ESTROGEL- estradiol gel, metered
ASCEND Therapeutics US, LLC
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use ESTROGEL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ESTROGEL.
EstroGel ® 0.06% (estradiol gel) for topical use Initial U.S. Approval: 1975 WARNING: ENDOMETRIAL CANCER, CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS, BREAST CANCER AND PROBABLE DEMENTIASee full prescribing information for complete boxed warningEstrogen-Alone Therapy
Estrogen Plus Progestin Therapy
RECENT MAJOR CHANGESINDICATIONS AND USAGEDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONDOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS1 pump depression of EstroGel 0.06% delivers 1.25 g of gel containing 0.75 mg estradiol ( 3) CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSADVERSE REACTIONSMost frequently occurring adverse reactions (≥5 percent) are: headache, flatulence and breast pain (
6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact ASCEND Therapeutics® US, LLC at 1-877-204-1013 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONSInducers and/or inhibitors of CYP3A4 may affect estrogen drug metabolism ( 7.1) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 8/2015 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: ENDOMETRIAL CANCER, CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS, BREAST CANCER AND PROBABLE DEMENTIA
Estrogen-Alone Therapy
Endometrial Cancer
There is an increased risk of endometrial cancer in a woman with a uterus who uses unopposed estrogens. Adding a progestin to estrogen therapy has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer. Adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed, persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)].
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
Estrogen-alone therapy should not be used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1, 5.3), and Clinical Studies ( 14.3, 14.4)] .
The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) estrogen-alone substudy reported increased risks of stroke and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 7.1 years of treatment with daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE) [0.625 mg]-alone, relative to placebo [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1), and Clinical Studies ( 14.3)].
The WHI Memory Study (WHIMS) estrogen-alone ancillary study of WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age or older during 5.2 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone, relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5), and Clinical Studies ( 14.4)] .
In the absence of comparable data, these risks should be assumed to be similar for other doses of CE and other dosage forms of estrogens.
Estrogens with or without progestins should be prescribed at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Estrogen Plus Progestin Therapy
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
Estrogen plus progestin therapy should not be used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1, 5.3), and Clinical Studies ( 14.3, 14.4)] .
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy reported increased risks of DVT, pulmonary embolism (PE), stroke and myocardial infarction (MI) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 5.6 years of treatment with daily oral CE (0.625 mg) combined with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) [2.5 mg], relative to placebo [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1), and Clinical Studies ( 14.3)].
The WHIMS estrogen plus progestin ancillary study of WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age or older during 4 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg) combined with MPA (2.5 mg), relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3), Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5), and Clinical Studies ( 14.4)].
Breast Cancer
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy also demonstrated an increased risk of invasive breast cancer [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2), and Clinical Studies ( 14.3)] .
In the absence of comparable data, these risks should be assumed to be similar for other doses of CE and MPA and other combinations and dosage forms of estrogens and progestins.
Estrogens with or without progestins should be prescribed at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Generally, when estrogen is prescribed for a postmenopausal woman with a uterus, a progestin should also be considered to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer. A woman without a uterus does not need progestin. In some cases, however, hysterectomized women with a history of endometriosis may need a progestin [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2, 5.14)] .
Use of estrogen-alone or in combination with a progestin, should be with the lowest effective dose and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman. Postmenopausal women should be reevaluated periodically as clinically appropriate to determine if treatment is still necessary.
2.1 Treatment of Moderate to Severe Vasomotor Symptoms due to Menopause
EstroGel 0.06% 1.25 g per day is the single approved dose for the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause. The lowest effective dose of EstroGel 0.06% for this indication has not been determined.
Before using the canister for the first time, it must be primed. Remove the large canister cover, and fully depress the pump 3 times. Discard the unused gel by thoroughly rinsing down the sink or placing it in the household trash. After priming, the pump is ready to use.
The recommended area of application is the arm. Apply a thin layer over the entire arm on the inside and outside from wrist to shoulder.
2.2 Treatment of Moderate to Severe Symptoms of Vulvar and Vaginal Atrophy due to Menopause
EstroGel 0.06% 1.25 g per day is the single approved dose for the treatment of moderate to severe symptoms of vulvar and vaginal atrophy due to menopause. The lowest effective dose of EstroGel 0.06% for this indication has not been determined. When prescribing solely for the treatment of moderate to severe symptoms of vulvar and vaginal atrophy, topical vaginal products should be considered.
Before using the canister for the first time, it must be primed. Remove the large canister cover, and fully depress the pump 3 times. Discard the unused gel by thoroughly rinsing down the sink or placing it in the household trash. After priming, the pump is ready to use.
The recommended area of application is the arm. Apply a thin layer over the entire arm on the inside and outside from wrist to shoulder.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
EstroGel 0.06% is an estradiol transdermal gel. One pump depression delivers 1.25 g of gel that contains 0.75 mg estradiol.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
EstroGel is contraindicated in women with any of the following conditions:
• Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
• Known, suspected, or history of breast cancer
• Known or suspected estrogen-dependent neoplasia
• Active DVT, PE, or history of these conditions
• Active arterial thromboembolic disease (for example, stroke and MI), or a history of these conditions
• Known anaphylactic reaction or angioedema to EstroGel
• Known liver impairment or disease
• Known protein C, protein S, or antithrombin deficiency, or other known thrombophilic disorders
• Known or suspected pregnancy
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiovascular Disorders
An increased risk of stroke and DVT has been reported with estrogen-alone therapy. An increased risk of PE, DVT, stroke and MI has been reported with estrogen plus progestin therapy. Should any of these occur or be suspected, estrogen with or without progestin therapy should be discontinued immediately.
Risk factors for arterial vascular disease (for example, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, tobacco use, hypercholesterolemia, and obesity) and/or venous thromboembolism (VTE) (for example, personal history or family history of VTE, obesity, and systemic lupus erythematosus) should be managed appropriately.
Stroke
In the WHI estrogen-alone substudy, a statistically significant increased risk of stroke was reported in women 50 to 79 years of age receiving daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone compared to women in the same age group receiving placebo (45 versus 33 per 10,000 women-years). The increase in risk was demonstrated in year 1 and persisted [see Clinical Studies ( 14.3)] . Should a stroke occur or be suspected, estrogen-alone therapy should be discontinued immediately.
Subgroup analysis of women 50 to 59 years of age suggest no increased risk of stroke for those women receiving CE (0.625 mg)-alone versus those receiving placebo (18 versus 21 per 10,000 women-years). 1
In the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy, a statistically significant increased risk of stroke was reported in women 50 to 79 years of age receiving daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) compared to women in the same age group receiving placebo (33 versus 25 per 10,000 women-years)
[see
Clinical Studies (
14.3)]
. The increase in risk was demonstrated after the first year and persisted.
