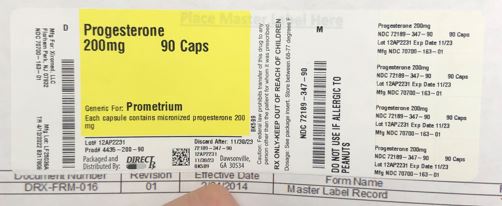
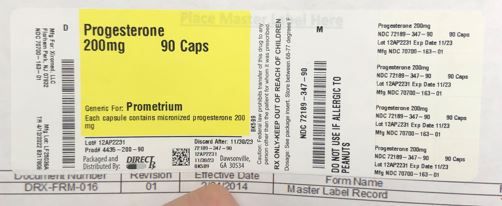
Label: PROGESTERONE capsule
- NDC Code(s): 72189-347-90
- Packager: Direct Rx
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 70700-163
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated April 27, 2022
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
DESCRIPTION
Progesterone capsules contain micronized progesterone for oral administration. Progesterone has a molecular weight of 314.47 and a molecular formula of C21H30O2. Progesterone (pregn-4-ene-3, 20-dione) is a white or creamy white, odorless, crystalline powder practically insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol, acetone and dioxane and sparingly soluble in vegetable oils, stable in air, melting between 126° and 131°C. The structural formula is:
[Chemical Structure]
Progesterone is synthesized from a starting material from a plant source and is chemically identical to progesterone of human ovarian origin. Progesterone capsules are available in multiple strengths to afford dosage flexibility for optimum management. Progesterone capsules contain 100 mg or 200 mg micronized progesterone and the following inactive ingredients: peanut oil, gelatin, glycerin, soya lecithin, titanium dioxide, and triglyderides medium chain.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Progesterone capsules are an oral dosage form of micronized progesterone which is chemically identical to progesterone of ovarian origin. The oral bioavailability of progesterone is increased through micronization.
Pharmacokinetics
A. Absorption
After oral administration of progesterone as a micronized soft-gelatin capsule formulation, maximum serum concentrations were attained within 3 hours. The absolute bioavailability of micronized progesterone is not known. Table 1 summarizes the mean pharmacokinetic parameters in postmenopausal women after five oral daily doses of progesterone capsules 100 mg as a micronized soft-gelatin capsule formulation.
TABLE 1. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Progesterone Capsules
Parameter Progesterone Capsules Daily Dose
100 mg 200 mg 300 mg*
Mean ± S.D.Cmax (ng/mL)
17.3 ± 21.9*
38.1 ± 37.8
60.6 ± 72.5
Tmax (hr)
1.5 ± 0.8
2.3 ± 1.4
1.7 ± 0.6
AUC (0-10) (ng × hr/mL)
43.3 ± 30.8
101.2 ± 66.0
175.7 ± 170.3
Serum progesterone concentrations appeared linear and dose proportional following multiple dose administration of progesterone capsules 100 mg over the dose range 100 mg per day to 300 mg per day in postmenopausal women. Although doses greater than 300 mg per day were not studied in females, serum concentrations from a study in male volunteers appeared linear and dose proportional between 100 mg per day and 400 mg per day. The pharmacokinetic parameters in male volunteers were generally consistent with those seen in postmenopausal women.
B. Distribution
Progesterone is approximately 96 percent to 99 percent bound to serum proteins, primarily to serum albumin (50 to 54 percent) and transcortin (43 to 48 percent).
C. Metabolism
Progesterone is metabolized primarily by the liver largely to pregnanediols and pregnanolones. Pregnanediols and pregnanolones are conjugated in the liver to glucuronide and sulfate metabolites. Progesterone metabolites which are excreted in the bile may be deconjugated and may be further metabolized in the intestine via reduction, dehydroxylation, and epimerization.
D. Excretion
The glucuronide and sulfate conjugates of pregnanediol and pregnanolone are excreted in the bile and urine. Progesterone metabolites are eliminated mainly by the kidneys. Progesterone metabolites which are excreted in the bile may undergo enterohepatic recycling or may be excreted in the feces.
E. Special Populations
The pharmacokinetics of progesterone capsules have not been assessed in low body weight or obese patients.
Hepatic Insufficiency: The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of progesterone capsules has not been studied.
Renal Insufficiency: The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of progesterone capsules has not been studied.
