Label: DOXY 100- TM DOXYCYCLINE injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
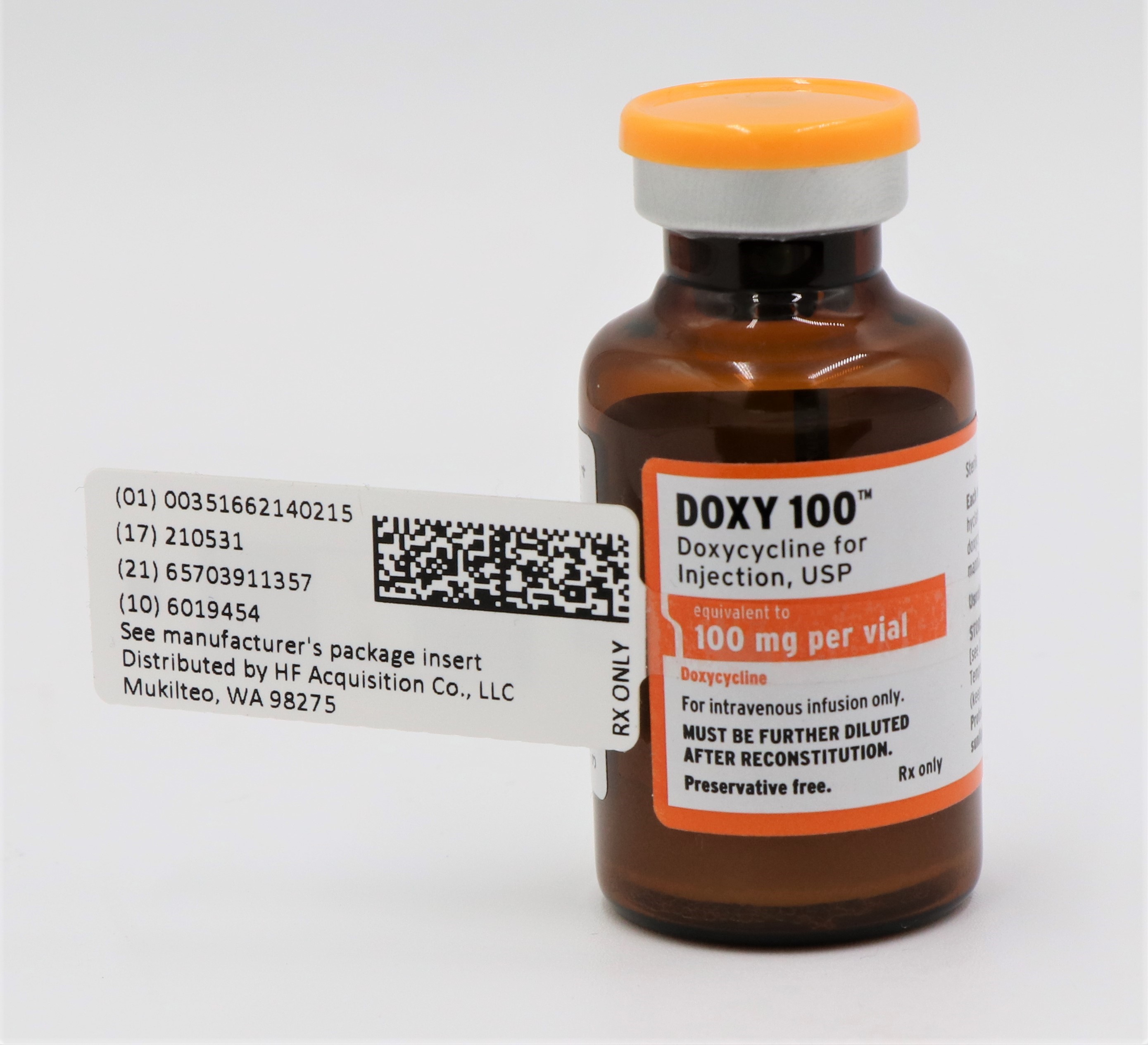
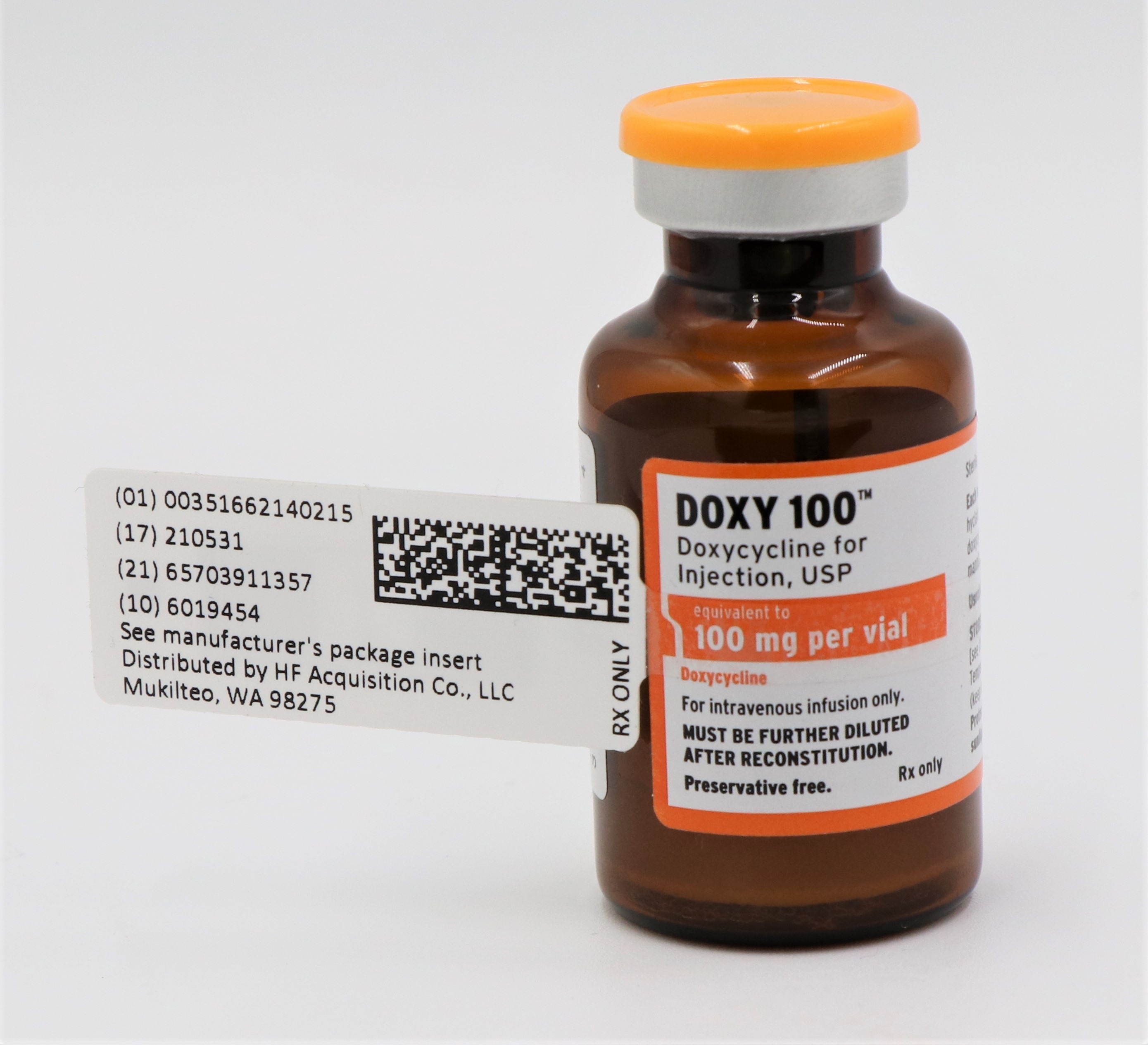
- NDC Code(s): 51662-1402-1, 51662-1402-2, 51662-1402-3
- Packager: HF Acquisition Co LLC, DBA HealthFirst
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 63323-130
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated January 30, 2024
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED
FOR INTRAVENOUS INFUSION ONLY
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Doxycycline for Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Doxycycline for Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
-
DESCRIPTION
Doxycycline hyclate is soluble in water and chars at 201°C without melting. The base doxycycline has a high degree of lipid solubility and a low affinity for calcium binding. It is highly stable in normal human serum.
