RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE- ranitidine hydrochloride capsule
AvKARE, Inc.
----------
Ranitidine Hydrochloride Capsules
DESCRIPTION
The active ingredient in Ranitidine Hydrochloride Capsules, 150 mg and 300 mg is ranitidine hydrochloride (HCl), USP, a histamine H 2-receptor antagonist. Chemically it is N-[2-[[[5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]thio]ethyl]- N’-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine, HCl. It has the following structural formula:
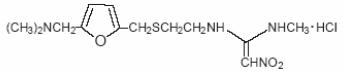
The molecular formula is C 13H 22N 4O 3S•HCl, representing a molecular weight of 350.87.
Ranitidine HCl is a white to pale yellow, crystalline substance that is soluble in water. It has a slightly bitter taste and sulfur-like odor.
Each Ranitidine Hydrochloride capsule, for oral administration, contains 167.4 mg or 334.8 mg of ranitidine hydrochloride equivalent to 150 mg or 300 mg of ranitidine, respectively. In addition, each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: Microcrystalline Cellulose, Sodium Starch Glycolate, Magnesium Stearate. The capsule shells contain Black Iron Oxide, Red Iron Oxide T3469, Yellow Iron Oxide T3506, Titanium Dioxide and Gelatin. The capsule shells are imprinted with edible ink.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Ranitidine is a competitive, reversible inhibitor of the action of histamine at the histamine H 2-receptors, including receptors on the gastric cells. Ranitidine does not lower serum Ca ++ in hypercalcemic states. Ranitidine is not an anticholinergic agent.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: Ranitidine is 50% absorbed after oral administration, compared to an intravenous (IV) injection with mean peak levels of 440 to 545 ng/mL occurring 2 to 3 hours after a 150 mg dose. Absorption is not significantly impaired by the administration of food or antacids. Propantheline slightly delays and increases peak blood levels of ranitidine, probably by delaying gastric emptying and transit time. In one study, simultaneous administration of high potency antacid (150 mmol) in fasting subjects has been reported to decrease the absorption of ranitidine.
Distribution: The volume of distribution is about 1.4 L/kg. Serum protein binding averages 15%.
Metabolism: In humans, the N-oxide is the principal metabolite in the urine; however, this amounts to <4% of the dose. Other metabolites are the S-oxide (1%) and the desmethyl ranitidine (1%). The remainder of the administered dose is found in the stool. Studies in patients with hepatic dysfunction (compensated cirrhosis) indicate that there are minor, but clinically insignificant, alterations in ranitidine half-life, distribution, clearance, and bioavailability.
Excretion: The principal route of excretion is the urine, with approximately 30% of the orally administered dose collected in the urine as unchanged drug in 24 hours. Renal clearance is about410 mL/min, indicating active tubular excretion. The elimination half-life is 2.5 to 3 hours. Fourpatients with clinically significant renal function impairment (creatinine clearance 25 to 35 mL/min) administered 50 mg of ranitidine intravenously had an average plasma half-life of 4.8 hours, a ranitidine clearance of 29 mL/min, and a volume of distribution of 1.76 L/kg. In general, these parameters appear to be altered in proportion to creatinine clearance (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
<content styleCode="bold italics">Geriatrics</content> Geriatrics
The plasma half-life is prolonged and total clearance is reduced in the elderly population due to a decrease in renal function. The elimination half-life is 3 to 4 hours. Peak levels average 526 ng/mL following a 150 mg twice daily dose and occur in about 3 hours (see PRECAUTIONS: Geriatric Useand DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Dosage Adjustment for Patients with Impaired Renal Function).
Pharmacodynamics
Serum concentrations necessary to inhibit 50% of stimulated gastric acidsecretion are estimated to be 36 to 94 ng/mL. Following a single oral dose of 150 mg, serum concentrations of ranitidine are in this range up to 12 hours. However, blood levels bear no consistent relationship to dose or degree of acid inhibition.
Antisecretory Activity
1. Effects on Acid Secretion: Ranitidine inhibits both daytime and nocturnal basal gastric acidsecretions as well as gastric acid secretion stimulated by food, betazole, and pentagastrin, as shown in Table 1:
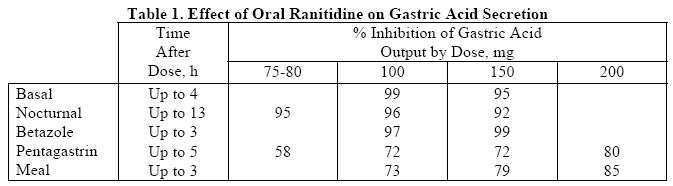
It appears that basal-, nocturnal-, and betazole-stimulated secretions are most sensitive to inhibition by ranitidine, responding almost completely to doses of 100 mg or less, while pentagastrin- and food-stimulated secretions are more difficult to suppress.
