DESCRIPTION
LEVEMIR® (insulin detemir [rDNA origin] injection) is a sterile solution of insulin detemir for use as an injection. Insulin detemir is a long-acting basal insulin analog, with up to 24 hours duration of action, produced by a process that includes expression of recombinant DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae followed by chemical modification.
Insulin detemir differs from human insulin in that the amino acid threonine in position B30 has been omitted, and a C14 fatty acid chain has been attached to the amino acid B29. Insulin detemir has a molecular formula of C267H402O76N64S6 and a molecular weight of 5916.9. It has the following structure:
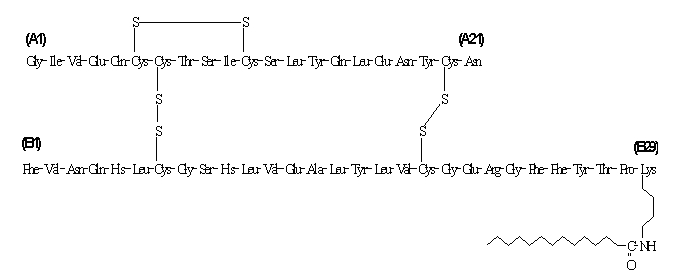
LEVEMIR is a clear, colorless, aqueous, neutral sterile solution. Each milliliter of LEVEMIR contains 100 U (14.2 mg/mL) insulin detemir, 65.4 mcg zinc, 2.06 mg m-cresol, 16.0 mg glycerol, 1.80 mg phenol, 0.89 mg disodium phosphate dihydrate, 1.17 mg sodium chloride, and water for injection. Hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust pH. LEVEMIR has a pH of approximately 7.4.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The primary activity of insulin detemir is the regulation of glucose metabolism. Insulins, including insulin detemir, exert their specific action through binding to insulin receptors.
Receptor-bound insulin lowers blood glucose by facilitating cellular uptake of glucose into skeletal muscle and fat and by inhibiting the output of glucose from the liver. Insulin inhibits lipolysis in the adipocyte, inhibits proteolysis, and enhances protein synthesis.
Pharmacodynamics
Insulin detemir is a soluble, long-acting basal human insulin analog with a relatively flat action profile. The mean duration of action of insulin detemir ranged from 5.7 hours at the lowest dose to 23.2 hours at the highest dose (sampling period 24 hours).
The prolonged action of LEVEMIR is mediated by the slow systemic absorption of insulin detemir molecules from the injection site due to strong self-association of the drug molecules and albumin binding. Insulin detemir is distributed more slowly to peripheral target tissues since insulin detemir in the bloodstream is highly bound to albumin.
Figure 1 shows glucose infusion rate results from a glucose clamp study in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Figure 1: Activity Profiles in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes in a 24-hour Glucose Clamp Study
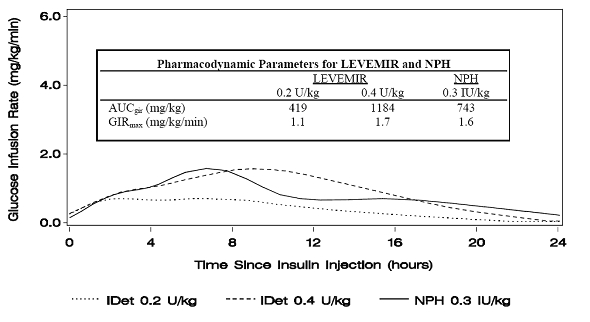
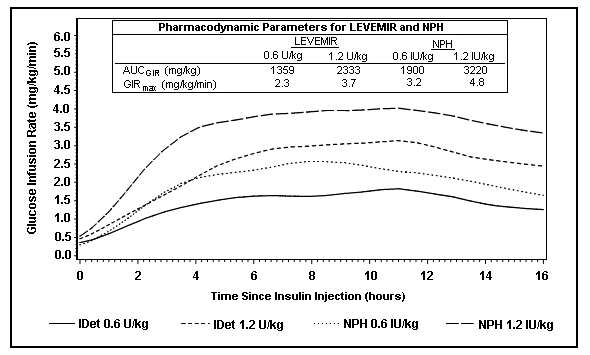
Figure 2 shows glucose infusion rate results from a 16-hour glucose clamp study in patients with type 2 diabetes. The clamp study was terminated at 16 hours according to protocol.
Figure 2: Activity Profiles in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in a 16-hour Glucose Clamp Study
For doses in the interval of 0.2 to 0.4 U/kg, LEVEMIR exerts more than 50% of its maximum effect from 3 to 4 hours up to approximately 14 hours after dose administration.
In a glucose clamp study, the overall glucodynamic effect (AUCGIR 0-24h) [mean mg/kg ± SD (CV)] of four separate subcutaneous injections in the thigh was 1702.6 ± 489 mg/kg (29%) in the LEVEMIR group and 1922.8 ± 765 mg/kg (40%) for NPH. The clinical significance of this difference has not been established.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After subcutaneous injection of insulin detemir in healthy subjects and in patients with diabetes, insulin detemir serum concentrations indicated a slower, more prolonged absorption over 24 hours in comparison to NPH human insulin.
Maximum serum concentration (Cmax) is reached between 6 and 8 hours after administration.
The absolute bioavailability of insulin detemir is approximately 60%.
Distribution and Elimination
More than 98% insulin detemir in the bloodstream is bound to albumin. LEVEMIR has a small apparent volume of distribution of approximately 0.1 L/kg. LEVEMIR, after subcutaneous administration, has a terminal half-life of 5 to7 hours depending on dose.
Special Populations
Children and Adolescents- The pharmacokinetic properties of LEVEMIR were investigated in children (6 to 12 years) and adolescents (13 to 17 years) and adults with type 1 diabetes. Similar to NPH human insulin, slightly higher plasma Area Under the Curve (AUC) and Cmax were observed in children by 10% and 24%, respectively, compared to adolescents and adults. There was no difference in pharmacokinetics between adolescents and adults.
Geriatrics- In a clinical trial investigating differences in pharmacokinetics of a single subcutaneous dose of LEVEMIR in young (25 to 35 years) versus elderly (≥68 years) healthy subjects, higher insulin AUC levels (up to 35%) were found in elderly subjects due to a reduced clearance. As with other insulin preparations, LEVEMIR should always be titrated according to individual requirements.
Gender- In controlled clinical trials, no clinically relevant difference between genders is seen in pharmacokinetic parameters based on subgroup analyses.
Race- In two trials in healthy Japanese and Caucasian subjects, there were no clinically relevant differences seen in pharmacokinetic parameters. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of LEVEMIR were investigated in a clamp trial comparing patients with type 2 diabetes of Caucasian, African-American, and Latino origin. Dose-response relationships were comparable for LEVEMIR in these three populations.
