FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Monitoring to Inform Dosage and Administration
Prior to dosing, withhold TEMODAR until patients have an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of 1.5 x 109/L or greater and a platelet count of 100 x 109/L or greater.
For concomitant radiotherapy, obtain a complete blood count prior to initiation of treatment and weekly during treatment.
For the 28-day treatment cycles, obtain a complete blood count prior to treatment on Day 1 and on Day 22 of each cycle. Perform complete blood counts weekly until recovery if the ANC falls below 1.5 x 109/L and the platelet count falls below 100 x 109/L.
For concomitant use with focal radiotherapy, obtain a complete blood count weekly and as clinically indicated.
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Dosage Modifications for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma
Administer TEMODAR either orally or intravenously once daily for 42 to 49 consecutive days during the concomitant use phase with focal radiotherapy, and then once daily on Days 1 to 5 of each 28-day cycle for 6 cycles during the maintenance use phase.
Provide Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) prophylaxis during the concomitant use phase and continue in patients who develop lymphopenia until resolution to Grade 1 or less [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Concomitant Use Phase:
The recommended dosage of TEMODAR is 75 mg/m2 either orally or intravenously once daily for 42 to 49 days in combination with focal radiotherapy. Focal radiotherapy includes the tumor bed or resection site with a 2 to 3 cm margin.
Other administration schedules have been used.
Obtain a complete blood count weekly. The recommended dosage modifications due to adverse reactions during concomitant use phase are provided in Table 1.
| Adverse Reaction | Interruption | Discontinuation |
|---|---|---|
| Absolute Neutrophil Count | Withhold TEMODAR if ANC is greater than or equal to 0.5 × 109/L and less than 1.5 × 109/L. | Discontinue TEMODAR if ANC is less than 0.5 × 109/L. |
| Resume TEMODAR at the same dose when ANC is greater than or equal to 1.5 × 109/L. | ||
| Platelet Count | Withhold TEMODAR if platelet count is greater than or equal to 10 × 109/L and less than 100 × 109/L. | Discontinue TEMODAR if platelet count is less than 10 × 109/L. |
| Resume TEMODAR at the same dose when platelet count is greater than or equal to 100 × 109/L. | ||
| Non-hematological Adverse Reaction (except for alopecia, nausea, vomiting) | Withhold TEMODAR if Grade 2 adverse reaction occurs. | Discontinue TEMODAR if Grade 3 or 4 adverse reaction occurs. |
| Resume TEMODAR at the same dose when resolution to Grade 1 or less. |
Single Agent Maintenance Use Phase:
Beginning 4 weeks after concomitant use phase completion, administer TEMODAR either orally or intravenously once daily on Days 1 to 5 of each 28-day cycle for 6 cycles. The recommended dosage of TEMODAR in the maintenance use phase is:
- Cycle 1: 150 mg/m2 per day on days 1 to 5.
- Cycles 2 to 6: May increase to 200 mg/m2 per day on days 1 to 5 before starting Cycle 2 if no dosage interruptions or discontinuations are required (Table 1). If the dose is not escalated at the onset of Cycle 2, do not increase the dose for Cycles 3 to 6.
Obtain a complete blood count on Day 22 and then weekly until the ANC is above 1.5 × 109/L and the platelet count is above 100 × 109/L. Do not start the next cycle until the ANC and platelet count exceed these levels.
The recommended dosage modifications due to adverse reactions during the maintenance use phase are provided in Table 2.
If TEMODAR is withheld, reduce the dose for the next cycle by 50 mg/m2 per day. Permanently discontinue TEMODAR in patients who are unable to tolerate a dose of 100 mg/m2 per day.
| Adverse Reactions | Interruption and Dose Reduction | Discontinuation |
|---|---|---|
| Absolute Neutrophil Count | Withhold TEMODAR if ANC less than 1 × 109/L. | Discontinue TEMODAR if unable to tolerate a dose of 100 mg/m2 per day. |
| When ANC is above 1.5 × 109/L, resume TEMODAR at reduced dose for the next cycle. | ||
| Platelet Count | Withhold TEMODAR if platelet less than 50 × 109/L. | Discontinue TEMODAR if unable to tolerate a dose of 100 mg/m2 per day. |
| When platelet count is above 100 × 109/L, resume TEMODAR at reduced dose for the next cycle. | ||
| Nonhematological Adverse Reactions (except for alopecia, nausea, vomiting) | Withhold TEMODAR if Grade 3 adverse reaction occurs. | Discontinue TEMODAR if recurrent Grade 3 adverse reaction occurs after dose reduction, if Grade 4 adverse reaction occurs, or if unable to tolerate a dose of 100 mg/m2 per day. |
| When resolved to Grade 1 or less, resume TEMODAR at reduced dose for the next cycle. |
2.3 Recommended Dosage and Dosage Modifications for Anaplastic Astrocytoma
Adjuvant Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Anaplastic Astrocytoma
Beginning 4 weeks after the end of radiotherapy, administer TEMODAR orally in a single dose on days 1 to 5 of a 28-day cycle for 12 cycles. The recommended dosage of TEMODAR is:
- Cycle 1: 150 mg/m2 per day on days 1 to 5.
- Cycles 2 to 12: 200 mg/m2 per day on days 1 to 5 if patient experienced no or minimal toxicity in Cycle 1. If the dose was not escalated at the onset of Cycle 2, do not increase the dose during Cycles 3 to 6.
The recommended complete blood count testing and dosage modifications due to adverse reactions during adjuvant treatment are provided above and in Table 2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Refractory Anaplastic Astrocytoma
The recommended initial dosage of TEMODAR is 150 mg/m2 once daily on Days 1 to 5 of each 28-day cycle. Increase the TEMODAR dose to 200 mg/m2 per day if the following conditions are met at the nadir and on Day 1 of the next cycle:
- ANC is greater than or equal to 1.5 × 109/L, and
- Platelet count is greater than or equal to 100 × 109/L.
Continue TEMODAR until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Obtain a complete blood count on Day 22 and then weekly until the ANC is above 1.5 x 109/L and the platelet count is above 100 x 109/L. Do not start the next cycle until the ANC and platelet count exceed these levels.
If the ANC is less than 1 × 109/L or the platelet count is less than 50 × 109/L during any cycle, reduce the TEMODAR dose for the next cycle by 50 mg/m2 per day. Permanently discontinue TEMODAR in patients who are unable to tolerate a dose of 100 mg/m2 per day.
2.4 Preparation and Administration
TEMODAR is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
TEMODAR capsules
Take TEMODAR at the same time each day. Administer TEMODAR consistently with respect to food (fasting vs. nonfasting) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. To reduce nausea and vomiting, take TEMODAR on an empty stomach or at bedtime and consider antiemetic therapy prior to and following TEMODAR administration.
Swallow TEMODAR capsules whole with water. Advise patients not to open, chew, or dissolve the contents of the capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
If capsules are accidentally opened or damaged, take precautions to avoid inhalation or contact with the skin or mucous membranes. In case of powder contact, wash the affected area with water immediately.
TEMODAR for injection
Bring the vial to room temperature prior to reconstitution with Sterile Water for Injection.
Reconstitute the vial with 41 mL of Sterile Water for Injection to yield a TEMODAR solution with a concentration of 2.5 mg/mL temozolomide. Reconstituted TEMODAR is a clear solution and essentially free of visible particles.
Gently swirl vial. Do not shake.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Discard if particulate matter or discoloration is observed.
Do not further dilute the reconstituted solution.
