Label: LILETTA- levonorgestrel intrauterine device
- NDC Code(s): 0023-5858-01
- Packager: Allergan, Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated June 29, 2023
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LILETTA® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LILETTA.
LILETTA (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
Initial U.S. Approval: 1968 (norgestrel)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Indications and Usage, Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (1.2) 06/2023 Dosage and Administration, Dosing Over Time (2.1) 06/2023 Dosage and Administration, Insertion Instructions (2.3) 11/2022 Dosage and Administration, Removal of LILETTA (2.6) 06/2023 Contraindications (4) 06/2023 Warnings and Precautions, Expulsion (5.6) 06/2023 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The initial release rate of levonorgestrel (LNG) is approximately 20 mcg/day and declines progressively to approximately 6.5 mcg/day after 8 years; LILETTA can be removed at any time but must be removed by the end of the eighth year. (2.1)
- To be inserted into the uterine cavity with the provided inserter by a trained healthcare professional using strict aseptic technique. Follow insertion instructions exactly as described. (2.3)
- Re-examination and evaluation should be considered 4 to 6 weeks after insertion and during routine care, or more often if clinically indicated. (2.5)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
One intrauterine system consisting of a T-shaped polyethylene frame with a drug reservoir containing 52 mg LNG, packaged within a sterile inserter. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Pregnancy (4)
- Use for post-coital contraception (emergency contraception) (4)
- Congenital or acquired uterine anomaly that distorts the uterine cavity and would be incompatible with correct IUS placement (4)
- Acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) (4)
- Postpartum endometritis or infected abortion in the past 3 months (4)
- Known or suspected uterine or cervical malignancy (4)
- Known or suspected breast cancer or other hormone-sensitive cancer (4)
- Uterine bleeding of unknown etiology (4)
- Untreated acute cervicitis or vaginitis or other lower genital tract infections (4)
- Acute liver disease or liver tumor (benign or malignant) (4)
- Increased susceptibility to pelvic infections (4)
- A previously inserted IUS that has not been removed (4)
- Hypersensitivity to any component of LILETTA (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Remove LILETTA if pregnancy occurs with LILETTA in place and LILETTA is in the uterus. If pregnancy occurs, there is increased risk of ectopic pregnancy (including loss of fertility), pregnancy loss, septic abortion (including septicemia, shock, and death), and premature labor and delivery. (5.1, 5.2)
- Severe infection or sepsis, including Group A streptococcal sepsis (GAS), have been reported following insertion of LNG-releasing IUSs; strict aseptic technique is essential during insertion. (5.3)
- Before using LILETTA, consider the risks of pelvic infection. (5.4)
- Perforation may occur and reduce contraceptive effectiveness or require surgery. Risk is increased if inserted in patients who have fixed retroverted uteri, are postpartum, or are lactating. (5.5)
- Partial or complete expulsion may occur. (5.6)
- Evaluate persistent enlarged ovarian follicles or ovarian cysts. (5.7)
- Bleeding patterns can become altered, may remain irregular, and amenorrhea may ensue. (5.8)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions reported in clinical studies (> 10% participants) are vulvovaginal mycotic infections, vaginal bacterial infections, acne, and nausea or vomiting. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie at 1-800-678-1605 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2023
- The initial release rate of levonorgestrel (LNG) is approximately 20 mcg/day and declines progressively to approximately 6.5 mcg/day after 8 years; LILETTA can be removed at any time but must be removed by the end of the eighth year. (2.1)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Contraception
1.2 Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Over Time
2.2 Timing of Insertion
2.3 Insertion Instructions
2.4 Patient Counseling and Record-Keeping
2.5 Patient Follow-Up
2.6 Removal of LILETTA
2.7 Continuation of Contraception after Removal
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ectopic Pregnancy
5.2 Intrauterine Pregnancy
5.3 Sepsis
5.4 Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or Endometritis
5.5 Perforation
5.6 Expulsion
5.7 Ovarian Cysts
5.8 Bleeding Pattern Alterations
5.9 Breast Cancer
5.10 Clinical Considerations for Use and Removal
5.11 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Information
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Study Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 LILETTA
11.2 Inserter
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Study on Contraception
14.2 Clinical Study on Treatment of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.2 Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
LILETTA is indicated for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding for up to 5 years in patients who choose to use intrauterine contraception as their method of contraception; replace after the end of the fifth year if continued treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding is needed.
-
2
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Over Time
LILETTA contains 52 mg of levonorgestrel (LNG). Initially, LNG is released in vivo at a rate of approximately 20 mcg/day. This rate decreases progressively to approximately 6.5 mcg/day after 8 years. The average in vivo release rate of LNG is approximately 13.5 mcg/day over a period of 8 years.
For contraception, remove LILETTA by the end of the eighth year. LILETTA can be replaced at the time of removal with a new LILETTA if continued contraceptive protection is desired.
For treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding, replace LILETTA by the end of the fifth year if continued use is needed.
2.2 Timing of Insertion
Refer to Table 1 for instructions on when to start use of LILETTA.
Table 1: When to Insert LILETTA Starting LILETTA in patients not currently using hormonal or intrauterine contraception
- LILETTA can be inserted any time there is reasonable certainty the patient is not pregnant. Consider the possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of LILETTA [see Contraindications (4)].
- If LILETTA is inserted after the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle, the patient should use a barrier method of contraception (such as condoms) or abstain from vaginal intercourse for 7 days after insertion to prevent pregnancy.
Switching to LILETTA from an oral, transdermal, or vaginal hormonal contraceptive - LILETTA may be inserted at any time during the hormone-free interval of the previous method.
- If LILETTA is inserted during active use of the previous method, continue that method for 7 days after LILETTA insertion or until the end of the current treatment cycle.
- If using continuous hormonal contraception, discontinue that method 7 days after LILETTA insertion.
Switching to LILETTA from an injectable progestin contraceptive - LILETTA may be inserted at any time.
- If LILETTA is inserted more than 3 months (13 weeks) after the last injection, the patient should use a barrier method of contraception (such as condoms) or abstain from vaginal intercourse for 7 days after insertion to prevent pregnancy.
Switching to LILETTA from a contraceptive implant or another IUS - Insert LILETTA on the same day the implant or IUS is removed.
- This switch to LILETTA may be at any time during the menstrual cycle. Back-up contraception is not needed.
Inserting LILETTA after pregnancy - After first-trimester abortion or miscarriage
- LILETTA may be inserted immediately after a first-trimester surgical or completed medical abortion or miscarriage, unless it is a septic abortion [see Contraindications (4)]. Back-up contraception is not needed.
- After childbirth or second-trimester abortion or miscarriage
- If immediate, insert LILETTA after expulsion/removal of the placenta, unless infection is present. [See Contraindication (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Back-up contraception is not needed.
- If not immediate:
- Delay inserting LILETTA a minimum of 4 weeks or until the uterus is fully involuted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- If the patient has not yet had a period, consider the possibility of ovulation and conception occurring prior to insertion of LILETTA [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and FDA-Approved Patient Labeling]. LILETTA can be inserted any time there is reasonable certainty the patient is not pregnant.
- If LILETTA is not inserted during the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle, the patient should use a barrier method of contraception (such as condoms) or abstain from vaginal intercourse for 7 days after insertion to prevent pregnancy [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Delay inserting LILETTA a minimum of 4 weeks or until the uterus is fully involuted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
2.3 Insertion Instructions
LILETTA (Figure 1a) is provided in a tray, sealed with a peel-off lid and is inserted into the uterine cavity with the provided inserter (Figure 1b) [see Description (11)] by carefully following the insertion instructions. Do not use if the seal of the sterile package is broken or appears compromised. Use strict aseptic techniques throughout the insertion procedure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. LILETTA is for single use only.
Note: The inserter provided with LILETTA (see Figure 1b) and the Insertion Instructions in this section are not applicable for immediate insertion after childbirth or second-trimester abortion or miscarriage. For immediate insertion, remove LILETTA from the inserter by pulling LILETTA out of the top of the inserter and insert according to accepted practice.
Figure 1a: LILETTA Intrauterine Contraceptive System (IUS)
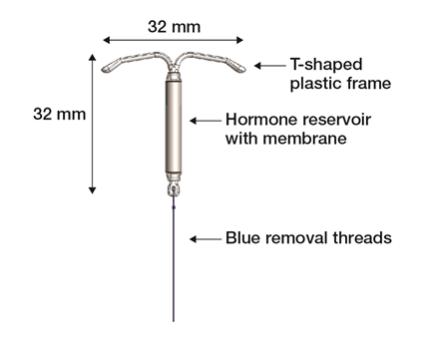
Figure 1b: LILETTA IUS with Inserter
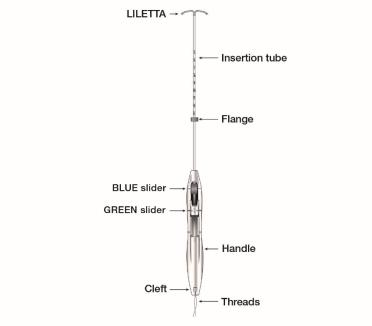
The LILETTA IUS is packaged partially preloaded within the inserter. The threads are passed through the insertion tube and exit through an opening in the handle at the cleft.
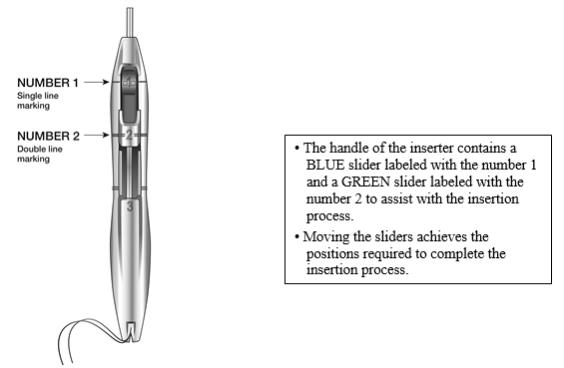
The handle of the inserter contains a BLUE slider labeled with the number 1 and a GREEN slider labeled with the number 2. The handle is labeled with the number 3. The sliders are labeled with the numbers 1 and 2, and the handle is labeled with the number 3 to assist with the insertion process (Figure 2). Moving the sliders achieves the positions required to complete the insertion process.
Figure 2: Inserter Sliders
Planning for Insertion
LILETTA should only be inserted by a trained healthcare professional. Healthcare professionals should become thoroughly familiar with the product, product educational materials, product insertion instructions, prescribing information, and patient labeling before attempting insertion of LILETTA.
Obtain a complete medical and social history to determine conditions that might influence the selection of LILETTA for contraception. If indicated, perform a physical examination and appropriate tests for genital or sexually transmitted infections.1 [See Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.10)].
Check the expiration date on the box before opening it. Do not insert LILETTA after the expiration date.
