VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE - vancomycin hydrochloride capsule
Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Vancomycin Hydrochloride Capsules, USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Vancomycin Hydrochloride Capsules, USP.
Vancomycin Hydrochloride Capsules, USP Initial U.S. Approval: 1986 To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of vancomycin hydrochloride capsules and other antibacterial drugs, vancomycin hydrochloride capsules should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. RECENT MAJOR CHANGESDosage and Administration (12/2011) Warnings and Precautions (12/2011) INDICATIONS AND USAGEDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
CONTRAINDICATIONSHypersensitivity to vancomycin (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSThe most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) were nausea (17%), abdominal pain (15%), and hypokalemia (13%). (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC, Medical Affairs at 1-800-551-7176 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONSNo drug interaction studies have been conducted. (7) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 5/2018 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Vancomycin Hydrochloride Capsules, USP are indicated for the treatment of C. difficile-associated diarrhea. Vancomycin hydrochloride capsules, USP are also used for the treatment of enterocolitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant strains). Parenteral administration of vancomycin is not effective for the above infections; therefore, vancomycin hydrochloride, USP must be given orally for these infections.
Orally administered vancomycin hydrochloride is not effective for other types of infections.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of vancomycin hydrochloride, USP and other antibacterial drugs, vancomycin hydrochloride, USP should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adults
Vancomycin hydrochloride capsules are used in treating C. difficile-associated diarrhea and staphylococcal enterocolitis.
- C. difficile-associated diarrhea: The recommended dose is 125 mg administered orally 4 times daily for 10 days.
- Staphylococcal enterocolitis: Total daily dosage is 500 mg to 2 g administered orally in 3 or 4 divided doses for 7 to 10 days.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Vancomycin hydrochloride 125 mg* capsules have a grey cap and opaque light-grey body imprinted with “VANCO” on the cap and “125 mg” on the body in black ink.
Vancomycin hydrochloride 250 mg* capsules have a green cap and turquoise body imprinted with “VANCO” on the cap and “250 mg” on the body in white ink.
*Equivalent to vancomycin.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Vancomycin hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to vancomycin.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Oral Use Only
This preparation for the treatment of colitis is for oral use only and is not systemically absorbed. Vancomycin hydrochloride capsules must be given orally for treatment of staphylococcal enterocolitis and Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. Orally administered vancomycin hydrochloride capsules are not effective for other types of infections.
Parenteral administration of vancomycin is not effective for treatment of staphylococcal enterocolitis and C. difficile-associated diarrhea. If parenteral vancomycin therapy is desired, use an intravenous preparation of vancomycin and consult the package insert accompanying that preparation.
5.2 Potential for Systemic Absorption
Clinically significant serum concentrations have been reported in some patients who have taken multiple oral doses of vancomycin for active C. difficile-associated diarrhea. Some patients with inflammatory disorders of the intestinal mucosa also may have significant systemic absorption of vancomycin. These patients may be at risk for the development of adverse reactions associated with higher doses of vancomycin; therefore, monitoring of serum concentrations of vancomycin may be appropriate in some instances, e.g., in patients with renal insufficiency and/or colitis or in those receiving concomitant therapy with an aminoglycoside antibiotic.
5.3 Nephrotoxicity
Nephrotoxicity (e.g., reports of renal failure, renal impairment, blood creatinine increased) has occurred following oral vancomycin hydrochloride therapy in randomized controlled clinical studies, and can occur either during or after completion of therapy.
The risk of nephrotoxicity is increased in patients >65 years of age [see Adverse Reactions, Clinical Trial Experience (6.1) and Use In Specific Populations, Geriatric Use (8.5)].
In patients >65 years of age, including those with normal renal function prior to treatment, renal function should be monitored during and following treatment with vancomycin hydrochloride to detect potential vancomycin induced nephrotoxicity.
5.4 Ototoxicity
Ototoxicity has occurred in patients receiving vancomycin. It may be transient or permanent. It has been reported mostly in patients who have been given excessive intravenous doses, who have an underlying hearing loss, or who are receiving concomitant therapy with another ototoxic agent, such as an aminoglycoside. Serial tests of auditory function may be helpful in order to minimize the risk of ototoxicity [see Adverse Reactions, Postmarketing Experience (6.2)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to vancomycin hydrochloride in 260 adult subjects in two Phase 3 clinical trials for the treatment of diarrhea associated with C. difficile. In both trials, subjects received vancomycin hydrochloride 125 mg orally four times daily. The mean duration of treatment was 9.4 days. The median age of patients was 67, ranging between 19 and 96 years of age. Patients were predominantly Caucasian (93%) and 52% were male.
Adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 5% of vancomycin hydrochloride-treated subjects are shown in Table 1. The most common adverse reactions associated with vancomycin hydrochloride (≥ 10%) were nausea, abdominal pain, and hypokalemia.
Table 1: Common (≥ 5%) Adverse Reactionsa for Vancomycin Hydrochloride Reported in Clinical Trials for Treatment of Diarrhea Associated with C. difficile
| System / Organ Class
| Adverse Reaction
| Vancomycin Hydrochloride % (N=260)
|
| Gastrointestinal disorders
| Nausea Abdominal pain Vomiting Diarrhea Flatulence | 17 15 9 9 8 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions
| Pyrexia Edema peripheral Fatigue | 9 6 5 |
| Infections and infestations
| Urinary tract infection | 8 |
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders
| Hypokalemia | 13 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
| Back pain | 6 |
| Nervous system disorders
| Headache | 7 |
| a Adverse reaction rates were derived from the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events. |
||
Nephrotoxicity (e.g., reports of renal failure, renal impairment, blood creatinine increased) occurred in 5% of subjects treated with vancomycin hydrochloride. Nephrotoxicity following vancomycin hydrochloride typically first occurred within one week after completion of treatment (median day of onset was Day 16). Nephrotoxicity following vancomycin hydrochloride occurred in 6% of subjects >65 years of age and 3% of subjects ≤65 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions, Nephrotoxicity (5.3)].
The incidences of hypokalemia, urinary tract infection, peripheral edema, insomnia, constipation, anemia, depression, vomiting, and hypotension were higher among subjects >65 years of age than in subjects ≤65 years of age [see Use In Specific Populations, Geriatric Use (8.5)].
Discontinuation of study drug due to adverse events occurred in 7% of subjects treated with vancomycin hydrochloride. The most common adverse events leading to discontinuation of vancomycin hydrochloride were C. difficile colitis (<1%), nausea (<1%), and vomiting (<1%).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of vancomycin hydrochloride. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Ototoxicity: Cases of hearing loss associated with intravenously administered vancomycin have been reported. Most of these patients had kidney dysfunction or a pre-existing hearing loss or were receiving concomitant treatment with an ototoxic drug [see Warnings and Precautions, Ototoxicity (5.4)]. Vertigo, dizziness, and tinnitus have been reported.
Hematopoietic: Reversible neutropenia, usually starting 1 week or more after onset of intravenous therapy with vancomycin or after a total dose of more than 25 g, has been reported for several dozen patients. Neutropenia appears to be promptly reversible when vancomycin is discontinued. Thrombocytopenia has been reported.
Miscellaneous: Patients have been reported to have had anaphylaxis, drug fever, chills, nausea, eosinophilia, rashes (including exfoliative dermatitis), Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and rare cases of vasculitis in association with the administration of vancomycin.
A condition has been reported that is similar to the IV-induced syndrome with symptoms consistent with anaphylactoid reactions, including hypotension, wheezing, dyspnea, urticaria, pruritus, flushing of the upper body (“Red Man Syndrome”), pain and muscle spasm of the chest and back. These reactions usually resolve within 20 minutes but may persist for several hours.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B – The highest doses of vancomycin tested were not teratogenic in rats given up to 200 mg/kg/day IV (1180 mg/m2 or 1 times the recommended maximum human dose based on body surface area) or in rabbits given up to 120 mg/kg/day IV (1320 mg/m2 or 1.1 times the recommended maximum human dose based on body surface area). No effects on fetal weight or development were seen in rats at the highest dose tested or in rabbits given 80 mg/kg/day (880 mg/m2 or 0.74 times the recommended maximum human dose based on body surface area).
In a controlled clinical study, the potential ototoxic and nephrotoxic effects of vancomycin on infants were evaluated when the drug was administered intravenously to pregnant women for serious staphylococcal infections complicating intravenous drug abuse. Vancomycin was found in cord blood. No sensorineural hearing loss or nephrotoxicity attributable to vancomycin was noted. One infant whose mother received vancomycin in the third trimester experienced conductive hearing loss that was not attributed to the administration of vancomycin. Because the number of subjects treated in this study was limited and vancomycin was administered only in the second and third trimesters, it is not known whether vancomycin causes fetal harm. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, vancomycin hydrochloride should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Vancomycin is excreted in human milk based on information obtained with the intravenous administration of vancomycin. However, systemic absorption of vancomycin is very low following oral administration of vancomycin hydrochloride [see Clinical Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. It is not known whether vancomycin is excreted in human milk, as no studies of vancomycin concentration in human milk after oral administration have been done. Caution should be exercised when vancomycin hydrochloride is administered to a nursing woman. Because of the potential for adverse events, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In clinical trials, 54% of vancomycin hydrochloride-treated subjects were >65 years of age. Of these, 40% were between the ages of >65 and 75, and 60% were >75 years of age.