Store reconstituted solution at room temperature (25°C [77°F]). Discard reconstituted solution if not used within 14 hours, including infusion time.
Withdraw up to 40 mL from each vial to make up the total dose and discard any unused portion. Transfer reconstituted solution from each vial into an empty 250 mL infusion bag.
Administer reconstituted solution using a pump over a period of 90 minutes. Administer TEMODAR by intravenous infusion only. Infusion over a shorter or longer period of time may result in suboptimal dosing. Flush the lines before and after each infusion. TEMODAR for injection may be administered in the same intravenous line with 0.9% Sodium Chloride injection only.
Because no data are available on the compatibility of TEMODAR for injection with other intravenous substances or additives, do not infuse other medications simultaneously through the same intravenous line.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Capsules:
- –
- 5 mg: opaque white bodies with green caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR.”
- –
- 20 mg: opaque white bodies with yellow caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR.”
- –
- 100 mg: opaque white bodies with pink caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR.”
- –
- 140 mg: opaque white bodies with blue caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR.”
- –
- 180 mg: opaque white bodies with orange caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR.”
- –
- 250 mg: opaque white bodies with white caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR.”
- For injection: 100 mg white to light tan or light pink lyophilized powder for reconstitution in a single-dose vial.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
TEMODAR is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity reactions to:
- temozolomide or any other ingredients in TEMODAR; and
- dacarbazine, since both temozolomide and dacarbazine are metabolized to the same active metabolite 5-(3-methyltriazen-1-yl)-imidazole-4-carboxamide.
Reactions to TEMODAR have included anaphylaxis [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myelosuppression
Myelosuppression, including pancytopenia, leukopenia, and anemia, some with fatal outcomes, have occurred with TEMODAR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)].
In MK-7365-006, myelosuppression usually occurred during the first few cycles of therapy and was generally not cumulative. The median nadirs occurred at 26 days for platelets (range: 21 to 40 days) and 28 days for neutrophils (range: 1 to 44 days). Approximately 10% of patients required hospitalization, blood transfusion, or discontinuation of therapy due to myelosuppression. Geriatric patients and women have been shown in clinical trials to have a higher risk of developing myelosuppression.
Obtain a complete blood count and monitor ANC and platelet counts before initiation of treatment and as clinically indicated during treatment. When TEMODAR is used in combination with radiotherapy, obtain a complete blood count prior to initiation of treatment, weekly during treatment, and as clinically indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.3)].
For severe myelosuppression, withhold TEMODAR and then resume at same or reduced dose, or permanently discontinue, based on occurrence [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.3)].
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
Fatal and severe hepatotoxicity have been reported in patients receiving TEMODAR. Perform liver tests at baseline, midway through the first cycle, prior to each subsequent cycle, and approximately two to four weeks after the last dose of TEMODAR.
5.3 Pneumocystis Pneumonia
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) has been reported in patients receiving TEMODAR. The risk of PCP is increased in patients receiving steroids or with longer treatment regimens of TEMODAR.
For patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma, provide PCP prophylaxis for all patients during the concomitant phase. Continue PCP prophylaxis in patients who experience lymphopenia, until resolution to Grade 1 or less [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Monitor all patients receiving TEMODAR for the development of lymphopenia and PCP.
5.4 Secondary Malignancies
The incidence of secondary malignancies is increased in patients treated with TEMODAR-containing regimens. Cases of myelodysplastic syndrome and secondary malignancies, including myeloid leukemia, have been observed following TEMODAR administration.
5.5 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, TEMODAR can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Adverse developmental outcomes have been reported in both pregnant patients and pregnant partners of male patients. Oral administration of temozolomide to rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryolethality and polymalformations at doses less than the maximum human dose based on body surface area.
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TEMODAR and for 6 months after the last dose. Because of potential risk of genotoxic effects on sperm, advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with TEMODAR and for 3 months after the last dose. Advise male patients not to donate semen during treatment with TEMODAR and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
5.6 Exposure to Opened Capsules
Advise patients not to open, chew or dissolve the contents of the TEMODAR capsules. Swallow capsules whole with a glass of water. If a capsule becomes damaged, avoid contact of the powder contents with skin or mucous membranes. In case of powder contact, wash affected area with water immediately [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. If TEMODAR capsules must be opened or the contents must be dissolved, this should be done by a professional trained in safe handling of hazardous drugs using appropriate equipment and safety procedures.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Pneumocystis Pneumonia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Secondary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma
The safety of TEMODAR was evaluated in study MK-7365-051 [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Severe or life-threatening adverse reactions occurred in 49% of patients treated with TEMODAR; the most common were fatigue (13%), convulsions (6%), headache (5%), and thrombocytopenia (5%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in patients treated with TEMODAR were alopecia, fatigue, nausea, anorexia, headache, constipation, and vomiting.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions in MK-7365-051.
| Adverse Reactions | Concomitant Use Phase | Maintenance Use Phase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiation Therapy and TEMODAR N=288* | Radiation Therapy Alone N=285 | TEMODAR N=224 |
||||
| All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades ≥3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥3 (%) |
|
| NOS = not otherwise specified. Note: Grade 5 (fatal) adverse reactions are included in the Grade ≥3 column. |
||||||
|
||||||
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||||
| Alopecia | 69 | 0 | 63 | 0 | 55 | 0 |
| Rash | 19 | 1 | 15 | 0 | 13 | 1 |
| General | ||||||
| Fatigue | 54 | 7 | 49 | 5 | 61 | 9 |
| Anorexia | 19 | 1 | 9 | <1 | 27 | 1 |
| Headache | 19 | 2 | 17 | 4 | 23 | 4 |
| Gastrointestinal System | ||||||
| Nausea | 36 | 1 | 16 | <1 | 49 | 1 |
| Vomiting | 20 | <1 | 6 | <1 | 29 | 2 |
| Constipation | 18 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 22 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 6 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 10 | 1 |
| Central and Peripheral Nervous System | ||||||
| Convulsions | 6 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 11 | 3 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of patients are presented below:
Central & Peripheral Nervous System: memory impairment, confusion
Eye: vision blurred
Gastrointestinal System: stomatitis, abdominal pain
General: weakness, dizziness
Immune System: allergic reaction
Injury: radiation injury not otherwise specified
Musculoskeletal System: arthralgia
Platelet, Bleeding, & Clotting: thrombocytopenia
Psychiatric: insomnia
Respiratory System: coughing, dyspnea
Special Senses Other: taste perversion
Skin & Subcutaneous Tissue: dry skin, pruritus, erythema
When laboratory abnormalities and adverse reactions were combined, Grade 3 or Grade 4 neutrophil abnormalities including neutropenic reactions were observed in 8% of patients, and Grade 3 or Grade 4 platelet abnormalities including thrombocytopenic reactions were observed in 14% of patients.
Newly Diagnosed Anaplastic Astrocytoma
The safety of TEMODAR for the adjuvant treatment of adults with newly diagnosed anaplastic astrocytoma was derived from published literature [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. The safety of TEMODAR for the adjuvant treatment of patients with newly diagnosed anaplastic astrocytoma was consistent with the known safety profile of TEMODAR.
Refractory Anaplastic Astrocytoma
The safety of TEMODAR was evaluated in study MK-7365-006 [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were nausea, vomiting, headache, fatigue, constipation, and convulsions.
