PROPOFOL- propofol injection, emulsion
Civica, Inc.
----------
PROPOFOL INJECTABLE EMULSION, USP
CONTAINS BENZYL ALCOHOL (see PRECAUTIONS section)
For IV Administration
Rx ONLY
Strict aseptic technique must always be maintained during handling. Propofol injectable emulsion is a single-access parenteral product (single patient infusion vial) which contains benzyl alcohol to inhibit the rate of growth of microorganisms, for up to 12 hours, in the event of accidental extrinsic contamination. However, propofol injectable emulsion can still support the growth of microorganisms, as it is not an antimicrobially preserved product under USP standards. Accordingly, strict aseptic technique must still be adhered to. Do not use if contamination is suspected. Discard unused drug product as directed within the required time limits. There have been reports in which failure to use aseptic technique when handling propofol injectable emulsion was associated with microbial contamination of the product and with fever, infection/sepsis, other life-threatening illness, and/or death.
There have been reports, in the literature and other public sources, of the transmission of bloodborne pathogens (such as Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, and HIV) from unsafe injection practices, and use of propofol vials intended for single use on multiple persons. Propofol injectable emulsion vials are never to be accessed more than once or used on more than one person.
DESCRIPTION
Propofol Injectable Emulsion is a sterile, nonpyrogenic emulsion containing 10 mg/mL of propofol suitable for intravenous administration. Propofol is chemically described as 2,6-diisopropylphenol. The structural formula is shown below:
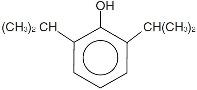
Molecular Formula: C12H180
Molecular Weight: 178.27
Propofol is slightly soluble in water and, thus, is formulated in a white, oil-in-water emulsion. The pKa is 11. The octanol/water partition coefficient for propofol is 6761:1 at a pH of 6 to 8.5. Each mL of Propofol Injectable Emulsion contains propofol 10 mg/mL; soybean oil (100 mg/mL); glycerol (22.5 mg/mL); egg lecithin (12 mg/mL); and benzyl alcohol, 1 mg/mL with sodium hydroxide to adjust pH. It is isotonic and has a pH of 6.5 to 8.5.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
General
Propofol is an intravenous general anesthetic and sedation drug for use in the induction and maintenance of anesthesia or sedation. Intravenous injection of a therapeutic dose of propofol induces, with minimal excitation, usually within 40 seconds from the start of injection (the time for one arm-brain circulation). As with other rapidly acting intravenous anesthetic agents, the half-time of the blood-brain equilibration is approximately 1 minute to 3 minutes, accounting for the rate of induction of anesthesia. The mechanism of action, like all general anesthetics, is poorly understood. However, propofol is thought to produce its sedative/anesthetic effects by the positive modulation of the inhibitory function of the neurotransmitter GABA through the ligand-gated GABAA receptors.
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamic properties of propofol are dependent upon the therapeutic blood propofol concentrations. Steady-state propofol blood concentrations are generally proportional to infusion rates. Undesirable side effects, such as cardiorespiratory depression, are likely to occur at higher blood concentrations which result from bolus dosing or rapid increases in infusion rates. An adequate interval (3 minutes to 5 minutes) must be allowed between dose adjustments in order to assess clinical effects.
The hemodynamic effects of propofol during induction of anesthesia vary. If spontaneous ventilation is maintained, the major cardiovascular effect is arterial hypotension (sometimes greater than a 30% decrease) with little or no change in heart rate and no appreciable decrease in cardiac output. If ventilation is assisted or controlled (positive pressure ventilation), there is an increase in the incidence and the degree of depression of cardiac output. Addition of an opioid, used as a premedicant, further decreases cardiac output and respiratory drive.
If anesthesia is continued by infusion of propofol, the stimulation of endotracheal intubation and surgery may return arterial pressure towards normal. However, cardiac output may remain depressed. Comparative clinical studies have shown that the hemodynamic effects of propofol during induction of anesthesia are generally more pronounced than with other intravenous (IV) induction agents.
Induction of anesthesia with propofol is frequently associated with apnea in both adults and pediatric patients. In adult patients who received propofol (2 mg/kg to 2.5 mg/kg), apnea lasted less than 30 seconds in 7% of patients, 30 seconds to 60 seconds in 24% of patients, and more than 60 seconds in 12% of patients. In pediatric patients from birth through 16 years of age assessable for apnea who received bolus doses of propofol (1 mg/kg to 3.6 mg/kg), apnea lasted less than 30 seconds in 12% of patients, 30 seconds to 60 seconds in 10% of patients, and more than 60 seconds in 5% of patients.
During maintenance of general anesthesia, propofol causes a decrease in spontaneous minute ventilation usually associated with an increase in carbon dioxide tension which may be marked depending upon the rate of administration and concurrent use of other medications (e.g., opioids, sedatives, etc.).
During monitored anesthesia care (MAC) sedation, attention must be given to the cardiorespiratory effects of propofol. Hypotension, oxyhemoglobin desaturation, apnea, and airway obstruction can occur, especially following a rapid bolus of propofol. During initiation of MAC sedation, slow infusion or slow injection techniques are preferable over rapid bolus administration. During maintenance of MAC sedation, a variable rate infusion is preferable over intermittent bolus administration in order to minimize undesirable cardiorespiratory effects. In the elderly, debilitated, or American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status (ASA-PS) III or IV patients, rapid (single or repeated) bolus dose administration should not be used for MAC sedation. (See WARNINGS.)
Clinical and preclinical studies suggest that propofol is rarely associated with elevation of plasma histamine levels.
Preliminary findings in patients with normal intraocular pressure indicate that propofol produces a decrease in intraocular pressure which may be associated with a concomitant decrease in systemic vascular resistance.
Clinical studies indicate that propofol when used in combination with hypocarbia increases cerebrovascular resistance and decreases cerebral blood flow, cerebral metabolic oxygen consumption, and intracranial pressure. Propofol does not affect cerebrovascular reactivity to changes in arterial carbon dioxide tension. (See Clinical Trials - Neuroanesthesia.)
Clinical studies indicate that propofol does not suppress the adrenal response to ACTH.
Animal studies and limited experience in susceptible patients have not indicated any propensity of propofol to induce malignant hyperthermia.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of propofol are well described by a three compartment linear model with compartments representing the plasma, rapidly equilibrating tissues, and slowly equilibrating tissues.
Following an IV bolus dose, there is rapid equilibration between the plasma and the brain, accounting for the rapid onset of anesthesia. Plasma levels initially decline rapidly as a result of both distribution and metabolic clearance. Distribution accounts for about half of this decline following a bolus of propofol. However, distribution is not constant over time, but decreases as body tissues equilibrate with plasma and become saturated. The rate at which equilibration occurs is a function of the rate and duration of the infusion. When equilibration occurs there is no longer a net transfer of propofol between tissues and plasma.
Discontinuation of the recommended doses of propofol after the maintenance of anesthesia for approximately one hour, or for sedation in the ICU for one day, results in a prompt decrease in blood propofol concentrations and rapid awakening. Longer infusions (10 days of ICU sedation) result in accumulation of significant tissue stores of propofol, such that the reduction in circulating propofol is slowed and the time to awakening is increased.
By daily titration of propofol dosage to achieve only the minimum effective therapeutic concentration, rapid awakening within 10 minutes to 15 minutes can occur even after long-term administration. If, however, higher than necessary infusion levels have been maintained for a long time, propofol redistribution from fat and muscle to the plasma can be a significant and slow recovery.
The figure below illustrates the fall of plasma propofol levels following infusions of various durations to provide ICU sedation.
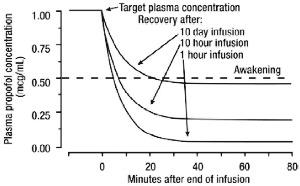
The large contribution of distribution (about 50%) to the fall of propofol plasma levels following brief infusions means that after very long infusions a reduction in the infusion rate is appropriate by as much as half the initial infusion rate in order to maintain a constant plasma level. Therefore, failure to reduce the infusion rate in patients receiving propofol for extended periods may result in excessively high blood concentrations of the drug. Thus, titration to clinical response and daily evaluation of sedation levels are important during use of propofol infusion for ICU sedation.
Adults:
Propofol clearance ranges from 23 mL/kg/min to 50 mL/kg/min (1.6 L/min to 3.4 L/min in 70 kg adults). It is chiefly eliminated by hepatic conjugation to inactive metabolites which are excreted by the kidney. A glucuronide conjugate accounts for about 50% of the administered dose. Propofol has a steady state volume of distribution (10-day infusion) approaching 60 L/kg in healthy adults. A difference in pharmacokinetics due to gender has not been observed. The terminal half-life of propofol after a 10-day infusion is 1 to 3 days.
Geriatrics:
With increasing patient age, the dose of propofol needed to achieve a defined anesthetic end point (dose-requirement) decreases. This does not appear to be an age-related change in pharmacodynamics or brain sensitivity, as measured by EEG burst suppression. With increasing patient age, pharmacokinetic changes are such that, for a given IV bolus dose, higher peak plasma concentrations occur, which can explain the decreased dose requirement. These higher peak plasma concentrations in the elderly can predispose patients to cardiorespiratory effects including hypotension, apnea, airway obstruction, and/or arterial oxygen desaturation. The higher plasma levels reflect an age-related decrease in volume of distribution and intercompartmental clearance. Lower doses are therefore recommended for initiation and maintenance of sedation and anesthesia in elderly patients. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Pediatrics:
The pharmacokinetics of propofol were studied in children between 3 years and 12 years of age who received propofol for periods of approximately 1 hour to 2 hours. The observed distribution and clearance of propofol in these children were similar to adults.
