Suicidality and Antidepressant Drugs
Antidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Anyone considering the use of Sertraline Hydrochloride Tablets or any other antidepressant in a child, adolescent, or young adult must balance this risk with the clinical need. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older. Depression and certain other psychiatric disorders are themselves associated with increases in the risk of suicide. Patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Families and caregivers should be advised of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Sertraline Hydrochloride Tablets are not approved for the treatment of major depressive disorder in pediatric patients. (See Warnings: Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk, Precautions: Information for Patients, and Precautions: Pediatric Use)
DESCRIPTION
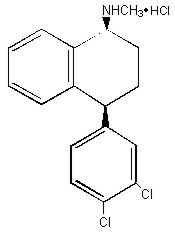
Sertraline is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) for oral administration. It has a molecular weight of 342.7. Sertraline hydrochloride has the following chemical name: (1S-cis)-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-N-methyl-1-naphthalenamine hydrochloride.
The empirical formula C17H17NCl2∙HCl is represented by the following structural formula:
Sertraline hydrochloride is a white crystalline powder that is slightly soluble in water and isopropyl alcohol, and sparingly soluble in ethanol.
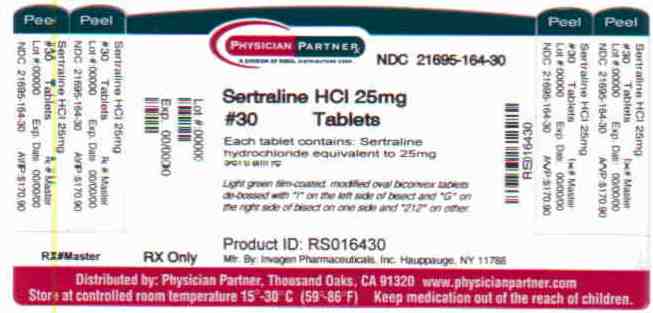
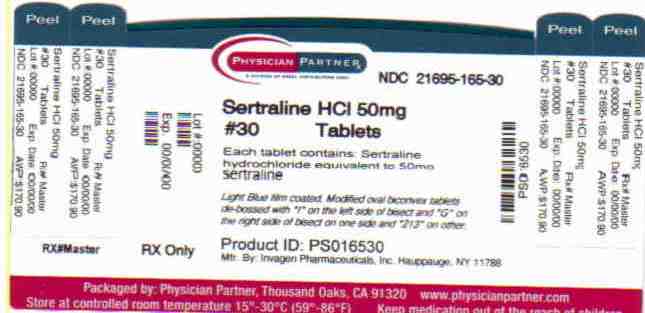
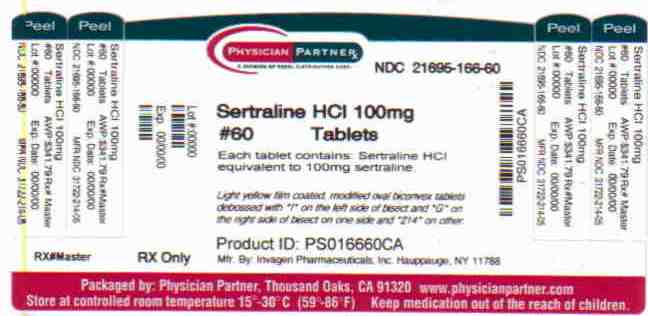
Sertraline is supplied for oral administration as scored tablets containing sertraline hydrochloride equivalent to 25, 50 and 100 mg of sertraline and the following inactive ingredients: D & C Yellow #10 aluminum lake (in 25 mg tablet), FD & C Blue #2 aluminum lake (in 25 mg & 50 mg tablets), magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, povidone K30, sodium starch glycolate, talc, titanium dioxide & yellow iron oxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacodynamics
The mechanism of action of sertraline is presumed to be linked to its inhibition of CNS neuronal uptake of serotonin (5HT). Studies at clinically relevant doses in man have demonstrated that sertraline blocks the uptake of serotonin into human platelets. In vitro studies in animals also suggest that sertraline is a potent and selective inhibitor of neuronal serotonin reuptake and has only very weak effects on norepinephrine and dopamine neuronal reuptake. In vitro studies have shown that sertraline has no significant affinity for adrenergic (alpha1, alpha2, beta), cholinergic, GABA, dopaminergic, histaminergic, serotonergic (5HT1A, 5HT1B, 5HT2), or benzodiazepine receptors; antagonism of such receptors has been hypothesized to be associated with various anticholinergic, sedative, and cardiovascular effects for other psychotropic drugs. The chronic administration of sertraline was found in animals to down regulate brain norepinephrine receptors, as has been observed with other drugs effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Sertraline does not inhibit monoamine oxidase.
Systemic Bioavailability
In man, following oral once-daily dosing over the range of 50 to 200 mg for 14 days, mean peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of sertraline occurred between 4.5 to 8.4 hours post-dosing. The average terminal elimination half-life of plasma sertraline is about 26 hours. Based on this pharmacokinetic parameter, steady-state sertraline plasma levels should be achieved after approximately one week of once-daily dosing. Linear dose-proportional pharmacokinetics were demonstrated in a single dose study in which the Cmax and area under the plasma concentration time curve (AUC) of sertraline were proportional to dose over a range of 50 to 200 mg. Consistent with the terminal elimination half-life, there is an approximately two-fold accumulation, compared to a single dose, of sertraline with repeated dosing over a 50 to 200 mg dose range. The single dose bioavailability of sertraline tablets is approximately equal to an equivalent dose of solution.
The effects of food on the bioavailability of the sertraline tablet and oral concentrate were studied in subjects administered a single dose with and without food. For the tablet, AUC was slightly increased when drug was administered with food but the Cmax was 25% greater, while the time to reach peak plasma concentration (Tmax) decreased from 8 hours post-dosing to 5.5 hours. For the oral concentrate, Tmax was slightly prolonged from 5.9 hours to 7.0 hours with food.
Metabolism
Sertraline undergoes extensive first pass metabolism. The principal initial pathway of metabolism for sertraline is N-demethylation.
N-desmethylsertraline has a plasma terminal elimination half-life of 62 to 104 hours. Both in vitro biochemical and in vivo pharmacological testing have shown N-desmethylsertraline to be substantially less active than sertraline. Both sertraline and N-desmethylsertraline undergo oxidative deamination and subsequent reduction, hydroxylation, and glucuronide conjugation. In a study of radiolabeled sertraline involving two healthy male subjects, sertraline accounted for less than 5% of the plasma radioactivity. About 40-45% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in urine in 9 days. Unchanged sertraline was not detectable in the urine. For the same period, about 40-45% of the administered radioactivity was accounted for in feces, including 12-14% unchanged sertraline.
Desmethylsertraline exhibits time-related, dose dependent increases in AUC (0-24 hour), Cmax and Cmin, with about a 5-9 fold increase in these pharmacokinetic parameters between day 1 and day 14.
Protein Binding
In vitro protein binding studies performed with radiolabeled 3H-sertraline showed that sertraline is highly bound to serum proteins (98%) in the range of 20 to 500 ng/mL. However, at up to 300 and 200 ng/mL concentrations, respectively, sertraline and N-desmethylsertraline did not alter the plasma protein binding of two other highly protein bound drugs, viz., warfarin and propranolol (see PRECAUTIONS).
Pediatric Pharmacokinetics
Sertraline pharmacokinetics were evaluated in a group of 61 pediatric patients (29 aged 6 to12 years, 32 aged 13 to 17 years). Patients included both males (N=28) and females (N=33). During 42 days of chronic sertraline dosing, sertraline was titrated up to 200 mg/day and maintained at that dose for a minimum of 11 days. On the final day of sertraline 200 mg/day, the 6-12 year old group exhibited a mean sertraline AUC (0-24 hr) of 3107 ng-hr/mL, mean Cmax of 165 ng/mL, and mean half-life of 26.2 hr. The 13-17 year old group exhibited a mean sertraline AUC (0-24 hr) of 2296 ng-hr/mL, mean Cmax of 123 ng/mL, and mean half-life of 27.8 hr. Higher plasma levels in the 6-12 year old group were largely attributable to patients with lower body weights. No gender associated differences were observed. By comparison, a group of 22 separately studied adults between 18 and 45 years of age (11 male, 11 female) received 30 days of 200 mg/day sertraline and exhibited a mean sertraline AUC (0-24 hr) of 2570 ng-hr/mL, mean Cmax of 142 ng/mL, and mean half-life of 27.2 hr. Relative to the adults, both the 6-12 year olds and the 13-17 year olds showed about 22% lower AUC (0-24 hr) and Cmax values when plasma concentration was adjusted for weight. These data suggest that pediatric patients metabolize sertraline with slightly greater efficiency than adults. Nevertheless, lower doses may be advisable for pediatric patients given their lower body weights, especially in very young patients, in order to avoid excessive plasma levels (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Age
Sertraline plasma clearance in a group of 16 (8 male, 8 female) elderly patients treated for 14 days at a dose of 100 mg/day was approximately 40% lower than in a similarly studied group of younger (25 to 32 y.o.) individuals. Steady-state, therefore, should be achieved after 2 to 3 weeks in older patients. The same study showed a decreased clearance of desmethylsertraline in older males, but not in older females.
