FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Asenapine is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia –related psychosis. [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1, 5.2)] .
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) is indicated for:
- Bipolar I disorder
[see Clinical Studies (
14.2)]
- Adjunctive treatment to lithium or valproate in adults
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Administration Instructions
Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) is a sublingual tablet. To ensure optimal absorption, patients should be instructed to place the tablet under the tongue and allow it to dissolve completely. The tablet will dissolve in saliva within seconds. Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) should not be split, crushed, chewed, or swallowed [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)] . Patients should be instructed to not eat or drink for 10 minutes after administration [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)] .
2.3 Bipolar I Disorder
Acute Treatment of Manic or Mixed Episodes:
The recommended starting dose of Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) is 5 mg twice daily when administered as adjunctive therapy with either lithium or valproate. Depending on the clinical response and tolerability in the individual patient, the dose can be increased to 10 mg twice daily. The safety of doses above 10 mg twice daily as adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate has not been evaluated in clinical trials. Adjunctive Therapy in Adults: The recommended starting dose of Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) is 5 mg twice daily when administered as adjunctive therapy with either lithium or valproate. Depending on the clinical response and tolerability in the individual patient, the dose can be increased to 10 mg twice daily. The safety of doses above 10 mg twice daily as adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate has not been evaluated in clinical trials.
For patients on asenapine, used as adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate, it is generally recommended that responding patients continue treatment beyond the acute episode.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Asenapine sublingual tablets, 5 mg, black cherry flavor, are White, Round, FFBE Tablets, debossed “Σ” on one side and “16” on the other side.
- Asenapine sublingual tablets, 10 mg, black cherry flavor, are White, Round, FFBE Tablets, debossed “Σ” on one side and “17” on the other side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Asenapine is contraindicated in patients with:
- Severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see Specific Populations ( 8.7), Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)]. Severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see Specific Populations ( 8.7), Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)].
- A history of hypersensitivity reactions to asenapine. Reactions have included anaphylaxis, angioedema, hypotension, tachycardia, swollen tongue, dyspnea, wheezing and rash [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6), Adverse Reactions ( 6)]. A history of hypersensitivity reactions to asenapine. Reactions have included anaphylaxis, angioedema, hypotension, tachycardia, swollen tongue, dyspnea, wheezing and rash [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6), Adverse Reactions ( 6)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of 17 placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk of death in the drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group.
Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Asenapine is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Asenapine is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)].
5.2 Cerebrovascular Adverse Events, Including Stroke, In Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
In placebo-controlled trials in elderly subjects with dementia, patients randomized to risperidone, aripiprazole, and olanzapine had a higher incidence of stroke and transient ischemic attacks, including fatal stroke. Asenapine is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)].
5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
A potentially fatal symptom complex sometimes referred to as Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) has been reported in association with administration of antipsychotic drugs. Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, delirium and autonomic instability. Additional signs may include elevated creatine phosphokinase, myoglobinuria (rhabdomyolysis), and acute renal failure. If NMS is suspected, immediately discontinue asenapine and provide intensive symptomatic treatment and monitoring.
5.4 Tardive Dyskinesia
Tardive dyskinesia, a syndrome consisting of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements, may develop in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs, including asenapine. The risk appears to be highest among the elderly, especially elderly women, but it is not possible to predict which patients are likely to develop the syndrome. Whether antipsychotic drug products differ in their potential to cause tardive dyskinesia is unknown.
The risk of tardive dyskinesia and the likelihood that it will become irreversible increase with the duration of treatment and the cumulative dose. The syndrome can develop after a relatively brief treatment period, even at low doses. It may also occur after discontinuation of treatment.
There is no known treatment for tardive dyskinesia, although the syndrome may remit, partially or completely, if antipsychotic treatment is discontinued. Antipsychotic treatment itself, however, may suppress (or partially suppress) the signs and symptoms of the syndrome, possibly masking the underlying process. The effect that symptomatic suppression has upon the long-term course of tardive dyskinesia is unknown.
Given these considerations, asenapine should be prescribed in a manner most likely to reduce the risk of tardive dyskinesia. Chronic antipsychotic treatment should generally be reserved for patients: (1)who suffer from a chronic illness that is known to respond to antipsychotic drugs; and (2) for whom alternative, effective, but potentially less harmful treatments are not available or appropriate. In patients who do require chronic treatment, use the lowest dose and the shortest duration of treatment producing a satisfactory clinical response should be sought. Periodically reassess the need for continued treatment.
If signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia appear in a patient on asenapine, drug discontinuation should be considered. However, some patients may require treatment with asenapine despite the presence of the syndrome.
5.5 Metabolic Changes
Atypical antipsychotic drugs, including asenapine, have caused metabolic changes, including hyperglycemia, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and body weight gain. Although all of the drugs in the class to date have been shown to produce some metabolic changes, each drug has its own specific risk profile.
Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus
Hyperglycemia, in some cases extreme and associated with ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar coma or death, has been reported in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics. There have been reports of hyperglycemia in patients treated with asenapine. Assess fasting plasma glucose before or soon after initiation of antipsychotic medication, and monitor periodically during long-term treatment.
Adult Patients: Pooled data from the short-term placebo-controlled bipolar mania trials are presented in Table 1.
| Bipolar I Disorder (3-weeks) | ||||
| Placebo | Asenapine | |||
| 5 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily | Asenapine
5 or 10 mg twice daily † |
||
| Mean Change from Baseline in Fasting Glucose at Endpoint | ||||
| Change from Baseline (mg/dL) (N*) | 0
(174) |
4.14.1 (84)(84) | 3.5
(81) | 1.7
(321) |
| Proportion of Patients with Shifts from Baseline to Endpoint | ||||
| Normal to High
<100 to ≥126 mg/dL (n/N**) | 2.4%
(3/126) |
0%0% (0/53)(0/53) | 1.7%
(1/60) | 1.8%
(4/224) |
| Borderline to High
≥100 and <126 to ≥126 mg/dL (n/N**) | 0%
(0/39) |
12.5%12.5% (3/24)(3/24) | 15.8%
(3/19) | 12.8%
(10/78) |
N* = Number of patients who had assessments at both Baseline and Endpoint.
N** = Number of patients at risk at Baseline with assessments at both Baseline and Endpoint.
Includes patients treated with flexible dose of asenapine 5 or 10 mg twice daily (N=379).
N* = Number of patients who had assessments at both Baseline and Endpoint.
N** = Number of patients at risk at Baseline with assessments at both Baseline and Endpoint.
†Includes patients treated with flexible dose of asenapine 5 or 10 mg twice daily (N=379).
In a 52-week, double-blind, comparator-controlled trial, the mean increase from baseline of fasting glucose was 2.4 mg/dL.
Dyslipidemia
Atypical antipsychotics cause adverse alterations in lipids. Before or soon after initiation of antipsychotic medication, obtain a fasting lipid profile at baseline and monitor periodically during treatment.
