BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: ADDICTION, ABUSE, and MISUSE; LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; ACCIDENTAL INGESTION; and NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets expose patients and other users to the risks of opioid addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death. Assess each patient’s risk prior to prescribing morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, and monitor all patients regularly for the development of these behaviors or conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur with use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets. Monitor for respiratory depression, especially during initiation of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets or following a dose increase. Instruct patients to swallow morphine sulfate extended-release tablets whole; crushing, chewing, or dissolving morphine sulfate extended-release tablets can cause rapid release and absorption of a potentially fatal dose of morphine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Accidental Ingestion
Accidental ingestion of even one dose of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, especially by children, can result in a fatal overdose of morphine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Prolonged use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. If opioid use is required for a prolonged period in a pregnant woman, advise the patient of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are indicated for the management of pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment and for which alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Limitations of Use
Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses, and because of the the greater risks of overdose and death with extended-release opioid formulations, reserve morphine sulfate extended-release tablets for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options (e.g., non-opioid analgesics or immediate-release opioids) are ineffective, not tolerated, or would be otherwise inadequate to provide sufficient management of pain.
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are not indicated as an as-needed (prn) analgesic.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2.1 Initial Dosing
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets should be prescribed only by healthcare professionals who are knowledgeable in the use of potent opioids for the management of chronic pain.
Initiate the dosing regimen for each patient individually, taking into account the patient's prior analgesic treatment experience and risk factors for addiction, abuse, and misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24 to 72 hours of initiating therapy with morphine sulfate extended-release tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets must be taken whole. Crushing, chewing, or dissolving morphine sulfate extended-release tablets will result in uncontrolled delivery of morphine and can lead to overdose or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Use of Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets as the First Opioid Analgesic
Initiate treatment with morphine sulfate extended-release tablets with 15 mg tablets orally every 8 or 12 hours.
Use of Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets in Patients who are not Opioid Tolerant
The starting dose for patients, who are not opioid-tolerant, is morphine sulfate extended-release tablets 15 mg orally every 12 hours. Patients who are opioid-tolerant are those receiving, for one week or longer, at least 60 mg oral morphine per day, 25 mcg transdermal fentanyl per hour, 30 mg oral oxycodone per day, 8 mg oral hydromorphone per day, 25 mg oral oxymorphone per day, or an equianalgesic dose of another opioid.
Use of higher starting doses in patients who are not opioid tolerant may cause fatal respiratory depression.
Conversion from Other Oral Morphine to Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets
Patients receiving other oral morphine formulations may be converted to morphine sulfate extended-release tablets by administering one-half of the patient's 24-hour requirement as morphine sulfate extended-release tablets on an every-12-hour schedule or by administering one-third of the patient's daily requirement as morphine sulfate extended-release tablets on an every-8-hour schedule.
Conversion from Other Opioids to Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets
There are no established conversion ratios for conversion from other opioids to morphine sulfate extended-release tablets defined by clinical trials. Discontinue all other around-the-clock opioid drugs when morphine sulfate extended-release tablets therapy is initiated and initiate dosing using morphine sulfate extended-release tablets 15 mg orally every 8 to 12 hours.
It is safer to underestimate a patient’s 24-hour oral morphine requirements and provide rescue medication (e.g., immediate-release morphine) than to overestimate the 24-hour oral morphine requirements and manage an adverse reaction. While useful tables of opioid equivalents are readily available, there is substantial inter-patient variability in the relative potency of different opioid drugs and products.
Conversion from Parenteral Morphine or Other Opioids (Parenteral or Oral) to Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets
When converting from parenteral morphine or other non-morphine opioids (parenteral or oral) to morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, consider the following general points:
Parenteral to oral morphine ratio: Between 2 to 6 mg of oral morphine may be required to provide analgesia equivalent to 1 mg of parenteral morphine. Typically, a dose of morphine that is approximately three times the previous daily parenteral morphine requirement is sufficient.
Other parenteral or oral non-morphine opioids to oral morphine sulfate: Specific recommendations are not available because of a lack of systematic evidence for these types of analgesic substitutions. Published relative potency data are available, but such ratios are approximations. In general, begin with half of the estimated daily morphine requirement as the initial dose, managing inadequate analgesia by supplementation with immediate-release morphine.
Conversion from Methadone to Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets
Close monitoring is of particular importance when converting methadone to other opioid agonists. The ratio between methadone and other opioid agonists may vary widely as a function of previous dose exposure. Methadone has a long half-life and can accumulate in the plasma.
2.2 Titration and Maintenance of Therapy
Individually titrate morphine sulfate extended-release tablets to a dose that provides adequate analgesia and minimizes adverse reactions. Continually reevaluate patients receiving morphine sulfate extended-release tablets to assess the maintenance of pain control and the relative incidence of adverse reactions, as well as monitoring for the development of addiction, abuse, or misuse. Frequent communication is important among the prescriber, other members of the healthcare team, the patient, and the caregiver/family during periods of changing analgesic requirements, including initial titration. During chronic therapy periodically reassess the continued need for the use of opioid analgesics.
Patients who experience breakthrough pain may require a dose increase of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, or may need rescue medication with an appropriate dose of an immediate-release analgesic. If the level of pain increases after dose stabilization, attempt to identify the source of increased pain before increasing the morphine sulfate extended-release tablets dose. Because steady-state plasma concentrations are approximated in 1 day, morphine sulfate extended-release tablets dosage adjustments may be done every 1 to 2 days.
If unacceptable opioid-related adverse reactions are observed, the subsequent doses may be reduced. Adjust the dose to obtain an appropriate balance between management of pain and opioid-related adverse reactions.