Organ Failure:
The pharmacokinetics of propofol do not appear to be different in people with chronic hepatic cirrhosis or chronic renal impairment compared to adults with normal hepatic and renal function. The effects of acute hepatic or renal failure on the pharmacokinetics of propofol have not been studied.
Clinical Trials
Anesthesia and Monitored Anesthesia Care (MAC) Sedation
Pediatric Anesthesia:
Propofol was studied in clinical trials which included cardiac surgical patients. Most patients were 3 years of age or older. The majority of the patients were healthy ASA-PS I or II patients. The range of doses in these studies are described in Tables 1 and 2.
|
Age Range |
Induction Dose |
Injection Duration |
|
Birth through 16 years |
2.5 mg/kg | 20 sec. |
| (1 mg/kg to 3.6 mg/kg) | (6 sec to 45 sec) |
| Age Range |
Maintenance Dosage | Duration |
|
2 months to 2 years | 199 mcg/kg/min (82 mcg/kg/min to 394 mcg/kg/min) |
65 minutes (12 minutes |
|
2 to 12 years |
188 mcg/kg/min |
69 minutes (23 minutes |
|
>12 through 16 years | 161 mcg/kg/min (84 mcg/kg/min to 359 mcg/kg/min) | 69 minutes (26 minutes to 251 minutes) |
Neuroanesthesia:
Propofol was studied in patients undergoing craniotomy for supratentorial tumors in two clinical trials. The mean lesion size (anterior/posterior x lateral) was 31 mm x 32 mm in one trial and 55 mm x 42 mm in the other trial respectively. Anesthesia was induced with a median propofol dose of 1.4 mg/kg (range: 0.9 mg/kg to 6.9 mg/kg) and maintained with a median maintenance propofol dose of 146 mcg/kg/min (range: 68 mcg/kg/min to 425 mcg/kg/min). The median duration of the propofol maintenance infusion was 285 minutes (range: 48 minutes to 622 minutes).
Propofol was administered by infusion in a controlled clinical trial to evaluate its effect on cerebrospinal fluid pressure (CSFP). The mean arterial pressure was maintained relatively constant over 25 minutes with a change from baseline of -4% ± 17% (mean ± SD). The change in CSFP was -46% ± 14%. As CSFP is an indirect measure of intracranial pressure (ICP), propofol, when given by infusion or slow bolus in combination with hypocarbia, is capable of decreasing ICP independent of changes in arterial pressure.
Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Sedation
Adult Patients:
Propofol was compared to benzodiazepines and opioids in clinical trials involving ICU patients. Of these, 302 received propofol and comprise the overall safety database for ICU sedation.
Across all clinical studies, the mean infusion maintenance rate for all propofol patients was 27 ± 21 mcg/kg/min. The maintenance infusion rates required to maintain adequate sedation ranged from 2.8 mcg/kg/min to 130 mcg/kg/min. The infusion rate was lower in patients over 55 years of age (approximately 20 mcg/kg/min) compared to patients under 55 years of age (approximately 38 mcg/kg/min). Although there are reports of reduced analgesic requirements, most patients received opioids for analgesia during maintenance of ICU sedation. In these studies, morphine or fentanyl was used as needed for analgesia. Some patients also received benzodiazepines and/or neuromuscular blocking agents. During long-term maintenance of sedation, some ICU patients were awakened once or twice every 24 hours for assessment of neurologic or respiratory function.
In Medical and Postsurgical ICU studies comparing propofol to benzodiazepine infusion or bolus, there were no apparent differences in maintenance of adequate sedation, mean arterial pressure, or laboratory findings. Like the comparators, propofol reduced blood cortisol during sedation while maintaining responsivity to challenges with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Case reports from the published literature generally reflect that propofol has been used safely in patients with a history of porphyria or malignant hyperthermia.
In hemodynamically stable head trauma patients ranging in age from 19 years to 43 years, adequate sedation was maintained with propofol or morphine. There were no apparent differences in adequacy of sedation, intracranial pressure, cerebral perfusion pressure, or neurologic recovery between the treatment groups. In literature reports of severely head-injured patients in Neurosurgical ICUs, propofol infusion and hyperventilation, both with and without diuretics, controlled intracranial pressure while maintaining cerebral perfusion pressure. In some patients, bolus doses resulted in decreased blood pressure and compromised cerebral perfusion pressure.
Propofol was found to be effective in status epilepticus which was refractory to the standard anticonvulsant therapies. For these patients, as well as for ARDS/respiratory failure and tetanus patients, sedation maintenance dosages were generally higher than those for other critically ill patient populations.
Pediatric Patients:
A single, randomized, controlled, clinical trial that evaluated the safety and effectiveness of propofol versus standard sedative agents (SSA) was conducted on 327 pediatric ICU patients. Patients were randomized to receive either propofol 2%, (113 patients), propofol 1%, (109 patients), or an SSA (e.g., lorazepam, chloral hydrate, fentanyl, ketamine, morphine, or phenobarbital). Propofol therapy was initiated at an infusion rate of 5.5 mg/kg/hr and titrated as needed to maintain sedation at a standardized level. The results of the study showed an increase in the number of deaths in patients treated with propofol as compared to SSAs. Of the 25 patients who died during the trial or within the 28-day follow-up period: 12 (11%) were in the propofol 2% treatment group, 9 (8%) were in the propofol 1% treatment group, and 4% were (4%) in the SSA treatment group. The differences in mortality rate between the groups were not statistically significant. Review of the deaths failed to reveal a correlation with underlying disease status or a correlation to the drug or a definitive pattern to the causes of death.
Cardiac Anesthesia
Propofol was evaluated in clinical trials involving patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).
In post-CABG (coronary artery bypass graft) patients, the maintenance rate of propofol administration was usually low (median 11 mcg/kg/min) due to the intraoperative administration of high opioid doses. Patients receiving propofol required 35% less nitroprusside than midazolam patients. During initiation of sedation in post-CABG patients, a 15% to 20% decrease in blood pressure was seen in the first 60 minutes. It was not possible to determine cardiovascular effects in patients with severely compromised ventricular function.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Propofol injectable emulsion is an IV general anesthetic and sedation drug that can be used as described in the table below.
|
Indication |
Approved Patient Population |
| Initiation and maintenance of Monitored Anesthesia Care (MAC) sedation | Adults only |
| Combined sedation and regional anesthesia | Adults only (see PRECAUTIONS) |
| Induction of General Anesthesia | Patients greater than or equal to 3 years of age |
| Maintenance of General Anesthesia | Patients greater than or equal to 2 months of age |
| Intensive Care Unit (ICU) sedation of intubated, mechanically ventilated patients | Adults only |
Safety, effectiveness and dosing guidelines for propofol have not been established for MAC Sedation in the pediatric population; therefore, it is not recommended for this use. (See PRECAUTIONS - Pediatric use.)
Propofol is not recommended for induction of anesthesia below the age of 3 years or for maintenance of anesthesia below the age of 2 months because its safety and effectiveness have not been established in those populations.
In the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), propofol can be administered to intubated, mechanically ventilated adult patients to provide continuous sedation and control of stress responses, only by persons skilled in the medical management of critically ill patients and trained in cardiovascular resuscitation and airway management.
Propofol is not indicated for use in Pediatric ICU sedation since the safety of this regimen has not been established. (See PRECAUTIONS -Pediatric use.)
Propofol is not recommended for obstetrics, including Cesarean section deliveries. Propofol crosses the placenta, and as with other general anesthetic agents, the administration of propofol may be associated with neonatal depression. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Propofol is not recommended for use in nursing mothers because propofol has been reported to be excreted in human milk, and the effects of oral absorption of small amounts of propofol are not known. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Propofol injectable emulsion is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to propofol or any of its components.
Propofol injectable emulsion is contraindicated in patients with allergies to eggs, egg products, soybeans or soy products.
WARNINGS
Use of propofol has been associated with both fatal and life-threatening anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions.
For general anesthesia or monitored anesthesia care (MAC) sedation, propofol should be administered only by persons trained in the administration of general anesthesia and not involved in the conduct of the surgical/diagnostic procedure. Sedated patients should be continuously monitored, and facilities for maintenance of a patent airway, providing artificial ventilation, administering supplemental oxygen, and instituting cardiovascular resuscitation must be immediately available. Patients should be continuously monitored for early signs of hypotension, apnea, airway obstruction, and/or oxygen desaturation. These cardiorespiratory effects are more likely to occur following rapid bolus administration, especially in the elderly, debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV patients.
For sedation of intubated, mechanically ventilated patients in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), propofol should be administered only by persons skilled in the management of critically ill patients and trained in cardiovascular resuscitation and airway management.