1 Should a stroke occur or be suspected, estrogen plus progestin therapy should be discontinued immediately.
Coronary Heart Disease
In the WHI estrogen-alone substudy, no overall effect on coronary heart disease (CHD) events (defined as nonfatal MI, silent MI, or CHD death) was reported in women receiving estrogen-alone compared to placebo 2[see Clinical Studies ( 14.3)].
Subgroup analyses of women 50 to 59 years of age suggest a statistically non-significant reduction in CHD events (CE [0.625 mg]-alone compared to placebo) in women with less than 10 years since menopause (8 versus 16 per 10,000 women-years). 1
In the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy, there was a statistically non-significant increased risk of CHD events reported in women receiving daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) compared to women receiving placebo (41 versus 34 per 10,000 women-years). 1 An increase in relative risk was demonstrated in year 1, and a trend toward decreasing relative risk was reported in years 2 through 5 [see Clinical Studies ( 14.3)].
In postmenopausal women with documented heart disease (n = 2,763, average 66.7 years of age), in a controlled clinical trial of secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease (Heart and Estrogen/Progestin Replacement Study [HERS]), treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) demonstrated no cardiovascular benefit. During an average follow-up of 4.1 years, treatment with CE plus MPA did not reduce the overall rate of CHD events in postmenopausal women with established coronary heart disease. There were more CHD events in the CE plus MPA-treated group than in the placebo group in year 1, but not during the subsequent years. Two thousand, three hundred twenty-one (2,321) women from the original HERS trial agreed to participate in an open-label extension of HERS, HERS II. Average follow‑up in HERS II was an additional 2.7 years, for a total of 6.8 years overall. Rates of CHD events were comparable among women in the CE plus MPA group and the placebo group in HERS, HERS II, and overall.
Venous Thromboembolism
In the WHI estrogen-alone substudy, the risk of VTE (DVT and PE) was increased for women receiving daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone compared to placebo (30 versus 22 per 10,000 women‑years), although only the increased risk of DVT reached statistical significance (23 versus 15 per 10,000 women-years). The increase in VTE risk was demonstrated during the first 2 years 3[see Clinical Studies ( 14.3)]. Should a VTE occur or be suspected, estrogen-alone therapy should be discontinued immediately.
In the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy, a statistically significant 2‑fold greater rate of VTE was reported in women receiving daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) compared to women receiving placebo (35 versus 17 per 10,000 women‑years). Statistically significant increases in risk for both DVT (26 versus 13 per 10,000 women-years) and PE (18 versus 8 per 10,000 women-years) were also demonstrated. The increase in VTE risk was demonstrated during the first year and persisted 4[see Clinical Studies ( 14.3)] . Should a VTE occur or be suspected, estrogen plus progestin therapy should be discontinued immediately.
If feasible, estrogens should be discontinued at least 4 to 6 weeks before any surgery of the type associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism, or during periods of prolonged immobilization.
5.2 Malignant Neoplasms
Endometrial Cancer
An increased risk of endometrial cancer has been reported with the use of unopposed estrogen therapy in women with a uterus. The reported endometrial cancer risk among unopposed estrogen users is about 2 to 12 times greater than in nonusers, and appears dependent on duration of treatment and on estrogen dose. Most studies show no significant increased risk associated with use of estrogens for less than 1 year. The greatest risk appears to be associated with prolonged use, with increased risks of 15- to 24‑fold for 5 to 10 years or more. This risk has been shown to persist for at least 8 to 15 years after estrogen therapy is discontinued.
Clinical surveillance of all women using estrogen-alone or estrogen plus progestin therapy is important. Adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding.
There is no evidence that the use of natural estrogens results in a different endometrial risk profile than synthetic estrogens of equivalent estrogen dose. Adding a progestin to estrogen therapy in postmenopausal women has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer.
Breast Cancer
The most important randomized clinical trial providing information about breast cancer in estrogen-alone users is the WHI substudy of daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone . In the WHI estrogen-alone substudy, after an average follow-up of 7.1 years, daily CE-alone was not associated with an increased risk of invasive breast cancer [relative risk (RR) 0.8])5[see Clinical Studies ( 14.3)].
The most important randomized clinical trial providing information about breast cancer in estrogen plus progestin users is the WHI substudy of daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg). After a mean follow-up of 5.6 years, the estrogen plus progestin substudy reported an increased risk of invasive breast cancer in women who took daily CE plus MPA.
In this substudy, prior use of estrogen-alone or estrogen plus progestin therapy was reported by 26 percent of the women. The relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.24, and the absolute risk was 41 versus 33 cases per 10,000 women-years, for CE plus MPA compared with placebo [see Clinical Studies ( 14.3)] . Among women who reported prior use of hormone therapy, the relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.86, and the absolute risk was 46 versus 25 cases per 10,000 women-years, for CE plus MPA compared with placebo. Among women who reported no prior use of hormone therapy, the relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.09, and the absolute risk was 40 versus 36 cases per 10,000 women‑years for CE plus MPA compared with placebo. In the same substudy, invasive breast cancers were larger, were more likely to be node positive, and were diagnosed at a more advanced stage in the CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) group compared with the placebo group. Metastatic disease was rare, with no apparent difference between the two groups. Other prognostic factors, such as histologic subtype, grade and hormone receptor status did not differ between the groups 6[see Clinical Studies ( 14.3)] .
Consistent with the WHI clinical trial, observational studies have also reported an increased risk of breast cancer for estrogen plus progestin therapy, and a smaller increased risk for estrogen-alone therapy, after several years of use. The risk increased with duration of use, and appeared to return to baseline over about 5 years after stopping treatment (only the observational studies have substantial data on risk after stopping). Observational studies also suggest that the risk of breast cancer was greater, and became apparent earlier, with estrogen plus progestin therapy as compared to estrogen-alone therapy. However, these studies have not generally found significant variation in the risk of breast cancer among different estrogen plus progestin combinations, doses, or routes of administration.
The use of estrogen-alone and estrogen plus progestin has been reported to result in an increase in abnormal mammograms requiring further evaluation.
All women should receive yearly breast examinations by a healthcare provider and perform monthly breast self-examinations. In addition, mammography examinations should be scheduled based on patient age, risk factors, and prior mammogram results.
Ovarian Cancer
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy reported a statistically non-significant increase in the risk of ovarian cancer. After an average follow-up of 5.6 years, the relative risk for ovarian cancer for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 1.58 (95 percent CI, 0.77-3.24). The absolute risk for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 4 versus 3 cases per 10,000 women-years. 7 In some epidemiologic studies, the use of estrogen plus progestin and estrogen-only products, in particular for 5 or more years, has been associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer. However, the duration of exposure associated with increased risk is not consistent across all epidemiologic studies, and some report no association.