Visually inspect the packaging containing LILETTA to verify that the packaging has not been damaged (e.g., torn, punctured, etc.). If the packaging has any visual damage that could compromise sterility, do not use the unit for insertion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Complete the pelvic examination, speculum placement, tenaculum placement, and sounding of the uterus before opening the LILETTA packaging.
Do not open the packaging to insert LILETTA if the following clinical findings occur:
- the cervix is unable to be properly visualized
- the uterus cannot be adequately instrumented (during sounding)
- the uterus sounds to less than 5.5 cm
Preparation for Insertion
Ensure all needed items for LILETTA insertion are readily available:
- Gloves
- Sterile speculum
- Sterile uterine sound
- Sterile tenaculum
- Antiseptic solution
- LILETTA with inserter tray, sealed with a peel-off lid
- Sterile, blunt-tipped scissors
Additional items may be useful:
- Local anesthesia, needle, and syringe
- Sterile os finder and/or cervical dilators
- Ultrasound with abdominal probe
Exclude pregnancy and confirm that there are no other contraindications to the insertion and use of LILETTA.
Follow the insertion instructions exactly as described to ensure proper insertion.
If you encounter cervical stenosis at any time during uterine sounding or LILETTA insertion, use cervical dilators, not force, to overcome resistance. If necessary, dilation, sounding, and insertion may be performed with ultrasound guidance.
Insertion may be associated with some pain and/or bleeding or vasovagal reactions (e.g., diaphoresis, syncope, bradycardia, or seizure), especially in patients with a predisposition to these conditions. Consider administering analgesics prior to insertion.
Use aseptic technique during the entire insertion procedure.
Insertion Procedure
The overall insertion process is conducted in 5 steps.
Step 1 – Preparation of Patient for Insertion
- With the patient comfortably in lithotomy position, do a bimanual exam to establish the size, shape, and position of the uterus and to evaluate any signs of uterine infection.
- Gently insert a speculum to visualize the cervix.
- Thoroughly cleanse the cervix and vagina with antiseptic solution.
- Administer cervical anesthetic, if needed.
- Apply a tenaculum to the cervix and use gentle traction to align the cervical canal with the uterine cavity. If the uterus is retroverted, it may be more appropriate to grasp the lower lip of the cervix. Keep the tenaculum in position and maintain gentle traction on the cervix throughout the insertion procedure.
- Carefully sound the uterus to measure its depth.
- The uterus should sound to a depth of at least 5.5 cm. Insertion of LILETTA into a uterine cavity that sounds to less than 5.5 cm may increase the incidence of expulsion, bleeding, pain, perforation, and possibly pregnancy. LILETTA should not be inserted if the uterus sounds to less than 5.5 cm.
- After ascertaining that the patient is appropriate for LILETTA, replace contaminated glove(s) and open the packaging containing LILETTA, noting the lot number.
Step 2 – Opening the Sterile LILETTA Packaging
- Remove the sealed tray containing LILETTA from the box.
- Inspect the sealed tray and do not use the product if the packaging, inserter, or IUS is damaged.
- Lay the tray on a flat surface with the peel-off lid side up.
- Remove peel-off lid.
Step 3 – Loading LILETTA into the Inserter
- To remove the inserter from the tray, grasp the handle below the sliders and twist gently (Figure 3).
- NOTE: Do not attempt to remove the inserter by pulling on the tube.
Figure 3: Removing Inserter from Tray

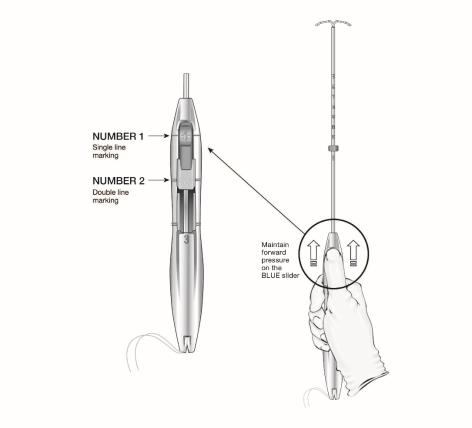
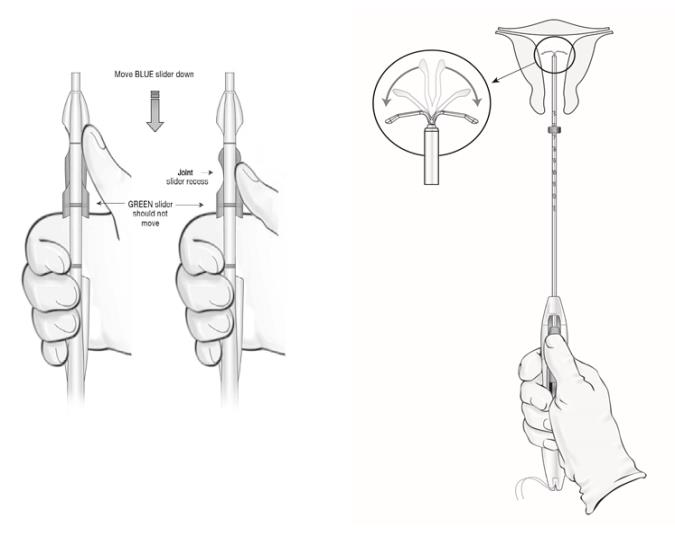
- Ensure both sliders (labeled 1 and 2) are fully forward (Figure 4):
- The BLUE slider (labeled with the number 1) has a single line marking that will align with the handle’s single line marking.
- The GREEN slider (labeled with the number 2) has a double line marking that will align with the handle’s double line marking.
- The BLUE slider (labeled with the number 1) has a single line marking that will align with the handle’s single line marking.
- Grip the handle keeping your thumb or finger in the groove of the BLUE slider (over the numeral 1) and apply forward pressure while ensuring both sliders are fully forward.
Figure 4: Sliders Completely Forward for Loading LILETTA
- Load LILETTA into the inserter:
- Ensure the arms of the IUS are horizontal (aligned to the horizontal plane of the handle and flange); adjust the rotation of the IUS as needed using the flat sterile surface of the tray.
- While maintaining forward pressure on the BLUE slider, gently pull the threads straight back to load LILETTA into the insertion tube. Ensure even tension is applied to both threads when pulling.
- Pull the threads upward or downward to lock the threads into the cleft at the bottom end of the handle (Figure 5); you must lock the threads in the cleft to prevent the IUS from moving out of the top of the insertion tube. Once the threads are locked in the cleft, stop holding the threads.
- After the IUS is loaded, continue to sustain forward pressure on the BLUE slider to maintain a hemispherical dome with the tips of the IUS.
- Ensure the arms of the IUS are horizontal (aligned to the horizontal plane of the handle and flange); adjust the rotation of the IUS as needed using the flat sterile surface of the tray.
- When correctly loaded, the IUS is completely within the insertion tube with the tips of the arms forming a hemispherical dome at the top of the tube (Figure 6).
- If the IUS is not correctly loaded, do not attempt insertion.
- To re-load LILETTA:
▪ Pull the BLUE slider back with your thumb until the groove becomes aligned with the GREEN slider to release the IUS.
▪ Manually pull the threads out of the cleft.
▪ Return the BLUE slider to the forward position and repeat the loading steps.
Figure 5: Locking the Threads in Cleft
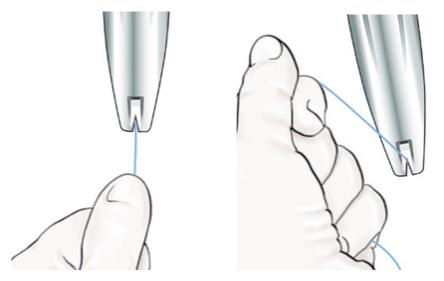
Figure 6: Close-up of Hemispherical Dome at Tip of Tube

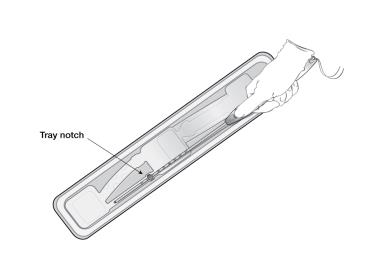
- Adjust the flange to the measured uterine depth based on sounding. To adjust, place the flat side of the flange in the tray notch (Figure 7) or against a sterile edge inside of the tray. Slide the insertion tube as necessary to move the flange to the correct measurement. Ensure the flat sides of the flange are in the same horizontal plane as the handle. If, at any step, there is a need to touch the flange or another sterile surface, sterile gloves should be used.
Figure 7: Adjusting the Flange
- If an adjustment to the curvature of the insertion tube is required to accommodate the anatomical orientation of the uterus, you may bend or straighten the insertion tube, but do not touch above the flange unless using sterile gloves. When bending the tube, avoid sharp bends to prevent kinking.
- Once the flange has been properly positioned, avoid contact of flange against objects that can change its position (e.g., tray, speculum, tenaculum, etc.).
Step 4 – Inserting LILETTA into the Uterus
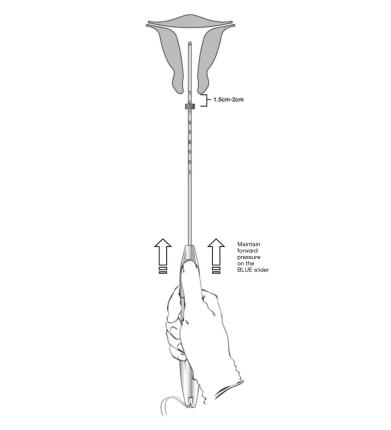
- Apply gentle traction on the tenaculum and continue to apply forward pressure on the BLUE slider while inserting the loaded insertion tube through the cervical os. Advance the tube until the upper edge of the flange is 1.5-2 cm from the external cervical os (Figure 8). Maintain forward pressure on the BLUE slider throughout the insertion process.
○ DO NOT advance flange to the cervix at this time.
○ DO NOT force the inserter. If necessary, dilate the cervical canal.
Figure 8: Advancing Insertion Tube until Flange is 1.5 to 2 cm from the External Cervix
● Using your thumb or finger, gently slide only the BLUE slider back. You will feel slight resistance initially to move the BLUE slider out of its starting position. Continue to move the BLUE slider back until you feel slight resistance again as the BLUE and GREEN sliders will merge together to form a joint slider recess. Do not move the BLUE slider any more than is necessary to create the recess. Maintain the GREEN slider so that the double line markings on the slider and the insertion handle remain aligned (Figure 9). This will allow the IUS arms to open in the lower uterine segment. Do not pull the sliders back any further as this could result in premature release of the IUS at the incorrect location.
Figure 9: Releasing and Opening the Arms of the IUS
- Wait 10-15 seconds to allow for the arms of the IUS to fully open.
- Without moving the sliders, advance the inserter until the flange touches the cervix. If fundal resistance is encountered, do not continue to advance. LILETTA is now in the fundal position (Figure 10).
- Note: Fundal position is important to prevent expulsions.
