FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution is indicated for the temporary relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis. Ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution is also indicated for the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
Patient Dosing
The recommended dose of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution is one drop four times a day to the affected eye(s) for relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis.
For the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction, one drop of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution should be applied to the affected eye four times daily beginning 24 hours after cataract surgery and continuing through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period.
2.2 Use with Other Topical Ophthalmic Medications
Ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution has been safely administered in conjunction with other ophthalmic medications such as antibiotics, alpha-agonists, beta blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, cycloplegics, and mydriatics. Drops should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.5% is supplied sterile in white opaque LDPE dropper bottles with white opaque plug and sealed with gray pantone opaque pilfer-proof caps as follows:
- 5 mL size bottle filled with 3 mL of solution
- 5 mL size bottle filled with 5 mL of solution
- 10 mL size bottle filled with 10 mL of solution
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in the formulation.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Delayed Healing
Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may slow or delay healing. Topical corticosteroids are also known to slow or delay healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical steroids may increase the potential for healing problems.
5.2 Cross-Sensitivity or Hypersensitivity
There is the potential for cross-sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, phenylacetic acid derivatives, and other NSAIDs. There have been reports of bronchospasm or exacerbation of asthma associated with the use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution in patients who have either a known hypersensitivity to aspirin/non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or a past medical history of asthma. Therefore, caution should be used when treating individuals who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs.
5.3 Increased Bleeding Time
With some NSAIDs, there exists the potential for increased bleeding time due to interference with thrombocyte aggregation. There have been reports that ocularly applied nonsteroidal anti- inflammatory drugs may cause increased bleeding of ocular tissues (including hyphemas) in conjunction with ocular surgery.
It is recommended that ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution be used with caution in patients with known bleeding tendencies or who are receiving other medications, which may prolong bleeding time.
5.4 Corneal Effects
Use of topical NSAIDs may result in keratitis. In some susceptible patients, continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration, or corneal perforation. These events may be sight threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs suggests that patients with complicated ocular surgeries, corneal denervation, corneal epithelial defects, diabetes mellitus, ocular surface diseases (e.g., dry eye syndrome), rheumatoid arthritis, or repeat ocular surgeries within a short period of time may be at increased risk for corneal adverse events which may become sight threatening. Topical NSAIDs should be used with caution in these patients.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs also suggests that use more than 1 day prior to surgery or use beyond 14 days post-surgery may increase patient risk for the occurrence and severity of corneal adverse events.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because cli nical studies are conducted under wi dely var ying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to t he rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect t he rates observed in practice.
The most fr equent adverse react ions reported with the use of k etorolac tro meth a mine ophthal mic solutio ns have been tra nsient stin gi ng and burni ng on instillation. These reactions were reported by up to 40% of patie nts partici pating in clinic al t rials.
Other adverse reactions occurring approxi mately 1 to 10% of the ti me during tre at ment with ketor olac tr ometh a mine ophthal mic solutio ns inc luded aller gic reactions, corneal ede ma, iritis, ocular inflammation, ocular ir rit ati on, super fici al ker atitis, and super ficial ocular in fectio ns.
Other adverse reactions reported rarely with the use of ketorolac tro metha mine ophthal mic solutio ns included: c orneal infiltrates, corneal ulcer, eye dry ness, headac hes, and visual disturbance (blurry vision).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.5% in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The reactions, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to topical ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.5% or a combination of these factors, include bronchospasm or exacerbation of asthma, corneal erosion, corneal perforation, corneal thinning, and epithelial breakdown [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects. P regnancy Category C
Pregnancy Category C: Ketorolac tr o metha min e, ad ministered during organogenesis, was not teratogenic in rabbits and rats at oral doses of 3.6 mg/kg/day and 10 mg/ kg/day, respectively. These doses are approxi mately 100 ti mes and 250 ti mes higher respectively than the max i m um recom mended hu man topical op hthal mic daily d ose of 2 mg (5 mg / mL x 0.05 mL/drop, x 4 drops x 2 eyes) to affected eyes on a mg/kg basis. Additionally, when ad ministered to rats after Day 17 of gestation at oral doses up to 1.5 mg/ k g/day (approxi mately 40 ti mes the typical hu man topical ophthal mic daily dose), ketorolac tro me tha mine resulted in dystocia and increased pup mortality. There are no adequate a nd well-controlled studies in pregnant w o men. Keto ro lac t ro met ham ine op htha lm ic so lut i on should be used during pregnancy only if the potential bene fit j usti fies the p otential risk to the fetus.
