LILETTA- levonorgestrel intrauterine device
Actavis Pharma, Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LILETTA® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LILETTA.
LILETTA (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Initial U.S. Approval: 1968 (norgestrel) INDICATIONS AND USAGELILETTA is a progestin-containing intrauterine system indicated for prevention of pregnancy for up to 6 years. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSThe most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials (> 10% users) are vulvovaginal mycotic infections, vaginal bacterial infections, acne, and nausea or vomiting. (6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 10/2019 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Over Time
LILETTA contains 52 mg of levonorgestrel (LNG). Initially, LNG is released at a rate of approximately 20 mcg/day. This rate decreases progressively to approximately 8.6 mcg/day after 6 years. The average in vivo release rate of LNG is approximately 14.3 mcg/day over a period of 6 years.
LILETTA can be removed at any time but must be removed by the end of the sixth year. LILETTA can be replaced at the time of removal with a new LILETTA if continued contraceptive protection is desired.
2.2 Timing of Insertion
Refer to Table 1 for instruction on when to start use of LILETTA.
| Starting LILETTA in women not currently using hormonal or intrauterine contraception
|
|
| Switching to Liletta from an oral, transdermal or vaginal hormonal contraceptive |
|
| Switching to LILETTA from an injectable progestin contraceptive |
|
| Switching to LILETTA from a contraceptive implant or another IUS |
|
| Inserting LILETTA after abortion or miscarriage | |
|
|
|
|
| Inserting LILETTA after Childbirth
|
|
2.3 Insertion Instructions
LILETTA (Figure 1) is provided in a sterile pouch [see Description (11)] and is inserted into the uterine cavity with the provided inserter (Figure 2) by carefully following the insertion instructions. Do not use if the seal of the sterile package is broken or appears compromised. Use strict aseptic techniques throughout the insertion procedure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. LILETTA is for single use only.
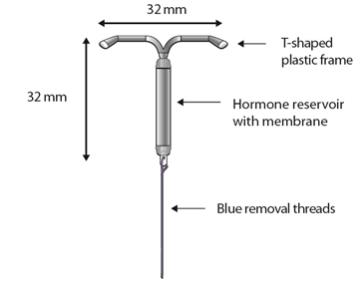
Figure 1 LILETTA Intrauterine Contraceptive System (IUS)
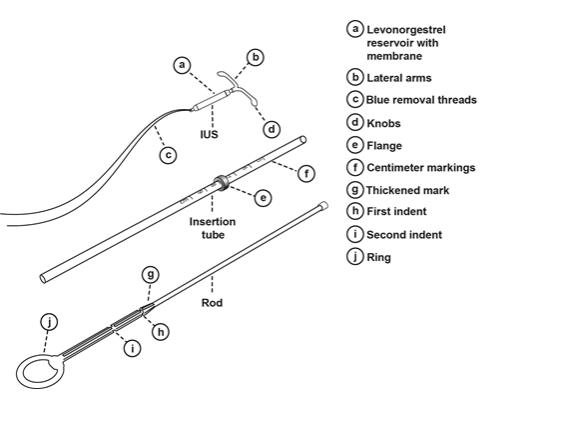
Figure 2: LILETTA IUS with Inserter
Insertion
LILETTA should only be inserted by a trained healthcare professional. Healthcare professionals should become thoroughly familiar with the product, product educational materials, product insertion instructions, prescribing information, and patient labeling before attempting insertion of LILETTA.
- Obtain a complete medical and social history to determine conditions that might influence the selection of LILETTA for contraception. If indicated, perform a physical examination and appropriate tests for genital or sexually transmitted infections. [See Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.10).]
- Check the expiration date on the box before opening it. Do not insert LILETTA after the expiration date.
- Visually inspect the packaging (sealed pouch) containing LILETTA to verify that the packaging has not been damaged (e.g., torn, punctured, etc.). If the packaging has any visual damage that could compromise sterility, do not use the unit for insertion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Ensure that the patient understands the contents of the Patient Information Booklet and obtain consent. A sample consent form that includes the lot number is on the last page of the Patient Information Booklet.
- Complete the pelvic examination, speculum placement, tenaculum placement, and sounding of the uterus before opening the LILETTA pouch.
- Do not open the pouch to insert LILETTA if:
○ the cervix is unable to be properly visualized
○ the uterus cannot be adequately instrumented (during sounding)
○ the uterus sounds to less than 5.5 cm
Planning for Insertion
- Ensure all needed items for LILETTA insertion are readily available:
- Gloves
- Sterile speculum
- Sterile uterine sound
- Sterile tenaculum
- Antiseptic solution
- LILETTA with inserter in sealed pouch
- Sterile, blunt-tipped scissors
- Additional items that may be useful could include:
- Local anesthesia, needle, and syringe
- Sterile os finder and/or cervical dilators
- Ultrasound with abdominal probe
- Local anesthesia, needle, and syringe
- Gloves
- Exclude pregnancy and confirm that there are no other contraindications to the insertion and use of LILETTA.
- Follow the insertion instructions exactly as described in order to ensure proper insertion.
- If you encounter cervical stenosis at any time during uterine sounding or LILETTA insertion, use cervical dilators, not force, to overcome resistance. If necessary, dilation, sounding, and insertion may be performed with ultrasound guidance.
- Insertion may be associated with some pain and/or bleeding or vasovagal reactions (e.g., diaphoresis, syncope, bradycardia, or seizure), especially in patients with a predisposition to these conditions. Consider administering analgesics prior to insertion.
Use aseptic technique during the entire insertion procedure. Loading and inserting LILETTA can be done with or without sterile gloves. If not using sterile gloves, complete all steps for loading the IUS (Steps 1-7) inside the pouch. Maintain sterility during LILETTA insertion; do not touch LILETTA or parts of any sterile instrument that will pierce tissue (e.g., a tenaculum on the cervix) or go into the uterine cavity. If, at any step, there is a need to touch a sterile surface, sterile gloves should be used.
Preparation for Insertion
- With the patient comfortably in lithotomy position, do a bimanual exam to establish the size, shape, and position of the uterus and to evaluate any signs of uterine infection.
- Gently insert a speculum to visualize the cervix.
- Thoroughly cleanse the cervix and vagina with antiseptic solution.
- Administer cervical anesthetic, if needed.
- Apply a tenaculum to the cervix and use gentle traction to align the cervical canal with the uterine cavity. If the uterus is retroverted, it may be more appropriate to grasp the lower lip of the cervix. Keep the tenaculum in position and maintain gentle traction on the cervix throughout the insertion procedure.
- Carefully sound the uterus to measure its depth.
- The uterus should sound to a depth of at least 5.5 cm. Insertion of LILETTA into a uterine cavity that sounds to less than 5.5 cm may increase the incidence of expulsion, bleeding, pain, perforation, and possibly pregnancy. LILETTA should not be inserted if the uterus sounds to less than 5.5 cm.
- After ascertaining that the patient is appropriate for LILETTA, replace contaminated glove(s) and open the pouch containing LILETTA.
Insertion Procedure
Loading the IUS into the Inserter
Step 1
- Place the LILETTA pouch on a flat surface with the clear side of the pouch facing up (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Place the LILETTA pouch on a flat surface.
- Open the sterile LILETTA pouch from the bottom (end with the rod ring) approximately 1/3 of the way until the lower ends of the IUS threads, the rod, and the insertion tube are exposed (Figure 4).
If using sterile gloves, you can open the pouch completely before putting on the sterile gloves.
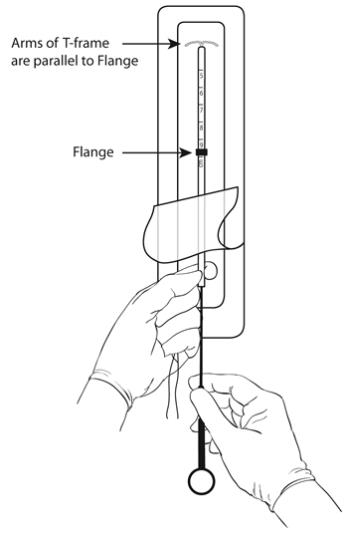
Figure 4: Release the threads from the flange and insert the rod.
Step 2
- Pull back the blue threads to dislodge them from the flange.
- Be careful to not pull the IUS down at the same time (Figure 4).