Renal impairment- Individuals with renal impairment showed no difference in pharmacokinetic parameters as compared to healthy volunteers. However, literature reports have shown that clearance of human insulin is decreased in renally impaired patients. Careful glucose monitoring and dose adjustments of insulin, including LEVEMIR, may be necessary in patients with renal dysfunction (see PRECAUTIONS, Renal Impairment).
Hepatic impairment- Individuals with severe hepatic dysfunction, without diabetes, were observed to have lower AUCs as compared to healthy volunteers. Careful glucose monitoring and dose adjustments of insulin, including LEVEMIR, may be necessary in patients with hepatic dysfunction (see PRECAUTIONS, Hepatic Impairment).
Pregnancy- The effect of pregnancy on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of LEVEMIR has not been studied (see PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy ).
Smoking- The effect of smoking on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of LEVEMIR has not been studied.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy and safety of LEVEMIR given once-daily at bedtime or twice-daily (before breakfast and at bedtime, before breakfast and with the evening meal, or at 12-hour intervals) was compared to that of once-daily or twice-daily NPH human insulin or once-daily insulin glargine in non-blinded, randomized, parallel studies of 6004 patients with diabetes (3724 with type 1, and 2280 with type 2). In general, patients treated with LEVEMIR achieved levels of glycemic control similar to those treated with NPH human insulin or insulin glargine, as measured by glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c).
Type 1 Diabetes – Adult
In one non-blinded clinical study (Study A, n=409), adult patients with type 1 diabetes were randomized to treatment with either LEVEMIR at 12-hour intervals, LEVEMIR morning and bedtime or NPH human insulin morning and bedtime. Insulin aspart was also administered before each meal. At 16 weeks of treatment, the combined LEVEMIR-treated patients had similar HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) reductions to NPH-treated patients (Table 1). Differences in timing of LEVEMIR administration (or flexible dosing) had no effect on HbA1c, FPG, body weight, or risk of having hypoglycemic episodes.
Overall glycemic control achieved with LEVEMIR was compared to that achieved with insulin glargine in a randomized, non-blinded, clinical study (Study B, n=320) in which patients with type 1 diabetes were treated for 26 weeks with either twice-daily (morning and bedtime) LEVEMIR or once-daily (bedtime) insulin glargine. Insulin aspart was administered before each meal. LEVEMIR-treated patients had a decrease in HbA1c similar to that of insulin glargine-treated patients.
In a randomized, controlled clinical study (Study C, n=749), patients with type 1 diabetes were treated with once-daily (bedtime) LEVEMIR or NPH human insulin, both in combination with human soluble insulin before each meal for 6 months. LEVEMIR and NPH human insulin had a similar effect on HbA1c.
| Study A | ||
| Treatment duration | 16 weeks | |
| Treatment in combination with | NovoLog® (insulin aspart) | |
| LEVEMIR | NPH | |
| Number of subjects treated | 276 | 133 |
| HbA1c (%) | ||
| Baseline | 8.64 | 8.51 |
| End of study adjusted mean | 7.76 | 7.94 |
| Mean change from baseline | -0.82 | -0.60 |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | ||
| End of study adjusted mean | 168 | 202 |
| Mean change from baseline | -42.48 | -10.80 |
| Daily Basal Insulin Dose (U/kg) | ||
| Prestudy mean | 0.36 | 0.39 |
| End of study mean | 0.49 | 0.45 |
| Daily Bolus Insulin Dose (U/kg) | ||
| Prestudy mean | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| End of study mean | 0.38 | 0.38 |
| Baseline values were included as covariates in an ANCOVA analysis. | ||
Type 1 Diabetes - Pediatric
In a non-blinded, randomized, controlled clinical study (Study D, n=347), pediatric patients (age range 6 to 17) with type 1 diabetes were treated for 26 weeks with a basal-bolus insulin regimen. LEVEMIR and NPH human insulin were administered once- or twice-daily (bedtime or morning and bedtime) according to pretrial dose regimen. Bolus insulin aspart was administered before each meal. LEVEMIR-treated patients had a decrease in HbA1c similar to that of NPH human insulin.
| Study D | ||
| Treatment duration | 26 weeks | |
| Treatment in combination with | NovoLog® (insulin aspart) | |
| LEVEMIR | NPH | |
| Number of subjects treated | 232 | 115 |
| HbA1c (%) | ||
| Baseline | 8.75 | 8.77 |
| End of study adjusted mean | 8.02 | 7.93 |
| Mean change from baseline | -0.72 | -0.80 |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | ||
| End of study adjusted mean | 151.92 | 172.44 |
| Mean change from baseline | -45.00 | -19.98 |
| Daily Basal Insulin Dose (U/kg) | ||
| Prestudy mean | 0.48 | 0.49 |
| End of study mean | 0.67 | 0.64 |
| Daily Bolus Insulin Dose (U/kg) | ||
| Prestudy mean | 0.52 | 0.47 |
| End of study mean | 0.52 | 0.51 |
Type 2 Diabetes – Adult
In a 24-week, non-blinded, randomized, clinical study (Study E, n=476), LEVEMIR administered twice-daily (before breakfast and evening) was compared to a similar regimen of NPH human insulin as part of a regimen of combination therapy with one or two of the following oral antidiabetes agents (metformin, insulin secretagogue, or α–glucosidase inhibitor). LEVEMIR and NPH similarly lowered HbA1c from baseline (Table 3).
| Study E | ||
| Treatment duration | 24 weeks | |
| Treatment in combination with | OAD | |
| LEVEMIR | NPH | |
| Number of subjects treated | 237 | 239 |
| HbA1c (%) | ||
| Baseline | 8.61 | 8.51 |
| End of study adjusted mean | 6.58 | 6.46 |
| Mean change from baseline | -1.84 | -1.90 |
| Proportion achieving HbA1c ≤ 7% | 70% | 74% |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | ||
| End of study adjusted mean | 119.16 | 113.40 |
| Mean change from baseline | -75.96 | -74.34 |
| Daily Insulin Dose (U/kg) | ||
| End of study mean | 0.77 | 0.52 |
In a 22-week, non-blinded, randomized, clinical study (Study F, n=395) in adults with Type 2 diabetes, LEVEMIR and NPH human insulin were given once- or twice-daily as part of a basal-bolus regimen. As measured by HbA1c or FPG, LEVEMIR had efficacy similar to NPH human insulin.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LEVEMIR is indicated for once- or twice-daily subcutaneous administration for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus or adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who require basal (long acting) insulin for the control of hyperglycemia.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
LEVEMIR is contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to insulin detemir or one of its excipients.
WARNINGS
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse effect of insulin therapy, including LEVEMIR. As with all insulins, the timing of hypoglycemia may differ among various insulin formulations.
Glucose monitoring is recommended for all patients with diabetes.
LEVEMIR is not to be used in insulin infusion pumps.