F. Food–Drug Interaction
Concomitant food ingestion increased the bioavailability of progesterone capsules relative to a fasting state when administered to postmenopausal women at a dose of 200 mg.
G. Drug Interactions
The metabolism of progesterone by human liver microsomes was inhibited by ketoconazole (IC50 < 0.1 μM). Ketoconazole is a known inhibitor of cytochrome P450 3A4, hence these data suggest that ketoconazole or other known inhibitors of this enzyme may increase the bioavailability of progesterone. The clinical relevance of the in vitro findings is unknown.
Coadministration of conjugated estrogens and progesterone capsules to 29 postmenopausal women over a 12-day period resulted in an increase in total estrone concentrations (Cmax 3.68 ng/mL to 4.93 ng/mL) and total equilin concentrations (Cmax 2.27 ng/mL to 3.22 ng/mL) and a decrease in circulating 17β estradiol concentrations (Cmax 0.037 ng/mL to 0.030 ng/mL). The half-life of the conjugated estrogens was similar with coadministration of progesterone capsules. Table 2 summarizes the pharmacokinetic parameters.
TABLE 2. Mean (± S.D.) Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Estradiol, Estrone, and Equilin Following Coadministration of Conjugated Estrogens 0.625 mg and Progesterone Capsules 200 mg for 12 Days to Postmenopausal Women
Conjugated Estrogens Conjugated Estrogens plus Progesterone Capsules
Drug Cmax
(ng/mL) Tmax
(hr) AUC(0-24h)
(ng × h/mL) Cmax
(ng/mL) Tmax
(hr) AUC(0-24h)
(ng × h/mL)*
Total estrogens is the sum of conjugated and unconjugated estrogen.Estradiol
0.037 ± 0.048
12.7 ± 9.1
0.676 ± 0.737
0.030 ± 0.032
17.32 ± 1.21
0.561 ± 0.572
Estrone Total*
3.68 ± 1.55
10.6 ± 6.8
61.3 ± 26.36
4.93 ± 2.07
7.5 ± 3.8
85.9 ± 41.2
Equilin Total
2.27 ± 0.95
6.0 ± 4.0
28.8 ± 13.0
3.22 ± 1.13
5.3 ± 2.6
38.1 ± 20.2
-
CLINICAL STUDIES
Effects on the endometrium
In a randomized, double-blind clinical trial, 358 postmenopausal women, each with an intact uterus, received treatment for up to 36 months. The treatment groups were: Progesterone capsules at the dose of 200 mg per day for 12 days per 28-day cycle in combination with conjugated estrogens 0.625 mg per day (n=120); conjugated estrogens 0.625 mg per day only (n=119); or placebo (n=119). The subjects in all three treatment groups were primarily Caucasian women (87 percent or more of each group). The results for the incidence of endometrial hyperplasia in women receiving up to 3 years of treatment are shown in Table 3. A comparison of the progesterone capsules plus conjugated estrogens treatment group to the conjugated estrogens only group showed a significantly lower rate of hyperplasia (6 percent combination product versus 64 percent estrogen alone) in the progesterone capsules plus conjugated estrogens treatment group throughout 36 months of treatment.
TABLE 3. Incidence of Endometrial Hyperplasia in Women Receiving 3 Years of Treatment
Endometrial Diagnosis Treatment Group
Conjugated Estrogens 0.625 mg
+ Progesterone Capsules 200 mg (cyclical) Conjugated Estrogens
0.625 mg
(alone) Placebo
Number of patients % of patients Number of patients % of patients Number of patients % of patients
n=117 n=115 n=116*
Most advanced result to least advanced result:
Adenocarcinoma > atypical hyperplasia > complex hyperplasia > simple hyperplasiaHYPERPLASIA *
7
6
74
64
3
3
Adenocarcinoma
0
0
0
0
1
1
Atypical hyperplasia
1
1
14
12
0
0
Complex hyperplasia
0
0
27
23
1
1
Simple hyperplasia
6
5
33
29
1
1
The times to diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia over 36 months of treatment are shown in Figure 1. This figure illustrates graphically that the proportion of patients with hyperplasia was significantly greater for the conjugated estrogens group (64 percent) compared to the conjugated estrogens plus progesterone capsules group (6 percent).