Step 3
- Hold the exposed end of the insertion tube containing the IUS (Figure 4) while keeping the end of the insertion tube with the IUS inside the packaging.
- Remove the rod from the pouch.
- Do not touch the end of the rod that will go into the insertion tube.
- Place the rod into the insertion tube (alongside the IUS threads) to about the 5 cm marking (Figure 4).
Step 4
- While holding the insertion tube and the rod firmly between the fingers and thumb of one hand, pull downward on both blue threads with the other hand to draw the IUS into the insertion tube (Figure 5).
- The arms of the IUS should be kept in a horizontal plane, parallel to the flat side of the flange (refer to Figure 4).
- Do not pull the IUS all of the way through the insertion tube; only pull the threads until the IUS is loaded at the top of the insertion tube. Note: If you accidentally remove the IUS completely out of the insertion tube, do not use or attempt to re-load.

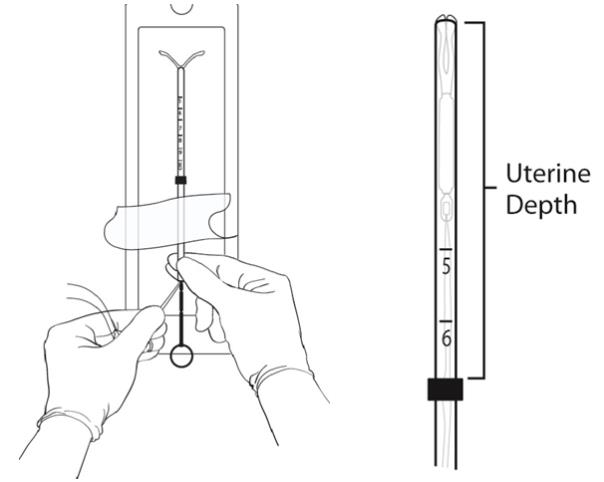
Step 5
- Hold the insertion tube and the rod firmly with one hand.
- With the other hand, adjust the position of the flange (through the sterile packaging if not using sterile gloves) by moving the tube to correspond to the sound measurement (Figure 6).
- The top end of the flange should be at the measurement corresponding to the sounded depth of the uterus.
Step 6
- Final IUS positioning: position the IUS in the tube so that the knobs of the lateral arms are opposed to each other and protrude slightly above the tip of the insertion tube to form a hemispherical dome (Figure 7).
- Hold the tube at its proximal end between your fingers and thumb of one hand.
- With the other hand, while pulling on the blue threads, slowly advance the rod forward to adjust the position of the IUS.
- When the IUS tips are in the correct position (slightly protruding), pinch and hold the proximal end of the tube firmly to maintain rod position.
- The proximal end of the insertion tube will be approximately at the top of the first indent on the rod (Figure 7).
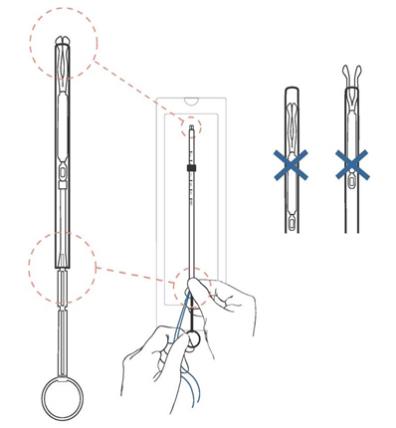
Figure 7: Final IUS Positioning
ENSURE A HEMISPHERICAL DOME IS ACHIEVED.
When the IUS is in the correct position, the lower end of the tube will be aligned approximately at the upper edge of the upper indent on the rod.
Step 7
Check to make sure the IUS is correctly loaded. You should note the following:
- The IUS is completely within the insertion tube with the knobs of the arms forming a hemispherical dome at the top of the tube.
- The top of the rod is touching the bottom of the IUS.
- The blue threads are hanging through the end of the insertion tube.
- The flange is marking the depth of the uterus based on pre-insertion sounding.
Step 8
Remove the loaded IUS insertion tube from the pouch while holding the lower end of the tube firmly between your fingers and thumb.
If not using sterile gloves, do not touch the flange and any part of the insertion tube above the flange during this step and through the IUS insertion procedure.
IUS Insertion into the Uterus
Step 1
- Apply gentle traction on the tenaculum to straighten the alignment of the cervical canal and uterine cavity.
- While still firmly pinching the proximal end of the insertion tube to maintain the IUS in the correct position (Hand A), slide the loaded IUS insertion tube through the cervical canal until the upper edge of the flange is approximately 1.5 – 2.0 cm from the cervix (Figure 8).
- DO NOT advance flange to the cervix at this step.
- DO NOT force the inserter. If necessary, dilate the cervical canal.

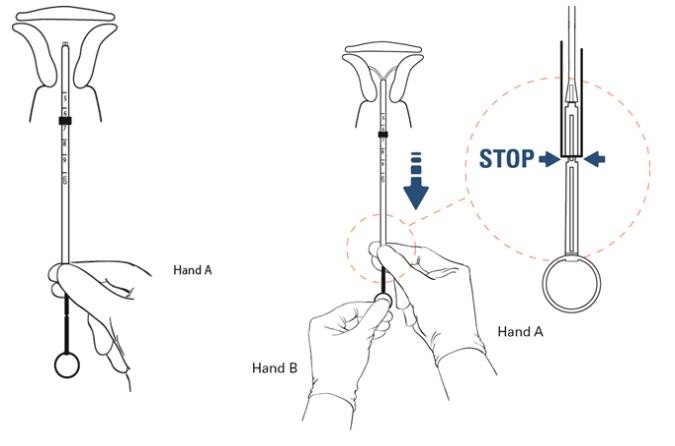
Step 2
- Release hold on the tenaculum.
- Hold the insertion tube with the fingers of one hand (Hand A) and the rod with the fingers of the other hand (Hand B).
- Hold the rod still (Hand B), relax the firmness of the pinch on the tube, and pull the insertion tube back with Hand A to the edge of the second indent of the rod (Figure 9).
- This will allow the IUS arms to open in the lower uterine segment.
Step 3
- Wait 10 – 15 seconds for the arms of the IUS to fully open.
Step 4
- Apply gentle traction with the tenaculum before advancing the IUS.
- With Hand A still holding the proximal end of the tube, advance both the insertion tube and rod simultaneously up to the uterine fundus (Figure 10). You will feel slight resistance when the IUS is at the fundus.
- The flange should be touching the cervix when the IUS reaches the uterine fundus.
- Note: Fundal positioning is important to prevent expulsion.
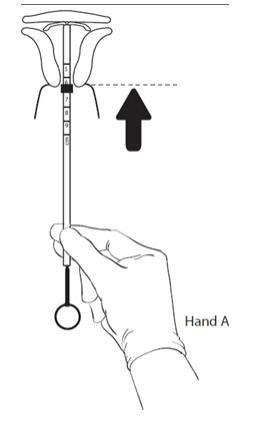
Figure 10: After 10 – 15 seconds, advance to the fundus while holding both the rod and the tube.
Step 5
- Hold the rod still (Hand B) while pulling the insertion tube back with Hand A to the ring of the rod (Figure 11).
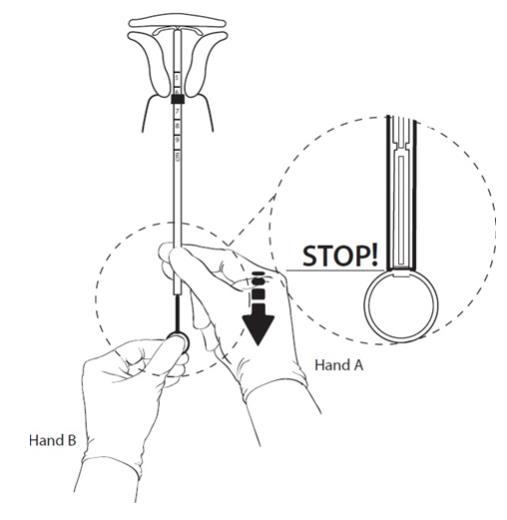
Figure 11: Hold the rod still and pull back the tube to the ring on the rod.
Step 6
- While holding the inserter tube with Hand A, withdraw the rod from the insertion tube all of the way out to prevent the rod from catching on the knot at the lower end of the IUS.