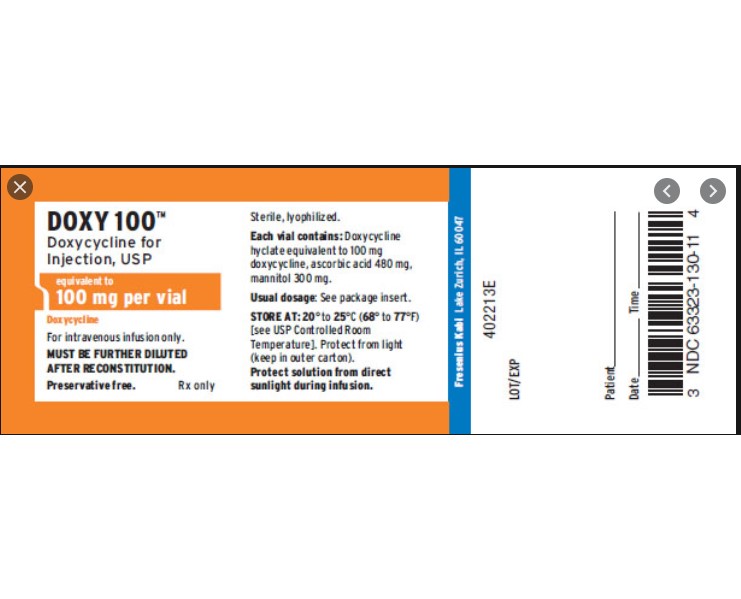
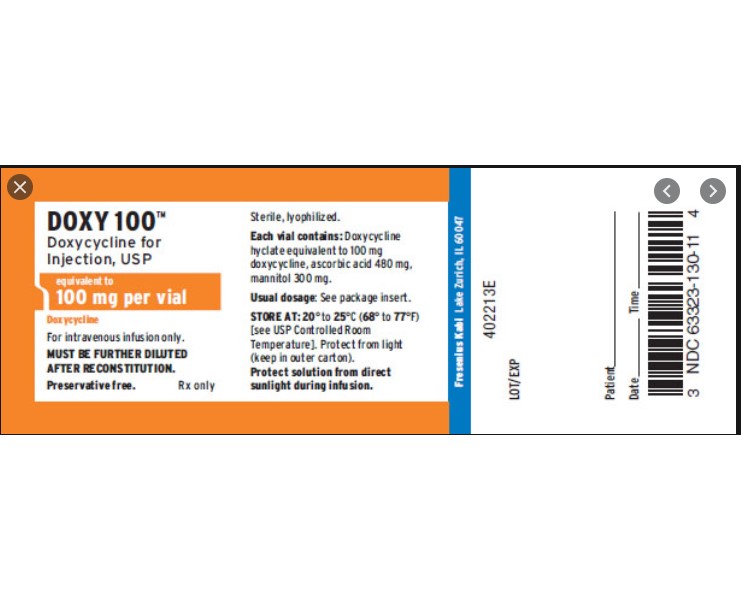
Each 100 mg vial contains: Doxycycline hyclate equivalent to 100 mg doxycycline; ascorbic acid 480 mg; mannitol 300 mg. pH of the reconstituted solution (10 mg/mL) is between 1.8 and 3.3.