[Figure 1]
Figure 1. Time to Hyperplasia in Women Receiving up to 36 Months of Treatment
The discontinuation rates due to hyperplasia over the 36 months of treatment are as shown in Table 4. For any degree of hyperplasia, the discontinuation rate for patients who received conjugated estrogens plus progesterone capsules was similar to that of the placebo only group, while the discontinuation rate for patients who received conjugated estrogens alone was significantly higher. Women who permanently discontinued treatment due to hyperplasia were similar in demographics to the overall study population.
TABLE 4. Discontinuation Rate Due to Hyperplasia Over 36 Months of Treatment
Most Advanced Biopsy Result Through 36 Months of Treatment Treatment Group
Conjugated Estrogens + Progestrone Capsules (cyclical) Conjugated Estrogens
(alone) Placebo
n=120 n=119 n=119
Number of patients % of patients Number of patients % of patients Number of patients % of patientsAdenocarcinoma
0
0
0
0
1
1
Atypical hyperplasia
1
1
10
8
0
0
Complex hyperplasia
0
0
21
18
1
1
Simple hyperplasia
1
1
13
11
0
0
Effects on secondary amenorrhea
In a single-center, randomized, double-blind clinical study that included premenopausal women with secondary amenorrhea for at least 90 days, administration of 10 days of progesterone capsules therapy resulted in 80 percent of women experiencing withdrawal bleeding within 7 days of the last dose of progesterone capsules, 300 mg per day (n=20), compared to 10 percent of women experiencing withdrawal bleeding in the placebo group (n=21).
In a multicenter, parallel-group, open label, postmarketing dosing study that included premenopausal women with secondary amenorrhea for at least 90 days, administration of 10 days of progesterone capsules during two 28-day treatment cycles, 300 mg per day (n=107) or 400 mg per day (n=99), resulted in 73.8 percent and 76.8 percent of women, respectively, experiencing withdrawal bleeding.
The rate of secretory transformation was evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical study in estrogen-primed postmenopausal women. Progesterone capsules administered orally for 10 days at 400 mg per day (n=22) induced complete secretory changes in the endometrium in 45 percent of women compared to 0 percent in the placebo group (n=23).
A second multicenter, parallel-group, open label postmarketing dosing study in premenopausal women with secondary amenorrhea for at least 90 days also evaluated the rate of secretory transformation. All subjects received daily oral conjugated estrogens over 3 consecutive 28-day treatment cycles and progesterone capsules, 300 mg per day (n=107) or 400 mg per day (n=99) for 10 days of each treatment cycle. The rate of complete secretory transformation was 21.5 percent and 28.3 percent, respectively.
Women's Health Initiative Studies
The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) enrolled approximately 27,000 predominantly healthy postmenopausal women in two substudies to assess the risks and benefits of daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE) [0.625 mg]-alone or in combination with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) [2.5 mg] compared to placebo in the prevention of certain chronic diseases. The primary endpoint was the incidence of coronary heart disease [(CHD) defined as nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI), silent MI and CHD death], with invasive breast cancer as the primary adverse outcome. A "global index" included the earliest occurrence of CHD, invasive breast cancer, stroke, pulmonary embolism (PE), endometrial cancer (only in the CE plus MPA substudy), colorectal cancer, hip fracture, or death due to other cause. These sub studies did not evaluate the effects of CE–alone or CE plus MPA on menopausal symptoms.
WHI Estrogen Plus Progestin Substudy
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy was stopped early. According to the predefined stopping rule, after an average follow-up of 5.6 years of treatment, the increased risk of breast cancer and cardiovascular events exceeded the specified benefits included in the "global index." The absolute excess risk of events in the "global index" was 19 per 10,000 women-years.
For those outcomes included in the WHI "global index" that reached statistical significance after 5.6 years of follow-up, the absolute excess risks per 10,000 women-years in the group treated with CE plus MPA were 7 more CHD events, 8 more strokes, 10 more PEs, and 8 more invasive breast cancers, while the absolute risk reductions per 10,000 women-years were 6 fewer colorectal cancers and 5 fewer hip fractures.
Results of the estrogen plus progestin substudy, which included 16,608 women (average 63 years of age, range 50 to 79; 83.9 percent White, 6.8 percent Black, 5.4 percent Hispanic, 3.9 percent Other) are presented in Table 5. These results reflect centrally adjudicated data after an average follow-up of 5.6 years.
