Label: OXYBUTYNIN CHLORIDE tablet, extended release
-
Contains inactivated NDC Code(s)
NDC Code(s): 71610-347-30, 71610-347-60 - Packager: Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 10135-610
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated October 10, 2019
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets.
OXYBUTYNIN chloride extended-release tablets, USP for oral use.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1975
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions (5) 02/2015
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Oxybutynin chloride extended release tablets, USP are a muscarinic antagonist indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency. (1)
- Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP are also indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with symptoms of detrusor overactivity associated with a neurological condition (e.g., spina bifida). (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP must be swallowed whole with the aid of liquids, and must not be chewed, divided, or crushed. Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP may be administered with or without food. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Extended-release tablets 5mg, 10mg and 15mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Angioedema: Angioedema has been reported with oxybutynin. If symptoms of angioedema occur, discontinue oxybutynin chloride immediately and initiate appropriate therapy. (5.1)
- Central Nervous System (CNS) effects: CNS effects have been reported with oxybutynin. If patient experiences anticholinergic CNS effects, consider dose adjustment or discontinuation of oxybutynin chloride. (5.2)
- Use with caution due to aggravation of symptoms:
° Pre-existing dementia in patients treated with cholinesterase inhibitors (5.2),
° Parkinson’s disease (5.2),
° Myasthenia Gravis (5.3), and
° Decreased gastrointestinal motility in patients with autonomic neuropathy. (5.4)
- Urinary Retention: Use with caution in patients with clinically significant bladder outflow obstruction because of the risk of urinary retention (5.5)
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions: Use with caution in patients with gastrointestinal obstructive disorders or decreased intestinal motility due to risk of gastric retention. Use with caution in patients with gastroesophageal reflux or in patients concurrently taking drugs that can exacerbate esophagitis. (5.6)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (incidence ≥5%) adverse reactions were dry mouth, constipation, diarrhea, headache, somnolence, and dizziness. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pediatric Use: oxybutynin chloride is not recommended in pediatric patients who cannot swallow the tablet whole without chewing, dividing, or crushing, or in children under the age of 6 years. (8.4)
- Renal or Hepatic Impairment: There have been no studies conducted in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. (8.6, 8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 2/2016
- Oxybutynin chloride extended release tablets, USP are a muscarinic antagonist indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency. (1)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adults
2.2 Pediatric Patients Aged 6 Years of Age and Older
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Angioedema
5.2 Central Nervous System Effects
5.3 Worsening of Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis
5.4 Worsening of Symptoms of Decreased Gastrointestinal Motility in Patients with Autonomic Neuropathy
5.5 Urinary Retention
5.6 Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis , Mutagenesis , Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED
16.1 Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP are a muscarinic antagonist indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency.
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP are also indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with symptoms of detrusor overactivity associated with a neurological condition (e.g., spina bifida).
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP must be swallowed whole with the aid of liquids, and must not be chewed, divided, or crushed.
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP may be administered with or without food.
2.1 Adults
The recommended starting dose of oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP is 5 or 10mg once daily at approximately the same time each day. Dosage may be adjusted in 5-mg increments to achieve a balance of efficacy and tolerability (up to a maximum of 30 mg/day). In general, dosage adjustment may proceed at approximately weekly intervals.
2.2 Pediatric Patients Aged 6 Years of Age and Older
The recommended starting dose of oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP is 5mg once daily at approximately the same time each day. Dosage may be adjusted in 5-mg increments to achieve a balance of efficacy and tolerability (up to a maximum of 20 mg/day).
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets are available as 5, 10 and 15 mg tablets for oral use:
5 mg: Purple, round, biconvex, coated tablets debossed with “A31” on one side and plain on the other side.
10 mg: Pink, round, biconvex, coated tablets debossed with “A32” on one side and plain on the other side.