Any change of insulin dose should be made cautiously and only under medical supervision. Changes in insulin strength, timing of dosing, manufacturer, type (e.g., regular, NPH, or insulin analogs), species (animal, human), or method of manufacture (rDNA versus animal-source insulin) may result in the need for a change in dosage.
Concomitant oral antidiabetic treatment may need to be adjusted.
Needles and Levemir FlexPen must not be shared.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Inadequate dosing or discontinuation of treatment may lead to hyperglycemia and, in patients with type 1 diabetes, diabetic ketoacidosis. The first symptoms of hyperglycemia usually occur gradually over a period of hours or days. They include nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, flushed dry skin, dry mouth, increased urination, thirst and loss of appetite as well as acetone breath. Untreated hyperglycemic events are potentially fatal.
LEVEMIR is not intended for intravenous or intramuscular administration. The prolonged duration of activity of insulin detemir is dependent on injection into subcutaneous tissue. Intravenous administration of the usual subcutaneous dose could result in severe hypoglycemia. Absorption after intramuscular administration is both faster and more extensive than absorption after subcutaneous administration.
LEVEMIR should not be diluted or mixed with any other insulin preparations (see PRECAUTIONS, Mixing of Insulins).
Insulin may cause sodium retention and edema, particularly if previously poor metabolic control is improved by intensified insulin therapy.
Lipodystrophy and hypersensitivity are among potential clinical adverse effects associated with the use of all insulins.
As with all insulin preparations, the time course of LEVEMIR action may vary in different individuals or at different times in the same individual and is dependent on site of injection, blood supply, temperature, and physical activity.
Adjustment of dosage of any insulin may be necessary if patients change their physical activity or their usual meal plan.
Hypoglycemia
As with all insulin preparations, hypoglycemic reactions may be associated with the administration of LEVEMIR. Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse effect of insulins. Early warning symptoms of hypoglycemia may be different or less pronounced under certain conditions, such as long duration of diabetes, diabetic nerve disease, use of medications such as beta-blockers, or intensified diabetes control (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions). Such situations may result in severe hypoglycemia (and, possibly, loss of consciousness) prior to patients’ awareness of hypoglycemia.
The time of occurrence of hypoglycemia depends on the action profile of the insulins used and may, therefore, change when the treatment regimen or timing of dosing is changed. In patients being switched from other intermediate or long-acting insulin preparations to once- or twice-daily LEVEMIR, dosages can be prescribed on a unit-to-unit basis; however, as with all insulin preparations, dose and timing of administration may need to be adjusted to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Changeover to LEVEMIR).
Renal Impairment
As with other insulins, the requirements for LEVEMIR may need to be adjusted in patients with renal impairment (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics).
Hepatic Impairment
As with other insulins, the requirements for LEVEMIR may need to be adjusted in patients with hepatic impairment (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics).
Injection Site and Allergic Reactions
As with any insulin therapy, lipodystrophy may occur at the injection site and delay insulin absorption. Other injection site reactions with insulin therapy may include redness, pain, itching, hives, swelling, and inflammation. Continuous rotation of the injection site within a given area may help to reduce or prevent these reactions. Reactions usually resolve in a few days to a few weeks. On rare occasions, injection site reactions may require discontinuation of LEVEMIR.
In some instances, these reactions may be related to factors other than insulin, such as irritants in a skin cleansing agent or poor injection technique.
Systemic allergy: Generalized allergy to insulin, which is less common but potentially more serious, may cause rash (including pruritus) over the whole body, shortness of breath, wheezing, reduction in blood pressure, rapid pulse, or sweating. Severe cases of generalized allergy, including anaphylactic reaction, may be life-threatening.
Intercurrent Conditions
Insulin requirements may be altered during intercurrent conditions such as illness, emotional disturbances, or other stresses.
Information for Patients
LEVEMIR must only be used if the solution appears clear and colorless with no visible particles (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Preparation and Handling). Patients should be informed about potential risks and advantages of LEVEMIR therapy, including the possible side effects. Patients should be offered continued education and advice on insulin therapies, injection technique, life-style management, regular glucose monitoring, periodic glycosylated hemoglobin testing, recognition and management of hypo- and hyperglycemia, adherence to meal planning, complications of insulin therapy, timing of dosage, instruction for use of injection devices and proper storage of insulin. Patients should be informed that frequent, patient-performed blood glucose measurements are needed to achieve effective glycemic control to avoid both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. Patients must be instructed on handling of special situations such as intercurrent conditions (illness, stress, or emotional disturbances), an inadequate or skipped insulin dose, inadvertent administration of an increased insulin dose, inadequate food intake, or skipped meals. Refer patients to the LEVEMIR "Patient Information" circular for additional information.
As with all patients who have diabetes, the ability to concentrate and/or react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Patients with diabetes should be advised to inform their health care professional if they are pregnant or are contemplating pregnancy (see PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy ).
Laboratory Tests
As with all insulin therapy, the therapeutic response to LEVEMIR should be monitored by periodic blood glucose tests. Periodic measurement of HbA1c is recommended for the monitoring of long-term glycemic control.
Drug Interactions
A number of substances affect glucose metabolism and may require insulin dose adjustment and particularly close monitoring.
The following are examples of substances that may reduce the blood-glucose-lowering effect of insulin: corticosteroids, danazol, diuretics, sympathomimetic agents (e.g., epinephrine, albuterol, terbutaline), isoniazid, phenothiazine derivatives, somatropin, thyroid hormones, estrogens, progestogens (e.g., in oral contraceptives).
The following are examples of substances that may increase the blood-glucose-lowering effect of insulin and susceptibility to hypoglycemia: oral antidiabetic drugs, ACE inhibitors, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine, MAO inhibitors, propoxyphene, salicylates, somatostatin analog (e.g., octreotide), and sulfonamide antibiotics.
Beta-blockers, clonidine, lithium salts, and alcohol may either potentiate or weaken the blood-glucose-lowering effect of insulin. Pentamidine may cause hypoglycemia, which may sometimes be followed by hyperglycemia. In addition, under the influence of sympatholytic medicinal products such as beta-blockers, clonidine, guanethidine, and reserpine, the signs of hypoglycemia may be reduced or absent.
The results of in-vitro and in-vivo protein binding studies demonstrate that there is no clinically relevant interaction between insulin detemir and fatty acids or other protein bound drugs.
Mixing of Insulins
If LEVEMIR is mixed with other insulin preparations, the profile of action of one or both individual components may change. Mixing LEVEMIR with insulin aspart, a rapid acting insulin analog, resulted in about 40% reduction in AUC(0-2h) and Cmax for insulin aspart compared to separate injections when the ratio of insulin aspart to LEVEMIR was less than 50%.