Use of propfol infusions for both adult and pediatric ICU sedation has been associated with a constellation of metabolic derangements and organ system failures, referred to as Propofol Infusion Syndrome, that have resulted in death. The syndrome is characterized by severe metabolic acidosis, hyperkalemia, lipemia, rhabdomyolysis, hepatomegaly, renal failure, ECG changes* and/or cardiac failure. The following appear to be major risk factors for the development of these events: decreased oxygen delivery to tissues; serious neurological injury and/or sepsis; high dosages of one or more of the following pharmacological agents: vasoconstrictors, steroids, inotropes and/or prolonged, high-dose infusions of propofol (greater than 5 mg/kg/h for greater than 48h). The syndrome has also been reported following large-dose, short-term infusions during surgical anesthesia. In the setting of prolonged need for sedation, increasing propofol dose requirements to maintain a constant level of sedation, or onset of metabolic acidosis during administration of a propofol infusion, consideration should be given to using alternative means of sedation.
*Coved ST segment elevation (similar to ECG changes of the Brugada syndrome).
Abrupt discontinuation of propofol prior to weaning or for daily evaluation of sedation levels should be avoided. This may result in rapid awakening with associated anxiety, agitation, and resistance to mechanical ventilation. Infusions of propofol injectable emulsion should be adjusted to maintain a light level of sedation through the weaning process or evaluation of sedation level. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Propofol injectable emulsion should not be coadministered through the same IV catheter with blood or plasma because compatibility has not been established. In vitro tests have shown that aggregates of the globular component of the emulsion vehicle have occurred with blood/plasma/serum from humans and animals. The clinical significance of these findings is not known.
There have been reports in which failure to use aseptic technique when handling propofol injectable emulsion was associated with microbial contamination of the product and with fever, infection, sepsis, other life-threatening illness, and death. Do not use if contamination is suspected. Discard unused drug product as directed within the required time limits. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION - Handling Procedures.)
There have been reports, in the literature and other public sources, of the transmission of bloodborne pathogens (such as Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, and HIV) from unsafe injection practices, and use of propofol vials intended for single use on multiple persons. Propofol injectable emulsion vial is never to be accessed more than once or used on more than one person.
Pediatric Neurotoxicity
Published animal studies demonstrate that the administration of anesthetic and sedation drugs that block NMDA receptors and/or potentiate GABA activity increase neuronal apoptosis in the developing brain and result in long-term cognitive deficits when used for longer than 3 hours. The clinical significance of these findings is not clear. However, based on the available data, the window of vulnerability to these changes is believed to correlate with exposures in the third trimester of gestation through the first several months of life, but may extend out to approximately three years of age in humans (see PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy, Pediatric Use; ANIMAL TOXICOLOGY AND/OR PHARMACOLOGY).
Some published studies in children suggest that similar deficits may occur after repeated or prolonged exposures to anesthetic agents early in life and may result in adverse cognitive or behavioral effects. These studies have substantial limitations, and it is not clear if the observed effects are due to the anesthetic/sedation drug administration or other factors such as the surgery or underlying illness.
Anesthetic and sedation drugs are a necessary part of the care of children needing surgery, other procedures, or tests that cannot be delayed, and no specific medications have been shown to be safer than any other. Decisions regarding the timing of any elective procedures requiring anesthesia should take into consideration the benefits of the procedure weighed against the potential risks.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Adult and Pediatric Patients: A lower induction dose and a slower maintenance rate of administration should be used in elderly, debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV patients. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.) Patients should be continuously monitored for early signs of hypotension and/or bradycardia. Apnea requiring ventilatory support often occurs during induction and may persist for more than 60 seconds. Propofol use requires caution when administered to patients with disorders of lipid metabolism such as primary hyperlipoproteinemia, diabetic hyperlipemia, and pancreatitis.
Very rarely the use of propofol may be associated with the development of a period of postoperative unconsciousness which may be accompanied by an increase in muscle tone.
This may or may not be preceded by a brief period of wakefulness. Recovery is spontaneous.
When propofol is administered to an epileptic patient, there is a risk of seizure during the recovery phase.
Attention should be paid to minimize pain on administration of propofol. Transient local pain can be minimized if the larger veins of the forearm or antecubital fossa are used. Pain during intravenous injection may also be reduced by prior injection of IV lidocaine (1 mL of a 1% solution). Pain on injection occurred frequently in pediatric patients (45%) when a small vein of the hand was utilized without lidocaine pretreatment. With lidocaine pretreatment or when antecubital veins were utilized, pain was minimal (incidence less than 10%) and well-tolerated. There have been reports in the literature indicating that the addition of lidocaine to propofol in quantities greater than 20 mg lidocaine/200 mg propofol results in instability of the emulsion which is associated with increases in globule sizes over time and (in rat studies) a reduction in anesthetic potency. Therefore, it is recommended that lidocaine be administered prior to propofol administration or that it be added to propofol immediately before administration and in quantities not exceeding 20 mg lidocaine/200 mg propofol.
Venous sequelae, i.e., phlebitis or thrombosis, have been reported rarely (less than 1%). In two clinical studies using dedicated intravenous catheters, no instances of venous sequelae were observed up to 14 days following induction.
Intra-arterial injection in animals did not induce local tissue effects. Accidental intra-arterial injection has been reported in patients, and, other than pain, there were no major sequelae.
Intentional injection into subcutaneous or perivascular tissues of animals caused minimal tissue reaction. During the post-marketing period, there have been rare reports of local pain, swelling, blisters, and/or tissue necrosis following accidental extravasation of propofol.
Perioperative myoclonia, rarely including convulsions and opisthotonos, has occurred in association with propofol administration.
Clinical features of anaphylaxis, including angioedema, bronchospasm, erythema, and hypotension, occur rarely following propofol administration.
There have been rare reports of pulmonary edema in temporal relationship to the administration of propofol, although a causal relationship is unknown.
Rarely, cases of unexplained postoperative pancreatitis (requiring hospital admission) have been reported after anesthesia in which propofol was one of the induction agents used. Due to a variety of confounding factors in these cases, including concomitant medications, a causal relationship to propofol is unclear.
Propofol has no vagolytic activity. Reports of bradycardia, asystole, and rarely, cardiac arrest have been associated with propofol. Pediatric patients are susceptible to this effect, particularly when fentanyl is given concomitantly. The intravenous administration of anticholinergic agents (e.g., atropine or glycopyrrolate) should be considered to modify potential increases in vagal tone due to concomitant agents (e.g., succinylcholine) or surgical stimuli.
Intensive Care Unit Sedation
Adult Patients:
(See WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION - Handling Procedures.) The administration of propofol should be initiated as a continuous infusion and changes in the rate of administration made slowly (greater than 5 min) in order to minimize hypotension and avoid acute overdosage. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Patients should be monitored for early signs of significant hypotension and/or cardiovascular depression, which may be profound. These effects are responsive to discontinuation of propofol, IV fluid administration, and/or vasopressor therapy. In the elderly, debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV patients, rapid (single or repeated) bolus administration should not be used during sedation in order to minimize undesirable cardiorespiratory depression, including hypotension, apnea, airway obstruction, and oxygen desaturation.
As with other sedative medications, there is wide interpatient variability in propofol dosage requirements, and these requirements may change with time.
Failure to reduce the infusion rate in patients receiving propofol for extended periods may result in excessively high blood concentrations of the drug. Thus, titration to clinical response and daily evaluation of sedation levels are important during use of propofol infusion for ICU sedation, especially when it is used for long durations.
Opioids and paralytic agents should be discontinued and respiratory function optimized prior to weaning patients from mechanical ventilation. Infusions of propofol should be adjusted to maintain a light level of sedation prior to weaning patients from mechanical ventilatory support. Throughout the weaning process, this level of sedation may be maintained in the absence of respiratory depression. Because of the rapid clearance of propofol, abrupt discontinuation of a patient's infusion may result in rapid awakening with associated anxiety, agitation, and resistance to mechanical ventilation, making weaning from mechanical ventilation difficult. It is therefore recommended that administration of propofol be continued in order to maintain a light level of sedation throughout the weaning process until 10 minutes to 15 minutes prior to extubation, at which time the infusion can be discontinued.
Since propofol injectable emulsion is formulated in an oil-in-water emulsion, elevations in serum triglycerides may occur when propofol is administered for extended periods of time. Patients at risk of hyperlipidemia should be monitored for increases in serum triglycerides or serum turbidity. Administration of propofol should be adjusted if fat is being inadequately cleared from the body. A reduction in the quantity of concurrently administered lipids is indicated to compensate for the amount of lipid infused as part of the propofol formulation; 1 mL of propofol contains approximately 0.1 g of fat (1.1 kcal).
The long-term administration of propofol to patients with renal failure and/or hepatic insufficiency has not been evaluated.
Neurosurgical Anesthesia:
When propofol is used in patients with increased intracranial pressure or impaired cerebral circulation, significant decreases in mean arterial pressure should be avoided because of the resultant decreases in cerebral perfusion pressure. To avoid significant hypotension and decreases in cerebral perfusion pressure, an infusion or slow bolus of approximately 20 mg every 10 seconds should be utilized instead of rapid, more frequent, and/or larger boluses of propofol. Slower induction, titrated to clinical responses, will generally result in reduced induction dosage requirements (1 mg/kg to 2 mg/kg). When increased ICP is suspected, hyperventilation and hypocarbia should accompany the administration of propofol. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Cardiac Anesthesia:
Slower rates of administration should be utilized in premedicated patients, geriatric patients, patients with recent fluid shifts, and patients who are hemodynamically unstable. Fluid deficits should be corrected prior to administration of propofol. In those patients where additional fluid therapy may be contraindicated, other measures, e.g., elevation of lower extremities, or use of pressor agents, may be useful to offset the hypotension which is associated with the induction of anesthesia with propofol.