2.3 Discontinuation of Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets
When the patient no longer requires therapy with morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, use a gradual downward titration of the dose to prevent signs and symptoms of withdrawal in the physically-dependent patient. Do not abruptly discontinue morphine sulfate extended-release tablets.
2.4 Administration of Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets must be taken whole. Crushing, chewing, or dissolving morphine sulfate extended-release tablets will result in uncontrolled delivery of morphine and can lead to overdose or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets 15 mg
Round, blue-colored, film-coated tablets bearing the symbol ABG on one side and 15 on the other
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets 30 mg
Round, lavender-colored, film-coated tablets bearing the symbol ABG on one side and 30 on the other
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets 60 mg
Round, orange-colored, film-coated tablets bearing the symbol ABG on one side and 60 on the other
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets 100 mg*
Round, gray-colored, film-coated tablets bearing the symbol ABG on one side and 100 on the other
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets 200 mg*
Capsule-shaped, green-colored, film-coated tablets bearing the symbol ABG on one side and 200 on the other
*100 mg and 200 mg tablets are for use in opioid-tolerant patients only
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with:
Significant respiratory depression
Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment
Known or suspected paralytic ileus
Hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylaxis) to morphine [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5.1 Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets contain morphine, a Schedule II controlled substance. As an opioid, morphine sulfate extended-release tablets expose its users to the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse. As modified-release products such as morphine sulfate extended-release tablets deliver the opioid over an extended period of time, there is a greater risk for overdose and death due to the larger amount of morphine present [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
Although the risk of addiction in any individual is unknown, it can occur in patients appropriately prescribed morphine sulfate extended-release tablets and in those who obtain the drug illicitly. Addiction can occur at recommended doses and if the drug is misused or abused.
Assess each patient’s risk for opioid addiction, abuse, or misuse prior to prescribing morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, and monitor all patients receiving opioids for development of these behaviors or conditions. Risks are increased in patients with a personal or family history of substance abuse (including drug or alcohol abuse or addiction) or mental illness (e.g., major depression). The potential for these risks should not, however, prevent the proper management of pain in any given patient. Patients at increased risk may be prescribed modified-release opioid formulations such as morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, but use in such patients necessitates intensive counseling about the risks of proper use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets along with intensive monitoring for signs of addiction, abuse, and misuse.
Abuse or misuse of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets by crushing, chewing, snorting, or injecting the dissolved product will result in the uncontrolled delivery of morphine and can result in overdose and death [see Overdosage (10)].
Opioid agonists such as morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are sought by drug abusers and people with addiction disorders and are subject to criminal diversion. Consider these risks when prescribing or dispensing morphine sulfate extended-release tablets. Strategies to reduce these risks include prescribing the drug in the smallest appropriate quantity and advising the patient on the proper disposal of unused drug [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Contact local state professional licensing board or state controlled substances authority for information on how to prevent and detect abuse or diversion of this product.
5.2 Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression has been reported with the use of modified-release opioids, even when used as recommended. Respiratory depression from opioid use, if not immediately recognized and treated, may lead to respiratory arrest and death. Management of respiratory depression may include close observation, supportive measures, and use of opioid antagonists, depending on the patient’s clinical status [see Overdosage (10)]. Carbon dioxide (CO2) retention from opioid-induced respiratory depression can exacerbate the sedating effects of opioids.
While serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression can occur at any time during the use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, the risk is greatest during the initiation of therapy or following a dose increase. Closely monitor patients for respiratory depression when initiating therapy with morphine sulfate extended-release tablets and following dose increases.
To reduce the risk of respiratory depression, proper dosing and titration of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are essential [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. Overestimating the morphine sulfate extended-release tablets dose when converting patients from another opioid product can result in a fatal overdose with the first dose.
Accidental ingestion of even one dose of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, especially by children, can result in respiratory depression and death due to an overdose of morphine.
5.3 Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Prolonged use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets during pregnancy can result in withdrawal signs in the neonate. Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, unlike opioid withdrawal syndrome in adults, may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. If opioid use is required for a prolonged period in a pregnant woman, advise the patient of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available.
Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome presents as irritability, hyperactivity and abnormal sleep pattern, high pitched cry, tremor, vomiting, diarrhea and failure to gain weight. The onset, duration, and severity of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome vary based on the specific opioid used, duration of use, timing and amount of last maternal use, and rate of elimination of the drug by the newborn.
5.4 Interactions with Central Nervous System Depressants
Hypotension, and profound sedation, coma or respiratory depression may result if morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are used concomitantly with other central nervous system (CNS) depressants (e.g., sedatives, anxiolytics, hypnotics, neuroleptics, other opioids).
When considering the use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets in a patient taking a CNS depressant, assess the duration of use of the CNS depressant and the patient’s response, including the degree of tolerance that has developed to CNS depression. Additionally, evaluate the patient’s use of alcohol and/or illicit drugs that cause CNS depression. If the decision to begin morphine sulfate extended-release tablets is made, start with the lowest possible dose, 15 mg every 12 hours, monitor patients for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, and consider using a lower dose of the concomitant CNS depressant [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.5 Use in Elderly, Cachectic, and Debilitated Patients
Life-threatening respiratory depression is more likely to occur in elderly, cachectic, or debilitated patients as they may have altered pharmacokinetics or altered clearance compared to younger, healthier patients. Monitor such patients closely, particularly when initiating and titrating morphine sulfate extended-release tablets and when morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are given concomitantly with other drugs that depress respiration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.6 Use in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease
Monitor patients with significant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or cor pulmonale, and patients having a substantially decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia, hypercapnia, or pre-existing respiratory depression for respiratory depression, particularly when initiating therapy and titrating with morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, as in these patients, even usual therapeutic doses of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets may decrease respiratory drive to the point of apnea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Consider the use of alternative non-opioid analgesics in these patients if possible.