Doxycycline for Injection, USP is a sterile, lyophilized powder prepared from a solution of doxycycline hyclate, ascorbic acid and mannitol in Water for Injection. Doxycycline hyclate is a broad spectrum antibiotic derived from oxytetracycline. It is meant for INTRAVENOUS use only after reconstitution. Doxycycline hyclate is a yellowish crystalline powder which is chemically designated 4-(Dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11, 12a-octahydro-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-de monohydrochloride, compound with ethyl alcohol (2:1), monohydrate. It has the following structural formula:
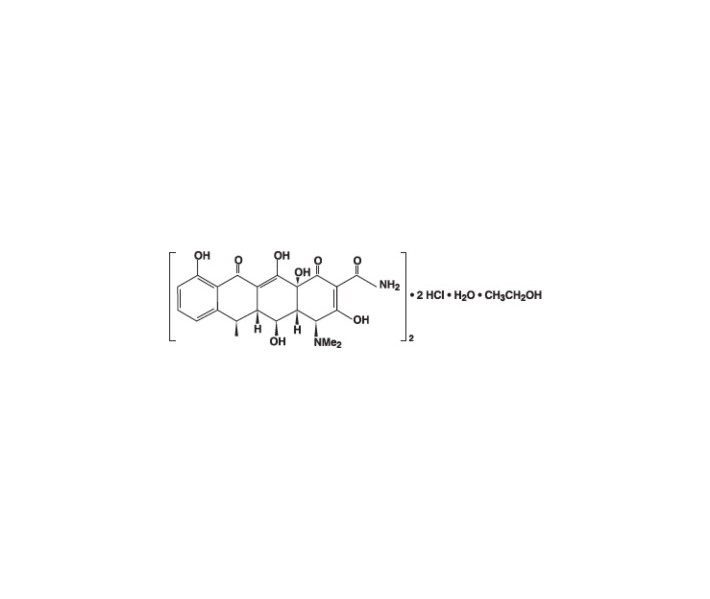

Doxycycline hyclate is soluble in water and chars at 201°C without melting. The base doxycycline has a high degree of lipid solubility and a low affinity for calcium binding. It is highly stable in normal human serum.
Each 100 mg vial contains: Doxycycline hyclate equivalent to 100 mg doxycycline; ascorbic acid 480 mg; mannitol 300 mg. pH of the reconstituted solution (10 mg/mL) is between 1.8 and 3.3.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Tetracyclines are readily absorbed and are bound to plasma proteins in varying degree. They are concentrated by the liver in the bile, and excreted in the urine and feces at high concentrations and in a biologically active form.
Following a single 100 mg dose administered in a concentration of 0.4 mg/mL in a one-hour infusion, normal adult volunteers averaged a peak of 2.5 mcg/mL, while 200 mg of a concentration of 0.4 mg/mL administered over two hours averaged a peak of 3.6 mcg/mL.
Excretion of doxycycline by the kidney is about 40 percent/72 hours in individuals with normal function (creatinine clearance about 75 mL/min). This percentage of excretion may fall as low as 1 to 5 percent/72 hours in individuals with severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance below 10 mL/min). Studies have shown no significant difference in serum half-life of doxycycline (range 18 to 22 hours) in individuals with normal and severely impaired renal function.
Hemodialysis does not alter this serum half-life of doxycycline.
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Doxycycline inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Doxycycline has bacteriostatic activity against a broad range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Resistance
Cross resistance with other tetracyclines is common.
Antimicrobial Activity
Doxycycline has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE).
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Acinetobacter species
Bartonella bacilliformis
Brucella species
Enterobacter aerogenes
Escherichia coli
Francisella tularensis
Haemophilus ducreyi
Haemophilus influenzae
Klebsiella granulomatis
Klebsiella species
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Shigella species
Vibrio cholerae
Campylobacter fetus
Yersinia pestis
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Bacillus anthracis
Listeria monocytogenes
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Anaerobic Bacteria
Clostridium species
Fusobacterium fusiforme
Propionibacterium acnes
Other Bacteria
Nocardiae and other aerobic Actinomyces species
Borrelia recurrentis
Chlamydophila psittaci
Chlamydia trachomatis
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Rickettsiae
Treponema pallidum
Treponema pallidum subspecies pertenue
Ureaplasma urealyticum
Parasites
Balantidium coli
Entamoeba species
Plasmodium falciparum*
*Doxycycline has been found to be active against the asexual erythrocytic forms of Plasmodium falciparum but not against the gametocytes of P. falciparum. The precise mechanism of action of the drug is not known.
Susceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.
-
INDICATIONS & USAGE
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Doxycycline for Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Doxycycline for Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Doxycycline for Injection, USP is indicated in infections caused by the following microorganisms:
Rickettsiae (Rocky Mountain spotted fever, typhus fever, and the typhus group, Q fever, rickettsial pox and tick fevers).
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (PPLO, Eaton Agent).
Agents of psittacosis and ornithosis.
Agents of lymphogranuloma venereum and granuloma inguinale.
The spirochetal agent of relapsing fever (Borrelia recurrentis).The following gram-negative microorganisms:
Haemophilus ducreyi (chancroid).
Yersinia pestis (formerly Pasteurella pestis) and Francisella tularensis (formerly Pasteurella tularensis).
Bartonella bacilliformis.
Bacteroides species.
Vibrio cholerae (formerly Vibrio comma) and Campylobacter fetus (formerly Vibrio fetus).
Brucella species (in conjunction with streptomycin).Because many strains of the following groups of microorganisms have been shown to be resistant to tetracyclines, culture and susceptibility testing are recommended.
Doxycycline is indicated for treatment of infections caused by the following gram-negative microorganisms when bacteriologic testing indicates appropriate susceptibility to the drug:
Escherichia coli.
Enterobacter aerogenes (formerly Aerobacter aerogenes).
Shigella species.
Acinetobacter species (formerly Mima species and Herellea species).
Haemophilus influenzae (respiratory infections).
Klebsiella species (respiratory and urinary infections).Doxycycline is indicated for treatment of infections caused by the following gram-positive microorganisms when bacteriologic testing indicates appropriate susceptibility to the drug:
Streptococcus species:
Up to 44 percent of strains of Streptococcus pyogenes and 74 percent of Enterococcus faecalis (formerly Streptococcus faecalis) have been found to be resistant to tetracycline drugs. Therefore, tetracyclines should not be used for streptococcal disease unless the organism has been demonstrated to be sensitive.
For upper respiratory infections due to group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, penicillin is the usual drug of choice, including prophylaxis of rheumatic fever.
Streptococcus pneumoniae (formerly Diplococcus pneumoniae).
Staphylococcus aureus, respiratory, skin and soft tissue infections. Tetracyclines are not the drugs of choice in the treatment of any type of staphylococcal infections.
Anthrax due to Bacillus anthracis, including inhalational anthrax (post-exposure): to reduce the incidence or progression of disease following exposure to aerosolized Bacillus anthracis.When penicillin is contraindicated, doxycycline is an alternative drug in the treatment of infections due to:
Neisseria gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis.
Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue (syphilis and yaws).
Listeria monocytogenes.
Clostridium species.
Fusobacterium fusiforme (Vincent's infection).
Actinomyces species.In acute intestinal amebiasis, doxycycline may be a useful adjunct to amebicides.
Doxycycline is indicated in the treatment of trachoma, although the infectious agent is not always eliminated, as judged by immunofluorescence.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
The use of drugs of the tetracycline class during tooth development (last half of pregnancy, infancy and childhood to the age of 8 years) may cause permanent discoloration of the teeth (yellow-gray-brown). This adverse reaction is more common during long-term use of the drugs but has been observed following repeated short-term courses. Enamel hypoplasia has also been reported. Use doxycycline in pediatric patients 8 years of age or less only when the potential benefits are expected to outweigh the risks in severe or life-threatening conditions (e.g., anthrax, Rocky Mountain spotted fever), particularly when there are no alternative therapies.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including doxycycline for injection, USP, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Severe skin reactions, such as exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) have been reported in patients receiving doxycycline (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). If severe skin reactions occur, doxycycline should be discontinued immediately and appropriate therapy should be instituted.
Intracranial hypertension (IH, pseudotumor cerebri) has been associated with the use of tetracyclines including doxycycline. Clinical manifestations of IH include headache, blurred vision, diplopia, and vision loss; papilledema can be found on fundoscopy. Women of childbearing age who are overweight or have a history of IH are at greater risk for developing tetracycline associated IH. Concomitant use of isotretinoin and doxycycline should be avoided because isotretinoin is also known to cause pseudotumor cerebri.