5.3 Probable Dementia
In the WHIMS estrogen-alone ancillary study of WHI, a population of 2,947 hysterectomized women 65 to 79 years of age was randomized to daily CE (0.625 mg)‑alone or placebo.
After an average follow-up of 5.2 years, 28 women in the estrogen-alone group and 19 women in the placebo group were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia for CE-alone versus placebo was 1.49 (95 percent CI, 0.83-2.66). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE-alone versus placebo was 37 versus 25 cases per 10,000 women-years 8[see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5), and Clinical Studies ( 14.4)] .
In the WHIMS estrogen plus progestin ancillary study of WHI, a population of 4,532 postmenopausal women 65 to 79 years of age was randomized to daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) or placebo. After an average follow-up of 4 years, 40 women in the CE plus MPA group and 21 women in the placebo group were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 2.05 (95 percent CI, 1.21-3.48). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 45 versus 22 cases per 10,000 women-years 8[see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5), and Clinical Studies ( 14.4)] .
When data from the two populations in the WHIMS estrogen-alone and estrogen plus progestin ancillary studies were pooled as planned in the WHIMS protocol, the reported overall relative risk for probable dementia was 1.76 (95 percent CI, 1.19-2.60). Since both ancillary studies were conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5), and Clinical Studies ( 14.4)] .
5.4 Gallbladder Disease
A 2- to 4-fold increase in the risk of gallbladder disease requiring surgery in postmenopausal women receiving estrogens has been reported.
5.5 Hypercalcemia
Estrogen administration may lead to severe hypercalcemia in patients with breast cancer and bone metastases. If hypercalcemia occurs, use of the drug should be stopped and appropriate measures taken to reduce the serum calcium level.
5.6 Visual Abnormalities
Retinal vascular thrombosis has been reported in patients receiving estrogens. Discontinue medication pending examination if there is sudden partial or complete loss of vision or a sudden onset of proptosis, diplopia, or migraine. If examination reveals papilledema or retinal vascular lesions, estrogens should be permanently discontinued.
5.7 Addition of a Progestin when a Woman has not had a Hysterectomy
Studies of the addition of a progestin for 10 or more days of a cycle of estrogen administration, or daily with estrogen in a continuous regimen, have reported a lowered incidence of endometrial hyperplasia than would be induced by estrogen treatment alone. Endometrial hyperplasia may be a precursor to endometrial cancer.
There are, however, possible risks that may be associated with the use of progestins with estrogens compared to estrogen‑alone regimens. These include an increased risk of breast cancer.
5.8 Elevated Blood Pressure
In a small number of case reports, substantial increases in blood pressure have been attributed to idiosyncratic reactions to estrogens. In a large, randomized, placebo‑controlled clinical trial, a generalized effect of estrogens on blood pressure was not seen.
5.9 Hypertriglyceridemia
In women with pre-existing hypertriglyceridemia, estrogen therapy may be associated with elevations of plasma triglycerides leading to pancreatitis. Consider discontinuation of treatment if pancreatitis occurs.
5.10 Hepatic Impairment and/or Past History of Cholestatic Jaundice
Estrogens may be poorly metabolized in women with impaired liver function. For women with a history of cholestatic jaundice associated with past estrogen use or with pregnancy, caution should be exercised, and in the case of recurrence, medication should be discontinued.
5.11 Hypothyroidism
Estrogen administration leads to increased thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) levels. Women with normal thyroid function can compensate for the increased TBG by making more thyroid hormone, thus maintaining free T 4 and T 3 serum concentrations in the normal range. Women dependent on thyroid hormone replacement therapy who are also receiving estrogens may require increased doses of their thyroid-replacement therapy. These women should have their thyroid function monitored in order to maintain an acceptable range.
5.12 Fluid Retention
Estrogens may cause some degree of fluid retention. Women with conditions that might be influenced by this factor, such as a cardiac or renal dysfunction, warrant careful observation when estrogen-alone is prescribed.
5.13 Hypocalcemia
Estrogen therapy should be used with caution in women with hypoparathyroidism as estrogen-induced hypocalcemia may occur.
5.14 Exacerbation of Endometriosis
A few cases of malignant transformation of residual endometrial implants have been reported in women treated post-hysterectomy with estrogen-alone therapy. For women known to have residual endometriosis post-hysterectomy, the addition of progestin should be considered.
5.15 Hereditary Angioedema
Exogenous estrogens may exacerbate symptoms of angioedema in women with hereditary angioedema.
5.16 Exacerbation of Other Conditions
Estrogen therapy may cause an exacerbation of asthma, diabetes mellitus, epilepsy, migraine, porphyria, systemic lupus erythematosus, and hepatic hemangiomas and should be used with caution in women with these conditions.
5.18 Moisturizer Lotion Application
Use of moisturizing lotion one hour after application of EstroGel 0.06% significantly increased estradiol absorption [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3)] .
5.19 Laboratory Tests
Serum follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and estradiol levels have not been shown to be useful in the management of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms and moderate to severe symptoms of vulvar and vaginal atrophy.
5.20 Drug-Laboratory Test Interactions
Accelerated prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and platelet aggregation time; increased platelet count; increased factors II, VII antigen, VIII antigen, VIII coagulant activity, IX, X, XII, VII-X complex, II-VII-X complex, and beta‑thromboglobulin; decreased levels of anti-factor Xa and antithrombin III, decreased antithrombin III activity; increased levels of fibrinogen and fibrinogen activity; increased plasminogen antigen and activity.
Increased thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) levels leading to increased circulating total thyroid hormone levels, as measured by protein-bound iodine (PBI), T 4 levels (by column or by radioimmunoassay) or T 3 levels by radioimmunoassay. T 3 resin uptake is decreased, reflecting the elevated TBG. Free T 4 and T 3 concentrations are unaltered. Women on thyroid-replacement therapy may require higher doses of thyroid hormone.
Other binding proteins may be elevated in serum (for example, corticosteroid-binding globulin [CBG], sex hormone-binding globulin [SHBG]), leading to increased total circulating corticosteroids and sex steroids, respectively. Free hormone concentrations, such as testosterone and estradiol, may be decreased. Other plasma proteins may be increased (angiotensinogen/renin substrate, alpha‑1‑antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin).
Increased plasma high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and HDL 2 cholesterol subfraction concentrations, reduced low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol concentration, increased triglyceride levels.