5.7 Hypotensive Effects
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets may cause severe hypotension including orthostatic hypotension and syncope in ambulatory patients. There is an increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent administration of certain CNS depressant drugs (e.g., phenothiazines or general anesthetics) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Monitor these patients for signs of hypotension after initiating or titrating the dose of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets. In patients with circulatory shock, morphine sulfate extended-release tablets may cause vasodilation that can further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure. Avoid the use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets in patients with circulatory shock.
5.8 Use in Patients with Head Injury or Increased Intracranial Pressure
Monitor patients taking morphine sulfate extended-release tablets who may be susceptible to the intracranial effects of CO2 retention (e.g., those with evidence of increased intracranial pressure or brain tumors) for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, particularly when initiating therapy with morphine sulfate extended-release tablets. Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets may reduce respiratory drive, and the resultant CO2 retention can further increase intracranial pressure. Opioids may also obscure the clinical course in a patient with a head injury.
Avoid the use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets in patients with impaired consciousness or coma.
5.9 Use in Patients with Gastrointestinal Conditions
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with paralytic ileus. Avoid the use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets in patients with other GI obstruction.
The morphine in morphine sulfate extended-release tablets may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis, for worsening symptoms. Opioids may cause increases in the serum amylase.
5.10 Use in Patients with Convulsive or Seizure Disorders
The morphine in morphine sulfate extended-release tablets may aggravate convulsions in patients with convulsive disorders, and may induce or aggravate seizures in some clinical settings. Monitor patients with a history of seizure disorders for worsened seizure control during morphine sulfate extended-release tablets therapy.
5.11 Avoidance of Withdrawal
Avoid the use of mixed agonist/antagonist (i.e., pentazocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol) or partial agonist (buprenorphine) analgesics in patients who have received or are receiving a course of therapy with a full opioid agonist analgesic, morphine sulfate extended-release tablets. In these patients, mixed agonists/antagonist and partial agonist analgesics may reduce the analgesic effect and/or may precipitate withdrawal symptoms.
When discontinuing morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, gradually taper the dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Do not abruptly discontinue morphine sulfate extended-release tablets.
5.12 Driving and Operating Machinery
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets may impair the mental or physical abilities needed to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating machinery. Warn patients not to drive or operate dangerous machinery unless they are tolerant to the effects of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets and know how they will react to the medication.
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
-
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Interactions with Other CNS Depressants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hypotensive Effect [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Gastrointestinal Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets may increase the risk of serious adverse reactions such as those observed with other opioid analgesics, including respiratory depression, apnea, respiratory arrest, circulatory depression, hypotension, or shock [see Overdosage (10)].
Most Frequently Observed Reactions
In clinical trials, the most common adverse reactions with morphine sulfate extended-release tablets were constipation, dizziness, sedation, nausea, vomiting, sweating, dysphoria, and euphoric mood.
Some of these effects seem to be more prominent in ambulatory patients and in those not experiencing severe pain.
Less Frequently Observed Reactions
Cardiovascular disorders: tachycardia, bradycardia, palpitations
Eye disorders: visual impairment, vision blurred, diplopia, miosis
Gastrointestinal disorders: dry mouth, diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation, dyspepsia
General disorders and administration site conditions: chills, feeling abnormal, edema, edema peripheral, weakness
Hepatobiliary disorders: biliary colic
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: anorexia
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: muscle rigidity, muscle twitching
Nervous system disorders: presyncope, syncope, headache, tremor, uncoordinated muscle movements, convulsion, intracranial pressure increased, taste alteration, paresthesia, nystagmus
Psychiatric disorders: agitation, mood altered, anxiety, depression, abnormal dreams, hallucination, disorientation, insomnia
Renal and urinary disorders: urinary retention, urinary hesitation, antidiuretic effects
Reproductive system and breast disorders: reduced libido and/or potency
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: laryngospasm
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: pruritus, urticaria, rash
Vascular disorders: flushing, hypotension, hypertension
6.2 Post-Marketing ExperienceThe following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets: amenorrhea, asthenia, bronchospasm, confusional state, drug hypersensitivity, fatigue, hyperalgesia, hypertonia, ileus, increased hepatic enzymes, intestinal obstruction, lethargy, malaise, pulmonary edema, thinking disturbances, somnolence, and vertigo.
Anaphylaxis has been reported with ingredients contained in morphine sulfate extended-release tablets. Advise patients how to recognize such a reaction and when to seek medical attention.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7.1 CNS Depressants
The concomitant use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets with other CNS depressants including sedatives, hypnotics, tranquilizers, general anesthetics, phenothiazines, other opioids, and alcohol can increase the risk of respiratory depression, profound sedation, coma, and death. Monitor patients receiving CNS depressants and morphine sulfate extended-release tablets for signs of respiratory depression, sedation, and hypotension.
When combined therapy with any of the above medications is considered, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
7.2 Interactions with Mixed Agonist/Antagonist and Partial Agonist Opioid Analgesics
Mixed agonist/antagonist (i.e., pentazocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol) and partial agonist (buprenorphine) analgesics may reduce the analgesic effect of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. Avoid the use of agonist/antagonist and partial agonist analgesics in patients receiving morphine sulfate extended-release tablets.
7.3 Muscle Relaxants
Morphine may enhance the neuromuscular blocking action of skeletal muscle relaxants and produce an increased degree of respiratory depression. Monitor patients receiving muscle relaxants and morphine sulfate extended-release tablets for signs of respiratory depression that may be greater than otherwise expected.