LEVEMIR should NOT be mixed or diluted with any other insulin preparations.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Standard 2-year carcinogenicity studies in animals have not been performed. Insulin detemir tested negative for genotoxic potential in the in-vitro reverse mutation study in bacteria, human peripheral blood lymphocyte chromosome aberration test, and the in-vivo mouse micronucleus test.
Preganancy Category C
Teratogenic effects
In a fertility and embryonic development study, insulin detemir was administered to female rats before mating, during mating, and throughout pregnancy at doses up to 300 nmol/kg/day (3 times the recommended human dose, based on plasma Area Under the Curve (AUC) ratio). Doses of 150 and 300 nmol/kg/day produced numbers of litters with visceral anomalies. Doses up to 900 nmol/kg/day (approximately 135 times the recommended human dose based on AUC ratio) were given to rabbits during organogenesis. Drug-dose related increases in the incidence of fetuses with gall bladder abnormalities such as small, bilobed, bifurcated and missing gall bladders were observed at a dose of 900 nmol/kg/day. The rat and rabbit embryofetal development studies that included concurrent human insulin control groups indicated that insulin detemir and human insulin had similar effects regarding embryotoxicity and teratogenicity.
Nursing mothers
It is unknown whether LEVEMIR is excreted in significant amounts in human milk. For this reason, caution should be exercised when LEVEMIR is administered to a nursing mother. Patients with diabetes who are lactating may require adjustments in insulin dose, meal plan, or both.
Pediatric use
In a controlled clinical study, HbA1c concentrations and rates of hypoglycemia were similar among patients treated with LEVEMIR and patients treated with NPH human insulin.
Geriatric use
Of the total number of subjects in intermediate and long-term clinical studies of LEVEMIR, 85 (type 1 studies) and 363 (type 2 studies) were 65 years and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. In elderly patients with diabetes, the initial dosing, dose increments, and maintenance dosage should be conservative to avoid hypoglycemic reactions. Hypoglycemia may be difficult to recognize in the elderly.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse events commonly associated with human insulin therapy include the following:
Body as Whole: allergic reactions (see PRECAUTIONS, Allergy).
Skin and Appendages: lipodystrophy, pruritus, rash. Mild injection site reactions occurred more frequently with LEVEMIR than with NPH human insulin and usually resolved in a few days to a few weeks (see PRECAUTIONS, Allergy).
Other:
Hypoglycemia: (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
In trials of up to 6 months duration in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the incidence of severe hypoglycemia with LEVEMIR was comparable to the incidence with NPH, and, as expected, greater overall in patients with type 1 diabetes (Table 4).
Weight gain:
In trials of up to 6 months duration in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, LEVEMIR was associated with somewhat less weight gain than NPH (Table 4). Whether these observed differences represent true differences in the effects of LEVEMIR and NPH insulin is not known, since these trials were not blinded and the protocols (e.g., diet and exercise instructions and monitoring) were not specifically directed at exploring hypotheses related to weight effects of the treatments compared. The clinical significance of the observed differences has not been established.
| Weight (kg) | Hypoglycemia (events/subject/month) | |||||
| Treatment | # of subjects | Baseline | End of treatment | Major | Minor | |
| Type 1 | ||||||
| Study A | LEVEMIR | N=276 | 75.0 | 75.1 | 0.045 | 2.184 |
| NPH | N=133 | 75.7 | 76.4 | 0.035 | 3.063 | |
| Study C | LEVEMIR | N=492 | 76.5 | 76.3 | 0.029 | 2.397 |
| NPH | N=257 | 76.1 | 76.5 | 0.027 | 2.564 | |
| Study D Pediatric | LEVEMIR | N=232 | N/A | N/A | 0.076 | 2.677 |
| NPH | N=115 | N/A | N/A | 0.083 | 3.203 | |
| Type 2 | ||||||
| Study E | LEVEMIR | N=237 | 82.7 | 83.7 | 0.001 | 0.306 |
| NPH | N=239 | 82.4 | 85.2 | 0.006 | 0.595 | |
| Study F | LEVEMIR | N=195 | 81.8 | 82.3 | 0.003 | 0.193 |
| NPH | N=200 | 79.6 | 80.9 | 0.006 | 0.235 | |
OVERDOSAGE
Hypoglycemia may occur as a result of an excess of insulin relative to food intake, energy expenditure, or both. Mild episodes of hypoglycemia usually can be treated with oral glucose. Adjustments in drug dosage, meal patterns, or exercise may be needed. More severe episodes with coma, seizure, or neurologic impairment may be treated with intramuscular/subcutaneous glucagon or concentrated intravenous glucose. After apparent clinical recovery from hypoglycemia, continued observation and additional carbohydrate intake may be necessary to avoid reoccurrence of hypoglycemia.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
LEVEMIR can be administered once- or twice-daily. The dose of LEVEMIR should be adjusted according to blood glucose measurements. The dosage of LEVEMIR should be individualized based on the physician’s advice, in accordance with the needs of the patient.
- For patients treated with Levemir once-daily, the dose should be administered with the evening meal or at bedtime.
- For patients who require twice-daily dosing for effective blood glucose control, the evening dose can be administered either with the evening meal, at bedtime, or 12 hours after the morning dose.
LEVEMIR should be administered by subcutaneous injection in the thigh, abdominal wall, or upper arm. Injection sites should be rotated within the same region. As with all insulins, the duration of action will vary according to the dose, injection site, blood flow, temperature, and level of physical activity.
Dose Determination for LEVEMIR
- For patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes on basal-bolus treatment, changing the basal insulin to LEVEMIR can be done on a unit-to-unit basis. The dose of LEVEMIR should then be adjusted to achieve glycemic targets. In some patients with type 2 diabetes, more LEVEMIR may be required than NPH insulin. In a clinical study, the mean dose at end of treatment was 0.77 U/kg for LEVEMIR and 0.52 IU/kg for NPH human insulin (see Table 3).
- For patients currently receiving only basal insulin, changing the basal insulin to LEVEMIR can be done on a unit-to-unit basis.
- For insulin-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes who are inadequately controlled on oral antidiabetic drugs, LEVEMIR should be started at a dose of 0.1 to 0.2 U/kg once-daily in the evening or 10 units once- or twice-daily, and the dose adjusted to achieve glycemic targets.
- As with all insulins, close glucose monitoring is recommended during the transition and in the initial weeks thereafter. Dose and timing of concurrent short-acting insulins or other concomitant antidiabetic treatment may need to be adjusted.
Preparation and Handling
LEVEMIR should be inspected visually prior to administration and should only be used if the solution appears clear and colorless.
LEVEMIR should not be mixed or diluted with any other insulin preparations.
After each injection, patients must remove the needle without recapping and dispose of it in a puncture-resistant container. Used syringes, needles, or lancets should be placed in “sharps” containers (such as red biohazard containers), hard plastic containers (such as detergent bottles), or metal containers (such as an empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.