Tables 4 and 5 summarize the adverse reactions and hematological laboratory abnormalities in MK-7365-006.
| Adverse Reactions | TEMODAR N=158 |
|
|---|---|---|
| All Reactions (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) |
|
| Gastrointestinal System | ||
| Nausea | 53 | 10 |
| Vomiting | 42 | 6 |
| Constipation | 33 | 1 |
| Diarrhea | 16 | 2 |
| General | ||
| Headache | 41 | 6 |
| Fatigue | 34 | 4 |
| Asthenia | 13 | 6 |
| Fever | 13 | 2 |
| Central and Peripheral Nervous System | ||
| Convulsions | 23 | 5 |
| Hemiparesis | 18 | 6 |
| Dizziness | 12 | 1 |
| Coordination abnormal | 11 | 1 |
| Amnesia | 10 | 4 |
| Insomnia | 10 | 0 |
| Cardiovascular | ||
| Edema peripheral | 11 | 1 |
| Resistance Mechanism | ||
| Infection viral | 11 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of patients are presented below:
Central and Peripheral Nervous System: paresthesia, somnolence, paresis, urinary incontinence, ataxia, dysphasia, convulsions local, gait abnormal, confusion
Endocrine: adrenal hypercorticism
Gastrointestinal System: abdominal pain, anorexia
General: back pain
Metabolic: weight increase
Musculoskeletal System: myalgia
Psychiatric: anxiety, depression
Reproductive Disorders: breast pain female
Respiratory System: upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, sinusitis, coughing
Skin & Appendages: rash, pruritus
Urinary System: urinary tract infection, micturition increased frequency
Vision: diplopia, vision abnormal1
- 1
- This term includes blurred vision; visual deficit; vision changes; and vision troubles.
| TEMODAR*,†
(%) |
|
|---|---|
| Decreased lymphocytes | 55 |
| Decreased platelets | 19 |
| Decreased neutrophils | 14 |
| Decreased leukocytes | 11 |
| Decreased hemoglobin | 4 |
Hematological Toxicities for Advanced Gliomas
In clinical trial experience with 110 to 111 females and 169 to 174 males (depending on measurements), females experienced higher rates of Grade 4 neutropenia (ANC <0.5 × 109/L) and thrombocytopenia (<20 × 109/L) than males in the first cycle of therapy (12% vs. 5% and 9% vs. 3%, respectively).
In the entire safety database for which hematologic data exist (N=932), 7% (4/61) and 10% (6/63) of patients >70 years experienced Grade 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia in the first cycle, respectively. For patients ≤70 years, 7% (62/871) and 6% (48/879) experienced Grade 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia in the first cycle, respectively. Pancytopenia, leukopenia, and anemia also occurred.
Injection Site Reactions
Adverse reactions that were reported in 35 patients who received TEMODAR for injection were pain, irritation, pruritus, warmth, swelling, and erythema at infusion site; petechiae; and hematoma.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of TEMODAR. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to the drug exposure.
Dermatologic: Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Immune System: Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Erythema multiforme, which resolved after discontinuation of TEMODAR and, in some cases, recurred upon rechallenge.
Hematopoietic: Prolonged pancytopenia, which may result in aplastic anemia and fatal outcomes.
Hepatobiliary: Fatal and severe hepatotoxicity, elevation of liver enzymes, hyperbilirubinemia, cholestasis, and hepatitis.
Infections: Serious opportunistic infections, including some cases with fatal outcomes, with bacterial, viral (primary and reactivated), fungal, and protozoan organisms.
Pulmonary: Interstitial pneumonitis, pneumonitis, alveolitis, and pulmonary fibrosis.
Endocrine: Diabetes insipidus.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], TEMODAR can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Available postmarketing reports describe cases of spontaneous abortions and congenital malformations, including polymalformations with central nervous system, facial, cardiac, skeletal, and genitourinary system anomalies with exposure to TEMODAR during pregnancy. These cases report similar adverse developmental outcomes to those observed in animal studies. Administration of TEMODAR to rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis caused numerous external, internal, and skeletal malformations at doses less than the maximum human dose based on body surface area (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Animal Data
Five consecutive days of oral administration of temozolomide at doses of 75 and 150 mg/m2 (0.38 and 0.75 times the human dose of 200 mg/m2) in rats and rabbits, respectively, during the period of organogenesis (Gestation Days 8-12) caused numerous malformations of the external and internal organs and skeleton in both species. In rabbits, temozolomide at the 150 mg/m2 dose (0.75 times the human dose of 200 mg/m2) caused embryolethality as indicated by increased resorptions.
8.2 Lactation
There are no data on the presence of TEMODAR or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on a breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including myelosuppression from temozolomide in the breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TEMODAR and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
TEMODAR can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating TEMODAR [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TEMODAR and for 6 months after the last dose.
Males
Because of the potential for embryofetal toxicity and genotoxic effects on sperm cells, advise male patients with pregnant partners or female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with TEMODAR and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Advise male patients not to donate semen during treatment with TEMODAR and for 3 months after the last dose.
Infertility
TEMODAR may impair male fertility [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Limited data from male patients show changes in sperm parameters during treatment with TEMODAR; however, no information is available on the duration or reversibility of these changes.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TEMODAR have not been established in pediatric patients. Safety and effectiveness of TEMODAR capsules were assessed, but not established, in 2 open-label studies in pediatric patients aged 3 to 18 years. In one study, 29 patients with recurrent brain stem glioma and 34 patients with recurrent high-grade astrocytoma were enrolled. In a second study conducted by the Children's Oncology Group (COG), 122 patients were enrolled, including patients with medulloblastoma/PNET (29), high grade astrocytoma (23), low grade astrocytoma (22), brain stem glioma (16), ependymoma (14), other CNS tumors (9), and non-CNS tumors (9). The adverse reaction profile in pediatric patients was similar to adults.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In MK-7365-051, 15% of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma were 65 years and older. This study did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine differences in effectiveness from younger patients. No overall differences in safety were observed between patients ≥65 years and younger patients.
The CATNON trial did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine differences in safety or effectiveness when compared to younger patients.
In MK-7365-006, 4% of patients with refractory anaplastic astrocytoma were 70 years and older. This study did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 70 years and older to determine differences in effectiveness from younger patients. Patients 70 years and older had a higher incidence of Grade 4 neutropenia (25%) and Grade 4 thrombocytopenia (20%) in the first cycle of therapy than patients less than 70 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In the entire safety database for which hematologic data exist (N=932), 7% (4/61) and 10% (6/63) of patients >70 years experienced Grade 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia in the first cycle, respectively. For patients ≤70 years, 7% (62/871) and 6% (48/879) experienced Grade 4 neutropenia or thrombocytopenia in the first cycle, respectively. Pancytopenia, leukopenia, and anemia also occurred.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) of 36 to 130 mL/min/m2 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The recommended dose of TEMODAR has not been established for patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr <36 mL/min/m2) or for patients with end-stage renal disease on dialysis.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh class A and B) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The recommended dose of TEMODAR has not been established for patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C).
10 OVERDOSAGE
Dose-limiting toxicity was myelosuppression and was reported with any dose but is expected to be more severe at higher doses. An overdose of 2000 mg per day for 5 days was taken by one patient and the adverse reactions reported were pancytopenia, pyrexia, multi-organ failure, and death. There are reports of patients who have taken more than 5 days of treatment (up to 64 days), with adverse reactions reported including myelosuppression, which in some cases was severe and prolonged, and infections and resulted in death. In the event of an overdose, monitor complete blood count and provide supportive measures as necessary.