15 mg: White, round, biconvex, coated tablets debossed with “A33” on one side and plain on the other side.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Oxybutynin chloride, USP is contraindicated in patients with urinary retention, gastric retention and other severe decreased gastrointestinal motility conditions, uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma.
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP are also contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug substance or other components of the product. There have been reports of hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and angiodema.
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Angioedema
Angioedema of the face, lips, tongue and/or larynx has been reported with oxybutynin. In some cases, angioedema occurred after the first dose. Angioedema associated with upper airway swelling may be life-threatening. If involvement of the tongue, hypopharynx, or larynx occurs, oxybutynin should be promptly discontinued and appropriate therapy and/or measures necessary to ensure a patent airway should be promptly provided.
5.2 Central Nervous System Effects
Oxybutynin is associated with anticholinergic central nervous system (CNS) effects [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. A variety of CNS anticholinergic effects have been reported, including hallucinations, agitation, confusion and somnolence. Patients should be monitored for signs of anticholinergic CNS effects, particularly in the first few months after beginning treatment or increasing the dose. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until they know how oxybutynin chloride affects them.
If a patient experiences anticholinergic CNS effects, dose reduction or drug discontinuation should be considered.
Oxybutynin chloride should be used with caution in patients with preexisting dementia treated with cholinesterase inhibitors due to the risk of aggravation of symptoms.
Oxybutynin chloride should be used with caution in patients with Parkinson’s disease due to the risk of aggravation of symptoms.
5.3 Worsening of Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis
Oxybutynin chloride should be used with caution in patients with myasthenia gravis due to the risk of symptom aggravation.
5.4 Worsening of Symptoms of Decreased Gastrointestinal Motility in Patients with Autonomic Neuropathy
Oxybutynin chloride should be used with caution in patients with autonomic neuropathy due to the risk of aggravation of symptoms of decreased gastrointestinal motility.
5.5 Urinary Retention
Oxybutynin chloride should be administered with caution to patients with clinically significant bladder outflow obstruction because of the risk of urinary retention [see Contraindications (4)].
5.6 Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Oxybutynin chloride should be administered with caution to patients with gastrointestinal obstructive disorders because of the risk of gastric retention [see Contraindications (4)].
Oxybutynin chloride, like other anticholinergic drugs, may decrease gastrointestinal motility and should be used with caution in patients with conditions such as ulcerative colitis and intestinal atony.
Oxybutynin chloride should be used with caution in patients who have gastroesophageal reflux and/or who are concurrently taking drugs (such as bisphosphonates) that can cause or exacerbate esophagitis.
As with any other nondeformable material, caution should be used when administering oxybutynin chloride to patients with preexisting severe gastrointestinal narrowing (pathologic or iatrogenic).
There have been rare reports of obstructive symptoms in patients with known strictures in association with the ingestion of other drugs in nondeformable controlled-release formulations.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety and efficacy of oxybutynin chloride extended-release (5 to 30 mg/day) was evaluated in 774 adult subjects who participated in five double-blind, controlled clinical trials. In four of the five studies, oxybutynin chloride immediate-release (5 to 20 mg/day in 199 subjects) was an active comparator. Adverse reactions reported by ≥ 1% of subjects are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Adverse Drug Reactions Reported by ≥ 1% of Oxybutynin Chloride-treated Adult Subjects in Five Double-blind, Controlled Clinical Trials of Oxybutynin Chloride System/Organ Class
Preferred TermOxybutynin Chloride
Extended-release
5 to 30 mg/day
N=774
%Oxybutynin Chloride
Immediate-release1
5 to 20 mg/day
N=199
%Psychiatric Disorders Insomnia 3 5.5 Nervous System Disorders Headache 7.5 8 Somnolence 5.6 14.1 Dizziness 5 16.6 Dysgeusia 1.6 1.5 Eye Disorders Vision blurred 4.3 9.6 Dry eye 3.1 2.5 Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders Cough 1.9 3 Oropharyngeal pain 1.9 1.5 Dry throat 1.7 2.5 Nasal dryness 1.7 4.5 Gastrointestinal Disorder Dry mouth 34.9 72.4 Constipation 8.7 15.1 Diarrhea 7.9 6.5 Dyspepsia 4.5 6 Nausea 4.5 11.6 Abdominal pain 1.6 2 Vomiting 1.3 1.5 Flatulence 1.2 2.5 Gastro-esophageal reflux disease 1 0.5 Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Dry skin 1.8 2.5 Pruritus 1.3 1.5 Renal and Urinary Disorders Dysuria 1.9 2 Urinary hesitation 1.9 8.5 Urinary retention 1.2 3 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatigue 2.6 3 Investigations Residual urine volume2 2.3 3.5 1 IR= immediate-release 2 The bundled term residual urine volume consists of the preferred terms residual urine volume and residual urine volume increased. The discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions was 4.4% with oxybutynin chloride extended-release compared to 0% with oxybutynin chloride immediate-release. The most frequent adverse reaction causing discontinuation of study medication was dry mouth (0.7%).