2. Effects on Other Gastrointestinal Secretions:
Pepsin: Oral ranitidine does not affect pepsin secretion. Total pepsin output is reduced in proportion to the decrease in volume of gastric juice.
Intrinsic Factor: Oral ranitidine has no significant effect on pentagastrin-stimulated intrinsic factor secretion.
Serum Gastrin: Ranitidine has little or no effect on fasting or postprandial serum gastrin.
Other Pharmacologic Actions
a. Gastric bacterial flora—increase in nitrate-reducing organisms, significance not known.
b. Prolactin levels—no effect in recommended oral or intravenous (IV) dosage, but small, transient, dose-related increases in serum prolactin have been reported after IV bolus injections of 100 mg or more.
c. Other pituitary hormones—no effect on serum gonadotropins, TSH, or GH. Possible impairment of vasopressin release.
d. No change in cortisol, aldosterone, androgen, or estrogen levels.
e. No antiandrogenic action.
f. No effect on count, motility, or morphology of sperm.
Clinical Trials
Active Duodenal Ulcer: In a multicenter, double-blind, controlled, US study of endoscopically diagnosed duodenal ulcers, earlier healing was seen in the patients treated with ranitidine as shown in Table 2:
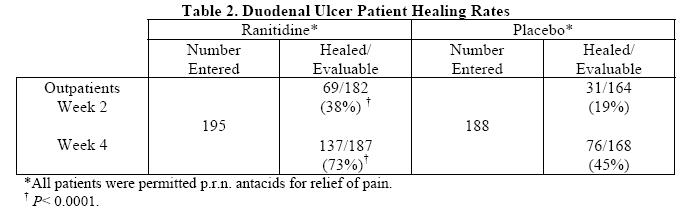
In these studies, patients treated with ranitidine reported a reduction in both daytime and nocturnal pain, and they also consumed less antacid than the placebo-treated patients.
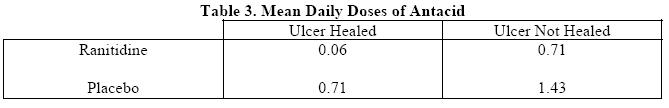
Foreign studies have shown that patients heal equally well with 150 mg b.i.d. and 300 mg h.s. (85% versus 84%, respectively) during a usual 4-week course of therapy. If patients require extended therapy of 8 weeks, the healing rate may be higher for 150 mg b.i.d. as compared to 300 mg h.s. (92% versus 87%, respectively).
Studies have been limited to short-term treatment of acute duodenal ulcer. Patients whose ulcershealed during therapy had recurrences of ulcers at the usual rates.
Maintenance Therapy in Duodenal Ulcer: Ranitidine has been found to be effective as maintenance therapy for patients following healing of acute duodenal ulcers. In two independent, double-blind, multicenter, controlled trials, the number of duodenal ulcers observed was significantly less in patients treated with ranitidine (150 mg h.s.) than in patients treated with placebo over a 12-month period.
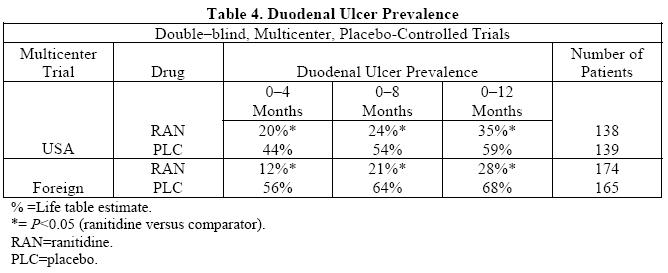
As with other H 2-antagonists, the factors responsible for the significant reduction in the prevalence of duodenal ulcers include prevention of recurrence of ulcers, more rapid healing of ulcers that may occur during maintenance therapy, or both.
Gastric Ulcer: In a multicenter, double-blind, controlled, US study of endoscopically diagnosedgastric ulcers, earlier healing was seen in the patients treated with ranitidine as shown in Table 5:
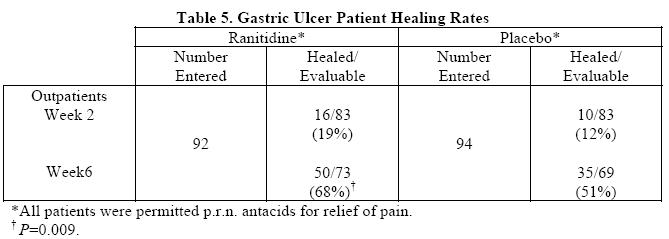
In this multicenter trial, significantly more patients treated with ranitidine became pain-free during therapy.