- Note: Ensure the tube is held firmly in place until the rod is completely pulled outside of the tube as there will be some slight resistance while removing the rod from the tube.
Step 7
- Completely remove the insertion tube.
Step 8
- Use blunt-tipped sharp scissors to cut the IUS threads perpendicular to the thread length, leaving about 3 cm outside of the cervix (Figure 12). Note: Do not cut threads at an angle as this may leave sharp ends.
- Do not apply tension or pull on the threads when cutting to prevent displacing the IUS.
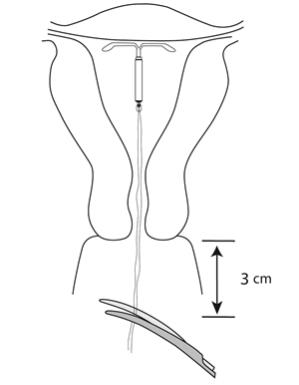
Figure 12: Cut the threads about 3 cm from the cervix
- Insertion of LILETTA is now complete.
Important information to consider during or after insertion:
- If you suspect the IUS is not in the correct position:
○ Check insertion with an ultrasound or other appropriate radiologic test.
○ If incorrect insertion is suspected, remove LILETTA. Do no reinsert the same LILETTA IUS after removal.
Difficult Insertion
- If insertion is difficult because the uterus cannot be appropriately instrumented, consider the following measures:
○ Use of cervical anesthesia to make sounding and manipulation more tolerable.
○ Use of dilators to dilate the cervix if needed to allow passage of the sound or inserter.
○ Abdominal ultrasound guidance during dilation and/or insertion.
○ If there is clinical concern, exceptional pain, or bleeding during or after insertion, take appropriate steps, such as physical examination and ultrasound, immediately to exclude uterine perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
2.4 Patient Counseling and Record-Keeping
- Keep a copy of the consent form and LILETTA lot number for your records.
- Counsel the patient on what to expect following LILETTA insertion. Give her the Patient Information Booklet, which includes the website address (www.LILETTA.com). Discuss expected bleeding patterns with LILETTA use. Review the signs and symptoms associated with infection, perforation, and expulsion that may occur with use of LILETTA [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
- Prescribe analgesics, if indicated.
2.5 Patient Follow-Up
Re-examine and evaluate patients 4 to 6 weeks after insertion and once a year thereafter, or more frequently if clinically indicated. The healthcare professional should check strings during each routine and follow-up visit.
2.6 Removal of LILETTA
Timing of Removal
- If pregnancy is desired, LILETTA can be removed at any time.
- If pregnancy is not desired, LILETTA can be removed at any time; however, a contraception method should be started prior to removal of LILETTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Counsel your patient that she is at risk of pregnancy if she has intercourse in the week prior to removal without use of a backup contraceptive method.
- LILETTA should be removed after 6 years. LILETTA can be replaced at the time of removal with a new LILETTA if continued contraceptive protection is desired.
Planning for Removal
- Ensure all needed items for LILETTA removal are readily available:
- Gloves
- Sterile speculum
- Sterile forceps
- Additional items that may be required could include:
- Local anesthetic, needle, and syringe
- Sterile os finder and/or cervical dilators
- Ultrasound with abdominal probe
- Sterile tenaculum
- Antiseptic solution
- Sterile long, narrow forceps or intrauterine thread retriever
- Local anesthetic, needle, and syringe
- Gloves
- Removal may be associated with some pain and/or bleeding or vasovagal reactions (e.g., syncope, bradycardia, or seizure), especially in patients with a predisposition to these conditions.
- After removal of LILETTA, examine the system to ensure that it is intact.
Removal Instructions
- With the patient comfortably in lithotomy position, place a speculum and visualize the cervix.
- When the threads of LILETTA are visible:
○ Remove the IUS by applying traction on the threads with forceps (Figure 13).
○ The arms of the device will fold upward as it is withdrawn from the uterus.
○ If the IUS cannot be removed with traction on the threads, perform an ultrasound examination to confirm location of the IUS, including assessment for partial or total perforation. If the IUS is in the uterus, use long, narrow forceps to grasp LILETTA. Consider use of a tenaculum, cervical anesthesia, cervical dilators, and/or ultrasound guidance as needed.
○ After removal, examine the system to ensure it is intact.
- If the threads of LILETTA are not visible:
○ Determine location of the IUS by ultrasound examination.
○ If the IUS is in the uterine cavity, thoroughly cleanse the cervix and vagina with antiseptic solution. Use a thread retriever to capture the threads or a long, narrow forceps (e.g., Alligator forceps) to grasp LILETTA. Consider use of a tenaculum, cervical anesthesia, cervical dilators, and/or ultrasound guidance as needed. If LILETTA cannot be removed using the above techniques, consider hysteroscopic evaluation for removal.
○ If the IUS is not in the uterine cavity, consider an abdominal x-ray or CT scan to evaluate if the IUS is in the abdominal cavity. Consider laparoscopic evaluation for removal, as clinically indicated.
○ After removal, examine the system to ensure it is intact.
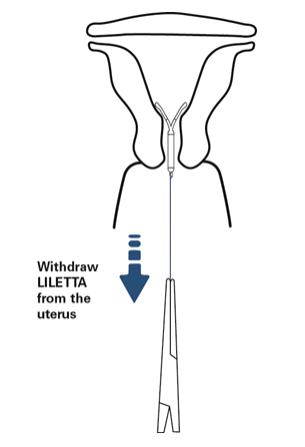
Figure 13: Removal of LILETTA
2.7 Continuation of Contraception After Removal
- If a patient wishes to continue using LILETTA or another intrauterine contraceptive, insertion can occur immediately after removal.
- If a patient with regular cycles wants to start a different birth control method, time the removal and initiation of a new method to ensure continuous contraception. Either remove LILETTA during the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle and start the new method or start the new method at least 7 days prior to removing LILETTA if removal is to occur at other times during the cycle.
- If a patient with irregular cycles or amenorrhea wants to start a different birth control method, start the new method at least 7 days before LILETTA removal.
- If LILETTA is removed but no other contraceptive method has already been started, the new contraceptive method can be started on the day LILETTA is removed. The patient should use a backup barrier method of contraception (e.g., condoms and spermicide) or abstain from vaginal intercourse for 7 days to prevent pregnancy.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
LILETTA is a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system consisting of a T-shaped polyethylene frame with a drug reservoir containing 52 mg levonorgestrel, packaged within a sterile inserter.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
LILETTA is contraindicated when one or more of the following conditions exist:
- Pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
- For use as post-coital contraception (emergency contraception)
- Congenital or acquired uterine anomaly, including fibroids, that distorts the uterine cavity and would be incompatible with correct IUS placement [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or endometritis or a history of PID unless there has been a subsequent intrauterine pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Infected abortion in the past 3 months [see Warning and Precautions (5.2.)]
- Known or suspected uterine or cervical neoplasia
- Known or suspected breast cancer or other hormone-sensitive cancer, now or in the past [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Uterine bleeding of unknown etiology [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Untreated acute cervicitis or vaginitis, including bacterial vaginosis, known chlamydial or gonococcal cervical infection, or other lower genital tract infections until infection is controlled [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Acute liver disease or liver tumor (benign or malignant)
- Conditions associated with increased susceptibility to pelvic infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- A previously inserted IUS that has not been removed
- A history of hypersensitivity reaction to any component of LILETTA. Reactions may include rash, urticaria, and angioedema [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ectopic Pregnancy
Evaluate women for ectopic pregnancy if they become pregnant with LILETTA in place because the likelihood of a pregnancy being ectopic is increased with LILETTA. Approximately half of pregnancies that occur with LILETTA in place are likely to be ectopic. Also consider the possibility of ectopic pregnancy in the case of lower abdominal pain, especially in association with missed menses or new onset bleeding in an amenorrheic woman. If an ectopic pregnancy is confirmed, LILETTA should be removed.
The incidence of ectopic pregnancy in the clinical trial with LILETTA, which excluded women with a history of ectopic pregnancy who did not have a subsequent intrauterine pregnancy, was approximately 0.12 per 100 women-years. The risk of ectopic pregnancy in women who have a history of ectopic pregnancy and use LILETTA is unknown. Women with a previous history of ectopic pregnancy, tubal surgery or pelvic infection have a higher risk of ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy may require surgery and may result in loss of fertility.