11 DESCRIPTION
Temozolomide is an alkylating drug. The chemical name of temozolomide is 3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-4-oxoimidazo[5,1-d]-as-tetrazine-8-carboxamide. The structural formula of temozolomide is:
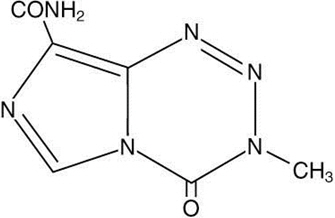
The material is a white to light tan or light pink powder with a molecular formula of C6H6N6O2 and a molecular weight of 194.15. The molecule is stable at acidic pH (<5) and labile at pH >7; hence TEMODAR can be administered orally and intravenously. The prodrug, temozolomide, is rapidly hydrolyzed to the active 5-(3-methyltriazen-1-yl) imidazole-4-carboxamide (MTIC) at neutral and alkaline pH values, with hydrolysis taking place even faster at alkaline pH.
TEMODAR capsules
TEMODAR (temozolomide) capsules for oral use contains either 5 mg, 20 mg, 100 mg, 140 mg, 180 mg, or 250 mg of temozolomide. The inactive ingredients are as follows:
- TEMODAR 5 mg: lactose anhydrous (132.8 mg), colloidal silicon dioxide (0.2 mg), sodium starch glycolate (7.5 mg), tartaric acid (1.5 mg), and stearic acid (3 mg).
- TEMODAR 20 mg: lactose anhydrous (182.2 mg), colloidal silicon dioxide (0.2 mg), sodium starch glycolate (11 mg), tartaric acid (2.2 mg), and stearic acid (4.4 mg).
- TEMODAR 100 mg: lactose anhydrous (175.7 mg), colloidal silicon dioxide (0.3 mg), sodium starch glycolate (15 mg), tartaric acid (3 mg), and stearic acid (6 mg).
- TEMODAR 140 mg: lactose anhydrous (246 mg), colloidal silicon dioxide (0.4 mg), sodium starch glycolate (21 mg), tartaric acid (4.2 mg), and stearic acid (8.4 mg).
- TEMODAR 180 mg: lactose anhydrous (316.3 mg), colloidal silicon dioxide (0.5 mg), sodium starch glycolate (27 mg), tartaric acid (5.4 mg), and stearic acid (10.8 mg).
- TEMODAR 250 mg: lactose anhydrous (154.3 mg), colloidal silicon dioxide (0.7 mg), sodium starch glycolate (22.5 mg), tartaric acid (9 mg), and stearic acid (13.5 mg).
The body of the capsules is made of gelatin and is opaque white. The cap is also made of gelatin, and the colors vary based on the dosage strength. The capsule body and cap are imprinted with pharmaceutical branding ink, which contains shellac, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, purified water, strong ammonia solution, potassium hydroxide, and ferric oxide.
- TEMODAR 5 mg: The green cap contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, iron oxide yellow, sodium lauryl sulfate, and FD&C Blue #2.
- TEMODAR 20 mg: The yellow cap contains gelatin, sodium lauryl sulfate, and iron oxide yellow.
- TEMODAR 100 mg: The pink cap contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, sodium lauryl sulfate, and iron oxide red.
- TEMODAR 140 mg: The blue cap contains gelatin, sodium lauryl sulfate, and FD&C Blue #2.
- TEMODAR 180 mg: The orange cap contains gelatin, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, titanium dioxide, and sodium lauryl sulfate.
- TEMODAR 250 mg: The white cap contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, and sodium lauryl sulfate.
TEMODAR for injection
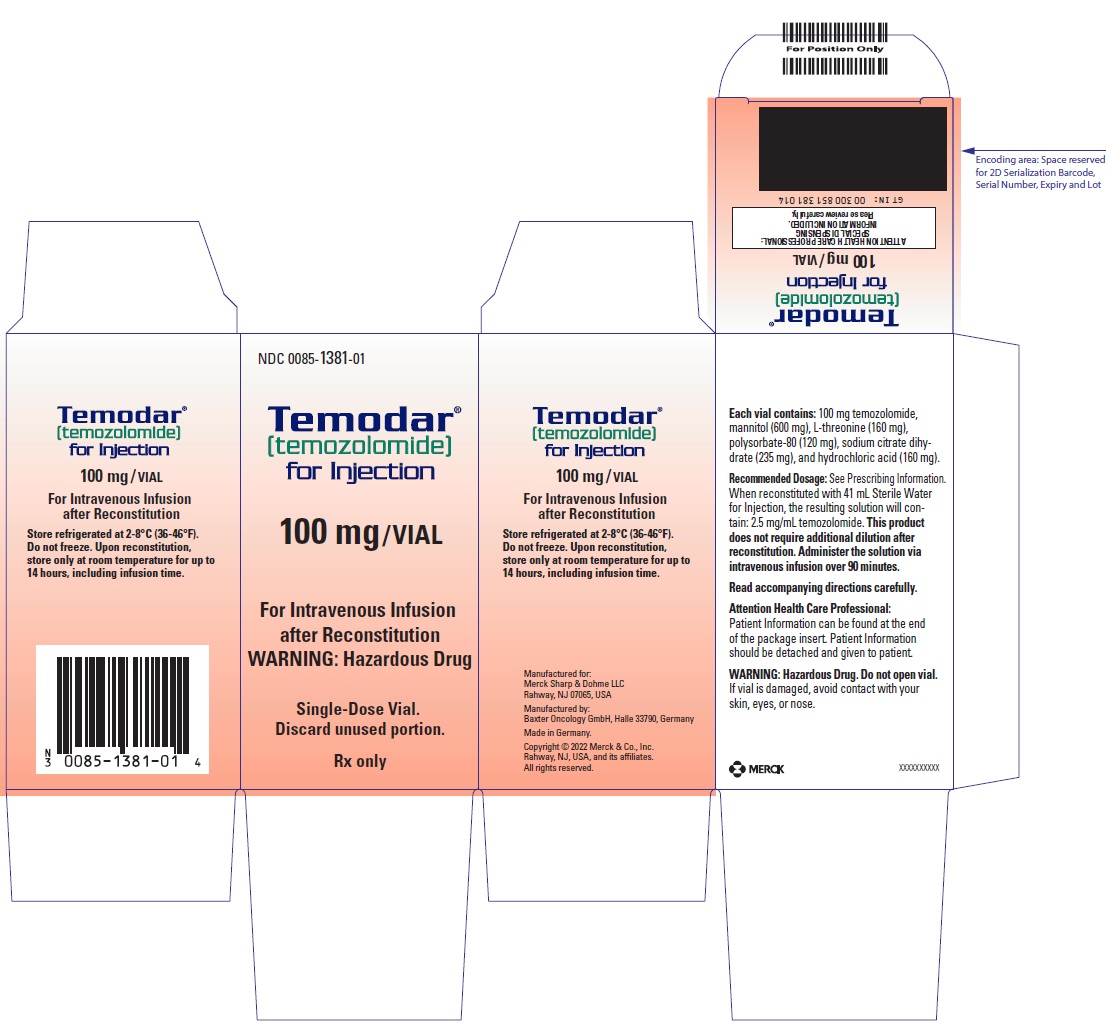
TEMODAR (temozolomide) for injection is for intravenous use. Each single-dose vial contains 100 mg of sterile and pyrogen-free lyophilized powder. The inactive ingredients are: mannitol (600 mg), L-threonine (160 mg), polysorbate 80 (120 mg), sodium citrate dihydrate (235 mg), and hydrochloric acid (160 mg).
