Label: SUCRALFATE tablet
-
Contains inactivated NDC Code(s)
NDC Code(s): 43353-061-60, 43353-061-70, 43353-061-94 - Packager: Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 0591-0780
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated May 2, 2014
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
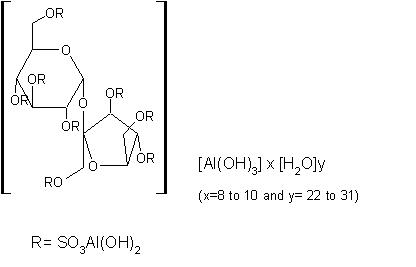
- DESCRIPTION
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Sucralfate is only minimally absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The small amounts of the sulfated disaccharide that are absorbed are excreted primarily in the urine.
Although the mechanism of sucralfate’s ability to accelerate healing of duodenal ulcers remains to be fully defined, it is known that it exerts its effect through a local, rather than systemic, action. The following observations also appear pertinent:
- Studies in human subjects and with animal models of ulcer disease have shown that sucralfate forms an ulcer-adherent complex with proteinaceous exudate at the ulcer site.
- In vitro, a sucralfate-albumin film provides a barrier to diffusion of hydrogen ions.
- In human subjects, sucralfate given in doses recommended for ulcer therapy inhibits pepsin activity in gastric juice by 32%.
- In vitro, sucralfate adsorbs bile salts.
These observations suggest that sucralfate’s antiulcer activity is the result of formation of an ulcer-adherent complex that covers the ulcer site and protects it against further attack by acid, pepsin, and bile salts. There are approximately 14-16 mEq of acid-neutralizing capacity per 1-g dose of sucralfate.
-
CLINICAL TRIALS
Acute Duodenal Ulcer
Over 600 patients have participated in well-controlled clinical trials worldwide. Multicenter trials conducted in the United States, both of them placebo-controlled studies with endoscopic evaluation at 2 and 4 weeks,showed:
STUDY 1 Treatment Groups Ulcer Healing/ No. Patients 2 wk 4 wk (Overall) Sucralfate 37/105 (35.2%) 82/109 (75.2%) Placebo 26/106 (24.5%) 68/107 (63.6%)
STUDY 2 Treatment Groups Ulcer Healing/ No. Patients 2 wk 4 wk (Overall) Sucralfate 8/24 (33%) 22/24 (92%) Placebo 4/31 (13%) 18/31 (58%) The sucralfate-placebo differences were statistically significant in both studies at 4 weeks but not at 2 weeks. The poorer result in the first study may have occurred because sucralfate was given 2 hours after meals and at bedtime rather than 1 hour before meals and at bedtime, the regimen used in international studies and in the second United States study. In addition, in the first study liquid antacid was utilized as needed, whereas in the second study antacid tablets were used.
Maintenance Therapy After Healing of Duodenal Ulcer
Two double-blind randomized placebo-controlled U.S. multicenter trials have demonstrated that sucralfate (1 g bid) is effective as maintenance therapy following healing of duodenal ulcers.
In one study, endoscopies were performed monthly for 4 months. Of the 254 patients who enrolled, 239 were analyzed in the intention-to-treat life table analysis presented below.
Duodenal Ulcer Recurrence Rate (%) Drug Months of Therapy n 1 2 3 4 Sucralfate 122 20* 30* 38† 42† Placebo 117 33 46 55 63 In this study, prn antacids were not permitted.
In the other study, scheduled endoscopies were performed at 6 and 12 months, but for-cause endoscopies were permitted as symptoms dictated. Median symptom scores between the sucralfate and placebo groups were not significantly different. A life table intention-to-treat analysis for the 94 patients enrolled in the trial had the following results:
- *
- P<0.002
Duodenal Ulcer Recurrence Rate (%) Drug n 6 Months 12 Months Sucralfate 48 19* 27* Placebo 46 54 65 In this study, prn antacids were permitted.
Data from placebo-controlled studies longer than 1 year are not available.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Sucralfate is indicated in:
- Short-term treatment (up to 8 weeks) of active duodenal ulcer. While healing with sucralfate may occur during the first week or two, treatment should be continued for 4 to 8 weeks unless healing has been demonstrated by x-ray or endoscopic examination.
- Maintenance therapy for duodenal ulcer patients at reduced dosage after healing of acute ulcers.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
PRECAUTIONS
Duodenal ulcer is a chronic, recurrent disease. While short-term treatment with sucralfate can result in complete healing of the ulcer, a successful course of treatment with sucralfate should not be expected to alter the posthealing frequency or severity of duodenal ulceration.
Special Populations: Chronic Renal Failure and Dialysis Patients
When sucralfate is administered orally, small amounts of aluminum are absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Concomitant use of sucralfate with other products that contain aluminum, such as aluminum-containing antacids, may increase the total body burden of aluminum. Patients with normal renal function receiving the recommended doses of sucralfate and aluminum-containing products adequately excrete aluminum in the urine. Patients with chronic renal failure or those receiving dialysis have impaired excretion of absorbed aluminum. In addition, aluminum does not cross dialysis membranes because it is bound to albumin and transferrin plasma proteins. Aluminum accumulation and toxicity (aluminum osteodystrophy, osteomalacia, encephalopathy) have been described in patients with renal impairment. Sucralfate should be used with caution in patients with chronic renal failure.