Women who use LILETTA should be informed about recognizing the signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy and promptly reporting them to their healthcare professional, and about the associated risks of ectopic pregnancy (e.g., the loss of fertility).
5.2 Intrauterine Pregnancy
If pregnancy occurs while using LILETTA, determine if LILETTA is in the uterus. If LILETTA is in the uterus, attempt to remove LILETTA because leaving it in place may increase the risk of spontaneous abortion and preterm labor. Removal of LILETTA or probing of the uterus may also result in spontaneous abortion. In the event of an intrauterine pregnancy with LILETTA, consider the following:
Septic Abortion
If a woman becomes pregnant with an IUS in place, septic abortion potentially including septicemia, septic shock, and death may occur. Septic abortion typically requires hospitalization and treatment with intravenous antibiotics. Septic abortion may result in spontaneous abortion or a medical indication for pregnancy termination. Should severe infection of the uterus occur, hysterectomy may be required, which will result in permanent infertility. LILETTA is contraindicated in patients who have has an infected abortion in the prior 3 months.
Continuation of Pregnancy
If a woman becomes pregnant with LILETTA in place and if LILETTA cannot be removed or the woman chooses not to have it removed, warn her that failure to remove LILETTA increases the risk of miscarriage, sepsis, premature labor, and premature delivery. Prenatal care should include counseling about these risks and that she should report immediately any flu-like symptoms, fever, chills, cramping, pain, bleeding, vaginal discharge or leakage of fluid, or any other symptom that suggests complications of the pregnancy.
5.3 Sepsis
Severe infection or sepsis, including Group A streptococcal sepsis (GAS), have been reported following insertion of LNG-releasing IUSs. In some cases, severe pain occurred within hours of insertion followed by sepsis within days. Because death from GAS is more likely if treatment is delayed, it is important to be aware of these rare but serious infections. Aseptic technique during insertion of LILETTA is essential in order to minimize serious infections such as GAS.
5.4 Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or Endometritis
Insertion of LILETTA is contraindicated in the presence of known or suspected PID or endometritis or a history of PID unless there has been a subsequent intrauterine pregnancy. As well, it is contraindicated in patients with untreated acute cervicitis or vaginitis (including bacterial vaginosis), known chlamydial or gonococcal cervical infection, or other known lower genital tract infections, until the infection is controlled. IUSs have been associated with an increased risk of PID, most likely due to organisms being introduced into the uterus during insertion. Assess risk factors for infection accordingly.
In the clinical trial with LILETTA, pelvic infection was diagnosed in 0.8% of women. Pelvic infection was diagnosed as PID in 0.5% of women and as endometritis in 0.3% of women. Infections occurred following variable duration of use. One woman diagnosed with PID and two women diagnosed with endometritis developed the infection within a week of LILETTA insertion. One case of endometritis was diagnosed at 39 days after LILETTA insertion. The remaining 11 cases of PID and endometritis were diagnosed more than six months after insertion, including one at 30 days after IUS removal.
Women who use LILETTA should be counseled to promptly notify a healthcare professional if they develop lower abdominal or pelvic pain, fever, chills, unusual or malodorous discharge, unexplained bleeding, genital lesions or sores, or dyspareunia. In such circumstances, perform a pelvic examination promptly to evaluate for possible pelvic infection. Remove LILETTA in cases of recurrent PID or endometritis, or if an acute pelvic infection is severe or does not respond to treatment.
Women at Increased Risk for PID or Endometritis
PID and endometritis are often associated with a sexually transmitted infection (STI), and LILETTA does not protect against STIs. The risk of PID or endometritis is greater for women who have multiple sexual partners, and for women whose sexual partner(s) have multiple sexual partners. Women who have had PID or endometritis are at increased risk for a recurrence or re-infection. Other risk factors for these infections include leukemia, acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), and illicit intravenous drug use.
Asymptomatic PID or Endometritis
PID or endometritis may be asymptomatic but still result in tubal damage and its sequelae.
Treatment of PID or Endometritis
Following a diagnosis of PID or endometritis, or suspected PID or endometritis, perform appropriate testing for sexually transmitted infection and initiate antibiotic therapy promptly. LILETTA does not need to be removed immediately if the woman needs ongoing contraception1. In the LILETTA clinical trial, 12 of the 14 women who developed PID or endometritis were successfully treated without removal of LILETTA (one of the 14 women developed PID 30 days after removal).
Reassess the woman in 48-72 hours. If no clinical improvement occurs, continue antibiotics and consider removal of LILETTA. If the woman wants to discontinue use, remove LILETTA after antibiotics have been started to avoid the potential risk for bacterial spread resulting from the removal procedure. Guidelines for PID or endometritis treatment are available from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), Atlanta, Georgia.1
Actinomycosis
Actinomycosis has been associated with IUS use. Symptomatic women with known actinomycosis infection should have LILETTA removed and receive antibiotics. Actinomycetes can be found in the genital tract cultures in healthy women without IUSs. The significance of actinomyces-like organisms on Pap test in an asymptomatic IUS user is unknown, and so this finding alone does not always require LILETTA removal and treatment. When possible, confirm a Pap test diagnosis with cultures.
5.5 Perforation
Perforation (total or partial, including penetration/embedment of LILETTA in the uterine wall or cervix) may occur, most often during insertion, although the perforation may not be detected until sometime later. Perforation may also occur at any time during IUS use. Perforation may reduce contraceptive efficacy and result in pregnancy. This may be associated with severe pain and continued bleeding.
The incidence of perforation during or following LILETTA insertion in the clinical trial, which excluded breastfeeding women, was 0.1%.
If perforation is suspected the IUS should be removed as soon as possible, surgery may be required. Delayed detection or removal of LILETTA in case of perforation may result in migration outside the uterine cavity, adhesions, peritonitis, intestinal perforations, intestinal obstruction, abscesses, and erosion of adjacent viscera.
In a large prospective comparative non-interventional cohort study with another IUS the incidence of uterine perforation was reported as 6.3 per 1,000 insertions for lactating women, compared to 1.0 per 1,000 insertions for non-lactating women.
The risk of perforation may be increased if LILETTA is inserted when the uterus is fixed retroverted or not completely involuted during the post-partum period. Delay LILETTA insertion a minimum of four weeks or until involution is complete following a delivery or a second trimester abortion.
5.6 Expulsion
Partial or complete expulsion of LILETTA may occur, resulting in the loss of contraceptive protection. In the clinical trial with LILETTA, an overall expulsion rate of 4.0% over 6 years was reported, with a rate of 2.2% in nulliparous women and 6.2% in parous women. The majority (73.5%) occur in the first 12 months, with 25.0% occurring in the first three months and 44.1% in the first six months, cumulatively. Expulsion may be associated with symptoms of bleeding or pain, or it may be asymptomatic and go unnoticed. LILETTA typically decreases menstrual bleeding over time; therefore, an increase in menstrual bleeding may be indicative of an expulsion. Consider further diagnostic imaging, such as sonography or X-ray, to confirm expulsion if LILETTA is not found in the uterus.
The risk of expulsion may be increased when the uterus is not completely involuted at the time of insertion. Delay LILETTA insertion a minimum of 4 weeks or until uterine involution is complete following a delivery or a second trimester abortion.
Remove a partially expelled LILETTA. If expulsion has occurred, a new LILETTA may be inserted within 7 days after the onset of a menstrual period after pregnancy has been ruled out.
5.7 Ovarian Cysts
Because the contraceptive effect of LILETTA is mainly due to its local effects within the uterus, ovulatory cycles with follicular rupture usually occur in women of fertile age using LILETTA. Sometimes atresia of the follicle is delayed and the follicle may continue to grow. Most ovarian cysts that occur during use of LNG-releasing IUSs are asymptomatic and disappear spontaneously during two to three months of observation. Cysts that cause clinical symptoms can result in pelvic or abdominal pain or dyspareunia. Symptomatic ovarian cysts occurred in 4.5% of subjects using LILETTA over the course of 6 years, and 0.3% of subjects discontinued use of LILETTA because of an ovarian cyst.