7.4 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
The effects of morphine may be potentiated by MAOIs. Monitor patients on concurrent therapy with an MAOI and morphine sulfate extended-release tablets for increased respiratory and central nervous system depression. MAOIs have been reported to potentiate the effects of morphine anxiety, confusion, and significant depression of respiration or coma. Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets should not be used in patients taking MAOIs or within 14 days of stopping such treatment.
7.5 Cimetidine
Cimetidine can potentiate morphine-induced respiratory depression. There is a report of confusion and severe respiratory depression when a patient undergoing hemodialysis was concurrently administered morphine and cimetidine. Monitor patients for respiratory depression when morphine sulfate extended-release tablets and cimetidine are used concurrently.
7.6 Diuretics
Morphine can reduce the efficacy of diuretics by inducing the release of antidiuretic hormone. Morphine may also lead to acute retention of urine by causing spasm of the sphincter of the bladder, particularly in men with enlarged prostates.
7.7 Anticholinergics
Anticholinergics or other medications with anticholinergic activity when used concurrently with opioid analgesics may result in increased risk of urinary retention and/or severe constipation, which may lead to paralytic ileus. Monitor patients for signs of urinary retention or reduced gastric motility when morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are used concurrently with anticholinergic drugs.
7.8 P-Glycoprotein (PGP) Inhibitors
PGP-inhibitors (e.g., quinidine) may increase the absorption/exposure of morphine sulfate by about two-fold. Therefore, monitor patients for signs of respiratory and central nervous system depression when morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are used concurrently with PGP inhibitors.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8.1 Pregnancy
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/neonatal adverse reactions
Prolonged use of opioid analgesics during pregnancy for medical or nonmedical purposes can result in physical dependence in the neonate and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome shortly after birth. Observe newborns for symptoms of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, such as poor feeding, diarrhea, irritability, tremor, rigidity, and seizures, and manage accordingly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Teratogenic Effects -Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
In humans, the frequency of congenital anomalies has been reported to be no greater than expected among the children of 70 women who were treated with morphine during the first four months of pregnancy or in 448 women treated with morphine anytime during pregnancy. Furthermore, no malformations were observed in the infant of a woman who attempted suicide by taking an overdose of morphine and other medication during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Several literature reports indicate that morphine administered subcutaneously during the early gestational period in mice and hamsters produced neurological, soft tissue and skeletal abnormalities. With one exception, the effects that have been reported were following doses that were maternally toxic and the abnormalities noted were characteristic of those observed when maternal toxicity is present. In one study, following subcutaneous infusion of doses greater than or equal to 0.15 mg/kg to mice, exencephaly, hydronephrosis, intestinal hemorrhage, split supraoccipital, malformed sternebrae, and malformed xiphoid were noted in the absence of maternal toxicity. In the hamster, morphine sulfate given subcutaneously on gestation day 8 produced exencephaly and cranioschisis. In rats treated with subcutaneous infusions of morphine during the period of organogenesis, no teratogenicity was observed. No maternal toxicity was observed in this study; however, increased mortality and growth retardation were seen in the offspring. In two studies performed in the rabbit, no evidence of teratogenicity was reported at subcutaneous doses up to 100 mg/kg.
Non-Teratogenic Effects
Infants born to mothers who have taken opioids chronically may exhibit neonatal withdrawal syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)], reversible reduction in brain volume, small size, decreased ventilatory response to CO2 and increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome. Morphine sulfate should be used by a pregnant woman only if the need for opioid analgesia clearly outweighs the potential risks to the fetus.
Controlled studies of chronic in utero morphine exposure in pregnant women have not been conducted. Published literature has reported that exposure to morphine during pregnancy in animals is associated with reduction in growth and a host of behavioral abnormalities in the offspring. Morphine treatment during gestational periods of organogenesis in rats, hamsters, guinea pigs and rabbits resulted in the following treatment-related embryotoxicity and neonatal toxicity in one or more studies: decreased litter size, embryo-fetal viability, fetal and neonatal body weights, absolute brain and cerebellar weights, delayed motor and sexual maturation, and increased neonatal mortality, cyanosis and hypothermia. Decreased fertility in female offspring, and decreased plasma and testicular levels of luteinizing hormone and testosterone, decreased testes weights, seminiferous tubule shrinkage, germinal cell aplasia, and decreased spermatogenesis in male offspring were also observed. Decreased litter size and viability were observed in the offspring of male rats administered morphine (25 mg/kg, IP) for 1 day prior to mating. Behavioral abnormalities resulting from chronic morphine exposure of fetal animals included altered reflex and motor skill development, mild withdrawal, and altered responsiveness to morphine persisting into adulthood.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
Opioids cross the placenta and may produce respiratory depression in neonates. Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are not for use in women during and immediately prior to labor, when shorter acting analgesics or other analgesic techniques are more appropriate. Opioid analgesics can prolong labor through actions that temporarily reduce the strength, duration, and frequency of uterine contractions. However, this effect is not consistent and may be offset by an increased rate of cervical dilatation, which tends to shorten labor.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Morphine is excreted in breast milk, with a milk to plasma morphine AUC ratio of approximately 2.5:1. The amount of morphine received by the infant varies depending on the maternal plasma concentration, the amount of milk ingested by the infant, and the extent of first pass metabolism.
Withdrawal signs can occur in breast-feeding infants when maternal administration of morphine is stopped.
Because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants from morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 18 have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
The pharmacokinetics of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets have not been studied in elderly patients. Clinical studies of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE SECTION
9.1 Controlled Substance
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets contain morphine, a Schedule II controlled substance with a high potential for abuse similar to other opioids including fentanyl, hydromorphone, methadone, oxycodone, and oxymorphone. Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets can be abused and is subject to misuse, addiction, and criminal diversion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
The high drug content in extended-release formulations adds to the risk of adverse outcomes from abuse and misuse.