Clinical studies with vancomycin hydrochloride in diarrhea associated with Clostridium difficile have demonstrated that geriatric subjects are at increased risk of developing nephrotoxicity following treatment with oral vancomycin hydrochloride, which may occur during or after completion of therapy. In patients >65 years of age, including those with normal renal function prior to treatment, renal function should be monitored during and following treatment with vancomycin hydrochloride to detect potential vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions, Nephrotoxicity (5.3); Adverse Reactions, Clinical Trial Experience (6.1) and Clinical Studies, Diarrhea Associated with Clostridium difficile (14.1)].
Patients >65 years of age may take longer to respond to therapy compared to patients ≤65 years of age [see Clinical Studies, Diarrhea Associated with Clostridium difficile (14.1)]. Clinicians should be aware of the importance of appropriate duration of vancomycin hydrochloride treatment in patients >65 years of age and not discontinue or switch to alternative treatment prematurely.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Supportive care is advised, with maintenance of glomerular filtration. Vancomycin is poorly removed by dialysis. Hemofiltration and hemoperfusion with polysulfone resin have been reported to result in increased vancomycin clearance.
To obtain up-to-date information about the treatment of overdose, a good resource is your certified Regional Poison Control Center. Telephone numbers of certified poison control centers are listed in the Physicians’ Desk Reference (PDR). In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug overdoses, interaction among drugs, and unusual drug kinetics.
11 DESCRIPTION
Vancomycin Hydrochloride Capsules, USP for oral administration contain chromatographically purified vancomycin hydrochloride (a white to slightly red or slightly brown semi-solid matrix), a tricyclic glycopeptide antibiotic derived from Amycolatopsis orientalis (formerly Nocardia orientalis); 500 mg of the base is equivalent to 0.34 mmol.
The 125 mg capsules contain vancomycin hydrochloride equivalent to 125 mg (0.08 mmol) vancomycin. The inactive ingredients are polyethylene glycol, black iron oxide, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide, and gelatin. The capsules are printed with ink containing shellac, propylene glycol, black iron oxide and potassium hydroxide.
The 250 mg capsules contain vancomycin hydrochloride equivalent to 250 mg (0.17 mmol) vancomycin. The inactive ingredients are polyethylene glycol, yellow iron oxide, black iron oxide, FD&C Blue No. 2, titanium dioxide, and gelatin. The capsules are printed with ink containing shellac, povidone, propylene glycol, titanium dioxide and sodium hydroxide.
Vancomycin hydrochloride is chemically designated as (Sa)-(3S,6R,7R,22R,23S,26S,36R,38aR)-44-[[2-O-(3-Amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-3-C-methyl-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-3-(carbamoylmethyl)-10,19-dichloro-2,3,4,5,6,7,23,24,25,26,36,37,38,38a-tetradecahydro-7,22,28,30,32-pentahydroxy-6-[(2R)-4-methyl-2-(methylamino)]valeramido]-2,5,24,38,39-pentaoxo-22H-8,11:18,21-dietheno-23,36-(iminomethano)-13,16:31,35-dimetheno-1H,16H-[1,6,9]oxadiazacyclohexadecino[4,5-m][10,2,16]benzoxadiazacyclotetracosine-26-carboxylic acid, monohydrochloride and has the following structural formula:
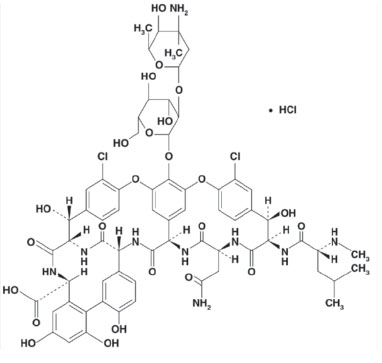
C66H75Cl2N9O24•HCl M.W. 1485.71
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Vancomycin is an antibacterial drug [see Clinical Pharmacology, Microbiology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Vancomycin is poorly absorbed after oral administration. During multiple dosing of 250 mg every 8 hours for 7 doses, fecal concentrations of vancomycin in volunteers exceeded 100 mg/kg in the majority of samples. No blood concentrations were detected and urinary recovery did not exceed 0.76%. In anephric subjects with no inflammatory bowel disease who received vancomycin oral solution 2 g for 16 days, blood concentrations of vancomycin were less than or equal to 0.66 mcg/mL in 2 of 5 subjects. No measurable blood concentrations were attained in the other 3 subjects. Following doses of 2 g daily, concentrations of drug were >3100 mg/kg in the feces and <1 mcg/mL in the serum of subjects with normal renal function who had C. difficile-associated diarrhea. After multiple-dose oral administration of vancomycin, measurable serum concentrations may occur in patients with active C. difficile-associated diarrhea, and, in the presence of renal impairment, the possibility of accumulation exists. It should be noted that the total systemic and renal clearances of vancomycin are reduced in the elderly [see Use in Specific Populations, Geriatric Use (8.5)].
