate, limbs and eyes as well as miscarriage have been reported after exposure to cyclophosphamide in the first trimester. Fetal growth retardation and toxic effects manifesting in the newborn, including leukopenia, anemia, pancytopenia, severe bone marrow hypoplasia, and gastroenteritis have been reported after exposure to cyclophosphamide.
Animal Data
Administration of cyclophosphamide to pregnant mice, rats, rabbits and monkeys during the period of organogenesis at doses at or below the dose in patients based on body surface area resulted in various malformations, which included neural tube defects, limb and digit defects and other skeletal anomalies, cleft lip and palate, and reduced skeletal ossification.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Cyclophosphamide is present in breast milk. Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, low hemoglobin, and diarrhea have been reported in infants breast fed by women treated with cyclophosphamide. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child from Cyclophosphamide Injection, advise lactating women not to breastfeed during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of Cyclophosphamide Injection [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
Cyclophosphamide Injection can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Cyclophosphamide Injection and for up to 1 year after completion of therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Males
Based on findings in genetic toxicity and animal reproduction studies, advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Cyclophosphamide Injection and for 4 months after completion of therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Infertility
Females
Amenorrhea, transient or permanent, associated with decreased estrogen and increased gonadotropin secretion develops in a proportion of women treated with cyclophosphamide. Affected patients generally resume regular menses within a few months after cessation of therapy. The risk of premature menopause with cyclophosphamide increases with age. Oligomenorrhea has also been reported in association with cyclophosphamide treatment.
Animal data suggest an increased risk of failed pregnancy and malformations may persist after discontinuation of cyclophosphamide as long as oocytes/follicles exist that were exposed to cyclophosphamide during any of their maturation phases. The exact duration of follicular development in humans is not known but may be longer than 12 months [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Males
Men treated with cyclophosphamide may develop oligospermia or azoospermia which are normally associated with increased gonadotropin but normal testosterone secretion.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Pre-pubescent girls treated with cyclophosphamide generally develop secondary sexual characteristics normally and have regular menses. Ovarian fibrosis with apparently complete loss of germ cells after prolonged cyclophosphamide treatment in late pre-pubescence has been reported. Girls treated with cyclophosphamide who have retained ovarian function after completing treatment are at increased risk of developing premature menopause.
Pre-pubescent boys treated with cyclophosphamide develop secondary sexual characteristics normally, but may have oligospermia or azoospermia and increased gonadotropin secretion. Some degree of testicular atrophy may occur. Cyclophosphamide-induced azoospermia is reversible in some patients, though the reversibility may not occur for several years after cessation of therapy.
8.5 Geriatric Use
There is insufficient data from clinical studies of cyclophosphamide available for patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac functioning, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
In patients with severe renal impairment, decreased renal excretion may result in increased plasma levels of cyclophosphamide and its metabolites. This may result in increased toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Monitor patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl =10 mL/min to 24 mL/min) for signs and symptoms of toxicity.
Cyclophosphamide and its metabolites are dialyzable although there are probably quantitative differences depending upon the dialysis system being used. In patients requiring dialysis, use of a consistent interval between cyclophosphamide administration and dialysis should be considered.
8.7 Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The alcohol content of Cyclophosphamide Injection should be taken into account when given to patients with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. Patients with severe hepatic impairment have reduced conversion of cyclophosphamide to the active 4-hydroxyl metabolite, potentially reducing efficacy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
No specific antidote for cyclophosphamide is known.
Overdosage should be managed with supportive measures, including appropriate treatment for any concurrent infection, myelosuppression, or cardiac toxicity should it occur.
Serious consequences of overdosage include manifestations of dose dependent toxicities such as myelosuppression, urotoxicity, cardiotoxicity (including cardiac failure), veno-occlusive hepatic disease, and stomatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, and 5.6)].
Patients who received an overdose should be closely monitored for the development of toxicities, and hematologic toxicity in particular.
Cyclophosphamide and its metabolites are dialyzable. Therefore, rapid hemodialysis is indicated when treating any suicidal or accidental overdose or intoxication.
Cystitis prophylaxis with mesna may be helpful in preventing or limiting urotoxic effects with cyclophosphamide overdose.
11 DESCRIPTION
Cyclophosphamide is a synthetic antineoplastic drug chemically related to the nitrogen mustards. The chemical name for cyclophosphamide is 2-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]tetrahydro-2H-1,3,2-oxazaphosphorine 2-oxide monohydrate, and has the following structural formula:
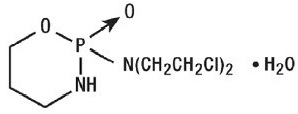
Cyclophosphamide has a molecular formula of C7H15Cl2N2O2P•H2O and a molecular weight of 279.1. Cyclophosphamide is soluble in water, saline, or ethanol.