Drug Interactions
Some studies have shown that simultaneous sucralfate administration in healthy volunteers reduced the extent of absorption (bioavailability) of single doses of the following: cimetidine, digoxin, fluoroquinolone antibiotics, ketoconazole, l-thyroxine, phenytoin, quinidine, ranitidine, tetracycline, and theophylline. Subtherapeutic prothrombin times with concomitant warfarin and sucralfate therapy have been reported in spontaneous and published case reports. However, two clinical studies have demonstrated no change in either serum warfarin concentration or prothrombin time with the addition of sucralfate to chronic warfarin therapy.
The mechanism of these interactions appears to be nonsystemic in nature, presumably resulting from sucralfate binding to the concomitant agent in the gastrointestinal tract. In all cases studied to date (cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, digoxin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and ranitidine), dosing the concomitant medication 2 hours before sucralfate eliminated the interaction. Because of the potential of sucralfate to alter the absorption of some drugs, sucralfate should be administered separately from other drugs when alterations in bioavailability are felt to be critical. In these cases, patients should be monitored appropriately.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Chronic oral toxicity studies of 24 months’ duration were conducted in mice and rats at doses up to 1 g/kg (12 times the human dose).
There was no evidence of drug-related tumorigenicity. A reproduction study in rats at doses up to 38 times the human dose did not reveal any indication of fertility impairment. Mutagenicity studies were not conducted.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects. Pregnancy Category B.
Teratogenicity studies have been performed in mice, rats, and rabbits at doses up to 50 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to sucralfate. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions to sucralfate in clinical trials were minor and only rarely led to discontinuation of the drug. In studies involving over 2700 patients treated with sucralfate tablets, adverse effects were reported in 129 (4.7%).
Constipation was the most frequent complaint (2%). Other adverse effects reported in less than 0.5% of the patients are listed below by body system:
Gastrointestinal: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, gastric discomfort, indigestion, flatulence, dry mouth
Dermatological: pruritus, rash
Nervous System: dizziness, insomnia, sleepiness, vertigo
Other: back pain, headache
Postmarketing reports of hypersensitivity reactions, including urticaria (hives), angioedema, respiratory difficulty, rhinitis, laryngospasm, and facial swelling have been reported in patients receiving sucralfate tablets. Similar events were reported with sucralfate suspension. However, a causal relationship has not been established.
Bezoars have been reported in patients treated with sucralfate. The majority of patients had underlying medical conditions that may predispose to bezoar formation (such as delayed gastric emptying) or were receiving concomitant enteral tube feedings.
Inadvertent injection of insoluble sucralfate and its insoluble excipients has led to fatal complications, including pulmonary and cerebral emboli. Sucralfate is not intended for intravenous administration.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Due to limited experience in humans with overdosage of sucralfate, no specific treatment recommendations can be given. Acute oral toxicity studies in animals, however, using doses up to 12 g/kg body weight, could not find a lethal dose. Sucralfate is only minimally absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Risks associated with acute overdosage should, therefore, be minimal. In rare reports describing sucralfate overdose, most patients remained asymptomatic. Those few reports where adverse events were described included symptoms of dyspepsia, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Active Duodenal Ulcer. The recommended adult oral dosage for duodenal ulcer is 1 g four times a day on an empty stomach.
Antacids may be prescribed as needed for relief of pain but should not be taken within one-half hour before or after sucralfate.
While healing with sucralfate may occur during the first week or two, treatment should be continued for 4 to 8 weeks unless healing has been demonstrated by x-ray or endoscopic examination.
Maintenance Therapy. The recommended adult oral dosage is 1 g twice a day.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Repackaged by Aphena Pharma Solutions - TN.
See Repackaging Information for available configurations.
Sucralfate 1-g tablets are supplied in bottles of 90, 100, 360 and 500.
Light blue, scored, oblong tablets are engraved WATSON 780 on one side and are blank with bisect on the other.
Prescribing Information as of June 2008AManufactured for:
Watson Laboratories, Inc.
Corona, CA 92880 USA
Manufactured by:
sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC
Kansas City, MO 64137 USA50088983
-
Repackaging Information
Please reference the How Supplied section listed above for a description of individual tablets or capsules. This drug product has been received by Aphena Pharma - TN in a manufacturer or distributor packaged configuration and repackaged in full compliance with all applicable cGMP regulations. The package configurations available from Aphena are listed below:
Count 1Gm 90 43353-061-60 120 43353-061-70 360 43353-061-94 Store between 20°-25°C (68°-77°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature. Dispense in a tight light-resistant container as defined by USP. Keep this and all drugs out of the reach of children.
Repackaged by:

Cookeville, TN 38506
20140502SC - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1Gm
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SUCRALFATE
sucralfate tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:43353-061(NDC:0591-0780) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SUCRALFATE (UNII: XX73205DH5) (SUCRALFATE - UNII:XX73205DH5) SUCRALFATE 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color BLUE (Light blue) Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL (Oblong) Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code WATSON;780 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:43353-061-60 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 2 NDC:43353-061-70 120 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 3 NDC:43353-061-94 360 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA018333 11/01/1996 Labeler - Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC (128385585) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC 128385585 Repack(43353-061)