HOW SUPPLIED
LEVEMIR is available in the following package sizes: each presentation containing 100 Units of insulin detemir per mL (U-100).
| 10 mL vial | NDC 0169-3687-12 |
| 3 mL PenFill® cartridges* | NDC 0169-3305-11 |
| 3 mL InnoLet® | NDC 0169-2312-11 |
| 3 mL FlexPen® | NDC 0169-6439-10 |
*LEVEMIR PenFill® cartridges are for use with Novo Nordisk 3 mL PenFill® cartridge compatible insulin delivery devices and NovoFine® disposable needles.
RECOMMENDED STORAGE
Unused LEVEMIR should be stored between 2° and 8°C (36° to 46° F). Do not freeze. Do not use LEVEMIR if it has been frozen.
Vials:
After initial use, vials should be stored in a refrigerator, never in a freezer. If refrigeration is not possible, the in-use vial can be kept unrefrigerated at room temperature, below 30°C (86°F), for up to 42 days, as long as it is kept as cool as possible and away from direct heat and light.
Unpunctured vials can be used until the expiration date printed on the label if they are stored in a refrigerator. Keep unused vials in the carton so they will stay clean and protected from light.
PenFill® cartridges, FlexPen® or InnoLet®:
After initial use, a cartridge (PenFill®) or a prefilled syringe (including FlexPen® or InnoLet®) may be used for up to 42 days if it is kept at room temperature, below 30°C (86°F). In-use cartridges and prefilled syringes in-use must NOT be stored in a refrigerator and must NOT be stored with the needle in place. Keep all cartridges and prefilled syringes away from direct heat and sunlight.
Not in-use (unopened) LEVEMIR PenFill®, FlexPen® or InnoLet® can be used until the expiration date printed on the label if they are stored in a refrigerator. Keep unused cartridges and prefilled syringes in the carton so they will stay clean and protected from light.
The storage conditions are summarized in the following table:
|
Not in-use (unopened) Room Temperature (below 30°C) |
Not in-use (unopened) Refrigerated |
In-use (opened) Room Temperature (below 30°C) |
|
| 10 mL vial | 42 days | Until expiration date |
42 days refrigerated/room temperature |
| 3 mL PenFill® cartridges | 42 days | Until expiration date | 42 days (Do not refrigerate) |
| 3 mL InnoLet® | 42 days | Until expiration date | 42 days (Do not refrigerate) |
| 3 mL FlexPen® | 42 days | Until expiration date | 42 days (Do not refrigerate) |
Date of issue: July 15, 2009
Version: 5
Novo Nordisk®, Levemir®, NovoLog®, FlexPen®, InnoLet®, PenFill®, and NovoFine® are registered trademarks owned by Novo Nordisk A/S.
© 2005/2009 Novo Nordisk Inc.
Levemir® is covered by US Patent Nos. 5,750,497; 5,866,538; 6,011,007; 6,869,930 and other patents pending.
FlexPen® is covered by US Patent Nos. 6,004,297; 6,235,004; 6,582,404 and other patents pending.
Manufactured for:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
Princeton, NJ 08540
www.novonordisk-us.com
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
PATIENT INFORMATION
Levemir® (LEV–uh-mere)
(insulin detemir [rDNA origin] injection)
Important:
Know your insulin. Do not change the type of insulin you use unless told to do so by your healthcare provider. The amount of insulin you take as well as the best time for you to take your insulin may need to change if you take a different type of insulin.
Make sure you know the type and strength of insulin prescribed for you.
Read the Patient Information that comes with Levemir before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your diabetes or your treatment. Make sure that you know how to manage your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider if you have any questions about managing your diabetes.
What is Levemir?
Levemir is a man-made long-acting insulin that is used to control high blood sugar in adults and children with diabetes mellitus.
Who should not use Levemir?
Do not take Levemir if:
- Your blood sugar is too low (hypoglycemia).
- You are allergic to anything in Levemir. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Levemir. Check with your healthcare provider if you are not sure.
Tell your healthcare provider:
- about all of your medical conditions. Medical conditions can affect your insulin needs and your dose of Levemir.
- if you are pregnant or breast-feeding. You and your healthcare provider should talk about the best way to manage your diabetes while you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Levemir has not been studied in pregnant or nursing women.
- about all medicines you take, including prescriptions and non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Your Levemir dose may change if you take other medicines.
How should I take Levemir?
Only use Levemir if it appears clear and colorless. There may be air bubbles. This is normal. If it looks cloudy, thickened, or colored, or if it contains solid particles do not use it and call Novo Nordisk at 1-800-727-6500.
Levemir comes in:
- 10 mL vials (small bottles) for use with a syringe
- 3 mL PenFill® cartridges for use with the Novo Nordisk 3 mL PenFill cartridge compatible insulin delivery devices and NovoFine® disposable needles. The cartridge delivery device can be used with a NovoPen® 3 PenMate®
- 3 mL Levemir FlexPen®
- 3 mL Levemir InnoLet
- Take Levemir exactly as prescribed.
- Levemir is a long-acting insulin. The effect of Levemir may last up to 24 hours after injection.
- Inject Levemir into the skin of your stomach area, upper arms, or thighs. Levemir may affect your blood sugar levels sooner if you inject it into the skin of your stomach area or upper arm. Never inject Levemir into a vein or into a muscle.
- Change (rotate) your injection site within the chosen area (for example, stomach or upper arm) with each dose. Do not inject into the exact same spot for each injection.
- If you take too much Levemir, your blood sugar may fall low (hypoglycemia). You can treat mild low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) by drinking or eating something sugary right away (fruit juice, sugar candies, or glucose tablets). It is important to treat low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) right away because it could get worse and you could pass out (become unconscious). If you pass out you will need help from another person or emergency medical services right away, and will need treatment with a glucagon injection or treatment at a hospital. See “What are the possible side effects of Levemir?” for more information on low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
- If you forget to take your dose of Levemir, your blood sugar may go too high (hyperglycemia). If high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) is not treated it can lead to serious problems, like loss of consciousness (passing out), coma or even death. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for treating high blood sugar. Know your symptoms of high blood sugar which may include:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Check your blood sugar levels. Ask your healthcare provider what your blood sugars should be and when you should check your blood sugar levels.
- Never mix Levemir with other insulin products.
- Never use Levemir in an insulin pump.
Your insulin dosage may need to change because of:
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Alcohol. Alcohol, including beer and wine, may affect your blood sugar when you take Levemir.
- Driving and operating machinery. You may have difficulty concentrating or reacting if you have low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Be careful when you drive a car or operate machinery. Ask your healthcare provider if it is alright to drive if you often have:
-
- low blood sugar
- decreased or no warning signs of low blood sugar
- low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Symptoms of low blood sugar may include:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
Serious allergic reaction (whole body reaction). Get medical help right away, if you develop a rash over your whole body, have trouble breathing, a fast heartbeat, or sweating.