Figure 10: Move LILETTA into the Fundal Position
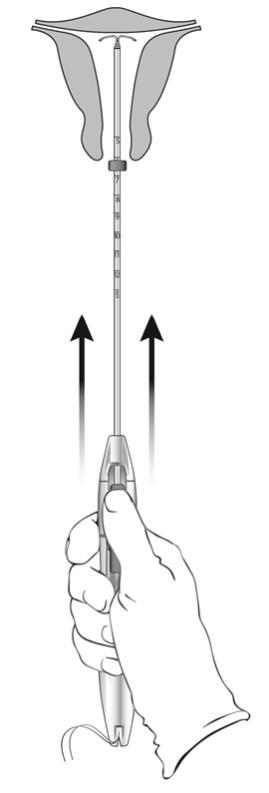
Step 5 – Releasing LILETTA and Procedure Completion
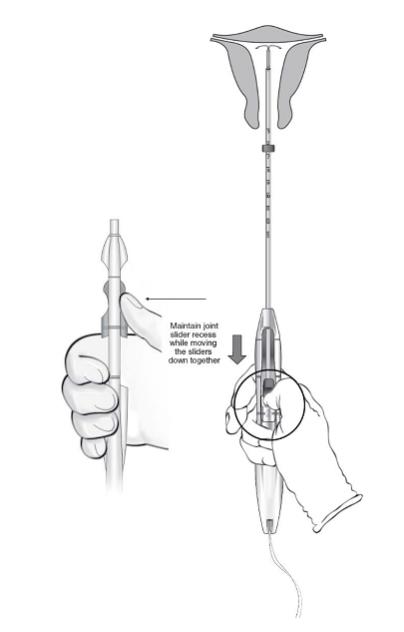
- While holding the inserter steady and maintaining its position relative to the cervix, move both sliders (BLUE and GREEN) together while maintaining the joint slider recess down toward the number 3 on the handle (Figure 11) until a click is heard and the GREEN indicator at the bottom of the handle is visible, signifying deployment (Figure 12).
Figure 11: Releasing LILETTA from the Inserter Tube
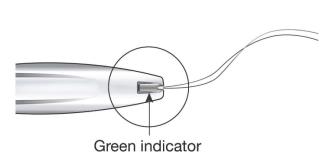
- Look at the cleft to ensure the threads were properly released (Figure 12); if not released or if a click is not heard, grasp the threads and gently pull the threads out of the cleft.
Figure 12: Green Indicator Visible and Threads Released from Cleft
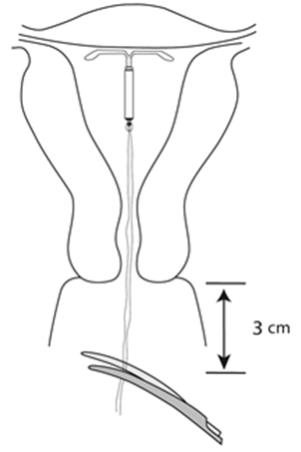
- Withdraw the inserter from the uterus.
- Use blunt-tipped sharp scissors to cut the IUS threads perpendicular to the thread length, leaving about 3 cm outside of the cervix (Figure 13). Note: Do not cut threads at an angle as this may leave sharp ends.
- Do not apply tension or pull on the threads when cutting to prevent displacing the IUS.
Figure 13: Cut the Threads about 3 cm from the Cervix
- Insertion of LILETTA is now complete.
Important information to consider during or after insertion:
If you suspect the IUS is not in the correct position, conduct the following procedures:
- Check insertion with an ultrasound or other appropriate radiologic test.
- If incorrect insertion is confirmed, remove LILETTA. Do not reinsert the same LILETTA IUS after removal.
Difficult Insertion
If insertion is difficult because the uterus cannot be appropriately instrumented, consider the following measures:
- Use of cervical anesthesia to make sounding and manipulation more tolerable.
- Use of dilators to dilate the cervix if needed to allow passage of the sound or inserter.
- Abdominal ultrasound guidance during dilation and/or insertion.
- If there is clinical concern, exceptional pain, or bleeding during or after insertion, take appropriate steps, such as physical examination and ultrasound, immediately to exclude uterine perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
2.4 Patient Counseling and Record-Keeping
Counsel the patient on what to expect following LILETTA insertion. Discuss expected bleeding patterns with LILETTA use. Review the signs and symptoms associated with infection, perforation, and expulsion that may occur with use of LILETTA [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Prescribe analgesics, if indicated.
2.5 Patient Follow-Up
The healthcare professional should consider re-examining and evaluating patients 4 to 6 weeks after insertion and during routine care, or more frequently if clinically indicated. The IUS threads should be checked during each evaluation.
2.6 Removal of LILETTA
Planning and Timing of Removal
If pregnancy is desired, LILETTA can be removed at any time.
If pregnancy is not desired, LILETTA can be removed at any time; however, a contraception method should be started prior to removal of LILETTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Counsel patients that they are at risk of pregnancy if they had intercourse in the week prior to removal without use of a backup contraceptive method.
For contraception, LILETTA should be removed after 8 years. LILETTA can be replaced at the time of removal with a new LILETTA if continued contraceptive protection is desired.
For treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding, LILETTA should be replaced at the end of the fifth year if continued treatment is needed.
Preparation for Removal
Ensure all needed items for LILETTA removal are readily available:
- Gloves
- Sterile speculum
- Sterile forceps
Additional items may be required:
- Local anesthetic, needle, and syringe
- Sterile os finder and/or cervical dilators
- Ultrasound with abdominal transducer
- Sterile tenaculum
- Antiseptic solution
- Sterile long, narrow forceps or intrauterine thread retriever
Removal may be associated with some pain and/or bleeding or vasovagal reactions (e.g., syncope, bradycardia, or seizure), especially in patients with a predisposition to these conditions.
After removal of LILETTA, examine the system to ensure that it is intact. The hormone cylinder may slide over and cover the horizontal arms, giving the appearance of missing arms. This does not require further intervention if the system is verified to be intact.
Breakage, embedment in the myometrium, or perforation of LILETTA can make removal difficult [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. IUS breakage may be associated with removal. Analgesia, paracervical anesthesia, cervical dilation, alligator forceps or other grasping instrument, or hysteroscopy may assist in removal.
Removal Procedure
With the patient comfortably in lithotomy position, place a speculum and visualize the cervix.
When the threads of LILETTA are visible:
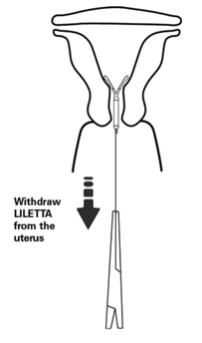
- Remove the IUS by applying gentle traction on the threads with forceps (Figure 14).
- The arms of the device will fold upward as it is withdrawn from the uterus.
- If the IUS cannot be removed with gentle traction on the threads, perform an ultrasound examination to confirm location of the IUS, including assessment for embedment in the myometrium or partial- or total-perforation. If the IUS is in the uterus, use long, narrow forceps to grasp LILETTA. Consider use of a tenaculum, cervical anesthesia, cervical dilators, and/or ultrasound guidance as needed.
- After removal, examine the system to ensure it is intact.
If the threads of LILETTA are not visible:
- Determine location of the IUS and exclude embedment or perforation by ultrasound examination [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
- If the IUS is in the uterine cavity, thoroughly cleanse the cervix and vagina with antiseptic solution. Use a thread retriever to capture the threads or a long, narrow forceps (e.g., Alligator forceps) to grasp LILETTA. Consider use of a tenaculum, cervical anesthesia, cervical dilators, and/or ultrasound guidance as needed. If LILETTA cannot be removed using the above techniques, consider hysteroscopic evaluation for removal.
- If the IUS is not in the uterine cavity, consider an abdominal x-ray or CT scan to evaluate if the IUS is in the abdominal cavity. Consider laparoscopic evaluation for removal, as clinically indicated.
- After removal, examine the system to ensure it is intact.
Figure 14: Removal of LILETTA
2.7 Continuation of Contraception after Removal
If a patient wishes to continue using LILETTA or another intrauterine contraceptive, insertion can occur immediately after removal.
If a patient with regular cycles wants to start a different birth control method, time the removal and initiation of a new method to ensure continuous contraception. Either remove LILETTA during the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle and start the new method or start the new method at least 7 days prior to removing LILETTA if removal is to occur at other times during the cycle.
If a patient with irregular cycles or amenorrhea wants to start a different birth control method, start the new method at least 7 days before LILETTA removal.
If LILETTA is removed but no other contraceptive method has already been started, the new contraceptive method can be started on the day LILETTA is removed. The patient should use a backup barrier method of contraception (e.g., condoms) or abstain from vaginal intercourse for 7 days to prevent pregnancy.
- LILETTA can be inserted any time there is reasonable certainty the patient is not pregnant. Consider the possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of LILETTA [see Contraindications (4)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4
CONTRAINDICATIONS
LILETTA is contraindicated when one or more of the following conditions exist:
Pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
For use as post-coital contraception (emergency contraception)
Congenital or acquired uterine anomaly, including leiomyomas, that distorts the uterine cavity and would be incompatible with correct IUS placement [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Postpartum endometritis or infected abortion in the past 3 months [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)]
Known or suspected uterine or cervical malignancy
Known or suspected breast cancer or other hormone-sensitive cancer, now or in the past [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
Uterine bleeding of unknown etiology [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
Untreated acute cervicitis or vaginitis, including bacterial vaginosis, known chlamydial or gonococcal cervical infection, or other lower genital tract infections until infection is controlled [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Acute liver disease or liver tumor (benign or malignant)
Conditions associated with increased susceptibility to pelvic infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
A previously inserted IUS that has not been removed
A history of hypersensitivity reaction to any component of LILETTA. Reactions may include rash, urticaria, and angioedema [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
5
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Ectopic Pregnancy
Evaluate patients for ectopic pregnancy if they become pregnant with LILETTA in place because the likelihood of a pregnancy being ectopic is increased with use of an IUS. Approximately half of pregnancies that occur with an IUS in place are likely to be ectopic. Also consider the possibility of ectopic pregnancy in the case of lower abdominal pain, especially in association with missed menses or new onset bleeding in an amenorrheic patient. If an ectopic pregnancy is confirmed, LILETTA should be removed.
The incidence of ectopic pregnancy in the clinical study on contraception with LILETTA, which excluded participants with a history of ectopic pregnancy who did not have a subsequent intrauterine pregnancy, was approximately 0.12 per 100 women-years. There were no ectopic pregnancies in the clinical study on heavy menstrual bleeding with LILETTA. The risk of ectopic pregnancy in patients who have a history of ectopic pregnancy and use LILETTA is unknown. Patients with a previous history of ectopic pregnancy, tubal surgery, or pelvic infection have a higher risk of ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy may require surgery and may result in loss of fertility.