Information for Patients
Risk of Drowsiness
Patients should be advised that performance of activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle, or hazardous machinery or signing legal documents may be impaired for some time after general anesthesia or sedation.
Effect of Anesthetic and Sedation Drugs on Early Brain Development
Studies conducted in young animals and children suggest repeated or prolonged use of general anesthetic or sedation drugs in children younger than 3 years may have negative effects on their developing brains. Discuss with parents and caregivers the benefits, risks, and timing and duration of surgery or procedures requiring anesthetic and sedation drugs (see WARNINGS, Pediatric Neurotoxicity).
Drug Interactions
The induction dose requirements of propofol may be reduced in patients with intramuscular or intravenous premedication, particularly with narcotics (e.g., morphine, meperidine, and fentanyl, etc.) and combinations of opioids and sedatives (e.g., benzodiazepines, barbiturates, chloral hydrate, droperidol, etc.). These agents may increase the anesthetic or sedative effects of propofol and may also result in more pronounced decreases in systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressures and cardiac output.
During maintenance of anesthesia or sedation, the rate of propofol administration should be adjusted according to the desired level of anesthesia or sedation and may be reduced in the presence of supplemental analgesic agents (e.g., nitrous oxide or opioids). The concurrent administration of potent inhalational agents (e.g., isoflurane, enflurane, and halothane) during maintenance with propofol has not been extensively evaluated. These inhalational agents can also be expected to increase the anesthetic or sedative and cardiorespiratory effects of propofol.
The concomitant use of valproate and propofol may lead to increased blood levels of propofol. Reduce the dose of propofol when co-administering with valproate. Monitor patients closely for signs of increased sedation or cardiorespiratory depression.
Propofol does not cause a clinically significant change in onset, intensity or duration of action of the commonly used neuromuscular blocking agents (e.g., succinylcholine and nondepolarizing muscle relaxants).
No significant adverse interactions with commonly used premedications or drugs used during anesthesia or sedation (including a range of muscle relaxants, inhalational agents, analgesic agents, and local anesthetic agents) have been observed in adults. In pediatric patients, administration of fentanyl concomitantly with propofol may result in serious bradycardia.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of propofol.
Mutagenesis: Propofol was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) using Salmonella typhimurium strains TA98, TA100, TA1535, TA1537 and TA1538. Propofol was not mutagenic in either the gene mutation/gene conversion test using Saccharomyces cerevisiae, or in vitro cytogenetic studies in Chinese hamsters. In the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay with Chinese hamsters propofol administration did not produce chromosome aberrations.
Impairment of Fertility: Female Wistar rats administered either 0, 10, or 15 mg/kg/day propofol intravenously from 2 weeks before pregnancy to day 7 of gestation did not show impaired fertility (0.65 and 1 times the human induction dose of 2.5 mg/kg based on body surface area). Male fertility in rats was not affected in a dominant lethal study at intravenous doses up to 15 mg/kg/day for 5 days.
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. In animal reproduction studies, decreased pup survival concurrent with increased maternal mortality was observed with intravenous administration of propofol to pregnant rats either prior to mating and during early gestation or during late gestation and early lactation at exposures less than the human induction dose of 2.5 mg/kg. In pregnant rats administered 15 mg/kg/day intravenous propofol (equivalent to the human induction dose) from two weeks prior to mating to early in gestation (Gestation Day 7), offspring that were allowed to mate had increased postimplantation losses. The pharmacological activity (anesthesia) of the drug on the mother is probably responsible for the adverse effects seen in the offspring.
Published studies in pregnant primates demonstrate that the administration of anesthetic and sedation drugs that block NMDA receptors and/or potentiate GABA activity during the period of peak brain development increases neuronal apoptosis in the developing brain of the offspring when used for longer than 3 hours. There are no data on pregnancy exposures in primates corresponding to periods prior to the third trimester in humans [See Data].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Pregnant rats were administered propofol intravenously at 0, 5, 10, and 15 mg/kg/day (0.3, 0.65, and 1 times the human induction dose of 2.5 mg/kg based on body surface area) during organogenesis (Gestational Days 6-15). Propofol did not cause adverse effects to the fetus at exposures up to 1 times the human induction dose despite evidence of maternal toxicity (decreased weight gain in all groups).
Pregnant rabbits were administered propofol intravenously at 0, 5, 10, and 15 mg/kg/day (0.65, 1.3, 2 times the human induction dose of 2.5 mg/kg based on body surface area comparison) during organogenesis (Gestation Days 6-18). Propofol treatment decreased total numbers of corpora lutea in all treatment groups but did not cause fetal malformations at any dose despite maternal toxicity (one maternal death from anesthesia-related respiratory depression in the high dose group).
Pregnant rats were administered propofol intravenously at 0, 10, and 15 mg/kg/day (0.65 and 1 times the human induction dose of 2.5 mg/kg based on body surface area) from late gestation through lactation (Gestation Day 16 to Lactation Day 22). Decreased pup survival was noted at all doses in the presence of maternal toxicity (deaths from anesthesia-induced respiratory depression). This study did not evaluate neurobehavioral function including learning and memory in the pups.
Pregnant rats were administered propofol intravenously at 0, 10, or 15 mg/kg/day (0.3 and 1 times the human induction dose of 2.5 mg/kg based on body surface area) from 2 weeks prior to mating to Gestational Day 7. Pup (F1) survival was decreased on Day 15 and 22 of lactation at maternally toxic doses of 10 and 15 mg/kg/day. When F1 offspring were allowed to mate, postimplantation losses were increased in the 15 mg/kg/day treatment group.
In a published study in primates, administration of an anesthetic dose of ketamine for 24 hours on Gestation Day 122 increased neuronal apoptosis in the developing brain of the fetus. In other published studies, administration of either isoflurane or propofol for 5 hours on Gestation Day 120 resulted in increased neuronal and oligodendrocyte apoptosis in the developing brain of the offspring. With respect to brain development, this time period corresponds to the third trimester of gestation in the human. The clinical significance of these findings is not clear; however, studies in juvenile animals suggest neuroapoptosis correlates with long-term cognitive deficits (see WARNINGS; Pediatric Neurotoxicity, PRECAUTIONS; Pediatric Use, and ANIMAL TOXICOLOGY AND/OR PHARMACOLOGY).
Labor and delivery
Propofol is not recommended for obstetrics, including cesarean section deliveries. Propofol crosses the placenta, and as with other general anesthetic agents, the administration of propofol may be associated with neonatal depression.
Nursing mothers
Propofol is not recommended for use in nursing mothers because propofol has been reported to be excreted in human milk and the effects of oral absorption of small amounts of propofol are not known.
Pediatric use
The safety and effectiveness of propofol have been established for induction of anesthesia in pediatric patients aged 3 years and older and for the maintenance of anesthesia aged 2 months and older.
Propofol is not recommended for the induction of anesthesia in patients younger than 3 years of age and for the maintenance of anesthesia in patients younger than 2 months of age as safety and effectiveness have not been established.
In pediatric patients, administration of fentanyl concomitantly with propofol may result in serious bradycardia (see PRECAUTIONS – General).
Propofol is not indicated for use in pediatric patients for ICU sedation or for MAC sedation for surgical, nonsurgical or diagnostic procedures as safety and effectiveness have not been established.
There have been anecdotal reports of serious adverse events and death in pediatric patients with upper respiratory tract infections receiving propofol for ICU sedation.
In one multicenter clinical trial of ICU sedation in critically ill pediatric patients that excluded patients with upper respiratory tract infections, the incidence of mortality observed in patients who received propofol (n=222) was 9%, while that for patients who received standard sedative agents (n=105) was 4%. While causality has not been established, propofol is not indicated for sedation in pediatric patients until further studies have been performed to document its safety in that population. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY – Pediatric Patients: and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
In pediatric patients, abrupt discontinuation following prolonged infusion may result in flushing of the hands and feet, agitation, tremulousness and hyperirritability. Increased incidences of bradycardia (5%), agitation (4%), and jitteriness (9%) have also been observed.
Published juvenile animal studies demonstrate that the administration of anesthetic and sedation drugs, such as propofol, that either block NMDA receptors or potentiate the activity of GABA during the period of rapid brain growth or synaptogenesis, results in widespread neuronal and oligodendrocyte cell loss in the developing brain and alterations in synaptic morphology and neurogenesis. Based on comparisons across species, the window of vulnerability to these changes is believed to correlate with exposures in the third trimester of gestation through the first several months of life, but may extend out to approximately 3 years of age in humans.
In primates, exposure to 3 hours of ketamine that produced a light surgical plane of anesthesia did not increase neuronal cell loss, however, treatment regimens of 5 hours or longer of isoflurane increased neuronal cell loss. Data from isoflurane-treated rodents and ketamine-treated primates suggest that the neuronal and oligodendrocyte cell losses are associated with prolonged cognitive deficits in learning and memory. The clinical significance of these nonclinical findings is not known, and healthcare providers should balance the benefits of appropriate anesthesia in pregnant women, neonates, and young children who require procedures with the potential risks suggested by the nonclinical data (see WARNINGS, Pediatric Neurotoxicity, Pregnancy, ANIMAL TOXICOLOGY AND/OR PHARMACOLOGY).