9.2 Abuse
All patients treated with opioids require careful monitoring for signs of abuse and addiction, since use of opioid analgesic products carries the risk of addiction even under appropriate medical use. Drug abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of an over-the-counter or prescription drug, even once, for its rewarding psychological or physiological effects. Drug abuse includes, but is not limited to the following examples: the use of a prescription or over-the-counter drug to get “high”, or the use of steroids for performance enhancement and muscle build up.
Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that develop after repeated substance use and include: a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling its use, persisting in its use despite harmful consequences, a higher priority given to drug use than to other activities and obligations, increased tolerance , and sometimes a physical withdrawal.
"Drug seeking" behavior is very common to addicts and drug abusers. Drug-seeking tactics include emergency calls or visits near the end of office hours, refusal to undergo appropriate examination, testing or referral, repeated claims of loss of prescriptions, tampering with prescriptions and reluctance to provide prior medical records or contact information for other treating physician(s). “Doctor shopping” (visiting multiple prescribers) to obtain additional prescriptions is common among drug abusers and people suffering from untreated addiction.
Preoccupation with achieving adequate pain relief can be appropriate behavior in a patient with poor pain control.
Abuse and addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance. Physicians should be aware that addiction may not be accompanied by concurrent tolerance and symptoms of physical dependence in all addicts. In addition, abuse of opioids can occur in the absence of true addiction.
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, like other opioids, can be diverted for non-medical use into illicit channels of distribution. Careful recordkeeping of prescribing information, including quantity, frequency, and renewal requests as required by state law, is strongly advised.
Proper assessment of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic reevaluation of therapy, and proper dispensing and storage are appropriate measures that help to reduce abuse of opioid drugs.
Risks Specific to Abuse of Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are for oral use only. Abuse of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets poses a risk of overdose and death. This risk is increased with concurrent abuse of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets with alcohol and other substances. Taking cut, broken, chewed, crushed, or dissolved morphine sulfate extended-release tablets enhances drug release and increases the risk of overdose and death.
Due to the presence of talc as one of the excipients in morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, parenteral abuse can be expected to result in local tissue necrosis, infection, pulmonary granulomas, and increased risk of endocarditis and valvular heart injury. Parenteral drug abuse is commonly associated with transmission of infectious diseases such as hepatitis and HIV.
9.3 Dependence
Both tolerance and physical dependence can develop during chronic opioid therapy. Tolerance is the need for increasing doses of opioids to maintain a defined effect such as analgesia (in the absence of disease progression or other external factors). Tolerance may occur to both the desired and undesired effects of drugs, and may develop at different rates for different effects.
Physical dependence results in withdrawal symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug. Withdrawal also may be precipitated through the administration of drugs with opioid antagonist activity, e.g., naloxone, nalmefene, mixed agonist/antagonist analgesics (pentazocine, butorphanol, nalbuphine), or partial agonists (buprenorphine). Physical dependence may not occur to a clinically significant degree until after several days to weeks of continued opioid usage.
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets should not be abruptly discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. If morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are abruptly discontinued in a physically-dependent patient, an abstinence syndrome may occur. Some or all of the following can characterize this syndrome: restlessness, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, yawning, perspiration, chills, myalgia, and mydriasis. Other signs and symptoms also may develop, including: irritability, anxiety, backache, joint pain, weakness, abdominal cramps, insomnia, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, or increased blood pressure, respiratory rate, or heart rate.
Infants born to mothers physically dependent on opioids will also be physically dependent and may exhibit respiratory difficulties and withdrawal signs [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
Clinical Presentation
Acute overdosage with morphine is manifested by respiratory depression, somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, constricted pupils, and, in some cases, pulmonary edema, bradycardia, hypotension, and death. Marked mydriasis rather than miosis may be seen due to severe hypoxia in overdose situations.
Treatment of Overdose
In case of overdose, priorities are the reestablishment of a patent and protected airway and institution of assisted or controlled ventilation if needed. Employ other supportive measures (including oxygen, vasopressors) in the management of circulatory shock and pulmonary edema as indicated. Cardiac arrest or arrhythmias will require advanced life support techniques.
The opioid antagonists, naloxone or nalmefene, are specific antidotes to respiratory depression resulting from opioid overdose. Opioid antagonists should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory or circulatory depression secondary to morphine overdose. Such agents should be administered cautiously to persons who are known, or suspected to be physically dependent on morphine sulfate extended-release tablets. In such cases, an abrupt or complete reversal of opioid effects may precipitate an acute withdrawal syndrome.
Because the duration of reversal would be expected to be less than the duration of action of morphine in morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, carefully monitor the patient until spontaneous respiration is reliably reestablished. Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets will continue to release morphine and add to the morphine load for 24 to 48 hours or longer following ingestion necessitating prolonged monitoring. If the response to opioid antagonists is suboptimal or not sustained, additional antagonist should be administered as directed in the product’s prescribing information.
In an individual physically dependent on opioids, administration of the usual dose of the antagonist will precipitate an acute withdrawal syndrome. The severity of the withdrawal symptoms experienced will depend on the degree of physical dependence and the dose of the antagonist administered. If a decision is made to treat serious respiratory depression in the physically dependent patient, administration of the antagonist should be begun with care and by titration with smaller than usual doses of the antagonist.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets are for oral use and contain morphine sulfate, an agonist at the mu-opioid receptor.
Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients common to all strengths: cetostearyl alcohol, hydroxyethyl cellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
The tablet strengths describe the amount of morphine per tablet as the pentahydrated sulfate salt (morphine sulfate).