Patients who use LILETTA should be informed about recognizing the signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy and promptly reporting them to their healthcare professional, and about the associated risks of ectopic pregnancy (e.g., loss of fertility).
5.2 Intrauterine Pregnancy
If pregnancy occurs while using LILETTA, determine if LILETTA is in the uterus. If LILETTA is in the uterus, attempt to remove LILETTA because leaving it in place may increase the risk of spontaneous abortion and preterm labor. Removal of LILETTA or probing of the uterus may also result in spontaneous abortion. In the event of an intrauterine pregnancy with LILETTA, consider the following:
Septic Abortion
If a patient becomes pregnant with an IUS in place, septic abortion—potentially including septicemia, septic shock, and death—may occur. Septic abortion typically requires hospitalization and treatment with intravenous antibiotics. Septic abortion may result in spontaneous abortion or a medical indication for pregnancy termination. Should severe infection of the uterus occur, hysterectomy may be required, which will result in permanent infertility. LILETTA is contraindicated in patients who have had an infected abortion in the prior 3 months.
Continuation of Pregnancy
If a patient becomes pregnant with LILETTA in place and if LILETTA cannot be removed or the patient chooses not to have it removed, warn the patient that failure to remove LILETTA increases the risk of miscarriage, sepsis, premature labor, and premature delivery. Prenatal care should include counseling about these risks and instructions to immediately report any flu-like symptoms, fever, chills, cramping, pain, bleeding, vaginal discharge or leakage of fluid, or any other symptom that suggests complications of the pregnancy.
5.3 Sepsis
Severe infection or sepsis, including Group A streptococcal sepsis (GAS), have been reported following insertion of LNG-releasing IUSs. In some cases, severe pain occurred within hours of insertion followed by sepsis within days. Because death from GAS is more likely if treatment is delayed, it is important to be aware of these rare but serious infections. Aseptic technique during insertion of LILETTA is essential to minimize serious infections such as GAS.
5.4 Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or Endometritis
Insertion of LILETTA is contraindicated in the presence of known or suspected PID or endometritis. As well, it is contraindicated in patients with untreated acute cervicitis or vaginitis (including bacterial vaginosis), known chlamydial or gonococcal cervical infection, or other known lower genital tract infections, until the infection is controlled. IUSs have been associated with an increased risk of PID, most likely due to organisms being introduced into the uterus during insertion. Assess risk factors for infection accordingly.
Patients who use LILETTA should be counseled to promptly notify a healthcare professional if they develop lower abdominal or pelvic pain, fever, chills, unusual or malodorous discharge, unexplained bleeding, genital lesions or sores, or dyspareunia. In such circumstances, perform a pelvic examination promptly to evaluate for possible pelvic infection. Remove LILETTA in cases of recurrent PID or endometritis, or if an acute pelvic infection is severe or does not respond to treatment.
In the clinical study on contraception with LILETTA, pelvic infection was diagnosed in 0.8% of participants. Pelvic infection was diagnosed as PID in 0.5% of participants and as endometritis in 0.3% of participants. Infections occurred following variable duration-of-use. One participant diagnosed with PID and two participants diagnosed with endometritis developed the infection within a week of LILETTA insertion. One case of endometritis was diagnosed at 39 days after LILETTA insertion. The remaining 11 cases of PID and endometritis were diagnosed more than six months after insertion, including one at 30 days after IUS removal. In the clinical study on heavy menstrual bleeding with LILETTA, there was one participant diagnosed with PID approximately 5 months after LILETTA insertion.
Patients at Increased Risk for PID or Endometritis
PID and endometritis are often associated with a sexually transmitted infection (STI), and LILETTA does not protect against STIs. The risk of PID or endometritis is greater for patients who have multiple sexual partners, and for patients whose sexual partner(s) have multiple sexual partners. Patients who have had PID or endometritis are at increased risk for recurrence or re-infection. Other risk factors for these infections include unprotected sex and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Asymptomatic PID or Endometritis
PID or endometritis may be asymptomatic but still result in tubal damage and its sequelae.
Treatment of PID or Endometritis
In IUS users with suspected or diagnosed PID or endometritis, obtain microbial specimens, including those for sexually transmitted infections, and initiate antibiotic treatment promptly. After initiation of antibiotic treatment, the IUS may be removed or kept in place. The patient should continue to receive antibiotic treatment according to current recommendations and should have close clinical follow-up. Guidelines for PID or endometritis treatment are available from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), Atlanta, Georgia. 1
If the patient opts for discontinuing IUS use, remove LILETTA after initiation of antibiotic treatment to avoid the potential risk for bacterial spread resulting from the removal procedure.
If the patient opts for ongoing IUS contraception, the patient may forego immediate removal of LILETTA after initiation of antibiotic treatment. However, the patient should have close clinical follow-up. If no clinical improvement occurs within 48–72 hours of initiating treatment, IUS removal is appropriate with continued antibiotic therapy, as indicated.
In the LILETTA clinical study on contraception, 12 of the 14 participants who developed PID or endometritis were successfully treated without removal of LILETTA (one of the 14 participants developed PID 30 days after removal).
Actinomycosis
Actinomycosis has been associated with IUS use. Symptomatic patients with known actinomycosis infection should have LILETTA removed and receive antibiotics. Actinomycetes can be found in the genital tract cultures in healthy patients without IUSs. The significance of actinomyces-like organisms on Pap test in an asymptomatic IUS user is unknown, and so this finding alone does not always require LILETTA removal and treatment. When possible, confirm a Pap test diagnosis with cultures.
5.5 Perforation
Perforation (total or partial, including penetration/embedment of LILETTA in the uterine wall or cervix) may occur, most often during insertion, although the perforation may not be detected until sometime later. Perforation may also occur at any time during IUS use. Perforation may reduce contraceptive efficacy and result in pregnancy. This may be associated with severe pain and continued bleeding.
The risk of perforation may be increased if an IUS is inserted when the uterus is fixed retroverted or not completely involuted during the post-partum period. Delay LILETTA insertion a minimum of four weeks or until involution is complete following a delivery or a second trimester abortion.
If perforation is suspected the IUS should be removed as soon as possible, surgery may be required. Delayed detection or removal of LILETTA in case of perforation may result in migration outside the uterine cavity, adhesions, peritonitis, intestinal perforations, intestinal obstruction, abscesses, and erosion of adjacent viscera.
In a large prospective comparative non-interventional cohort study with another IUS the incidence of uterine perforation was reported as 6.3 per 1,000 insertions for lactating participants, compared to 1.0 per 1,000 insertions for non-lactating participants.
The incidence of perforation during or following LILETTA insertion in the clinical studies, which excluded breastfeeding participants, was 0.1%.
5.6 Expulsion
Partial or complete expulsion of LILETTA may occur, resulting in the loss of contraceptive protection. In the clinical study on contraception with LILETTA, an overall expulsion rate of 4.1% over 8 years was reported, with a rate of 2.4% in nulliparous participants and 6.4% in parous participants. The majority (70.4%) occur in the first 12 months, with 23.9% occurring in the first three months and 42.3% in the first six months, cumulatively. Risk of expulsion is increased for patients with a history of heavy menstrual bleeding or greater than normal BMI at the time of insertion. In the clinical study on heavy menstrual bleeding with LILETTA, 8.6% of participants experienced expulsions, with two-thirds occurring within the first 90 days. About 90% of the expulsions occurred in overweight or obese participants.
Expulsion may be associated with symptoms of bleeding or pain, or it may be asymptomatic and go unnoticed. LILETTA typically decreases menstrual bleeding over time; therefore, an increase in menstrual bleeding may be indicative of an expulsion. Consider further diagnostic imaging, such as sonography or X-ray, to confirm expulsion if LILETTA is not found in the uterus.
The risk of expulsion is increased with insertions performed immediately after delivery; it appears to be increased with insertions performed after second-trimester abortion, based on limited data.
Remove a partially expelled LILETTA. If expulsion has occurred, a new LILETTA may be inserted when there is reasonable certainty the patient is not pregnant.
5.7 Ovarian Cysts
The contraceptive effect of LILETTA is mainly due to its local effects within the uterus; therefore, ovulatory cycles with follicular rupture usually occur in patients of fertile age using LILETTA. Most ovarian cysts that occur during use of LNG-releasing IUSs are asymptomatic and disappear spontaneously during two to three months of observation. Cysts that cause clinical symptoms can result in pelvic or abdominal pain or dyspareunia. In the clinical study on contraception, symptomatic ovarian cysts occurred in 4.7% of participants using LILETTA over the course of 8 years, and 0.3% of participants discontinued use of LILETTA because of an ovarian cyst. In the clinical study on heavy menstrual bleeding, symptomatic ovarian cysts occurred in 1.0% of participants using LILETTA over the course of 6 months.
Evaluate persistent ovarian cysts. Surgical intervention is not usually required, but may be necessary in some cases, and occurred in 1 (0.06%) of participants in the LILETTA study. Discuss this risk with patients, as indicated.
5.8 Bleeding Pattern Alterations
LILETTA can alter the bleeding pattern and result in spotting, irregular bleeding, heavy bleeding, oligomenorrhea, and amenorrhea. During the first three to six months of LILETTA use, the number of bleeding and spotting days may increase and irregular bleeding patterns may develop. Thereafter, the number of bleeding and spotting days usually decreases but bleeding may remain irregular.
Contraception Study
The amenorrhea rates observed in the LILETTA clinical study on contraception are shown in Table 2. The bleeding and spotting days, based on 28-day cycle equivalents, are shown in Table 3. In this study, 2.5% of participants discontinued LILETTA due to bleeding complaints.
Table 2: Amenorrhea Rates Last 90-Day Interval of Year Year 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Amenorrhea Rate* 19% 27% 37% 37% 40% 40% 39% 39% *Amenorrhea is defined as no bleeding and/or spotting.
Table 3: Bleeding and Spotting Days per 28-Day Cycle Equivalent 28-Day Cycle Equivalent
N*Cycle 1
N=1,691Cycle 4
N=1,593Cycle 7
N=1,519Cycle 13
N=1,395Cycle 26
N=1,109Days on treatment 1-28 85-112 169-196 337-364 674-728 Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Number of bleeding days 5.8 5.2 2.3 3.3 1.6 2.7 1.2 2.4 0.8 1.8 Number of spotting days 9.0 5.9 4.3 4.2 3.2 3.6 2.7 3.4 1.9 2.8 *N includes all LILETTA participants in the clinical study on contraception.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding Study
The amenorrhea rates observed in the LILETTA clinical study on heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) are shown in Table 4. Amenorrhea developed in 19% of LILETTA study participants by Cycle 6.
Table 4: Amenorrhea Rates for 28-Day Treatment Cycles 28-Day Cycle
NBaseline
N=87Cycle 1
N=87Cycle 2
N=88Cycle 3
N=88Cycle 4
N=82Cycle 5
N=82Cycle 6
N=79Amenorrhea Rate* 0% 3% 8% 11% 13% 17% 19% *Amenorrhea is defined as no bleeding and/or spotting. Percentages within each cycle are based on the number of participants who completed the cycle.