TABLE 5. Relative and Absolute Risk Seen in the Estrogen Plus Progestin Substudy of WHI at an Average of 5.6 Years*, †
Event Relative Risk CE/MPA versus Placebo (95% nCI ‡) CE/MPA
n = 8,506 Placebo
n = 8,102
Absolute Risk per 10,000 Women-Years*
Adapted from numerous WHI publications. WHI publications can be viewed at www.nhlbi.nih.gov/whi.
†
Results are based on centrally adjudicated data.
‡
Nominal confidence intervals unadjusted for multiple looks and multiple comparisons.
§
Not included in Global Index.
¶
Includes metastatic and non-metastatic breast cancer with the exception of in situ breast cancer.
#
All deaths, except from breast or colorectal cancer, definite or probable CHD, PE or cerebrovascular disease.
Þ
A subset of the events was combined in a "global index" defined as the earliest occurrence of CHD events, invasive breast cancer, stroke, pulmonary embolism, endometrial cancer, colorectal cancer, hip fracture, or death due to other causes.CHD events
1.23 (0.99-1.53)
41
34
Non-fatal MI
1.28 (1.00-1.63)
31
25
CHD death
1.10 (0.70-1.75)
8
8
All stroke
1.31 (1.03-1.88)
33
25
Ischemic Stroke
1.44 (1.09-1.90)
26
18
Deep vein thrombosis §
1.95 (1.43-2.67)
26
13
Pulmonary embolism
2.13 (1.45-3.11)
18
8
Invasive breast cancer ¶
1.24 (1.01-1.54)
41
33
Colorectal cancer
0.61 (0.42-0.87)
10
16
Endometrial cancer
0.81 (0.48-1.36)
6
7
Cervical cancer
1.44 (0.47-4.42)
2
1
Hip fracture
0.67 (0.47-0.96)
11
16
Vertebral fractures
0.65 (0.46-0.92)
11
17
Lower arm/wrist fractures
0.71 (0.59-0.85)
44
62
Total fractures
0.76 (0.69-0.83)
152
199
Overall mortality #
1.00 (0.83-1.19)
52
52
Global Index Þ
1.13 (1.02-1.25)
184
165
Timing of the initiation of estrogen plus progestin therapy relative to the start of menopause may affect the overall risk benefit profile. The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy stratified for age showed in women 50 to 59 years of age a non-significant trend toward reducing risk of overall mortality [hazard ratio (HR) 0.69 (95 percent CI, 0.44-1.07)].
Women's Health Initiative Memory Study
The estrogen plus progestin Women's Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS), an ancillary study of WHI, enrolled 4,532 predominantly healthy postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older (47 percent were 65 to 69 years of age; 35 percent were 70 to 74 years of age; and 18 percent were 75 years of age and older) to evaluate the effects of daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) on the incidence of probable dementia (primary outcome) compared to placebo.
After an average follow-up of 4 years, the relative risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 2.05 (95 percent CI, 1.21 – 3.48). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 45 versus 22 per 10,000 women-years. Probable dementia as defined in this study included Alzheimer's disease (AD), vascular dementia (VaD) and mixed type (having features of both AD and VaD). The most common classification of probable dementia in the treatment group and the placebo group was AD. Since the ancillary study was conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women. (See WARNINGS, PROBABLE DEMENTIA and PRECAUTIONS, GERIATRIC USE.)
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Progesterone capsules should not be used in women with any of the following conditions:
1.
Progesterone capsules should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to its ingredients. Progesterone capsules contain peanut oil and should never be used by patients allergic to peanuts.
2.
Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding.
3.
Known, suspected, or history of breast cancer.
4.
Active deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism or history of these conditions.
5.
Active arterial thromboembolic disease (for example, stroke and myocardial infarction), or a history of these conditions.
6.
Known liver dysfunction or disease.
7.