The 15 mg tablets also contain: FD&C Blue No. 2, lactose monohydrate, polysorbate 80
The 30 mg tablets also contain: D&C Red No. 7, FD&C Blue No. 1, lactose monohydrate, polysorbate 80
The 60 mg tablets also contain: D&C Red No. 30, D&C Yellow No. 10, hydroxypropyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate
The 100 mg tablets also contain: black iron oxide
The 200 mg tablets also contain: D&C Yellow No. 10, FD&C Blue No. 1, hydroxypropyl cellulose
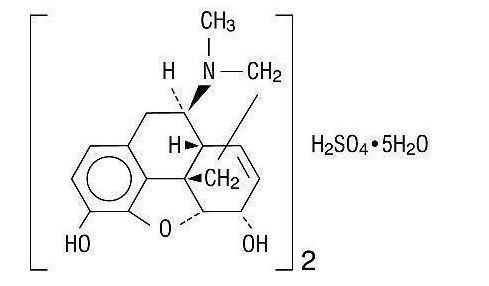
Morphine sulfate is an odorless, white, crystalline powder with a bitter taste. It has a solubility of 1 in 21 parts of water and 1 in 1000 parts of alcohol, but is practically insoluble in chloroform or ether. The octanol: water partition coefficient of morphine is 1.42 at physiologic pH and the pKb is 7.9 for the tertiary nitrogen (mostly ionized at pH 7.4). Its structural formula is:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Morphine sulfate, an opioid agonist, is relatively selective for the mu receptor, although it can interact with other opioid receptors at higher doses. In addition to analgesia, the widely diverse effects of morphine sulfate include analgesia, dysphoria, euphoria, somnolence, respiratory depression, diminished gastrointestinal motility, altered circulatory dynamics, histamine release, physical dependence, and alterations of the endocrine and autonomic nervous systems.
Morphine produces both its therapeutic and its adverse effects by interaction with one or more classes of specific opioid receptors located throughout the body. Morphine acts as a full agonist, binding with and activating opioid receptors at sites in the peri-aqueductal and peri-ventricular grey matter, the ventro-medial medulla and the spinal cord to produce analgesia.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Plasma Level-Analgesia Relationships
While plasma morphine-efficacy relationships can be demonstrated in non-tolerant individuals, they are influenced by a wide variety of factors and are not generally useful as a guide to the clinical use of morphine. Dosages of morphine should be chosen and must be titrated on the basis of clinical evaluation of the patient and the balance between therapeutic and adverse effects.
CNS Depressant/Alcohol Interaction
Additive pharmacodynamic effects may be expected when morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are used in conjunction with alcohol, other opioids, or illicit drugs that cause central nervous system depression.
Effects on the Central Nervous System
The principal actions of therapeutic value of morphine are analgesia and sedation. Specific CNS opiate receptors for endogenous compounds with opioid-like activity have been identified throughout the brain and spinal cord and are likely to play a role in the expression of analgesic effects.
Morphine produces respiratory depression by direct action on brainstem respiratory centers. The mechanism of respiratory depression involves a reduction in the responsiveness of the brainstem respiratory centers to increases in carbon dioxide tension, and to electrical stimulation.
Morphine depresses the cough reflex by direct effect on the cough center in the medulla. Morphine causes miosis, even in total darkness. Pinpoint pupils are a sign of narcotic overdose but are not pathognomonic (e.g., pontine lesions of hemorrhagic or ischemic origins may produce similar findings). Marked mydriasis rather than miosis may be seen with worsening hypoxia.
Effects on the Gastrointestinal Tract and Other Smooth Muscle
Morphine causes a reduction in motility associated with an increase in smooth muscle tone in the antrum of the stomach and in the duodenum. Digestion of food is delayed in the small intestine and propulsive contractions are decreased. Propulsive peristaltic waves in the colon are decreased, while tone may be increased to the point of spasm. The end result is constipation. Morphine can cause a marked reduction in gastric, biliary and pancreatic secretions, spasm of the sphincter of Oddi, and transient elevations in serum amylase.
Effects on the Cardiovascular System
Morphine produces peripheral vasodilation which may result in orthostatic hypotension. Release of histamine can occur and may contribute to opioid-induced hypotension. Manifestations of histamine release and/or peripheral vasodilation may include pruritus, flushing, red eyes, and sweating.
Effects on the Endocrine System
Opioids inhibit the secretion of ACTH, cortisol, testosterone, and luteinizing hormone (LH) in humans. They also stimulate prolactin, growth hormone (GH) secretion, and pancreatic secretion of insulin and glucagon.
Effects on the Immune System
Opioids have been shown to have a variety of effects on components of the immune system in in vitro and animal models. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Overall, the effects of opioids appear to be modestly immunosuppressive.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are an extended-release tablet containing morphine sulfate. Morphine is released from morphine sulfate extended-release tablets somewhat more slowly than from immediate-release oral preparations. Following oral administration of a given dose of morphine, the amount ultimately absorbed is essentially the same whether the source is morphine sulfate extended-release tablets or an immediate-release formulation. Because of pre-systemic elimination (i.e., metabolism in the gut wall and liver) only about 40% of the administered dose reaches the central compartment.
Absorption
The oral bioavailability of morphine is approximately 20 to 40%. When morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are given on a fixed dosing regimen, steady-state is achieved in about a day.
Food Effect
The effect of food upon the systemic bioavailability of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets has not been systematically evaluated for all strengths. One study, conducted with the 30 mg morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, showed no significant differences in Cmax and AUC (0-24h) values, whether the tablet was taken while fasting or with a high-fat breakfast.
