DECITABINE - decitabine injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
NorthStar RxLLC
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use DECITABINE FOR INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DECITABINE FOR INJECTION
DECITABINE for injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval:[2006] INDICATIONS AND USAGEDecitabine for injection is a nucleoside metabolic inhibitor indicated for treatment of adult patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) including previously treated and untreated, de novo and secondary MDS of all French-American-British subtypes (refractory anemia, refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts, refractory anemia with excess blasts, refractory anemia with excess blasts in transformation, and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia) and intermediate-1, intermediate-2, and high‑risk International Prognostic Scoring System groups. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Administer decitabine for injection at a dose of 15 mg/m2by continuous intravenous infusion over 3 hours repeated every 8 hours for 3 days. Repeat cycle every 6 weeks. (2.1)
Administer decitabine for injection at a dose of 20 mg/m2by continuous intravenous infusion over 1 hour repeated daily for 5 days. Repeat cycle every 4 weeks. (2.2) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSFor Injection: 50 mg of decitabine as a lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSNone (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions (> 50%) are neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and pyrexia. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact NorthStar Rx LLC at 1‑800-206-7821 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSLactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2) (8) See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 3/2022 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Decitabine for injection is indicated for treatment of adult patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) including previously treated and untreated, de novo and secondary MDS of all French-American-British subtypes (refractory anemia, refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts, refractory anemia with excess blasts, refractory anemia with excess blasts in transformation, and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia) and intermediate-1, intermediate-2, and high-risk International Prognostic Scoring System groups.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Starting Dosage
Pre-Medications and Baseline Testing
- Consider pre-medicating for nausea with antiemetics.
- Conduct baseline laboratory testing: CBC with platelets, serum hepatic panel, and serum creatinine.
Decitabine for injection Regimen Options
Three Day Regimen
Administer Decitabine for injection at a dose of 15 mg/m2by continuous intravenous infusion over 3 hours repeated every 8 hours for 3 days. Repeat cycles every 6 weeks upon hematologic recovery (ANC at least 1,000/μL and platelets at least 50,000/μL) for a minimum of 4 cycles. A complete or partial response may take longer than 4 cycles. Delay and reduce dose for hematologic toxicity (see Dose Modifications for Toxicity).
Five Day Regimen
Administer Decitabine for injection at a dose of 20 mg/m2 by continuous intravenous infusion over 1 hour daily for 5 days. Delay and reduce dose for hematologic toxicity (see Dose Modifications for Toxicity). Repeat cycles every 6 weeks upon hematologic recovery (ANC at least 1,000/μL and platelets at least 50,000/μL) for a minimum of 4 cycles. A complete or partial response may take longer than 4 cycles.
2.2 Dose Modifications for Toxicity
If hematologic recovery from a previous decitabine for injection treatment cycle requires more than 6 weeks, delay the next cycle of decitabine for injection therapy and reduce decitabine for injection dose temporarily by following this algorithm:
- Recovery requiring more than 6, but less than 8 weeks – delay decitabine for injection dosing for up to 2 weeks and reduce the dose temporarily to 11 mg/m2every 8 hours (33 mg/m2/day, 99 mg/m2/cycle) upon restarting therapy.
- Recovery requiring more than 8, but less than 10 weeks - Perform bone marrow aspirate to assess for disease progression. In the absence of progression, delay the decitabine for injection dose up to 2 more weeks and reduce the dose to 11 mg/m2every 8 hours (33 mg/m2/day, 99 mg/m2/cycle) upon restarting therapy, then maintain or increase dose in subsequent cycles as clinically indicated.
Delay subsequent decitabine for injection treatment for any the following non-hematologic toxicities and do not restart until toxicities resolve:
- Serum creatinine greater than or equal to 2 mg/dL
- SGPT, total bilirubin greater than or equal to 2 times ULN
- Active or uncontrolled infection
2.3 Instructions for Intravenous Administration
Decitabine is a cytotoxic drug and caution should be exercised when handling and preparing decitabine for injection1.
Aseptically reconstitute decitabine for injection with room temperature (20°C to 25°C) 10 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP. Upon reconstitution, the final concentration of the reconstituted decitabine for injection solution is 5 mg/mL. You must dilute the reconstituted solution with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Dextrose Injection prior to administration. Temperature of the diluent (0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Dextrose Injection) depends on time of administration after preparation.
For Administration Within 15 Minutes of Preparation
If decitabine for injection is intended to be administered within 15 minutes from the time of preparation, dilute the reconstituted solution with room temperature (20°C - 25°C) 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Dextrose Injection to a final concentration of 0.1 mg/mL- 1 mg/mL.
For Delayed Administration
If decitabine for injection is intended to be administered after 15 minutes of preparation, dilute the reconstituted solution with cold (2°C - 8°C) 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Dextrose Injection to a final concentration of 0.1 mg/mL- 1 mg/mL. Store at 2°C - 8°C for up to 4 hours. Diluted stored solution must be used within 4 hours from the time of preparation.