Impaired glucose tolerance.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Disorders [see Boxed Warning, and Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)]
- Malignant Neoplasms [see Boxed Warning, and Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
EstroGel was studied in 2 well-controlled, 12-week clinical trials. Incidence of adverse drug reactions ≥5 percent for 1.25 g EstroGel 0.06% and placebo is given in Table 1.
|
Body System/
|
EstroGel 0.06%
|
Placebo
|
|
BODY AS A WHOLE |
||
|
Headache |
9.5 |
2.7 |
|
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM |
||
|
Flatulence |
5.4 |
4.1 |
|
UROGENITAL SYSTEM |
||
|
Breast pain |
10.7 |
8.2 |
In 2 controlled clinical trials, application site reactions were reported by 0.6 percent of patients who received 1.25 g of EstroGel. Other skin reactions, such as pruritus and rash, were also noted.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of EstroGel. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Genitourinary system
Endometrial cancer
Breast
Pain; tenderness; breast cancer
Cardiovascular
Deep vein thrombosis; myocardial ischemia; phlebitis
Gastrointestinal
Nausea; abdominal distension; diarrhea; stomach discomfort
Skin
Alopecia; rash; pruritus; application site: dryness, pain, discoloration, reaction, rash
Eyes
Retinal vein occlusion
Central nervous system
Headache; dizziness; insomnia; hypoesthesia; meningioma; aphasia; bradyphrenia; paresthesia
Miscellaneous
Drug ineffective; hot flush; arthralgia; night sweats; drug effect decreased; pain in extremity; fatigue; weight increased; pain; hypersensitivity; dyspnea; malignant mesenchymoma; angioedema; hepatitis acute; face edema; accidental exposure; myoclonus; gait disturbance; flushing
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted for EstroGel.
7.1 Metabolic Interactions
In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that estrogens are metabolized partially by cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4). Therefore, inducers or inhibitors of CYP3A4 may affect estrogen drug metabolism. Inducers of CYP3A4, such as St. John’s wort ( Hypericum perforatum) preparations, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and rifampin, may reduce plasma concentrations of estrogens, possibly resulting in a decrease in therapeutic effects and/or changes in the uterine bleeding profile. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 such as erythromycin, clarithromycin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir, and grapefruit juice may increase plasma concentrations of estrogen and may result in side effects.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
EstroGel should not be used during pregnancy [see Contraindications ( 4)]. There appears to be little or no increased risk of birth defects in children born to women who have used estrogens and progestins as an oral contraceptive inadvertently during early pregnancy.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
EstroGel should not be used during lactation. Estrogen administration to nursing women has been shown to decrease the quantity and quality of the breast milk. Detectable amounts of estrogen have been identified in the milk of women receiving estrogen therapy. Caution should be exercised when EstroGel is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
EstroGel is not indicated in children. Clinical studies have not been conducted in the pediatric population.
8.5 Geriatric Use
There have not been sufficient numbers of geriatric women involved in studies utilizing EstroGel to determine whether those over 65 years of age differ from younger subjects in their response to EstroGel.
The Women’s Health Initiative Studies
In the WHI estrogen-alone substudy (daily CE [0.625 mg]-alone versus placebo), there was a higher relative risk of stroke in women greater than 65 years of age [see Clinical Studies ( 14.3)] .
In the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy (daily CE [0.625 mg] plus MPA [2.5 mg] versus placebo), there was a higher relative risk of nonfatal stroke and invasive breast cancer in women greater than 65 years of age
[see
Clinical Studies (
14.3)]
.
The Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study
In the WHIMS ancillary studies of postmenopausal women 65 to 79 years of age, there was an increased risk of developing probable dementia in women receiving estrogen-alone or estrogen plus progestin when compared to placebo [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3), and Clinical Studies ( 14.4)] .
Since both ancillary studies were conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women 8[see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3), and Clinical Studies ( 14.4)] .
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of estrogen may cause nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, abdominal pain, drowsiness and fatigue, and withdrawal bleeding may occur in women. Treatment of overdose consists of discontinuation of EstroGel together with institution of appropriate symptomatic care.
11 DESCRIPTION
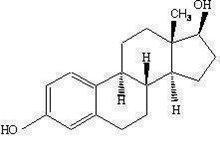
EstroGel (estradiol gel) contains 0.06 percent estradiol in an absorptive hydroalcoholic gel base for topical application. It is a clear, colorless gel, which is odorless when dry. One pump depression of EstroGel delivers 1.25 g of gel containing 0.75 mg estradiol.
Estradiol is a white crystalline powder, chemically described as estra‑1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol. It has an empirical formula of C 18H 24O 2 and molecular weight of 272.39. The structural formula is:
The active component of the gel is estradiol. The remaining components of the gel (purified water, alcohol, triethanolamine and carbomer 934P) are pharmacologically inactive.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
EstroGel provides systemic estrogen therapy by releasing estradiol, the major estrogenic hormone secreted by the human ovary.
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Endogenous estrogens are largely responsible for the development and maintenance of the female reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics. Although circulating estrogens exist in a dynamic equilibrium of metabolic interconversions, estradiol is the principal intracellular human estrogen and is substantially more potent than its metabolites, estrone and estriol, at the receptor level.
The primary source of estrogen in normally cycling adult women is the ovarian follicle, which secretes 70 to 500 mcg of estradiol daily, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. After menopause, most endogenous estrogen is produced by conversion of androstenedione, secreted by the adrenal cortex, to estrone in the peripheral tissues. Thus, estrone and the sulfate‑conjugated form, estrone sulfate, are the most abundant circulating estrogens in postmenopausal women.
Estrogens act through binding to nuclear receptors in estrogen-responsive tissues. To date, two estrogen receptors have been identified. These vary in proportion from tissue to tissue.
Circulating estrogens modulate the pituitary secretion of the gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and FSH through a negative feedback mechanism. Estrogens act to reduce the elevated levels of these hormones seen in postmenopausal women.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Estradiol is transported across intact skin and into the systemic circulation by a passive diffusion process. The rate of diffusion across the stratum corneum is the rate-limiting factor. When EstroGel is applied to the skin, it dries in 2 to 5 minutes.
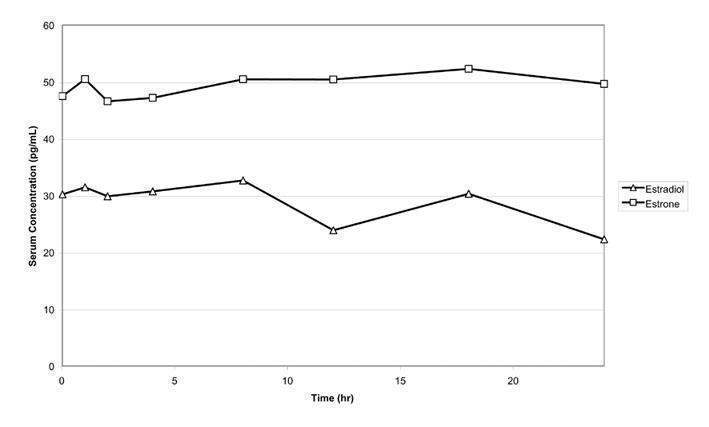
EstroGel 1.25 g (containing 0.75 mg of estradiol) was administered to 24 postmenopausal women once daily on the posterior surface of 1 arm from wrist to shoulder for 14 consecutive days. Mean maximal serum concentrations of estradiol and estrone on Day 14 were 46.4 pg/mL and 64.2 pg/mL, respectively. The time‑averaged serum estradiol and estrone concentrations over the 24-hour dose interval after administration of 1.25 g EstroGel on Day 14 are 28.3 pg/mL and 48.6 pg/mL, respectively. Mean concentration-time profiles for unadjusted estradiol and estrone on Day 14 are shown in Figure 1.