Although IH typically resolves after discontinuation of treatment, the possibility for permanent visual loss exists. If visual disturbance occurs during treatment, prompt ophthalmologic evaluation is warranted. Since intracranial pressure can remain elevated for weeks after drug cessation patients should be monitored until they stabilize.
Photosensitivity manifested by an exaggerated sunburn reaction has been observed in some individuals taking tetracyclines. Patients apt to be exposed to direct sunlight or ultraviolet light, should be advised that this reaction can occur with tetracycline drugs, and treatment should be discontinued at the first evidence of skin erythema.
The anti-anabolic action of the tetracyclines may cause an increase in BUN. Studies to date indicate that this does not occur with the use of doxycycline in patients with impaired renal function.
-
PRECAUTIONS
The use of drugs of the tetracycline class during tooth development (last half of pregnancy, infancy and childhood to the age of 8 years) may cause permanent discoloration of the teeth (yellow-gray-brown). This adverse reaction is more common during long-term use of the drugs but has been observed following repeated short-term courses. Enamel hypoplasia has also been reported. Use doxycycline in pediatric patients 8 years of age or less only when the potential benefits are expected to outweigh the risks in severe or life-threatening conditions (e.g., anthrax, Rocky Mountain spotted fever), particularly when there are no alternative therapies.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including doxycycline for injection, USP, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Severe skin reactions, such as exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) have been reported in patients receiving doxycycline (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). If severe skin reactions occur, doxycycline should be discontinued immediately and appropriate therapy should be instituted.
Intracranial hypertension (IH, pseudotumor cerebri) has been associated with the use of tetracyclines including doxycycline. Clinical manifestations of IH include headache, blurred vision, diplopia, and vision loss; papilledema can be found on fundoscopy. Women of childbearing age who are overweight or have a history of IH are at greater risk for developing tetracycline associated IH. Concomitant use of isotretinoin and doxycycline should be avoided because isotretinoin is also known to cause pseudotumor cerebri.
Although IH typically resolves after discontinuation of treatment, the possibility for permanent visual loss exists. If visual disturbance occurs during treatment, prompt ophthalmologic evaluation is warranted. Since intracranial pressure can remain elevated for weeks after drug cessation patients should be monitored until they stabilize.
Photosensitivity manifested by an exaggerated sunburn reaction has been observed in some individuals taking tetracyclines. Patients apt to be exposed to direct sunlight or ultraviolet light, should be advised that this reaction can occur with tetracycline drugs, and treatment should be discontinued at the first evidence of skin erythema.
The anti-anabolic action of the tetracyclines may cause an increase in BUN. Studies to date indicate that this does not occur with the use of doxycycline in patients with impaired renal function.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Gastrointestinal
Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, glossitis, dysphagia, enterocolitis and inflammatory lesions (with monilial overgrowth) in the anogenital region, and pancreatitis. Hepatotoxicity has been reported rarely. These reactions have been caused by both the oral and parenteral administration of tetracyclines. Superficial discoloration of the adult permanent dentition, reversible upon drug discontinuation and professional dental cleaning has been reported. Permanent tooth discoloration and enamel hypoplasia may occur with drugs of the tetracycline class when used during tooth development (see WARNINGS).
Skin
Maculopapular and erythematous rashes. Exfoliative dermatitis has been reported but is uncommon. Photosensitivity is discussed above (see WARNINGS).
Renal Toxicity
Rise in BUN has been reported and is apparently dose related (see WARNINGS).
Immune
Hypersensitivity reactions including urticaria, angioneurotic edema, anaphylaxis, anaphylactoid purpura, pericarditis and exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Other
Bulging fontanels in infants and intracranial hypertension in adults (see WARNINGS).
Blood
Hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia and eosinophilia have been reported.
When given over prolonged periods, tetracyclines have been reported to produce brown-black microscopic discoloration of thyroid glands. No abnormalities of thyroid function studies are known to occur.