Liver Disease
As might be predicted from its primary site of metabolism, liver impairment can affect the elimination of sertraline. In patients with chronic mild liver impairment (N=10, 8 patients with Child-Pugh scores of 5-6 and 2 patients with Child-Pugh scores of 7-8) who received 50 mg sertraline per day maintained for 21 days, sertraline clearance was reduced, resulting in approximately 3-fold greater exposure compared to age-matched volunteers with no hepatic impairment (N=10). The exposure to desmethylsertraline was approximately 2-fold greater compared to age-matched volunteers with no hepatic impairment. There were no significant differences in plasma protein binding observed between the two groups. The effects of sertraline in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment have not been studied. The results suggest that the use of sertraline in patients with liver disease must be approached with caution. If sertraline is administered to patients with liver impairment, a lower or less frequent dose should be used (see PRECAUTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Renal Disease
Sertraline is extensively metabolized and excretion of unchanged drug in urine is a minor route of elimination. In volunteers with mild to moderate (CLcr =30-60 mL/min), moderate to severe (CLcr =10-29 mL/min) or severe (receiving hemodialysis) renal impairment (N=10 each group), the pharmacokinetics and protein binding of 200 mg sertraline per day maintained for 21 days were not altered compared to age-matched volunteers (N=12) with no renal impairment. Thus sertraline multiple dose pharmacokinetics appear to be unaffected by renal impairment (see PRECAUTIONS).
Major Depressive Disorder
The efficacy of sertraline as a treatment for major depressive disorder was established in two placebo-controlled studies in adult outpatients meeting DSM-III criteria for major depressive disorder. Study 1 was an 8-week study with flexible dosing of sertraline in a range of 50 to 200 mg/day; the mean dose for completers was 145 mg/day. Study 2 was a 6-week fixed-dose study, including sertraline doses of 50, 100, and 200 mg/day. Overall, these studies demonstrated sertraline to be superior to placebo on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and the Clinical Global Impression Severity and Improvement scales. Study 2 was not readily interpretable regarding a dose response relationship for effectiveness.
Study 3 involved depressed outpatients who had responded by the end of an initial 8-week open treatment phase on sertraline 50-200 mg/day. These patients (N=295) were randomized to continuation for 44 weeks on double-blind sertraline 50-200 mg/day or placebo. A statistically significantly lower relapse rate was observed for patients taking sertraline compared to those on placebo. The mean dose for completers was 70 mg/day. Analyses for gender effects on outcome did not suggest any differential responsiveness on the basis of sex.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
The effectiveness of sertraline for the treatment of PMDD was established in two double-blind, parallel group, placebo-controlled flexible dose trials (Studies 1 and 2) conducted over 3 menstrual cycles. Patients in Study 1 met DSM-III-R criteria for Late Luteal Phase Dysphoric Disorder (LLPDD), the clinical entity now referred to as Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD) in DSM-IV. Patients in Study 2 met DSM-IV criteria for PMDD. Study 1 utilized daily dosing throughout the study, while Study 2 utilized luteal phase dosing for the 2 weeks prior to the onset of menses. The mean duration of PMDD symptoms for these patients was approximately 10.5 years in both studies. Patients on oral contraceptives were excluded from these trials; therefore, the efficacy of sertraline in combination with oral contraceptives for the treatment of PMDD is unknown.
Efficacy was assessed with the Daily Record of Severity of Problems (DRSP), a patient-rated instrument that mirrors the diagnostic criteria for PMDD as identified in the DSM-IV, and includes assessments for mood, physical symptoms, and other symptoms. Other efficacy assessments included the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD-17), and the Clinical Global Impression Severity of Illness (CGI-S) and Improvement (CGI-I) scores.
In Study 1, involving n=251 randomized patients, sertraline treatment was initiated at 50 mg/day and administered daily throughout the menstrual cycle. In subsequent cycles, patients were dosed in the range of 50-150 mg/day on the basis of clinical response and toleration. The mean dose for completers was 102 mg/day. Sertraline administered daily throughout the menstrual cycle was significantly more effective than placebo on change from baseline to endpoint on the DRSP total score, the HAMD-17 total score, and the CGI-S score, as well as the CGI-I score at endpoint.
In Study 2, involving n=281 randomized patients, sertraline treatment was initiated at 50 mg/day in the late luteal phase (last 2 weeks) of each menstrual cycle and then discontinued at the onset of menses. In subsequent cycles, patients were dosed in the range of 50-100 mg/day in the luteal phase of each cycle, on the basis of clinical response and toleration. Patients who were titrated to 100 mg/day received 50 mg/day for the first 3 days of the cycle, then 100 mg/day for the remainder of the cycle. The mean sertraline dose for completers was 74 mg/day. Sertraline administered in the late luteal phase of the menstrual cycle was significantly more effective than placebo on change from baseline to endpoint on the DRSP total score and the CGI-S score, as well as the CGI-I score at endpoint.
There was insufficient information to determine the effect of race or age on outcome in these studies.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Major Depressive Disorder
Sertraline is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder in adults.
The efficacy of sertraline hydrochloride in the treatment of a major depressive episode was established in six to eight week controlled trials of adult outpatients whose diagnoses corresponded most closely to the DSM-III category of major depressive disorder (see Clinical Trials under CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
A major depressive episode implies a prominent and relatively persistent depressed or dysphoric mood that usually interferes with daily functioning (nearly every day for at least 2 weeks); it should include at least 4 of the following 8 symptoms: change in appetite, change in sleep, psychomotor agitation or retardation, loss of interest in usual activities or decrease in sexual drive, increased fatigue, feelings of guilt or worthlessness, slowed thinking or impaired concentration, and a suicide attempt or suicidal ideation.
The antidepressant action of sertraline hydrochloride in hospitalized depressed patients has not been adequately studied.
The efficacy of sertraline hydrochloride in maintaining an antidepressant response for up to 44 weeks following 8 weeks of open-label acute treatment (52 weeks total) was demonstrated in a placebo-controlled trial. The usefulness of the drug in patients receiving sertraline for extended periods should be reevaluated periodically (see Clinical Trials under CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
Sertraline is indicated for the treatment of premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) in adults.
The efficacy of sertraline in the treatment of PMDD was established in 2 placebo-controlled trials of female adult outpatients treated for 3 menstrual cycles who met criteria for the DSM-III-R/IV category of PMDD (see Clinical Trials under CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
The essential features of PMDD include markedly depressed mood, anxiety or tension, affective lability, and persistent anger or irritability. Other features include decreased interest in activities, difficulty concentrating, lack of energy, change in appetite or sleep, and feeling out of control. Physical symptoms associated with PMDD include breast tenderness, headache, joint and muscle pain, bloating and weight gain. These symptoms occur regularly during the luteal phase and remit within a few days following onset of menses; the disturbance markedly interferes with work or school or with usual social activities and relationships with others. In making the diagnosis, care should be taken to rule out other cyclical mood disorders that may be exacerbated by treatment with an antidepressant.
The effectiveness of sertraline in long-term use, that is, for more than 3 menstrual cycles, has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials. Therefore, the physician who elects to use sertraline for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Concomitant use in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) is contraindicated (see WARNINGS). Concomitant use in patients taking pimozide is contraindicated (see PRECAUTIONS).
Sertraline hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to sertraline or any of the inactive ingredients in sertraline hydrochloride tablets.
WARNINGS
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
Patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), both adult and pediatric, may experience worsening of their depression and/or the emergence of suicidal ideation and behavior (suicidality) or unusual changes in behavior, whether or not they are taking antidepressant medications, and this risk may persist until significant remission occurs.
Suicide is a known risk of depression and certain other psychiatric disorders, and these disorders themselves are the strongest predictors of suicide. There has been a long-standing concern, however, that antidepressants may have a role in inducing worsening of depression and the emergence of suicidality in certain patients during the early phases of treatment. Pooled analyses of short-term placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and others) showed that these drugs increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults (ages 18-24) with major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older.
The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in children and adolescents with MDD, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 24 short-term trials of 9 antidepressant drugs in over 4400 patients. The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in adults with MDD or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 295 short-term trials (median duration of 2 months) of 11 antidepressant drugs in over 77,000 patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidality among drugs, but a tendency toward an increase in the younger patients for almost all drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidality across the different indications, with the highest incidence in MDD. The risk differences (drug vs placebo), however, were relatively stable within age strata and across indications. The risk differences (drug-placebo differences in the number of cases of suicidality per 1000 patients treated) are provided in Table 1.
| Age Range | Drug-Placebo Difference in Number of Cases of Suicidality per 1000 Patients Treated |
| Increases Compared to Placebo | |
| <18 | 14 additional cases |
| 18–24 | 5 additional cases |
| Decreases Compared to Placebo | |
| 25–64 | 1 fewer case |
| ≥65 | 6 fewer cases |
No suicides occurred in any of the pediatric trials. There were suicides in the adult trials, but the number was not sufficient to reach any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
It is unknown whether the suicidality risk extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond several months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with depression that the use of antidepressants can delay the recurrence of depression.