Cyclophosphamide Injection is a sterile, colorless to slightly yellow clear solution available in clear glass vials for single-dose use. Vials of Cyclophosphamide Injection are available in two presentations:
- 500 mg per 2.5 mL vial contains 500 mg anhydrous cyclophosphamide (equivalent to 534 mg cyclophosphamide monohydrate) and 10 mg citric acid dissolved in dehydrated alcohol (1.69 grams).
- 1 g per 5 mL vial contains 1 gram anhydrous cyclophosphamide (equivalent to 1.07 g cyclophosphamide monohydrate) and 20 mg citric acid dissolved in dehydrated alcohol (3.38 grams).
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action is thought to involve cross-linking of tumor cell DNA.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cyclophosphamide is biotransformed principally in the liver to active alkylating metabolites by a mixed function microsomal oxidase system. These metabolites interfere with the growth of susceptible rapidly proliferating malignant cells.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following intravenous (IV) administration, elimination half-life (t½) ranges from 3 to 12 hours with total body clearance (CL) values of 4 to 5.6 L/h. Pharmacokinetics are linear over the dose range used clinically. When cyclophosphamide was administered at 4 g/m2 over a 90 minutes infusion, saturable elimination in parallel with first-order renal elimination describe the kinetics of the drug.
Distribution
Approximately 20% of cyclophosphamide is protein bound, with no dose dependent changes. Some metabolites are protein bound to an extent greater than 60%. Volume of distribution approximates total body water (30 to 50 L).
Metabolism
The liver is the major site of cyclophosphamide activation. Approximately 75% of the administered dose of cyclophosphamide is activated by hepatic microsomal cytochrome P450s including CYP2A6, 2B6, 3A4, 3A5, 2C9, 2C18 and 2C19, with 2B6 displaying the highest 4-hydroxylase activity. Cyclophosphamide is activated to form 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide, which is in equilibrium with its ring-open tautomer aldophosphamide. 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide and aldophosphamide can undergo oxidation by aldehyde dehydrogenases to form the inactive metabolites 4-ketocyclophosphamide and carboxyphosphamide, respectively. Aldophosphamide can undergo β-elimination to form active metabolites phosphoramide mustard and acrolein. This spontaneous conversion can be catalyzed by albumin and other proteins. Less than 5% of cyclophosphamide may be directly detoxified by side chain oxidation, leading to the formation of inactive metabolites 2-dechloroethylcyclophosphamide. At high doses, the fraction of parent compound cleared by 4-hydroxylation is reduced resulting in non-linear elimination of cyclophosphamide in patients. Cyclophosphamide appears to induce its own metabolism. Auto-induction results in an increase in the total clearance, increased formation of 4-hydroxyl metabolites and shortened t1/2 values following repeated administration at 12- to 24-hour interval.
Elimination
Cyclophosphamide is primarily excreted as metabolites. 10 to 20% is excreted unchanged in the urine and 4% is excreted in the bile following IV administration.
Special Populations
Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide were determined following one-hour intravenous infusion to renally impaired patients. The results demonstrated that the systemic exposure to cyclophosphamide increased as the renal function decreased. Mean dose-corrected AUC increased by 38% in the moderate renal group, (Creatinine clearance (CrCl of 25 to 50 mL/min), by 64% in the severe renal group (CrCl of 10 to 24 mL/min) and by 23% in the hemodialysis group (CrCl of < 10mL/min) compared to the control group. The increase in exposure was significant in the severe group (p>0.05); thus, patients with severe renal impairment should be closely monitored for toxicity [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
The dialyzability of cyclophosphamide was investigated in four patients on long-term hemodialysis. Dialysis clearance calculated by arterial-venous difference and actual drug recovery in dialysate averaged 104 mL/min, which is in the range of the metabolic clearance of 95 mL/min for the drug. A mean of 37% of the administered dose of cyclophosphamide was removed during hemodialysis. The elimination half-life (t1/2) was 3.3 hours in patients during hemodialysis, a 49% reduction of the 6.5 hours to t1/2reported in uremic patients. Reduction in t1/2, larger dialysis clearance than metabolic clearance, high extraction efficiency, and significant drug removal during dialysis, suggest that cyclophosphamide is dialyzable.