Use the diluted, refrigerated solution within 4 hours from the time of preparation or discard.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration
prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if there is evidence
of particulate matter or discoloration.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myelosuppression
Fatal and serious myelosuppression occurs in decitabine for injection -treated patients. Myelosuppression (anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia) is the most frequent cause of decitabine for injection dose reduction, delay, and discontinuation. Neutropenia of any grade occurred in 90% of decitabine for injection-treated patients with grade 3 or 4 occurring in 87% of patients. Thrombocytopenia of any grade occurred in 89% of patients with grade 3 or 4 occurring in 85% of patients. Grade 3 or 4 febrile neutropenia occurred in 23% of patients. Anemia of any grade occurred in 82% of patients. Perform complete blood count with platelets at baseline, prior to each cycle, and as needed to monitor response and toxicity. Manage toxicity using dose-delay, dose-reduction, growth factors, and anti-infective therapies as needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Myelosuppression and worsening neutropenia may occur more frequently in the first or second treatment cycles, and may not necessarily indicate progression of underlying MDS.
5.2 Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Decitabine for injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Based on its mechanism of action, decitabine alters DNA synthesis and is expected to result in adverse reproductive effects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. In preclinical studies in mice and rats, decitabine was teratogenic, fetotoxic, and embryotoxic. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if a patient becomes pregnant while receiving this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. Advise women of childbearing potential to avoid becoming pregnant while taking decitabine for injection and for 6 months following the last dose. Advise men with female partners of childbearing potential to avoid fathering a child while receiving treatment with decitabine for injection, and for 3 months following the last dose, Counsel patients of childbearing potential to use effective contraception during this time [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of decitabine for injection was studied in 3 single-arm studies (N = 66, N = 98, N = 99) and 1 controlled supportive care study (N = 83 decitabine for injection, N = 81 supportive care). The data described below reflect exposure to decitabine for injection in 83 patients in the MDS trial. In the trial, patients received 15 mg/m2 intravenously every 8 hours for 3 days every 6 weeks. The median number of decitabine for injection cycles was 3 (range 0 to 9). Most Commonly Occurring Adverse Reactions: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, fatigue, pyrexia, nausea, cough, petechiae, constipation, diarrhea, and hyperglycemia.
Adverse Reactions Most Frequently (≥ 1%) Resulting in Clinical Intervention and or Dose Modification in the Phase 3 Trials in the Decitabine for Injection Arm:
- Discontinuation: thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, pneumonia, Mycobacterium avium complex infection, cardio-respiratory arrest, increased blood bilirubin, intracranial hemorrhage, abnormal liver function tests.
- Dose Delayed: neutropenia, pulmonary edema, atrial fibrillation, central line infection, febrile neutropenia.
- Dose Reduced: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, lethargy, edema, tachycardia, depression, pharyngitis.
Table 1 presents all adverse reactions occurring in at least 5% of patients in the decitabine for injection group and at a rate greater than supportive care.
|
| Decitabine for Injection
N = 83 (%) | Supportive Care
N = 81 (%) |
|
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders
|
|
|
|
| Neutropenia | 75 (90) | 58 (72) |
|
| Thrombocytopenia | 74 (89) | 64 (79) |
|
| Anemia NOS | 68 (82) | 60 (74) |
|
| Febrile neutropenia | 24 (29) | 5 (6) |
|
| Leukopenia NOS | 23 (28) | 11 (14) |
|
| Lymphadenopathy | 10 (12) | 6 (7) |
|
| Thrombocythemia | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Cardiac disorders
| |||
| Pulmonary edema NOS | 5 (6) | 0 (0) |
|
| Eye disorders
| |||
| Vision blurred | 5 (6) | 0 (0) |
|
| Gastrointestinal disorders
| |||
| Nausea | 35 (42) | 13 (16) |
|
| Constipation | 29 (35) | 11 (14) |
|
| Diarrhea NOS | 28 (34) | 13 (16) |
|
| Vomiting NOS | 21 (25) | 7 (9) |
|
| Abdominal pain NOS | 12 (14) | 5 (6) |
|
| Oral mucosal petechiae | 11 (13) | 4 (5) |
|