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Temozolomide is not directly active but undergoes rapid nonenzymatic conversion at physiologic pH to the reactive compound 5-(3-methyltriazen-1-yl)-imidazole-4-carboxamide (MTIC). The cytotoxicity of MTIC is thought to be primarily due to DNA alkylation, mainly at the O6 and N7 positions of guanine, which causes DNA double strand breaks and results in programmed cell death.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Temozolomide exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following a single oral dose of 150 mg/m2, the mean Cmax is 7.5 mcg/mL for temozolomide and 282 ng/mL for MTIC. The mean AUC is 23.4 mcg∙hr/mL for temozolomide and 864 ng∙hr/mL for MTIC.
Following a single 90-minute intravenous infusion of 150 mg/m2, the mean Cmax is 7.3 mcg/mL for temozolomide and 276 ng/mL for MTIC. The mean AUC is 24.6 mcg∙hr/mL for temozolomide and 891 ng∙hr/mL for MTIC.
Temozolomide exhibits linear kinetics over the therapeutic dosing range of 75 mg/m2/day to 250 mg/m2/day.
Absorption
The median Tmax is 1 hour.
Effect of Food
The mean temozolomide Cmax and AUC decreased by 32% and 9%, respectively, and median Tmax increased by 2-fold (from 1 to 2.25 hours) when TEMODAR capsules were administered after a modified high-fat breakfast (587 calories comprised of 1 fried egg, 2 strips of bacon, 2 slices of toast, 2 pats of butter, and 8 oz whole milk).
Distribution
Temozolomide has a mean (CV%) apparent volume of distribution of 0.4 L/kg (13%). The mean percent bound of drug-related total radioactivity is 15%.
Elimination
Clearance of temozolomide is approximately 5.5 L/hr/m2 and the mean elimination half-life is 1.8 hours.
Metabolism
Temozolomide is spontaneously hydrolyzed at physiologic pH to the active species, MTIC and to temozolomide acid metabolite. MTIC is further hydrolyzed to 5-amino-imidazole-4-carboxamide (AIC), which is known to be an intermediate in purine and nucleic acid biosynthesis, and to methylhydrazine, which is believed to be the active alkylating species. Cytochrome P450 enzymes play a minor role in the metabolism of temozolomide and MTIC. Relative to the AUC of temozolomide, the exposure to MTIC and AIC is 2.4% and 23%, respectively.
Excretion
Approximately 38% of the administered temozolomide total radioactive dose is recovered over 7 days: 38% in urine and 0.8% in feces. The majority of the recovered radioactivity in urine is unchanged temozolomide (6%), AIC (12%), temozolomide acid metabolite (2.3%), and unidentified polar metabolite(s) (17%).
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of temozolomide were observed based on age (range: 19 to 78 years), gender, smoking status (smoker vs. non-smoker), creatinine clearance (CLcr) of 36 to 130 mL/min/m2, or mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh class A and B). The pharmacokinetics of temozolomide has not been studied in patients with CLcr <36 mL/min/m2, end-stage renal disease on dialysis, or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C).
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of temozolomide or MTIC were observed when co-administered with ranitidine.
No clinically significant differences in the clearance of temozolomide or MTIC were predicted when co-administered with the following drugs: valproic acid, dexamethasone, prochlorperazine, phenytoin, carbamazepine, ondansetron, histamine-2-receptor antagonists, or phenobarbital.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Temozolomide is carcinogenic in rats at doses less than the maximum recommended human dose. Temozolomide induced mammary carcinomas in both males and females at doses 0.13 to 0.63 times the maximum human dose (25-125 mg/m2) when administered orally on 5 consecutive days every 28 days for 6 cycles. Temozolomide also induced fibrosarcomas of the heart, eye, seminal vesicles, salivary glands, abdominal cavity, uterus, and prostate, carcinomas of the seminal vesicles, schwannomas of the heart, optic nerve, and harderian gland, and adenomas of the skin, lung, pituitary, and thyroid at doses 0.5 times the maximum daily dose. Mammary tumors were also induced following 3 cycles of temozolomide at the maximum recommended daily dose.
Temozolomide is a mutagen and a clastogen. In a reverse bacterial mutagenesis assay (Ames assay), temozolomide increased revertant frequency in the absence and presence of metabolic activation. Temozolomide was clastogenic in human lymphocytes in the presence and absence of metabolic activation.
Temozolomide impairs male fertility. Temozolomide caused syncytial cells/immature sperm formation at doses of 50 and 125 mg/m2 (0.25 and 0.63 times the human dose of 200 mg/m2) in rats and dogs, respectively, and testicular atrophy in dogs at 125 mg/m2.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Toxicology studies in rats and dogs identified a low incidence of hemorrhage, degeneration, and necrosis of the retina at temozolomide doses equal to or greater than 125 mg/m2 (0.63 times the human dose of 200 mg/m2). These changes were most commonly seen at doses where mortality was observed.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma
The efficacy of TEMODAR was evaluated in MK-7365-051 (NCT00006353), a randomized (1:1), multicenter, open-label trial. Eligible patients were required to have newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Patients were randomized to receive either radiation therapy alone or concomitant TEMODAR 75 mg/m2 once daily starting the first day of radiation therapy and continuing until the last day of radiation therapy for 42 days (with a maximum of 49 days), followed by TEMODAR 150 mg/m2 or 200 mg/m2 once daily on Days 1 to 5 of each 28-day cycle, starting 4 weeks after the end of radiation therapy and continuing for 6 cycles. In both arms, focal radiation therapy was delivered as 60 Gy/30 fractions and included radiation to the tumor bed or resection site with a 2- to 3-cm margin. PCP prophylaxis was required during the concomitant phase regardless of lymphocyte count and continued until recovery of lymphocyte count to Grade 1 or less. The major efficacy outcome measure was overall survival.
A total of 573 patients were randomized, 287 to TEMODAR and radiation therapy and 286 to radiation therapy alone. At the time of disease progression, TEMODAR was administered as salvage therapy in 161 patients of the 282 (57%) in the radiation therapy alone arm and 62 patients of the 277 (22%) in the TEMODAR and radiation therapy arm.
The addition of concomitant and maintenance TEMODAR to radiation therapy for the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma showed a statistically significant improvement in overall survival compared to radiotherapy alone (Figure 1). The hazard ratio (HR) for overall survival was 0.63 (95% CI: 0.52, 0.75) with a log-rank P<0.0001 in favor of the TEMODAR arm. The median overall survival was 14.6 months in the TEMODAR arm and 12.1 months for radiation therapy alone arm.
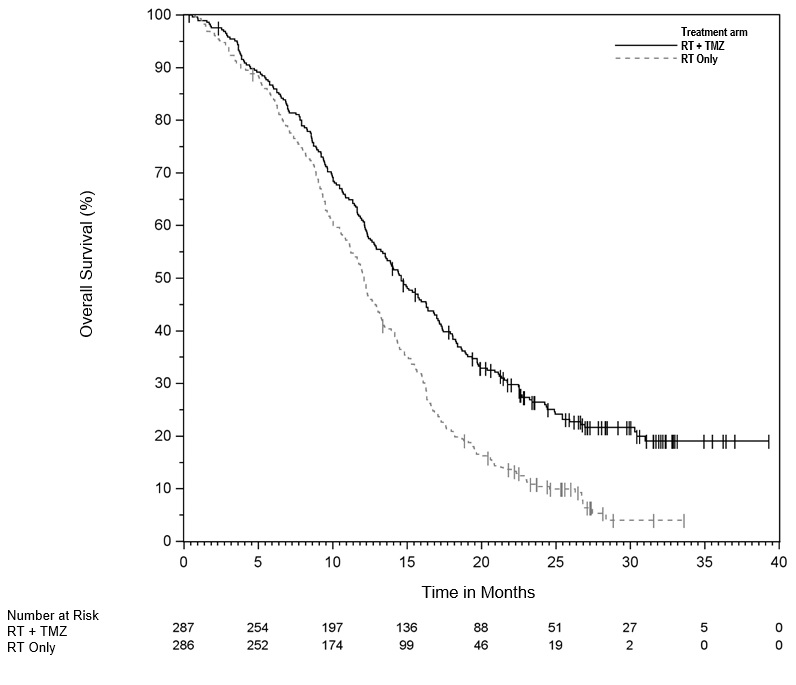 |
14.2 Anaplastic Astrocytoma
Newly Diagnosed Anaplastic Astrocytoma
The efficacy of TEMODAR for the adjuvant treatment of newly diagnosed anaplastic astrocytoma was derived from studies of TEMODAR in the published literature. TEMODAR was evaluated in CATNON (NCT00626990), a randomized, open-label, multicenter trial, where the major efficacy outcome measure was overall survival.