Adult Patients: Pooled data from the short-term, placebo-controlled bipolar mania trials are presented in Table 3.
| Bipolar I Disorder (3-weeks) | ||||
| Placebo | Asenapine | |||
| 5 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily | 5 or 10 mg twice daily † | ||
| Mean Change from Baseline (mg/dL) | ||||
|
Total CholesterolTotal Cholesterol (N*)(N*) | -1.6
(278) | -1.6
(108) | -4.7
(95) | -0.5
(525) |
| LDL (N*) | 1.4
(271) | -2.5
(101) | -4.1
(94) | -0.3
(499) |
| HDL (N*) | 0.2
(278) | 0.1
(108) | 0.7
(95) | 0.7
(525) |
| Fasting triglycerides (N*) | -16.9
(222) | 3.9
(89) | -8.5
(85) | -3.0
(411) |
| Proportion of Patients with Shifts from Baseline to Endpoint | ||||
| Total cholesterol
Normal to High <200 to >240 (mg/dL) (n/N*) | 1.2
(2/174) | 3.0
(2/66) | 0
(0/63) | 2.1
(7/333) |
| LDL
Normal to High <100 to >160 (mg/dL) (n/N*) | 1.9
(2/108) | 2.4
(1/41) | 0
(0/41) | 0.5
(1/223) |
|
HDLHDL
Normal to Low
40 to <40 (mg/dL) (n/N*)
Normal to Low
| 7.4
(16/215) | 4.1
(4/97) | 5.1
(4/78) | 7.0
(29/417) |
| Fasting triglycerides
Normal to High <150 to >200 (mg/dL) (n/N*) | 4.6
(7/153) | 8.2
(5/61) | 1.6
(1/64) | 6.2
(17/273) |
N* = Number of subjects who had assessments at both Baseline and Endpoint.
Includes patients treated with flexible dose of asenapine 5 or 10 mg twice daily (N=379).
N* = Number of subjects who had assessments at both Baseline and Endpoint.
†Includes patients treated with flexible dose of asenapine 5 or 10 mg twice daily (N=379).
In short-term, placebo-controlled bipolar mania trials, the proportion of patients with total cholesterol elevations >240 mg/dL (at Endpoint) was 7.8% for asenapine-treated patients versus 7.9% for placebo-treated patients. The proportion of patients with elevations in triglycerides >200 mg/dL (at Endpoint) was 13.1% for asenapine-treated patients versus 8.6% for placebo-treated patients.
Weight Gain
Weight gain has been observed in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics, including asenapine. Monitor weight at baseline and frequently thereafter.
Adult Patients: Pooled data on mean changes in body weight and the proportion of subjects meeting a weight gain criterion of >7% of body weight from the short-term, placebo-controlled bipolar mania trials are presented in Table 5.
| Bipolar I Disorder (3-weeks) | |||||
| Placebo | Asenapine | ||||
| 5 mg twice daily | 10 mg twice daily | 5 or 10 mg twice daily † | |||
| Change from Baseline (kg) (N*) | 0.2
(288) | 1.4
(110) | 1.3
(98) | 1.3
(544) |
|
| Proportion of Patients with a >7% Increase in Body Weight | |||||
| % with >7% increase in body weight | 0.4% | 6.4% | 1.0% | 5.5% | |
N* = Number of subjects who had assessments at both Baseline and Endpoint.
Includes patients treated with flexible dose of asenapine 5 or 10 mg twice daily (N=379).
N* = Number of subjects who had assessments at both Baseline and Endpoint.
†Includes patients treated with flexible dose of asenapine 5 or 10 mg twice daily (N=379).
In a 52-week, double-blind, comparator-controlled adult trial, the mean weight gain from baseline was 0.9 kg. The proportion of patients with a 7% increase in body weight (at Endpoint) was 14.7%. Table 6 provides the mean weight change from baseline and the proportion of patients with a weight gain of 7% categorized by Body Mass Index (BMI) at baseline. Adult Patients: In a 52-week, double-blind, comparator-controlled adult trial, the mean weight gain from baseline was 0.9 kg. The proportion of patients with a >7% increase in body weight (at Endpoint) was 14.7%. Table 6 provides the mean weight change from baseline and the proportion of patients with a weight gain of >7% categorized by Body Mass Index (BMI) at baseline.
| BMI <23
Asenapine N=295 | BMI 23 - ≤27
Asenapine N=290 | BMI >27
Asenapine N=302 |
|
| Mean change from Baseline (kg) | 1.7 | 1 | 0 |
| % with ≥7% increase in body weight | 22% | 13% | 9% |
5.6 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions have been observed in patients treated with asenapine. In several cases, these reactions occurred after the first dose. These hypersensitivity reactions included: anaphylaxis, angioedema, hypotension, tachycardia, swollen tongue, dyspnea, wheezing and rash.
5.7 Orthostatic Hypotension, Syncope, and Other Hemodynamic Effects
Atypical antipsychotics cause orthostatic hypotension and syncope. Generally, the risk is greatest during initial dose titration and when increasing the dose. In short-term bipolar mania adult trials, syncope was reported in 0.2% (1/620) of patients treated with therapeutic doses (5 mg or 10 mg twice daily) of asenapine, compared to 0% (0/329) of patients treated with placebo. During adult pre-marketing clinical trials with asenapine, including long-term trials without comparison to placebo, syncope was reported in 0.6% (11/1953) of patients treated with asenapine.
Orthostatic vital signs should be monitored in patients who are vulnerable to hypotension (elderly patients, patients with dehydration, hypovolemia, concomitant treatment with antihypertensive medications, patients with known cardiovascular disease (history of myocardial infarction or ischemic heart disease, heart failure, or conduction abnormalities), and patients with cerebrovascular disease. Asenapine should be used cautiously when treating patients who receive treatment with other drugs that can induce hypotension, bradycardia, respiratory or central nervous system depression [see Drug Interactions ( 7.1)] . Monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be considered in all such patients, and a dose reduction should be considered if hypotension occurs.
5.8 Falls
Asenapine may cause somnolence, postural hypotension, motor and sensory instability, which may lead to falls and, consequently, fractures or other injuries. For patients with diseases, conditions, or medications that could exacerbate these effects, complete fall risk assessments when initiating antipsychotic treatment and recurrently for patients on long-term antipsychotic therapy.
5.9 Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis
In clinical trial and postmarketing experience, leukopenia and neutropenia have been reported temporally related to antipsychotic agents, including asenapine. Agranulocytosis (including fatal cases) has been reported with other agents in the class.
Possible risk factors for leukopenia/neutropenia include pre-existing low white blood cell count (WBC) or absolute neutrophil count (ANC) and history of drug induced leukopenia/neutropenia. In patients with a pre-existing low WBC or ANC or a history of drug-induced leukopenia or neutropenia, perform a complete blood count (CBC) during the first few months of therapy. In such patients, consider discontinuation of asenapine at the first sign of a clinically significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors.
Monitor patients with clinically significant neutropenia for fever or other symptoms or signs of infection and treat promptly if such symptoms or signs occur. Discontinue asenapine in patients with severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count <1000/mm 3) and follow their WBC until recovery.
5.10 QT Prolongation
The effects of asenapine on the QT/QTc interval were evaluated in a dedicated adult QT study. This trial involved asenapine doses of 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, and 20 mg twice daily, and placebo, and was conducted in 151 clinically stable patients with another indication, with electrocardiographic assessments throughout the dosing interval at baseline and steady state. At these doses, asenapine was associated with increases in QTc interval ranging from 2 to 5 msec compared to placebo. No patients treated with asenapine experienced QTc increases ≥60 msec from baseline measurements, nor did any patient experience a QTc of ≥500 msec.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) measurements were taken at various time points during the asenapine clinical trial program (5 mg or 10 mg twice daily doses). Post-baseline QT prolongations exceeding 500 msec were reported at comparable rates for asenapine and placebo in these short-term trials. There were no reports of Torsade de Pointes or any other adverse reactions associated with delayed ventricular repolarization.
The use of asenapine should be avoided in combination with other drugs known to prolong QTc including Class 1A antiarrhythmics (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) or Class 3 antiarrhythmics (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol), antipsychotic medications (e.g., ziprasidone, chlorpromazine, thioridazine), and antibiotics (e.g., gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin). Asenapine should also be avoided in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias and in other circumstances that may increase the risk of the occurrence of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death in association with the use of drugs that prolong the QTc interval, including bradycardia; hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia; and presence of congenital prolongation of the QT interval.
