NORTRIPTYLINE HYDROCHLORIDE- nortriptyline hydrochloride capsule
REMEDYREPACK INC.
----------
DESCRIPTION
Nortriptyline hydrochloride is 1-Propanamine, 3-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-N-methyl-, hydrochloride.
The structural formula is as follows:
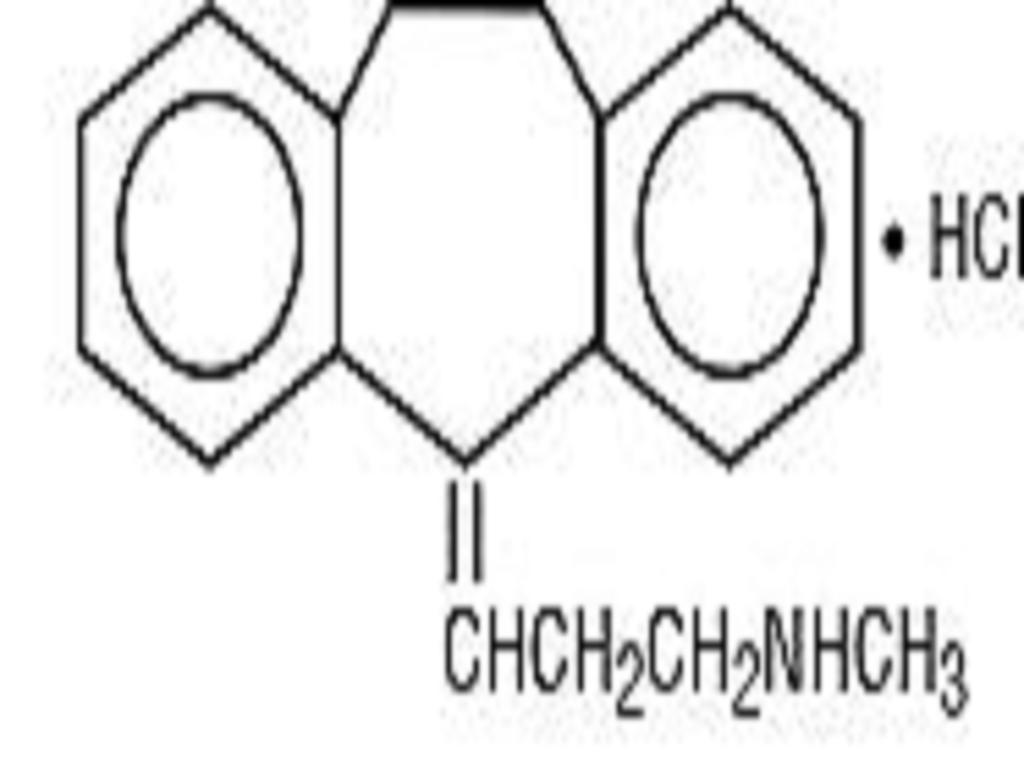
C19H21NHCl M.W. 299.8
Each capsule, for oral administration, contains nortriptyline hydrochloride equivalent to 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg or 75 mg nortriptyline.
In addition, each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, D&C Yellow #10 aluminum lake, FD&C Blue #1 aluminum lake, FD&C Blue #2 aluminum lake, FD&C Red #40 aluminum lake, gelatin, iron oxide black, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, shellac glaze, silicone fluid, sodium lauryl sulfate, and titanium dioxide. The 10 mg, 25 mg and 75 mg capsules also contain D&C Yellow #10, FD&C Blue #1, and FD&C Yellow #6.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The mechanism of mood elevation by tricyclic antidepressants is at present unknown. Nortriptyline hydrochloride is not a monoamine oxidase inhibitor. It inhibits the activity of such diverse agents as histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and acetylcholine. It increases the pressor effect of norepinephrine but blocks the pressor response of phenethylamine. Studies suggest that nortriptyline hydrochloride interferes with the transport, release, and storage of catecholamines. Operant conditioning techniques in rats and pigeons suggest that nortriptyline hydrochloride has a combination of stimulant and depressant properties.