Known or suspected pregnancy. -
WARNINGS
1. Cardiovascular disorders
An increased risk of pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), stroke, and myocardial infarction has been reported with estrogen plus progestin therapy. Should any of these occur or be suspected, estrogen with progestin therapy should be discontinued immediately.Risk factors for arterial vascular disease (for example, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, tobacco use, hypercholesterolemia, and obesity) and/or venous thromboembolism (for example, personal history or family history of venous thromboembolism [VTE], obesity, and systemic lupus erythematosus) should be managed appropriately.
a. Stroke
In the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) estrogen plus progestin substudy, a statistically significant increased risk of stroke was reported in women 50 to 79 years of age receiving daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) compared to women in the same age group receiving placebo (33 versus 25 per 10,000 women-years). The increase in risk was demonstrated after the first year and persisted. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.) Should a stroke occur or be suspected, estrogen plus progestin therapy should be discontinued immediately.b. Coronary Heart Disease
In the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy, there was a statistically non-significant increased risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) events (defined as nonfatal myocardial infarction [MI], silent MI, or CHD death) reported in women receiving daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) compared to women receiving placebo (41 versus 34 per 10,000 women-years). An increase in relative risk was demonstrated in year 1 and a trend toward decreasing relative risk was reported in years 2 through 5. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)In postmenopausal women with documented heart disease (n = 2,763, average age 66.7 years), in a controlled clinical trial of secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease (Heart and Estrogen/Progestin Replacement Study [HERS]), treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) demonstrated no cardiovascular benefit. During an average follow-up of 4.1 years, treatment with CE plus MPA did not reduce the overall rate of CHD events in postmenopausal women with established coronary heart disease. There were more CHD events in the CE plus MPA-treated group than in the placebo group in year 1, but not during the subsequent years. Two thousand, three hundred and twenty-one (2,321) women from the original HERS trial agreed to participate in an open-label extension of HERS, HERS II. Average follow-up in HERS II was an additional 2.7 years, for a total of 6.8 years overall. Rates of CHD events were comparable among women in the CE plus MPA group and the placebo group in HERS, HERS II, and overall.
c. Venous Thromboembolism
In the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy, a statistically significant 2-fold greater rate of VTE (DVT and pulmonary embolism [PE]) was reported in women receiving daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) compared to women receiving placebo (35 versus 17 per 10,000 women-years). Statistically significant increases in risk for both DVT (26 versus 13 per 10,000 women-years) and PE (18 versus 8 per 10,000 women-years) were also demonstrated. The increase in VTE risk was demonstrated during the first year and persisted. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.) Should a VTE occur or be suspected, estrogen plus progestin therapy should be discontinued immediately.If feasible, estrogens with progestins should be discontinued at least 4 to 6 weeks before surgery of the type associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism, or during periods of prolonged immobilization.
2. Malignant neoplasms
a. Breast Cancer
The most important randomized clinical trial providing information about breast cancer in estrogen plus progestin users is the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) substudy of daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg). After a mean follow-up of 5.6 years, the estrogen plus progestin substudy reported an increased risk of invasive breast cancer in women who took daily CE plus MPA. In this substudy, prior use of estrogen-alone or estrogen plus progestin therapy was reported by 26 percent of the women. The relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.24 (95 percent nCI, 1.01-1.54), and the absolute risk was 41 versus 33 cases per 10,000 women-years, for CE plus MPA compared with placebo.Among women who reported prior use of hormone therapy, the relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.86, and the absolute risk was 46 versus 25 cases per 10,000 women-years, for estrogen plus progestin compared with placebo. Among women who reported no prior use of hormone therapy, the relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.09, and the absolute risk was 40 versus 36 cases per 10,000 women-years for CE plus MPA compared with placebo. In the same substudy, invasive breast cancers were larger, were more likely to be node positive, and were diagnosed at a more advanced stage in the CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) group compared with the placebo group. Metastatic disease was rare, with no apparent difference between the two groups. Other prognostic factors such as histologic subtype, grade and hormone receptor status did not differ between the groups. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
Consistent with the WHI clinical trials, observational studies have also reported an increased risk of breast cancer for estrogen plus progestin therapy, and a smaller increased risk for estrogen-alone therapy, after several years of use. The risk increased with duration of use, and appeared to return to baseline over about 5 years after stopping treatment (only the observational studies have substantial data on risk after stopping). Observational studies also suggest that the risk of breast cancer was greater, and became apparent earlier, with estrogen plus progestin therapy as compared to estrogen-alone therapy. However, these studies have not generally found significant variation in the risk of breast cancer among different estrogen plus progestin combinations, doses, or routes of administration.