All patients being treated with antidepressants for any indication should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, and unusual changes in behavior, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases.
The following symptoms, anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, and mania, have been reported in adult and pediatric patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder as well as for other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric. Although a causal link between the emergence of such symptoms and either the worsening of depression and/or the emergence of suicidal impulses has not been established, there is concern that such symptoms may represent precursors to emerging suicidality.
Consideration should be given to changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing the medication, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidality or symptoms that might be precursors to worsening depression or suicidality, especially if these symptoms are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient’s presenting symptoms.
If the decision has been made to discontinue treatment, medication should be tapered, as rapidly as is feasible, but with recognition that abrupt discontinuation can be associated with certain symptoms (see PRECAUTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION—Discontinuation of Treatment with Sertraline Hydrochloride Tablets, for a description of the risks of discontinuation of Sertraline Hydrochloride Tablets).
Families and caregivers of patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder or other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric, should be alerted about the need to monitor patients for the emergence of agitation, irritability, unusual changes in behavior, and the other symptoms described above, as well as the emergence of suicidality, and to report such symptoms immediately to health care providers. Such monitoring should include daily observation by families and caregivers. Prescriptions for sertraline hydrochloride should be written for the smallest quantity of tablets consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder
A major depressive episode may be the initial presentation of bipolar disorder. It is generally believed (though not established in controlled trials) that treating such an episode with an antidepressant alone may increase the likelihood of precipitation of a mixed/manic episode in patients at risk for bipolar disorder. Whether any of the symptoms described above represent such a conversion is unknown. However, prior to initiating treatment with an antidepressant, patients with depressive symptoms should be adequately screened to determine if they are at risk for bipolar disorder; such screening should include a detailed psychiatric history, including a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression. It should be noted that Sertraline Hydrochloride is not approved for use in treating bipolar depression.
Cases of serious sometimes fatal reactions have been reported in patients receiving sertraline hydrochloride, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), in combination with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). Symptoms of a drug interaction between an SSRI and an MAOI include: hyperthermia, rigidity, myoclonus, autonomic instability with possible rapid fluctuations of vital signs, mental status changes that include confusion, irritability, and extreme agitation progressing to delirium and coma. These reactions have also been reported in patients who have recently discontinued an SSRI and have been started on an MAOI. Some cases presented with features resembling neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Therefore, sertralineshould not be used in combination with an MAOI, or within 14 days of discontinuing treatment with an MAOI. Similarly, at least 14 days should be allowed after stopping sertralinebefore starting an MAOI.
The concomitant use of sertraline hydrochloride with MAOIs intended to treat depression is contraindicated (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS – Potential for Interaction with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors ).
Serotonin Syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)- like Reactions:
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome or Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)-like reactions have been reported with SNRIs and SSRIs alone, including sertraline hydrochloride treatment, but particularly with concomitant use of serotonergic drugs (including triptans) and with drugs which impair metabolism of serotonin (including MAOIs), or with antipsychotics or other dopamine antagonists. Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination) and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Serotonin syndrome, in its most severe form can resemble neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which includes hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, autonomic instability with possible rapid fluctuation of vital signs, and mental status changes. Patients should be monitored for the emergence of serotonin syndrome or NMS-like signs and symptoms.
The concomitant use of sertraline hydrochloride with MAOIs intended to treat depression is contraindicated.
If concomitant treatment of SNRIs and SSRIs, including sertraline hydrochloride, with a 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor agonist (triptan) is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases.
The concomitant use of SNRIs and SSRIs, including serteraline hydrochloride, with serotonin precursors (such as tryptophan) is not recommended.
Treatment with sertraline hydrochloride and any concomitant serotonergic or antidopaminergic agents, including antipsychotics, should be discontinued immediately if the above events occur and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
PRECAUTIONS
Activation of Mania/Hypomania
During premarketing testing, hypomania or mania occurred in approximately 0.4% of sertraline hydrochloride treated patients.
Weight Loss
Significant weight loss may be an undesirable result of treatment with sertraline for some patients, but on average, patients in controlled trials had minimal, 1 to 2 pound weight loss, versus smaller changes on placebo. Only rarely have sertraline patients been discontinued for weight loss.
Seizure
Sertraline hydrochloride has not been evaluated in patients with a seizure disorder. These patients were excluded from clinical studies during the product’s premarket testing. No seizures were observed among approximately 3000 patients treated with sertraline hydrochloride in the development program for major depressive disorder. However, 4 patients out of approximately 1800 (220 <18 years of age) exposed during the development program for another disorder experienced seizures, representing a crude incidence of 0.2%. Three of these patients were adolescents, two with a seizure disorder and one with a family history of seizure disorder, none of whom were receiving anticonvulsant medication. Accordingly, sertraline should be introduced with care in patients with a seizure disorder.
Discontinuation of Treatment with Sertraline
During marketing of Sertraline hydrochloride and other SSRIs and SNRIs (Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors), there have been spontaneous reports of adverse events occurring upon discontinuation of these drugs, particularly when abrupt, including the following: dysphoric mood, irritability, agitation, dizziness, sensory disturbances (e.g. paresthesias such as electric shock sensations), anxiety, confusion, headache, lethargy, emotional lability, insomnia, and hypomania. While these events are generally self-limiting, there have been reports of serious discontinuation symptoms.
Patients should be monitored for these symptoms when discontinuing treatment with Sertraline hydrochloride. A gradual reduction in the dose rather than abrupt cessation is recommended whenever possible. If intolerable symptoms occur following a decrease in the dose or upon discontinuation of treatment, then resuming the previously prescribed dose may be considered. Subsequently, the physician may continue decreasing the dose but at a more gradual rate (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Abnormal Bleeding
SSRIs and SNRIs, including sertraline hydrochloride, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Concomitant use of aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, warfarin, and other anticoagulants may add to this risk. Case reports and epidemiological studies (case-control and cohort design) have demonstrated an association between use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding. Bleeding events related to SSRIs and SNRIs use have ranged from ecchymoses, hematomas, epistaxis, and petechiae to life-threatening hemorrhages.
Patients should be cautioned about the risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of sertraline hydrochloride and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation.
Weak Uricosuric Effect
Sertraline Hydrochloride is associated with a mean decrease in serum uric acid of approximately 7%. The clinical significance of this weak uricosuric effect is unknown.
Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
Clinical experience with sertraline hydrochloride in patients with certain concomitant systemic illness is limited. Caution is advisable in using sertraline in patients with diseases or conditions that could affect metabolism or hemodynamic responses.
Patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction or unstable heart disease were excluded from clinical studies during the product’s premarket testing. However, the electrocardiograms of 774 patients who received sertraline in double-blind trials were evaluated and the data indicate that sertraline is not associated with the development of significant ECG abnormalities.
Sertraline administered in a flexible dose range of 50 to 200 mg/day (mean dose of 89 mg/day) was evaluated in a post-marketing, placebo-controlled trial of 372 randomized subjects with a DSM-IV diagnosis of major depressive disorder and recent history of myocardial infarction or unstable angina requiring hospitalization. Exclusions from this trial included, among others, patients with uncontrolled hypertension, need for cardiac surgery, history of CABG within 3 months of index event, severe or symptomatic bradycardia, non-atherosclerotic cause of angina, clinically significant renal impairment (creatinine > 2.5 mg/dl), and clinically significant hepatic dysfunction. Sertraline hydrochloride treatment initiated during the acute phase of recovery (within 30 days post-MI or post-hospitalization for unstable angina) was indistinguishable from placebo in this study on the following week 16 treatment endpoints: left ventricular ejection fraction, total cardiovascular events (angina, chest pain, edema, palpitations, syncope, postural dizziness, CHF, MI, tachycardia, bradycardia, and changes in BP), and major cardiovascular events involving death or requiring hospitalization (for MI, CHF, stroke, or angina).
Sertraline hydrochloride is extensively metabolized by the liver. In patients with chronic mild liver impairment, sertraline clearance was reduced, resulting in increased AUC, Cmax and elimination half-life. The effects of sertraline in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment have not been studied. The use of sertraline in patients with liver disease must be approached with caution. If sertraline is administered to patients with liver impairment, a lower or less frequent dose should be used (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Since sertraline is extensively metabolized, excretion of unchanged drug in urine is a minor route of elimination. A clinical study comparing sertraline pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers to that in patients with renal impairment ranging from mild to severe (requiring dialysis) indicated that the pharmacokinetics and protein binding are unaffected by renal disease. Based on the pharmacokinetic results, there is no need for dosage adjustment in patients with renal impairment (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Interference with Cognitive and Motor Performance
In controlled studies, sertraline did not cause sedation and did not interfere with psychomotor performance. (See Information for Patients.)
Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia may occur as a result of treatment with SSRIs and SNRIs, including sertraline hydrochloride. In many cases, this hyponatremia appears to be the result of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). Cases with serum sodium lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported. Elderly patients may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia with SSRIs and SNRIs. Also, patients taking diuretics or who are otherwise volume depleted may be at greater risk (see GERIATRIC USE ). Discontinuation of sertraline hydrochloride should be considered in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia and appropriate medical intervention should be instituted.
Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls. Signs and symptoms associated with more severe and/or acute cases have included hallucination, syncope, seizure, coma, respiratory arrest, and death.
Platelet Function
There have been rare reports of altered platelet function and/or abnormal results from laboratory studies in patients taking sertraline hydrochloride. While there have been reports of abnormal bleeding or purpura in several patients taking sertraline, it is unclear whether sertraline hydrochloride had a causative role.
Information for Patients
Prescribers or other health professionals should inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with sertraline hydrochloride and should counsel them in its appropriate use. A patient Medication Guide about 'Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and other Serious Mental Illness, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions' is available for sertraline hydrochloride. The prescriber or health professional should instruct patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide and should assist them in understanding its contents. Patients should be given the opportunity to discuss the contents of the Medication Guide and to obtain answers to any questions they may have. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of this document.
Patients should be advised of the following issues and asked to alert their prescriber if these occur while taking sertraline hydrochloride.
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
Patients, their families, and their caregivers should be encouraged to be alert to the emergence of anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, mania, other unusual changes in behavior, worsening of depression, and suicidal ideation, especially early during antidepressant treatment and when the dose is adjusted up or down. Families and caregivers of patients should be advised to look for the emergence of such symptoms on a day-to-day basis, since changes may be abrupt. Such symptoms should be reported to the patient’s prescriber or health professional, especially if they are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient’s presenting symptoms. Symptoms such as these may be associated with an increased risk for suicidal thinking and behavior and indicate a need for very close monitoring and possibly changes in the medication.
Patients should be cautioned about the risk of serotonin syndrome with the concomitant use of SNRIs and SSRIs, including sertraline hydrochloride, and triptans, tramadol, or other serotonergic agents.
Patients should be told that although sertraline has not been shown to impair the ability of normal subjects to perform tasks requiring complex motor and mental skills in laboratory experiments, drugs that act upon the central nervous system may affect some individuals adversely. Therefore, patients should be told that until they learn how they respond to sertraline hydrochloride they should be careful doing activities when they need to be alert, such as driving a car or operating machinery.
Patients should be cautioned about the concomitant use of sertraline and NSAIDs, aspirin, warfarin, or other drugs that affect coagulation since the combined use of psychotropic drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and these agents has been associated with an increased risk of bleeding.
Patients should be told that although sertraline hydrochloride has not been shown in experiments with normal subjects to increase the mental and motor skill impairments caused by alcohol, the concomitant use of sertraline hydrochloride and alcohol is not advised.
Patients should be told that while no adverse interaction of sertraline hydrochloride with over-the-counter (OTC) drug products is known to occur, the potential for interaction exists. Thus, the use of any OTC product should be initiated cautiously according to the directions of use given for the OTC product.
Patients should be advised to notify their physician if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during therapy.
Patients should be advised to notify their physician if they are breast feeding an infant.
Potential Effects of Coadministration of Drugs Highly Bound to Plasma Proteins
Because sertraline is tightly bound to plasma protein, the administration of sertraline hydrochloride to a patient taking another drug which is tightly bound to protein (e.g., warfarin, digitoxin) may cause a shift in plasma concentrations potentially resulting in an adverse effect. Conversely, adverse effects may result from displacement of protein bound sertraline by other tightly bound drugs.
In a study comparing prothrombin time AUC (0-120 hr) following dosing with warfarin (0.75 mg/kg) before and after 21 days of dosing with either sertraline (50-200 mg/day) or placebo, there was a mean increase in prothrombin time of 8% relative to baseline for sertraline compared to a 1% decrease for placebo (p<0.02). The normalization of prothrombin time for the sertraline hydrochloride group was delayed compared to the placebo group. The clinical significance of this change is unknown. Accordingly, prothrombin time should be carefully monitored when sertraline therapy is initiated or stopped.
Cimetidine
In a study assessing disposition of sertraline hydrochloride (100 mg) on the second of 8 days of cimetidine administration (800 mg daily), there were significant increases in sertraline hydrochloride mean AUC (50%), Cmax (24%) and half-life (26%) compared to the placebo group. The clinical significance of these changes is unknown.
CNS Active Drugs
In a study comparing the disposition of intravenously administered diazepam before and after 21 days of dosing with either sertraline (50 to 200 mg/day escalating dose) or placebo, there was a 32% decrease relative to baseline in diazepam clearance for the sertraline hydrochloride group compared to a 19% decrease relative to baseline for the placebo group (p<0.03). There was a 23% increase in Tmax for desmethyldiazepam in the sertraline group compared to a 20% decrease in the placebo group (p<0.03). The clinical significance of these changes is unknown.
In a placebo-controlled trial in normal volunteers, the administration of two doses of sertraline hydrochloride did not significantly alter steady-state lithium levels or the renal clearance of lithium.
Nonetheless, at this time, it is recommended that plasma lithium levels be monitored following initiation of sertraline hydrochloride therapy with appropriate adjustments to the lithium dose.
In a controlled study of a single dose (2 mg) of pimozide, 200 mg sertraline (q.d.) co-administration to steady state was associated with a mean increase in pimozide AUC and Cmax of about 40%, but was not associated with any changes in EKG. Since the highest recommended pimozide dose (10 mg) has not been evaluated in combination with sertraline, the effect on QT interval and PK parameters at doses higher than 2 mg at this time are not known. While the mechanism of this interaction is unknown, due to the narrow therapeutic index of pimozide and due to the interaction noted at a low dose of pimozide, concomitant administration of sertraline hydrochloride and pimozide should be contraindicated (see CONTRAINDICATIONS ).
Results of a placebo-controlled trial in normal volunteers suggest that chronic administration of sertraline 200 mg/day does not produce clinically important inhibition of phenytoin metabolism. Nonethless, at this time, it is recommended that plasma phenytoin concentrations be monitored following initiation of sertraline hydrochloride therapy with appropriate adjustments to the phenytoin dose, practiculary in patients with multiple underlying medical conditions and/or those receiving multiple concomitant medications.
The effect of sertraline on valproate levels has not been evaluated in clinical trials. In the absence of such data, it is recommended that plasma valproate levels be monitored following initiation of sertraline therapy with appropriate adjustments to the valproate dose.
The risk of using sertraline in combination with other CNS active drugs has not been systematically evaluated. Consequently, caution is advised if the concomitant administration of sertraline and such drugs is required.
There is limited controlled experience regarding the optimal timing of switching from other drugs effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder and premenstrual dysphoric disorder to sertraline. Care and prudent medical judgment should be exercised when switching, particularly from long-acting agents. The duration of an appropriate washout period which should intervene before switching from one selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) to another has not been established.
Drugs Metabolized by P450 3A4
In three separate in vivo interaction studies, sertraline was co-administered with cytochrome P450 3A4 substrates, terfenadine, carbamazepine, or cisapride under steady-state conditions. The results of these studies indicated that sertraline did not increase plasma concentrations of terfenadine, carbamazepine, or cisapride. These data indicate that sertraline’s extent of inhibition of P450 3A4 activity is not likely to be of clinical significance. Results of the interaction study with cisapride indicate that sertraline 200 mg (q.d.) induces the metabolism of cisapride (cisapride AUC and Cmax were reduced by about 35%).
Drugs Metabolized by P450 2D6
Many drugs effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder, e.g., the SSRIs, including sertraline, and most tricyclic antidepressant drugs effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder inhibit the biochemical activity of the drug metabolizing isozyme cytochrome P450 2D6 (debrisoquin hydroxylase), and, thus, may increase the plasma concentrations of co-administered drugs that are metabolized by P450 2D6. The drugs for which this potential interaction is of greatest concern are those metabolized primarily by 2D6 and which have a narrow therapeutic index, e.g., the tricyclic antidepressant drugs effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder and the Type 1C antiarrhythmics propafenone and flecainide. The extent to which this interaction is an important clinical problem depends on the extent of the inhibition of P450 2D6 by the antidepressant and the therapeutic index of the co-administered drug. There is variability among the drugs effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder in the extent of clinically important 2D6 inhibition, and in fact sertraline at lower doses has a less prominent inhibitory effect on 2D6 than some others in the class. Nevertheless, even sertraline has the potential for clinically important 2D6 inhibition. Consequently, concomitant use of a drug metabolized by P450 2D6 with sertraline hydrochloride may require lower doses than usually prescribed for the other drug. Furthermore, whenever sertraline hydrochloride is withdrawn from co-therapy, an increased dose of the co-administered drug may be required (see Tricyclic Antidepressant Drugs Effective in the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder under PRECAUTIONS).