Refractory Anaplastic Astrocytoma
The efficacy of TEMODAR was evaluated in Study MK-7365-006, a single-arm, multicenter trial. Eligible patients had anaplastic astrocytoma at first relapse and a baseline Karnofsky performance status (KPS) of 70 or greater. Patients had previously received radiation therapy and may also have previously received a nitrosourea with or without other chemotherapy. Fifty-four patients had disease progression on prior therapy with both a nitrosourea and procarbazine and their malignancy was considered refractory to chemotherapy (refractory anaplastic astrocytoma population). TEMODAR capsules were given on Days 1 to 5 of each 28-day cycle at a starting dose of 150 mg/m2/day. If ANC was ≥1.5 × 109/L and platelet count was ≥100 × 109/L at the nadir and on Day 1 of the next cycle, the TEMODAR dose was increased to 200 mg/m2/day. The major efficacy outcome measure was progression-free survival at 6 months and the additional efficacy outcome measures were overall survival and overall response rate.
In the refractory anaplastic astrocytoma population (n=54), the median age was 42 years (range: 19 to 76); 65% were male; and 72% had a KPS of >80. Sixty-three percent of patients had surgery other than a biopsy at the time of initial diagnosis. Of those patients undergoing resection, 73% underwent a subtotal resection and 27% underwent a gross total resection. Eighteen percent of patients had surgery at the time of first relapse. The median time from initial diagnosis to first relapse was 13.8 months (range: 4.2 months to 6.3 years).
In the refractory anaplastic astrocytoma population, the overall response rate (CR+PR) was 22% (12 of 54 patients) and the complete response rate was 9% (5 of 54 patients). The median duration of all responses was 50 weeks (range: 16 to 114 weeks) and the median duration of complete responses was 64 weeks (range: 52 to 114 weeks). In this population, progression-free survival at 6 months was 45% (95% CI: 31%, 58%) and progression-free survival at 12 months was 29% (95% CI: 16%, 42%). Median progression-free survival was 4.4 months. Overall survival at 6 months was 74% (95% CI: 62%, 86%) and 12-month overall survival was 65% (95% CI: 52%, 78%). Median overall survival was 15.9 months.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
TEMODAR is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
TEMODAR capsules
TEMODAR capsules are supplied in child-resistant sachets containing the following capsule strengths:
5 mg: opaque white bodies with green caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR”. They are supplied as follows:
- 5-count – NDC 0085-3004-03
- 14-count – NDC 0085-3004-04
20 mg: opaque white bodies with yellow caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR”. They are supplied as follows:
- 5-count – NDC 0085-1519-03
- 14-count – NDC 0085-1519-04
100 mg: opaque white bodies with pink caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR”. They are supplied as follows:
- 5-count – NDC 0085-1366-03
- 14-count – NDC 0085-1366-04
140 mg: opaque white bodies with blue caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR”. They are supplied as follows:
- 5-count – NDC 0085-1425-03
- 14-count – NDC 0085-1425-04
180 mg: opaque white bodies with orange caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR”. They are supplied as follows:
- 5-count – NDC 0085-1430-03
- 14-count – NDC 0085-1430-04
250 mg: opaque white bodies with white caps. The capsule body is imprinted with two stripes, the dosage strength, and the Schering-Plough logo. The cap is imprinted with “TEMODAR”. They are supplied as follows:
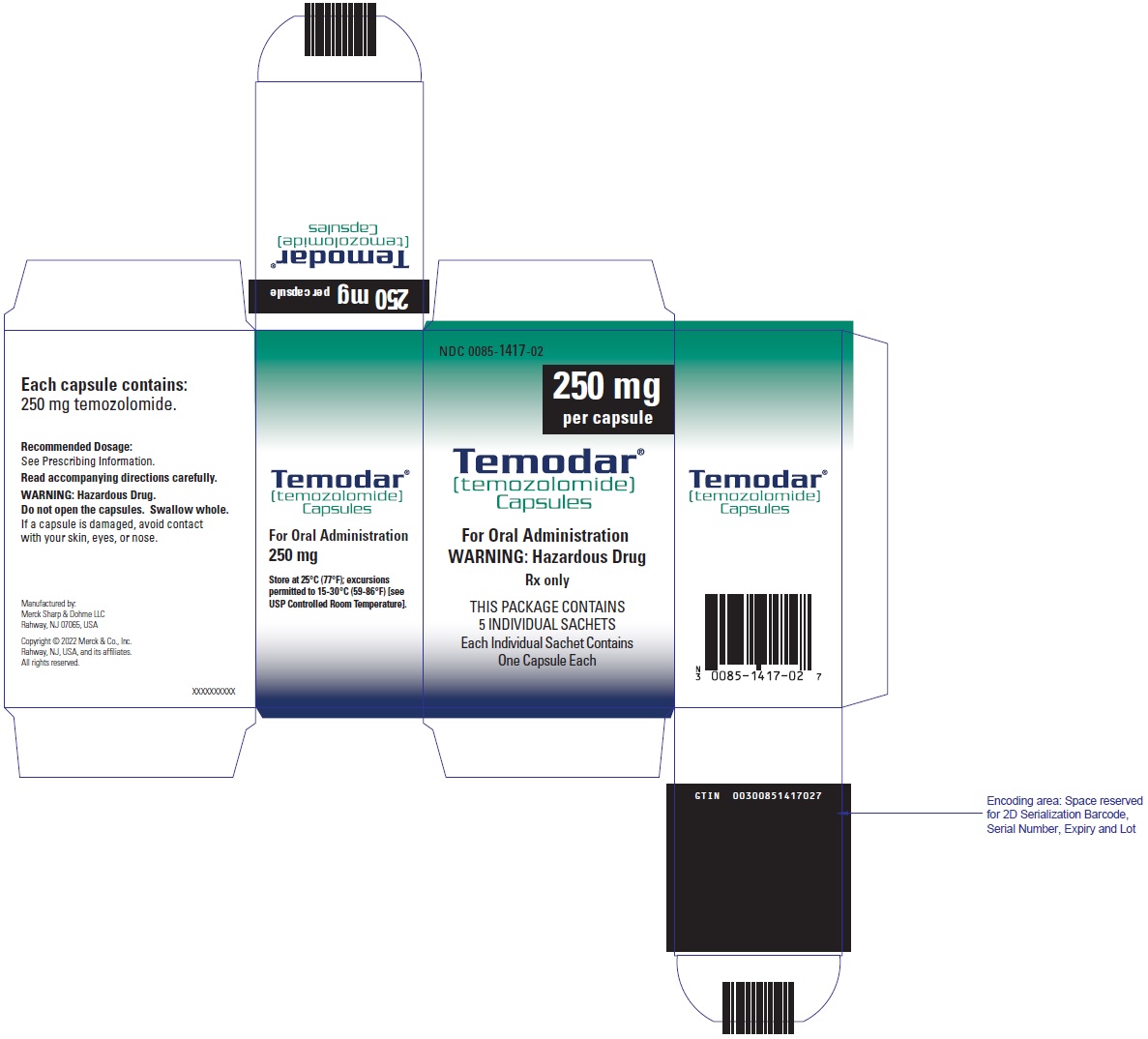
- 5-count – NDC 0085-1417-02
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Myelosuppression
Inform patients that TEMODAR can cause low blood cell counts and the need for frequent monitoring of blood cell counts. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for bleeding, fever, or other signs of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hepatotoxicity
Advise patients of the increased risk of hepatotoxicity and to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs or symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Inform patients that they will have periodic liver enzyme tests during treatment and following the last dose of TEMODAR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Pneumocystis Pneumonia
Advise patients of the increased risk of Pneumocystis pneumonia and to contact their healthcare provider immediately for new or worsening pulmonary symptoms. Inform patients that prophylaxis for Pneumocystis pneumonia may be needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Secondary Malignancies
Advise patients of the increased risk of myelodysplastic syndrome and secondary malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Exposure to Opened Capsules
Advise patient to not open, chew, or dissolve the capsules. If capsules are accidentally opened or damaged, advise patients to take rigorous precautions with capsule contents to avoid inhalation or contact with the skin or mucous membranes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. In case of powder contact, wash the affected area with water immediately [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TEMODAR and for 6 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise male patients with pregnant partners or female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with TEMODAR and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Advise male patients not to donate semen during treatment with TEMODAR and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with TEMODAR and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise males of reproductive potential that TEMODAR may impair fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Distributed by: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC
Rahway, NJ 07065, USA
For patent information: www.msd.com/research/patent
Copyright © 1999-2023 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, and its affiliates.