Maintenance of Healing of Gastric Ulcers: In two multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebocontrolled, 12-month trials conducted in patients whose gastric ulcers had been previously healed, ranitidine 150 mg h.s. was significantly more effective than placebo in maintaining healing of gastric ulcers.
Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions (such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome): Ranitidine inhibits gastric acid secretion and reduces occurrence of diarrhea, anorexia, and pain in patients with pathological hypersecretion associated with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, systemic mastocytosis, and other pathological hypersecretory conditions (e.g., postoperative, “short-gut” syndrome, idiopathic). Use of ranitidine was followed by healing of ulcers in 8 of 19 (42%) patients who were intractable to previous therapy.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): In two multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 6-week trials performed in the United States and Europe, ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d. was more effective than placebo for the relief of heartburn and other symptoms associated with GERD. Ranitidine-treated patients consumed significantly less antacid than did placebo-treated patients.
The US trial indicated that ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d. significantly reduced the frequency of heartburn attacks and severity of heartburn pain within 1 to 2 weeks after starting therapy. The improvement was maintained throughout the 6-week trial period. Moreover, patient response rates demonstrated that the effect on heartburn extends through both the day and night time periods.
In two additional US multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2 week trials, ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d was shown to provide relief of heartburn pain within 24 hours of initiating therapy and a reduction in the frequency of severity of heartburn.
Erosive Esophagitis: In two multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, 12-week trials performed in the United States, ranitidine 150 mg q.i.d. was significantly more effective than placebo in healing endoscopically diagnosed erosive esophagitis and in relieving associated heartburn.The erosive esophagitis healing rates were as follows:
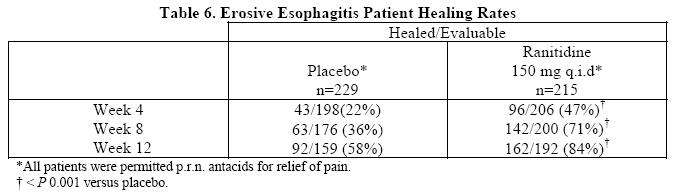
No additional benefit in healing of esophagitis or in relief of heartburn was seen with a ranitidine dose of 300 mg q.i.d.
Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis: In two multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, 48-week trials conducted in patients whose erosive esophagitis had been previously healed, ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d. was significantly more effective than placebo in maintaining healing of erosive esophagitis.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ranitidine is Indicated in:
- Short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer. Most patients heal within 4 weeks. Studies available to date have not assessed the safety of ranitidine in uncomplicated duodenal ulcer for periods of more than 8 weeks.
- Maintenance therapy for duodenal ulcer patients at reduced dosage after healing of acute ulcers. No placebo-controlled comparative studies have been carried out for periods of longer than 1 year.
- The treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions (e.g., Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and systemic mastocytosis).
- Short-term treatment of active, benign gastric ulcer. Most patients heal within 6 weeks and the usefulness of further treatment has not been demonstrated. Studies available to date have not assessed the safety of ranitidine in uncomplicated benign gastric ulcer for periods of more than 6 weeks.
- Maintenance therapy for gastric ulcer patients at reduced dosage after healing of acute ulcers. Placebo-controlled studies have been carried out for 1 year.
- Treatment of GERD. Symptomatic relief commonly occurs within 24 hours after starting therapy with ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d.
- Treatment of endoscopically diagnosed erosive esophagitis. Symptomatic relief of heartburn commonly occurs within 24 hours of therapy initiation with ranitidine 150 mg q.i.d.
- Maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis. Placebo-controlled trials have been carried out for 48 weeks.
Concomitant antacids should be given as needed for pain relief to patients with active duodenal ulcer; active, benign gastric ulcer; hypersecretory states; GERD; and erosive esophagitis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Ranitidine is contraindicated for patients known to have hypersensitivity to the drug or any of the ingredients (see PRECAUTIONS).
PRECAUTIONS
General
- Symptomatic response to therapy with ranitidine does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy.
- Since ranitidine is excreted primarily by the kidney, dosage should be adjusted in patients with impaired renal function (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Caution should be observed in patients with hepatic dysfunction since ranitidine is metabolized in the liver.