The use of estrogen plus progestin has been reported to result in an increase in abnormal mammograms requiring further evaluation. All women should receive yearly breast examinations by a healthcare provider and perform monthly breast self-examinations. In addition, mammography examinations should be scheduled based on patient age, risk factors, and prior mammogram results.
b. Endometrial Cancer
An increased risk of endometrial cancer has been reported with the use of unopposed estrogen therapy in a woman with a uterus. The reported endometrial cancer risk among unopposed estrogen users is about 2 to 12 times greater than in non-users, and appears dependent on duration of treatment and on estrogen dose. Most studies show no significant increased risk associated with the use of estrogens for less than 1 year. The greatest risk appears associated with prolonged use, with increased risks of 15- to 24-fold for 5 to 10 years or more and this risk has been shown to persist for at least 8 to 15 years after estrogen therapy is discontinued.Clinical surveillance of all women using estrogen plus progestin therapy is important. Adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in all cases of undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding. There is no evidence that the use of natural estrogens results in a different endometrial risk profile than synthetic estrogens of equivalent estrogen dose. Adding a progestin to estrogen therapy in postmenopausal women has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer.
c. Ovarian Cancer
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy reported a statistically non-significant increased risk of ovarian cancer. After an average follow-up of 5.6 years, the relative risk for ovarian cancer for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 1.58 (95 percent nCI, 0.77 – 3.24). The absolute risk for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 4 versus 3 cases per 10,000 women-years. In some epidemiologic studies, the use of estrogen plus progestin and estrogen-only products, in particular for 5 or more years, has been associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer. However, the duration of exposure associated with increased risk is not consistent across all epidemiologic studies and some report no association.3. Probable dementia
In the estrogen plus progestin Women's Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS), an ancillary study of WHI, a population of 4,532 postmenopausal women 65 to 79 years of age was randomized to daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) or placebo.In the WHIMS estrogen plus progestin ancillary study, after an average follow-up of 4 years, 40 women in the CE plus MPA group and 21 women in the placebo group were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia for estrogen plus progestin versus placebo was 2.05 (95 percent CI, 1.21-3.48). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 45 versus 22 cases per 10,000 women-years. It is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and PRECAUTIONS, GERIATRIC USE.)
4. Vision abnormalities
Retinal vascular thrombosis has been reported in patients receiving estrogen. Discontinue estrogen plus progestin therapy pending examination if there is sudden partial or complete loss of vision, or if there is a sudden onset of proptosis, diplopia or migraine. If examination reveals papilledema or retinal vascular lesions, estrogen plus progestin therapy should be permanently discontinued. -
HOW SUPPLIED
Progesterone capsules, 100 mg are off-white, ovoid, capsules with "PR1" marked.
NDC 70700-162-01, Bottle of 100 capsules
Progesterone capsules, 200 mg are off-white, ovoid, capsules with "PR2" marked.
NDC 70700-163-01, Bottle of 100 capsules
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from excessive moisture.
Dispense in tight, light-resistant container as defined in USP/NF, accompanied by a Patient Insert.
Keep out of reach of children.
- OVERDOSAGE
-
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Prevention of Endometrial Hyperplasia
Progesterone capsules should be given as a single daily dose at bedtime, 200 mg orally for 12 days sequentially per 28-day cycle, to a postmenopausal woman with a uterus who is receiving daily conjugated estrogens tablets.Treatment of Secondary Amenorrhea
Progesterone capsules may be given as a single daily dose of 400 mg at bedtime for 10 days.Some women may experience difficulty swallowing progesterone capsules. For these women, progesterone capsules should be taken with a glass of water while in the standing position.
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PROGESTERONE
progesterone capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:72189-347(NDC:70700-163) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PROGESTERONE (UNII: 4G7DS2Q64Y) (PROGESTERONE - UNII:4G7DS2Q64Y) PROGESTERONE 200 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MEDIUM-CHAIN TRIGLYCERIDES (UNII: C9H2L21V7U) GELATIN, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2G86QN327L) PEANUT OIL (UNII: 5TL50QU0W4) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) LECITHIN, SOYBEAN (UNII: 1DI56QDM62) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Product Characteristics Color white Score no score Shape OVAL Size 16mm Flavor Imprint Code PR2 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:72189-347-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 04/14/2022 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA205229 04/14/2022 Labeler - Direct Rx (079254320) Registrant - Direct Rx (079254320) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Direct Rx 079254320 relabel(72189-347)