Serotonergic Drugs
Based on the mechanism of action of SNRIs and SSRIs, including sertraline hydrochloride, and the potential for serotonin syndrome, caution is advised when SNRIs and SSRIs, including sertraline hydrochloride, are coadministered with other drugs that may affect the serotonergic neutrotransmitter systems, such as triptans, linezolid (an antibiotic which is a reversible non-selective MAOI), lithium, tramadol, or St. John’s Wort (see WARNINGS-Serotonin Syndrome). The concomitant use of sertraline hydrochloride with other SSRIs, SNRIs or tryptophan is not recommended (see PRECAUTIONS – Drug Interactions).
Triptans
There have been rare post marketing reports of serotonin syndrome with use of an SNRI or an SSRI and a triptan. If concomitant treatment of SNRIs and SSRIs, including sertraline hydrochloride, with a triptan is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases (see WARNINGS – Serotonin Syndrome).
Sumatriptan
There have been rare post marketing reports describing patients with weakness, hyperreflexia, and incoordination following the use of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) and sumatriptan. If concomitant treatment with sumatriptan and an SSRI (e.g., citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline) is clinically warranted, appropriate observation of the patient is advised.
Tricyclic Antidepressant Drugs Effective in the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder (TCAs)
The extent to which SSRI–TCA interactions may pose clinical problems will depend on the degree of inhibition and the pharmacokinetics of the SSRI involved. Nevertheless, caution is indicated in the co-administration of TCAs with sertraline, because sertraline may inhibit TCA metabolism. Plasma TCA concentrations may need to be monitored, and the dose of TCA may need to be reduced, if a TCA is co-administered with sertraline (see Drugs Metabolized by P450 2D6 under PRECAUTIONS).
Hypoglycemic Drugs
In a placebo-controlled trial in normal volunteers, administration of sertraline for 22 days (including 200 mg/day for the final 13 days) caused a statistically significant 16% decrease from baseline in the clearance of tolbutamide following an intravenous 1000 mg dose. Sertraline administration did not noticeably change either the plasma protein binding or the apparent volume of distribution of tolbutamide, suggesting that the decreased clearance was due to a change in the metabolism of the drug. The clinical significance of this decrease in tolbutamide clearance is unknown.
Atenolol
Sertraline (100 mg) when administered to 10 healthy male subjects had no effect on the beta-adrenergic blocking ability of atenolol.
Digoxin
In a placebo-controlled trial in normal volunteers, administration of sertraline for 17 days (including 200 mg/day for the last 10 days) did not change serum digoxin levels or digoxin renal clearance.
Microsomal Enzyme Induction
Preclinical studies have shown sertraline to induce hepatic microsomal enzymes. In clinical studies, sertraline was shown to induce hepatic enzymes minimally as determined by a small (5%) but statistically significant decrease in antipyrine half-life following administration of 200 mg/day for 21 days. This small change in antipyrine half-life reflects a clinically insignificant change in hepatic metabolism.
Drugs That Interfere With Hemostasis (Non-selective NSAIDs, Aspirin, Warfarin, etc.)
Serotonin release by platelets plays an important role in hemostasis. Epidemiological studies of the case-control and cohort design that have demonstrated an association between the use of psychotropic drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of upper gastrointestinal bleeding have also shown that concurrent use of an NSAID or aspirin may potentiate this risk of bleeding. These studies have also shown that concurrent use of an NSAID or aspirin may potentiate this risk of bleeding. Altered anticoagulant effects, including increased bleeding, have been reported when SSRIs or SNRIs are coadministered with warfarin. Patients receiving warfarin therapy should be carefully monitored when sertraline hydrochloride is initiated or discontinued.
Electroconvulsive Therapy
There are no clinical studies establishing the risks or benefits of the combined use of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) and sertraline hydrochloride.
Alcohol
Although sertraline did not potentiate the cognitive and psychomotor effects of alcohol in experiments with normal subjects, the concomitant use of sertraline and alcohol is not recommended.
Carcinogenesis
Lifetime carcinogenicity studies were carried out in CD-1 mice and Long-Evans rats at doses up to 40 mg/kg/day. These doses correspond to 1 times (mice) and 2 times (rats) the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m2 basis. There was a dose-related increase of liver adenomas in male mice receiving sertraline at 10-40 mg/kg (0.25-1.0 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). No increase was seen in female mice or in rats of either sex receiving the same treatments, nor was there an increase in hepatocellular carcinomas. Liver adenomas have a variable rate of spontaneous occurrence in the CD-1 mouse and are of unknown significance to humans. There was an increase in follicular adenomas of the thyroid in female rats receiving sertraline at 40 mg/kg (2 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis); this was not accompanied by thyroid hyperplasia. While there was an increase in uterine adenocarcinomas in rats receiving sertraline at 10-40 mg/kg (0.5-2.0 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) compared to placebo controls, this effect was not clearly drug related.
Mutagenesis
Sertraline had no genotoxic effects, with or without metabolic activation, based on the following assays: bacterial mutation assay; mouse lymphoma mutation assay; and tests for cytogenetic aberrations in vivo in mouse bone marrow and in vitro in human lymphocytes.
Impairment of Fertility
A decrease in fertility was seen in one of two rat studies at a dose of 80 mg/kg (4 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis).
Pregnancy–Pregnancy Category C
Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits at doses up to 80 mg/kg/day and 40 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses correspond to approximately 4 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m2 basis. There was no evidence of teratogenicity at any dose level. When pregnant rats and rabbits were given sertraline during the period of organogenesis, delayed ossification was observed in fetuses at doses of 10 mg/kg (0.5 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) in rats and 40 mg/kg (4 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) in rabbits.
When female rats received sertraline during the last third of gestation and throughout lactation, there was an increase in the number of stillborn pups and in the number of pups dying during the first 4 days after birth. Pup body weights were also decreased during the first four days after birth. These effects occurred at a dose of 20 mg/kg (1 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). The no effect dose for rat pup mortality was 10 mg/kg (0.5 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). The decrease in pup survival was shown to be due to in utero exposure to sertraline. The clinical significance of these effects is unknown. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Sertraline hydrochloride should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Pregnancy-Nonteratogenic Effects
Neonates exposed to sertraline and other SSRIs or SNRIs, late in the third trimester have developed complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding. These findings are based on postmarketing reports. Such complications can arise immediately upon delivery. Reported clinical findings have included respiratory distress, cyanosis, apnea, seizures, temperature instability, feeding difficulty, vomiting, hypoglycemia, hypotonia, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, tremor, jitteriness, irritability, and constant crying. These features are consistent with either a direct toxic effect of SSRIs and SNRIs or, possibly, a drug discontinuation syndrome. It should be noted that, in some cases, the clinical picture is consistent with serotonin syndrome (see WARNINGS).
Infants exposed to SSRIs in late pregnancy may have an increased risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN). (PPHN) occurs in 1-2 per 1,000 live births in the general population and is associated with substantial neonatal morbidity and mortality. In a retrospective case-control study of 377 women whose infants were born with PPHN and 836 women whose infants were born healthy, the risk for developing PPHN was approximately six-fold higher for infants exposed to SSRIs after the 20th week of gestation compared to infants who had not been exposed to antidepressants during pregnancy. There is currently no corroborative evidence regarding the risk for PPHN following exposure to SSRIs in pregnancy; this is the first study that has investigated the potential risk. The study did not include enough cases with exposure to individual SSRIs to determine if all SSRIs posed similar levels of PPHN risk.
When treating a pregnant woman with sertraline during the third trimester, the physician should carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of treatment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Physicians should note that in a prospective longitudinal study of 201 women with a history of major depression who were euthyrnic in the context of antidepressant therapy at the beginning of pregnancy, women who discontinued antidepressant medication during pregnancy were more likely to experience a relapse of major depression than women who continued antidepressant medication.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether, and if so in what amount, sertraline or its metabolites are excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when sertraline is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients with major depressive disorder have not been established (see BOX WARNING and WARNINGS, Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk). Two placebo controlled trials (n=373) in pediatric patients with MDD have been conducted with sertraline hydrochloride, and the data were not sufficient to support a claim for use in pediatric patients. Anyone considering the use of sertraline hydrochloride tablets in a child or adolescent must balance the potential risks with the clinical need.
