DESCRIPTION
Each teaspoonful (5 mL) of hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex extended release (ER) oral suspension contains hydrocodone polistirex equivalent to 10 mg of hydrocodone bitartrate and chlorpheniramine polistirex equivalent to 8 mg of chlorpheniramine maleate. Hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension provides up to 12-hour relief per dose. Hydrocodone is a centrally-acting narcotic antitussive. Chlorpheniramine is an antihistamine. Hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is for oral use only.
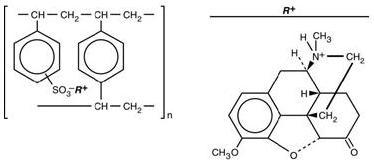
Hydrocodone Polistirex
Sulfonated styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer complex with 4,5α-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-one.
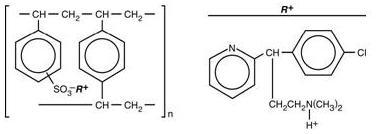
Chlorpheniramine Polistirex
Sulfonated styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer complex with 2-[p-chloro-α-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-benzyl]pyridine.
Inactive Ingredients
Ascorbic acid, D&C Yellow No. 10, flavors, high fructose corn syrup, modified food starch, methylparaben, polysorbate 80, polyvinyl acetate, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium ascorbate, sodium metabisulfite, sodium polystyrene sulfonate, sucrose, triacetin, xanthan gum.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Hydrocodone is a semisynthetic narcotic antitussive and analgesic with multiple actions qualitatively similar to those of codeine. The precise mechanism of action of hydrocodone and other opiates is not known; however, hydrocodone is believed to act directly on the cough center. In excessive doses, hydrocodone, like other opium derivatives, will depress respiration. The effects of hydrocodone in therapeutic doses on the cardiovascular system are insignificant. Hydrocodone can produce miosis, euphoria, and physical and psychological dependence.
Chlorpheniramine is an antihistamine drug (H1 receptor antagonist) that also possesses anticholinergic and sedative activity. It prevents released histamine from dilating capillaries and causing edema of the respiratory mucosa.
Hydrocodone release from hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is controlled by an extended-release drug delivery system, which combines an ion-exchange polymer matrix with a diffusion rate-limiting permeable coating. Chlorpheniramine release is prolonged by use of an ion-exchange polymer system.
Following multiple dosing with hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension, hydrocodone mean (S.D.) peak plasma concentrations of 22.8 (5.9) ng/mL occurred at 3.4 hours. Chlorpheniramine mean (S.D.) peak plasma concentrations of 58.4 (14.7) ng/mL occurred at 6.3 hours following multiple dosing. Peak plasma levels obtained with an immediate-release syrup occurred at approximately 1.5 hours for hydrocodone and 2.8 hours for chlorpheniramine. The plasma half-lives of hydrocodone and chlorpheniramine have been reported to be approximately 4 and 16 hours, respectively.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is indicated for relief of cough and upper respiratory symptoms associated with allergy or a cold in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is contraindicated in patients with a known allergy or sensitivity to hydrocodone or chlorpheniramine.
The use of hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is contraindicated in children less than 6 years of age due to the risk of fatal respiratory depression.
WARNINGS
Contains sodium metabisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown and probably low. Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in asthmatic than in nonasthmatic people.
Respiratory Depression
As with all narcotics, hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension produces dose-related respiratory depression by directly acting on brain stem respiratory centers. Hydrocodone affects the center that controls respiratory rhythm and may produce irregular and periodic breathing. Caution should be exercised when hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is used postoperatively and in patients with pulmonary disease, or whenever ventilatory function is depressed. If respiratory depression occurs, it may be antagonized by the use of naloxone hydrochloride and other supportive measures when indicated (see OVERDOSAGE).
Head Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure
The respiratory depressant effects of narcotics and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, other intracranial lesions, or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. Furthermore, narcotics produce adverse reactions, which may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries.
Acute Abdominal Conditions
The administration of narcotics may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions.
Obstructive Bowel Disease
Chronic use of narcotics may result in obstructive bowel disease especially in patients with underlying intestinal motility disorder.
Pediatric Use
The use of hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is contraindicated in children less than 6 years of age (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
In pediatric patients, as well as adults, the respiratory center is sensitive to the depressant action of narcotic cough suppressants in a dose-dependent manner. Caution should be exercised when administering hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension to pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Overdose or concomitant administration of hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension with other respiratory depressants may increase the risk of respiratory depression in pediatric patients. Benefit to risk ratio should be carefully considered, especially in pediatric patients with respiratory embarrassment (e.g., croup) (see PRECAUTIONS).
PRECAUTIONS
General
Caution is advised when prescribing this drug to patients with narrow-angle glaucoma, asthma, or prostatic hypertrophy.
Special Risk Patients
As with any narcotic agent, hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension should be used with caution in elderly or debilitated patients and those with severe impairment of hepatic or renal function, hypothyroidism, Addison's disease, prostatic hypertrophy, or urethral stricture. The usual precautions should be observed and the possibility of respiratory depression should be kept in mind.
Information for Patients
As with all narcotics, hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension may produce marked drowsiness and impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery; patients should be cautioned accordingly. Hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension must not be diluted with fluids or mixed with other drugs as this may alter the resin-binding and change the absorption rate, possibly increasing the toxicity.