Evaluate persistent ovarian cysts. Surgical intervention is not usually required, but may be necessary in some cases. Discuss this risk with patients who use LILETTA.
5.8 Bleeding Pattern Alterations
LILETTA can alter the bleeding pattern and result in spotting, irregular bleeding, heavy bleeding, oligomenorrhea, and amenorrhea. During the first three to six months of LILETTA use, the number of bleeding and spotting days may increase and irregular bleeding patterns may develop. Thereafter, the number of bleeding and spotting days usually decreases but bleeding may remain irregular.
In the LILETTA clinical trial, amenorrhea developed in approximately 19% of LILETTA users by the end of the first year of use, 27% by the end of the second year of use, 37% by the end of the third year of use, 37% by the end of the fourth year of use, 40% by the end of the fifth year of use, and 40% by the end of the sixth year of use. In the trial, 2.3% of LILETTA subjects discontinued due to bleeding complaints. Table 2 shows the bleeding and spotting days based on 28-day cycle equivalents.
| 28-Day Cycle Equivalent | Cycle 1
N=1,691 | Cycle 4
N=1,593 | Cycle 7
N=1,519 | Cycle 13
N=1,395 | Cycle 26
N=1,108 |
|||||
| Days on treatment | 1-28 | 85-112 | 169-196 | 337-364 | 674-728 | |||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| Number of
bleeding days | 5.8 | 5.2 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 1.6 | 2.7 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 1.8 |
| Number of
spotting days | 9.0 | 5.9 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 3.2 | 3.6 | 2.7 | 3.4 | 1.9 | 2.8 |
Note: Includes all LILETTA subjects.
In the LILETTA clinical trial, 537 of 538 (99.8%) women evaluated experienced menses after LILETTA removal. This excludes fourteen women who became pregnant (9 women), had a hysterectomy (3 women), were considered menopausal after removal (1 woman), or had ovulatory dysfunction (1 woman).
If a significant change in bleeding develops during prolonged use, conduct diagnostic tests to assess possible endometrial pathology. Consider the possibility of pregnancy if menstruation does not occur within six weeks of the onset of a previous menstruation. After excluding pregnancy, repeat pregnancy tests are generally not necessary in amenorrheic women unless indicated, by other signs of pregnancy or pelvic pain.
5.9 Breast Cancer
Women who currently have or have had breast cancer, or have a suspicion of breast cancer, should not use hormonal contraception, including LILETTA, because some breast cancers are hormone-sensitive [see Contraindications (4)].
Spontaneous reports of breast cancer have been received during postmarketing experience with LNG-releasing IUSs. Observational studies have not provided consistent evidence of an increased risk of breast cancer with use of a LNG-releasing IUS.
5.10 Clinical Considerations for Use and Removal
Obtain a complete medical and social history, including partner status, to determine conditions that might influence the selection of an IUS for contraception.
Exclude underlying endometrial pathology (e.g. polyps or cancer) prior to the insertion of LILETTA in women with persistent or uncharacteristic bleeding because irregular bleeding/spotting is common during the first months of LILETTA use and may preclude adequate assessment after insertion. LILETTA is contraindicated in women with uterine bleeding of unknown etiology.
Exclude underlying congenital or acquired uterine anomalies, including fibroids, that distort the uterine cavity and would be incompatible with correct IUS placement [see Contraindications (4)].
Ensure a previously inserted IUS has been removed prior to insertion of LILETTA [see Contraindications (4)].
Assess whether the woman is at increased risk of infection (e.g., leukemia, acquired immune deficiency syndrome [AIDS], IV drug abuse), or has a history of PID unless there has been a subsequent intrauterine pregnancy. LILETTA does not protect against HIV/STI transmission [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Use LILETTA with caution after careful assessment if any of the following conditions exist, and consider removal of the IUS if any of them arise during use:
- Coagulopathy or use of anticoagulants
- Migraine, focal migraine with asymmetrical visual loss or other symptoms indicating transient cerebral ischemia
- Exceptionally severe or frequent headache
- Marked increase of blood pressure
- Severe arterial disease such as stroke or myocardial infarction
Consider removing LILETTA if any of the following conditions arise during use [see Contraindications (4)]:
- Uterine or cervical malignancy
- Jaundice
If the threads are not visible or are significantly shortened, they may have broken or retracted into the cervical canal or uterus. Consider the possibility that the IUS may have been displaced, (for example, expulsed or perforated the uterus) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6)]. Exclude pregnancy and verify the location of LILETTA by an appropriate diagnostic method, e.g. ultrasonography, X-ray, or gentle exploration of the cervical canal with a suitable instrument [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)]. If LILETTA is displaced, remove it. A new LILETTA may be inserted at that time or during the next menses if it is certain that conception has not occurred. If LILETTA is in place with no evidence of perforation, no intervention is indicated.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious or important adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Ectopic Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Intrauterine Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Group A Streptococcal Sepsis (GAS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or Endometritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Expulsion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Ovarian Cysts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Bleeding Pattern Alterations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure of 1,751 generally healthy 16- to 45-year-old women to LILETTA in a large, multi-center contraceptive trial conducted in the US, including 1,401 exposed for 1 year and 402 subjects who completed 6 years of use; 58% were nulliparous (mean age 25.1 ± 4.3 years) and 42% were parous (mean age 30.3 ± 6.1 years). Most women who received LILETTA were Caucasian (78.4%) or Black/African American (13.3%); 14.7% of women were of Hispanic ethnicity. The clinical trial had no upper or lower weight or body mass index (BMI) limit. Mean BMI of LILETTA subjects was 26.9 kg/m2 (range 15.8 – 61.6 kg/m2); 25.1% had a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, of which 5.3% had a BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2. The data cover more than 68,000 28-day cycles of LILETTA exposure. The frequencies of reported adverse drug reactions represent crude incidences.
The most common adverse reactions during the LILETTA clinical trial (occurring in ≥ 5% of users) are shown in Table 3. The most common adverse reactions during the first year of use were acne (11.4%), bacterial vaginitis (9.0%) and vulvovaginal mycotic infection (7.9%).
| Adverse Reaction | % LILETTA Subjects (N = 1,751) |
| Vulvovaginal mycotic infections | 19.2% |
| Vaginal bacterial infections | 18.6% |
| Acne | 15.3% |
| Nausea or vomiting | 10.3% |
| Abdominal discomfort or pain | 9.9% |
| Headache | 9.5% |
| Breast tenderness or pain | 9.5% |
| Dyspareunia | 9.3% |
| Anxiety | 8.8% |
| Pelvic discomfort or pain | 8.4% |
| Depression | 8.3% |
| Dysmenorrhea | 6.4% |
| Mood changes | 6.3% |
| Weight increased | 5.9% |
| Back pain | 5.9% |
| Vaginal discharge | 5.4% |
In the contraceptive clinical trial, 19.2% of LILETTA users discontinued prematurely due to an adverse reaction. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were expulsion (4.0%) and bleeding complaints (2.3%). The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation during the first year of use were expulsion (2.9%) and acne (0.7%). The next most common adverse reactions causing discontinuation were acne (1.4%), dysmenorrhea (1.0%), weight increased (1.0%), menorrhagia (0.9%), mood swings (0.8%), uterine spasm (0.7%), dyspareunia (0.6%) and pelvic pain (0.6%). Two women discontinued the clinical trial due to PID and one due to endometritis.
In the clinical trial, serious adverse reactions related to LILETTA were ectopic pregnancies, ovarian cysts, and IUS perforation requiring a laparoscopic surgery.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of LNG-releasing IUSs. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Arterial thrombotic and venous thromboembolic events, including cases of pulmonary emboli, deep vein thrombosis and stroke
- Device breakage
- Hypersensitivity (including rash, urticaria, and angioedema)
- Increased blood pressure
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
LILETTA is contraindicated for use in pregnant women because there is no need for pregnancy prevention in a woman who is already pregnant and LILETTA may cause adverse pregnancy outcomes. If a woman becomes pregnant with LILETTA in place, there is an increased risk of miscarriage, sepsis, premature labor, and premature delivery. Published studies report no harmful effects on fetal development associated with long-term use of contraceptive doses of oral progestins in a pregnant woman. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with LILETTA.