Nonterato genic Effect s: Because of the known effects of prostaglandin-inhibiting drugs on the fetal c ardio vascul ar syst em (closure of the ductus art eriosu s), the use of keto ro lac t ro met ham ine op htha lm ic so lut i on during late pregnancy should be avoided.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution is administered to a nursing woman.
11 DESCRIPTION
Keto ro lac t ro met ham ine op htha lm ic so lut i on 0.5% is a m ember of the pyrrolo-pyrrole group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for ophthal mic use. Its che mical na me is (±)-5-Benzoyl-2, 3-dihydro-1H pyrrolizi ne-1-carboxylic acid co m pound with 2-a mino-2-(hydroxy methyl)-1,3-propanediol ( 1:1) and it has the following structure:
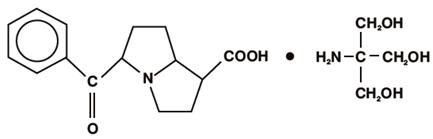
Keto ro lac t ro met ham ine op htha lm ic so lut i on is supplied as a sterile isotonic aqueous 0.5% solution, with a pH of 7.4. Keto ro lac t ro met ham ine op htha lm ic so lut i on is a race mic m ixture of R-(+) and S-(-)- ketor olac tro metha mine. Ketorol ac tro methamine may exist in t hree cr ystal for ms. All for ms are equally soluble in water. The pKa of ketorolac is 3.5. This white to o ff-white c rystalline su bstance discolors on prolonged exposure to light. The m o lecular weight of ketorolac tro metha mine is 376.41. The os molality of keto ro lac t ro met ham ine op htha lm ic so lut i on is 290 m O s mol/kg.
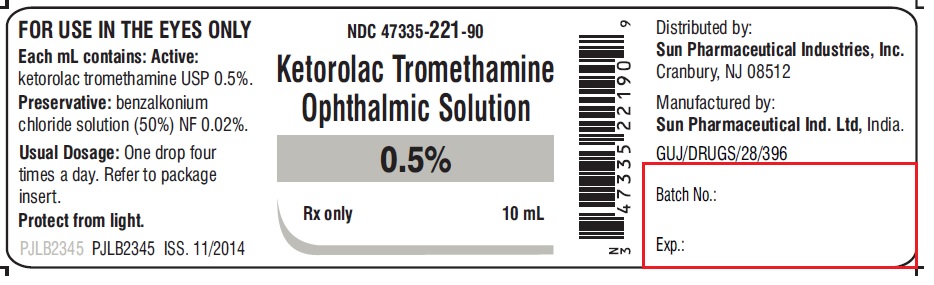
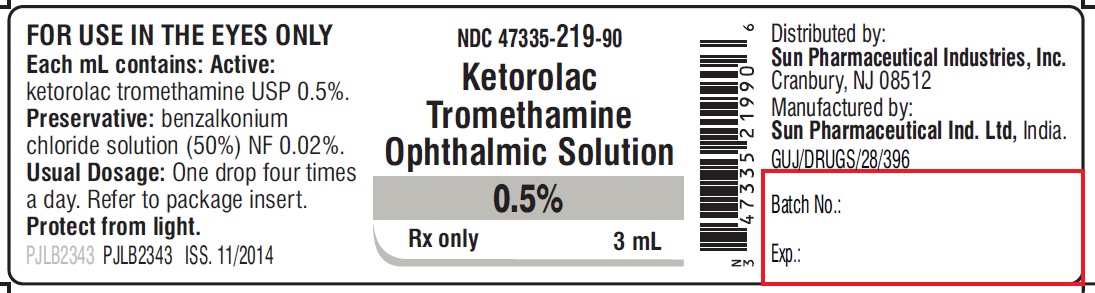
Each mL of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution contains: Active: ketorolac tromethamine USP 0.5%. Preservative: benzalkonium chloride solution (50%) NF 0.02%. Inactives: edetate disodium USP 0.1%; octoxynol 40; water for injection USP; sodium chloride USP; hydrochloric acid NF and/or sodium hydroxide NF to adjust the pH.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ketorolac tr o metha mine is a nonsteroidal ant i-inflammatory drug which, when a d ministered syste micall y, has de monstrated anal gesic, a nti-inflam matory, and anti-pyretic activity. The mechani sm of its action is thought to be due to i ts ability to inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Two drops of 0.5% ketorolac tro metha mine ophthal mic solution instilled into the eyes of patients 12 hours and 1 hour prior to cataract extraction achieved a mean ketorolac concentration of 95 ng/ mL in the aqueous h u mor of 8 of 9 eyes tested (range 40 to 170 ng/mL).