- Rare reports suggest that ranitidine may precipitate acute porphyric attacks in patients with acute porphyria. Ranitidine should therefore be avoided in patients with a history of acute porphyria.
Laboratory Tests
False-positive tests for urine protein with MULTISTIX ® may occur during ranitidine therapy, and therefore testing with sulfosalicylic acid is recommended.
Drug Interactions
Although ranitidine has been reported to bind weakly to cytochrome P-450 in vitro, recommended doses of the drug do not inhibit the action of the cytochrome P-450-linked oxygenase enzymes in the liver. However, there have been isolated reports of drug interactions that suggest that ranitidine may affect the bioavailability of certain drugs by some mechanism as yet unidentified (e.g., a pH-dependent effect on absorption or a change in volume of distribution).
Increased or decreased prothrombin times have been reported during concurrent use of ranitidine and warfarin. However, in human pharmacokinetic studies with dosages of ranitidine up to 400 mg per day, no interaction occurred; ranitidine had no effect on warfarin clearance or prothrombin time. The possibility of an interaction with warfarin at dosages of ranitidine higher than 400 mg per day has not been investigated.
In a ranitidine-triazolam drug-drug interaction study, triazolam plasma concentrations were higher during b.i.d. dosing of ranitidine than triazolam given alone. The mean area under the triazolam concentration time curve (AUC) values in 18- to 60-year-old subjects were 10% and 28% higher following administration of 75 mg and 150 mg ranitidine tablets, respectively, than triazolam given alone. In subjects older than 60 years of age, the mean AUC values were approximately 30% higher following administration of 75 mg and 150 mg ranitidine tablets. It appears that there were no changes in pharmacokinetics of triazolam and α-hydroxytriazolam, a major metabolite, and in their elimination. Reduced gastric acidity due to ranitidine may have resulted in an increase in the availability of triazolam. The clinical significance of this triazolam and ranitidine pharmacokinetic interaction is unknown.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
There was no indication of tumorigenic or carcinogenic effects in life-span studies in mice and rats at dosages up to 2000 mg/kg per day.
Ranitidine was not mutagenic in standard bacterial tests ( Salmonella, Escherichia coli) for mutagenicity at concentrations up to the maximum recommended for these assays.
In a dominant lethal assay, a single oral dose of 1000 mg/kg to male rats was without effect on the outcome of two matings per week for the next 9 weeks.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category B: Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits at doses up to 160 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to ranitidine. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Ranitidine is secreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when ranitidine is administered to a nursing mother.
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects enrolled in US and foreign controlled clinical trials of oral formulations of ranitidine, for which there were subgroup analyses, 4197 were 65 and over, while 899 were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, caution should be exercised in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics: Geriatric Use and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Dosage Adjustments for Patients with impaired Renal Function).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following have been reported as events in clinical trials or in the routine management of patients treated with ranitidine. The relationship to therapy with ranitidine has been unclear in many cases. Headache, sometimes severe, seems to be related to administration of ranitidine.
Central Nervous System:
Rarely, malaise, dizziness, somnolence, insomnia, and vertigo. Rare cases of reversible mental confusion, agitation, depression, and hallucinations have been reported, predominantly in severely ill elderly patients. Rare cases of reversible blurred vision suggestive of a change in accommodation have been reported. Rare reports of reversible involuntary motor disturbances have been received.
Cardiovascular:
As with other H 2-blockers, rare reports of arrhythmias such as tachycardia, bradycardia, atrioventricular block and premature ventricular beats.
Gastrointestinal:
Constipation, diarrhea, nausea/vomiting, abdominal discomfort/pain, and rare reports of pancreatitis.
Hepatic:
There have been occasional reports of hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed hepatitis, with or without jaundice. In such circumstances, ranitidine should be immediately discontinued. These events are usually reversible, but in rare circumstances death has occurred. Rare cases of hepatic failure have also been reported. In normal volunteers, SGPT values were increased to at least twice the pretreatment levels in 6 of 12 subjects receiving 100 mg q.i.d. intravenously for 7 days, and in 4 of 24 subjects receiving 50 mg q.i.d. intravenously for 5 days.
Musculoskeletal:
Rare reports of arthralgias and myalgias.
Hematologic:
Blood count changes (leukopenia, granulocytopenia, and thrombocytopenia) have occurred in a few patients. These were usually reversible. Rare cases of agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, sometimes with marrow hypoplasia, and aplastic anemia and exceedingly rare cases of acquired immune hemolytic anemia have been reported.