The background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2-4% and of miscarriage is 15-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Published studies report the presence of LNG in human milk. Small amounts of progestins (approximately 0.1% of the total maternal doses) were detected in the breast milk of nursing mothers who used other LNG-releasing IUSs. Isolated cases of decreased milk production have been reported with another LNG-releasing IUS. The infant’s developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for LILETTA, underlying maternal conditions, and any potential adverse effects from LILETTA on the infant.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Assess pregnancy status prior to inserting LILETTA, as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of LILETTA have been established in females of reproductive potential. The safety and effectiveness are expected to be the same for postpubertal females under the age of 16 as for users 16 years and older. The LILETTA clinical trial included 11 subjects that were 16 to 7 years of age; no differences in safety or effectiveness were identified in these subjects through 6 years of use of LILETTA. Use of this product is not indicated before menarche.
8.5 Geriatric Use
LILETTA is not indicated in women after menopause and has not been studied in this population.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic disease on the disposition of LNG released from LILETTA [see Contraindications (4)].
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 LILETTA
LILETTA (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) contains 52 mg of levonorgestrel, a progestin, and is intended to provide an initial release rate of 20.1 mcg/day of levonorgestrel.
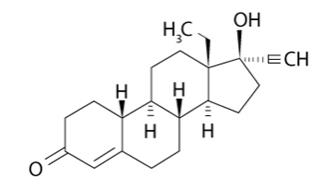
Levonorgestrel USP, (-)-13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one, the active ingredient in LILETTA, is the levorotatory form of norgestrel, which consists of a racemic mixture of S-(-)-norgestrel (levonorgestrel) and L-(+)-norgestrel (dextronorgestrel). It has a molecular weight of 312.45, a molecular formula of C21H28O2, and the following structural formula:
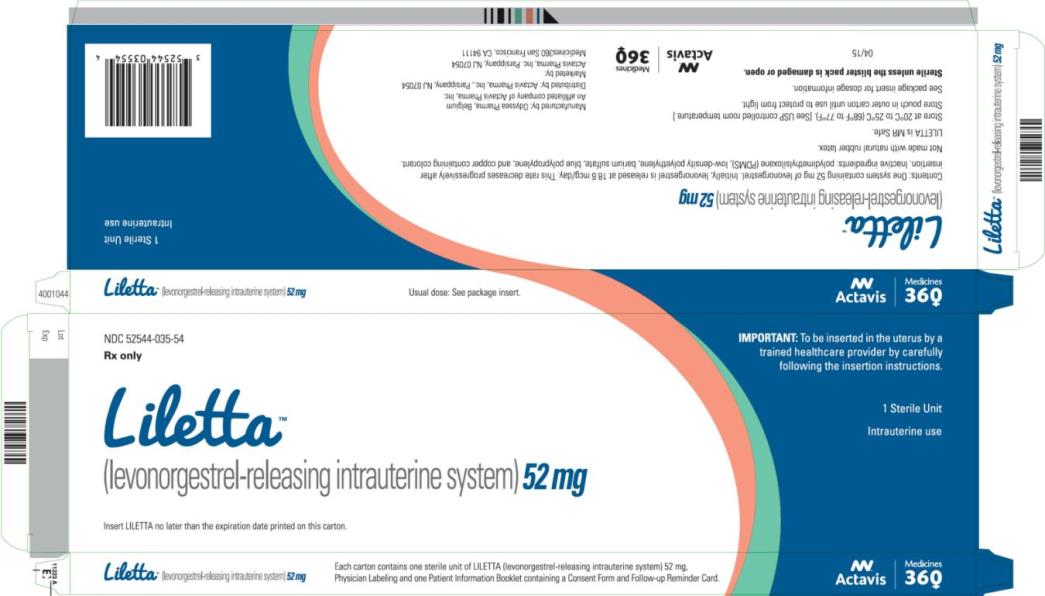
LILETTA consists of a T-shaped polyethylene frame (T-frame) with a drug reservoir around the vertical stem (Figure 14). The T-frame has a loop at one end of the vertical stem and two horizontal arms at the other end. The drug reservoir consists of a cylinder, made of a mixture of 52 mg levonorgestrel and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) formed from silicone base, tetra-n-propyl silicate, and stannous octoate. The drug reservoir is covered by a translucent PDMS membrane. The low-density polyethylene of the T-frame is compounded with barium sulfate, which makes it radio-opaque. A blue polypropylene monofilament removal thread is attached to an eyelet at the end of the vertical stem of the T-frame. The polypropylene of the removal thread contains a copper-containing pigment as a colorant. The components of LILETTA, including its packaging, are not manufactured using natural rubber latex.

Figure 14: Diagram of LILETTA
11.2 Inserter
The inserter device provided with LILETTA is a single-use, disposable, sterile insertion system (tube, flange, rod; Figure 15), partially preloaded with the IUS product for intrauterine administration.
Once LILETTA has been inserted, the inserter is discarded.

Figure 15: Diagram of Inserter
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The local mechanism by which continuously released LNG provides contraception has not been conclusively demonstrated. Studies of LNG-releasing IUSs suggest several mechanisms for pregnancy prevention: prevention of fertilization due to the thickening of the cervical mucus, which inhibits sperm passage through the cervix, and inhibition of sperm mobility and function (capacitation), and alteration of the endometrium.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
LILETTA has mainly local progestogenic effects in the uterine cavity which change the endometrium and may lead to alterations in the menstrual bleeding pattern [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. High local concentrations of LNG lead to morphological changes including stromal pseudo-decidualization, glandular atrophy, a leukocytic infiltration, and a decrease in glandular and stromal mitoses.
In clinical trials with other LNG-releasing IUSs with an LNG release rate similar to LILETTA, approximately 45-75% of menstrual cycles were ovulatory.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Low doses of LNG are administered into the uterine cavity with the LILETTA intrauterine delivery system. The initial in vivo release rate is 20.1 mcg/day and decreases to 17.5 mcg/day at 1 year, 15.2 mcg/day at 2 years, 13.2 mcg/day at 3 years, 11.4 at 4 years, 9.9 mcg/day at 5 years, and 8.6 mcg/day at 6 years.
In the phase 3 clinical trial, systemic plasma LNG concentrations were assessed in a subset of subjects through Month 30 and in all subjects in the trial at Month 36 and after. Plasma LNG concentrations following insertion of LILETTA are shown in Table 4.
| 7 Days (n = 40) | 6 Months (n = 36) | 12 Months (n = 33) | 24 Months (n = 30) | 36 Months (n = 894) | 48 Months (n = 737) | 60 Months (n = 531) | 72 Months (n = 191) |
| 252 ± 123 | 195 ± 68 | 168 ± 51 | 150 ± 47 | 132 ± 54 | 114 ± 52 | 101 ± 43 | 93 ± 45 |
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of LNG at steady-state following oral administration is reported to be approximately 1.8 L/kg. It is about 98.9% protein-bound, principally to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and, to a lesser extent, serum albumin.
Elimination
The elimination half-life of LNG after a single oral administration is approximately 13.9 ± 3.2 hours. Metabolic clearance rates may differ among individuals by several-fold, and this may account in part for wide individual variations in LNG concentrations seen in individuals using LNG–containing contraceptive products.
Metabolism
Following absorption, LNG is conjugated at the 17β-OH position to form sulfate conjugates and, to a lesser extent, glucuronide conjugates in serum. Significant amounts of conjugated and unconjugated 3α, 5β-tetrahydrolevonorgestrel are also present in serum, along with much smaller amounts of 3α, 5α-tetrahydrolevonorgestrel and 16β-hydroxylevonorgestrel. In vitro studies have demonstrated that oxidative metabolism of LNG is catalyzed by CYP enzymes, especially CYP3A4.
Excretion
About 45% of LNG and its metabolites are excreted in the urine and about 32% are excreted in feces, mostly as glucuronide conjugates.
Specific Populations
Racial or Ethnic Groups:
The effect of race on plasma LNG concentrations after LILETTA insertion was assessed in 731 (80%) White subjects, 106 (12%) Black subjects, 40 (4%) Asian subjects, 8 (1%) American Indian/Alaska Native subjects, 21 (2%) multiple-race subjects. Race does not appear to affect LNG concentrations following LILETTA insertion [see Clinical Studies (14)].