All rights reserved.
uspi-mk7365-mtl-2309r024
| Patient Information | ||
|---|---|---|
| TEMODAR® (tem-o-dar) (temozolomide) capsules | TEMODAR® (tem-o-dar) (temozolomide) for injection |
|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 9/2023 | |
| What is TEMODAR? | ||
| TEMODAR is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with certain brain cancer tumors. | ||
| It is not known if TEMODAR is safe and effective in children. | ||
| Do not take TEMODAR if you: | ||
|
||
| Before taking or receiving TEMODAR, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | ||
|
||
| Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | ||
| Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | ||
| How should I take TEMODAR? | ||
| TEMODAR may be taken 2 different ways: | ||
|
||
| There are 2 common dosing schedules for taking or receiving TEMODAR depending on the type of brain cancer tumor that you have. | ||
|
||
|
||
| TEMODAR capsules: | ||
|
||
| TEMODAR for injection: | ||
|
||
| What are the possible side effects of TEMODAR? | ||
| TEMODAR can cause serious side effects, including: | ||
|
||
| Common side effects of TEMODAR include: | ||
|
|
|
| Additional side effects seen with TEMODAR for injection include: | ||
|
||
| TEMODAR can affect fertility in males and may affect your ability to father a child. Talk with your healthcare provider if fertility is a concern for you. | ||
| Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. | ||
| These are not all the possible side effects of TEMODAR. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. | ||
| Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||
| How should I store TEMODAR capsules? | ||
|
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of TEMODAR. | ||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use TEMODAR for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give TEMODAR to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about TEMODAR that is written for health professionals. | ||
| What are the ingredients in TEMODAR? | ||
| TEMODAR capsules: | ||
| Active ingredient: temozolomide | ||
| Inactive ingredients: lactose anhydrous, colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium starch glycolate, tartaric acid, stearic acid. | ||
| The body of the capsules is made of gelatin and is opaque white. The cap is also made of gelatin, and the colors vary based on the dosage strength. The capsule body and cap are imprinted with pharmaceutical branding ink, which contains shellac, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, purified water, strong ammonia, potassium hydroxide, and ferric oxide. | ||
| TEMODAR 5 mg: The green cap contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, iron oxide yellow, sodium lauryl sulfate, and FD&C Blue #2. | ||
| TEMODAR 20 mg: The yellow cap contains gelatin, sodium lauryl sulfate, and iron oxide yellow. | ||
| TEMODAR 100 mg: The pink cap contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, sodium lauryl sulfate, and iron oxide red. | ||
| TEMODAR 140 mg: The blue cap contains gelatin, sodium lauryl sulfate, and FD&C Blue #2. | ||
| TEMODAR 180 mg: The orange cap contains gelatin, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, titanium dioxide, and sodium lauryl sulfate. | ||
| TEMODAR 250 mg: The white cap contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, and sodium lauryl sulfate. | ||
| TEMODAR for injection: | ||
| Active ingredient: temozolomide. | ||
| Inactive ingredients: mannitol, L-threonine, polysorbate 80, sodium citrate dihydrate, and hydrochloric acid. | ||
| Distributed by: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, Rahway, NJ 07065, USA | ||
| For patent information: www.msd.com/research/patent | ||
| The trademarks depicted herein are owned by their respective companies. | ||
| Copyright © 1999-2023 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, and its affiliates.