The bleeding and spotting days, based on 28-day cycle equivalents, are shown in Table 5. In this study, 3.8% of LILETTA participants discontinued due to bleeding complaints.
Table 5: Bleeding and Spotting Days from Baseline to Treatment Cycle 3 and Cycle 6 28-Day Cycle
N*Baseline
N=87Cycle 3
N=88Cycle 6
N=79Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Number of Bleeding Days 4.9 1.5 3.7 3.8 2.2 3.5 Number of Spotting Days 1.8 1.1 7.3 7.0 5.1 5.8 *N includes participants with at least one complete 28-day cycle of product-use. Calculations are based on complete 28-day cycles (at least 23 days in length).
Resumption of Menses After Discontinuation
In the LILETTA clinical study on contraception, 651 of 652 (99.8%) participants 16-35 years of age at enrollment that were evaluated resumed menses after LILETTA removal. This excludes twelve participants (9 became pregnant, 2 had a hysterectomy, and 1 had ovulatory dysfunction).
Other Bleeding Pattern Changes
If a significant change in bleeding develops during prolonged use, conduct diagnostic tests to assess possible endometrial pathology. Consider the possibility of pregnancy, including ectopic pregnancy, if menstruation does not occur within six weeks of the onset of a previous menstruation. After excluding pregnancy, repeat pregnancy tests are generally not necessary in amenorrheic patients unless indicated by other signs of pregnancy or pelvic pain.
5.9 Breast Cancer
Patients who currently have or have had breast cancer, or have a suspicion of breast cancer, should not use hormonal contraception, including LILETTA, because some breast cancers are hormone-sensitive [see Contraindications (4)].
Spontaneous reports of breast cancer have been received during postmarketing experience with LNG-releasing IUSs. Observational studies have not provided consistent evidence of an increased risk of breast cancer with use of an LNG-releasing IUS.
5.10 Clinical Considerations for Use and Removal
Obtain a complete medical and social history, including partner status, to determine conditions that might influence the selection of an IUS for contraception.
Exclude underlying endometrial pathology (e.g., polyps or cancer) prior to the insertion of LILETTA in patients with persistent or uncharacteristic bleeding because irregular bleeding/spotting is common during the first months of LILETTA use and may preclude adequate assessment after insertion. LILETTA is contraindicated in patients with uterine bleeding of unknown etiology.
Exclude underlying congenital or acquired uterine anomalies, including leiomyomas, that distort the uterine cavity and would be incompatible with correct IUS placement [see Contraindications (4)].
Ensure a previously inserted IUS has been removed prior to insertion of LILETTA [see Contraindications (4)].
Assess whether the patient is at increased risk of pelvic infection (e.g., unprotected sex, history of PID, or acquired immune deficiency syndrome [AIDS]). LILETTA does not protect against HIV/STI transmission [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Use LILETTA with caution after careful assessment if any of the following conditions exist, and consider removal of the IUS if any of them arise during use:
- Coagulopathy or use of anticoagulants
- Migraine, focal migraine with asymmetrical visual loss, or other symptoms indicating transient cerebral ischemia
- Exceptionally severe or frequent headache
- Marked increase of blood pressure
- Severe arterial disease such as stroke or myocardial infarction
Consider removing LILETTA if any of the following conditions arise during use [see Contraindications (4)]:
- Uterine or cervical malignancy
- Jaundice
If the threads are not visible or are significantly shortened, they may have broken or retracted into the cervical canal or uterus. Consider the possibility that the IUS may have been displaced, (e.g., expulsed or perforated the uterus) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6)]. Exclude pregnancy and verify the location of LILETTA by an appropriate diagnostic method (e.g., ultrasonography, X-ray, or gentle exploration of the cervical canal with a suitable instrument) [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)]. If LILETTA is displaced, remove it. A new LILETTA may be inserted at that time or during the next menses if it is certain that conception has not occurred. If LILETTA is in place with no evidence of perforation, no intervention is indicated.
- Coagulopathy or use of anticoagulants
-
6
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious or important adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
Ectopic Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Intrauterine Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Group A Streptococcal Sepsis (GAS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or Endometritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Expulsion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Ovarian Cysts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
Bleeding Pattern Alterations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Study Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure of 1,751 generally healthy participants, 16 to 45 years of age, to LILETTA in a large, multi-center contraceptive study conducted in the US. Participants included 1,401 exposed for 1 year and 380 who completed 8 years of use; 58% were nulliparous (mean age 25.1 ± 4.3 years) and 42% were parous (mean age 30.3 ± 6.1 years). Most participants who received LILETTA were Caucasian (78.4%) or Black/African American (13.3%); 14.7% of participants were of Hispanic ethnicity. Mean BMI of LILETTA participants was 26.9 kg/m2 (range 15.8 – 61.6 kg/m2); 25.1% had a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 of which 5.3% had a BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2. The data cover more than 80,221 28-day cycles of LILETTA exposure. The frequencies of reported adverse drug reactions represent crude incidences.
The most common adverse reactions during the LILETTA clinical study on contraception (occurring in ≥ 5% of participants) are shown in Table 6. The most common adverse reactions during the first year of use were acne (11.4%), bacterial vaginitis (9.0%), and vulvovaginal mycotic infection (7.9%).
Table 6: Adverse Reactions in ≥ 5% of LILETTA Participants in the Phase 3 Clinical Study on Contraception Adverse Reaction % LILETTA Participants (N = 1,751) Vulvovaginal mycotic infections 20.2% Vaginal bacterial infections 19.2% Acne 15.5% Nausea or vomiting 10.5% Headache 10.1% Breast tenderness or pain 10.1% Abdominal discomfort or pain 10.0% Dyspareunia 9.6% Anxiety 9.6% Depression 9.1% Pelvic discomfort or pain 8.7% Dysmenorrhea 7.3% Mood changes 6.5% Back pain 6.5% Weight increased 6.1% Vaginal discharge 5.8% In the clinical study, 20.1% of LILETTA participants discontinued prematurely due to an adverse reaction. The most common adverse reactions reported by participants as reason for discontinuation were expulsion (4.1%), bleeding complaints (2.5%), acne (1.4%), dysmenorrhea (1.0%), weight increased (1.0%), mood swings (0.8%), uterine spasm (0.7%), dyspareunia (0.6%) and pelvic pain (0.6%). Two participants discontinued the clinical study due to PID and one due to endometritis. The most common adverse reactions reported by participants as reason for discontinuation during the first year of use were expulsion (2.9%) and acne (0.7%).
In the clinical study, serious adverse reactions related to LILETTA were ectopic pregnancies, ovarian cysts, and IUS perforation requiring laparoscopic surgery.
In the LILETTA clinical study on heavy menstrual bleeding, which included 105 participants who were 18- to 50-years old, the adverse reaction profile was consistent with the adverse reaction profile for LILETTA participants in the contraception study as shown in Table 6. Approximately 11% of LILETTA study participants discontinued prematurely due to an adverse reaction. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were expulsions (4.8%) and bleeding pattern alterations (3.8%).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of LNG-releasing IUSs. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Arterial thrombotic and venous thromboembolic events, including cases of pulmonary emboli, deep vein thrombosis, and stroke
- Hypersensitivity (including rash, urticaria, and angioedema)
- Increased blood pressure
- Dizziness
- Device breakage
- Arterial thrombotic and venous thromboembolic events, including cases of pulmonary emboli, deep vein thrombosis, and stroke
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
LILETTA is contraindicated for use in pregnant patients and LILETTA may cause adverse pregnancy outcomes. If a patient becomes pregnant with LILETTA in place, there is an increased risk of miscarriage, sepsis, premature labor, and premature delivery. Published studies report no harmful effects on fetal development associated with long-term use of contraceptive doses of oral progestins in a pregnant patient. There have been isolated cases of virilization of the external genitalia of the female fetus following local exposure to LNG during pregnancy with an LNG IUS in place. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with LILETTA.
The background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2-4% and of miscarriage is 15-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Published studies report the presence of LNG in human milk. Small amounts of progestins (approximately 0.1% of the total maternal doses) were detected in the breast milk of nursing mothers who used other LNG-releasing IUSs. Isolated cases of decreased milk production have been reported with another LNG-releasing IUS. There are no reports of adverse effects in breastfed infants with maternal use of progestin-only contraceptives. The infant’s developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for LILETTA, underlying maternal conditions, and any potential adverse effects from LILETTA on the infant.
The incidence of uterine perforation appears higher in lactating patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Assess pregnancy status prior to inserting LILETTA, as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of LILETTA have been established in females of reproductive potential. The safety and effectiveness are expected to be the same for postpubertal females under the age of 16 as for users 16 years and older. The LILETTA clinical study on contraception included 11 participants who were 16 to 17 years of age; no differences in safety or effectiveness were identified in these participants through 8 years of use of LILETTA. Use of this product is not indicated before menarche.
8.5 Geriatric Use
LILETTA is not indicated in patients after menopause and has not been studied in this population.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic disease on the disposition of LNG released from LILETTA [see Contraindications (4)].
-
11
DESCRIPTION
11.1 LILETTA
LILETTA (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) contains 52 mg of levonorgestrel, a progestin, and is intended to provide an initial release rate of 20.4 mcg/day of levonorgestrel.
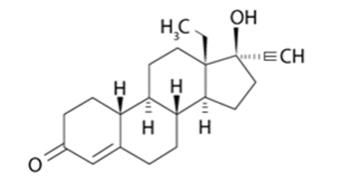
Levonorgestrel USP, (-)-13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one, the active ingredient in LILETTA, is the levorotatory form of norgestrel, which consists of a racemic mixture of D-(–)-norgestrel (levonorgestrel) and L-(+)-norgestrel (dextronorgestrel). It has a molecular weight of 312.45, a molecular formula of C21H28O2, and the following structural formula:
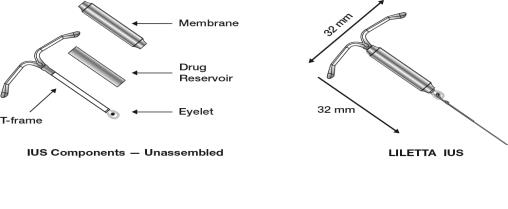
LILETTA consists of a T-shaped polyethylene frame (T-frame) with a drug reservoir around the vertical stem (Figure 15). The T-frame has a loop at one end of the vertical stem and two horizontal arms at the other end. The drug reservoir consists of a cylinder, made of a mixture of 52 mg levonorgestrel and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) formed from silicone base, tetra-n-propyl silicate, and stannous octoate. The drug reservoir is covered by a translucent PDMS membrane. The low-density polyethylene of the T-frame is compounded with barium sulfate, which makes it radio-opaque. A blue polypropylene monofilament removal thread is attached to an eyelet at the end of the vertical stem of the T-frame. The polypropylene of the removal thread contains a copper-containing pigment as a colorant. The components of LILETTA, including its packaging, are not manufactured using natural rubber latex.