BMI/Body Weight:
The effect of BMI on LNG exposure was assessed in 673 non-obese (BMI ≤ 30 kg/m2) and 219 obese women (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2). Plasma LNG concentrations were approximately 24-32% lower in obese subjects than in non-obese subjects based on data collected from Months 36 to 72. However, since LILETTA has a mainly local progestogenic effect in the uterine cavity, the clinical relevance of the reduced systemic exposure is unclear [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Contraceptive effect of LILETTA is mediated via the direct release of LNG into the uterine cavity and is unlikely to be affected by drug interactions via enzyme induction or inhibition.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Trial on Contraception
LILETTA was studied in a multicenter, randomized, open-label clinical trial conducted in the US that enrolled 1,910 generally healthy women aged 16 to 45 years, 1,751 of whom received LILETTA. LILETTA was inserted in 1,011 (58%) nulliparous and 740 (42%) parous women. Women with a history of ectopic pregnancy, PID, or trophoblastic disease without a subsequent intrauterine pregnancy, who were less than 4 weeks post-pregnancy, had HIV, or were not in a mutually monogamous relationship at study entry were excluded. The demographic profile of enrolled women who received LILETTA are as follows: Caucasian 78.4%, Black or African American 13.3%, Asian 3.9%, American Indian or Alaska Native 1.2%, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander 0.3%; 2.9% identified multiple races; 14.7% indicated Hispanic ethnicity. The clinical trial had no upper or lower weight or BMI limit and the BMI range was 15.8 – 61.6 kg/m2. The mean BMI of LILETTA subjects was 26.9 kg/m2; 24% were overweight, 24% were obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2), and 5% were morbidly obese (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2).
The pregnancy rate calculated as the Pearl Index (PI) in women aged 16 to 35 years, inclusive, was the primary efficacy endpoint used to assess contraceptive reliability. The PI was calculated based on 28-day equivalent exposure cycles; evaluable cycles excluded those in which back-up contraception was used unless a pregnancy occurred in that cycle. The Year 1 PI was based on two pregnancies and the cumulative 6-year pregnancy rate was calculated by the life table method, based on a total of nine pregnancies that occurred after the onset of treatment and within 7 days after LILETTA removal or expulsion. Table 5 shows the annual PI for each of the six years and the calculated cumulative life table pregnancy rates through years 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6.
| LILETTA Clinical Trial | Number of 28-Day Cycles of Exposure
By Year | Year-by-Year
Pearl Index Pregnancy Rate (95% CI) | Cumulative 28-Day Cycles of Exposure | Cumulative Year
Life Table Pregnancy Rate (95% CI) |
| Year 1 | 17,175 | 0.15 (0.02, 0.55) | 17,175 | 0.14 (0.04, 0.57) |
| Year 2 | 14,205 | 0.37 (0.10, 0.94) | 31,380 | 0.49 (0.22, 1.09) |
| Year 3 | 11,760 | 0.11 (0.00, 0.62) | 43,140 | 0.59 (0.28, 1.25) |
| Year 4 | 9,891 | 0.13 (0.00, 0.73) | 53,031 | 0.72 (0.36, 1.45) |
| Year 5 | 8,335 | 0.16 (0.00, 0.87) | 61,366 | 0.87 (0.44, 1.70) |
| Year 6 | 5,091 | 0.00 (0.00, 0.9) | 66,457 | 0.7 (0.44, 1.70) |
Conception rates after the removal of LILETTA were assessed and appeared consistent with conception rates in the general population of women having regular unprotected sexual intercourse for 12 months.
Of 191 women who desired pregnancy after study discontinuation, 79% conceived within 6 months after removal of LILETTA, and 85% conceived within 12 months after removal of LILETTA.
15 REFERENCES
(1) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), (2019). CDC-STD Treatment [online] Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment/default.htm
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
LILETTA (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system), containing 52 mg levonorgestrel, is packaged together with an inserter in a peelable pouch, and is available in a carton of one sterile unit. NDC # 52544-035-54.
LILETTA is supplied sterile. LILETTA is sterilized with ethylene oxide. Do not re-sterilize. Do not use if the inner pouch is damaged or opened. Insert before the end of the month shown on the pouch. Store at 20°C – 25°C (68°F – 77°F), with excursions permitted between 15°C – 30°C (59°F – 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store pouch in outer carton until use to protect from light.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
- Advise the patient that this product does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Advise the patient about the risks of ectopic pregnancy, including the loss of fertility. Advise her to recognize and report to her healthcare professional promptly any symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, including lower abdominal pain, especially in association with missed periods [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1).]
- Advise the patient that if pregnancy occurs while using LILETTA:
○ LILETTA will likely need to be removed because leaving it in place may increase the risk of spontaneous abortion and preterm labor; however, removal of LILETTA or probing of the uterus may also result in spontaneous abortion. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2).]
○ Report promptly to her healthcare professional any symptoms that suggest complications of the pregnancy, including flu-like symptoms, fever, chills, cramping, pain, bleeding, and vaginal discharge or leakage of fluid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
○ Septic abortion may occur. Advise her that if LILETTA cannot be removed or she chooses not to have it removed, there may be an increased risk of miscarriage, sepsis, premature labor, and premature delivery. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2).]
- Advise the patient that severe infection or sepsis, including Group A streptococcal sepsis (GAS), can occur within the first few days after LILETTA is inserted. Advise her to contact a healthcare professional immediately if she develops severe pain or fever shortly after LILETTA is inserted. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3).]
- Advise the patient about the possibility of PID or endometritis and that these infections can cause tubal damage leading to ectopic pregnancy or infertility, or infrequently can necessitate hysterectomy, or cause death. Advise the patient to recognize and report to her healthcare professional any of the following signs and symptoms of possible infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]:
○ lower abdominal or pelvic pain or tenderness
○ fever
○ chills
○ unusual or malodorous vaginal discharge
○ atypical or unexplained bleeding (prolonged or heavy bleeding)
○ genital lesions or sores.
○ dyspareunia
- Advise the patient that perforation may occur, most often during insertion, although the perforation may not be detected until sometime later. Advise her that if perforation occurs, LILETTA will have to be located and removed. Surgery may be required. Advise her that delayed detection or removal of LILETTA in case of perforation may result in [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]:
| ○ migration of the IUS outside the uterine cavity | ○ intestinal perforations |
| ○ adhesions | ○ intestinal obstruction |
| ○ peritonitis | ○ abscesses |
| ○ erosion of adjacent viscera |
- Review the signs and symptoms of LILETTA expulsion with the patient. Advise the patient on how she can check that the threads still protrude from her cervix, and not to pull on them. Advise her that there is no contraceptive protection if LILETTA is displaced or expelled [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6).]
- Advise the patient that excessive pain or vaginal bleeding during insertion, worsening pain or bleeding after insertion, or the inability to feel the threads may occur with perforation and expulsion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6).]
- Advise the patient regarding the risk of ovarian cysts and that cysts can cause clinical symptoms including pelvic pain, abdominal pain or dyspareunia and infrequently will need surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7).]
- Advise the patient that irregular or prolonged bleeding and spotting, and/or cramps may occur during the first three to six months after insertion. If her symptoms continue or are severe, she should report them to her healthcare professional [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8).]
- Advise the patient to contact her healthcare professional if she experiences any of the following symptoms or conditions:
| ○ A stroke or heart attack | ○ Possible exposure to sexually transmitted infections (STIs) |
| ○ Very severe or migraine headaches | ○ Unusual vaginal discharge or genital sores |
| ○ Unexplained fever | ○ Severe vaginal bleeding or bleeding that lasts a long time, or if she misses a menstrual period |
| ○ Yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes, as these may be signs of serious liver problems | ○ Inability to feel LILETTA's threads |
| ○ Pregnancy or suspected pregnancy | |
| ○ Pelvic pain or pain during sex | |
| ○ She or her partner becomes HIV positive |
- Inform the patient that LILETTA is compatible with MRI and should not interfere with imaging [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Complete the Follow-Up Reminder Card and give it to the patient.
LILETTA® and its design are registered trademarks of Odyssea Pharma SPRL, an Allergan affiliate.
Manufactured by:
Odyssea Pharma, SPRL, Belgium
An affiliated company of Allergan USA, Inc.
Distributed by:
Allergan USA, Inc. Irvine, CA 92612
Marketed by:
Allergan USA, Inc.