The serum concentrations of estradiol following 2.5 g EstroGel applications (1.25 g on each arm from wrist to shoulder) appeared to reach steady state after the third daily application.
Distribution
The distribution of exogenous estrogens is similar to that of endogenous estrogens. Estrogens are widely distributed in the body and are generally found in higher concentrations in the sex hormone target organs. Estrogens circulate in blood largely bound to SHBG and albumin.
Metabolism
Exogenous estrogens are metabolized in the same manner as endogenous estrogens. Circulating estrogens exist in a dynamic equilibrium of metabolic interconversions. These transformations take place mainly in the liver. Estradiol is converted reversibly to estrone, and both can be converted to estriol, which is a major urinary metabolite. Estrogens also undergo enterohepatic recirculation via sulfate and glucuronide conjugation in the liver, biliary secretion of conjugates into the intestine, and hydrolysis in the intestine followed by reabsorption. In postmenopausal women, a significant proportion of the circulating estrogens exist as sulfate conjugates, especially estrone sulfate, which serves as a circulating reservoir for the formation of more active estrogens. Although the clinical significance has not been determined, estradiol from EstroGel does not go through first‑pass liver metabolism.
Excretion
Estradiol, estrone, and estriol are excreted in the urine along with glucuronide and sulfate conjugates.
The apparent terminal exponential half-life for estradiol was about 36 hours following administration of 1.25 g EstroGel.
Use in Specific Populations
No pharmacokinetic studies were conducted in special populations, including patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
Effect of Application Site Washing
The effect of application site washing on the serum concentrations of estradiol was determined in 24 healthy postmenopausal women who applied 1.25 g of EstroGel once daily for 14 consecutive days. Site washing 1 hour after the application resulted in a 22 percent mean decrease in average 24-hour serum concentrations of estradiol.
Potential for Estradiol Transfer
The effect of estradiol transfer was evaluated in 24 healthy postmenopausal women who topically applied 1.25 g of EstroGel once daily on the posterior surface of 1 arm from wrist to shoulder for a period of 14 consecutive days. On each day, 1 hour after gel application, a cohort of 24 non-dosed healthy postmenopausal females directly contacted the dosed cohort at the site of gel application for 15 minutes. No change in endogenous mean serum concentrations of estradiol was observed in the non-dosed cohort after direct skin-to-skin contact with subjects administered EstroGel.
Effect of Moisturizer Lotion/Sunscreen on Estradiol Absorption
The effect of sunscreen and moisturizer lotion on estradiol absorption from 0.06% estradiol topical gel was evaluated in a randomized, open-label, three-period crossover study in 42 healthy postmenopausal women. The study results showed that repeated daily application of sunscreen for 7 days at 1 hour after the administration of 0.06% estradiol topical gel decreased the mean AUC 0-24h and C max of estradiol by 16%. Repeated daily application of moisturizer lotion for 7 days at 1 hour after the administration of 0.06% estradiol topical gel increased the mean AUC 0-24h and C max of estradiol by 38% and 73%, respectively.
The effect of daily application of sunscreen/moisturizer lotion on estradiol absorption, when sunscreen/moisturizer lotion is applied before administration of 0.06% estradiol topical gel, was not studied.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Effects on Vasomotor Symptoms
In a placebo-controlled study, 145 postmenopausal women between 29 and 67 years of age (81.4 percent were White) were randomly assigned to receive 1.25 g of EstroGel (containing 0.75 mg of estradiol) or placebo gel for 12 weeks. Efficacy was assessed at 4 and 12 weeks of treatment. A statistically significant reduction in the frequency and severity of moderate to severe hot flushes was shown at Weeks 4 and 12. (See Table 2)
|
Number of Hot Flushes/Day (Moderate to Severe) |
Severity Score/Day (Mild, Moderate, Severe) |
|||
|
Placebo n=73 |
EstroGel 0.06% 1.25 g n=72 |
Placebo n=73 |
EstroGel 0.06% 1.25 g n=72 |
|
|
Baseline Mean (SD) |
|
|
|
|
|
Week 4* Mean (SD) Mean change from baseline (SD) Diff. vs placebo P value † |
-5.06 (4.91) |
-5.91 (3.68) 0.85 0.019 ‡ |
-0.31 (0.62) |
-0.63 (0.71) 0.32 0.005 ‡ |
|
Week 12* Mean (SD) Mean change from baseline (SD) Diff. vs placebo P value † |
-5.84 (4.52) |
-7.55 (3.52) 1.71 0.043 ‡ |
-0.54 (0.84) |
-1.03 (0.94) 0.49 <0.001 ‡ |
14.2 Effects on Vulvar and Vaginal Atrophy
Results of the vaginal wall cytology showed a significant ( P≤0.001) increase from baseline in the percent of superficial epithelial cells at Week 12 for 1.25 g EstroGel. In contrast, no significant change from baseline was observed in the placebo group.
14.3 Women’s Health Initiative Studies
The WHI enrolled approximately 27,000 predominantly healthy postmenopausal women in two substudies to assess the risks and benefits of daily oral CE (0.625 mg)‑alone or in combination with MPA (2.5 mg) compared to placebo in the prevention of certain chronic diseases. The primary endpoint was the incidence of CHD (defined as nonfatal MI, silent MI, and CHD death), with invasive breast cancer as the primary adverse outcome. A “global index” included the earliest occurrence of CHD, invasive breast cancer, stroke, PE, endometrial cancer (only in the CE plus MPA substudy), colorectal cancer, hip fracture, or death due to other causes. These substudies did not evaluate the effects of CE-alone or CE plus MPA on menopausal symptoms.