Sertraline pharmacokinetics were evaluated in a group of 61 pediatric patients between 6 and 17 years of age and revealed similar drug exposures to those of adults when plasma concentration was adjusted for weight (see Pharmacokinetics under CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Approximately 600 pediatric patients between 6 and 17 years of age have received sertraline in clinical trials, both controlled and uncontrolled. The adverse event profile observed in these patients was generally similar to that observed in adult studies with sertraline hydrochloride (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). As with other SSRIs, decreased appetite and weight loss have been observed in association with the use of sertraline hydrochloride. In a pooled analysis of two 10-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, flexible dose (50-200 mg) outpatient trials for major depressive disorder (n=373), there was a difference in weight change between sertraline and placebo of roughly 1 kilogram, for both children (ages 6-11) and adolescents (ages 12-17), in both cases representing a slight weight loss for sertraline compared to a slight gain for placebo. At baseline the mean weight for children was 39.0 kg for sertraline and 38.5 kg for placebo. At baseline the mean weight for adolescents was 61.4 kg for sertraline and 62.5 kg for placebo. There was a bigger difference between sertraline and placebo in the proportion of outliers for clinically important weight loss in children than in adolescents. For children, about 7% had a weight loss > 7% of body weight compared to none of the placebo patients; for adolescents, about 2% had a weight loss > 7% of body weight compared to about 1% of the placebo patients. A subset of these patients who completed the randomized controlled trials (sertraline n=99, placebo n=122) were continued into a 24-week, flexible-dose, open-label, extension study. A mean weight loss of approximately 0.5 kg was seen during the first eight weeks of treatment for subjects with first exposure to sertraline during the open-label extension study, similar to the mean weight loss observed among sertraline treated subjects during the first eight weeks of the randomized controlled trials. The subjects continuing in the open label study began gaining weight compared to baseline by week 12 of sertraline treatment. Those subjects who completed 34 weeks of sertraline treatment (10 weeks in a placebo controlled trial + 24 weeks open label, n=68), had weight gain that was similar to that expected using data from age-adjusted peers. Regular monitoring of weight and growth is recommended if treatment of a pediatric patient with an SSRI is to be continued long term. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients with major depressive disorder have not been established.
The risks, if any, that may be associated with sertraline hydrochloride’s use beyond 1 year in children and adolescents have not been systematically assessed. The prescriber should be mindful that the evidence relied upon to conclude that sertraline is safe for use in children and adolescents derives from clinical studies that were 10 to 52 weeks in duration and from the extrapolation of experience gained with adult patients. In particular, there are no studies that directly evaluate the effects of long-term sertraline use on the growth, development, and maturation of children and adolescents. Although there is no affirmative finding to suggest that sertraline possesses a capacity to adversely affect growth, development or maturation, the absence of such findings is not compelling evidence of the absence of the potential of sertraline to have adverse effects in chronic use (see WARNINGS – Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk).
Geriatric Use
U.S. geriatric clinical studies of sertraline hydrochloride in major depressive disorder included 663 sertraline-treated subjects ≥ 65 years of age, of those, 180 were ≥ 75 years of age. No overall differences in the pattern of adverse reactions were observed in the geriatric clinical trial subjects relative to those reported in younger subjects (see ADVERSE REACTIONS), and other reported experience has not identified differences in safety patterns between the elderly and younger subjects. As with all medications, greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. There were 947 subjects in placebo-controlled geriatric clinical studies of sertraline hydrochloride in major depressive disorder. No overall differences in the pattern of efficacy were observed in the geriatric clinical trial subjects relative to those reported in younger subjects.
Other Adverse Events in Geriatric Patients. In 354 geriatric subjects treated with sertraline in placebo-controlled trials, the overall profile of adverse events was generally similar to that shown in Table 2. Urinary tract infection was the only adverse event not appearing in Table 2 and reported at an incidence of at least 2% and at a rate greater than placebo in placebo-controlled trials.
SSRIS and SNRIs, including sertraline hydrochloride, have been associated with cases of clinically significant hyponatremia in elderly patients, who may be at greater risk for this adverse event (see PRECAUTIONS, Hyponatremia).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
During its premarketing assessment, multiple doses of sertraline hydrochloride were administered to over 4000 adult subjects as of February 18, 2000. The conditions and duration of exposure to sertraline hydrochloride varied greatly, and included (in overlapping categories) clinical pharmacology studies, open and double-blind studies, uncontrolled and controlled studies, inpatient and outpatient studies, fixed-dose and titration studies, and studies for multiple indications, including major depressive disorder and PMDD.
Untoward events associated with this exposure were recorded by clinical investigators using terminology of their own choosing. Consequently, it is not possible to provide a meaningful estimate of the proportion of individuals experiencing adverse events without first grouping similar types of untoward events into a smaller number of standardized event categories.
In the tabulations that follow, a World Health Organization dictionary of terminology has been used to classify reported adverse events. The frequencies presented, therefore, represent the proportion of the over 4000 adult individuals exposed to multiple doses of sertraline hydrochloride who experienced a treatment-emergent adverse event of the type cited on at least one occasion while receiving sertraline hydrochloride. An event was considered treatment-emergent if it occurred for the first time or worsened while receiving therapy following baseline evaluation. It is important to emphasize that events reported during therapy were not necessarily caused by it.
The prescriber should be aware that the figures in the tables and tabulations cannot be used to predict the incidence of side effects in the course of usual medical practice where patient characteristics and other factors differ from those that prevailed in the clinical trials. Similarly, the cited frequencies cannot be compared with figures obtained from other clinical investigations involving different treatments, uses, and investigators. The cited figures, however, do provide the prescribing physician with some basis for estimating the relative contribution of drug and non-drug factors to the side effect incidence rate in the population studied.
Incidence in Placebo-Controlled Trials
Table 2 enumerates the most common treatment-emergent adverse events associated with the use of sertraline hydrochloride (incidence of at least 5% for sertraline hydrochloride and at least twice that for placebo) for the treatment of adult patients with major depressive disorder/other* in placebo-controlled clinical trials. Most patients in major depressive disorder/other* and PMDD studies received doses of 50 to 200 mg/day.
Patients in the PMDD study with daily dosing throughout the menstrual cycle received doses of 50 to 150 mg/day, and in the PMDD study with dosing during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle received doses of 50 to 100 mg/day.
TABLE 2
MOST COMMON TREATMENT-EMERGENT ADVERSE EVENTS:
INCIDENCE IN PLACEBO-CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIALS
|
Percentage of Patients Reporting Event |
||||||
|
Major Depressive Disorder/Other* |
PMDD Daily Dosing |
PMDD Luteal Phase Dosing(2) |
||||
|
Body System/Adverse Event |
Sertraline Hydrochloride (N=861) |
Placebo (N=853) |
Sertraline Hydrochloride (N=121) |
Placebo (N=122) |
Sertraline Hydrochloride (N=136) |
Placebo (N=127) |
|
Autonomic Nervous System Disorders | ||||||
|
Ejaculation Failure(1) |
7 |
<1 |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Mouth Dry |
16 |
9 |
6 |
3 |
10 |
3 |
|
Sweating Increased |
8 |
3 |
6 |
<1 |
3 |
0 |
|
Center. & Periph. Nerv. System Disorders | ||||||
|
Somnolence |
13 |
6 |
7 |
<1 |
2 |
0 |
|
Tremor |
11 |
3 |
2 |
0 |
<1 |
<1 |
|
Dizziness |
12 |
7 |
6 |
3 |
7 |
5 |
|
General | ||||||
|
Fatigue |
11 |
8 |
16 |
7 |
10 |
<1 |
|
Pain |
1 |
2 |
6 |
<1 |
3 |
2 |
|
Malaise |
<1 |
1 |
9 |
5 |
7 |
5 |
|
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||||
|
Abdominal Pain |
2 |
2 |
7 |
<1 |
3 |
3 |
|
Anorexia |
3 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
5 |
0 |
|
Constipation |
8 |
6 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
|
Diarrhea/Loose Stools |
18 |
9 |
13 |
3 |
13 |
7 |
|
Dyspepsia |
6 |
3 |
7 |
2 |
7 |
3 |
|
Nausea |
26 |
12 |
23 |
9 |
13 |
3 |
|
Psychiatric Disorders | ||||||
|
Agitation |
6 |
4 |
2 |
<1 |
1 |
0 |
|
Insomnia |
16 |
9 |
17 |
11 |
12 |
10 |
|
Libido Decreased |
1 |
<1 |
11 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
(1)Primarily ejaculatory delay. Denominator used was for male patients only (N=271 sertraline hydrochloride major depressive disorder/other*; N=271 placebo major depressive disorder/other*; No male patients in PMDD studies.
*Major depressive disorder and other premarketing controlled trials.
(2)The luteal phase and daily dosing PMDD trials were not designed for making direct comparisons between the two dosing regimens. Therefore, a comparison between the two dosing regimens of the PMDD trials of incidence rates shown in Table 2 should be avoided.
Associated with Discontinuation in Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials
Table 3 lists the adverse events associated with discontinuation of sertraline treatment (incidence at least twice that for placebo and at least 1% for sertraline in clinical trials) in major depressive disorder/other*and PMDD.