Medicines360
Irvine, CA 92612
San Francisco, CA 94111
© 2019 Allergan and Medicines360. All rights reserved.
| PATIENT INFORMATION
LILETTA (lye-LET-uh) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) |
| Read this Patient Information carefully before you decide if LILETTA is right for you. This information does not take the place of talking with your gynecologist or other healthcare professional. If you have any questions about LILETTA, ask your healthcare professional. You should also learn about other birth control methods to choose the one that is best for you. |
| LILETTA does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). |
What is LILETTA?
Two thin threads are attached to the stem (lower end) of LILETTA. The threads are the only part of LILETTA you can feel when LILETTA is in your uterus; however, unlike a tampon string, the threads do not extend outside your body.  |
| What if I need birth control for more than 6 years?
LILETTA must be removed after 6 years. Your healthcare professional can place a new LILETTA during the same office visit if you choose to continue using LILETTA. |
| What if I want to stop using LILETTA?
LILETTA is intended for use up to 6 years, but you can stop using LILETTA at any time by asking your healthcare professional to remove it. You could become pregnant as soon as LILETTA is removed, so you should use another method of birth control if you do not want to become pregnant. Talk to your healthcare professional about the best birth control methods for you, because your new method may need to be started 7 days before LILETTA is removed to prevent pregnancy. |
| What if I change my mind about birth control and want to become pregnant in less than 6 years?
Your healthcare professional can remove LILETTA at any time. You could become pregnant as soon as LILETTA is removed. About 6 out of 7 women who want to become pregnant will become pregnant sometime in the first year after LILETTA is removed. |
| How does LILETTA work?
LILETTA may work in several ways including thickening cervical mucus, inhibiting sperm movement, reducing sperm survival, and thinning the lining of your uterus. It is not known exactly how these actions work together to prevent pregnancy. 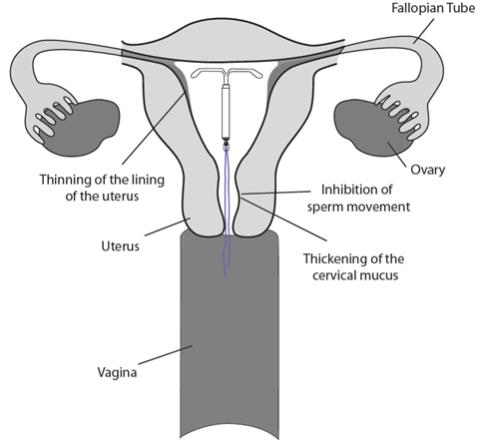 |
| How well does LILETTA work for contraception?
The following chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who use different methods of birth control. Each box on the chart contains a list of birth control methods that are similar in effectiveness. The most effective methods are at the top of the chart. The box on the bottom of the chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who do not use birth control and are trying to get pregnant. LILETTA, an intrauterine system (IUS), is also known as an intrauterine device (IUD), which is described in the box at the top of the chart.  |
| Who might use LILETTA?
You might choose LILETTA if you:
|
Do not use LILETTA if you:
|
Before having LILETTA placed, tell your healthcare professional if you have or have had any medical conditions, including those listed below:
|
| How is LILETTA placed?
LILETTA is placed by your healthcare professional during an in-office visit. First, your healthcare professional will examine your pelvis to find the exact position of your uterus. Your healthcare professional will then clean your vagina and cervix with an antiseptic solution and slide a plastic tube containing LILETTA through the cervix into your uterus. Your healthcare professional will then remove the plastic tube and leave LILETTA in your uterus. Your healthcare professional will trim the threads to the right length. You may experience pain, bleeding, or dizziness during and after placement. If your symptoms do not pass within 30 minutes after placement, LILETTA may not have been placed correctly. Your healthcare professional will examine you to see if LILETTA needs to be removed or replaced. |
| Should I check that LILETTA is in place?
Yes, you should check that LILETTA is in proper position by feeling the threads. It is a good habit to do this 1 time a month. Your healthcare professional should teach you how to check that LILETTA is in place. First, wash your hands with soap and water. You can check by reaching up to the top of your vagina with clean fingers to feel the threads. Do not pull on the threads. If you feel more than just the threads or if you cannot feel the threads, LILETTA may not be in the right position and may not prevent pregnancy. Use non-hormonal back-up birth control (such as condoms and spermicide) and ask your healthcare professional to check that LILETTA is still in the right place. |
| How soon after placement of LILETTA should I return to my healthcare professional?
Call your healthcare professional if you have any questions or concerns (see “When should I call my healthcare professional?”). Otherwise, you should return to your healthcare professional for a follow-up visit 4 to 6 weeks after LILETTA is placed to make sure that LILETTA is in the right position. |
| Can I use tampons with LILETTA?
Yes, tampons may be used with LILETTA |
| What if I become pregnant while using LILETTA?
Call your healthcare professional right away if you think you are pregnant. If possible, also do a urine pregnancy test. If you get pregnant while using LILETTA, you may have an ectopic pregnancy. This means that the pregnancy is not in the uterus. Unusual vaginal bleeding or abdominal pain especially with missed periods may be a sign of ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency that often requires surgery. Ectopic pregnancy can cause internal bleeding, infertility, and even death. There are also risks if you get pregnant while using LILETTA and the pregnancy is in the uterus. Severe infection, miscarriage, premature labor, premature delivery, and even death can occur with pregnancies that continue with an intrauterine system (IUS). Because of this, your healthcare professional may try to remove LILETTA, even though removing it may cause a miscarriage. If LILETTA cannot be removed, talk with your healthcare professional about the benefits and risks of continuing the pregnancy. If you continue your pregnancy, see your healthcare professional regularly. Call your healthcare professional right away if you get flu-like symptoms, fever, chills, cramping, pain, bleeding, vaginal discharge, or fluid leaking from your vagina. These may be signs of infection. It is not known if LILETTA can cause long-term effects on the fetus if it stays in place during a pregnancy. |
| How will LILETTA change my periods?
For the first 3 to 6 months, your period may become irregular and the number of bleeding days may increase. You may also have frequent spotting or light bleeding and cramping. Some women have heavy bleeding during this time. After you have used LILETTA for a while, the number of bleeding and spotting days is likely to lessen. For some women, menstrual periods will stop altogether. When LILETTA is removed, your menstrual periods will likely return to their former pattern. |
| Is it safe to breastfeed while using LILETTA?
You may use LILETTA when you are breastfeeding if more than 6 weeks have passed since you had your baby. If you are breastfeeding, LILETTA is not likely to affect the quality or amount of your breast milk or the health of your nursing baby. However, isolated cases of decreased milk production have been reported among women using progestin-only birth control pills. The risk of LILETTA becoming attached to (embedded) or going through the wall of the uterus is increased when LILETTA is placed in breastfeeding women. |
| Will LILETTA interfere with sexual intercourse?
You and your partner should not feel LILETTA during intercourse. LILETTA is placed in the uterus, not in the vagina. In some cases, your partner may feel the threads. If this occurs, or if you or your partner experience pain during sex, talk with your healthcare professional. |
| Can I have a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedure with LILETTA in place?
LILETTA should not interfere with imaging. |
| What are the possible side effects of LILETTA?
LILETTA can cause serious side effects, including:
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to Allergan at 1-800-678-1605. |
| After LILETTA has been inserted, when should I call my healthcare professional?
Call your healthcare professional if you have any concerns about LILETTA. Be sure to call if you:
|
| General information about the safe and effective use of LILETTA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare professional for information about LILETTA that is written for health professionals. For more information, go to www.LILETTA.com or call 1-855-LILETTA (1-855-545-3882). |
| LILETTA® and its design are registered trademarks of Odyssea Pharma SPRL, an Allergan affiliate. Manufactured by: Odyssea Pharma, SPRL, Belgium An affiliated company of Allergan USA, Inc. Distributed by: Allergan USA, Inc. Irvine, CA 92612 Marketed by: Allergan USA, Inc. Medicines360 Irvine, CA 92612 San Francisco, CA 94111 © 2019 Allergan and Medicines360. All rights reserved. Allergan® and its design are trademarks of Allergan, Inc. |
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration 10/2019
V1.0PPI5858
| LILETTA
levonorgestrel intrauterine device |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Actavis Pharma, Inc. (119723554) |