| Stomatitis | 10 (12) | 5 (6) |
|
| Dyspepsia | 10 (12) | 1 (1) |
|
| Ascites | 8 (10) | 2 (2) |
|
| Gingival bleeding | 7 (8) | 5 (6) |
|
| Hemorrhoids | 7 (8) | 3 (4) |
|
| Loose stools | 6 (7) | 3 (4) |
|
| Tongue ulceration | 6 (7) | 2 (2) |
|
| Dysphagia | 5 (6) | 2 (2) |
|
| Oral soft tissue disorder NOS | 5 (6) | 1 (1) |
|
| Lip ulceration | 4 (5) | 3 (4) |
|
| Abdominal distension | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Abdominal pain upper | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Gastro-esophageal reflux disease | 4 (5) | 0 (0) |
|
| Glossodynia | 4 (5) | 0 (0) |
|
| General disorders and administrative site disorders
| |||
| Pyrexia | 44 (53) | 23 (28) |
|
| Edema peripheral | 21 (25) | 13 (16) |
|
| Rigors | 18 (22) | 14 (17) |
|
| Edema NOS | 15 (18) | 5 (6) |
|
| Pain NOS | 11 (13) | 5 (6) |
|
| Lethargy | 10 (12) | 3 (4) |
|
| Tenderness NOS | 9 (11) | 0 (0) |
|
| Fall | 7 (8) | 3 (4) |
|
| Chest discomfort | 6 (7) | 3 (4) |
|
| Intermittent pyrexia | 5 (6) | 3 (4) |
|
| Malaise | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Crepitations NOS | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Catheter site erythema | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Catheter site pain | 4 (5) | 0 (0) |
|
| Injection site swelling | 4 (5) | 0 (0) |
|
| Hepatobiliary disorders
| |||
| Hyperbilirubinemia | 12 (14) | 4 (5) |
|
| Infections and infestations
| |||
| Pneumonia NOS | 18 (22) | 11 (14) |
|
| Cellulitis | 10 (12) | 6 (7) |
|
| Candidal infection NOS | 8 (10) | 1 (1) |
|
| Catheter related infection | 7 (8) | 0 (0) |
|
| Urinary tract infection NOS | 6 (7) | 1 (1) |
|
| Staphylococcal infection | 6 (7) | 0 (0) |
|
| Oral candidiasis | 5 (6) | 2 (2) |
|
| Sinusitis NOS | 4 (5) | 2 (2) |
|
| Bacteremia | 4 (5) | 0 (0) |
|
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
| |||
| Transfusion reaction | 6 (7) | 3 (4) |
|
| Abrasion NOS | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Investigations
| |||
| Cardiac murmur NOS | 13 (16) | 9 (11) |
|
| Blood alkaline phosphatase NOS increased | 9 (11) | 7 (9) |
|
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 8 (10) | 7 (9) |
|
| Blood urea increased | 8 (10) | 1 (1) |
|
| Blood lactate dehydrogenase increased | 7 (8) | 5 (6) |
|
| Blood albumin decreased | 6 (7) | 0 (0) |
|
| Blood bicarbonate increased | 5 (6) | 1 (1) |
|
| Blood chloride decreased | 5 (6) | 1 (1) |
|
| Protein total decreased | 4 (5) | 3 (4) |
|
| Blood bicarbonate decreased | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Blood bilirubin decreased | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders
| |||
| Hyperglycemia NOS | 27 (33) | 16 (20) |
|
| Hypoalbuminemia | 20 (24) | 14 (17) |
|
| Hypomagnesemia | 20 (24) | 6 (7) |
|
| Hypokalemia | 18 (22) | 10 (12) |
|
| Hyponatremia | 16 (19) | 13 (16) |
|
| Appetite decreased NOS | 13 (16) | 12 (15) |
|
| Anorexia | 13 (16) | 8 (10) |
|
| Hyperkalemia | 11 (13) | 3 (4) |
|
| Dehydration | 5 (6) | 4 (5) |
|
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
| |||
| Arthralgia | 17 (20) | 8 (10) |
|
| Pain in limb | 16 (19) | 8 (10) |
|
| Back pain | 14 (17) | 5 (6) |
|
| Chest wall pain | 6 (7) | 1 (1) |
|
| Musculoskeletal discomfort | 5 (6) | 0 (0) |
|
| Myalgia | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Nervous system disorders
| |||
| Headache | 23 (28) | 11 (14) |
|
| Dizziness | 15 (18) | 10 (12) |
|
| Hypoesthesia | 9 (11) | 1 (1) |
|
| Psychiatric disorders
| |||
| Insomnia | 23 (28) | 11 (14) |
|
| Confusional state | 10 (12) | 3 (4) |
|
| Anxiety | 9 (11) | 8 (10) |
|
| Renal and urinary disorders
| |||
| Dysuria | 5 (6) | 3 (4) |
|
| Urinary frequency | 4 (5) | 1 (1) |
|
| Respiratory, thoracic and Mediastinal disorders
| |||
| Cough | 33 (40) | 25 (31) |
|
| Pharyngitis | 13 (16) | 6 (7) |
|
| Crackles lung | 12 (14) | 1 (1) |
|
| Breath sounds decreased | 8 (10) | 7 (9) |
|
| Hypoxia | 8 (10) | 4 (5) |
|
| Rales | 7 (8) | 2 (2) |
|
| Postnasal drip | 4 (5) | 2 (2) |
|
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
| |||
| Ecchymosis | 18 (22) | 12 (15) |
|
| Rash NOS | 16 (19) | 7 (9) |
|
| Erythema | 12 (14) | 5 (6) |
|
| Skin lesion NOS | 9 (11) | 3 (4) |
|
| Pruritis | 9 (11) | 2 (2) |
|
| Alopecia | 7 (8) | 1 (1) |
|
| Urticaria NOS | 5 (6) | 1 (1) |
|
| Swelling face | 5 (6) | 0 (0) |
|
| Vascular disorders
| |||
| Petechiae | 32 (39) | 13 (16) |
|
| Pallor | 19 (23) | 10 (12) |
|
| Hypotension NOS | 5 (6) | 4 (5) |
|
| Hematoma NOS | 4 (5) | 3 (4) |
|
In a single-arm MDS study (N=99) decitabine for injection was dosed at 20 mg/m2intravenous, infused over one hour daily for 5 consecutive days of a 4 week cycle. Table 2 presents all adverse reactions occurring in at least 5% of patients.