The following adverse reactions were reported by <1% of oxybutynin chloride extended-release treated patients and at a higher incidence than placebo in clinical trials: Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: anorexia, fluid retention; Vascular disorders: hot flush; Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: dysphonia; Gastrointestinal Disorders: dysphagia, frequent bowel movements; General disorders and administration site conditions: chest discomfort, thirst.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported from worldwide postmarketing experience with oxybutynin chloride. Because postmarketing reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Psychiatric Disorders: psychotic disorder, agitation, hallucinations, memory impairment; Nervous System
Disorders: convulsions; Eye Disorders: glaucoma; Cardiac Disorders: arrhythmia, tachycardia, QT interval prolongation; Vascular Disorders: flushing; Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: rash; Rena and Urinary Disorders: impotence; General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema with airway obstruction, urticaria, and face edema; anaphylactic reactions requiring hospitalization for emergency treatment; Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: fall.
Additional adverse events reported with some other oxybutynin chloride formulations include: cycloplegia, mydriasis, and suppression of lactation.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
The concomitant use of oxybutynin with other anticholinergic drugs or with other agents which produce dry mouth, constipation, somnolence (drowsiness), and/or other anticholinergic-like effects may increase the frequency and/or severity of such effects.
Anticholinergic agents may potentially alter the absorption of some concomitantly administered drugs due to anticholinergic effects on gastrointestinal motility. This may be of concern for drugs with a narrow therapeutic index. Anticholinergic agents may also antagonize the effects of prokinetic agents, such as metoclopramide.
Mean oxybutynin chloride plasma concentrations were approximately 2 fold higher when oxybutynin chloride was administered with ketoconazole, a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor. Other inhibitors of the cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme system, such as antimycotic agents (e.g., itraconazole and miconazole) or macrolide antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin and clarithromycin), may alter oxybutynin mean pharmacokinetic parameters (i.e., C and AUC). The clinical relevance of such potential interactions is not known. Caution should be used when such drugs are co-administered.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies using oxybutynin chloride in pregnant women. Oxybutynin chloride should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the risk to the patient and fetus. Women who become pregnant during oxybutynin chloride treatment are encouraged to contact their physician.
Risk Summary
Based on animal data, oxybutynin is predicted to have a low probability of increasing the risk of adverse developmental effects above background risk.
Animal Data
Reproduction studies with oxybutynin chloride in the mouse, rat, hamster, and rabbit showed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the animal fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether oxybutynin is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when oxybutynin chloride is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of oxybutynin chloride were studied in 60 children in a 24-week, open-label, non-randomized trial. Patients were aged 6 to 15 years, all had symptoms of detrusor overactivity in association with a neurological condition (e.g., spina bifida), all used clean intermittent catheterization, and all were current users of oxybutynin chloride. Study results demonstrated that administration of oxybutynin chloride 5 to 20 mg/day was associated with an increase from baseline in mean urine volume per catheterization from 108 mL to 136 mL, an increase from baseline in mean urine volume after morning awakening from 148 mL to 189 mL, and an increase from baseline in the mean percentage of catheterizations without a leaking episode from 34% to 51%.