5.11 Hyperprolactinemia
Like other drugs that antagonize dopamine D 2 receptors, asenapine can elevate prolactin levels, and the elevation can persist during chronic administration. Hyperprolactinemia may suppress hypothalamic GnRH, resulting in reduced pituitary gonadotropin secretion. This, in turn, may inhibit reproductive function by impairing gonadal steroidogenesis in both female and male patients. Galactorrhea, amenorrhea, gynecomastia, and impotence have been reported in patients receiving prolactin-elevating compounds. Long-standing hyperprolactinemia when associated with hypogonadism may lead to decreased bone density in both female and male subjects. In asenapine adult pre-marketing clinical trials, the incidences of adverse events related to abnormal prolactin levels were 0.4% versus 0% for placebo.
Tissue culture experiments indicate that approximately one-third of human breast cancers are prolactin-dependent , a factor of potential importance if the prescription of these drugs is considered in a patient with previously-detected breast cancer. Neither clinical studies nor epidemiologic studies conducted to date have shown an association between chronic administration of this class of drugs and tumorigenesis in humans, but the available evidence is too limited to be conclusive. Tissue culture experiments indicate that approximately one-third of human breast cancers are prolactin-dependent in vitro, a factor of potential importance if the prescription of these drugs is considered in a patient with previously-detected breast cancer. Neither clinical studies nor epidemiologic studies conducted to date have shown an association between chronic administration of this class of drugs and tumorigenesis in humans, but the available evidence is too limited to be conclusive.
5.12 Seizures
Seizures were reported in 0% and 0.3% (0/572, 1/379) of adult patients treated with doses of 5 mg and 10 mg twice daily of asenapine, respectively, compared to 0% (0/203) of patients treated with placebo in pre-marketing short-term bipolar mania trials. During adult pre-marketing clinical trials with asenapine, including long-term trials without comparison to placebo, seizures were reported in 0.3% (5/1953) of patients treated with asenapine.
As with other antipsychotic drugs, asenapine should be used with caution in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions that potentially lower the seizure threshold. Conditions that lower the seizure threshold may be more prevalent in patients 65 years or older.As with other antipsychotic drugs, asenapine should be used with caution in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions that potentially lower the seizure threshold. Conditions that lower the seizure threshold may be more prevalent in patients 65 years or older.
5.13 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
Somnolence was reported in patients treated with asenapine. It was usually transient with the highest incidence reported during the first week of treatment. In short-term, placebo-controlled bipolar mania adult trials of therapeutic doses (5-10 mg twice daily), somnolence was reported in 23% (145/620) of patients on asenapine compared to 5% (18/329) of placebo patients. In another study, somnolence occurred at a lower rate in the 5 mg twice daily dose 20% (24/122) versus the 10 mg twice daily dose 26% (31/119) compared to 4% (5/126) in placebo patients. During adult pre-marketing clinical trials with asenapine, including long-term trials without comparison to placebo, somnolence was reported in 18% (358/1953) of patients treated with asenapine. Somnolence led to discontinuation in 0.6% (12/1953) of patients in short-term, placebo-controlled trials.
Patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including motor vehicles, until they are reasonably certain that asenapine therapy does not affect them adversely.
5.14 Body Temperature Regulation
Atypical antipsychotics may disrupt the body’s ability to reduce core body temperature. In the pre-marketing short-term placebo-controlled trials for acute bipolar I disorder and another indication, the incidence of adverse reactions suggestive of body temperature increases was low (≤1%) and comparable to placebo (0%). During pre-marketing clinical trials with asenapine, including long-term trials without comparison to placebo, the incidence of adverse reactions suggestive of body temperature increases (pyrexia and feeling hot) was ≤1%.
Strenuous exercise, exposure to extreme heat, dehydration, and anticholinergic medications may contribute to an elevation in core body temperature; use asenapine with caution in patient who may experience these conditions.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Use in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1 and 5.2)]
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3)]
- Tardive Dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4)]
- Metabolic Changes [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Contraindications, Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6)]
- Orthostatic Hypotension, Syncope, and other Hemodynamic Effects [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7)]
- Falls [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.8)]
- Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9)]
- QT Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.10)]
- Hyperprolactinemia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.11)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.12)]
- Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.13)]
- Body Temperature Regulation [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.14)]
- Dysphagia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.15)]
The most common adverse reactions (≥5% and at least twice the rate of placebo) reported during the adjunctive therapy trial in bipolar I disorder in adults were somnolence and oral hypoesthesia. The rates were lower at the 5 mg twice daily dose than the 10 mg twice daily dose for all of these most common adverse reactions.
The adult information below is derived from a clinical trial database for asenapine consisting of over 5355 patients and/or healthy subjects exposed to one or more sublingual doses of asenapine. A total of 1427 asenapine-treated patients were treated for at least 24 weeks and 785 asenapine-treated patients had at least 52 weeks of exposure at therapeutic doses.
The stated frequencies of adverse reactions represent the proportion of individuals who experienced a treatment-emergent adverse event of the type listed. A reaction was considered treatment emergent if it occurred for the first time or worsened while receiving therapy following baseline evaluation.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adjunctive Therapy in Adult Patients with Bipolar Mania: The following findings are based on a 12 week placebo-controlled trial (with a 3 week efficacy endpoint) in adult patients with bipolar mania in which sublingual asenapine was administered in doses of 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily as adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate.
Adverse Reactions Associated with Discontinuation of Treatment: Approximately 16% (25/158) of asenapine-treated patients discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction, compared with about 11% (18/166) on placebo. The most common adverse reactions associated with discontinuation in subjects treated with asenapine (rates at least 1% and at least twice the placebo rate) were depression (2.5%), suicidal ideation (2.5%), bipolar I disorder (1.9%), insomnia (1.9%) and depressive symptoms (1.3%).
Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence of 2% or More Among Asenapine-Treated (Adjunctive) Bipolar I Patients: Adverse reactions associated with the use of asenapine (incidence of 2% or greater, rounded to the nearest percent, and asenapine incidence greater than placebo) that occurred during acute adjunctive therapy at 3 weeks, a time when most of the patients were still participating in the trial, are shown in Table 11.
| System Organ Class/Preferred Term |
Placebo N=166 % |
Asenapine 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily* N=158 % |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Dyspepsia | 2 | 3 |
| Oral hypoesthesia | 0 | 5 |
| General disorders | ||
| Fatigue | 2 | 4 |
| Edema peripheral | <1 | 3 |
| Investigations | ||
| Increased weight | 0 | 3 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Dizziness | 2 | 4 |
| Other extrapyramidal symptoms (excluding akathisia) † | 5 | 6 |
| Somnolence ‡ | 10 | 22 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||
| Insomnia | 8 | 10 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hypertension | <1 | 3 |
* Asenapine 5 mg to 10 mg twice daily with flexible dosing.
† Extrapyramidal symptoms included: dystonia, parkinsonism, oculogyration, and tremor (excluding akathisia).
‡ Somnolence includes the following events: somnolence and sedation.
Dystonia: Symptoms of dystonia, prolonged abnormal contractions of muscle groups, may occur in susceptible individuals during the first few days of treatment. Dystonic symptoms include: spasm of the neck muscles, sometimes progressing to tightness of the throat, swallowing difficulty, difficulty breathing, and/or protrusion of the tongue. While these symptoms can occur at low doses, they occur more frequently and with greater severity with high potency and at higher doses of first generation antipsychotic drugs. An elevated risk of acute dystonia is observed in males and younger age groups [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.3), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.4), and Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)].