|
| Decitabine for injection
N = 99 (%) |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders
|
|
| Anemia | 31 (31%) |
| Febrile neutropenia | 20 (20%) |
| Leukopenia | 6 (6%) |
| Neutropenia | 38 (38%) |
| Pancytopenia | 5 (5%) |
| Thrombocythemia | 5 (5%) |
| Thrombocytopenia | 27 (27%) |
| Cardiac disorders
| |
| Cardiac failure congestive | 5 (5%) |
| Tachycardia | 8 (8%) |
| Ear and labyrinth disorders
| |
| Ear pain | 6 (6%) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders
| |
| Abdominal pain | 14 (14%) |
| Abdominal pain upper | 6 (6%) |
| Constipation | 30 (30%) |
| Diarrhea | 28 (28%) |
| Dyspepsia | 10 (10%) |
| Dysphagia | 5 (5%) |
| Gastro-esophageal reflux disease | 5 (5%) |
| Nausea | 40 (40%) |
| Oral pain | 5 (5%) |
| Stomatitis | 11 (11%) |
| Toothache | 6 (6%) |
| Vomiting | 16 (16%) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions
| |
| Asthenia | 15 (15%) |
| Chest pain | 6 (6%) |
| Chills | 16 (16%) |
| Fatigue | 46 (46%) |
| Mucosal inflammation | 9 (9%) |
| Edema | 5 (5%) |
| Edema peripheral | 27 (27%) |
| Pain | 5 (5%) |
| Pyrexia | 36 (36%) |
| Infections and infestations
| |
| Cellulitis | 9 (9%) |
| Oral candidiasis | 6 (6%) |
| Pneumonia | 20 (20%) |
| Sinusitis | 6 (6%) |
| Staphylococcal bacteremia | 8 (8%) |
| Tooth abscess | 5 (5%) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 10 (10%) |
| Urinary tract infection | 7 (7%) |
| Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
| |
| Contusion | 9 (9%) |
| Investigations
| |
| Blood bilirubin increased | 6 (6%) |
| Breath sounds abnormal | 5 (5%) |
| Weight decreased | 9 (9%) |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders
| |
| Anorexia | 23 (23%) |
| Decreased appetite | 8 (8%) |
| Dehydration | 8 (8%) |
| Hyperglycemia | 6 (6%) |
| Hypokalemia | 12 (12%) |
| Hypomagnesemia | 5 (5%) |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
| |
| Arthralgia | 17 (17%) |
| Back pain | 18 (18%) |
| Bone pain | 6 (6%) |
| Muscle spasms | 7 (7%) |
| Muscular weakness | 5 (5%) |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 5 (5%) |
| Myalgia | 9 (9%) |
| Pain in extremity | 18 (18%) |
| Nervous system disorders
| |
| Dizziness | 21 (21%) |
| Headache | 23 (23%) |
| Psychiatric disorders
| |
| Anxiety | 9 (9%) |
| Confusional state | 8 (8%) |
| Depression | 9 (9%) |
| Insomnia | 14 (14%) |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
| |
| Cough | 27 (27%) |
| Dyspnea | 29 (29%) |
| Epistaxis | 13 (13%) |
| Pharyngolaryngeal pain | 8 (8%) |
| Pleural effusion | 5 (5%) |
| Sinus congestion | 5 (5%) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
| |
| Dry skin | 8 (8%) |
| Ecchymosis | 9 (9%) |
| Erythema | 5 (5%) |
| Night sweats | 5 (5%) |
| Petechiae | 12 (12%) |
| Pruritus | 9 (9%) |
| Rash | 11 (11%) |
| Skin lesion | 5 (5%) |
| Vascular disorders
| |
| Hypertension | 6 (6%) |
| Hypotension | 11 (11%) |
| 1 In this single arm study, investigators reported adverse events based on clinical signs and symptoms rather than predefined laboratory abnormalities. Thus not all laboratory abnormalities were recorded as adverse events. |
No overall difference in safety was detected between patients > 65 years of age and younger patients in these myelodysplasia trials. No significant gender differences in safety or efficacy were detected. Patients with renal or hepatic dysfunction were not studied. Insufficient numbers of non-white patients were available to draw conclusions in these clinical trials.
Serious adverse reactions that occurred in patients receiving decitabine for injection regardless of causality, not previously reported in Tables 1 and 2 include:
- Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: myelosuppression, splenomegaly.
- Cardiac Disorders: myocardial infarction, cardio-respiratory arrest, cardiomyopathy, atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: gingival pain, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
- General Disorders and Administrative Site Conditions: chest pain, catheter site hemorrhage.
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: cholecystitis.
- Infections and Infestations: fungal infection, sepsis, bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, peridiverticular abscess, respiratory tract infection, pseudomonal lung infection, Mycobacterium avium complex infection.
- Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications: post procedural pain, post procedural hemorrhage.
- Nervous System Disorders: intracranial hemorrhage.
- Psychiatric Disorders: mental status changes.
- Renal and Urinary Disorders: renal failure, urethral hemorrhage.
- Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: hemoptysis, lung infiltration, pulmonary embolism, respiratory arrest, pulmonary mass.
- Allergic Reaction: Hypersensitivity (anaphylactic reaction) to decitabine for injection has been reported in a Phase 2 trial.
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of decitabine for injection. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cases of Sweet's Syndrome (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) have been reported.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drug interaction studies with decitabine have not been conducted. In vitro studies in human liver microsomes suggest that decitabine is unlikely to inhibit or induce cytochrome P450 enzymes. In vitro metabolism studies have suggested that decitabine is not a substrate for human liver cytochrome P450 enzymes. As plasma protein binding of decitabine is negligible (<1%), interactions due to displacement of more highly protein bound drugs from plasma proteins are not expected.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Based on findings from human data, animal studies, and the mechanism of action, decitabine for injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
Limited published data on decitabine for injection use throughout the first trimester during pregnancy describe adverse developmental outcomes including major birth defects (structural abnormalities). In animal reproduction studies, administration of decitabine to pregnant mice and rats during organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes and was teratogenic, fetotoxic, and embryotoxic starting at doses approximately 7% of the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in the U.S. general population is 2-4% and 15-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies, respectively.
Data
Human Data
A single published case report of decitabine pregnancy exposure in a 39-year old woman with a hematologic malignancy described multiple structural abnormalities after 6 cycles of therapy in the 18th week of gestation. These abnormalities included
holoprosencephaly, absence of nasal bone, mid-facial deformity, cleft lip and palate, polydactyly and rocker-bottom feet. The pregnancy was terminated.
Animal Data
In utero exposure to decitabine causes temporal related defects in the rat and/or mouse, which include growth suppression, exencephaly, defective skull bones, rib/sternabrae defects, phocomelia, digit defects, micrognathia, gastroschisis, micromelia. Decitabine inhibits proliferation and increases apoptosis of neural progenitor cells of the fetal CNS and induces palatal clefting in the developing murine fetus. Studies in mice have also shown that decitabine administration during osteoblastogenesis (day 10 of gestation) induces bone loss in offspring.
In mice exposed to single IP (intraperitoneal) injections (0, 0.9 and 3.0 mg/m2, approximately 2% and 7% of the recommended daily clinical dose, respectively) over gestation days 8, 9, 10 or 11, no maternal toxicity was observed but reduced fetal survival was observed after treatment at 3 mg/m2 and decreased fetal weight was observed at both dose levels. The 3 mg/m2 dose elicited characteristic fetal defects for each treatment day, including supernumerary ribs (both dose levels), fused vertebrae and ribs, cleft palate, vertebral defects, hind-limb defects and digital defects of fore- and hind-limbs.
In rats given a single IP injection of 2.4, 3.6 or 6 mg/m2 (approximately 5, 8, or 13% the daily recommended clinical dose, respectively) on gestation days 9-12, no maternal toxicity was observed. No live fetuses were seen at any dose when decitabine was injected on gestation day 9. A significant decrease in fetal survival and reduced fetal weight at doses greater than 3.6 mg/m2 was seen when decitabine was given on gestation day 10. Increased incidences of vertebral and rib anomalies were seen at all dose levels, and induction of exophthalmia, exencephaly, and cleft palate were observed at 6.0 mg/m2. Increased incidence of foredigit defects was seen in fetuses at doses greater than 3.6 mg/m2. Reduced size and ossification of long bones of the fore-limb and hind-limb were noted at 6.0 mg/m2.
The effect of decitabine on postnatal development and reproductive capacity was evaluated in mice administered a single 3 mg/m2 IP injection (approximately 7% the recommended daily clinical dose) on day 10 of gestation. Body weights of males and females exposed in utero to decitabine were significantly reduced relative to controls at all postnatal time points. No consistent effect on fertility was seen when female mice exposed in utero were mated to untreated males. Untreated females mated to males exposed in utero showed decreased fertility at 3 and 5 months of age (36% and 0% pregnancy rate, respectively). Follow up studies indicated that treatment of pregnant mice with decitabine on gestation day 10 was associated with a reduced pregnancy rate resulting from effects on sperm production in the F1-generation.
8.2 Lactation
There are no data on the presence of decitabine or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from decitabine for injection in a nursing child, advise lactating women to avoid breastfeeding during treatment with decitabine for injection and for at least 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Conduct pregnancy testing of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating decitabine for injection.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to avoid pregnancy and use effective contraception while receiving decitabine for injection and for 6 months following the last dose.
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception while receiving treatment with decitabine for injection and for 3 months following the last dose. [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Infertility
Based on findings of decitabine in animals, male fertility may be compromised by treatment with decitabine for injection [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of decitabine for injection in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients exposed to decitabine for injection in the controlled clinical trial, 61 of 83 patients were age 65 and over, while 21 of 83 patients were age 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no known antidote for overdosage with decitabine for injection. Higher doses are associated with increased myelosuppression including prolonged neutropenia and thrombocytopenia. Standard supportive measures should be taken in the event of an overdose.