Urodynamic results were consistent with clinical results. Administration of oxybutynin chloride resulted in an increase from baseline in mean maximum cystometric capacity from 185 mL to 254 mL, a decrease from baseline in mean detrusor pressure at maximum cystometric capacity from 44 cm H O to 33 cm H O, and a reduction in the percentage of patients demonstrating uninhibited detrusor contractions (of at least 15 cm H O) from 60% to 28%.
The pharmacokinetics of oxybutynin chloride in these patients were consistent with those reported for adults [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets are not recommended in pediatric patients who cannot swallow the tablet whole without chewing, dividing, or crushing, or in children under the age of 6.
8.5 Geriatric Use
The rate and severity of anticholinergic effects reported by patients less than 65 years old and those 65 years and older were similar. The pharmacokinetics of oxybutynin chloride were similar in all patients studied (up to 78 years of age).
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
The continuous release of oxybutynin from oxybutynin chloride should be considered in the treatment of overdosage. Patients should be monitored for at least 24 hours. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. Activated charcoal as well as a cathartic may be administered.
Overdosage with oxybutynin chloride has been associated with anticholinergic effects including central nervous system excitation, flushing, fever, dehydration, cardiac arrhythmia, vomiting, and urinary retention.
Ingestion of 100 mg oxybutynin chloride in association with alcohol has been reported in a 13-year-old boy who experienced memory loss, and a 34-year-old woman who developed stupor, followed by disorientation and agitation on awakening, dilated pupils, dry skin, cardiac arrhythmia, and retention of urine. Both patients fully recovered with symptomatic treatment.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Oxybutynin chloride) is an antispasmodic, muscarinic antagonist. Each oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablet, USP contains 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg of oxybutynin chloride USP, formulated as a once-a day controlled-release tablet for oral administration. Oxybutynin chloride, USP is administered as a racemate of R- and S-enantiomers.
Chemically, oxybutynin chloride, USP is d,l (racemic) 4-diethylamino-2-butynyl phenylcyclohexylglycolate hydrochloride. The empirical formula of oxybutynin chloride, USP is C22H31NO3 •HCl.
Its structural formula is:
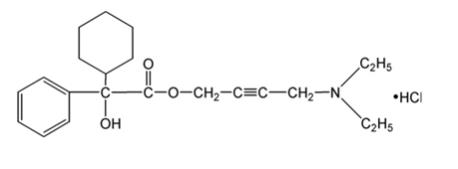
Oxybutynin chloride, USP is a white crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 393.9. It is readily soluble in water and acids, but relatively insoluble in alkalis.
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, USP also contains the following inert ingredients: hydrogenated vegetable oil, hypromellose, isopropyl alcohol, lactose monohydrate, methacrylic acid copolymer, microcrystalline cellulose, polysorbate 80, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc and triethyl citrate. The 5 mg tablets also contain D&C Red #27 and FD&C Blue #1. The 10mg tablets also contain FD&C Red #40 and FD&C Yellow #6.
USP Dissolution Test is pending.
System Components and Performance
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablet, USP uses a pH-independent hydrophilic matrix and pH dependent enteric coating to deliver oxybutynin chloride, USP at a controlled rate over approximately 24 hours. The oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablet, USP comprises of an inner core made of the drug, rate controlling pH independent polymer and other excipients. The tablet core is then coated with pH dependent enteric coating polymer. When tablets will be exposed to an acidic environment such as the stomach, the drug release will be minimal due to outer enteric coating of the pH dependent polymer. The outer enteric coating upon reaching an environment of pH 5.5 and above will start to dissolve and the polymer in the inner core tablet will hydrate to form a gel layer and the drug releases via diffusion process.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Oxybutynin relaxes bladder smooth muscle. Oxybutynin chloride exerts a direct antispasmodic effect on smooth muscle and inhibits the muscarinic action of acetylcholine on smooth muscle. No blocking effects occur at skeletal neuromuscular junctions or autonomic ganglia (antinicotinic effects).