Extrapyramidal Symptoms: In the short-term, placebo-controlled bipolar mania adult trials, data was objectively collected on the Simpson Angus Rating Scale for extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), the Barnes Akathisia Scale (for akathisia) and the Assessments of Involuntary Movement Scales (for dyskinesias). The mean change from baseline for the all-asenapine 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily treated group was comparable to placebo in each of the rating scale scores.
In short-term placebo-controlled bipolar mania adult trials, the incidence of EPS-related events, excluding events related to akathisia, for asenapine-treated patients was 8% versus 4% for placebo; and the incidence of akathisia-related events for asenapine-treated patients was 7% versus 3% for placebo. The incidence rates of all EPS events (including akathisia) were lower at the 5 mg twice daily dose (11% of N=122) than the 10 mg twice daily dose (25% of N=119) in another study.
Other Findings: Oral hypoesthesia and/or oral paresthesia may occur directly after administration of asenapine and usually resolves within 1 hour.
Laboratory Test Abnormalities:
Transaminases: Transient elevations in serum transaminases (primarily ALT) in the short-term bipolar mania adult trials were more common in treated patients. In short-term, placebo-controlled bipolar adult mania trials, the mean increase in transaminase levels for asenapine-treated patients was 6.1 units/L compared to a decrease of 3.9 units/L in placebo-treated patients. The proportion of patients with transaminase elevations ≥3 times upper limit of normal (ULN) (at Endpoint) was 2.1% for asenapine-treated patients versus 0.7% for placebo-treated patients. The incidence rate of transaminase elevations ≥3 times ULN is 3% of N=95 for 10 mg twice daily dose, and 0% of N=108 for the 5 mg twice daily dose and 0% of N=115 for placebo in another study.
In a 52-week, double-blind, comparator-controlled trial that included primarily adult patients, the mean increase from baseline of ALT was 1.7 units/L.
Prolactin: In short-term, placebo-controlled bipolar mania adult trials, the mean increase in prolactin levels was 6.7 ng/mL for asenapine-treated patients compared to a decrease of 1.0 ng/mL for placebo-treated patients. The proportion of patients with prolactin elevations ≥4 times ULN (at Endpoint) were 2.0% for asenapine-treated patients versus 0.8% for placebo-treated patients.
In a long-term (52-week), double-blind, comparator-controlled adult trial, the mean decrease in prolactin from baseline for asenapine-treated patients was 26.9 ng/mL.
Creatine Kinase (CK): The proportion of adult patients with CK elevations >3 times ULN at any time were 6.4% and 11.1% for patients treated with asenapine 5 mg twice daily and 10 mg twice daily, respectively, as compared to 6.7% for placebo-treated patients in pre-marketing short-term, fixed-dose trials in bipolar mania and another indication. The clinical relevance of this finding is unknown.
Other Adverse Reactions Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation of Asenapine: Following is a list of MedDRA terms that reflect adverse reactions reported by patients treated with sublingual asenapine at multiple doses of ≥5 mg twice daily during any phase of a trial within the database of adult patients. The reactions listed are those that could be of clinical importance, as well as reactions that are plausibly drug-related on pharmacologic or other grounds. Reactions already listed for adult patients in other parts of Adverse Reactions ( 6) , or those considered in Contraindications ( 4), Warnings and Precautions ( 5) or Overdosage ( 10) are not included. Reactions are further categorized by MedDRA system organ class and listed in order of decreasing frequency according to the following definitions: those occurring in at least 1/100 patients (frequent) (only those not already listed in the tabulated results from placebo-controlled trials appear in this listing); those occurring in 1/100 to 1/1000 patients (infrequent); and those occurring in fewer than 1/1000 patients (rare).
Blood and lymphatic disorders: infrequent: anemia;
rare: thrombocytopenia
Cardiac disorders: infrequent: temporary bundle branch block
Eye disorders: infrequent:
accommodation disorder
Gastrointestinal disorders: infrequent: swollen tongue
General disorders: rare: idiosyncratic drug reaction
Investigations: infrequent: hyponatremia
Nervous system disorders: infrequent: dysarthria
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of asenapine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. In many cases, the occurrence of these adverse reactions led to discontinuation of therapy.
- Application site reactions, primarily in the sublingual area, have been reported. These application site reactions included oral ulcers, blisters, peeling/sloughing, and inflammation.
- Choking has been reported by patients, some of whom may have also experienced oropharyngeal muscular dysfunction or hypoesthesia.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sigmapharm Laboratories, LLC, Pharmacovigilance at 1-855-332-0731 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs Having Clinically Important Drug Interactions with Asenapine
| Concomitant Drug Name or Drug Class | Clinical Rationale | Clinical Recommendation |
| Antihypertensive Drugs | Because of its α 1-adrenergic antagonism with potential for inducing hypotension, asenapine may enhance the effects of certain antihypertensive agents [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7)] . | Monitor blood pressure and adjust dosage of antihypertensive drug accordingly. |
| Strong CYP1A2 Inhibitors (e.g., Fluvoxamine) | Asenapine is metabolized by CYP1A2. Marginal increase of asenapine exposure was observed when asenapine is used with fluvoxamine at 25 mg administered twice daily [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)]. However, the tested fluvoxamine dose was suboptimal. Full therapeutic dose of fluvoxamine is expected to cause a greater increase in asenapine exposure. | Dosage reduction for asenapine based on clinical response may be necessary. |
| CYP2D6 substrates and inhibitors (e.g., paroxetine) | Asenapine may enhance the inhibitory effects of paroxetine on its own metabolism. Concomitant use of paroxetine with asenapine increased the paroxetine exposure by 2-fold as compared to use paroxetine alone [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)]. | Reduce paroxetine dose by half when paroxetine is used in combination with asenapine. |
7.2 Drugs Having No Clinically Important Interactions with Asenapine
No dosage adjustment of asenapine is necessary when administered concomitantly with paroxetine (see Table 12 in Drug Interactions ( 7.1) for paroxetine dosage adjustment), imipramine, cimetidine, valproate, lithium, or a CYP3A4 inducer (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampin).
In addition, valproic acid and lithium pre-dose serum concentrations collected from an adjunctive therapy study were comparable between asenapine-treated patients and placebo-treated patients indicating a lack of effect of asenapine on valproic and lithium plasma levels.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to asenapine during pregnancy. For more information contact the National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics at 1-866-961-2388 or visit http://womensmentalhealth.org/clinical-and-research-programs/pregnancyregistry/.
Risk Summary
Neonates exposed to antipsychotic drugs during the third trimester of pregnancy are at risk for extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms. Studies have not been conducted with asenapine in pregnant women. There are no available human data informing the drug-associated risk. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. However, the background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2-4% and of miscarriage is 15-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies. No teratogenicity was observed in animal reproduction studies with intravenous administration of asenapine to rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses 0.7 and 0.4 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 10 mg sublingually twice daily. In a pre-and post-natal study in rats, intravenous administration of asenapine at doses up to 0.7 times the MRHD produced increases in post-implantation loss and early pup deaths, and decreases in subsequent pup survival and weight gain [see Data]. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms, including agitation, hypertonia, hypotonia, tremor, somnolence, respiratory distress and feeding disorder have been reported in neonates who were exposed to antipsychotic drugs during the third trimester of pregnancy. These symptoms have varied in severity. Some neonates recovered within hours or days without specific treatment; others required prolonged hospitalization. Monitor neonates for extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms and manage symptoms appropriately.
Data
Animal Data
In animal studies, asenapine increased post-implantation loss and decreased pup weight and survival at doses similar to or less than recommended clinical doses. In these studies there was no increase in the incidence of structural abnormalities caused by asenapine.