11 DESCRIPTION
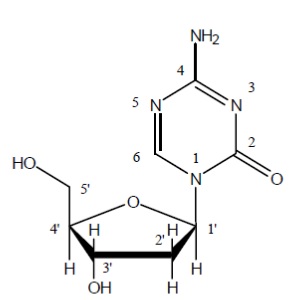
Decitabine for Injection contains decitabine (5-aza-2'-deoxycitidine), an analogue of the natural nucleoside 2'-deoxycytidine. Decitabine is a fine, white to almost white powder with the molecular formula of C8H12N4O4 and a molecular weight of 228.21. Its chemical name is 4-amino-1-(2-deoxy-β-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)-1,3,5-triazin-2(1H)-one and it has the following structural formula:
image
Decitabine is slightly soluble in ethanol/water (50/50), methanol/water (50/50) and methanol; sparingly soluble in water and soluble in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO).
Decitabine for injection a sterile, white to off white lyophilized powder/cake, supplied in a clear, colorless glass vial. Each 20 mL, single dose, glass vial contains 50 mg decitabine, 68 mg monobasic potassium phosphate (potassium dihydrogen phosphate) and 11.6 mg sodium hydroxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Decitabine is believed to exert its antineoplastic effects after phosphorylation and direct incorporation into DNA and inhibition of DNA methyltransferase, causing hypomethylation of DNA and cellular differentiation or apoptosis. Decitabine inhibits DNA methylation in vitro, which is achieved at concentrations that do not cause major suppression of DNA synthesis. Decitabine-induced hypomethylation in neoplastic cells may restore normal function to genes that are critical for the control of cellular differentiation and proliferation. In rapidly dividing cells, the cytotoxicity of decitabine may also be attributed to the formation of covalent adducts between DNA methyltransferase and decitabine incorporated into DNA. Non-proliferating cells are relatively insensitive to decitabine.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Decitabine has been shown to induce hypomethylation both in vitro and in vivo. However, there have been no studies of decitabine ‑ induced hypomethylation and pharmacokinetic parameters.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic parameters were evaluated in patients. Eleven patients received 20 mg/m2infused over 1 hour intravenously (treatment Option 2). Fourteen patients received 15 mg/m2infused over 3 hours (treatment Option 1). PK parameters are shown in Table 3. Plasma concentration-time profiles after discontinuation of infusion showed a biexponential decline. The CL of decitabine was higher following treatment Option 2. Upon repeat doses there was no systemic accumulation of decitabine or any changes in PK parameters. Population PK analysis (N=35) showed that the cumulative AUC per cycle for treatment Option 2 was 2.3-fold lower than the cumulative AUC per cycle following treatment Option 1.
|
* N=14, **N=11, ***N=35 Cumulative AUC per cycle |
|||||
| Dose
| Cmax
| AUC0-∞
| T1/2
| CL
| AUCCumulative***
|
|
| (ng/mL)
| (ng·h/mL)
| (h)
| (L/h/m2)
| (ng·h/mL)
|
| 15 mg/m2 3-hr infusion every 8 hours for 3 days (Option 1)*
| 73.8 | 163 | 0.62 | 125 | 1332 |
| (66) | (62) | (49) | (53) | (1010-1730) |
|
| 20 mg/m2 1-hr infusion daily for 5 days (Option 2)**
| 147 | 115 | 0.54 | 210 | 570 |
| (49) | (43) | (43) | (47) | (470-700) |
|
The exact route of elimination and metabolic fate of decitabine is not known in humans. One of the pathways of elimination of decitabine appears to be deamination by cytidine deaminase found principally in the liver but also in granulocytes, intestinal epithelium and whole blood.
Specific Populations
Patients with Renal Impairment
There are no data on the use of decitabine for injection in patients with renal impairment; therefore, if decitabine for injection is administered to these patients, monitor them frequently for excessive toxicity.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
There are no data on the use of decitabine for injection in patients with hepatic impairment; therefore, if decitabine for injection is administered to these patients, monitor them frequently for excessive toxicity.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with decitabine have not been conducted.
The mutagenic potential of decitabine was tested in several in vitro and in vivo systems. Decitabine increased mutation frequency in L5178Y mouse lymphoma cells, and mutations were produced in an Escherichia coli lac-I transgene in colonic DNA of decitabine-treated mice. Decitabine caused chromosomal rearrangements in larvae of fruit flies.