- Reactions at the injection site (local allergic reaction). You may get redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site. If you keep having skin reactions or they are serious, talk to your healthcare provider. You may need to stop using Levemir and use a different insulin. Do not inject insulin into skin that is red, swollen, or itchy.
-
Skin thickens or pits at the injection site (lipodystrophy). Change (rotate) where you inject your insulin to help to prevent these skin changes from happening. Do not inject insulin into this type of skin.
- Swelling of your hands and feet.
- Vision changes
- Low potassium in your blood (hypokalemia)
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Levemir?
All Unopened Levemir:
- Keep all unopened Levemir in the refrigerator between 36° to 46°F (2° to 8°C).
- Do not freeze. Do not use Levemir if it has been frozen.
- Keep unopened Levemir in the carton to protect from light.
Levemir in use:
- Vials
-
- Keep in the refrigerator or at room temperature below 86°F (30°C) for up to 42 days.
- Keep vials away from direct heat or light.
- Throw away an opened vial after 42 days of use, even if there is insulin left in the vial.
- Unopened vials can be used until the expiration date on the Levemir label, if the medicine has been stored in a refrigerator.
- Levemir FlexPen
-
- Keep at room temperature below 86°F (30°C) for up to 42 days.
- Do not store a Levemir FlexPen that you are using in the refrigerator.
- Keep Levemir FlexPen away from direct heat or light.
- Throw away a used Levemir FlexPen after 42 days, even if there is insulin left in the syringe.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in the patient leaflet. Do not use Levemir for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Levemir to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Levemir. If you would like more information about Levemir or diabetes, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Levemir that is written for healthcare professionals. Call 1-800-727-6500 or visit www.novonordisk-us.com for more information.
Helpful information for people with diabetes is published by the American Diabetes Association, 1701 N Beauregard Street, Alexandria, VA 22311 and on www.diabetes.org.
Levemir ingredients include:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
All Levemir vials and Levemir FlexPen are latex free.
Date of Issue: May 22, 2009
Version: 4
Levemir® , PenFill® , FlexPen® , NovoPen® , NovoFine® , PenMate® , are trademarks of Novo Nordisk A/S.
Levemir® is covered by US Patent Nos. 5,750,497, 5,866,538, 6,011,007, 6,869,930, and other patents pending.
FlexPen® is covered by US Patent Nos. 6,582,404, 6,004,297, 6,235,004, and other patents pending.
PenFill® is covered by US Patent Nos. 6,126,646, 5,693,027, DES 347894, and other patents pending.
© 2005-2009 Novo Nordisk Inc.
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
For information about Levemir® contact:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
100 College Road West,
Princeton, New Jersey 08540
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Levemir® 10 mL vial (100 units/mL, U-100)
Levemir® 3 mL PenFill® cartridge (100 units/mL, U-100)
How should I prepare and deliver the injection using different delivery devices?
Using the 10 mL vial:
- At your first use, remove the tamper-resistant cap from the vial. If the cap has already been removed, do not use this vial and return it to your pharmacy.
- Wipe the rubber membrane with an alcohol swab.
- Do not roll or shake the vial. Vigorous shaking right before the dose is drawn into the syringe may cause bubbles or froth, which could cause dosage errors. The insulin should be used only if it is clear and colorless.
- Pull back the plunger on your syringe until the black tip reaches the marking for the number of units you will inject.
- Push the needle through the rubber membrane into the vial.
- Push the plunger all the way in. This inserts air into the vial.
- Turn the vial and syringe upside down together and slowly pull the plunger back to a few units beyond the correct dose.
- If there are air bubbles, tap the syringe gently with your finger to raise the air bubbles to the needle. Then slowly push the plunger to the correct unit marking.
- Lift the vial off the syringe.
- Inject right away.
- The syringe and vial should be disposed of properly without recapping the needle. After each injection, patients must remove the needle without recapping and dispose of it in a puncture-resistant container. Used syringes, needles, or lancets should be placed in sharps containers (such as red biohazard containers), hard plastic containers (such as detergent bottles), or metal containers (such as an empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.
- Read the instruction manuals for the 3 mL PenFill® cartridge compatible delivery device* before the device is used.
- The insulin should be used only if it is clear and colorless. Insert the PenFill® cartridge into the 3 mL PenFill® cartridge compatible delivery device*.
- Place the needle onto the 3 mL PenFill® cartridge compatible delivery device* immediately before use
- Airshots should be done prior to each injection. Directions for performing an airshot and setting the dose are provided in your insulin delivery device instruction manual.
- Discard needle after each dose. The needle should not be recapped to avoid needlesticks. After each injection, patients must remove the needle without recapping and dispose of it in a puncture-resistant container. Used syringes, needles, or lancets should be placed in sharps containers (such as red biohazard containers), hard plastic containers (such as detergent bottles), or metal containers (such as an empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.
- Airshots should be done prior to each injection. Directions for performing an airshot and setting the dose are provided in your insulin delivery device instruction manual.
- To avoid needle sticks, do not recap the needle. Throw away the needle safely after each injection
- Pinch your skin between two fingers, push the needle into the skinfold, and push the plunger to inject the insulin under your skin. The needle should be perpendicular to the skin. This means the needle will be straight in.
- Keep the needle under your skin for at least 6 seconds to make sure you have injected all the insulin.
- If blood appears after you pull the needle from your skin, press the injection site lightly with a finger. Do not rub the area.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Levemir® 3 mL InnoLet (100 units/mL, U-100)
LEVEMIR InnoLet (3 mL) directions for use
LEVEMIR InnoLet is a disposable dial-a-dose insulin delivery system able to deliver 1 to a maximum of 50 units. The dose can be adjusted in increments of 1 unit. LEVEMIR InnoLet is designed for use with NovoFine® single-use needles. LEVEMIR InnoLet is not recommended for the blind or severely visually impaired patients without the assistance of a sighted individual trained in the proper use of the product.
Please read and follow these instructions completely each time you use this device. If you do not follow these instructions completely, you may get too much or too little insulin.
Every time you give an injection using LEVEMIR InnoLet:
- Use a new needle
-
Prime to make sure the InnoLet is ready to dose
- Make sure you got your full dose
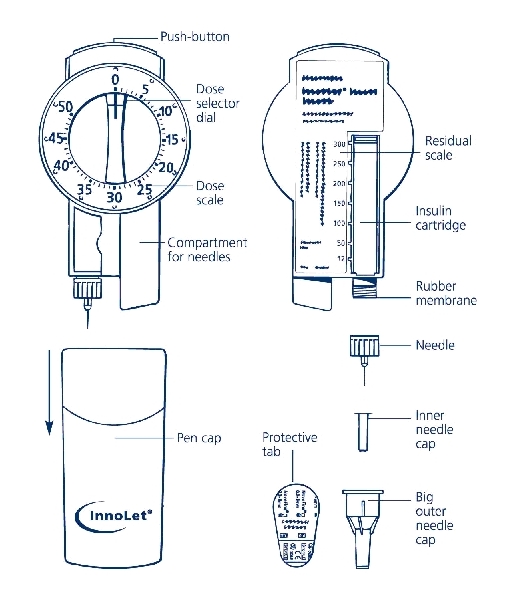
Figure of Innolet and Needles
1. PREPARING THE LEVEMIR INNOLET
a. Pull off the cap.
b. Wipe the rubber membrane with an alcohol swab.