-
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
NOTE: Rapid administration is to be avoided. Parenteral therapy is indicated only when oral therapy is not indicated. Oral therapy should be instituted as soon as possible. If intravenous therapy is given over prolonged periods of time, thrombophlebitis may result.
The usual dosage and frequency of administration of Doxycycline for Injection (100 to 200 mg/day) differs from that of the other tetracyclines (1 to 2 g/day). Exceeding the recommended dosage may result in an increased incidence of side effects.
Studies to date have indicated that doxycycline hyclate at the usual recommended doses does not lead to excessive accumulation of the antibiotic in patients with renal impairment.
Adults
The usual dosage of doxycycline for injection is 200 mg on the first day of treatment administered in one or two infusions. Subsequent daily dosage is 100 to 200 mg depending upon the severity of infection, with 200 mg administered in one or two infusions.
In the treatment of primary and secondary syphilis, the recommended dosage is 300 mg daily for at least 10 days.
In the treatment of inhalational anthrax (post-exposure) the recommended dose is 100 mg of doxycycline, twice a day. Parenteral therapy is only indicated when oral therapy is not indicated and should not be continued over a prolonged period of time. Oral therapy should be instituted as soon as possible. Therapy must continue for a total of 60 days.
Pediatric Patients
For all pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg with severe or life-threatening infections (e.g., anthrax, Rocky Mountain spotted fever), the recommended dosage is 2.2 mg/kg of body weight administered every 12 hours. Children weighing 45 kg or more should receive the adult dose (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
For pediatric patients with less severe disease (greater than 8 years of age and weighing less than 45 kg), the recommended dosage schedule is 4.4 mg/kg of body weight divided into two doses on the first day of treatment, followed by a maintenance dose of 2.2 mg/kg of body weight (given as a single daily dose or divided into twice daily doses). For pediatric patients weighing over 45 kg, the usual adult dose should be used.
In the treatment of inhalational anthrax (post-exposure) the recommended dose is 2.2 mg/kg of body weight, twice a day in children weighing less than 45 kg. Parenteral therapy is only indicated when oral therapy is not indicated and should not be continued over a prolonged period of time. Oral therapy should be instituted as soon as possible. Therapy must continue for a total of 60 days.
General
The duration of infusion may vary with the dose (100 to 200 mg/day), but is usually one to four hours. A recommended minimum infusion time for 100 mg of a 0.5 mg/mL solution is one hour. Therapy should be continued for at least 24 to 48 hours after symptoms and fever have subsided. The therapeutic antibacterial serum activity will usually persist for 24 hours following recommended dosage.
Intravenous solutions should not be injected intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Caution should be taken to avoid the inadvertent introduction of the intravenous solution into the adjacent soft tissue.
-
PREPARATION OF SOLUTION
To prepare a solution containing 10 mg/mL, the contents of the vial should be reconstituted with 10 mL (for the 100 mg/vial container) of Sterile Water for Injection or any of the 10 intravenous infusion solutions listed below. Each 100 mg of doxycycline for injection (i.e., withdraw entire solution from the 100 mg vial) is further diluted with 100 mL to 1,000 mL of the intravenous solutions listed below:
Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
5% Dextrose Injection, USP
Ringer's Injection, USP
Invert Sugar, 10% in Water
Lactated Ringer's Injection, USP
Dextrose 5% in Lactated Ringer's
Normosol-M ® in D5-W
Normosol-R ® in D5-W
Plasma-Lyte ® 56 in 5% Dextrose
Plasma-Lyte ® 148 in 5% DextroseThis will result in desired concentrations of 0.1 to 1 mg/mL. Concentrations lower than 0.1 mg/mL or higher than 1 mg/mL are not recommended.
Stability
Doxycycline is stable for 48 hours in solution when diluted with Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, to concentrations between 1 mg/mL and 0.1 mg/mL and stored at 25°C. Doxycycline in these solutions is stable under fluorescent light for
48 hours, but must be protected from direct sunlight during storage and infusion. Reconstituted solutions (1 to 0.1 mg/mL) may be stored up to 72 hours prior to start of infusion if refrigerated and protected from sunlight and artificial light. Infusion must then be completed within 12 hours. Solutions must be used within these time periods or discarded.