Figure 15: Diagram of LILETTA
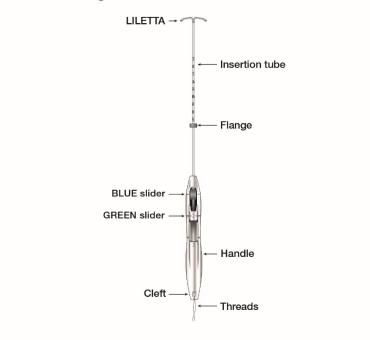
11.2 Inserter
The inserter device provided with LILETTA is a single-use, disposable, sterile insertion system (tube, flange, handle; Figure 16), partially preloaded with the IUS product for intrauterine administration.
Once LILETTA has been inserted, the inserter is discarded.
Figure 16: Diagram of Inserter
-
12
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The local mechanism by which continuously released LNG provides contraception has not been conclusively demonstrated. Studies of LNG-releasing IUSs suggest several mechanisms for pregnancy prevention: prevention of fertilization due to the thickening of the cervical mucus, which inhibits sperm passage through the cervix, and inhibition of sperm mobility and function (capacitation), and alteration of the endometrium.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
LILETTA has mainly local progestogenic effects in the uterine cavity which change the endometrium and may lead to alterations in the menstrual bleeding pattern [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. High local concentrations of LNG lead to morphological changes including stromal pseudo-decidualization, glandular atrophy, a leukocytic infiltration, and a decrease in glandular and stromal mitoses.
In clinical studies with other LNG-releasing IUSs with an LNG release rate similar to LILETTA, approximately 45-75% of menstrual cycles were ovulatory.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Low doses of LNG are administered into the uterine cavity with the LILETTA intrauterine delivery system. The initial in vivo release rate is 20.4 mcg/day and decreases to 17.7 mcg/day at 1 year, 15.3 mcg/day at 2 years, 13.3 mcg/day at 3 years, 11.5 mcg/day at 4 years, 10.0 mcg/day at 5 years, 8.7 mcg/day at 6 years, 7.5 mcg/day at 7 years, and 6.5 mcg/day at 8 years.
In the clinical study on contraception, systemic plasma LNG concentrations were assessed in a subset of participants through Month 30 and in all participants in the study at Month 36 and after. Plasma LNG concentrations following insertion of LILETTA are shown in Table 7.
Table 7: Plasma LNG Concentrations (mean ± SD, pg/mL) Following LILETTA Insertion 7 Days
(n=40)6 Months
(n=36)12 Months
(n=33)24 Months
(n=30)36 Months
(n=914)48 Months
(n=793)60 Months
(n=608)72 Months
(n=243)84 Months (n=211) 96 Months (n=142) 252±123 195±68 168±51 150±47 132±54 114±52 101±42 92±43 90±38 88±37 Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of LNG at steady-state following oral administration is reported to be approximately 1.8 L/kg. It is about 98.9% protein-bound, principally to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and, to a lesser extent, serum albumin.
Elimination
The elimination half-life of LNG after a single oral administration is approximately 13.9 ± 3.2 hours. Metabolic clearance rates may differ among individuals by several-fold, and this may account in part for wide individual variations in LNG concentrations seen in individuals using LNG–containing contraceptive products.
Metabolism
Following absorption, LNG is conjugated at the 17β-OH position to form sulfate conjugates and, to a lesser extent, glucuronide conjugates in serum. Significant amounts of conjugated and unconjugated 3α, 5β-tetrahydrolevonorgestrel are also present in serum, along with much smaller amounts of 3α, 5α-tetrahydrolevonorgestrel and 16β-hydroxylevonorgestrel. In vitro studies have demonstrated that oxidative metabolism of LNG is catalyzed by CYP enzymes, especially CYP3A4.
Excretion
About 45% of LNG and its metabolites are excreted in the urine and about 32% are excreted in feces, mostly as glucuronide conjugates.
Specific Populations
Racial or Ethnic Groups:
The effect of race on plasma LNG concentrations after LILETTA insertion was assessed in 731 (80%) White participants, 106 (12%) Black participants, 40 (4%) Asian participants, 8 (1%) American Indian/Alaska Native participants, and 21 (2%) multiple-race participants. Race does not appear to affect LNG concentrations following LILETTA insertion [see Clinical Studies (14)].
BMI/Body Weight:
The effect of BMI on LNG exposure was assessed in 687 non-obese (BMI < 30 kg/m2) and 225 obese participants (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2). Plasma LNG concentrations were approximately 21-34% lower in obese participants than in non-obese participants based on data collected from Months 36 to 96. However, since LILETTA has a mainly local progestogenic effect in the uterine cavity, the clinical relevance of the reduced systemic exposure is unclear [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Contraceptive effect of LILETTA is mediated via the direct release of LNG into the uterine cavity and is unlikely to be affected by drug interactions via enzyme induction or inhibition.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14
CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Study on Contraception
The efficacy of LILETTA for contraception was studied in a multicenter, randomized, open-label clinical study conducted in the US that enrolled 1,910 generally healthy participants aged 16 to 45 years, 1,751 of whom received LILETTA. LILETTA was inserted in 1,011 (58%) nulliparous and 740 (42%) parous participants. Participants with a history of ectopic pregnancy, PID, or trophoblastic disease without a subsequent intrauterine pregnancy, who were less than 4 weeks post-pregnancy, had HIV, or were not in a mutually monogamous relationship at study entry were excluded. The demographic profile of enrolled participants who received LILETTA are as follows: White 78.4%, Black or African American 13.3%, Asian 3.9%, American Indian or Alaska Native 1.2%, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander 0.3%; 2.9% identified multiple races; 14.7% indicated Hispanic ethnicity. The clinical study had no limit on weight (minimum or maximum) or BMI (range was 15.8 – 61.6 kg/m2). The mean BMI of LILETTA participants was 26.9 kg/m2; 24% were overweight, 24% were obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2), and 5% were morbidly obese (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2).
The pregnancy rate calculated as the Pearl Index (PI) in participants 16 to 35 years of age, inclusive, was the primary efficacy endpoint used to assess contraceptive reliability. The PI was calculated based on 28-day equivalent exposure cycles; evaluable cycles excluded those in which back-up contraception was used unless a pregnancy occurred in that cycle. The Year 1 PI was based on two pregnancies and the cumulative 8-year pregnancy rate was calculated by the life table method, based on a total of eleven pregnancies that occurred after the onset of treatment and within 7 days after LILETTA removal or expulsion. Table 8 shows the annual PI for each of the eight years and the calculated cumulative life table pregnancy rates through years 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8. For Year 7 and Year 8, participants who were more than 39 years of age at the beginning of the respective study year were excluded from the efficacy analysis.
Table 8: Contraceptive Efficacy: Pregnancy Rates LILETTA Clinical Study Number of 28-Day Cycles of Exposure
By YearYear-by-Year
Pearl Index
Pregnancy Rate (95% CI)Cumulative 28-Day Cycles of Exposure Cumulative Year
Life Table
Pregnancy Rate
(95% CI)Year 1 17,175 0.15 (0.02, 0.55) 17,175 0.14 (0.04, 0.57) Year 2 14,205 0.37 (0.10, 0.94) 31,380 0.50 (0.22, 1.10) Year 3 11,760 0.11 (0.00, 0.62) 43,140 0.60 (0.29, 1.27) Year 4 9,891 0.13 (0.00, 0.73) 53,031 0.73 (0.36, 1.48) Year 5 8,337 0.16 (0.00, 0.87) 61,368 0.89 (0.45, 1.74) Year 6 6,916 0.00 (0.00, 0.69) 68,284 0.89 (0.45, 1.74) Year 7* 5,280 0.49 (0.06, 1.78) 73,564 1.37 (0.71, 2.62) Year 8* 3,657 0.00 (0.00, 1.31) 77,221 1.37 (0.71, 2.62) *Excludes participants >39 years of age at the beginning of the respective year.
Conception rates after the removal of LILETTA were assessed and appeared consistent with conception rates in the general population having regular unprotected sexual intercourse for 12 months.
Of 244 participants who desired pregnancy after study discontinuation, 63.1% conceived within 6 months after removal of LILETTA and 83.2% conceived within 12 months after removal of LILETTA.
14.2 Clinical Study on Treatment of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
The efficacy of LILETTA in the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding was studied in a non-comparative, open-label clinical study conducted in the US. The study enrolled 105 generally healthy participants 18 to 50 years of age, with no contraindications to LILETTA, and with confirmed heavy menstrual bleeding (≥ 80 mL menstrual blood loss [MBL] per menses) determined using the alkaline hematin method. Participants with any structural (e.g., leiomyomas > 2 cm in greatest diameter or more than 3 leiomyomas > 1.5 cm in greatest diameter) or diagnosed pathophysiologic conditions that may cause heavy uterine bleeding were excluded.
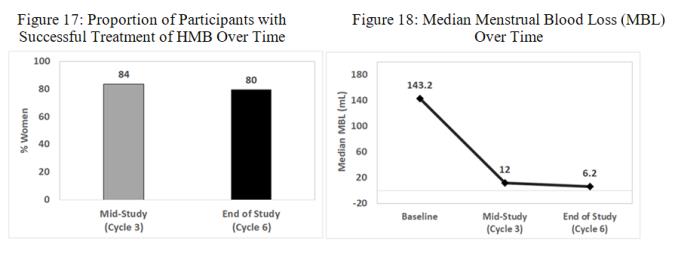
The study population was 64.8% White, 23.8% African American, and 11.4% Other; 9.5% of enrolled participants were of Hispanic ethnicity. The median BMI was 29.7 kg/m2 (with 23.8% overweight and 48.6% obese). The median baseline MBL was 143.2 mL.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of women with successful treatment, defined as (1) an end-of-study MBL volume < 80 mL and (2) ≥ 50% reduction in MBL from baseline to end-of-study.
Treatment outcomes with LILETTA are summarized in Figures 17 and 18. The proportion of participants meeting both criteria defining successful treatment was 80% at the end of the study, with a 95% confidence interval of 71-88% (Figure 17). The quantitative reduction in median MBL volume from baseline to mid-study and to end-of-study is shown in Figure 18. The median MBL percent reduction from baseline to mid-study was 91% and to end-of-study was 96%.
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
LILETTA (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system), containing 52 mg levonorgestrel, is supplied partially preloaded within the inserter and packaged in a clear plastic tray with lid. LILETTA is available in a carton of one sterile unit. NDC # 0023-5858-01.