Hepatic Impairment
Total body clearance (CL) of cyclophosphamide is decreased by 40% in patients with severe hepatic impairment and elimination half-life (t1/2) is prolonged by 64%. Mean CL and t1/2were 45 ± 8.6 L/kg and 12.5 ± 1.0 hours respectively, in patients with severe hepatic impairment and 63 ± 7.6 L/kg and 7.6 ± 1.4 hours respectively in the control group [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Cyclophosphamide administered by different routes, including intravenous, subcutaneous or intraperitoneal injection, or in drinking water, caused tumors in both mice and rats. In addition to leukemia and lymphoma, benign and malignant tumors were found at various tissue sites, including urinary bladder, mammary gland, lung, liver, and injection site [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Cyclophosphamide was mutagenic and clastogenic in multiple in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology studies.
Cyclophosphamide is genotoxic in male and female germ cells. Animal data indicate that exposure of oocytes to cyclophosphamide during follicular development may result in a decreased rate of implantations and viable pregnancies, and in an increased risk of malformations. Male mice and rats treated with cyclophosphamide show alterations in male reproductive organs (e.g., decreased weights, atrophy, changes in spermatogenesis), and decreases in reproductive potential (e.g., decreased implantations and increased post-implantation loss) and increases in fetal malformations when mated with untreated females [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Cyclophosphamide Injection is a colorless to slightly yellow clear solution available in clear glass vials for single-dose use. Discard unused portion.
Cyclophosphamide Injection:
NDC 55150-270-01 500 mg/2.5 mL (200 mg/mL) in 30 mL vial, carton of 1
NDC 55150-271-01 1 g/5 mL (200 mg/mL) in 50 mL vial, carton of 1
Storage:
Store vials at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Cyclophosphamide is a hazardous drug. Follow special handling and disposal procedures.1
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient of the following:
Myelosuppression, Immunosuppression, and Infections
- Inform patients of the possibility of myelosuppression, immunosuppression, and infections. Explain the need for routine blood cell counts. Instruct patients to monitor their temperature frequently and immediately report any occurrence of fever [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Urinary Tract and Renal Toxicity
- Advise the patient to report urinary symptoms (patients should report if their urine has turned a pink or red color) and the need for increasing fluid intake and frequent voiding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Cardiotoxicity
- Advise patients to contact a health care professional immediately for any of the following: new onset or worsening shortness of breath, cough, swelling of the ankles/legs, palpitations, weight gain of more than 5 pounds in 24 hours, dizziness or loss of consciousness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Pulmonary Toxicity
- Warn patients of the possibility of developing non-infectious pneumonitis. Advise patients to report promptly any new or worsening respiratory symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Alcohol Content
- Explain to patients the possible effects of the alcohol content in Cyclophosphamide Injection, including possible effects on the central nervous system. Patients in whom alcohol should be avoided or minimized should consider the alcohol content of Cyclophosphamide Injection. Alcohol could impair their ability to drive or use machines immediately after infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Inform female patients of the risk to a fetus and potential loss of the pregnancy. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or if pregnancy is suspected [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for up to 1 year after completion of therapy [See Warning and Precautions (5.8) and Use in Specific Population (8.1, 8.3)].Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months after completion of therapy. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation
- Advise lactating women not to breastfeed during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of Cyclophosphamide Injection [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
- Cyclophosphamide Injection may impair fertility in males and females of reproductive potential [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3, 8.4)].
Common Adverse Reactions
- Explain to patients that side effects such as nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, impaired wound healing, amenorrhea, premature menopause, sterility and hair loss may be associated with cyclophosphamide administration. Other undesirable effects (including, e.g., dizziness, blurred vision, visual impairment) could affect the ability to drive or use machines [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Distributed by:
AuroMedics Pharma LLC
279 Princeton-Hightstown Rd.
E. Windsor, NJ 08520
Manufactured by:
Eugia Pharma Specialities Limited
Medchal-Malkajgiri District - 500101
India
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL- 500 mg per 2.5 mL (200 mg per mL) - Container Label
Rx only NDC 55150-270-01
Cyclophosphamide
Injection
500 mg per 2.5 mL
(200 mg per mL)
For Intravenous Infusion
After Dilution
HAZARDOUS AGENT
Single-Dose Vial – Discard Unused Portion
AUROMEDICS

PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-500 mg per 2.5 mL (200 mg per mL) - Container-Carton (1 Vial)
Rx only NDC 55150-270-01
Cyclophosphamide
Injection
500 mg per 2.5 mL
(200 mg per mL)
HAZARDOUS AGENT
For Intravenous Infusion
After Dilution
Single-Dose Vial – Discard Unused Portion AUROMEDICS