One drop of 0.5% ketorolac tro metha mine ophthal mic solution was instilled into 1 eye and 1 drop of vehicle into the other eye TID in 26 healthy subjects. Five (5) of 26 subjects had dete ctable concent ratio ns of ketorol ac in th eir plas ma (range 11 to 23 ng/mL) at Day 10 during topical ocular treat ment. The range of concent rations following TID dosing of 0.5% ketorolac tro metha mi ne ophthal mic solution are approxi mately 4 to 8% of the steady state mean min i m um plas ma concentration observed following four ti mes daily oral a d ministration of 10 mg ketorolac in hu mans (290 ± 70 ng/mL).
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis,Impairment of Fertility
Ketorolac tr o metha mine was not ca rcinogenic in either rats given up to 5 mg/kg/day orally for 24 months or in mice given 2 mg /kg/day orally for 18 months. These doses are approximately 125 ti mes and 50 ti mes higher respectively than the maxi m um re com mended h u man topical ophthal mic daily dose given as QID for itching to affected eyes on a mg/kg basis.
Ketorolac tromethamine was not mutagenic in vitro in the Ames assay or in forward mutation assays. Si milarly, it did not result in an in vitro increase in unscheduled DNA synthesis or an in vivo i ncrea se in chro moso me breakage in mice. However, ketorolac trometha mine did result in an increased incide nce in chro mosomal ab err atio ns in Chinese ha mster ovary cells.
Ketorol ac t ro metha mine did not i mpair fe rtility when ad ministered orally to male and fe male rats at doses up to 9 mg/kg/day and 16 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses are respectively 225 and 400 ti mes higher than the typical h u man topical ophthal mic daily dose.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Two controlled clinical studies sho wed that k etorolac tro metha mine ophthal mic solution was significa ntly more effective than its vehicle in relieving ocular itching caused by seasonal all ergic conjuncti vitis.
Two controlled clinical studies sho wed that pati ents t reated for two weeks with ket o rolac tro metha mi ne ophthal mic solution were less likely to have measurable signs of inflammation (cell and flare) than patients treated with its ve hicle.
Results from clinical studies indicate that k etorolac tro metha mine has no significant effect upon intraocular pressure; ho wever, chan ges in intraoc ular pressure may occur following cataract surgery.