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules are indicated for the relief of symptoms of depression. Endogenous depressions are more likely to be alleviated than are other depressive states.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The use of nortriptyline hydrochloride or other tricyclic antidepressants concurrently with a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor is contraindicated. Hyperpyretic crises, severe convulsions, and fatalities have occurred when similar tricyclic antidepressants were used in such combinations. It is advisable to have discontinued the MAO inhibitor for at least two weeks before treatment with nortriptyline hydrochloride is started. Patients hypersensitive to nortriptyline hydrochloride should not be given the drug.
Cross-sensitivity between nortriptyline and other dibenzazepines is a possibility.
Nortriptyline hydrochloride is contraindicated during the acute recovery period after myocardial infarction.
WARNINGS
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in children and adolescents with MDD, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 24 short-term trials of 9 antidepressant drugs in over 4400 patients. The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in adults with MDD or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 295 short-term trials (median duration of 2 months) of 11 antidepressant drugs in over 77,000 patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidality among drugs, but a tendency toward an increase in the younger patients for almost all drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidality across the different indications, with the highest incidence in MDD. The risk differences (drug vs placebo), however, were relatively stable within age strata and across indications. These risk differences (drug-placebo difference in the number of cases of suicidality per 1000 patients treated) are provided in Table 1.
Table 1
AgeDrug-Placebo Difference in Number of CasesRangeof Suicidality per 1000 Patients TreatedIncreases Compared to Placebo< 1814 additional cases18-245 additional casesDecreases Compared to Placebo25-641 fewer case656 fewer casesNo suicides occurred in any of the pediatric trials. There were suicides in the adult trials, but the number was not sufficient to reach any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
It is unknown whether the suicidality risk extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond several months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with depression that the use of antidepressants can delay the recurrence of depression.
All patients being treated with antidepressants for any indication should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, and unusual changes in behavior, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases.
The following symptoms, anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, and mania, have been reported in adult and pediatric patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder as well as for other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric. Although a causal link between the emergence of such symptoms and either the worsening of depression and/or the emergence of suicidal impulses has not been established, there is concern that such symptoms may represent precursors to emerging suicidality.
Consideration should be given to changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing the medication, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidality or symptoms that might be precursors to worsening depression or suicidality, especially if these symptoms are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms.
Families and caregivers of patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder or other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric, should be alerted about the need to monitor patients for the emergence of agitation, irritability, unusual changes in behavior, and the other symptoms described above, as well as the emergence of suicidality, and to report such symptoms immediately to health care providers.Such monitoring should include daily observation by families and caregivers. Prescriptions for nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules should be written for the smallest quantity of capsules consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder
Patients with cardiovascular disease should be given nortriptyline hydrochloride only under close supervision because of the tendency of the drug to produce sinus tachycardia and to prolong the conduction time. Myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, and strokes have occurred. The antihypertensive action of guanethidine and similar agents may be blocked. Because of its anticholinergic activity, nortriptyline hydrochloride should be used with great caution in patients who have glaucoma or a history of urinary retention. Patients with a history of seizures should be followed closely when nortriptyline hydrochloride is administered, inasmuch as this drug is known to lower the convulsive threshold. Great care is required if nortriptyline hydrochloride is given to hyperthyroid patients or to those receiving thyroid medication, since cardiac arrhythmias may develop.
Excessive consumption of alcohol in combination with nortriptyline therapy may have a potentiating effect, which may lead to the danger of increased suicidal attempts or overdosage, especially in patients with histories of emotional disturbances or suicidal ideation.
The concomitant administration of quinidine and nortriptyline may result in a significantly longer plasma half-life, higher AUC, and lower clearance of nortriptyline.
Use in Pregnancy
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Prescribers or other health professionals should inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules and should counsel them in its appropriate use. A patient Medication Guide aboutAntidepressant Medicines, Depression and other Serious Mental Illnesses, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actionsis available for nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules. The prescriber or health professional should instruct patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide and should assist them in understanding its contents. Patients should be given the opportunity to discuss the contents of the Medication Guide and to obtain answers to any questions they may have. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of this document.
Patients should be advised of the following issues and asked to alert their prescriber if these occur while taking nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules.
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
Patients, their families, and their caregivers should be encouraged to be alert to the emergence of anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, mania, other unusual changes in behavior, worsening of depression, and suicidal ideation, especially early during antidepressant treatment and when the dose is adjusted up or down. Families and caregivers of patients should be advised to look for the emergence of such symptoms on a day-to-day basis, since changes may be abrupt. Such symptoms should be reported to the patient's prescriber or health professional, especially if they are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms. Symptoms such as these may be associated with an increased risk for suicidal thinking and behavior and indicate a need for very close monitoring and possibly changes in the medication.