Endocrine:
Controlled studies in animals and man have shown no stimulation of any pituitary hormone by ranitidine and no antiandrogenic activity, and cimetidine-induced gynecomastia and impotence in hypersecretory patients have resolved when ranitidine has been substituted. However, occasional cases of gynecomastia, impotence, and loss of libido have been reported in male patients receiving ranitidine, but the incidence did not differ from that in the general population.
Integumentary:
Rash, including rare cases of erythema multiforme, and, rarely, alopecia.
Other:
Rare cases of hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., bronchospasm, fever, rash, eosinophilia), anaphylaxis, angioneurotic edema, and small increases in serum creatinine.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS contact AvKARE, Inc. at 1-855-361-3993; email
drugsafety@avkare.com; or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or
www.fda.gov/medwatch.
OVERDOSAGE
There has been limited experience with overdosage. Reported acute ingestions of up to 18 g orally have been associated with transient adverse effects similar to those encountered in normal clinical experience (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). In addition, abnormalities of gait and hypotension have been reported.
When overdosage occurs, the usual measures to remove unabsorbed material from the gastrointestinal tract, clinical monitoring, and supportive therapy should be employed.
Studies in dogs receiving dosages of ranitidine in excess of 225 mg/kg per day have shown muscular tremors, vomiting, and rapid respiration. Single oral doses of 1000 mg/kg in mice and rats were not lethal. Intravenous LD 50 values in mice and rats were 77 and 83 mg/kg, respectively.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Active Duodenal Ulcer:
The current recommended adult oral dosage of ranitidine for duodenal ulcer is 150 mg twice daily. An alternative dosage of 300 mg once daily after the evening meal or at bedtime can be used for patients in whom dosing convenience is important. The advantages of one treatment regimen compared to the other in a particular patient population have yet to be demonstrated (see Clinical Trials: Active Duodenal Ulcer). Smaller doses have been shown to be equally effective in inhibiting gastric acid secretion in US studies, and several foreign trials have shown that 100 mg b.i.d. is as effective as the 150 mg dose.
Antacid should be given as needed for relief of pain (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics).
Maintenance of Healing Duodenal Ulcers:
The current recommended adult oral dosage is 150 mg at bedtime.
Pathological Hypersecretory Conditions (such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome):
The current recommended adult oral dosage is 150 mg twice a day. In some patients it may be necessary to administer ranitidine 150 mg doses more frequently. Dosages should be adjusted to individual patient needs, and should continue as long as clinically indicated. Dosages up to 6 g/day have been employed in patients with severe disease.
Benign Gastric Ulcer:
The current recommended adult oral dosage is 150 mg twice a day.
Maintenance of Healing of Gastric Ulcers:
The current recommended adult oral dosage is 150 mg at bedtime.
GERD:
The current recommended adult oral dosage is 150 mg twice a day.
Erosive Esophagitis:
The current recommended adult oral dosage is 150 mg four times a day.
Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis :
The current recommended adult oral dosage is 150 mg twice a day.
Dosage Adjustment for Patients With Impaired Renal Function
On the basis of experience with a group of subjects with severely impaired renal function treated with ranitidine, the recommended dosage in patients with a creatinine clearance <50 mL per minute is 150 mg every 24 hours. Should the patient’s condition require, the frequency of dosing may be increased to every 12 hours or even further with caution. Hemodialysis reduces the level of circulating ranitidine. Ideally, the dosing schedule should be adjusted so that the timing of a scheduled dose coincides with the end of hemodialysis.
Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, therefore caution should be exercised in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics: Geriatric Useand PRECAUTIONS: Geriatric Use).
HOW SUPPLIED
Ranitidine Hydrochloride Capsules 150 mg are Size 3, opaque light brown hard gelatin capsules imprinted “CD” and “129” in black edible ink. The capsules are supplied in bottles of 500 (NDC 42291-735-50)
Ranitidine Hydrochloride Capsules 300 mg are Size 1, opaque light brown hard gelatin capsulesimprinted “CD” and “130” in black edible ink. The capsules are supplied in bottles of 500 (NDC 42291-736-50)
Store at controlled room temperature 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F) (see USP) in a dry place. Protect from light.
Dispense in a tight, light resistant container.
Manufactured for:
AvKARE, Inc.
Pulaski, TN 38478
Mfg. Rev. 0205
AV 11/16 (P)
| RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
ranitidine hydrochloride capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
ranitidine hydrochloride capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - AvKARE, Inc. (796560394) |