In male mice given IP injections of 0.15, 0.3 or 0.45 mg/m2decitabine (approximately 0.3% to 1% the recommended clinical dose) 3 times a week for 7 weeks, decitabine did not affect survival, body weight gain or hematological measures (hemoglobin and WBC counts). Testes weights were reduced, abnormal histology was observed and significant decreases in sperm number were found at doses ≥ 0.3 mg/m2. In females mated to males dosed with ≥ 0.3 mg/m2decitabine, pregnancy rate was reduced and preimplantation loss was significantly increased.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Controlled Trial in Myelodysplastic Syndrome
A randomized open-label, multicenter, controlled trial evaluated 170 adult patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) meeting French-American-British (FAB) classification criteria and International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) High-Risk, Intermediate-2 and Intermediate-1 prognostic scores. Eighty-nine patients were randomized to decitabine for injection therapy plus supportive care (only 83 received decitabine for injection), and 81 to Supportive Care (SC) alone. Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) were not intended to be included. Of the 170 patients included in the study, independent review (adjudicated diagnosis) found that 12 patients (9 in the decitabine for injection arm and 3 in the SC arm) had the diagnosis of AML at baseline. Baseline demographics and other patient characteristics in the Intent-to-Treat (ITT) population were similar between the 2 groups, as shown in Table 4.
| Demographic or Other Patient
Characteristic | Decitabine for Injection
| Supportive Care
|
|
| N = 89
| N= 81
|
| Age (years)
| ||
| Mean (±SD) | 69±10 | 67±10 |
| Median (IQR) | 70 (65-76) | 70 (62-74) |
| (Range: min-max) | (31-85) | (30-82) |
| Gender n (%)
| ||
| Male | 59 (66) | 57 (70) |
| Female | 30 (34) | 24 (30) |
| Race n (%)
| ||
| White | 83 (93) | 76 (94) |
| Black | 4 (4) | 2 (2) |
| Other | 2 (2) | 3 (4) |
| Weeks Since MDS Diagnosis
| ||
| Mean (±SD) | 86±131 | 77±119 |
| Median (IQR) | 29 (10-87) | 35 (7-98) |
| (Range: min-max) | (2-667) | (2-865) |
| Previous MDS Therapy n (%)
| ||
| Yes | 27 (30) | 19 (23) |
| No | 62 (70) | 62 (77) |
| RBC Transfusion Status n (%)
| ||
| Independent | 23 (26) | 27 (33) |
| Dependent | 66 (74) | 54 (67) |
| Platelet Transfusion Status n (%)
| ||
| Independent | 69 (78) | 62 (77) |
| Dependent | 20 (22) | 19 (23) |
| IPSS Classification n (%)
| ||
| Intermediate–1 | 28 (31) | 24 (30) |
| Intermediate–2 | 38 (43) | 36 (44) |
| High Risk | 23 (26) | 21 (26) |
| FAB Classification n (%)
| ||
| RA | 12 (13) | 12 (15) |
| RARS | 7 (8) | 4 (5) |
| RAEB | 47 (53) | 43 (53) |
| RAEB-t | 17 (19) | 14 (17) |
| CMML | 6 (7) | 8 (10) |
Patients randomized to the decitabine for injection arm received decitabine for injection intravenously infused at a dose of 15 mg/m2over a 3-hour period, every 8 hours, for 3 consecutive days. This cycle was repeated every 6 weeks, depending on the patient's clinical response and toxicity. Supportive care consisted of blood and blood product transfusions, prophylactic antibiotics, and hematopoietic growth factors. The study endpoints were overall response rate (complete response + partial response) and time to AML or death. Responses were classified using the MDS International Working Group (IWG) criteria; patients were required to be RBC and platelet transfusion independent during the time of response. Response criteria are given in Table 5:
|
* Cheson BD, Bennett JM, et al. Report of an International Working Group to Standardize Response Criteria for MDS. Blood . 2000; 96:3671-3674. |
||
| Complete Response (CR) ≥ 8 weeks
| Bone Marrow
| On repeat aspirates:
• < 5% myeloblasts • No dysplastic changes |
| Peripheral Blood
| In all samples during response:
• Hgb > 11 g/dL (no transfusions or erythropoietin) • ANC ≥ 1500/μL (no growth factor) • Platelets ≥ 100,000/ μL (no thrombopoietic agent) • No blasts and no dysplasia |
|
| Partial Response (PR) ≥ 8 weeks
| Bone Marrow
| On repeat aspirates:
• ≥ 50% decrease in blasts over pretreatment values OR • Improvement to a less advanced MDS FAB classification |
| Peripheral Blood
| Same as for CR
|
|
The overall response rate (CR+PR) in the ITT population was 17% in decitabine for injection-treated patients and 0% in the SC group (p<0.001). (See Table 6) The overall response rate was 21% (12/56) in decitabine for injection-treated patients considered evaluable for response (i.e., those patients with pathologically confirmed MDS at baseline who received at least 2 cycles of treatment). The median duration of response (range) for patients who responded to decitabine for injection was 288 days (116-388) and median time to response (range) was 93 days (55-272). All but one of the decitabine for injection-treated patients who responded did so by the fourth cycle. Benefit was seen in an additional 13% of decitabine for injection-treated patients who had hematologic improvement, defined as a response less than PR lasting at least 8 weeks, compared to 7% of SC patients. Decitabine for injection treatment did not significantly delay the median time to AML or death versus supportive care.
|
**p-value <0.001 from two-sided Fisher's Exact Test comparing Decitabine for Injection vs. Supportive Care. |
||
| Parameter
| Decitabine for Injection
| Supportive Care
|
|
| N=89
| N=81
|
| Overall Response Rate (CR+PR) †
| 15 (17%) **
| 0 (0%)
|
| Complete Response (CR) | 8 (9%) | 0 (0%) |
| Partial Response (PR) | 7 (8%) | 0 (0%) |
| Duration of Response
| ||
| Median time to (CR+PR) response - Days (range) | 93 (55-272) | NA |
| Median Duration of (CR+PR) response - Days (range) | 288 (116-388) | NA |
All patients with a CR or PR were RBC and platelet transfusion independent in the absence of growth factors.