LILETTA is supplied sterile. LILETTA is sterilized with ethylene oxide. Do not re-sterilize. Do not use if the packaging is damaged, or if the packaging is opened. Insert before the end of the month shown on the packaging. Store at 20°C – 25°C (68°F – 77°F), with excursions permitted between 15°C – 30°C (59°F – 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store the sealed tray with peel-off lid in outer carton until use to protect from light.
-
17
PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Advise patients that this product does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Advise patients about the risks of ectopic pregnancy, including the loss of fertility. Advise them to recognize and report promptly to their healthcare professional any symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, including lower abdominal pain, especially in association with missed periods [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Advise patients about the following concerns and precautions if pregnancy occurs while using LILETTA:
- LILETTA will likely need to be removed because leaving it in place may increase the risk of spontaneous abortion and preterm labor; however, removal of LILETTA or probing of the uterus may also result in spontaneous abortion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Report promptly to their healthcare professional any symptoms that suggest complications of the pregnancy, including flu-like symptoms, fever, chills, cramping, pain, bleeding, and vaginal discharge or leakage of fluid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Septic abortion may occur. Advise them that if LILETTA cannot be removed or they choose not to have it removed, there may be an increased risk of miscarriage, sepsis, premature labor, and premature delivery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Advise patients that severe infection or sepsis, including Group A streptococcal sepsis (GAS), can occur within the first few days after LILETTA is inserted. Advise them to contact a healthcare professional immediately if they develop severe pain or fever shortly after LILETTA is inserted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Advise patients about the possibility of PID or endometritis and that these infections can cause tubal damage leading to ectopic pregnancy or infertility, or infrequently can necessitate hysterectomy, or cause death. Advise the patient to recognize and report to their healthcare professional any of the following signs and symptoms of possible infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]:
- lower abdominal or pelvic pain or tenderness
- fever
- chills
- unusual or malodorous vaginal discharge
- atypical or unexplained bleeding (prolonged or heavy bleeding)
- genital lesions or sores.
- dyspareunia
Advise patients that perforation may occur, most often during insertion, although the perforation may not be detected until sometime later. Perforation may also occur at any time during IUS use. Advise them that if perforation occurs, LILETTA will have to be located and removed. Surgery may be required. Advise them that delayed detection or removal of LILETTA in case of perforation may have the following results [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]:
- migration of IUS outside the uterus
- intestinal perforations
- adhesions
- intestinal obstruction
- peritonitis
- erosion of adjacent viscera
- abscesses
- loss of contraceptive protection
Review with patients the signs and symptoms of LILETTA expulsion. Advise patients on how they can check that the threads still protrude from their cervix, and not to pull on them. Advise them that there is no contraceptive protection if LILETTA is displaced or expelled [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Advise patients that excessive pain or vaginal bleeding during insertion, worsening pain or bleeding after insertion, or the inability to feel the threads may occur with perforation and expulsion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6)].
Advise patients regarding the risk of ovarian cysts and that cysts can cause clinical symptoms including pelvic pain, abdominal pain or dyspareunia and infrequently will need surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Advise patients that irregular or prolonged bleeding and spotting, and/or cramps may occur during the first three to six months after insertion. If their symptoms continue or are severe, they should report them to their healthcare professional [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Advise patients to contact their healthcare professional if they experience any of the following symptoms or conditions:
- Stroke or heart attack
- Very severe or migraine headaches
- Unexplained fever
- Yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes, as these may be signs of serious liver problems
- Pregnancy or suspected pregnancy
- Severe vaginal bleeding or bleeding that lasts a long time, or if they miss a menstrual period
- Pelvic pain or pain during sex
- Patient or partner becomes HIV positive
- Possible exposure to sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Unusual or malodorous vaginal discharge
- Genital sores
- Inability to feel LILETTA's threads
Inform patients that LILETTA is compatible with MRI and should not interfere with imaging [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
LILETTA and its design are trademarks of Odyssea Pharma SPRL, an AbbVie company.
Medicines360 and its design are trademarks of Medicines360.
Manufactured by:
Odyssea Pharma, SPRL, Belgium
An affiliated company of AbbVieDistributed by:
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, Illinois 60064Marketed by:
AbbVie Inc. Medicines360
North Chicago, IL 60064 San Francisco, CA 94105© 2023 AbbVie and Medicines360. All rights reserved.
V4.1USPI5858
- LILETTA will likely need to be removed because leaving it in place may increase the risk of spontaneous abortion and preterm labor; however, removal of LILETTA or probing of the uterus may also result in spontaneous abortion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
LILETTA (lye-LET-uh)
(levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
Read this Patient Information carefully before you decide if LILETTA is right for you. This information does not take the place of talking with your gynecologist or other healthcare professional. If you have any questions about LILETTA, ask your healthcare professional. You should also learn about other birth control methods to choose the one that is best for you. LILETTA does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). What is LILETTA?
- LILETTA is a hormone-releasing system placed in your uterus by your healthcare professional to prevent pregnancy for up to 8 years.
- LILETTA can also help with heavy periods, also known as heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB), for up to 5 years.
- LILETTA can be removed by your healthcare professional at any time.
- LILETTA can be used whether or not you have given birth to a child.
Two thin threads are attached to the stem (lower end) of LILETTA. The threads are the only part of LILETTA you can feel when LILETTA is in your uterus; however, unlike a tampon string, the threads do not extend outside your body.

LILETTA is small and flexible What if I need birth control for more than 8 years?
LILETTA must be removed after 8 years. Your healthcare professional can place a new LILETTA during the same office visit if you choose to continue using LILETTA.What if I need treatment for heavy menstrual flow for more than 5 years?
For continued treatment of heavy menstrual flow after 5 years, your healthcare professional can remove LILETTA and place a new LILETTA during the same office visit.What if I want to stop using LILETTA?
LILETTA is intended for use as birth control for up to 8 years, but you can stop using LILETTA at any time by asking your healthcare professional to remove it. You could become pregnant as soon as LILETTA is removed, so you should use another method of birth control if you do not want to become pregnant. Talk to your healthcare professional about the best birth control methods for you, because your new method may need to be started 7 days before LILETTA is removed to prevent pregnancy.What if I change my mind about birth control and want to become pregnant in less than 8 years?
Your healthcare professional can remove LILETTA at any time. You could become pregnant as soon as LILETTA is removed. About 5 out of 6 patients who want to become pregnant will become pregnant sometime in the first year after LILETTA is removed.How does LILETTA work for birth control?
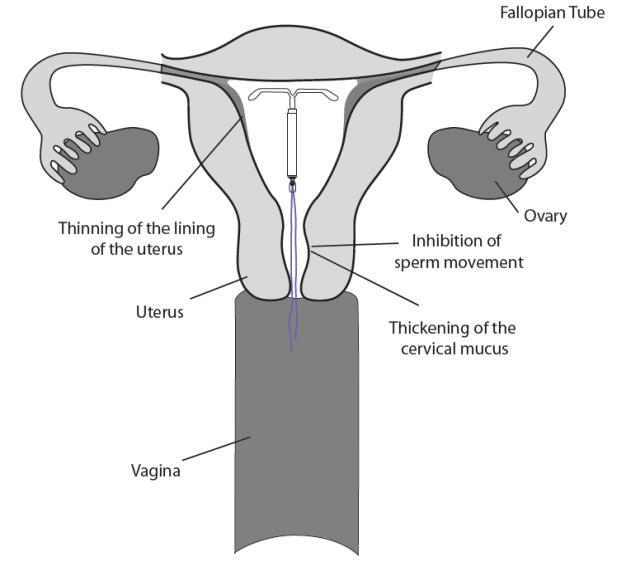
LILETTA may work in several ways including thickening cervical mucus, inhibiting sperm movement, reducing sperm survival, and thinning the lining of your uterus. It is not known exactly how these actions work together to prevent pregnancy.
How does LILETTA work for heavy menstrual bleeding?
The hormone in LILETTA, levonorgestrel, acts by controlling the monthly development of the womb (uterus) lining, making it thinner, so that there is less bleeding every month.How well does LILETTA work for birth control?
The following chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for patients who use different methods of birth control. Each box on the chart contains a list of birth control methods that are similar in effectiveness. The most effective methods are at the top of the chart. The box on the bottom of the chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for patients who do not use birth control and are trying to get pregnant.
LILETTA, an intrauterine system (IUS), is also known as an intrauterine device (IUD), which is shown in the box at the top of the chart.
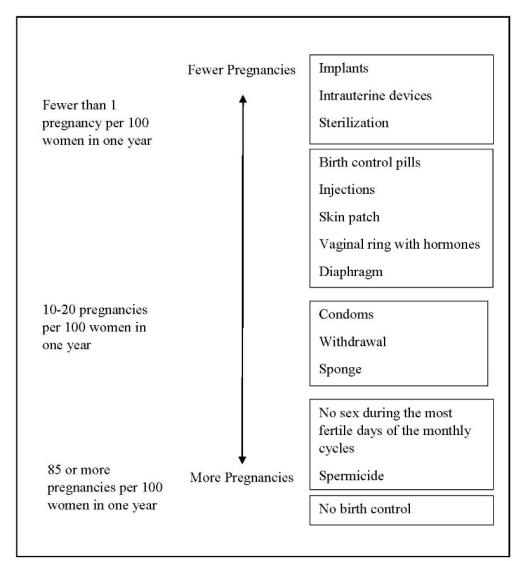
How well does LILETTA work for treating heavy menstrual bleeding?
In the clinical trial performed in patients with heavy menstrual bleeding and treated with LILETTA, the majority of (or 8 out of 10) patients were treated successfully. That is, their menstrual cycle blood loss was reduced to less than 80 mL and reduced by more than half by the end of treatment at six months.Who might use LILETTA?
You might choose LILETTA if you are willing to use a birth control method that is placed in the uterus, and want birth control with the following features:- long-term birth control that provides a low chance of getting pregnant (less than 1 in 100)
- works continuously for up to 8 years
- is reversible
- does not need to be taken daily
- does not contain estrogen
- treats heavy menstrual bleeding
Do not use LILETTA if you have any of the following conditions: - you are or might be pregnant; LILETTA cannot be used as an emergency contraceptive
- a serious pelvic infection called pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- an untreated lower genital infection now
- a serious pelvic infection after an abortion or pregnancy within the last 3 months
- a condition or behavior that can allow you to get infections more easily, such as those listed below:
○ problems with your immune system
○ having multiple sexual partners or your partner has multiple sexual partners
○ history of PID
- cancer of the uterus or cervix, known or suspected
- bleeding from the vagina that has not been explained
- short-term (acute) liver disease or a liver tumor
- breast cancer or any other cancer that is sensitive to progestin (a female hormone), now or in the past
- an intrauterine contraceptive system in your uterus already
- a condition of the uterus that changes the shape of the uterine cavity, such as large fibroid tumors
- an allergy to levonorgestrel, silicone, polyethylene, or barium sulfate
Before having LILETTA placed, tell your healthcare professional if you have or had any medical conditions, including those listed below:
- any of the conditions listed above
- you recently had a baby, or you are breastfeeding
- heart attack
- stroke
- heart disease you were born with, or problems with your heart valves
- blood clotting problems, or condition for which you take medicine to reduce clotting
- high blood pressure
- severe migraine headaches
- severe or frequent headaches
- AIDS, HIV, or any other sexually transmitted infection
How is LILETTA placed?