Asenapine was not teratogenic in reproduction studies in rats and rabbits at intravenous doses up to 1.5 mg/kg in rats and 0.44 mg/kg in rabbits administered during organogenesis. These doses are 0.7 and 0.4 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 10 mg twice daily given sublingually on a mg/m 2 basis. Plasma levels of asenapine were measured in the rabbit study, and the area under the curve (AUC) at the highest dose tested was 2 times that in humans receiving the MRHD.
In a study in which rats were treated from day 6 of gestation through day 21 postpartum with intravenous doses of asenapine of 0.3, 0.9, and 1.5 mg/kg/day (0.15, 0.4, and 0.7 times the MRHD of 10 mg twice daily given sublingually on a mg/m 2 basis), increases in post-implantation loss and early pup deaths were seen at all doses, and decreases in subsequent pup survival and weight gain were seen at the two higher doses. A cross-fostering study indicated that the decreases in pup survival were largely due to prenatal drug effects. Increases in post-implantation loss and decreases in pup weight and survival were also seen when pregnant rats were dosed orally with asenapine.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Lactation studies have not been conducted to assess the presence of asenapine in human milk, the effects of asenapine on the breastfed infant, or the effects of asenapine on milk production. Asenapine is excreted in rat milk. The development and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for asenapine and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from asenapine or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of asenapine in pediatric patients below the age of 10 years of age have not been evaluated.
Juvenile Animal Data
Subcutaneous administration of asenapine to juvenile rats for 56 days from day 14 of age to day 69 of age at 0.4, 1.2, and 3.2 mg/kg/day (0.2, 0.6 and 1.5 times the maximum recommended human dose of 10 mg twice daily given sublingually on a mg/m 2 basis) resulted in significant reduction in body weight gain in animals of both sexes at all dose levels from the start of dosing until weaning. Body weight gain remained reduced in males to the end of treatment, however, recovery was observed once treatment ended. Neurobehavioral assessment indicated increased motor activity in animals at all dose levels following the completion of treatment, with the evidence of recovery in males. There was no recovery after the end of treatment in female activity pattern as late as day 30 following the completion of treatment (last retesting). Therefore, a No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) for the juvenile animal toxicity of asenapine could not be determined. There were no treatment-related effects on the startle response, learning/memory, organ weights, microscopic evaluations of the brain and, reproductive performance (except for minimally reduced conception rate and fertility index in males and females administered 1.2 and 3.2 mg/kg/day).
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of asenapine in the treatment of bipolar mania did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether or not they respond differently than younger patients. Of the approximately 2250 patients in pre-marketing clinical studies of asenapine, 1.1% (25) were 65 years of age or over. Multiple factors that might increase the pharmacodynamic response to asenapine, causing poorer tolerance or orthostasis, could be present in elderly patients, and these patients should be monitored carefully. Based on a pharmacokinetic study in elderly patients, dosage adjustments are not recommended based on age alone [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)].
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with asenapine are at an increased risk of death compared to placebo. Asenapine is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning].
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment for asenapine is required on the basis of a patient’s renal function (mild to severe renal impairment, glomerular filtration rate between 15 and 90 mL/minute). The exposure of asenapine was similar among subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment and subjects with normal renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)] . The effect of renal function on the excretion of other metabolites and the effect of dialysis on the pharmacokinetics of asenapine has not been studied.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Asenapine is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) because asenapine exposure is 7-fold higher in subjects with severe hepatic impairment than the exposure observed in subjects with normal hepatic function.
No dosage adjustment for asenapine is required in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A and B) because asenapine exposure is similar to that in subjects with normal hepatic function [see Contraindications ( 4) and Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)].
8.8 Other Specific Populations
No dosage adjustment for asenapine is required on the basis of a patient’s sex, race (Caucasian and Japanese), or smoking status [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)] .
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.2 Abuse
Asenapine has not been systematically studied in animals or humans for its abuse potential or its ability to induce tolerance or physical dependence. Thus, it is not possible to predict the extent to which a CNS-active drug will be misused, diverted and/or abused once it is marketed. Patients should be evaluated carefully for a history of drug abuse, and such patients should be observed carefully for signs that they are misusing or abusing asenapine (e.g., drug-seeking behavior, increases in dose).
10 OVERDOSAGE
Human Experience: In adult pre-marketing clinical studies involving more than 3350 patients and/or healthy subjects, accidental or intentional acute overdosage of asenapine was identified in 3 patients. Among these few reported cases of overdose, the highest estimated ingestion of asenapine was 400 mg. Reported adverse reactions at the highest dosage included agitation and confusion.
Management of Overdosage: There is no specific antidote to asenapine. The possibility of multiple drug involvement should be considered. An electrocardiogram should be obtained and management of overdose should concentrate on supportive therapy, maintaining an adequate airway, oxygenation and ventilation, and management of symptoms. Consult with a Certified Poison Control Center for up-to-date guidance and advice on the management of overdosage (1-800-222-1222.)
Hypotension and circulatory collapse should be treated with appropriate measures, such as intravenous fluids and/or sympathomimetic agents (epinephrine and dopamine should not be used, since beta stimulation may worsen hypotension in the setting of asenapine-induced alpha blockade). In case of severe extrapyramidal symptoms, anticholinergic medication should be administered. Close medical supervision and monitoring should continue until the patient recovers.
11 DESCRIPTION
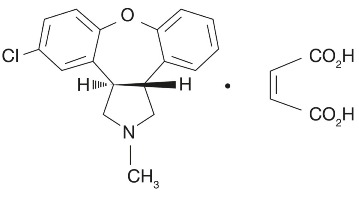
Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) contains asenapine maleate which is an atypical antipsychotic that is available for sublingual administration. Asenapine belongs to the class dibenzo-oxepino pyrroles. The chemical designation is (3a RS,12b RS)-5-Chloro-2-methyl-2,3,3a,12b-tetrahydro-1 Hdibenzo[2,3:6,7]oxepino[4,5- c]pyrrole (2 Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1). Its molecular formula is C 17H 16ClNO⋅C 4H 4O 4 and its molecular weight is 401.84 (free base: 285.8). The chemical structure is:
Asenapine maleate is a white to off-white powder.
Asenapine sublingual tablet(s), black cherry flavor, is supplied for sublingual administration in tablets containing 5 mg or 10 mg asenapine; inactive ingredients include copovidone, crospovidone, polyoxyl 35 castor oil, mannitol, magnesium stearate, citric acid, butylated hydroxytoluene, silicon dioxide, sodium bicarbonate and black cherry flavor. Black cherry flavor contains maltodextrin, artificial flavors, propylene glycol, triethyl citrate, and caramel color.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Asenapine exhibits high affinity for serotonin 5-HT 1A, 5-HT 1B, 5-HT 2A, 5-HT 2B, 5-HT 2C, 5-HT 5A, 5-HT 6, and 5-HT 7 receptors (Ki values of 2.5, 2.7, 0.07, 0.18, 0.03, 1.6, 0.25, and 0.11 nM, respectively), dopamine D 2A, D 2B, D 3, D 4, and D 1 receptors (Ki values of 1.3, 1.4, 0.42, 1.1, and 1.4 nM, respectively), α 1A, α 2A, α 2B, and α 2C -adrenergic receptors (Ki values of 1.2, 1.2, 0.33 and 1.2 nM, respectively), and histamine H 1 receptors (Ki value 1.0 nM), and moderate affinity for H 2 receptors (Ki value of 6.2 nM). In in vitro assays asenapine acts as an antagonist at these receptors. Asenapine has no appreciable affinity for muscarinic cholinergic receptors (e.g., Ki value of 8128 nM for M 1).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following a single 5 mg dose of asenapine, the mean C max was approximately 4 ng/mL and was observed at a mean t max of 1 hour. Elimination of asenapine is primarily through direct glucuronidation by UGT1A4 and oxidative metabolism by cytochrome P450 isoenzymes (predominantly CYP1A2). Following an initial more rapid distribution phase, the mean terminal half-life is approximately 24 hrs. With multiple-dose twice-daily dosing, steady-state is attained within 3 days. Overall, steady-state asenapine pharmacokinetics are similar to single-dose pharmacokinetics.