Distribution
Once absorbed, morphine is distributed to skeletal muscle, kidneys, liver, intestinal tract, lungs, spleen, and brain. Morphine also crosses placental membranes and has been found in breast milk. The volume of distribution (Vd) for morphine is approximately 3 to 4 liters per kilogram and morphine is 30 to 35% reversibly bound to plasma proteins.
Metabolism
The major pathways of morphine metabolism include glucuronidation to produce metabolites including morphine-3-glucuronide, M3G (about 50%) and morphine-6-glucuronide, M6G (about 5 to 15%) and sulfation in the liver to produce morphine-3-etheral sulfate. A small fraction (less than 5%) of morphine is demethylated. M6G has been shown to have analgesic activity but crosses the blood-brain barrier poorly, while M3G has no significant analgesic activity.
Excretion
The elimination of morphine occurs primarily as renal excretion of M3G and its effective half-life after intravenous administration is normally 2 to 4 hours. Approximately 10% of the dose is excreted unchanged in urine. In some studies involving longer periods of plasma sampling, a longer terminal half-life of about 15 hours was reported. A small amount of the glucuronide conjugate is excreted in the bile, and there is some minor enterohepatic recycling.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets have not been studied in elderly patients.
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets have not been studied in pediatric patients below the age of 18.
Gender
A gender analysis of pharmacokinetic data from healthy subjects taking morphine sulfate extended-release tablets indicated that morphine concentrations were similar in males and females.
Race
Chinese subjects given intravenous morphine had a higher clearance when compared to Caucasian subjects (1852 +/- 116 ml/min compared to 1495 +/- 80 ml/min).
Hepatic Impairment
Morphine pharmacokinetics are altered in individuals with cirrhosis. Clearance was found to decrease with a corresponding increase in half-life. The M3G and M6G to morphine plasma AUC ratios also decreased in these subjects, indicating diminished metabolic activity. Adequate studies of the pharmacokinetics of morphine in patients with severe hepatic impairment have not been conducted.
Renal Impairment
Morphine pharmacokinetics are altered in patients with renal failure. The AUC is increased and clearance is decreased and the metabolites, M3G and M6G, may accumulate to much higher plasma levels in patients with renal failure as compared to patients with normal renal function. Adequate studies of the pharmacokinetics of morphine in patients with severe renal impairment have not been conducted.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: Studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of morphine have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis: No formal studies to assess the mutagenic potential of morphine have been conducted. In the published literature, morphine was found to be mutagenic in vitro increasing DNA fragmentation in human T-cells. Morphine was reported to be mutagenic in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay and positive for the induction of chromosomal aberrations in mouse spermatids and murine lymphocytes. Mechanistic studies suggest that the in vivo clastogenic effects reported with morphine in mice may be related to increases in glucocorticoid levels produced by morphine in this species. In contrast to the above positive findings, in vitro studies in the literature have also shown that morphine did not induce chromosomal aberrations in human leukocytes or translocations or lethal mutations in Drosophila.
Impairment of Fertility: No formal nonclinical studies to assess the potential of morphine to impair fertility have been conducted. Several nonclinical studies from the literature have demonstrated adverse effects on male fertility in the rat from exposure to morphine. One study in which male rats were administered morphine sulfate subcutaneously prior to mating (up to 30 mg/kg twice daily) and during mating (20 mg/kg twice daily) with untreated females, a number of adverse reproductive effects including reduction in total pregnancies, higher incidence of pseudopregnancies, and reduction in implantation sites were seen. Studies from the literature have also reported changes in hormonal levels (i.e., testosterone, luteinizing hormone, serum corticosterone) following treatment with morphine. These changes may be associated with the reported effects on fertility in the rat.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets 15 mg are round, blue-colored, film-coated tablets bearing the symbol ABG on one side and 15 on the other. They are supplied as follows:
NDC 42858-801-01: opaque plastic bottles containing 100 tablets
Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets 30 mg are round, lavender-colored, film-coated tablets bearing the symbol ABG on one side and 30 on the other. They are supplied as follows:
NDC 42858-802-01: opaque plastic bottles containing 100 tablets
Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets 60 mg are round, orange-colored, film-coated tablets bearing the symbol ABG on one side and 60 on the other. They are supplied as follows:
NDC 42858-803-01: opaque plastic bottles containing 100 tablets
Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets 100 mg are round, gray-colored, film-coated tablets bearing the symbol ABG on one side and 100 on the other. They are supplied as follows:
NDC 42858-804-01: opaque plastic bottles containing 100 tablets
Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets 200 mg are capsule-shaped, green-colored, film-coated tablets bearing the symbol ABG on one side and 200 on the other. They are supplied as follows:
NDC 42858-805-01: opaque plastic bottles containing 100 tablets
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container.
CAUTION
DEA FORM REQUIRED
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
-
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
Inform patients that the use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, even when taken as recommended, can result in addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Instruct patients not to share morphine sulfate extended-release tablets with others and to take steps to protect morphine sulfate extended-release tablets from theft or misuse.
Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Inform patients of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression, including information that the risk is greatest when starting morphine sulfate extended-release tablets or when the dose is increased, and that it can occur even at recommended doses [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Advise patients how to recognize respiratory depression and to seek medical attention if breathing difficulties develop.
Accidental Ingestion
Inform patients that accidental ingestion, especially in children, may result in respiratory depression or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Instruct patients to take steps to store morphine sulfate extended-release tablets securely and to dispose of unused morphine sulfate extended-release tablets by flushing the tablets down the toilet.
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Inform female patients of reproductive potential that prolonged use of morphine sulfate extended-release tablets during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Interactions with Alcohol and other CNS Depressants
Inform patients that potentially serious additive effects may occur if morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are used with alcohol or other CNS depressants, and not to use such drugs unless supervised by a health care provider.