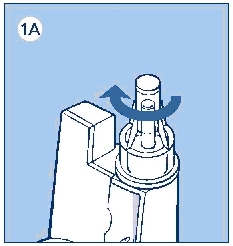
c. Remove the protective tab from the disposable needle and screw the needle onto the InnoLet (see diagram 1A). Never place a disposable needle on your InnoLet until you are ready to give an injection. Remove the needle from InnoLet immediately after the use. If the needle is not removed, some liquid may leak from the LEVEMIR InnoLet.
d. Giving the air shot before each injection
Small amounts of air may collect in the needle and insulin reservoir during normal use. To avoid injecting air and to ensure proper dosing, dial 2 units by turning the dose selector clockwise. Hold the LEVEMIR InnoLet with the needle pointing up and tap the LEVEMIR InnoLet gently with your finger so any air bubbles collect in the top of the reservoir. Remove both the plastic outer and inner needle cap.
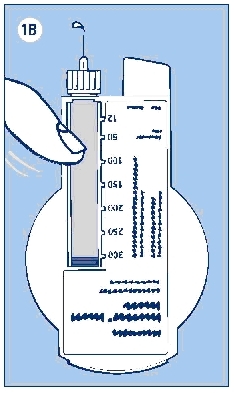
e. With the needle pointing up, press the push button as far as it will go and the dose selector returns to zero. See if a drop of insulin appears at the needle tip (see Figure 1B). If not, repeat the procedure until insulin appears.
Before the first use of LEVEMIR InnoLet, you may need to perform up to 6 airshots to get a droplet of insulin at the needle tip. If you need to make more than 6 airshots, do not use the LEVEMIR InnoLet, and contact Novo Nordisk® at 1-800-727-6500. A small air bubble may remain but it will not be injected because the operating mechanism prevents the reservoir from being completely emptied.
2. SETTING THE DOSE
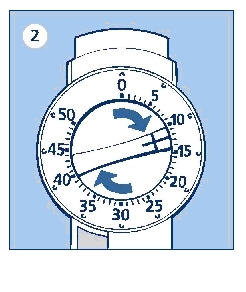
Always check that the push button is fully depressed and the dose selector is set at 0. Hold the LEVEMIR InnoLet® in front of you and dial the dose selector clockwise to set the required dose. Do not put your hand over the push button when dialing the dose. If the button is not allowed to rise freely, insulin will be pushed out of the needle. You will hear a click for every single unit dialed. Do not rely on the clicking sound as a means for setting your dose. If you have set a wrong dose, simply dial the dose selector forward or backwards until the right number of dose has been set.
50 units is the maximum dose.
3. GIVING THE INJECTION
Use the injection technique recommended by your doctor or health care professionals.
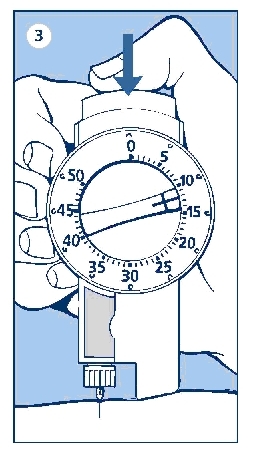
a. Check that you have set the proper dose and depress the push button as far as it will go. Make sure not to block the dose selector while injecting, as the dose selector must be allowed to return to zero when you press the push button. When depressing the push button, you may hear a clicking sound. Do not rely on this clicking sound as a means of confirming delivery of your dose.
After making the injection, unscrew the needle and discard appropriately. After each injection, you must remove the needle before replacing the device cap and dispose of the needle in a puncture-resistant container. Used syringes, needles, or lancets should be placed in “sharps” containers (such as red biohazard containers), hard plastic containers (such as detergent bottles), or metal containers (such as an empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.
It is important that you use a new needle for each injection. Health care professionals, relatives, and other caregivers, should follow general precautionary measures for removal and disposal of needles to eliminate the risk of unintended needlestick.
4. LATER (SUBSEQUENT) INJECTIONS
Always check that the push button is fully depressed before using the LEVEMIR InnoLet® again. If not, turn the dose selector until the push button is completely down. Then proceed as stated in steps 1-3.
The numbers on the insulin reservoir can be used to estimate the amount of insulin left in the LEVEMIR InnoLet. Do not use these numbers to measure the insulin dose. You cannot set a dose greater than the number of units remaining in the reservoir.
5. FUNCTION CHECK
If you think that your LEVEMIR InnoLet is not working properly, follow this procedure:
a. Screw on a new NovoFine needle
b. Perform air shot as described in 1. PREPARING THE LEVEMIR INNOLET®, steps (d) through (e) and Figure 1B
c. Put the outer needle cap onto the needle
d. Dispense 20 units into the needle cap.
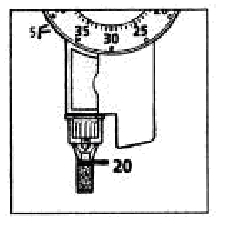
The insulin will fill the lower part of the cap (as shown in the figure above).
If the LEVEMIR InnoLet has released too much or too little insulin, repeat the test. If it happens again, do not use your LEVEMIR InnoLet and contact Novo Nordisk at 1-800-727-6500.
6. IMPORTANT NOTES
- If you need to perform more than 6 air shots before the first use of the disposable LEVEMIR InnoLet to get a droplet of insulin at the needle tip, do not use your LEVEMIR InnoLet and contact Novo Nordisk at 1-800-727-6500.
- Remember to perform an air shot before each injection. See figure 1B.
- Do not drop, damage, or crush the disposable LEVEMIR InnoLet.
- Remember to keep the disposable LEVEMIR InnoLet with you. Don’t leave it in a car or other location where it can get too hot or too cold.
- LEVEMIR InnoLet is not supplied with needles. NovoFine® disposable needles are designed and recommended for use with Novo Nordisk® insulin delivery devices, including LEVEMIR InnoLet.
- Never place a disposable needle on the LEVEMIR InnoLet until you are ready to use it. Remove the needle right after the use without recapping.
- Discard the needle after each injection. After each injection, remove the needle before replacing the device cap and dispose the needle in a puncture-resistant container. Used syringes, needles, or lancets should be placed in “sharps” containers (such as red biohazard containers), hard plastic containers (such as detergent bottles), or metal containers (such as an empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.