LILETTA is placed by your healthcare professional during an in-office visit.
First, your healthcare professional will examine your pelvis to find the exact position of your uterus. Your healthcare professional will then clean your vagina and cervix with an antiseptic solution and slide a plastic tube containing LILETTA through the cervix into your uterus. Your healthcare professional will then remove the plastic tube and leave LILETTA in your uterus. Your healthcare professional will trim the threads to the right length.
You may experience pain, bleeding, or dizziness during and after placement. If your symptoms do not pass within 30 minutes after placement, LILETTA may not have been placed correctly. Your healthcare professional will examine you to see if LILETTA needs to be removed or replaced.Should I check that LILETTA is in place?
Yes, you should check that LILETTA is in proper position by feeling the threads. It is a good habit to do this 1 time a month. Your healthcare professional should teach you how to check that LILETTA is in place. First, wash your hands with soap and water. You can check by reaching up to the top of your vagina with clean fingers to feel the threads. Do not pull on the threads.
If you feel more than just the threads or if you cannot feel the threads, LILETTA may not be in the right position and may not prevent pregnancy. Use non-hormonal back-up birth control (such as condoms) and ask your healthcare professional to check that LILETTA is still in the right place.How soon after placement of LILETTA should I return to my healthcare professional?
Call your healthcare professional if you have any questions or concerns (see “When should I call my healthcare professional?”). Generally, patients have a follow-up visit 4 to 6 weeks after LILETTA is placed to make sure that LILETTA is in the right position, and routine visits thereafter. Follow-up plans may vary according to patient needs.Can I use tampons or menstrual cups with LILETTA?
Yes, tampons or menstrual cups may be used with LILETTA. Change tampons or menstrual cups with care to avoid pulling the threads of LILETTA. If you think you may have pulled LILETTA out of place, avoid intercourse or use a non-hormonal back-up birth control (such as condoms), and contact your healthcare professional.What if I become pregnant while using LILETTA?
Call your healthcare professional right away if you think you are pregnant. If possible, also do a urine pregnancy test. If you get pregnant while using LILETTA, you may have an ectopic pregnancy. This means that the pregnancy is not in the uterus. Unusual vaginal bleeding or abdominal pain, especially with missed periods, may be a sign of ectopic pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency that often requires surgery. Ectopic pregnancy can cause internal bleeding, infertility, and even death.
There are also risks if you get pregnant while using LILETTA and the pregnancy is in the uterus. Severe infection, miscarriage, premature labor, premature delivery, and even death can occur with pregnancies that continue with an intrauterine system (IUS). Because of this, your healthcare professional may try to remove LILETTA, even though removing it may cause a miscarriage. If LILETTA cannot be removed, talk with your healthcare professional about the benefits and risks of continuing the pregnancy.
If you continue your pregnancy, see your healthcare professional regularly. Call your healthcare professional right away if you get flu-like symptoms, fever, chills, cramping, pain, bleeding, vaginal discharge, or fluid leaking from your vagina. These may be signs of infection.
It is not known if LILETTA can cause long-term effects on the fetus if it stays in place during a pregnancy.How will LILETTA change my periods?
For the first 3 to 6 months, your period may become irregular and the number of bleeding days may increase. You may also have frequent spotting or light bleeding and cramping. Some patients have heavy bleeding during this time. After you have used LILETTA for a while, the number of bleeding and spotting days is likely to lessen. For some patients, menstrual periods will stop altogether. When LILETTA is removed, your menstrual periods will likely return to their former pattern.Is it safe to breastfeed while using LILETTA?
You may use LILETTA when you are breastfeeding. LILETTA is not likely to affect the quality or amount of your breast milk or the health of your nursing baby. However, isolated cases of decreased milk production have been reported among patients using progestin-only birth control pills. The risk of LILETTA becoming attached to (embedded) or going through the wall of the uterus is increased when LILETTA is inserted while you are breastfeeding.Will LILETTA interfere with sexual intercourse?
You and your partner should not feel LILETTA during intercourse. LILETTA is placed in the uterus, not in the vagina. In some cases, your partner may feel the threads. If this occurs, or if you or your partner experience pain during sex, talk with your healthcare professional.Can I have a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedure with LILETTA in place?
Yes, LILETTA should not interfere with imaging. Tell your healthcare professional you have an intrauterine contraceptive in place.What are the possible side effects of LILETTA?
LILETTA can cause serious side effects, including those listed below:
-
ectopic pregnancy. If you get pregnant while using LILETTA, you might have an ectopic pregnancy. This means that the pregnancy is not in the uterus. Unusual vaginal bleeding or abdominal pain, especially with missed periods, may be a sign of ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency that often requires surgery. Ectopic pregnancy can cause internal bleeding, infertility, and even death.
-
intrauterine pregnancy risks. There are also risks if you get pregnant while using LILETTA and the pregnancy is in the uterus. Severe infection, miscarriage, premature labor, premature delivery, and even death can occur with pregnancies that continue with an intrauterine system (IUS). Because of this, your healthcare professional may try to remove LILETTA, even though removing it may cause a miscarriage. If LILETTA cannot be removed, talk with your healthcare professional about the benefits and risks of continuing the pregnancy. If, after seeing your healthcare professional, you choose to continue your pregnancy, see your healthcare professional regularly. Call your healthcare professional right away if you get flu-like symptoms, fever, chills, cramping, pain, bleeding, vaginal discharge, or fluid leaking from your vagina. These may be signs of infection. It is not known if LILETTA can cause long-term effects on the fetus if it stays in place during a pregnancy.
-
life-threatening infection. Life-threatening infection can occur within the first few days after LILETTA is placed. Call your healthcare professional immediately if you develop severe pain or fever shortly after LILETTA is placed.
-
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or endometritis. Some IUS users get a serious pelvic infection called pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or endometritis. PID and endometritis may be sexually transmitted. You have a higher chance of getting PID or endometritis if you or your partner have sex with other partners. PID or endometritis can cause serious problems such as infertility, ectopic pregnancy, or pelvic pain that does not go away. PID is usually treated with antibiotics. More serious cases of PID or endometritis may require surgery. Removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) is sometimes needed. In rare cases, infections that start as PID or endometritis can even cause death.
Tell your healthcare professional right away if you have any of these signs of PID or endometritis: long-lasting or heavy bleeding, unusual or foul-smelling vaginal discharge, low abdominal or pelvic pain, painful sex, genital lesions or sores, chills, or fever.
-
perforation. LILETTA may partially go into the wall of the uterus (become embedded) or go completely through the wall of the uterus (perforate). If this occurs, LILETTA may no longer prevent pregnancy. If perforation occurs, LILETTA may move outside the uterus and can cause internal scarring, infection, or damage to other organs. You may need surgery to have LILETTA removed if it is embedded or perforation occurs. The risk of perforation is increased in breastfeeding patients.
-
expulsion. LILETTA may come out of your uterus (expulsion). Expulsion occurs in about 4 out of 100 patients, most often in the first year of use. You may become pregnant if LILETTA comes out. If you think that LILETTA has come out, use another birth control method (such as condoms) or do not have sex (vaginal intercourse) until you are seen by a healthcare professional.
-
cysts on the ovary. Some patients using LILETTA develop a cyst on the ovary. These cysts usually disappear on their own in 2 to 3 months. However, a cyst can cause pain and sometimes will need surgery.
- changes in bleeding. You may have bleeding and spotting between menstrual periods, especially during the first 3 to 6 months. Sometimes the bleeding is heavier than usual at first. Over time the bleeding often becomes lighter than usual and may be irregular. Call your healthcare professional if the bleeding remains heavier than usual or increases after it has been light for a while.
• acne • vaginal discharge • headache • vaginal bacterial infection • breast pain • yeast infection of your vulva and vagina (vulvovaginal) • abdominal pain • nausea or vomiting • pelvic pain • weight increase • menstrual-like cramping • mood changes • pain during sex • anxiety • back pain • depression -
Pain, bleeding, or dizziness during and after placement. If these symptoms do not stop within 30 minutes after placement, LILETTA may not have been placed correctly, or they may be symptoms of perforation or expulsion. Your healthcare professional will examine you to see if LILETTA needs to be removed or replaced.
- Missed menstrual periods. About 2 out of 10 patients stop having periods after 1 year of LILETTA use. If you have any concerns that you may be pregnant while using LILETTA, do a urine pregnancy test and call your healthcare professional. When LILETTA is removed, your menstrual periods will usually return to your previous pattern.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to AbbVie at 1-800-678-1605.After LILETTA has been placed, when should I call my healthcare professional?
Call your healthcare professional if you have any concerns about LILETTA. Be sure to call if you have any of the conditions listed below:- are pregnant or think you are pregnant
- pelvic pain or pain during sex
- unusual or foul-smelling vaginal discharge or genital sores
- unexplained fever, chills, or flu-like symptoms
- might be exposed to sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- concern that LILETTA may have come out or expelled
- cannot feel LILETTA's threads
- very severe or migraine headaches
- yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (these may be signs of liver problems)
- stroke or heart attack
- you or your partner become HIV positive
- severe vaginal bleeding, bleeding that lasts a long time, or you miss your period
General information about the safe and effective use of LILETTA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet.
You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare professional for information about LILETTA that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.LILETTA.com or call 1-855-LILETTA (1-855-545-3882).LILETTA and its design are trademarks of Odyssea Pharma SPRL, an AbbVie company.
Medicines360 and its design are trademarks of Medicines360.
Manufactured by:
Odyssea Pharma, SPRL, Belgium
An affiliated company of AbbVie
Distributed by:
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, Illinois 60064
Marketed by:
AbbVie Inc. Medicines360
North Chicago, IL 60064 San Francisco, CA 94105
© 2023 AbbVie and Medicines360. All rights reserved.This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration 06/2023
V4.0PPI5858
- LILETTA is a hormone-releasing system placed in your uterus by your healthcare professional to prevent pregnancy for up to 8 years.
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LILETTA
levonorgestrel intrauterine deviceProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0023-5858 Route of Administration INTRAUTERINE Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LEVONORGESTREL (UNII: 5W7SIA7YZW) (LEVONORGESTREL - UNII:5W7SIA7YZW) LEVONORGESTREL 52 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DIMETHICONE (UNII: 92RU3N3Y1O) BARIUM SULFATE (UNII: 25BB7EKE2E) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0023-5858-01 1 in 1 CARTON 05/31/2016 1 1 in 1 TRAY; Type 4: Device Coated/Impregnated/Otherwise Combined with Drug Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA206229 05/31/2016 Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497)