Benzyl alcohol, a component of this product, has been associated with serious adverse events and death, particularly in pediatric patients. The "gasping syndrome", (characterized by central nervous system depression, metabolic acidosis, gasping respirations, and high levels of benzyl alcohol and its metabolites found in the blood and urine) has been associated with benzyl alcohol dosages >99 mg/kg/day in neonates and low-birthweight neonates. Additional symptoms may include gradual neurological deterioration, seizures, intracranial hemorrhage, hematologic abnormalities, skin breakdown, hepatic and renal failure, hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiovascular collapse.
Although normal therapeutic doses of this product deliver amounts of benzyl alcohol that are substantially lower than those reported in association with the "gasping syndrome", the minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. Premature and low-birthweight infants, as well as patients receiving high dosages, may be more likely to develop toxicity. Practitioners administering this and other medications containing benzyl alcohol should consider the combined daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from all sources.
Geriatric use
The effect of age on induction dose requirements for propofol was assessed in an open-label study involving 211 unpremedicated patients with approximately 30 patients in each decade between the ages of 16 and 80. The average dose to induce anesthesia was calculated for patients up to 54 years of age and for patients 55 years of age or older. The average dose to induce anesthesia in patients up to 54 years of age was 1.99 mg/kg and in patients above 54 it was 1.66 mg/kg. Subsequent clinical studies have demonstrated lower dosing requirements for subjects greater than 60 years of age.
A lower induction dose and a slower maintenance rate of administration of propofol should be used in elderly patients. In this group of patients, rapid (single or repeated) bolus administration should not be used in order to minimize undesirable cardiorespiratory depression including hypotension, apnea, airway obstruction, and/or oxygen desaturation. All dosing should be titrated according to patient condition and response. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION – Elderly, Debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV Patients: and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY – Geriatrics.)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc. at 1-877-845-0689 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
General
Adverse event information is derived from controlled clinical trials and worldwide marketing experience. In the description below, rates of the more common events represent US/Canadian clinical study results. Less frequent events are also derived from publications and marketing experience in over 8 million patients; there are insufficient data to support an accurate estimate of their incidence rates. These studies were conducted using a variety of premedicants, varying lengths of surgical/diagnostic procedures, and various other anesthetic/sedative agents. Most adverse events were mild and transient.
Anesthesia and MAC Sedation in Adults
The following estimates of adverse events for propofol include data from clinical trials in general anesthesia/MAC sedation (N=2,889 adult patients). The adverse events listed below as probably causally related are those events in which the actual incidence rate in patients treated with propofol was greater than the comparator incidence rate in these trials. Therefore, incidence rates for anesthesia and MAC sedation in adults generally represent estimates of the percentage of clinical trial patients which appeared to have probable causal relationship.
The adverse experience profile from reports of 150 patients in the MAC sedation clinical trials is similar to the profile established with Propofol during anesthesia (see below). During MAC sedation clinical trials, significant respiratory events included cough, upper airway obstruction, apnea, hypoventilation, and dyspnea.
Anesthesia in Pediatric Patients
Generally the adverse experience profile from reports of 506 propofol pediatric patients from 6 days through 16 years of age in the US/Canadian anesthesia clinical trials is similar to the profile established with propofol during anesthesia in adults (see Pediatric percentages [Peds %] below). Although not reported as an adverse event in clinical trials, apnea is frequently observed in pediatric patients.
ICU Sedation in Adults
The following estimates of adverse events include data from clinical trials in ICU sedation (N=159 adult patients). Probably related incidence rates for ICU sedation were determined by individual case report form review. Probable causality was based upon an apparent dose response relationship and/or positive responses to rechallenge. In many instances the presence of concomitant disease and concomitant therapy made the causal relationship unknown. Therefore, incidence rates for ICU sedation generally represent estimates of the percentage of clinical trial patients which appeared to have a probable causal relationship.
| Anesthesia/MAC Sedation | ICU Sedation | |
| Cardiovascular: | Bradycardia | Bradycardia |
| Arrhythmia [Peds: 1.2%] | ||
| Tachycardia Nodal [Peds: 1.6%] | ||
| Hypotension* [Peds: 17%] (see also CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY) | Decreased Cardiac Output | |
| Hypertension [Peds: 8%] | Hypotension 26% | |
| Central Nervous System: | Movement* [Peds: 17%] | |
| Injection Site: | Burning/Stinging or Pain, 17.6% [Peds: 10%] | |
| Metabolic/Nutritional: | Hyperlipemia* | |
| Respiratory: | Apnea (see also CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY) | Respiratory Acidosis During Weaning* |
| Skin and Appendages: | Rash [Peds: 5%] | |
| Pruritus [Peds: 2%] |
Events without an * or % had an incidence of 1% to 3%
*Incidence of events 3% to 10%
| Anesthesia/MAC Sedation | ICU Sedation | |
| Body as a Whole: | Anaphylaxis/Anaphylactoid Reaction Perinatal Disorder Tachycardia Bigeminy Bradycardia Premature Ventricular Contractions Hemorrhage ECG Abnormal Arrhythmia Atrial Fever Extremities Pain Anticholinergic Syndrome | |
| Cardiovascular: | Premature Atrial Contractions Syncope | |
| Central Nervous System: | Hypertonia/Dystonia, Paresthesia | Agitation |
| Digestive: | Hypersalivation Nausea | |
| Hemic/Lymphatic: | Leukocytosis | |
| Injection Site: | Phlebitis Pruritus | |
| Metabolic: | Hypomagnesemia | |
| Musculoskeletal: | Myalgia | |
| Nervous: | Dizziness Agitation Chills Somnolence Delirium | |
| Respiratory: | Wheezing Cough Laryngospasm Hypoxia | Decreased Lung Function |
| Skin and Appendages: | Flushing, Pruritus | |
| Special Senses: | Amblyopia Vision Abnormal | |
| Urogenital: | Cloudy Urine | Green Urine |
|
Anesthesia/MAC Sedation |
ICU Sedation |
|
| Body as a Whole: | Asthenia, Awareness, Chest Pain, Extremities Pain, Fever, Increased Drug Effect, Neck Rigidity/Stiffness, Trunk Pain | Fever, Sepsis, Trunk Pain, Whole Body Weakness |
| Cardiovascular: | Arrhythmia, Atrial Fibrillation, Atrioventricular Heart Block, Bigeminy, Bleeding, Bundle Branch Block, Cardiac Arrest, ECG Abnormal, Edema, Extrasystole, Heart Block, Hypertension, Myocardial Infarction, Myocardial Ischemia, Premature Ventricular Contractions, ST Segment Depression, Supraventricular Tachycardia, Tachycardia, Ventricular Fibrillation | Arrhythmia, Atrial Fibrillation, Bigeminy, Cardiac Arrest, Extrasystole, Right Heart Failure, ventricular Tachycardia |
|
Central Nervous System: | Abnormal Dreams, Agitation, Amorous Behavior, Anxiety, Bucking/Jerking/Thrashing, Chills/Shivering/Clonic/Myoclonic Movement, Combativeness, Confusion, Delirium, Depression, Dizziness, Emotional Lability, Euphoria, Fatigue, Hallucinations, Headache, Hypotonia, Hysteria, Insomnia, Moaning, Neuropathy, Opisthotonos, Rigidity, Seizures, Somnolence, Tremor, Twitching |
Chills/Shivering, Intracranial Hypertension, Seizures, Somnolence, Thinking Abnormal |
| Digestive: | Cramping, Diarrhea, Dry Mouth, Enlarged Parotid, Nausea, Swallowing, Vomiting | Ileus, Liver Function Abnormal |
| Hematologic/Lymphatic: | Coagulation Disorder, Leukocytosis | |
| Injection Site: | Hives/Itching, Phlebitis, Redness/Discoloration | |
| Metabolic/Nutritional: | Hyperkalemia, Hyperlipemia | BUN Increased, Creatinine Increased, Dehydration, Hyperglycemia, Metabolic Acidosis, Osmolality Increased |
| Respiratory: | Bronchospasm, Burning in Throat, Cough, Dyspnea, Hiccough, Hyperventilation, Hypoventilation, Hypoxia, Laryngospasm, Pharyngitis, Sneezing, Tachypnea, Upper Airway Obstruction |
Hypoxia |
| Skin and Appendages: | Conjunctival Hyperemia, Diaphoresis, Urticaria | Rash |
| Special Senses: | Diplopia, Ear Pain, Eye Pain, Nystagmus, Taste Perversion, Tinnitus | |
| Urogenital: | Oliguria, Urine Retention | Kidney Failure |
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
There are reports of the abuse of propofol for recreational and other improper purposes, which have resulted in fatalities and other injuries. Instances of self-administration of propofol by healthcare professionals have also been reported, which have resulted in fatalities and other injuries. Inventories of propofol should be stored and managed to prevent the risk of diversion, including restriction of access and accounting procedures as appropriate to the clinical setting.
OVERDOSAGE
If overdosage occurs, propofol administration should be discontinued immediately. Overdosage is likely to cause cardiorespiratory depression. Respiratory depression should be treated by artificial ventilation with oxygen. Cardiovascular depression may require repositioning of the patient by raising the patient's legs, increasing the flow rate of intravenous fluids, and administering pressor agents and/or anticholinergic agents.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
NOTE: CONTAINS BENZYL ALCOHOL (see PRECAUTIONS section)
Propofol blood concentrations at steady state are generally proportional to infusion rates, especially in individual patients. Undesirable effects such as cardiorespiratory depression are likely to occur at higher blood concentrations which result from bolus dosing or rapid increases in the infusion rate. An adequate interval (3 minutes to 5 minutes) must be allowed between dose adjustments to allow for and assess the clinical effects.