Patients should be advised to measure hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension with an accurate measuring device. A household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and could lead to overdosage, especially when a half a teaspoon is measured. A pharmacist can recommend an appropriate measuring device and can provide instructions for measuring the correct dose.
Shake well before using.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Cough Reflex
Hydrocodone suppresses the cough reflex; as with all narcotics, caution should be exercised when hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is used postoperatively, and in patients with pulmonary disease.
Drug Interactions
Patients receiving narcotics, antihistaminics, antipsychotics, antianxiety agents, or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension may exhibit an additive CNS depression. When combined therapy is contemplated, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced.
The use of MAO inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants with hydrocodone preparations may increase the effect of either the antidepressant or hydrocodone.
The concurrent use of other anticholinergics with hydrocodone may produce paralytic ileus.
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, and reproductive studies have not been conducted with hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects - Pregnancy Category C
Hydrocodone has been shown to be teratogenic in hamsters when given in doses 700 times the human dose. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Babies born to mothers who have been taking opioids regularly prior to delivery will be physically dependent. The withdrawal signs include irritability and excessive crying, tremors, hyperactive reflexes, increased respiratory rate, increased stools, sneezing, yawning, vomiting, and fever. The intensity of the syndrome does not always correlate with the duration of maternal opioid use or dose.
Labor and Delivery
As with all narcotics, administration of hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension to the mother shortly before delivery may result in some degree of respiratory depression in the newborn, especially if higher doses are used.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
The use of hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is contraindicated in children less than 6 years of age (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and ADVERSE REACTIONS, Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders).
Hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension should be used with caution in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older (see WARNINGS, Pediatric Use).
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Nausea and vomiting may occur; they are more frequent in ambulatory than in recumbent patients. Prolonged administration of hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension may produce constipation.
Nervous System Disorders
Sedation, drowsiness, mental clouding, lethargy, impairment of mental and physical performance, anxiety, fear, dysphoria, euphoria, dizziness, psychic dependence, mood changes.
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Ureteral spasm, spasm of vesical sphincters, and urinary retention have been reported with opiates.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders
Dryness of the pharynx, occasional tightness of the chest, and respiratory depression (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension may produce dose-related respiratory depression by acting directly on brain stem respiratory centers (see OVERDOSAGE). Use of hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension in children less than 6 years of age has been associated with fatal respiratory depression. Overdose with hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension in children 6 years of age and older, in adolescents, and in adults has been associated with fatal respiratory depression.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is a Schedule III narcotic. Psychic dependence, physical dependence and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of narcotics; therefore, hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension should be prescribed and administered with caution. However, psychic dependence is unlikely to develop when hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is used for a short time for the treatment of cough. Physical dependence, the condition in which continued administration of the drug is required to prevent the appearance of a withdrawal syndrome, assumes clinically significant proportions only after several weeks of continued oral narcotic use, although some mild degree of physical dependence may develop after a few days of narcotic therapy.
OVERDOSAGE
Signs and Symptoms
Serious overdosage with hydrocodone is characterized by respiratory depression (a decrease in respiratory rate and/or tidal volume, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, cyanosis), extreme somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, and sometimes bradycardia and hypotension. Although miosis is characteristic of narcotic overdose, mydriasis may occur in terminal narcosis or severe hypoxia. In severe overdosage apnea, circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest and death may occur. The manifestations of chlorpheniramine overdosage may vary from central nervous system depression to stimulation.
Treatment
Primary attention should be given to the reestablishment of adequate respiratory exchange through provision of a patent airway and the institution of assisted or controlled ventilation. The narcotic antagonist naloxone hydrochloride is a specific antidote for respiratory depression which may result from overdosage or unusual sensitivity to narcotics including hydrocodone. Therefore, an appropriate dose of naloxone hydrochloride should be administered, preferably by the intravenous route, simultaneously with efforts at respiratory resuscitation. Since the duration of action of hydrocodone in this formulation may exceed that of the antagonist, the patient should be kept under continued surveillance and repeated doses of the antagonist should be administered as needed to maintain adequate respiration. For further information, see full prescribing information for naloxone hydrochloride. An antagonist should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory depression. Oxygen, intravenous fluids, vasopressors and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated. Gastric emptying may be useful in removing unabsorbed drug.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
It is important that hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension is measured with an accurate measuring device (see PRECAUTIONS, Information for Patients). A household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and could lead to overdosage, especially when half a teaspoon is to be measured. It is strongly recommended that an accurate measuring device be used. A pharmacist can provide an appropriate measuring device and can provide instructions for measuring the correct dose.
Shake well before using.
HOW SUPPLIED
Hydrocodone polistirex and chlorpheniramine polistirex ER oral suspension, equivalent to 10 mg of hydrocodone bitartrate and 8 mg of chlorpheniramine maleate per 5 mL is a yellow viscous suspension.
NDC 54868-6196-0 473 mL bottle
Storage:
Shake well. Dispense in a well-closed container.
Store at 20 to 25°C (68 to 77°F); excursions permitted from 15 to 30°C (59 to 86°F)
[see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Distributed by:
Par Pharmaceutical Companies, Inc.
Spring, Valley, NY 10977
LB8072
Rev 00 OS235-01-72-01
I 04/10
Relabeling of "Additional Barcode Label" by:
Physicians Total Care, Inc.
Tulsa, OK 74146