Responses occurred in patients with an adjudicated baseline diagnosis of AML.
14.2 Single-arm Studies in Myelodysplastic Syndrome
Three open-label, single-arm, multicenter studies were conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of decitabine for injection in MDS patients with any of the FAB subtypes. In one study conducted in North America, 99 patients with IPSS Intermediate-1, Intermediate-2, or high risk prognostic scores received decitabine for injection by intravenous infusion at a dose of 20 mg/m2IV over 1-hour daily, on days 1-5 of week 1 every 4 weeks (1 cycle). The results were consistent with the results of the controlled trial and summarized in Table 8.
| Demographic or Other Patient Characteristic
| Decitabine for injection
|
|
| N = 99
|
| Age (years)
| |
| Mean (±SD) | 71±9 |
| Median (Range: min-max) | 72 (34-87) |
| Gender n (%)
| |
| Male | 71 (72) |
| Female | 28 (28) |
| Race n (%)
| |
| White | 86 (87) |
| Black | 6 (6) |
| Asian | 4 (4) |
| Other | 3 (3) |
| Days From MDS Diagnosis to First Dose
| |
| Mean (±SD) | 444±626 |
| Median (Range: min-max) | 154 (7-3079) |
| Previous MDS Therapy n (%) | |
| Yes | 27 (27) |
| No | 72 (73) |
| RBC Transfusion Status n (%)
| |
| Independent | 33 (33) |
| Dependent | 66 (67) |
| Platelet Transfusion Status n (%)
| |
| Independent | 84 (85) |
| Dependent | 15 (15) |
| IPSS Classification n (%)
| |
| Low Risk | 1 (1) |
| Intermediate–1 | 52 (53) |
| Intermediate–2 | 23 (23) |
| High Risk | 23 (23) |
| FAB Classification n (%)
| |
| RA | 20 (20) |
| RARS | 17 (17) |
| RAEB | 45 (45) |
| RAEB-t | 6 (6) |
| CMML | 11 (11) |
| Parameter
| Decitabine for injection
|
| N=99
|
|
| Overall Response Rate (CR+PR)
| 16 (16%)
|
| Complete Response (CR) | 15 (15%) |
| Partial Response (PR) | 1 (1%) |
| Duration of Response
| |
| Median time to (CR+PR) response - Days (range) | 162 (50-267) |
| Median Duration of (CR+PR) response - Days (range) | 443 (72-722+) |
| + indicates censored observation | |
| * Cheson BD, Bennett JM, et al. Report of an International Working Group to Standardize Response Criteria for MDS. Blood . 2000; 96:3671-3674. |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Decitabine for injection is a sterile, white to off white lyophilized powder/cake, supplied as 50 mg single-dose vial individually packaged in a carton. NDC 16714-749-01.
Storage
Store vials at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise women of childbearing potential to avoid pregnancy and to use effective contraception while receiving decitabine for injection and for 6 months after last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Advise men not to father a child while receiving treatment with decitabine for injection, and for 3 months after the last dose. Advise men with female partners of childbearing potential to use effective contraception [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Advise patients to avoid breastfeeding while receiving decitabine for injection and for at 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)]. Advise patients of the risk of myelosuppression and to report any symptoms of infection, anemia, or bleeding to their healthcare provider as soon as possible. Advise patients for the need for laboratory monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Manufactured for:
Northstar Rx LLC, Memphis, TN 38141.
Manufactured by:
Cipla Ltd., Verna Goa, India.
Issued: 1/2019
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 16714-749-01
Decitabine for Injection
50 mg per vial
FOR INTRAVENOUS INFUSION ONLY
WARNING: Cytotoxic agent.
Single Dose Sterile Vial –
Discard Unused Portion
Storage: Store vials at 25°C (77°F);
excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C
(59°F to 86°F). (see insert)
NORTHSTAR
NDC 16714-749-01
Decitabine
for Injection
50 mg per vial
FOR INTRAVENOUS INFUSION ONLY
WARNING: Cytotoxic agent.
Single Dose Sterile Vial –
Discard Unused Portion
Store vials at 25°C (77°F);
excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C
(59°F to 86°F). (see insert)
NORTHSTAR

| DECITABINE
decitabine injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - NorthStar RxLLC (830546433) |
| Registrant - Cipla Ltd. Goa (650072015) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cipla Ltd. Goa | 650072015 | MANUFACTURE(16714-749) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| scinopharm Taiwan Limited | 657484726 | API MANUFACTURE(16714-749) | |