All rights reserved. |
||
| usppi-mk7365-mtl-2309r013 For more information, go to www.TEMODAR.com or call 1-877-888-4231. |
||
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg Capsule Sachet Carton
NDC 0085-3004-03
5 mg
per capsule
Temodar®
[temozolomide]
Capsules
For Oral Administration
WARNING: Hazardous Drug
Rx only
THIS PACKAGE CONTAINS
5 INDIVIDUAL SACHETS
Each Individual Sachet Contains
One Capsule Each
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mg Capsule Sachet Carton
NDC 0085-1519-03
20 mg
per capsule
Temodar®
[temozolomide]
Capsules
For Oral Administration
WARNING: Hazardous Drug
Rx only
THIS PACKAGE CONTAINS
5 INDIVIDUAL SACHETS
Each Individual Sachet Contains
One Capsule Each
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg Capsule Sachet Carton
NDC 0085-1366-03
100 mg
per capsule
Temodar®
[temozolomide]
Capsules
For Oral Administration
WARNING: Hazardous Drug
Rx only
THIS PACKAGE CONTAINS
5 INDIVIDUAL SACHETS
Each Individual Sachet Contains
One Capsule Each
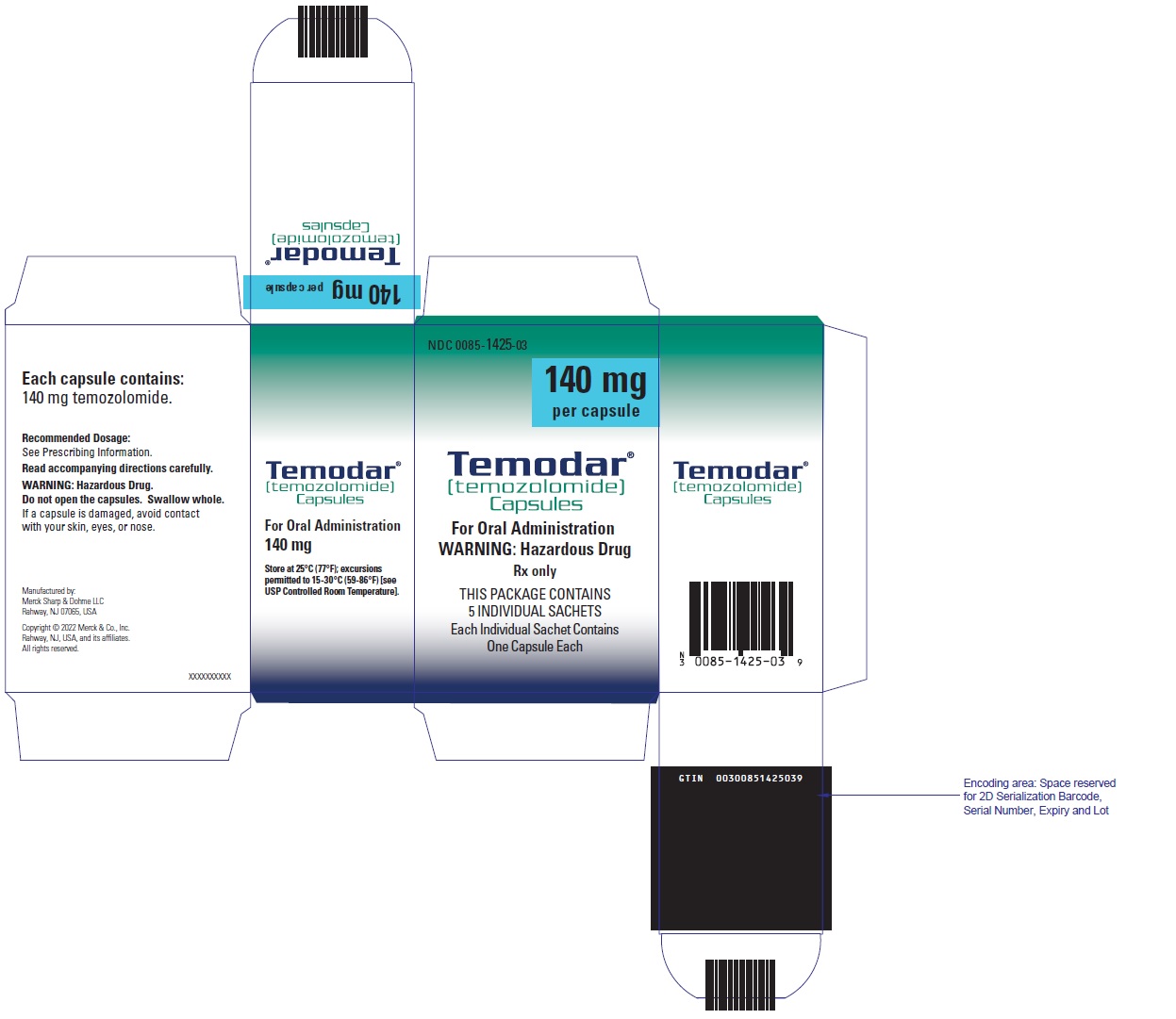
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 140 mg Capsule Sachet Carton
NDC 0085-1425-03
140 mg
per capsule
Temodar®
[temozolomide]
Capsules
For Oral Administration
WARNING: Hazardous Drug
Rx only
THIS PACKAGE CONTAINS
5 INDIVIDUAL SACHETS
Each Individual Sachet Contains
One Capsule Each
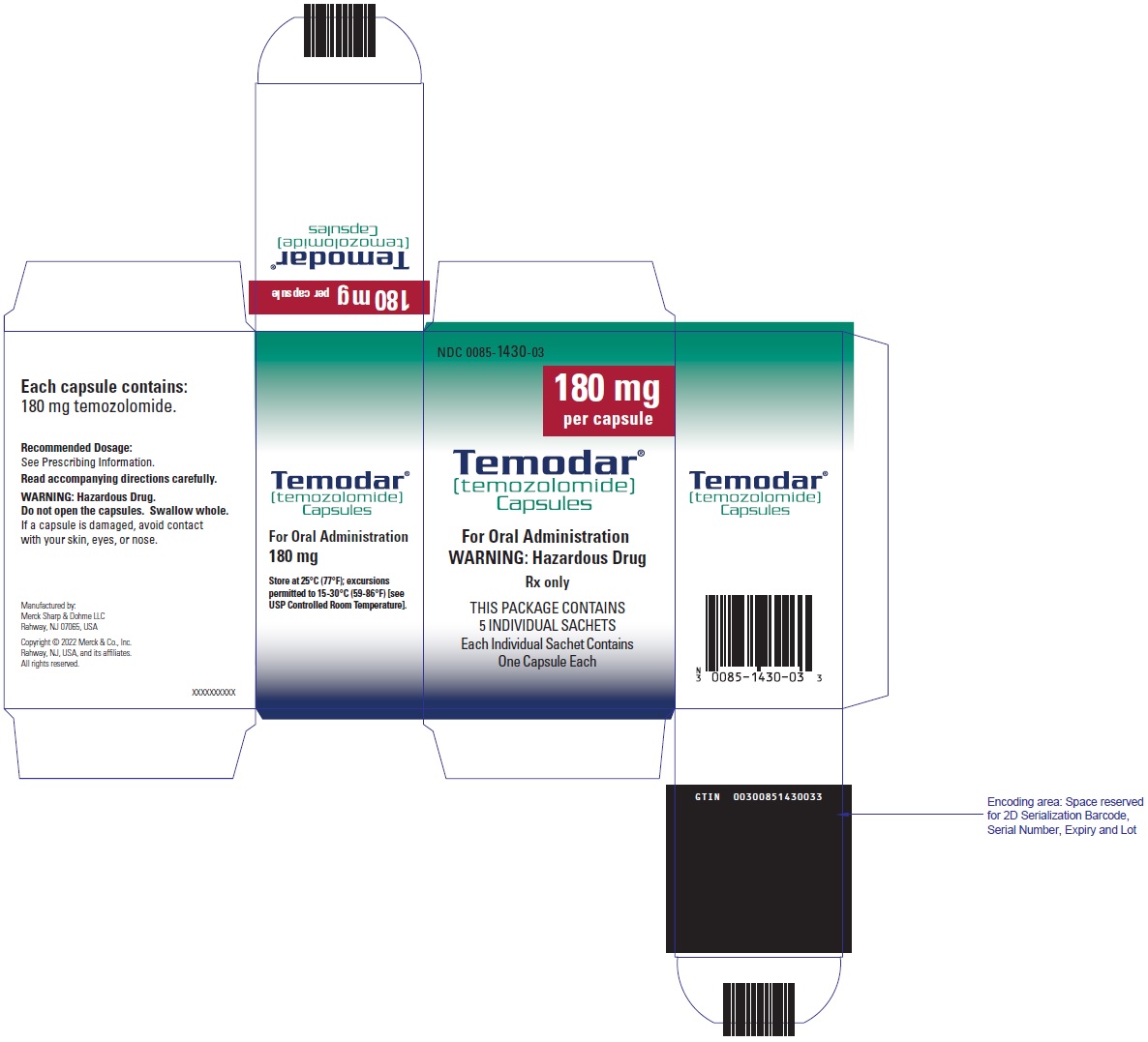
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 180 mg Capsule Sachet Carton
NDC 0085-1430-03
180 mg
per capsule
Temodar®
[temozolomide]
Capsules
For Oral Administration
WARNING: Hazardous Drug
Rx only
THIS PACKAGE CONTAINS
5 INDIVIDUAL SACHETS
Each Individual Sachet Contains
One Capsule Each