Antimuscarinic activity resides predominantly in the R-isomer. A metabolite, desethyloxybutynin, has pharmacological activity similar to that of oxybutynin in in vitro studies.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In patients with conditions characterized by involuntary bladder contractions, cystometric studies have demonstrated that oxybutynin increases bladder (vesical) capacity, diminishes the frequency of uninhibited contractions of the detrusor muscle, and delays the initial desire to void.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following the first dose of oxybutynin chloride, oxybutynin plasma concentrations rise for 4 to 6 hours; thereafter steady concentrations are maintained for up to 24 hours, minimizing fluctuations between peak and trough concentrations associated with oxybutynin.
The relative bioavailabilities of R- and S-oxybutynin from oxybutynin chloride are 156% and 187%, respectively, compared with oxybutynin. The mean pharmacokinetic parameters for R- and S-oxybutynin are summarized in Table 2. The plasma concentration-time profiles for R- and S-oxybutynin are similar in shape; Figure 1 shows the profile for R-oxybutynin.
Table 2: Mean (SD) R- and S- Oxybutynin Pharmacokinetic Parameters Following a Single Dose of Oxybutynin Chloride 10mg (n=43) Parameters (units) R-Oxybutynin S-Oxybutynin Cmax (ng/mL) 1 (0.6) 1.8 (1) Tmax (h) 12.7 (5.4) 11.8 (5.3) t1/2(h) 13.2 (6.2) 12.4 (6.1) AUC(0-48)( ng•h/mL) 18.4 (10.3) 34.2 (16.9) AUCinf (ng•h/mL) 21.3 (12.2) 39.5 (21.2) 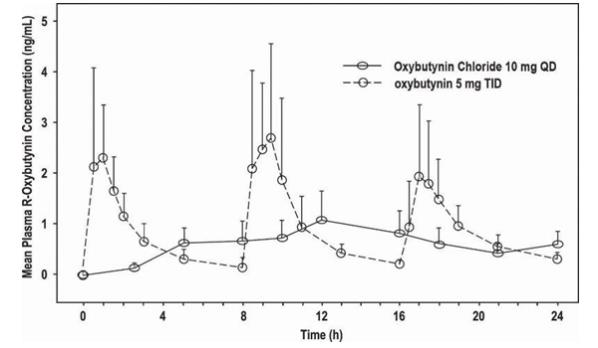
Figure 1: Mean R-oxybutynin plasma concentrations following a single dose of oxybutynin chloride 10 mg and oxybutynin 5 mg administered every 8 hours (n=23 for each treatment).
Steady-state oxybutynin plasma concentrations are achieved by Day 3 of repeated oxybutynin chloride dosing, with no observed drug accumulation or change in oxybutynin and desethyloxybutynin pharmacokinetic parameters.
Oxybutynin chloride steady-state pharmacokinetics were studied in 19 children aged 5 to 15 years with detrusor overactivity associated with a neurological condition (e.g., spina bifida). The children were on oxybutynin chloride total daily dose ranging from 5 to 20 mg (0.10 to 0.77 mg/kg). Sparse sampling technique was used to obtain serum samples. When all available data are normalized to an equivalent of 5 mg per day of oxybutynin chloride, the mean pharmacokinetic parameters derived for R- and S- oxybutynin and R- and S-desethyloxybutynin are summarized in Table 3. The plasma-time concentration profiles for R- and S-oxybutynin are similar in shape; Figure 2 shows the profile for R-oxybutynin when all available data are normalized to an equivalent of 5 mg per day.