- Throw away the empty LEVEMIR InnoLet without the needle attached.
- Always carry an extra LEVEMIR InnoLet with you in case your LEVEMIR InnoLet you are using is damaged or lost.
- To avoid possible transmission of disease, do not share your LEVEMIR InnoLet with anyone, even if you attach a new needle.
- Novo Nordisk is not responsible for harm due to using this insulin delivery system with products not recommended by Novo Nordisk.
- Keep this disposable LEVEMIR InnoLet out of the reach of children.
LEVEMIR® FlexPen®
Introduction
Please read the following instructions carefully before using your Levemir® FlexPen®.
Levemir FlexPen is a disposable dial-a-dose insulin pen. You can select doses from 1 to 60 units in increments of 1 unit. Levemir FlexPen is designed to be used with NovoFine® needles.
Δ Levemir FlexPen should not be used by people who are blind or have severe visual problems without the help of a person who has good eyesight and who is trained to use the Levemir FlexPen the right way.
Getting ready
Make sure you have the following items:
- Levemir FlexPen
- New NovoFine needle
- Alcohol swab
Preparing your Levemir FlexPen
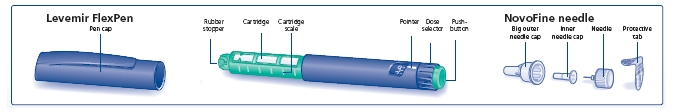
Wash your hands with soap and water. Before you start to prepare your injection, check the label to make sure that you are taking the right type of insulin. This is especially important if you take more than 1 type of insulin. Levemir should look clear.
A. Pull off the pen cap (see diagram A).
Wipe the rubber stopper with an alcohol swab.
B. Attaching the needle
Remove the protective tab from a disposable needle.
Screw the needle tightly onto your FlexPen. It is important that the needle is put on straight (see diagram B).

Never place a disposable needle on your Levemir FlexPen until you are ready to take your injection.
C. Pull off the big outer needle cap (see diagram C).
D. Pull off the inner needle cap and dispose of it (see diagram D).
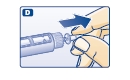
Δ Always use a new needle for each injection to help ensure sterility and prevent blocked needles.
Δ Be careful not to bend or damage the needle before use.
Δ To reduce the risk of unexpected needle sticks, never put the inner needle cap back on the needle.
Giving the airshot before each injection:
Before each injection small amounts of air may collect in the cartridge during normal use. To avoid injecting air and to ensure proper dosing:
E. Turn the dose selector to select 2 units (see diagram E).

F. Hold your Levemir FlexPen with the needle pointing up. Tap the cartridge gently with your finger a few times to make any air bubbles collect at the top of the cartridge (see diagram F).
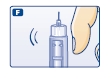
G. Keep the needle pointing upwards, press the push-button all the way in (see diagram G). The dose selector returns to 0.
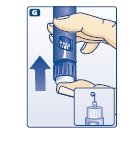
A drop of insulin should appear at the needle tip. If not, change the needle and repeat the procedure no more than 6 times.
If you do not see a drop of insulin after 6 times, do not use the Levemir FlexPen and contact Novo Nordisk at 1-800-727-6500.
A small air bubble may remain at the needle tip, but it will not be injected.
Selecting your dose
Check and make sure that the dose selector is set at 0.
H. Turn the dose selector to the number of units you need to inject. The pointer should line up with your dose.
The dose can be corrected either up or down by turning the dose selector in either direction until the correct dose lines up with the pointer (see diagram H). When turning the dose selector, be careful not to press the push-button as insulin will come out.

I. Insert the needle into your skin.
Inject the dose by pressing the push-button all the way in until the 0 lines up with the pointer (see diagram I). Be careful only to push the button when injecting.
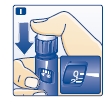
J. Keep the needle in the skin for at least 6 seconds, and keep the push-button pressed all the way in until the needle has been pulled out from the skin (see diagram J).
This will make sure that the full dose has been given. You may see a drop of Levemir at the needle tip. This is normal and has no effect on the dose you just received. If blood appears after you take the needle out of your skin, press the injection site lightly with a finger. Do not rub the area.
After the injection
Do not recap the needle. Recapping can lead to a needle stick injury. Remove the needle from the Levemir FlexPen after each injection. This helps to prevent infection, leakage of insulin, and will help to make sure you inject the right dose of insulin.
The Levemir FlexPen prevents the cartridge from being completely emptied. It is designed to deliver 300 units.
Δ Put the needle and any empty Levemir FlexPen or any used Levemir FlexPen still containing insulin in a sharps container or some type of hard plastic or metal container with a screw top such as a detergent bottle or empty coffee can. These containers should be sealed and thrown away the right way. Check with your healthcare provider about the right way to throw away used syringes and needles. There may be local or state laws about how to throw away used needles and syringes. Do not throw away used needles and syringes in household trash or recycling bins.
K. Put the pen cap on the Levemir FlexPen and store the Levemir FlexPen without the needle attached (see diagram K).
Diagram K: Replacing the pen cap
Function Check
If your Levemir FlexPen is not working the right way, follow the steps below:
L.
- Screw on a new NovoFine needle.
- Remove the big outer needle cap and the inner needle cap.
- Do an airshot as described in “Giving the airshot before each injection”.
- Put the big outer needle cap onto the needle. Do not put on the inner needle cap.
- Turn the dose selector so the dose indicator window shows 20 units.
- Hold the Levemir FlexPen so the needle is pointing down.
- Press the push-button all the way in.
Maintenance
Your FlexPen is designed to work accurately and safely. It must be handled with care. Avoid dropping your FlexPen as it may damage it. If you are concerned that your FlexPen is damaged, use a new one. You can clean the outside of your FlexPen by wiping it with a damp cloth. Do not soak or wash your FlexPen as it may damage it. Do not refill your FlexPen.
Δ Remove the needle from the Levemir FlexPen after each injection. This helps to ensure sterility, prevent leakage of insulin, and will help to make sure you inject the right dose of insulin for future injections.
Δ Be careful when handling used needles to avoid needle sticks and transfer of infectious diseases.
Δ Keep your Levemir FlexPen and needles out of the reach of children.
Δ Use Levemir FlexPen as directed to treat your diabetes. Needles and Levemir FlexPen must not be shared.
Δ Always use a new needle for each injection.
Δ Novo Nordisk is not responsible for harm due to using this insulin pen with products not recommended by Novo Nordisk.
Δ As a precautionary measure, always carry a spare insulin delivery device in case your Levemir FlexPen is lost or damaged.
Δ Remember to keep the disposable Levemir FlexPen with you. Do not leave it in a car or other location where it can get too hot or too cold.