Absorption: Following sublingual administration, asenapine is rapidly absorbed with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 0.5 to 1.5 hours. The absolute bioavailability of sublingual asenapine at 5 mg is 35%. Increasing the dose from 5 mg to 10 mg twice daily (a two-fold increase) results in less than linear (1.7 times) increases in both the extent of exposure and maximum concentration. The absolute bioavailability of asenapine when swallowed is low (<2% with an oral tablet formulation).
The intake of water several (2 or 5) minutes after asenapine administration resulted in decreased asenapine exposure. Therefore, eating and drinking should be avoided for 10 minutes after administration [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1)] .
Distribution: Asenapine is rapidly distributed and has a large volume of distribution (approximately 20 - 25 L/kg), indicating extensive extravascular distribution. Asenapine is highly bound (95%) to plasma proteins, including albumin and α 1-acid glycoprotein.
Metabolism and Elimination: Direct glucuronidation by UGT1A4 and oxidative metabolism by cytochrome P450 isoenzymes (predominantly CYP1A2) are the primary metabolic pathways for asenapine.
Asenapine is a high clearance drug with a clearance after intravenous administration of 52 L/h. In this circumstance, hepatic clearance is influenced primarily by changes in liver blood flow rather than by changes in the intrinsic clearance, i.e., the metabolizing enzymatic activity. Following an initial more rapid distribution phase, the terminal half-life of asenapine is approximately 24 hours. Steady-state concentrations of asenapine are reached within 3 days of twice daily dosing.
After administration of a single dose of [ 14C]-labeled asenapine, about 90% of the dose was recovered; approximately 50% was recovered in urine, and 40% recovered in feces. About 50% of the circulating species in plasma have been identified. The predominant species was asenapine N +-glucuronide; others included N-desmethylasenapine, N-desmethylasenapine N-carbamoyl glucuronide, and unchanged asenapine in smaller amounts. Asenapine activity is primarily due to the parent drug.
In vitro studies indicate that asenapine is a substrate for UGT1A4, CYP1A2 and to a lesser extent CYP3A4 and CYP2D6. Asenapine is a weak inhibitor of CYP2D6. Asenapine does not cause induction of CYP1A2 or CYP3A4 activities in cultured human hepatocytes. Coadministration of asenapine with known inhibitors, inducers or substrates of these metabolic pathways has been studied in a number of drug-drug interaction studies [see Drug Interactions ( 7.1)].
Food: A crossover study in 26 healthy adult male subjects was performed to evaluate the effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of a single 5 mg dose of asenapine. Consumption of food immediately prior to sublingual administration decreased asenapine exposure by 20%; consumption of food 4 hours after sublingual administration decreased asenapine exposure by about 10%. These effects are probably due to increased hepatic blood flow.
In clinical trials establishing the efficacy and safety of asenapine, patients were instructed to avoid eating for 10 minutes following sublingual dosing. There were no other restrictions with regard to the timing of meals in these trials [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1)].
Water: In clinical trials establishing the efficacy and safety of asenapine, patients were instructed to avoid drinking for 10 minutes following sublingual dosing. The effect of water administration following 10 mg sublingual asenapine dosing was studied at different time points of 2, 5, 10, and 30 minutes in 15 healthy adult male subjects. The exposure of asenapine following administration of water 10 minutes after sublingual dosing was equivalent to that when water was administered 30 minutes after dosing. Reduced exposure to asenapine was observed following water administration at 2 minutes (19% decrease) and 5 minutes (10% decrease) [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1)].
Drug Interaction Studies:
Effects of other drugs on the exposure of asenapine are summarized in Figure 1. In addition, a population pharmacokinetic analysis indicated that the concomitant administration of lithium had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of asenapine.
Figure 1: Effect of Other Drugs on Asenapine Pharmacokinetics
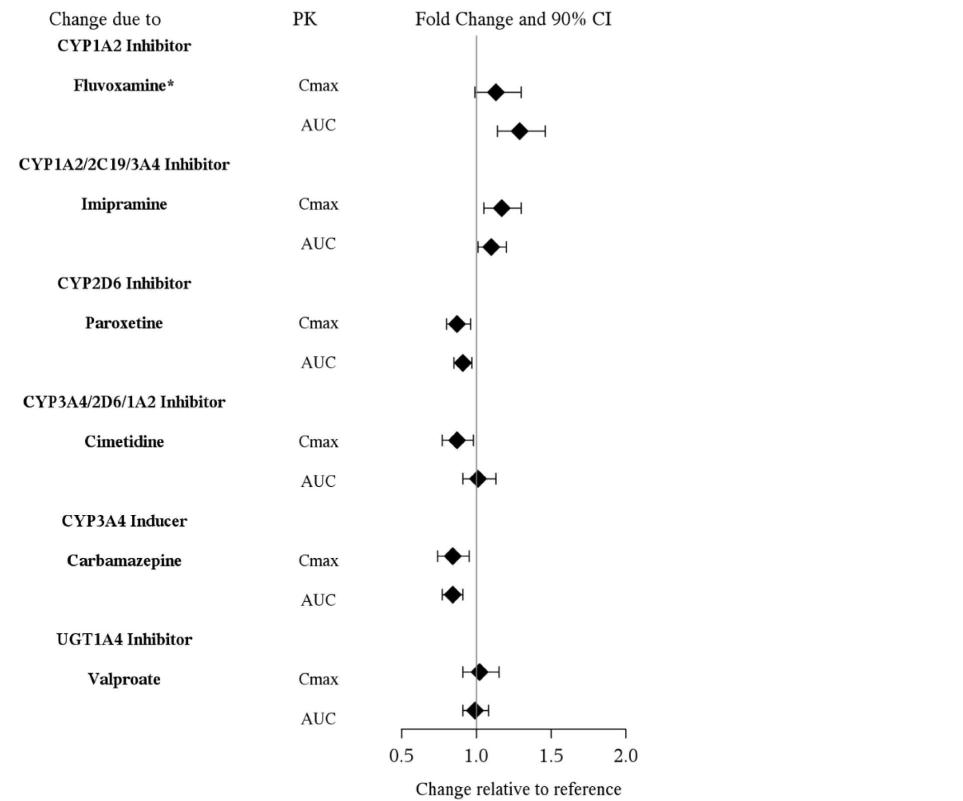
*: When a low dose of 25 mg twice daily fluvoxamine was co-administered with asenapine, a 29% increase in asenapine exposure was observed. Concomitant use of a therapeutic dose of fluvoxamine may cause greater increases in asenapine exposure.
The effects of asenapine on the pharmacokinetics of other co-administered drugs are summarized in Figure 2. Coadministration of paroxetine with asenapine caused a two-fold increase in the maximum plasma concentrations and systemic exposure of paroxetine. Asenapine enhances the inhibitory effects of paroxetine on its own metabolism by CYP2D6.