Doxycycline, when diluted with Ringer's Injection, USP, or Invert Sugar, 10% in Water, to a concentration between 1 mg/mL and 0.1 mg/mL, must be completely infused within 12 hours after reconstitution to ensure adequate stability. During infusion, the solution must be protected from direct sunlight. Reconstituted solutions (1 to 0.1 mg/mL) may be stored up to 72 hours prior to start of infusion if refrigerated and protected from sunlight and artificial light. Infusion must then be completed within 12 hours. Solutions must be used within these time periods or discarded.
Diluted solutions (0.1 to 1 mg/mL) prepared using Normosol-M ® in D5-W; Normosol-R ® in D5-W; Plasma-Lyte ® 56 in 5% Dextrose; or Plasma-Lyte ® 148 in 5% Dextrose may also be stored up to 12 hours prior to start of infusion, if refrigerated and protected from sunlight and artificial light. The infusion must be completed within 12 hours. Solutions must be used within these time periods or discarded.
When diluted with Lactated Ringer's Injection, USP, or Dextrose 5% in Lactated Ringer's, infusion of the solution (ca. 1 mg/mL) or lower concentrations (not less than 0.1 mg/mL) must be completed within six hours after reconstitution to ensure adequate stability. During infusion, the solution must be protected from direct sunlight. Solutions must be used within this time period or discarded.
Solutions of doxycycline for injection, at a concentration of 10 mg/mL in Sterile Water for Injection, when frozen immediately after reconstitution are stable for eight weeks when stored at –20°C. If the product is warmed, care should be taken to avoid heating it after the thawing is complete. Once thawed the solution should not be refrozen.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
DOXY 100(TM) DOXYCYCLINE FOR INJECTION, USP is supplied in the following dosage forms.
NDC 51662-1402-1
DOXY 100(TM) DOXYCYCLINE FOR INJECTION, USP 100mg per VIAL 20mL VIALNDC 51662-1402-2
DOXY 100(TM) DOXYCYCLINE FOR INJECTION, USP 100mg per VIAL 20mL VIAL, 1 VIAL PER POUCH
NDC 51662-1402-3
DOXY 100(TM) DOXYCYCLINE FOR INJECTION, USP 100mg per VIAL 20mL VIAL, 1 VIAL PER POUCH, 10 POUCHES PER BOX
HF Acquisition Co LLC, DBA HealthFirst
Mukilteo, WA 98275Also supplied in the following manufacture supplied dosage forms
Doxycycline for Injection, USP, sterile powder, supplied as follows:
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
PROTECT FROM LIGHT.
Retain in carton until time of use.
The brand names mentioned in this document are the trademarks of their respective owners.

Lake Zurich, IL 60047
www.fresenius-kabi.com/us
45824K
Revised: July 2019
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL, VIAL LABELING
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL, SERIALIZED VIAL LABELING
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 51662-1402-2 POUCH LABELING
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 51662-1402-3 SERIALIZED BOX LABELING
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DOXY 100(TM) DOXYCYCLINE
doxy 100(tm) doxycycline injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:51662-1402(NDC:63323-130) Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DOXYCYCLINE HYCLATE (UNII: 19XTS3T51U) (DOXYCYCLINE ANHYDROUS - UNII:334895S862) DOXYCYCLINE ANHYDROUS 100 mg in 10 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ASCORBIC ACID (UNII: PQ6CK8PD0R) 480 mg in 10 mL MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) 300 mg in 10 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:51662-1402-1 10 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/07/2019 2 NDC:51662-1402-3 10 in 1 BOX 03/16/2022 2 NDC:51662-1402-2 1 in 1 POUCH 2 10 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA062475 10/07/2019 Labeler - HF Acquisition Co LLC, DBA HealthFirst (045657305) Registrant - HF Acquisition Co LLC, DBA HealthFirst (045657305) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations HF Acquisition Co LLC, DBA HealthFirst 045657305 relabel(51662-1402)