WHI Estrogen-Alone Substudy
The WHI estrogen-alone substudy was stopped early because an increased risk of stroke was observed, and it was deemed that no further information would be obtained regarding the risks and benefits of estrogen-alone in predetermined primary endpoints. Results of the estrogen-alone substudy, which included 10,739 women (average 63 years of age, range 50-79; 75.3 percent White, 15.1 percent Black, 6.1 percent Hispanic, 3.6 percent Other), after an average follow-up of 7.1 years are presented in Table 3.
|
|||
|
Event |
Relative Risk
|
CE n = 5,310 |
Placebo n = 5,429 |
|
Absolute Risk per 10,000 Women-Years |
|||
|
CHD events ‡ |
0.95 (0.78-1.16) |
54 |
57 |
|
Non-fatal MI‡ |
0.91 (0.73-1.14) |
40 |
43 |
|
CHD death‡ |
1.01 (0.71-1.43) |
16 |
16 |
|
All strokes ‡ Ischemic stroke‡ |
1.33 (1.05-1.68) 1.55 (1.19-2.01) |
45 38 |
33 25 |
|
1.47 (1.06-2.06) |
23 |
15 |
|
|
Pulmonary embolism ‡ |
1.37 (0.90-2.07) |
14 |
10 |
|
Invasive breast cancer ‡ |
0.80 (0.62-1.04) |
28 |
34 |
|
Colorectal cancer ‡ |
1.08 (0.75-1.55) |
17 |
16 |
|
Hip fracture ‡ |
0.65 (0.45-0.94) |
12 |
19 |
|
0.64 (0.44-0.93) |
11 |
18 |
|
|
0.58 (0.47-0.72) |
35 |
59 |
|
|
0.71 (0.64-0.80) |
144 |
197 |
|
|
1.08 (0.88-1.32) |
53 |
50 |
|
|
1.04 (0.88-1.22) |
79 |
75 |
|
|
Global index Þ |
1.02 (0.92-1.13) |
206 |
201 |
For those outcomes included in the WHI “global index” that reached statistical significance, the absolute excess risk per 10,000 women-years in the group treated with CE-alone was 12 more strokes, while the absolute risk reduction per 10,000 women‑years was 7 fewer hip fractures. 9 The absolute excess risk of events included in the "global index" was a non-significant 5 events per 10,000 women-years. There was no difference between the groups in terms of all-cause mortality .
No overall difference for primary CHD events (nonfatal MI, silent MI and CHD death) and invasive breast cancer in women receiving CE-alone compared with placebo was reported in final centrally adjudicated results from the estrogen-alone substudy, after an average follow-up of 7.1 years. See Table 3.
Centrally adjudicated results for stroke events from the estrogen-alone substudy, after an average follow-up of 7.1 years, reported no significant difference in the distribution of stroke subtype or severity, including fatal strokes, in women receiving estrogen-alone compared to placebo. Estrogen-alone therapy increased the risk of ischemic stroke, and this excess risk was present in all subgroups of women examined. 10 See Table 3.
Timing of initiation of estrogen-alone therapy relative to the start of menopause may affect the overall risk benefit profile. The WHI estrogen-alone substudy stratified by age showed in women 50 to 59 years of age a non-significant trend toward reduced risk for CHD
[hazard ratio (HR) 0.63 (95 percent CI, 0.36-1.09)] and overall mortality
[HR 0.71 (95 percent CI, 0.46-1.11)].
WHI Estrogen Plus Progestin Substudy
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy was stopped early. According to the predefined stopping rule, after an average follow-up of 5.6 years of treatment, the increased risk of invasive breast cancer and cardiovascular events exceeded the specified benefits included in the “global index.” The absolute excess risk of events included in the “global index” was 19 per 10,000 women-years.
For those outcomes included in the WHI “global index” that reached statistical significance after 5.6 years of follow-up, the absolute excess risks per 10,000 women-years in the group treated with CE plus MPA were 7 more CHD events, 8 more strokes, 10 more PEs, and 8 more invasive breast cancers, while the absolute risk reduction per 10,000 women-years were 6 fewer colorectal cancers and 5 fewer hip fractures .
Results of the CE plus MPA substudy, which included 16,608 women (average 63 years of age, range 50-79; 83.9 percent White, 6.8 percent Black, 5.4 percent Hispanic, 3.9 percent Other), are presented in Table 4. These results reflect centrally adjudicated data after an average follow-up of 5.6 years.
|
|||
|
Event |
Relative Risk
|
CE/MPA
|
Placebo
|
|
Absolute Risk per 10,000
|
|||
|
CHD events
|
1.23 (0.99-1.53)
|
41
|
34
|
|
All strokes
|
1.31 (1.03-1.68)
|
33
|
25
|
|
Deep vein thrombosis § |
1.95 (1.43-2.67) |
26 |
13 |
|
Pulmonary embolism |
2.13 (1.45-3.11) |
18 |
8 |
|
Invasive breast cancer ¶ |
1.24 (1.01-1.54) |
41 |
33 |
|
Colorectal cancer |
0.61 (0.42-0.87) |
10 |
16 |
|
Endometrial cancer § |
0.81 (0.48-1.36) |
6 |
7 |
|
Cervical cancer § |
1.44 (0.47-4.42) |
2 |
1 |
|
Hip fracture |
0.67 (0.47-0.96) |
11 |
16 |
|
Vertebral fractures § |
0.65 (0.46-0.92) |
11 |
17 |
|
Lower arm/wrist fractures § |
0.71 (0.59-0.85) |
44 |
62 |
|
Total fractures |
0.76 (0.69-0.83) |
152 |
199 |
|
Overall mortality # |
1.00 (0.83-1.19) |
52 |
52 |
|
Global Index Þ |
1.13 (1.02-1.25) |
184 |
165 |
Timing of initiation of estrogen plus progestin therapy relative to the start of menopause may affect the overall risk benefit profile. The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy stratified by age showed in women 50 to 59 years of age a non-significant trend toward reduced risk for overall mortality [HR 0.69 (95 percent CI, 0.44-1.07)].
14.4 Women's Health Initiative Memory Study
The WHIMS estrogen-alone ancillary study of WHI enrolled 2,947 predominantly healthy hysterectomized postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older (45 percent were 65 to 69 years of age, 36 percent were 70 to 74 years of age, and 19 percent were 75 years of age and older) to evaluate the effects of daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone on the incidence of probable dementia (primary outcome) compared to placebo.
After an average follow-up of 5.2 years, the relative risk of probable dementia for CE-alone versus placebo was 1.49 (95 percent CI, 0.83-2.66). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE-alone versus placebo was 37 versus 25 cases per 10,000 women-years. Probable dementia as defined in the study included Alzheimer’s disease (AD), vascular dementia (VaD) and mixed type (having features of both AD and VaD). The most common classification of probable dementia in the treatment group and the placebo group was AD. Since the ancillary study was conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3), and Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5)].
The WHIMS estrogen plus progestin ancillary study enrolled 4,532 predominantly healthy postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older (47 percent were 65 to 69 years of age, 35 percent were 70 to 74 years of age, and 18 percent were 75 years of age and older) to evaluate the effects of daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) on the incidence of probable dementia (primary outcome) compared to placebo.
After an average follow-up of 4 years, the relative risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 2.05 (95 percent CI, 1.21-3.48). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE plus MPA versus placebo was 45 versus 22 cases per 10,000 women-years. Probable dementia as defined in the study included AD, VaD and mixed type (having features of both AD and VaD). The most common classification of probable dementia in the treatment group and the placebo group was AD. Since the ancillary study was conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3), and Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5)].