The use of nortriptyline hydrochloride in schizophrenic patients may result in an exacerbation of the psychosis or may activate latent schizophrenic symptoms. If the drug is given to overactive or agitated patients, increased anxiety and agitation may occur. In manic-depressive patients, nortriptyline hydrochloride may cause symptoms of the manic phase to emerge.
Troublesome patient hostility may be aroused by the use of nortriptyline hydrochloride. Epileptiform seizures may accompany its administration, as is true of other drugs of its class.
When it is essential, the drug may be administered with electroconvulsive therapy, although the hazards may be increased. Discontinue the drug for several days, if possible, prior to elective surgery.
Both elevation and lowering of blood sugar levels have been reported.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Administration of reserpine during therapy with a tricyclic antidepressant has been shown to produce a "stimulating" effect in some depressed patients.
Close supervision and careful adjustment of the dosage are required when nortriptyline hydrochloride is used with other anticholinergic drugs and sympathomimetic drugs.
Concurrent administration of cimetidine and tricyclic antidepressants can produce clinically significant increases in the plasma concentrations of the tricyclic antidepressant. The patient should be informed that the response to alcohol may be exaggerated.
A case of significant hypoglycemia has been reported in a type II diabetic patient maintained on chlorpropamide (250 mg/day), after the addition of nortriptyline (125 mg/day).
Drugs Metabolized by P450 2D6
Concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants with drugs that can inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 may require lower doses than usually prescribed for either the tricyclic antidepressant or the other drug. Furthermore, whenever one of these other drugs is withdrawn from co-therapy, an increased dose of tricyclic antidepressant may be required. It is desirable to monitor TCA plasma levels whenever a TCA is going to be coadministered with another drug known to be an inhibitor of P450 2D6.
PEDIATRIC USE
Safety and effectiveness in the pediatric population have not been established (see BOX WARNING and WARNINGS, Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk). Anyone considering the use of nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules in a child or adolescent must balance the potential risks with the clinical need.
GERIATRIC USE
Clinical studies of nortriptyline hydrochloride did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience indicates that, as with other tricyclic antidepressants, hepatic adverse events (characterized mainly by jaundice and elevated liver enzymes) are observed very rarely in geriatric patients and deaths associated with cholestatic liver damage have been reported in isolated instances. Cardiovascular function, particularly arrhythmias and fluctuations in blood pressure, should be monitored. There have also been reports of confusional states following tricyclic antidepressant administration in the elderly. Higher plasma concentrations of the active nortriptyline metabolite, 10-hydroxynortriptyline, have also been reported in elderly patients. As with other tricyclic antidepressants, dose selection for an elderly patient should usually be limited to the smallest effective total daily dose (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Note - Included in the following list are a few adverse reactions that have not been reported with this specific drug. However, the pharmacologic similarities among the tricyclic antidepressant drugs require that each of the reactions be considered when nortriptyline is administered.
Cardiovascular - Hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, palpitation, myocardial infarction, arrhythmias, heart block, stroke.
Gastrointestinal - Nausea and vomiting, anorexia, epigastric distress, diarrhea, peculiar taste, stomatitis, abdominal cramps, black-tongue.
Withdrawal Symptoms - Though these are not indicative of addiction, abrupt cessation of treatment after prolonged therapy may produce nausea, headache, and malaise.
OVERDOSAGE
Deaths may occur from overdosage with this class of drugs. Multiple drug ingestion (including alcohol) is common in deliberate tricyclic antidepressant overdose. As the management is complex and changing, it is recommended that the physician contact a poison control center for current information on treatment. Signs and symptoms of toxicity develop rapidly after tricyclic antidepressant overdose, therefore, hospital monitoring is required as soon as possible.
Manifestations
Critical manifestations of overdose include: cardiac dysrhythmias, severe hypotension, shock, congestive heart failure, pulmonary edema, convulsions, and CNS depression, including coma. Changes in the electrocardiogram, particularly in QRS axis or width, are clinically significant indicators of tricyclic antidepressant toxicity.