Important Administration Instructions
Instruct patients how to properly take morphine sulfate extended-release tablets, including the following:
- Swallowing morphine sulfate extended-release tablets whole
- Not crushing, chewing, or dissolving the tablets
- Using morphine sulfate extended-release tablets exactly as prescribed to reduce the risk of life-threatening adverse reactions (e.g., respiratory depression)
- Not discontinuing morphine sulfate extended-release tablets without first discussing the need for a tapering regimen with the prescriber
Hypotension
Inform patients that morphine sulfate extended-release tablets may cause orthostatic hypotension and syncope. Instruct patients how to recognize symptoms of low blood pressure and how to reduce the risk of serious consequences should hypotension occur (e.g., sit or lie down, carefully rise from a sitting or lying position).
Driving or Operating Heavy Machinery
Inform patients that morphine sulfate extended-release tablets may impair the ability to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating heavy machinery. Advise patients not to perform such tasks until they know how they will react to the medication.
Constipation
Advise patients of the potential for severe constipation, including management instructions and when to seek medical attention.
Anaphylaxis
Inform patients that anaphylaxis has been reported with ingredients contained in morphine sulfate extended-release tablets. Advise patients how to recognize such a reaction and when to seek medical attention.
Pregnancy
Advise female patients that morphine sulfate extended-release tablets can cause fetal harm and to inform the prescriber if they are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
Healthcare professionals can telephone Rhodes Pharmaceuticals L.P. (1-888-827-0616) for information on this product.
Disposal of Unused Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets
Advise patients to flush the unused tablets down the toilet when morphine sulfate extended-release tablets are no longer needed.
Marketed by:
Rhodes Pharmaceuticals L.P.
Coventry, RI 02816
Manufactured by:
Purdue Pharmaceuticals, L.P.
Wilson, NC 27893
302942-0B
Rev. 05/2014
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release (ER) Tablets, CII
Morphine sulfate ER tablets are:
A strong prescription pain medicine that contains an opioid (narcotic) that is used to manage pain severe enough to require daily around-the-clock, long-term treatment with an opioid, when other pain treatments such as non-opioid pain medicines or immediate-release opioid medicines do not treat your pain well enough or you cannot tolerate them.
A long-acting (extended-release) opioid pain medicine that can put you at risk for overdose and death. Even if you take your dose correctly as prescribed you are at risk for opioid addiction, abuse, and misuse that can lead to death.
Not for use to treat pain that is not around-the-clock.
Important information about morphine sulfate ER tablets:
Get emergency help right away if you take too much morphine sulfate ER tablets (overdose). When you first start taking morphine sulfate ER tablets, when your dose is changed, or if you take too much (overdose), serious or life-threatening breathing problems that can lead to death may occur.
Never give anyone else your morphine sulfate ER tablets. They could die from taking it. Store morphine sulfate ER tablets away from children and in a safe place to prevent stealing or abuse. Selling or giving away morphine sulfate ER tablets is against the law.
Do not take morphine sulfate ER tablets if you have:
severe asthma, trouble breathing, or other lung problems.
a bowel blockage or have narrowing of the stomach or intestines.
Before taking morphine sulfate ER tablets, tell your healthcare provider if you have a history of:
head injury, seizures
liver, kidney, thyroid problems
problems urinating
pancreas or gallbladder problems
abuse of street or prescription drugs, alcohol addiction, or mental health problems.
Tell your healthcare provider if you are:
pregnant or planning to become pregnant. Prolonged use of morphine sulfate ER tablets during pregnancy can cause withdrawal symptoms in your newborn baby that could be life-threatening if not recognized and treated.
breastfeeding. Morphine sulfate ER tablets pass into breast milk and may harm your baby.
taking prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements. Taking morphine sulfate ER tablets with certain other medicines can cause serious side effects.
When taking morphine sulfate ER tablets:
Do not change your dose. Take morphine sulfate ER tablets exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Take your prescribed dose every 8 to 12 hours, as directed by your healthcare provider. Do not take more than your prescribed dose. If you miss a dose, take your next dose at the usual time.
Swallow morphine sulfate ER tablets whole. Do not cut, break, chew, crush, dissolve, snort, or inject morphine sulfate ER tablets because this may cause you to overdose and die.
Call your healthcare provider if the dose you are taking does not control your pain.
Do not stop taking morphine sulfate ER tablets without talking to your healthcare provider.
After you stop taking morphine sulfate ER tablets, flush any unused tablets down the toilet.
While taking morphine sulfate ER tablets DO NOT:
Drive or operate heavy machinery, until you know how morphine sulfate ER tablets affect you. Morphine sulfate ER tablets can make you sleepy, dizzy, or lightheaded.
Drink alcohol or use prescription or over-the-counter medicines that contain alcohol. Using products containing alcohol during treatment with morphine sulfate ER tablets may cause you to overdose and die.
The possible side effects of morphine sulfate ER tablets are:
constipation, nausea, sleepiness, vomiting, tiredness, headache, dizziness, abdominal pain. Call your healthcare provider if you have any of these symptoms and they are severe.
Get emergency medical help if you have:
trouble breathing, shortness of breath, fast heartbeat, chest pain, swelling of your face, tongue or throat, extreme drowsiness, light-headedness when changing positions, or you are feeling faint.
These are not all the possible side effects of morphine sulfate ER tablets. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. For more information go to dailymed.nlm.nih.gov
Manufactured for: Rhodes Pharmaceuticals L.P., Coventry, RI 02816, http://www.rhodespharma.com or call 1-888-827-0616
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: April 2014