Figure 2: Effect of Asenapine on Other Drug Pharmacokinetics
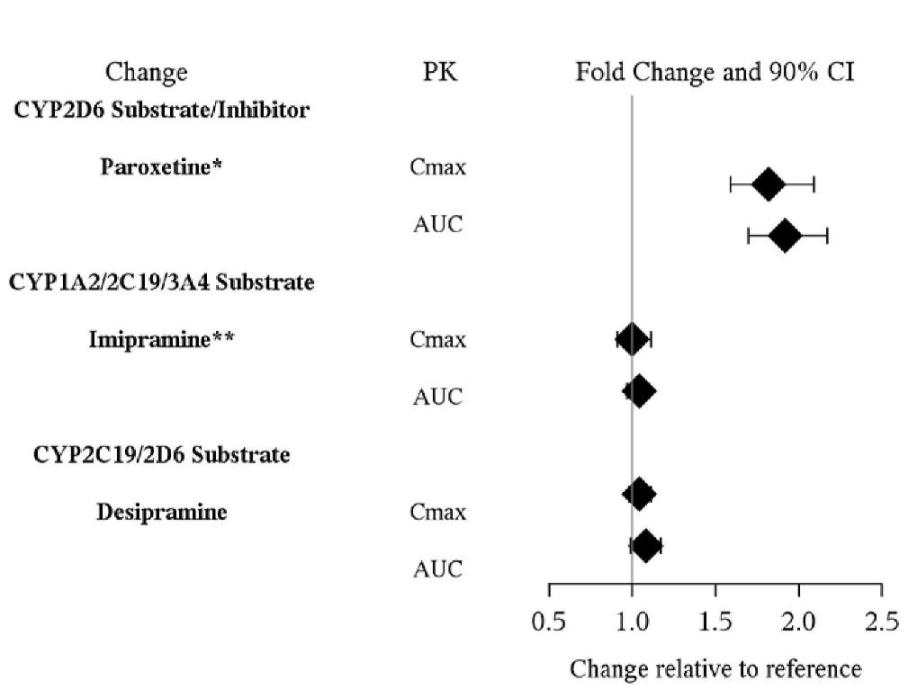
*: Asenapine may enhance the inhibitory effects of paroxetine on its own metabolism.
**: In vivo, Asenapine appears to be at most a weak inhibitor of CYP2D6. Following coadministration of dextromethorphan and asenapine in healthy subjects, the ratio of dextrorphan/dextromethorphan (DX/DM) as a marker of CYP2D6 activity was measured. Indicative of CYP2D6 inhibition, treatment with asenapine 5 mg twice daily decreased the DX/DM ratio of 0.43. In the same study, treatment with paroxetine 20 mg daily decreased the DX/DM ratio to 0.032. In a separate study, coadministration of a single 75 mg dose of imipramine with a single 5 mg dose of asenapine did not affect the plasma concentrations of the metabolite dispiramine (a CYP2D6 substrate).
Studies in Special Populations:
Exposures of asenapine in special populations are summarized in Figure 3. Additionally, based on population pharmacokinetic analysis, no effects of sex, race, BMI, and smoking status on asenapine exposure were observed. Exposure in elderly patients is 30-40% higher as compared to adults.
Figure 3: Effect of Intrinsic Factors on Asenapine Pharmacokinetics
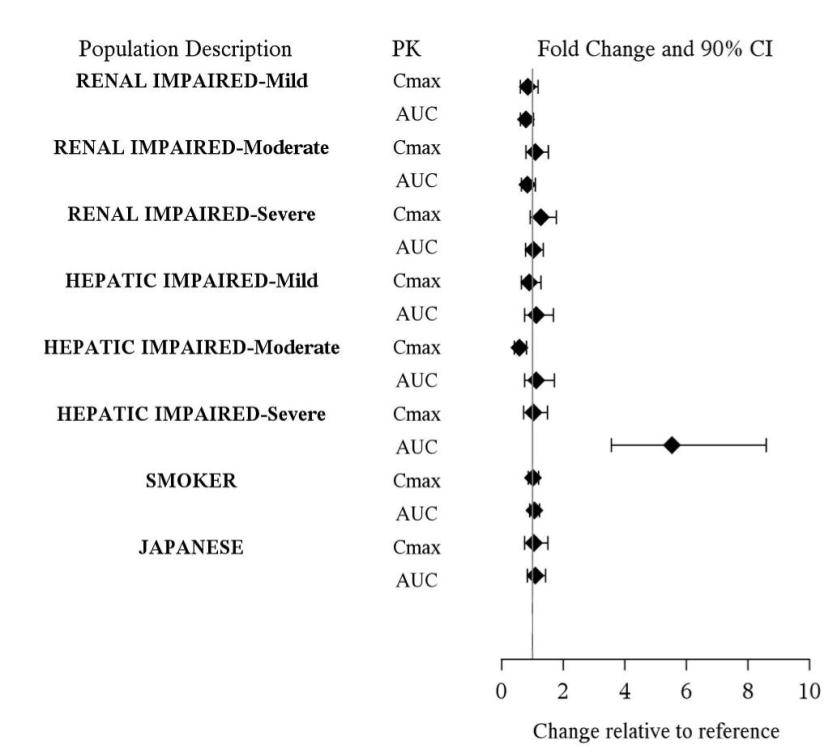
*: Results are based on a cross-trial comparison.
The data shown for renal and hepatic impairment are relative to subjects with normal renal and hepatic function, respectively.
The data shown for smoker are relative to non-smoker.
The data shown for Japanese are relative to Caucasian.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: In a lifetime carcinogenicity study in CD-1 mice asenapine was administered subcutaneously at doses up to those resulting in plasma levels (AUC) estimated to be 5 times those in humans receiving the MRHD of 10 mg twice daily. The incidence of malignant lymphomas was increased in female mice, with a no-effect dose resulting in plasma levels estimated to be 1.5 times those in humans receiving the MRHD. The mouse strain used has a high and variable incidence of malignant lymphomas, and the significance of these results to humans is unknown. There were no increases in other tumor types in female mice. In male mice, there were no increases in any tumor type.
In a lifetime carcinogenicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats, asenapine did not cause any increases in tumors when administered subcutaneously at doses up to those resulting in plasma levels (AUC) estimated to be 5 times those in humans receiving the MRHD.
Mutagenesis: No evidence for genotoxic potential of asenapine was found in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay, the in vitro forward gene mutation assay in mouse lymphoma cells, the in vitro chromosomal aberration assays in human lymphocytes, the in vitro sister chromatid exchange assay in rabbit lymphocytes, or the in vivo micronucleus assay in rats.
Impairment of Fertility: Asenapine did not impair fertility in rats when tested at doses up to 11 mg/kg twice daily given orally. This dose is 10 times the maximum recommended human dose of 10 mg twice daily given sublingually on a mg/m 2 basis.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Efficacy of asenapine was established in the following trials:
- One flexible-dose, short-term trial in adult patients with manic or mixed episode associated with bipolar I disorder as adjunctive treatment to lithium or valproate [see Clinical Studies ( 14.2)]
14.2 Bipolar I Disorder
Adjunctive Therapy:The efficacy of asenapine as an adjunctive therapy in acute mania was established in a 12-week, placebo-controlled trial with a 3-week primary efficacy endpoint involving 326 adult patients with a manic or mixed episode of Bipolar I Disorder, with or without psychotic features, who were partially responsive to lithium or valproate monotherapy after at least 2 weeks of treatment. All patients randomized to asenapine were initially administered 5 mg twice daily, and the dose could be adjusted within the dose range of 5 to 10 mg twice daily from Day 2 onward based on efficacy and tolerability. Asenapine was statistically superior to placebo in the reduction of manic symptoms (measured by the YMRS total score) as an adjunctive therapy to lithium or valproate monotherapy at Week 3 (Trial 5 Adjunctive in Table 14).
| Study Number | Treatment Group | Primary Efficacy Measure: YMRS Total Score | ||
| Mean Baseline Score (SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline (SE) | Placebo-subtracted Difference a (95% CI) | ||
| Trial 5 (Adjunctive) | Asenapine 5-10 mg* twice daily + lithium/Valproate | 28.0 (5.6) | -10.3 (0.8) | -2.4 (-4.4, -0.3) |
| Lithium/Valproate | 28.2 (5.8) | -7.9 (0.8) | -- | |
SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error; LS Mean: least-squares mean; CI: confidence interval, not adjusted for multiple comparisons. a Difference (drug minus placebo) in least-squares mean change from baseline. * Doses that are demonstrated to be effective.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Asenapine sublingual tablets are supplied as:
5 mg Tablets, black cherry flavor
White, Round, FFBE Tablets, debossed “Σ” on one side and “16” on the other side.