Shake well before use. Do not use if there is evidence of excessive creaming or aggregation, if large droplets are visible, or if there are other forms of phase separation indicating that the stability of the product has been compromised. Slight creaming, which should disappear after shaking, may be visible upon prolonged standing.
When administering propofol by infusion, syringe or volumetric pumps are recommended to provide controlled infusion rates. When infusing propofol to patients undergoing magnetic resonance imaging, metered control devices may be utilized if mechanical pumps are impractical.
Changes in vital signs indicating a stress response to surgical stimulation or the emergence from anesthesia may be controlled by the administration of 25 mg (2.5 mL) to 50 mg (5 mL) incremental boluses and/or by increasing the infusion rate of propofol.
For minor surgical procedures (e.g., body surface) nitrous oxide (60% to 70%) can be combined with a variable rate propofol infusion to provide satisfactory anesthesia. With more stimulating surgical procedures (e.g., intra-abdominal), or if supplementation with nitrous oxide is not provided, administration rate(s) of propofol and/or opioids should be increased in order to provide adequate anesthesia.
Infusion rates should always be titrated downward in the absence of clinical signs of light anesthesia until a mild response to surgical stimulation is obtained in order to avoid administration of propofol at rates higher than are clinically necessary. Generally, rates of 50 mcg/kg/min to 100 mcg/kg/min in adults should be achieved during maintenance in order to optimize recovery times.
Other drugs that cause CNS depression (e.g., sedatives, anesthetics, and opioids) can increase CNS depression induced by propofol. Morphine premedication (0.15 mg/kg) with nitrous oxide 67% in oxygen has been shown to decrease the necessary propofol injection maintenance infusion rate and therapeutic blood concentrations when compared to non-narcotic (lorazepam) premedication.
Induction of General Anesthesia
Adult Patients:
Most adult patients under 55 years of age and classified as ASA-PS I or II require 2 mg/kg to 2.5 mg/kg of propofol for induction when unpremedicated or when premedicated with oral benzodiazepines or intramuscular opioids. For induction, propofol should be titrated (approximately 40 mg every 10 seconds) against the response of the patient until the clinical signs show the onset of anesthesia. As with other general anesthetics, the amount of intravenous opioid and/or benzodiazepine premedication will influence the response of the patient to an induction dose of propofol.
Elderly, Debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV Patients:
It is important to be familiar and experienced with the intravenous use of propofol before treating elderly, debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV patients. Due to the reduced clearance and higher blood concentrations, most of these patients require approximately 1 mg/kg to 1.5 mg/kg (approximately 20 mg every 10 seconds) of propofol for induction of anesthesia according to their condition and responses. A rapid bolus should not be used, as this will increase the likelihood of undesirable cardiorespiratory depression including hypotension, apnea, airway obstruction, and/or oxygen desaturation. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Pediatric Patients:
Most patients aged 3 years through 16 years and classified ASA-PS I or II require 2.5 mg/kg to 3.5 mg/kg of propofol for induction when unpremedicated or when lightly premedicated with oral benzodiazepines or intramuscular opioids. Within this dosage range, younger pediatric patients may require higher induction doses than older pediatric patients. As with other general anesthetics, the amount of intravenous opioid and/or benzodiazepine premedication will influence the response of the patient to an induction dose of propofol.
A lower dosage is recommended for pediatric patients classified as ASA-PS III or IV. Attention should be paid to minimize pain on injection when administering propofol to pediatric patients. Boluses of propofol may be administered via small veins if pretreated with lidocaine or via antecubital or larger veins. (See PRECAUTIONS - General.)
Neurosurgical Patients:
Slower induction is recommended using boluses of 20 mg every 10 seconds. Slower boluses or infusions of propofol for induction of anesthesia, titrated to clinical responses, will generally result in reduced induction dosage requirements (1 mg/kg to 2 mg/kg). (See PRECAUTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Cardiac Anesthesia:
Propofol has been well-studied in patients with coronary artery disease, but experience in patients with hemodynamically significant valvular or congenital heart disease is limited. As with other general anesthetics and sedation drugs, propofol in healthy patients causes a decrease in blood pressure that is secondary to decreases in preload (ventricular filling volume at the end of the diastole) and afterload (arterial resistance at the beginning of the systole). The magnitude of these changes is proportional to the blood and effect site concentrations achieved. These concentrations depend upon the dose and speed of the induction and maintenance infusion rates.
In addition, lower heart rates are observed during maintenance with propofol, possibly due to reduction of the sympathetic activity and/or resetting of the baroreceptor reflexes. Therefore, anticholinergic agents should be administered when increases in vagal tone are anticipated.
As with other anesthetic agents, propofol reduces myocardial oxygen consumption. Further studies are needed to confirm and delineate the extent of these effects on the myocardium and the coronary vascular system.
Morphine premedication (0.15 mg/kg) with nitrous oxide 67% in oxygen has been shown to decrease the necessary propofol maintenance infusion rates and therapeutic blood concentrations when compared to non-narcotic (lorazepam) premedication. The rate of propofol administration should be determined based on the patient's premedication and adjusted according to clinical responses.
A rapid bolus induction should be avoided. A slow rate of approximately 20 mg every 10 seconds until induction onset (0.5 mg/kg to 1.5 mg/kg) should be used. In order to assure adequate anesthesia, when propofol is used as the primary agent, maintenance infusion rates should not be less than 100 mcg/kg/min and should be supplemented with analgesic levels of continuous opioid administration. When an opioid is used as the primary agent, propofol maintenance rates should not be less than 50 mcg/kg/min, and care should be taken to ensure amnesia. Higher doses of propofol will reduce the opioid requirements (see TABLE 4. CARDIAC ANESTHESIA TECHNIQUES). When propofol is used as the primary anesthetic, it should not be administered with the high-dose opioid technique as this may increase the likelihood of hypotension. (See PRECAUTIONS - Cardiac Anesthesia: .)
| Primary Agent | Rate | Secondary Agent/Rate (Following Induction with Primary Agent) |
| PROPOFOL | OPIOIDa/0.05 mcg/kg/min to 0.075 mcg/kg/min (no bolus) |
|
| Preinduction Anxiolysis | 25 mcg/kg/min | |
| Induction | 0.5-1.5 mg/kg over 60 sec | |
| Maintenance (Titrated to Clinical Response) | 100 mcg/kg/min to 150 mcg/kg/min | |
| OPIOIDb | PROPOFOL/50 mcg/kg/min to 100 mcg/kg/min (no bolus) |
|
| Induction | 25 mcg/kg to 50 mcg/kg | |
| Maintenance | 0.2 mcg/kg/min to 0.3 mcg/kg/min |
aOPIOID is defined in terms of fentanyl equivalents, i.e.,
1 mcg of fentanyl
= 5 mcg of alfentanil (for bolus)
= 10 mcg of alfentanil (for maintenance)
or
= 0.1 mcg of sufentanil
bCare should be taken to ensure amnesia
Maintenance of General Anesthesia
Propofol has been used with a variety of agents commonly used in anesthesia such as atropine, scopolamine, glycopyrrolate, diazepam, depolarizing and nondepolarizing muscle relaxants, and opioid analgesics, as well as with inhalational and regional anesthetic agents.
In the elderly, debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV patients, rapid bolus doses should not be used, as this will increase cardiorespiratory effects including hypotension, apnea, airway obstruction, and oxygen desaturation.
Adult Patients:
In adults, anesthesia can be maintained by administering propofol by infusion or intermittent IV bolus injection. The patient's clinical response will determine the infusion rate or the amount and frequency of incremental injections.
Continuous Infusion:
Propofol 100 mcg/kg/min to 200 mcg/kg/min administered in a variable rate infusion with 60% to 70% nitrous oxide and oxygen provides anesthesia for patients undergoing general surgery. Maintenance by infusion of propofol should immediately follow the induction dose in order to provide satisfactory or continuous anesthesia during the induction phase. During this initial period following the induction dose, higher rates of infusion are generally required (150 mcg/kg/min to 200 mcg/kg/min) for the first 10 minutes to 15 minutes. Infusion rates should subsequently be decreased 30% to 50% during the first half-hour of maintenance. Generally, rates of 50 mcg/kg/min to 100 mcg/kg/min in adults should be achieved during maintenance in order to optimize recovery times.
Other drugs that cause CNS depression (e.g., sedatives, anesthetics, and opioids) can increase the CNS depression induced by propofol.
Intermittent Bolus:
Increments of propofol 25 mg (2.5 mL) to 50 mg (5 mL) may be administered with nitrous oxide in adult patients undergoing general surgery. The incremental boluses should be administered when changes in vital signs indicate a response to surgical stimulation or light anesthesia.
Pediatric Patients:
Propofol administered as a variable rate infusion supplemented with nitrous oxide 60% to 70% provides satisfactory anesthesia for most children 2 months of age or older, ASA-PS I or II, undergoing general anesthesia.
In general, for the pediatric population, maintenance by infusion of propofol at a rate of 200 mcg/kg/min to 300 mcg/kg/min should immediately follow the induction dose. Following the first half-hour of maintenance, infusion rates of 125 mcg/kg/min to 150 mcg/kg/min are typically needed. Propofol injectable emulsion should be titrated to achieve the desired clinical effect. Younger pediatric patients may require higher maintenance infusion rates than older pediatric patients. (See TABLE 2. PEDIATRIC MAINTENANCE OF ANESTHESIA, Clinical Trials.)