Table 3: Mean ± SD R- and S-Oxybutynin and R- and S-Desethyloxybutynin Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Children Aged 5-15 Following Administration of 5 to 20 mg Oxybutynin Chloride Once Daily (n=19), All Available Data Normalized to an Equivalent of Oxybutynin Chloride 5 mg Once Daily R-Oxybutynin S-Oxybutynin R-Desethyloxybutynin S-Desethyloxybutynin Cmax (ng/mL) 0.7 ± 0.4 1.3 ± 0.8 7.8 ± 3.7 4.2 ± 2.3 Tmax (h) 5 5 5 5 AUC (ng•h/mL) 12.8 ± 7 23.7 ± 14.4 125.1 ± 66.7 73.6 ± 47.7 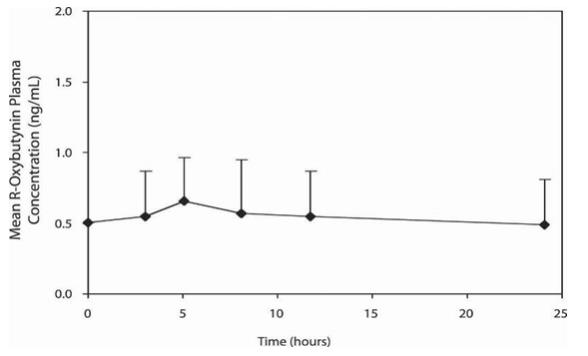
Figure 2: Mean steady-state (± SD) R-oxybutynin plasma concentrations following administration of 5 to 20 mg Oxybutynin Chloride once daily in children aged 5 to 15. Plot represents all available data normalized to an equivalent of Oxybutynin Chloride 5 mg once daily.
Food Effects
The rate and extent of absorption and metabolism of oxybutynin are similar under fed and fasted conditions.
Distribution
Oxybutynin is widely distributed in body tissues following systemic absorption. The volume of distribution is 193 L after intravenous administration of 5 mg oxybutynin chloride. Both enantiomers of oxybutynin are highly bound (>99%) to plasma proteins. Both enantiomers of N-desethyloxybutynin are also highly bound (>97%) to plasma proteins. The major binding protein is alpha-1 acid glycoprotein.
Metabolism
Oxybutynin is metabolized primarily by the cytochrome P450 enzyme systems, particularly CYP3A4 found mostly in the liver and gut wall. Its metabolic products include phenylcyclohexylglycolic acid, which is pharmacologically inactive, and desethyloxybutynin, which is pharmacologically active.
Following oxybutynin chloride administration, plasma concentrations of R- and S-desethyloxybutynin are 73% and 92%, respectively, of concentrations observed with oxybutynin.
Excretion
Oxybutynin is extensively metabolized by the liver, with less than 0.1% of the administered dose excreted unchanged in the urine. Also, less than 0.1% of the administered dose is excreted as the metabolite desethyloxybutynin.
Dose Proportionality
Pharmacokinetic parameters of oxybutynin and desethyloxybutynin (C and AUC) following administration of 5 to 20 mg of oxybutynin chloride are dose proportional.
Use in Specific Populations
Pediatric
The pharmacokinetics of oxybutynin chloride were evaluated in 19 children aged 5 to 15 years with detrusor overactivity associated with a neurological condition (e.g., spina bifida). The pharmacokinetics of oxybutynin chloride in these pediatric patients were consistent with those reported for adults (see Tables 2 and 3, and Figures 1 and 2 above).
Gender
There are no significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of oxybutynin in healthy male and female volunteers following administration of oxybutynin chloride.
Race
Available data suggest that there are no significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of oxybutynin based on race in healthy volunteers following administration of oxybutynin chloride.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis , Mutagenesis , Impairment of Fertility
A 24-month study in rats at dosages of oxybutynin chloride of 20, 80, and 160 mg/kg/day showed no evidence of carcinogenicity. These doses are approximately 6, 25, and 50 times the maximum human exposure, based on a human equivalent dose taking into account normalization of body surface area.