When data from the two populations were pooled as planned in the WHIMS protocol, the reported overall relative risk for probable dementia was 1.76 (95 percent CI, 1.19-2.60). Differences between groups became apparent in the first year of treatment. It is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3), and Use in Specific Populations ( 8.5)].
15 REFERENCES
- Rossouw JE, et al. Postmenopausal Hormone Therapy and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease by Age and Years Since Menopause. JAMA. 2007;297:1465-1477.
- Hsia J, et al. Conjugated Equine Estrogens and Coronary Heart Disease. Arch Int Med. 2006;166:357-365.
- Curb JD, et al. Venous Thrombosis and Conjugated Equine Estrogen in Women Without a Uterus. Arch Int Med. 2006;166:772-780.
- Cushman M, et al. Estrogen Plus Progestin and Risk of Venous Thrombosis. JAMA. 2004;292:1573-1580.
- Stefanick ML, et al. Effects of Conjugated Equine Estrogens on Breast Cancer and Mammography Screening in Postmenopausal Women With Hysterectomy. JAMA. 2006;295:1647-1657.
- Chlebowski RT, et al. Influence of Estrogen Plus Progestin on Breast Cancer and Mammography in Healthy Postmenopausal Women. JAMA. 2003;289:3234-3253.
- Anderson GL, et al. Effects of Estrogen Plus Progestin on Gynecologic Cancers and Associated Diagnostic Procedures. JAMA. 2003;290:1739-1748.
- Shumaker SA, et al. Conjugated Equine Estrogens and Incidence of Probable Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Postmenopausal Women. JAMA. 2004;291:2947-2958.
- Jackson RD, et al. Effects of Conjugated Equine Estrogen on Risk of Fractures and BMD in Postmenopausal Women With Hysterectomy: Results From the Women's Health Initiative Randomized Trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2006;21:817-828. Hendrix SL, et al. Effects of Conjugated Equine Estrogen on Stroke in the Women's Health Initiative. Circulation. 2006;113:2425-2434.
- Hendrix SL, et al. Effects of Conjugated Equine Estrogen on Stroke in the Women's Health Initiative. Circulation. 2006;113:2425-2434.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
EstroGel is a clear, colorless, hydroalcoholic 0.06 percent estradiol gel supplied in a non‑aerosol, metered-dose pump. The pump consists of an LDPE inner liner encased in rigid plastic with a resealable polypropylene cap. Two pump sizes are available, a 50-gram (1.75 oz), and a 25-gram (0.88 oz). Each individually packaged 50-gram pump contains 50 grams of gel and is capable of delivering 32 metered 1.25-g doses. Each individually packaged 25-gram pump contains 25 grams of gel and is capable of delivering 14 metered 1.25-g doses. One pump depression (1.25 g EstroGel) contains 0.75 mg estradiol.
NDC: 17139-617-40............................. (50-gram pump)
NDC: 17139-617-20............................. (25-gram sample pump)
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use)
17.1 Vaginal Bleeding
Inform postmenopausal women of the importance of reporting vaginal bleeding to their healthcare provider as soon as possible [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)] .
17.2 Possible Serious Adverse Reactions with Estrogen-Alone Therapy
Inform postmenopausal women of the possible serious adverse reactions of estrogen-alone therapy including Cardiovascular Disorders, Malignant Neoplasms, and Probable Dementia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1, 5.2, 5.3)].
17.3 Possible Less Serious but Common Adverse Reactions with Estrogen-Alone Therapy
Inform postmenopausal women of possible less serious adverse reactions of estrogen-alone therapy such as headache, breast pain and tenderness, nausea and vomiting.
Manufactured for:
ASCEND Therapeutics
® US, LLC
Herndon, VA 20170
By DPT Laboratories
San Antonio, TX 78215
129911Rev082014
Utilizes EHG
® Technology
©2014 ASCEND Therapeutics
® US, LLC
Patient Information
EstroGel ® 0.06% (ĕs’ trə jĕl)
(estradiol gel)
Read this Patient Information before you start using EstroGel, and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your menopausal symptoms or your treatment.
|
What is the most important information I should know about EstroGel (an estrogen hormone)?
|
What is EstroGel?
EstroGel is a prescription medicine gel that contains estradiol (an estrogen hormone).
What is EstroGel used for?
EstroGel is used after menopause to:
-
Reduce moderate to severe hot flashes
Estrogens are hormones made by a woman’s ovaries. The ovaries normally stop making estrogens when a woman is between 45 and 55 years old. This drop in body estrogen levels causes the “change of life” or menopause (the end of monthly menstrual periods). Sometimes, both ovaries are removed during an operation before natural menopause takes place. The sudden drop in estrogen levels causes “surgical menopause.”
When the estrogen levels begin dropping, some women develop very uncomfortable symptoms, such as feelings of warmth in the face, neck, and chest, or sudden strong feelings of heat and sweating (“hot flashes” or “hot flushes”). In some women, the symptoms are mild, and they will not need to use estrogens. In other women, symptoms can be more severe. You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly about whether you still need treatment with EstroGel.
-
Treat moderate to severe menopausal changes in and around the vagina
You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly about whether you still need treatment with EstroGel to control these problems. If you use EstroGel only to treat your menopausal changes in and around your vagina, talk with your healthcare provider about whether a topical vaginal product would be better for you.
Who should not use EstroGel?
Do not start using EstroGel if you:
-
have unusual vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding after menopause may be a warning sign of cancer of the uterus (womb). Your healthcare provider should check any unusual vaginal bleeding to find out the cause.
-
currently have or have had certain cancers
Estrogens may increase the chance of getting certain types of cancer, including cancer of the breast or uterus. If you have or have had cancer, talk with your healthcare provider about whether you should use EstroGel.
- had a stroke or heart attack
- currently have or have had blood clots
- currently have or have had liver problems
- have been diagnosed with a bleeding disorder
-
are allergic to EstroGel or any of its ingredients
See the list of ingredients in EstroGel at the end of this leaflet.
-
think you may be pregnant
EstroGel is not for pregnant women. If you think you may be pregnant, you should have a pregnancy test and know the results. Do not use EstroGel if the test is positive and talk to your healthcare provider.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before I use EstroGel?
Before you use EstroGel, tell your healthcare provider if you:
-
have any unusual vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding after menopause may be a warning sign of cancer of the uterus (womb). Your healthcare provider should check any unusual vaginal bleeding to find out the cause.
-
have any other medical conditions
Your healthcare provider may need to check you more carefully if you have certain conditions, such as asthma (wheezing), epilepsy (seizures), diabetes, migraine, endometriosis, lupus, angioedema (swelling of face and tongue), or problems with your heart, liver, thyroid, kidneys, or high calcium levels in your blood .