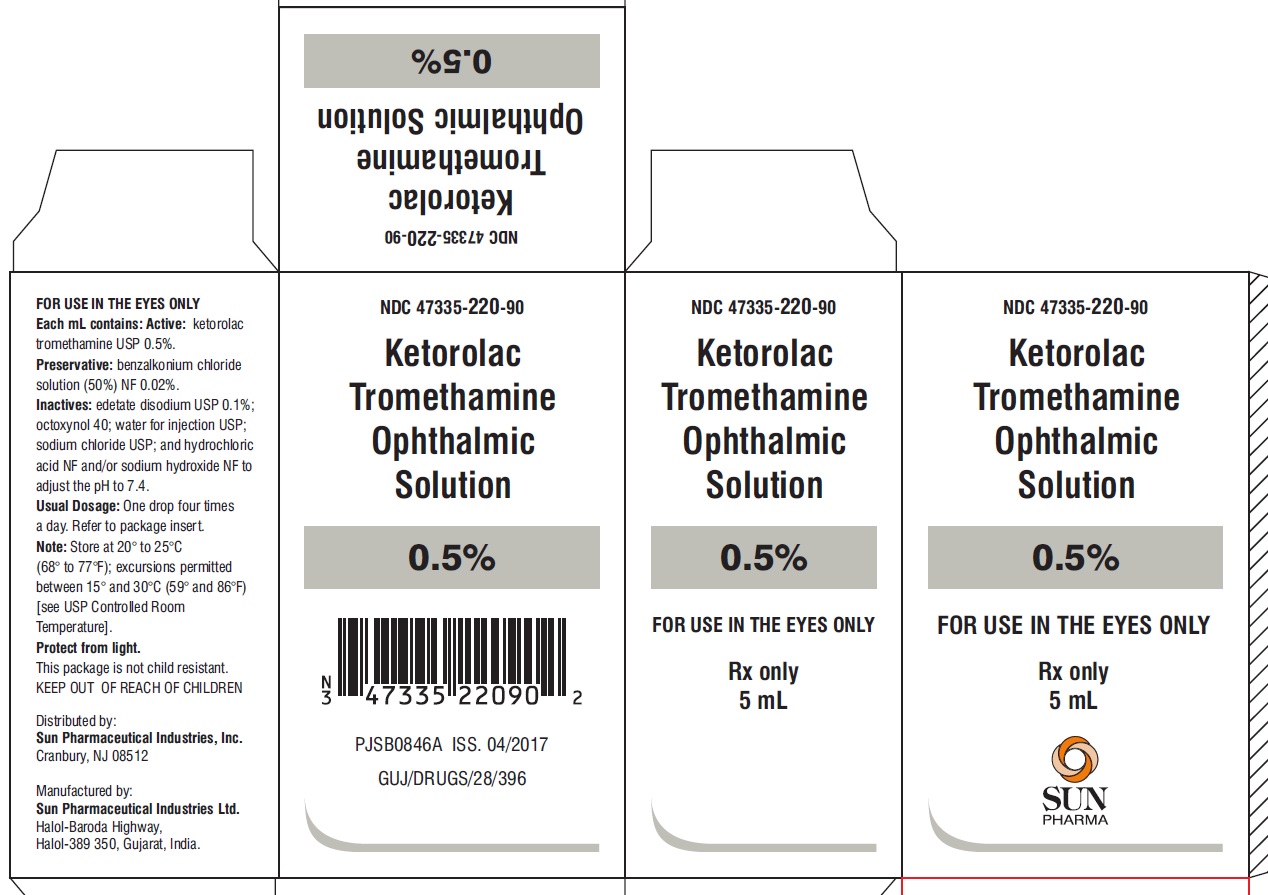
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.5% is supplied sterile in white opaque LDPE dropper bottles with white opaque plug and sealed with gray pantone opaque pilfer-proof caps as follows:
3 mL in 5 mL bottle NDC 47335-219-90
5 mL in 5 mL bottle NDC 47335-220-90
10 mL in 10 mL bottle NDC 47335-221-90
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Slow or Delayed Healing
Patie nts sh ould be in fo r med of the possibility that slow or delayed healing may occur while using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
17.2 Avoiding Contamination of the Product
Patie nts sh ould be in str ucted to avoid allow ing the tip of the bottle to co ntact the eye or surrounding structures because this could cause the tip to beco me cont a m inated by common bacteria kn own to cause ocular infections. Serious da mage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions.
Also, to avoid the potential for cross-conta mina tion, the patient should be advised to use one bottle for e ach eye foll owing bil ate ral ocular s u rgery. The use of the s a me bottle of topic al eye drops for both eyes following bilateral ocular surgery is not recom mend ed.
17.3 Contact Lens Wear
Patients should be advised that keto ro lac t ro met ham ine op htha lm ic so lut i on should not be ad ministered while wearing contact lenses.