TABLE 3
MOST COMMON ADVERSE EVENTS ASSOCIATED WITH DISCONTINUATION
IN PLACEBO-CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIALS
|
Adverse Event |
Major Depressive Disorder/ Other* (N=861) |
PMDD Daily Dosing (N=121) |
PMDD Luteal Phase Dosing (N=136) |
|
Abdominal Pain |
– |
– |
– |
|
Agitation |
1% |
– |
– |
|
Anxiety |
– |
– |
– |
|
Diarrhea/ Loose Stools |
2% |
2% |
– |
|
Dizziness |
– |
– |
– |
|
Dry Mouth |
1% |
– |
– |
|
Dyspepsia |
– |
– |
– |
|
Ejaculation Failure(1) |
1% |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Fatigue |
– |
– |
– |
|
Headache |
2% |
– |
– |
|
Hot Flushes |
– |
– |
1% |
|
Insomnia |
1% |
– |
1% |
|
Nausea |
4% |
2% |
1% |
|
Nervousness |
– |
2% |
– |
|
Palpitation |
– |
– |
1% |
|
Somnolence |
1% |
– |
– |
|
Tremor |
2% |
– |
– |
(1)
Primarily ejaculatory delay. Denominator used was for male patients only
(N=271 major depressive disorder/other*; No male patients in PMDD studies.
*Major depressive disorder and other premarketing controlled trials.
Male and Female Sexual Dysfunction with SSRIs
Although changes in sexual desire, sexual performance and sexual satisfaction often occur as manifestations of a psychiatric disorder, they may also be a consequence of pharmacologic treatment. In particular, some evidence suggests that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can cause such untoward sexual experiences. Reliable estimates of the incidence and severity of untoward experiences involving sexual desire, performance and satisfaction are difficult to obtain, however, in part because patients and physicians may be reluctant to discuss them. Accordingly, estimates of the incidence of untoward sexual experience and performance cited in product labeling, are likely to underestimate their actual incidence.
Table 4 below displays the incidence of sexual side effects reported by at least 2% of patients taking sertraline hydrochloride in placebo-controlled trials.
TABLE 4
|
Adverse Event |
Sertraline |
Placebo |
|
Ejaculation failure*(primarily delayed ejaculation) |
14% |
1% |
|
Decreased libido** |
6% |
1% |
*Denominator used was for male patients only (N=1118 sertraline; N=926 placebo)
**Denominator used was for male and female patients (N=2799 sertraline hydrochloride; N=2394 placebo)
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies examining sexual dysfunction with sertraline treatment.
Priapism has been reported with all SSRIs.
While it is difficult to know the precise risk of sexual dysfunction associated with the use of SSRIs, physicians should routinely inquire about such possible side effects.
Other Adverse Events in Pediatric Patients
In over 600 pediatric patients treated with sertraline, the overall profile of adverse events was generally similar to that seen in adult studies. However, the following adverse events, from controlled trials, not appearing in Tables 2 and 3, were reported at an incidence of at least 2% and occurred at a rate of at least twice the placebo rate (N=281 patients treated with sertraline): fever, hyperkinesia, urinary incontinence, aggressive reaction, sinusitis, epistaxis and purpura.
Other Events Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation of Sertraline Hydrochloride
Following is a list of treatment-emergent adverse events reported during premarketing assessment of sertraline hydrochloride in clinical trials (over 4000 adult subjects) except those already listed in the previous tables or elsewhere in labeling.
In the tabulations that follow, a World Health Organization dictionary of terminology has been used to classify reported adverse events. The frequencies presented, therefore, represent the proportion of the over 4000 adult individuals exposed to multiple doses of sertraline hydrochloride who experienced an event of the type cited on at least one occasion while receiving sertraline hydrochloride. All events are included except those already listed in the previous tables or elsewhere in labeling and those reported in terms so general as to be uninformative and those for which a causal relationship to sertraline hydrochloride treatment seemed remote. It is important to emphasize that although the events reported occurred during treatment with sertraline, they were not necessarily caused by it.
Events are further categorized by body system and listed in order of decreasing frequency according to the following definitions: frequent adverse events are those occurring on one or more occasions in at least 1/100 patients; infrequent adverse events are those occurring in 1/100 to 1/1000 patients; rare events are those occurring in fewer than 1/1000 patients. Events of major clinical importance are also described in the PRECAUTIONS section.
Autonomic Nervous System Disorders–Frequent: impotence; Infrequent: flushing, increased saliva, cold clammy skin, mydriasis; Rare: pallor, glaucoma, priapism, vasodilation.
Body as a Whole–General Disorders–Rare: allergic reaction, allergy.
Cardiovascular–Frequent: palpitations, chest pain; Infrequent: hypertension, tachycardia, postural dizziness, postural hypotension, periorbital edema, peripheral edema, hypotension, peripheral ischemia, syncope, edema, dependent edema; Rare: precordial chest pain, substernal chest pain, aggravated hypertension, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disorder.
Central and Peripheral Nervous System Disorders–Frequent: hypertonia, hypoesthesia; Infrequent: twitching, confusion, hyperkinesia, vertigo, ataxia, migraine, abnormal coordination, hyperesthesia, leg cramps, abnormal gait, nystagmus, hypokinesia; Rare: dysphonia, coma, dyskinesia, hypotonia, ptosis, choreoathetosis, hyporeflexia.
Disorders of Skin and Appendages–Infrequent: pruritus, acne, urticaria, alopecia, dry skin, erythematous rash, photosensitivity reaction, maculopapular rash; Rare: follicular rash, eczema, dermatitis, contact dermatitis, bullous eruption, hypertrichosis, skin discoloration, pustular rash.
Endocrine Disorders–Rare: exophthalmos, gynecomastia.
Gastrointestinal Disorders–Frequent: appetite increased; Infrequent: dysphagia, tooth caries aggravated, eructation, esophagitis, gastroenteritis; Rare: melena, glossitis, gum hyperplasia, hiccup, stomatitis, tenesmus, colitis, diverticulitis, fecal incontinence, gastritis, rectum hemorrhage, hemorrhagic peptic ulcer, proctitis, ulcerative stomatitis, tongue edema, tongue ulceration.
General–Frequent: back pain, asthenia, malaise, weight increase; Infrequent: fever, rigors, generalized edema; Rare: face edema, aphthous stomatitis.
Hearing and Vestibular Disorders–Rare: hyperacusis, labyrinthine disorder.
Hematopoietic and Lymphatic–Rare: anemia, anterior chamber eye hemorrhage.
Liver and Biliary System Disorders–Rare: abnormal hepatic function.
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders–Infrequent: thirst; Rare: hypoglycemia, hypoglycemia reaction.
Musculoskeletal System Disorders–Frequent: myalgia; Infrequent: arthralgia, dystonia, arthrosis, muscle cramps, muscle weakness.
Psychiatric Disorders–Frequent: yawning, other male sexual dysfunction, other female sexual dysfunction; Infrequent: depression, amnesia, paroniria, teeth-grinding, emotional lability, apathy, abnormal dreams, euphoria, paranoid reaction, hallucination, aggressive reaction, aggravated depression, delusions; Rare: withdrawal syndrome, suicide ideation, libido increased, somnambulism, illusion.
Reproductive–Infrequent: menstrual disorder, dysmenorrhea, intermenstrual bleeding, vaginal hemorrhage, amenorrhea, leukorrhea; Rare: female breast pain, menorrhagia, balanoposthitis, breast enlargement, atrophic vaginitis, acute female mastitis.
Respiratory System Disorders–Frequent: rhinitis; Infrequent: coughing, dyspnea, upper respiratory tract infection, epistaxis, bronchospasm, sinusitis; Rare: hyperventilation, bradypnea, stridor, apnea, bronchitis, hemoptysis, hypoventilation, laryngismus, laryngitis.
Special Senses–Frequent: tinnitus; Infrequent: conjunctivitis, earache, eye pain, abnormal accommodation; Rare: xerophthalmia, photophobia, diplopia, abnormal lacrimation, scotoma, visual field defect.
Urinary System Disorders–Infrequent: micturition frequency, polyuria, urinary retention, dysuria, nocturia, urinary incontinence; Rare: cystitis, oliguria, pyelonephritis, hematuria, renal pain, strangury.
Laboratory Tests
In man, asymptomatic elevations in serum transaminases (SGOT [or AST] and SGPT [or ALT]) have been reported infrequently (approximately 0.8%) in association with sertraline hydrochloride administration. These hepatic enzyme elevations usually occurred within the first 1 to 9 weeks of drug treatment and promptly diminished upon drug discontinuation.
Sertraline hydrochloride therapy was associated with small mean increases in total cholesterol (approximately 3%) and triglycerides (approximately 5%), and a small mean decrease in serum uric acid (approximately 7%) of no apparent clinical importance.
The safety profile observed with sertraline treatment in patients with major depressive disorder, and PMDD is similar.