Oxybutynin chloride showed no increase of mutagenic activity when tested in Schizosaccharomyces pompholiciformis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Salmonella typhimurium test systems.
Reproduction studies with oxybutynin chloride in the mouse, rat, hamster, and rabbit showed no evidence of impaired fertility.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Oxybutynin chloride was evaluated for the treatment of patients with overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency in three controlled efficacy studies. The majority of patients were Caucasian (89%) and female (91.9%) with a mean age of 59 years (range, 18 to 98 years). Entry criteria required that patients have urge or mixed incontinence (with a predominance of urge) as evidenced by ≥ 6 urge incontinence episodes per week and ≥ 10 micturitions per day. Study 1 was a fixed-dose escalation design, whereas the other two studies used a dose-adjustment design in which each patient’s final dose was adjusted to a balance between improvement of incontinence symptoms and tolerability of side effects. All three studies included patients known to be responsive to oxybutynin or other anticholinergic medications, and these patients were maintained on a final dose for up to 2 weeks.
The efficacy results for the three controlled trials are presented in the following tables and figures.
Number of Urge Urinary Incontinence Episodes Per Week Study 1 n Oxybutynin
Chloriden Placebo Mean Baseline 34 15.9 16 20.9 Mean (SD) Change from Baseline † 34 -15.8 (8.9) 16 -7.6 (8.6) 95% Confidence Interval for Difference (-13.6, -2.8)* (Oxybutynin Chloride – Placebo) * The difference between oxybutynin chloride and placebo was statistically significant. †Covariate adjusted mean with missing observations set to baseline values 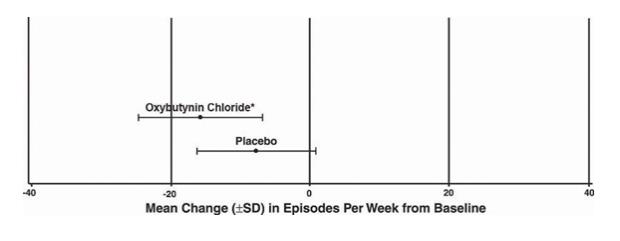
Number of Urge Urinary Incontinence Episodes Per Week Study 2 n Oxybutynin
Chloriden Oxybutynin Mean Baseline 53 27.6 52 23 Mean (SD) Change from Baseline † 53 -17.6 (11.9) 52 -19.4 (11.9) 95% Confidence Interval for Difference (-2.8,6.5) (Oxybutynin Chloride – Oxybutynin) †Covariate adjusted mean with missing observations set to baseline values 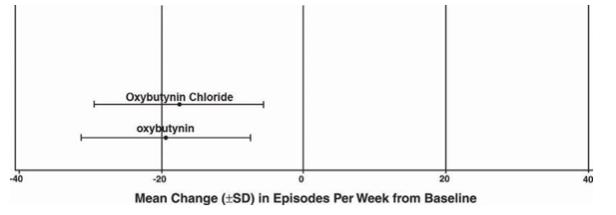
Study 3 n Oxybutynin
Chloriden Oxybutynin Mean Baseline 111 18.9 115 19.5 Mean (SD) Change from Baseline † 111 -14.5 (8.7) 115 -13.8 (8.6) 95% Confidence Interval for Difference (-3, 1.6)** (Oxybutynin Chloride – Oxybutynin) ** The difference between oxybutynin chloride and oxybutynin fulfilled the criteria for comparable efficacy. †Covariate adjusted mean with missing observations set to baseline values 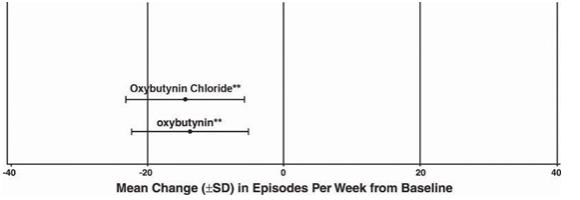
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED
Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets USP, 5 mg, are supplied as purple, round, biconvex, coated tablets debossed with “A31” on one side and plain on the other side.