Monitored Anesthesia Care (MAC) Sedation
Adult Patients:
When propofol is administered for MAC sedation, rates of administration should be individualized and titrated to clinical response. In most patients, the rates of propofol injectable emulsion administration will be in the range of 25 mcg/kg/min to 75 mcg/kg/min.
During initiation of MAC sedation, slow infusion or slow injection techniques are preferable over rapid bolus administration. During maintenance of MAC sedation, a variable rate infusion is preferable over intermittent bolus dose administration. In the elderly, debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV patients, rapid (single or repeated) bolus dose administration should not be used for MAC sedation. (See WARNINGS.) A rapid bolus injection can result in undesirable cardiorespiratory depression including hypotension, apnea, airway obstruction, and oxygen desaturation.
Initiation of MAC Sedation:
For initiation of MAC sedation, either an infusion or a slow injection method may be utilized while closely monitoring cardiorespiratory function. With the infusion method, sedation may be initiated by infusing propofol injectable emulsion at 100 mcg/kg/min to 150 mcg/kg/min (6 mg/kg/h to 9 mg/kg/h) for a period of 3 minutes to 5 minutes and titrating to the desired clinical effect while closely monitoring respiratory function. With the slow injection method for initiation, patients will require approximately 0.5 mg/kg administered over 3 minutes to 5 minutes and titrated to clinical responses. When propofol is administered slowly over 3 minutes to 5 minutes, most patients will be adequately sedated, and the peak drug effect can be achieved while minimizing undesirable cardiorespiratory effects occurring at high plasma levels.
In the elderly, debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV patients, rapid (single or repeated) bolus dose administration should not be used for MAC sedation. (See WARNINGS.) The rate of administration should be over 3 minutes to 5 minutes and the dosage of propofol injectable emulsion should be reduced to approximately 80% of the usual adult dosage in these patients according to their condition, responses, and changes in vital signs. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Maintenance of MAC Sedation:
For maintenance of sedation, a variable rate infusion method is preferable over an intermittent bolus dose method. With the variable rate infusion method, patients will generally require maintenance rates of 25 mcg/kg/min to 75 mcg/kg/min (1.5 mg/kg/h to 4.5 mg/kg/h) during the first 10 minutes to 15 minutes of sedation maintenance. Infusion rates should subsequently be decreased over time to 25 mcg/kg/min to 50 mcg/kg/min and adjusted to clinical responses. In titrating to clinical effect, allow approximately 2 minutes for onset of peak drug effect.
Infusion rates should always be titrated downward in the absence of clinical signs of light sedation until mild responses to stimulation are obtained in order to avoid sedative administration of propofol at rates higher than are clinically necessary.
If the intermittent bolus dose method is used, increments of propofol injectable emulsion 10 mg (1 mL) or 20 mg (2 mL) can be administered and titrated to desired clinical effect. With the intermittent bolus method of sedation maintenance, there is increased potential for respiratory depression, transient increases in sedation depth, and prolongation of recovery.
In the elderly, debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV patients, rapid (single or repeated) bolus dose administration should not be used for MAC sedation. (See WARNINGS.) The rate of administration and the dosage of propofol should be reduced to approximately 80% of the usual adult dosage in these patients according to their condition, responses, and changes in vital signs. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Propofol can be administered as the sole agent for maintenance of MAC sedation during surgical/diagnostic procedures. When propofol sedation is supplemented with opioid and/or benzodiazepine medications, these agents increase the sedative and respiratory effects of propofol and may also result in a slower recovery profile. (See PRECAUTIONS - Drug interactions.)
ICU Sedation:
(See WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION - Handling Procedures.)
Abrupt discontinuation of propofol prior to weaning or for daily evaluation of sedation levels should be avoided. This may result in rapid awakening with associated anxiety, agitation, and resistance to mechanical ventilation. Infusions of propofol should be adjusted to assure a minimal level of sedation is maintained throughout the weaning process and when assessing the level of sedation. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Adult Patients:
For intubated, mechanically ventilated adult patients, Intensive Care Unit (ICU) sedation should be initiated slowly with a continuous infusion in order to titrate to desired clinical effect and minimize hypotension. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Most adult ICU patients recovering from the effects of general anesthesia or deep sedation will require maintenance rates of 5 mcg/kg/min to 50 mcg/kg/min (0.3 mg/kg/h to 3 mg/kg/h) individualized and titrated to clinical response. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.) With medical ICU patients or patients who have recovered from the effects of general anesthesia or deep sedation, the rate of administration of 50 mcg/kg/min or higher may be required to achieve adequate sedation. These higher rates of administration may increase the likelihood of patients developing hypotension. Administration should not exceed 4 mg/kg/hour unless the benefits outweight the risks. (See WARNINGS.)
Dosage and rate of administration should be individualized and titrated to the desired effect, according to clinically relevant factors including the patient’s underlying medical problems, preinduction and concomitant medications, age, ASA-PS classification, and level of debilitation of the patient. The elderly, debilitated, and ASA-PS III or IV patients may have exaggerated hemodynamic and respiratory responses to rapid bolus doses. (See WARNINGS.)
Propofol should be individualized according to the patient's condition and response, blood lipid profile, and vital signs. (See PRECAUTIONS - Intensive Care Unit Sedation.) For intubated, mechanically ventilated adult patients, Intensive Care Unit (ICU) sedation should be initiated slowly with a continuous infusion in order to titrate to desired clinical effect and minimize hypotension. When indicated, initiation of sedation should begin at 5 mcg/kg/min (0.3 mg/kg/h). The infusion rate should be increased by increments of 5 mcg/kg/min to 10 mcg/kg/min (0.3 mg/kg/h to 0.6 mg/kg/h) until the desired level of sedation is achieved. A minimum period of 5 minutes between adjustments should be allowed for onset of peak drug effect. Most adult patients require maintenance rates of 5 mcg/kg/min to 50 mcg/kg/min (0.3 mg/kg/h to 3 mg/kg/h) or higher. Administration should not exceed 4 mg/kg/hour unless the benefits outweigh the risks (see WARNINGS). Dosages of propofol should be reduced in patients who have received large dosages of narcotics. The propofol dosage requirement may also be reduced by adequate management of pain with analgesic agents. As with other sedative medications, there is interpatient variability in dosage requirements, and these requirements may change with time. (See SUMMARY OF DOSAGE GUIDELINES.) Evaluation of level of sedation and assessment of CNS function should be carried out daily throughout maintenance to determine the minimum dose of propofol required for sedation (see Clinical Trials - Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Sedation). Bolus administration of 10 mg or 20 mg should only be used to rapidly increase depth of sedation in patients where hypotension is not likely to occur. Patients with compromised myocardial function, intravascular volume depletion, or abnormally low vascular tone (e.g., sepsis) may be more susceptible to hypotension. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
SUMMARY OF DOSAGE GUIDELINES
Dosages and rates of administration in the following table should be individualized and titrated to clinical response. Safety and dosing requirements for induction of anesthesia in pediatric patients have only been established for children 3 years of age or older. Safety and dosing requirements for the maintenance of anesthesia have only been established for children 2 months of age and older.
For complete dosage information, see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.
| INDICATION | DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION |
|
Induction of General Anesthesia: |
Healthy Adults Less Than 55 Years of Age:
Elderly, Debilitated, or ASA-PS III or IV Patients:
Cardiac Anesthesia:
Neurosurgical Patients:
Pediatric Patients - healthy, from 3 years to 16 years of age: (see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric use and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pediatrics:) |
|
Maintenance of General Anesthesia: |
Infusion
Healthy Adults Less Than 55 Years of Age:
Elderly, Debilitated, ASA-PS III or IV Patients:
Cardiac Anesthesia: Most patients require: Low-Dose Propofol with Primary Opioid – 50mcg/kg/min to 100 mcg/kg/min. (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Table 4)
Neurosurgical Patients:
Pediatric Patients - healthy, from 2 months of age to 16 years of age: (see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric use and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pediatrics) |
| Maintenance of General Anesthesia: |
Intermittent Bolus
Healthy Adults Less Than 55 Years of Age: |
| Initiation of MAC Sedation: |
Healthy Adults Less Than 55 Years of Age:
Elderly, Debilitated, Neurosurgical, or ASA-PS III or IV Patients: |
| Maintenance of MAC Sedation: |
Healthy Adults Less Than 55 Years of Age:
In Elderly, Debilitated, Neurosurgical, or ASA-PS III or IV Patients: |
| Initiation and Maintenance of ICU Sedation in Intubated, Mechanically Ventilated Adult Patients: |
Adult Patients - Because of the residual effects of previous anesthetic or sedative agents, in most patients the initial infusion should be 5 mcg/kg/min (0.3 mg/kg/h) for at least 5 minutes. Subsequent increments of 5 mcg/kg/min to 10 mcg/kg/min (0.3mg/kg/k to 0.6 mg/kg/h) over 5 minutes to 10 minutes may be used until desired clinical effect is achieved. Maintenance rates of 5 mcg/kg/min to 50 mcg/kg/min (0.3 mg/kg/h to 3 mg/kg/h) or higher may be required. Administration should not exceed 4 mg/kg/hour unless the benefits outweigh the risks (see WARNINGS). Evaluation of clinical effect and assessment of CNS function should be carried out daily throughout maintenance to determine the minimum dose of Propofol required for sedation. The tubing and any unused Propofol drug product should be discarded after 12 hours because Propofol contains no preservatives and is capable of supporting growth of microorganisms (see WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). |
Administration with Lidocaine: If lidocaine is to be administered to minimize pain on injection of propofol injectable emulsion, it is recommended that it be administered prior to propofol injectable emulsion administration or that it be added to propofol injectable emulsion immediately before administration and in quantities not exceeding 20 mg lidocaine/200 mg propofol injectable emulsion.