Other Events Observed During the Post marketing Evaluation of Sertraline Hydrochloride
Reports of adverse events temporally associated with sertraline hydrochloride that have been received since market introduction, that are not listed above and that may have no causal relationship with the drug, include the following: acute renal failure, anaphylactoid reaction, angioedema, blindness, optic neuritis, cataract, increased coagulation times, bradycardia, AV block, atrial arrhythmias, QT-interval prolongation, ventricular tachycardia (including torsade de pointes-type arrhythmias), hypothyroidism, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia and pancytopenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, lupus-like syndrome, serum sickness, hyperglycemia, galactorrhea, hyperprolactinemia, extrapyramidal symptoms, oculogyric crisis, serotonin syndrome, psychosis, pulmonary hypertension, severe skin reactions, which potentially can be fatal, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, vasculitis, photosensitivity and other severe cutaneous disorders, rare reports of pancreatitis, and liver events—clinical features (which in the majority of cases appeared to be reversible with discontinuation of sertraline hydrochloride) occurring in one or more patients include: elevated enzymes, increased bilirubin, hepatomegaly, hepatitis, jaundice, abdominal pain, vomiting, liver failure and death.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Physical and Psychological Dependence
In a placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized study of the comparative abuse liability of sertraline hydrochloride, alprazolam, and d-amphetamine in humans, sertraline hydrochloride did not produce the positive subjective effects indicative of abuse potential, such as euphoria or drug liking, that were observed with the other two drugs. Premarketing clinical experience with sertraline hydrochloride did not reveal any tendency for a withdrawal syndrome or any drug-seeking behavior. In animal studies sertraline hydrochloride does not demonstrate stimulant or barbiturate-like (depressant) abuse potential. As with any CNS active drug, however, physicians should carefully evaluate patients for history of drug abuse and follow such patients closely, observing them for signs of sertraline hydrochloride misuse or abuse (e.g., development of tolerance, incrementation of dose, drug-seeking behavior).
OVERDOSAGE
Human Experience
Of 1,027 cases of overdose involving sertraline hydrochloride worldwide, alone or with other drugs, there were 72 deaths (circa 1999). Among 634 overdoses in which sertraline hydrochloride was the only drug ingested, 8 resulted in fatal outcome, 75 completely recovered, and 27 patients experienced sequelae after overdosage to include alopecia, decreased libido, diarrhea, ejaculation disorder, fatigue, insomnia, somnolence and serotonin syndrome. The remaining 524 cases had an unknown outcome. The most common signs and symptoms associated with non-fatal sertraline hydrochloride overdosage were somnolence, vomiting, tachycardia, nausea, dizziness, agitation and tremor.
The largest known ingestion was 13.5 grams in a patient who took sertraline hydrochloride alone and subsequently recovered. However, another patient who took 2.5 grams of sertraline hydrochloride alone experienced a fatal outcome.
Other important adverse events reported with sertraline hydrochloride overdose (single or multiple drugs) include bradycardia, bundle branch block, coma, convulsions, delirium, hallucinations, hypertension, hypotension, manic reaction, pancreatitis, QT-interval prolongation, serotonin syndrome, stupor and syncope.
Overdose Management
Treatment should consist of those general measures employed in the management of overdosage with any antidepressant.
Ensure an adequate airway, oxygenation and ventilation. Monitor cardiac rhythm and vital signs. General supportive and symptomatic measures are also recommended. Induction of emesis is not recommended. Gastric lavage with a large-bore orogastric tube with appropriate airway protection, if needed, may be indicated if performed soon after ingestion, or in symptomatic patients.
Activated charcoal should be administered. Due to large volume of distribution of this drug, forced diuresis, dialysis, hemoperfusion and exchange transfusion are unlikely to be of benefit. No specific antidotes for sertraline are known.
In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug involvement. The physician should consider contacting a poison control center on the treatment of any overdose. Telephone numbers for certified poison control centers are listed in the Physicians’ Desk Reference(PDR).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Major Depressive Disorder and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Sertraline treatment should be administered at a dose of 50 mg once daily.
While a relationship between dose and effect has not been established for major depressive disorder, patients were dosed in a range of 50-200 mg/day in the clinical trials demonstrating the effectiveness of sertraline hydrochloride for the treatment of this indication. Consequently, a dose of 50 mg, administered once daily, is recommended as the initial therapeutic dose. Patients not responding to a 50 mg dose may benefit from dose increases up to a maximum of 200 mg/day. Given the 24 hour elimination half-life of sertraline hydrochloride, dose changes should not occur at intervals of less than 1 week.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
Sertraline treatment should be initiated with a dose of 50 mg/day, either daily throughout the menstrual cycle or limited to the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, depending on physician assessment.
While a relationship between dose and effect has not been established for PMDD, patients were dosed in the range of 50-150 mg/day with dose increases at the onset of each new menstrual cycle (see Clinical Trials under CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). Patients not responding to a 50 mg/day dose may benefit from dose increases (at 50 mg increments/menstrual cycle) up to 150 mg/day when dosing daily throughout the menstrual cycle, or 100 mg/day when dosing
during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. If a 100 mg/day dose has been established with luteal phase dosing, a 50 mg/day titration step for three days should be utilized at the beginning of each luteal phase dosing period.
Sertraline should be administered once daily, either in the morning or evening.
Major Depressive Disorder
It is generally agreed that acute episodes of major depressive disorder require several months or longer of sustained pharmacologic therapy beyond response to the acute episode. Systematic evaluation of sertraline has demonstrated that its antidepressant efficacy is maintained for periods of up to 44 weeks following 8 weeks of initial treatment at a dose of 50-200 mg/day (mean dose of 70 mg/day) (see Clinical Trials under CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). It is not known whether the dose of sertraline hydrochloride needed for maintenance treatment is identical to the dose needed to achieve an initial response. Patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the need for maintenance treatment.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
The effectiveness of sertraline in long-term use, that is, for more than 3 menstrual cycles, has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials. However, as women commonly report that symptoms worsen with age until relieved by the onset of menopause, it is reasonable to consider continuation of a responding patient. Dosage adjustments, which may include changes between dosage regimens (e.g., daily throughout the menstrual cycle versus during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle), may be needed to maintain the patient on the lowest effective dosage and patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the need for continued treatment.
Switching Patients to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI and initiation of therapy with sertraline hydrochloride. In addition, at least 14 days should be allowed after stopping sertraline before starting an MAOI (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS).
Dosage for Hepatically Impaired Patients
The use of sertraline in patients with liver disease should be approached with caution. The effects of sertraline in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment have not been studied. If sertraline is administered to patients with liver impairment, a lower or less frequent dose should be used (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and PRECAUTIONS).
Treatment of Pregnant Women During the Third Trimester
Neonates exposed to sertraline hydrochloride and other SSRIs or SNRIs, late in the third trimester have developed complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding (see PRECAUTIONS). When treating pregnant women with sertraline during the third trimester, the physician should carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of treatment. The physician may consider tapering sertraline in the third trimester.
Discontinuation of Treatment with Sertraline
Symptoms associated with discontinuation of sertraline and other SSRIs and SNRIs, have been reported (see PRECAUTIONS). Patients should be monitored for these symptoms when discontinuing treatment. A gradual reduction in the dose rather than abrupt cessation is recommended whenever possible. If intolerable symptoms occur following a decrease in the dose or upon discontinuation of treatment, then resuming the previously prescribed dose may be considered. Subsequently, the physician may continue decreasing the dose but at a more gradual rate.
HOW SUPPLIED
Sertraline hydrochloride tablets capsular-shaped scored tablets, containing sertraline hydrochloride equivalent to 25, 50 and 100 mg of sertraline, are packaged in bottles.
Store at 20º- 25ºC (68º- 77ºF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
MEDICATION GUIDE
Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and other Serious Mental Illnesses, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions
Read the Medication Guide that comes with you or your family member's antidepressant medicine. This Medication Guide is only about the risk of suicidal thoughts and actions with antidepressant medicines.
Talk to your, or your family member"s, healthcare provider about:
· all risks and benefits of treatment with antidepressant medicines
· all treatment choices for depression or other serious mental illness
What is the most important information I should know about antidepressant medicines, depression and other serious mental illnesses, and suicidal thoughts or actions?
1. Antidepressant medicines may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, teenagers, and young adults when the medicine is first started.
2. Depression and other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts and actions. Some people may have a particularly high risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions.
These include people who have (or have a family history of) bipolar illness (also called manic-depressive illness) or suicidal thoughts or actions.
3. How can I watch for and try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions in myself or a family member?
· Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is first started or when the dose is changed.
· Call the health care provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
· Keep all follow-up visits with the healthcare provider as scheduled. Call the healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you or your family member has any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
· Thoughts about suicide or dying
· Attempts to commit suicide
· New or worse depression
· New or worse anxiety
· Feeling very agitated or restless
· Panic attacks
· Trouble sleeping (insomnia)
· New or worse irritability
· Acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
· Acting on dangerous impulses
· An extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
· Other unusual changes in behavior or mood
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What else do I need to know about antidepressant medicines?
· Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to a healthcare provider. Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can cause other symptoms.
· Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and also the risks of not treating it. Patients and their families or other caregivers should discuss all treatment choices with the healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
· Antidepressant medicines have other side effects. Talk to the healthcare provider about the side effects of the medicine prescribed for you or your family member.
· Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines. Know all of the medicines that you or your family member takes. Keep a list of all medicines to show the healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
· Not all antidepressant medicines prescribed for children are FDA approved for use in children. Talk to your child"s healthcare provider for more information.
This medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for all antidepressants.