Other signs of overdose may include: confusion, restlessness, disturbed concentration, transient visual hallucinations, dilated pupils, agitation, hyperactive reflexes, stupor, drowsiness, muscle rigidity, vomiting, hypothermia, hyperpyrexia, or any of the acute symptoms listed under ADVERSE REACTIONS. There have been reports of patients recovering from nortriptyline overdoses of up to 525 mg.
Management
General
Obtain an ECG and immediately initiate cardiac monitoring. Protect the patient
Gastrointestinal Decontamination
All patients suspected of tricyclic antidepressant overdose should receive gastrointestinal decontamination. This should include large volume gastric lavage followed by activated charcoal. If consciousness is impaired, the airway should be secured prior to lavage. EMESIS IS CONTRAINDICATED.
Cardiovascular
A maximal limb-lead QRS duration of0.10 seconds may be the best indication of the severity of the overdose. Intravenous sodium bicarbonate should be used to maintain the serum pH in the range of 7.45 to 7.55. If the pH response is inadequate, hyperventilation may also be used. Concomitant use of hyperventilation and sodium bicarbonate should be done with extreme caution, with frequent pH monitoring. A pH > 7.60 or a pCO2 < 20 mmHg is undesirable. Dysrhythmias unresponsive to sodium bicarbonate therapy/hyperventilation may respond to lidocaine, bretylium or phenytoin. Type 1A and 1C antiarrhythmics are generally contraindicated (e.g., quinidine, disopyramide, and procainamide).
In rare instances, hemoperfusion may be beneficial in acute refractory cardiovascular instability in patients with acute toxicity. However, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, exchange transfusions, and forced diuresis generally have been reported as ineffective in tricyclic antidepressant poisoning.
CNS
In patients with CNS depression, early intubation is advised because of the potential for abrupt deterioration. Seizures should be controlled with benzodiazepines, or if these are ineffective, other anticonvulsants (e.g., phenobarbital, phenytoin). Physostigmine is not recommended except to treat life-threatening symptoms that have been unresponsive to other therapies, and then only in consultation with a poison control center
Psychiatric Follow-up
Since overdosage is often deliberate, patients may attempt suicide by other means during the recovery phase. Psychiatric referral may be appropriate.
Pediatric Management
The principles of management of child and adult overdosages are similar. It is strongly recommended that the physician contact the local poison control center for specific pediatric treatment.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Nortriptyline hydrochloride is not recommended for children.
Lower than usual dosages are recommended for elderly patients and adolescents. Lower dosages are also recommended for outpatients than for hospitalized patients who will be under close supervision. The physician should initiate dosage at a low level and increase it gradually, noting carefully the clinical response and any evidence of intolerance. Following remission, maintenance medication may be required for a longer period of time at the lowest dose that will maintain remission.
If a patient develops minor side effects, the dosage should be reduced. The drug should be discontinued promptly if adverse effects of a serious nature or allergic manifestations occur.
Usual Adult Dose
Elderly and Adolescent Patients
30 to 50 mg/day, in divided doses, or the total daily dosage may be given once a day.
HOW SUPPLIED
Nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules USP, equivalent to 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg or 75 mg base, are available as follows:
Nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules USP, 10 mg: #3 capsules with a white body and an orange cap, imprinted "TEVA" on the cap and "10mg"-"0810" on the body, in bottles of 100, 500, and 1000.
Nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules USP, 25 mg: #4 capsules with a white body and an orange cap, imprinted "TEVA"-"TEVA" on the cap and "25mg"-"0811" on the body, in bottles of 100, 500, and 1000.
Nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules USP, 50 mg: #1 capsules with a white body and a white cap, imprinted "TEVA" on the cap and "50mg"-"0812" on the body, in bottles of 100, 500, and 1000.
Nortriptyline hydrochloride capsules USP, 75 mg: #1 capsules with an orange body and an orange cap, imprinted "TEVA" on the cap and "75mg"-"0813" on the body, in bottles of 100, 500, and 1000.
Store at 20to 25(68to 77[See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense contents in a tight container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required).
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA
Sellersville, PA 18960
Rev. U 7/2010
| NORTRIPTYLINE HYDROCHLORIDE
nortriptyline hydrochloride capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - REMEDYREPACK INC. (829572556) |