They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100: NDC 10135-0609-01
Bottles of 500: NDC 10135-0609-05Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets USP, 10 mg, are supplied as pink, round, biconvex, coated tablets debossed with “A32” on one side and plain on the other side.
They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100: NDC 10135-0610-01
Bottles of 500: NDC 10135-0610-05Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets USP, 15 mg, are supplied as white, round, biconvex, coated tablets debossed with “A33” on one side and plain on the other side.
They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100: NDC 10135-0611-01
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Patients should be informed that oxybutynin may produce angioedema that could result in life threatening airway obstruction. Patients should be advised to promptly discontinue oxybutynin therapy and seek immediate medical attention if they experience swelling of the tongue, edema of the laryngopharynx, or difficulty breathing.
- Patients should be informed that anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) agents such as oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets, may produce clinically significant adverse reactions related to anticholinergic activity such as:
° Urinary retention and constipation
° Heat prostration due to decreased sweating. Heat prostration can occur when anticholinergic medicines are administered in the presence of high environmental temperature.
- Patients should be informed that anticholinergic medicines such as oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets may produce drowsiness (somnolence), dizziness or blurred vision. Patients should be advised to exercise caution in decisions to engage in potentially dangerous activities until oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets effects have been determined.
- Patients should be informed that alcohol may enhance the drowsiness caused by anticholinergic agents such as oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets.
- Patients should be informed that oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets should be swallowed whole with the aid of liquids. Patients should not chew, divide, or crush tablets. The medication is contained within a nonabsorbable shell designed to release the drug at a controlled rate. The tablet shell is eliminated from the body; patients should not be concerned if they occasionally notice in their stool something that looks like a tablet.
- Oxybutynin chloride extended-release tablets should be taken at approximately the same time each day.
For more information call 1-877-835-5472 or visit www.amneal.com
* Trademarks are the property of their respective owners.Manufactured for and Distributed by:
Marlex Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
New Castle, DE 19720
Made in U.S.A.Rev. 02/16AN
- Patients should be informed that oxybutynin may produce angioedema that could result in life threatening airway obstruction. Patients should be advised to promptly discontinue oxybutynin therapy and seek immediate medical attention if they experience swelling of the tongue, edema of the laryngopharynx, or difficulty breathing.
-
Repackaging Information
Please reference the How Supplied section listed above for a description of individual tablets. This drug product has been received by Aphena Pharma - TN in a manufacturer or distributor packaged configuration and repackaged in full compliance with all applicable cGMP regulations. The package configurations available from Aphena are listed below:
Count 10 mg 30 71610-347-30 90 71610-347-60 Store between 20°-25°C (68°-77°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature. Dispense in a tight light-resistant container as defined by USP. Keep this and all drugs out of the reach of children.
Repackaged by:

Cookeville, TN 38506
20191010JH - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
OXYBUTYNIN CHLORIDE
oxybutynin chloride tablet, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:71610-347(NDC:10135-610) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength OXYBUTYNIN CHLORIDE (UNII: L9F3D9RENQ) (OXYBUTYNIN - UNII:K9P6MC7092) OXYBUTYNIN CHLORIDE 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength METHACRYLIC ACID - ETHYL ACRYLATE COPOLYMER (1:1) TYPE A (UNII: NX76LV5T8J) HYDROGENATED COTTONSEED OIL (UNII: Z82Y2C65EA) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (UNII: ND2M416302) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TRIETHYL CITRATE (UNII: 8Z96QXD6UM) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color PINK Score no score Shape ROUND Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code A;32 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:71610-347-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/27/2019 2 NDC:71610-347-60 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/27/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA204010 02/01/2016 Labeler - Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC (128385585) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC 128385585 REPACK(71610-347)