Child-resistant packaging
Bottle of 10 tablets NDC 42794-016-22
Bottle of 30 tablets NDC 42794-016-08
Bottle of 60 tablets NDC 42794-016-10
10 mg Tablets, black cherry flavor
White, Round, FFBE Tablets, debossed “Σ” on one side and “17” on the other side.
Child-resistant packaging
Bottle of 10 tablets NDC 42794-017-22
Bottle of 30 tablets NDC 42794-017-08
Bottle of 60 tablets NDC 42794-017-10
Storage
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F). Store Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) in its original container.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use).
Dosage and Administration
Counsel patients on proper sublingual administration of Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) and advise them to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use). When initiating treatment with asenapine, provide dosage escalation instructions [see Dosage and Administration ( 2)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Counsel patients on the signs and symptoms of a serious allergic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, itching, swelling of the face, tongue or throat, feeling lightheaded etc.) and to seek immediate emergency assistance if they develop any of these signs and symptoms [see Contraindications ( 4), Warnings and Precautions ( 5.6) and Adverse Reactions ( 6)].
Application Site Reactions
Inform patients that application site reactions, primarily in the sublingual area, including oral ulcers, blisters, peeling/sloughing and inflammation have been reported. Instruct patients to monitor for these reactions [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.2)]. Inform patients that numbness or tingling of the mouth or throat may occur directly after administration of Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) and usually resolves within 1 hour [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.1)] .
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Counsel patients about a potentially fatal symptom complex sometimes referred to as Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) that has been reported in association with administration of antipsychotic drugs. Patients should contact their health care provider or report to the emergency room if they experience the following signs and symptoms of NMS, including hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, and evidence of autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia) [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3)] .
Tardive Dyskinesia
Counsel patients on the signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia and to contact their health care provider if these abnormal movements occur [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.4)].
Metabolic Changes (Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus, Dyslipidemia, and Weight Gain)
Educate patients about the risk of metabolic changes, how to recognize symptoms of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and diabetes mellitus, and the need for specific monitoring, including blood glucose, lipids, and weight [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.5)].
Orthostatic Hypotension
Educate patients about the risk of orthostatic hypotension (symptoms include feeling dizzy or lightheaded upon standing) especially early in treatment, and also at times of re-initiating treatment or increases in dose [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7)].
Leukopenia/Neutropenia
Advise patients with a pre-existing low WBC or a history of drug induced leukopenia/neutropenia they should have their CBC monitored while taking asenapine [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.9)].
Hyperprolactinemia
Counsel patients on the signs and symptoms of Hyperprolactinemia and to contact their health care provider if these abnormalities occur [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.11)].
Interference with Cognitive and Motor Performance
Caution patients about performing activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating hazardous machinery or operating a motor vehicle, until they are reasonably certain that asenapine therapy does not affect them adversely [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.13)].
Heat Exposure and Dehydration
Counsel patients regarding appropriate care in avoiding overheating and dehydration [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.14)].
Concomitant Medications
Advise patients to inform their health care provider if they are taking, or plan to take, any prescription or over-the-counter medications since there is a potential for interactions [see Drug Interactions ( 7.1)].
Pregnancy
Advise patients that asenapine may cause fetal harm as well as extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms in a neonate. Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider with a known or suspected pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1)].
Pregnancy Registry
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to asenapine during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1)].
Sigmapharm Laboratories, LLC
Bensalem, PA 19020
OS017-11 REV.1220
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
ASENAPINE
SUBLINGUAL TABLETS
Read these Instructions for Use before you start using Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
IMPORTANT:
- For sublingual (under your tongue) use only
- Do not remove tablet until ready to administer.
- Use dry hands when handling tablet.
Directions for taking your Asenapine sublingual tablet(s):
Step 1: Gently remove the tablet from the bottle. Do not split, cut or crush the tablet.
Step 2: Place the whole tablet under tongue and allow it to dissolve completely (see Figure A).
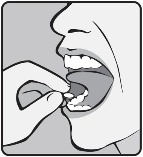
Figure A
Do not chew or swallow the tablet.
Do not eat or drink for 10 minutes (See Figure B).
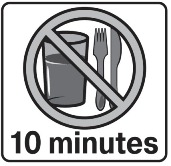
Figure B
Storing Asenapine sublingual tablet(s):
Store Asenapine sublingual tablet(s) at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C), in the container it comes in.
These Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Sigmapharm Laboratories, LLC
Bensalem, PA 19020
OS017-11 REV.1220
Revised: December 2020
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 MG 10 COUNT CONTAINER LABEL
Prinicipal Display Panel - 5 mg 10 count Container Label
NDC 42794- 016-22
Asenapine Sublingual Tablets
5 mg
Do not split, cut or crush tablet. Do not chew or swallow tablet.
DISPENSE ONLY IN ORIGINAL CONTAINER.
Black Cherry
Flavor
Rx only
10 Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 MG 30 COUNT CONTAINER LABEL
Prinicipal Display Panel - 5 mg 30 count Container Label
NDC 42794- 016-18
Asenapine Sublingual Tablets
5 mg
Do not split, cut or crush tablet. Do not chew or swallow tablet.
DISPENSE ONLY IN ORIGINAL CONTAINER.
Black Cherry
Flavor
Rx only
30 Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 MG 60 COUNT CONTAINER LABEL
Prinicipal Display Panel - 5 mg 60 count Container Label
NDC 42794- 016-10
Asenapine Sublingual Tablets
5 mg
Do not split, cut or crush tablet. Do not chew or swallow tablet.
DISPENSE ONLY IN ORIGINAL CONTAINER.
Black Cherry
Flavor
Rx only
60 Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 MG 10 COUNT CONTAINER LABEL
Prinicipal Display Panel - 10 mg 10 count Container Label
NDC 42794- 017-22
Asenapine Sublingual Tablets
10 mg
Do not split, cut or crush tablet. Do not chew or swallow tablet.
DISPENSE ONLY IN ORIGINAL CONTAINER.
Black Cherry
Flavor
Rx only
10 Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 MG 30 COUNT CONTAINER LABEL
Prinicipal Display Panel - 10 mg 30 count Container Label
NDC 42794- 017-08
Asenapine Sublingual Tablets
10 mg
Do not split, cut or crush tablet. Do not chew or swallow tablet.
DISPENSE ONLY IN ORIGINAL CONTAINER.
Black Cherry
Flavor
Rx only
30 Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 MG 60 COUNT CONTAINER LABEL
Prinicipal Display Panel - 10 mg 60 count Container Label
NDC 42794- 017-10
Asenapine Sublingual Tablets
10 mg
Do not split, cut or crush tablet. Do not chew or swallow tablet.
DISPENSE ONLY IN ORIGINAL CONTAINER.
Black Cherry
Flavor
Rx only
60 Tablets