17.4 Intercurrent Ocular Conditions
Patients should be advised that if they develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trau ma or infection) or have ocular surgery, they should i mmediately seek their physician’s advice concerning the continued use of keto ro lac t ro met ham ine op htha lm ic so lut i on.
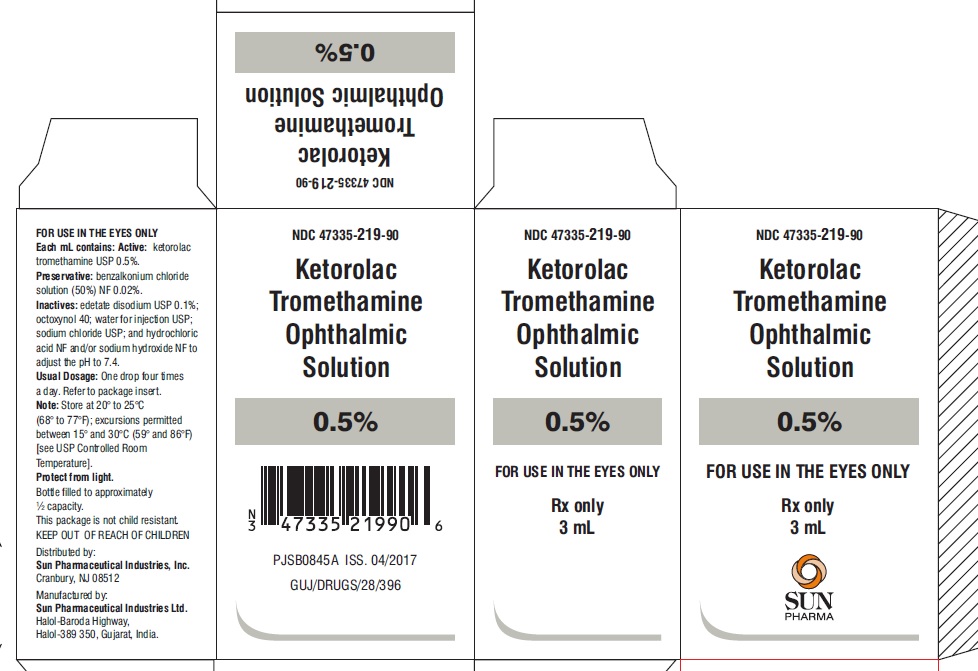
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL -label-3 mL
NDC 47335-219-90
Ketorolac Tromethamine Ophthalmic Solution
0.5%
Rx only
3 mL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL -Carton- 3 mL
NDC 47335-219-90
Ketorolac Tromethamine Ophthalmic Solution
0.5%
FOR USE IN THE EYES ONLY
Rx only
3 mL
SUN PHARMA
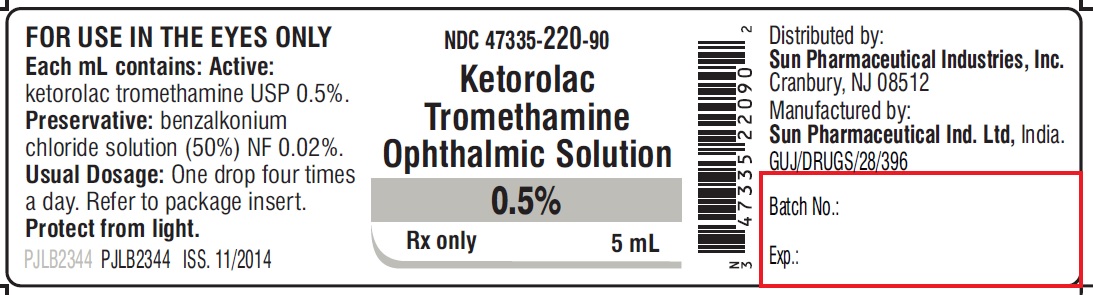
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL -Label -5 mL
NDC 47335-220-90
Ketorolac Tromethamine Ophthalmic Solution
0.5%
Rx only
5mL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL -Carton -5 mL
NDC 47335-220-90
Ketorolac Tromethamine Ophthalmic Solution
0.5%
FOR USE IN THE EYES ONLY
Rx only
5 mL
SUN PHARMA