Compatibility and Stability: Propofol injectable emulsion should not be mixed with other therapeutic agents prior to administration.
Dilution Prior to Administration: Propofol injectable emulsion is provided as a ready-to-use formulation. However, should dilution be necessary, it should only be diluted with 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, and it should not be diluted to a concentration less than 2 mg/mL because it is an emulsion. In diluted form it has been shown to be more stable when in contact with glass than with plastic (95% potency after 2 hours of running infusion in plastic).
Administration with Other Fluids: Compatibility of propofol injectable emulsion with the coadministration of blood/serum/plasma has not been established. (See WARNINGS.) When administered using a y-type infusion set, propofol injectable emulsion has been shown to be compatible with the following intravenous fluids.
- 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
- Lactated Ringers Injection, USP
- Lactated Ringers and 5% Dextrose Injection
- 5% Dextrose and 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose and 0.2% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
Handling Procedures
General
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
Clinical experience with the use of in-line filters and propofol during anesthesia or ICU/MAC sedation is limited. Propofol should only be administered through a filter with a pore size of 5 micron or greater unless it has been demonstrated that the filter does not restrict the flow of propofol and/or cause the breakdown of the emulsion. Filters should be used with caution and where clinically appropriate. Continuous monitoring is necessary due to the potential for restricted flow and/or breakdown of the emulsion.
Do not use if there is evidence of separation of the phases of the emulsion.
Rare cases of self-administration of propofol by health care professionals have been reported, including some fatalities. (See DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE.)
Strict aseptic technique must always be maintained during handling. Propofol injectable emulsion is a single-access parenteral product (single patient infusion vial) which contains benzyl alcohol to inhibit the rate of growth of microorganisms, up to 12 hours, in the event of accidental extrinsic contamination. However, propofol injectable emulsion can still support the growth of microorganisms as it is not an antimicrobially preserved product under USP standards. Accordingly, strict aseptic technique must still be adhered to. Do not use if contamination is suspected. Discard unused drug product as directed within the required time limits (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION - Handling Procedures). There have been reports in which failure to use aseptic technique when handling propofol injectable emulsion was associated with microbial contamination of the product and with fever, infection/sepsis, other life-threatening illness, and/or death.
There have been reports, in the literature and other public sources, of the transmission of bloodborne pathogens (such as Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, and HIV) from unsafe injection practices, and use of propofol vials intended for single use on multiple persons. Propofol injectable emulsion vial is never to be accessed more than once or used on more than one person.
Guidelines for Aseptic Technique for General Anesthesia/MAC Sedation
Propofol must be prepared for use just prior to initiation of each individual anesthetic/sedative procedure. The vial rubber stopper should be disinfected using 70% isopropyl alcohol. Propofol should be drawn into a sterile syringe immediately after a vial is opened. When withdrawing propofol from vials, a sterile vent spike should be used. The syringe(s) should be labeled with appropriate information including the date and time the vial was opened. Administration should commence promptly and be completed within 12 hours after the vial has been opened.
Propofol must be prepared for single-patient use only. Any unused propofol drug product, reservoirs, dedicated administration tubing and/or solutions containing propofol must be discarded at the end of the anesthetic procedure or at 12 hours, whichever occurs sooner. The IV line should be flushed every 12 hours and at the end of the anesthetic procedure to remove residual propofol.
Guidelines for Aseptic Technique for ICU Sedation
Propofol must be prepared for single-patient use only. Strict aseptic techniques must be followed. The vial rubber stopper should be disinfected using 70% isopropyl alcohol. A sterile vent spike and sterile tubing must be used for administration of propofol. As with other lipid emulsions, the number of IV line manipulations should be minimized. Administration should commence promptly and must be completed within 12 hours after the vial has been spiked. The tubing and any unused propofol drug product must be discarded after 12 hours.
If propofol is transferred to a syringe prior to administration, it should be drawn into a sterile syringe immediately after a vial is opened. When withdrawing propofol from a vial, a sterile vent spike should be used. The syringe should be labeled with appropriate information including the date and time the vial was opened. Administration should commence promptly and be completed within 12 hours after the vial has been opened. Propofol injectable emulsion should be discarded and administration lines changed after 12 hours.
HOW SUPPLIED
Propofol Injectable Emulsion, USP Vials containing 10 mg/mL of propofol, is available as follows:
20 mL single dose vial in cartons of 10. NDC 72572-583-10.
50 mL single-patient infusion vial in cartons of 20. NDC 72572-584-20.
100 mL single-patient infusion vial in cartons of 10. NDC 72572-585-10.
Propofol undergoes oxidative degradation, in the presence of oxygen, and is therefore packaged under nitrogen to eliminate this degradation path.
Store between 4° to 25°C (40° to 77°F). DO NOT FREEZE. Shake well before use.
ANIMAL TOXICOLOGY AND/OR PHARMACOLOGY
Published studies in animals demonstrate that the use of anesthetic agents during the period of rapid brain growth or synaptogenesis results in widespread neuronal and oligodendrocyte cell loss in the developing brain and alterations in synaptic morphology and neurogenesis. Based on comparisons across species, the window of vulnerability to these changes is believed to correlate with exposures in the third trimester through the first several months of life, but may extend out to approximately 3 years of age in humans.
In primates, exposure to 3 hours of an anesthetic regimen that produced a light surgical plane of anesthesia did not increase neuronal cell loss, however, treatment regimens of 5 hours or longer increased neuronal cell loss. Data in rodents and in primates suggest that the neuronal and oligodendrocyte cell losses are associated with subtle but prolonged cognitive deficits in learning and memory. The clinical significance of these nonclinical findings is not known, and healthcare providers should balance the benefits of appropriate anesthesia in neonates and young children who require procedures against the potential risks suggested by the nonclinical data (see WARNINGS, Pediatric Neurotoxicity, PRECAUTIONS; Pregnancy, Pediatric Use).
Mfd for: Civica, Inc.
Lehi, Utah 84043
Mfd by: Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
Cherry Hill, New Jersey 08003
Revised: May 2020
462-874-00
Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 72572-583-01 Rx Only
Propofol
Injectable Emulsion, USP
200 mg per 20 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Intravenous Administration
Contains Benzyl Alcohol
20 mL – For Single Patient Use Only
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING

NDC 72572-583-10 Rx Only
Propofol
Injectable Emulsion, USP
200 mg per 20 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Intravenous Administration
Contains Benzyl Alcohol
For Single Patient Use Only
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING
10 x 20 mL Vials

Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 72572-584-01 Rx Only
Propofol
Injectable Emulsion, USP
500 mg per 50 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Intravenous Administration
Contains Benzyl Alcohol
50 mL – For Single Patient Use Only
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING
NDC 72525-584-20 Rx Only
Propofol
Injectable Emulsion, USP
500 mg per 50 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Intravenous Administration
Contains Benzyl Alcohol
For Single Patient Use Only
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING
20 x 50 mL Vials
Package/Label Display Panel
NDC 72572-585-01 Rx Only
Propofol
Injectable Emulsion, USP
1 gram per 100 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Intravenous Administration
Contains Benzyl Alcohol
100 mL – For Single Patient Use Only
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING

NDC 72572-585-10 Rx Only
Propofol
Injectable Emulsion, USP
1 gram per 100 mL
(10 mg per mL)
For Intravenous Administration
Contains Benzyl Alcohol
For Single Patient Use Only
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING
10 x 100 mL Vials
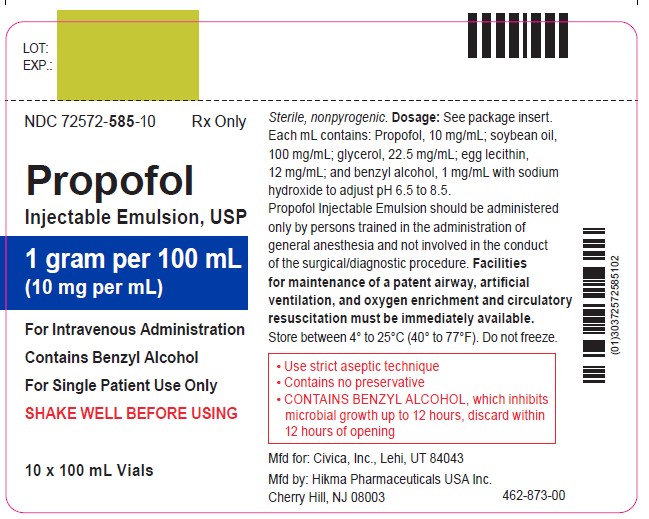
| PROPOFOL
propofol injection, emulsion |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| PROPOFOL
propofol injection, emulsion |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| PROPOFOL
propofol injection, emulsion |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Civica, Inc. (081373942) |
| Registrant - Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc. (946499746) |