-
are going to have surgery or will be on bed rest
Your healthcare provider will let you know if you need to stop using EstroGel.
-
are breastfeeding
The hormone in EstroGel can pass into your breast milk.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicines may affect how EstroGel works. EstroGel may also affect how your other medicines work. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use EstroGel?
For detailed instructions, see the step-by-step instructions for using EstroGel at the end of this Patient Information.
- Use EstroGel exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- EstroGel is for skin use only.
- EstroGel contains alcohol, which is flammable. Avoid fire, flame or smoking until EstroGel has dried.
- You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly (for example, every 3 to 6 months) about the dose you are taking and whether you still need treatment with EstroGel.
What are the possible side effects of EstroGel?
Side effects are grouped by how serious they are and how often they happen when you are treated.
Serious, but less common side effects include:
- heart attack
- stroke
- blood clots
- dementia
- breast cancer
- cancer of the lining of the uterus (womb)
- cancer of the ovary
- high blood pressure
- high blood glucose
- gallbladder disease
- liver problems
- changes in your thyroid hormone levels
- enlargement of benign tumors (“fibroids”)
Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following warning signs or any other unusual symptoms that concern you:
- new breast lumps
- unusual vaginal bleeding
- changes in vision or speech
- sudden new severe headaches
- severe pains in your chest or legs with or without shortness of breath, weakness and fatigue
Less serious, but common side effects include:
- headache
- breast pain
- stomach or abdominal cramps, bloating
- nausea and vomiting
- hair loss
- fluid retention
- vaginal yeast infection
These are not all of the possible side effects of EstroGel. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effects that bother you or do not go away. You may report side effects to ASCEND Therapeutics
® US, LLC at 1‑877-204-1013 or to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What can I do to lower my chances of a serious side effect with EstroGel?
- Talk with your healthcare provider regularly about whether you should continue using EstroGel.
- If you have a uterus, talk with your healthcare provider about whether the addition of a progestin is right for you.
- The addition of a progestin is generally recommended for women with a uterus to reduce the chance of getting cancer of the uterus (womb).
- See your healthcare provider right away if you get vaginal bleeding while using EstroGel.
- Have a pelvic exam, breast exam and mammogram (breast x-ray) every year unless your healthcare provider tells you something else.
- If members of your family have had breast cancer or if you have ever had breast lumps or an abnormal mammogram (breast x-ray), you may need to have breast exams more often.
- If you have high blood pressure, high cholesterol (fat in the blood), diabetes, are overweight, or if you use tobacco, you may have higher chances of getting heart disease.
Ask your healthcare provider for ways to lower your chances of getting heart disease.
How should I store EstroGel?
- Store EstroGel at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep EstroGel and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of EstroGel
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use EstroGel for conditions for which it was not prescribed. Do not give EstroGel to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This patient leaflet summarizes the most important information about EstroGel. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist. You can ask for information about EstroGel that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to
www.estrogel.com, or call ASCEND Therapeutics
® US, LLC at 1-877-204-1013.
What are the ingredients in EstroGel?
Active ingredient: estradiol
Inactive ingredients: purified water, alcohol, triethanolamine, and carbomer 934P.
Instructions for Use
EstroGel ® 0.06% (ĕs’ trə jĕl)
(estradiol gel)
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using EstroGel and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your menopausal symptoms or your treatment.
You will need the following supplies to use EstroGel: See Figure A.
Figure A
EstroGel is supplied in a metered-dose pump that delivers a measured amount of estradiol to your skin each time you press the pump.
EstroGel is available in 2 sizes:
- a 50-gram canister
- a 25-gram canister
Your healthcare provider will prescribe the size canister that is right for you. The instructions below are the same for both canister sizes.
Step 1. Priming the EstroGel pump
- Before using the EstroGel pump for the first time, the pump must be primed. The EstroGel canister contains enough medicine to allow you to prime the pump before you use it for the first time.
- Remove the large cap from the canister and the small cap from the tip of the pump. See Figure B.
Figure B
- Slowly push the pump all the way down 3 times. Do not use any EstroGel that came out while priming. Wash it down the sink to avoid accidental exposure to others.
- After priming, the EstroGel pump is ready to use. One complete press of the pump will give the same amount of EstroGel each time.
Step 2. Applying EstroGel to your skin
- Do not allow other people to apply EstroGel to your skin for you.
- Apply EstroGel to clean, dry, unbroken skin.
- Apply EstroGel after your bath or shower. If you go swimming, try to leave as much time as possible between using your EstroGel and going swimming.
- Remove the small cover on the tip of the pump if you have not done so already. See Figure C.
Figure C
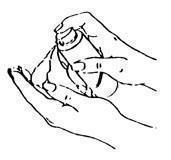
- To use EstroGel, press the EstroGel pump firmly and fully 1 time into the palm of your hand. See Figure D.
Figure D
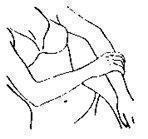
- Using your hand, apply EstroGel to the skin of your other arm.
See Figure E.
Spread the gel as thinly as possible over the entire area on the inside and outside of your arm from your wrist to your shoulder. See Figure F.
Figure E
Figure F
- Do not apply EstroGel directly to your breasts or in and around your vagina.
- Do not massage or rub in EstroGel. Allow the gel to dry for 5 minutes before you get dressed.
Step 3. After you use EstroGel
- Place the small cap back on the tip of the pump. Place the large cap over the top of the canister.
- Wash your hands right away with soap and water after applying EstroGel. This will lower the chance that the medicine will spread from your hands to other people.
- Do not allow others to make contact with the area of skin where you applied the gel for at least 1 hour after application.
- EstroGel is flammable until dry. Let EstroGel dry before smoking or going near an open flame.
Step 4. Throwing away used EstroGel canisters
- The EstroGel 50-gram canister contains enough medicine to allow for priming your canister with 3 full pump depressions and delivery of 32 daily doses. After you have first primed your canister and used 32 doses, you will need to throw away the canister. Do not use the canister for more than 32 doses even though the canister may not be completely empty. You may not get the correct dose.
-
The EstroGel 25-gram canister contains enough medicine to allow for priming your canister with 3 full pump depressions and delivery of 14 daily doses. After you have first primed your canister and used 14 doses, you will need to throw away the canister. Do not use the canister for more than 14 doses even though the canister may not be completely empty. You may not get the correct dose.
This Patient Information and Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
ASCEND Therapeutics ® US, LLC
Herndon, VA 20170
By DPT Laboratories
San Antonio, TX 78215
129911Rev082014
Utilizes EHG ® Technology
©2014 ASCEND Therapeutics ® US, LLC
Revised: 8/2014
| ESTROGEL
estradiol gel, metered |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - ASCEND Therapeutics US, LLC (133780051) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPT Laboratories, Ltd. | 832224526 | manufacture(17139-613) | |