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of action
The bactericidal action of vancomycin against Staphylococcus aureus and the vegetative cells of Clostridium difficile results primarily from inhibition of cell-wall biosynthesis. In addition, vancomycin alters bacterial-cell-membrane permeability and RNA synthesis.
Mechanism of resistance
Staphylococcus aureus
S. aureus isolates with vancomycin minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) as high as 1024 mcg/mL have been reported.
The exact mechanism of this resistance is not clear but is believed to be due to cell wall thickening and potentially the transfer of genetic material.
Clostridium difficile
Isolates of C. difficile generally have vancomycin MICs of <1 mcg/mL, however vancomycin MICs ranging from 4 mcg/mL to 16 mcg/mL have been reported. The
mechanism which mediates C. difficile’s decreased susceptibility to vancomycin has not been fully elucidated.
Vancomycin has been shown to be active against susceptible isolates of the following bacteria in clinical infections as described in the Indications and Usage section.
Gram-positive bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant isolates) associated with enterocolitis
Anaerobic Gram-positive bacteria
Clostridium difficile isolates associated with C. difficile associated diarrhea
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term carcinogenesis studies in animals have been conducted.
At concentrations up to 1000 mcg/mL, vancomycin had no mutagenic effect in vitro in the mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay or the primary rat hepatocyte unscheduled DNA synthesis assay. The concentrations tested in vitro were above the peak plasma vancomycin concentrations of 20 to 40 mcg/mL usually achieved in humans after slow infusion of the maximum recommended dose of 1 g. Vancomycin had no mutagenic effect in vivo in the Chinese hamster sister chromatid exchange assay (400 mg/kg IP) or the mouse micronucleus assay (800 mg/kg IP).
No definitive fertility studies have been conducted.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Diarrhea Associated with Clostridium difficile
In two trials, vancomycin hydrochloride 125 mg orally four times daily for 10 days was evaluated in 266 adult subjects with C. difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD). Enrolled subjects were 18 years of age or older and received no more than 48 hours of treatment with oral vancomycin hydrochloride or oral/intravenous metronidazole in the 5 days preceding enrollment. CDAD was defined as ≥3 loose or watery bowel movements within the 24 hours preceding enrollment, and the presence of either C. difficile toxin A or B, or pseudomembranes on endoscopy within the 72 hours preceding enrollment. Subjects with fulminant C. difficile disease, sepsis with hypotension, ileus, peritoneal signs or severe hepatic disease were excluded.
Efficacy analyses were performed on the Full Analysis Set (FAS), which included randomized subjects who received at least one dose of vancomycin hydrochloride and had any postdosing investigator evaluation data (N=259; 134 in Trial 1 and 125 in Trial 2).
The demographic profile and baseline CDAD characteristics of enrolled subjects were similar in the two trials. Vancomycin hydrochloride-treated subjects had a median age of 67 years, were mainly white (93%), and male (52%). CDAD was classified as severe (defined as 10 or more unformed bowel movements per day or WBC ≥15000/mm3) in 25% of subjects, and 47% were previously treated for CDAD.
Efficacy was assessed by using clinical success, defined as diarrhea resolution and the absence of severe abdominal discomfort due to CDAD, on Day 10. An additional efficacy endpoint was the time to resolution of diarrhea, defined as the beginning of diarrhea resolution that was sustained through the end of the prescribed active treatment period.
The results for clinical success for vancomycin hydrochloride-treated subjects in both trials are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Clinical Success Rates (Full Analysis Set)
| | Clinical Success Rate | 95% Confidence Interval |
| Vancomycin Hydrochloride % (N)
| |
|
| Trial 1 | 81.3 (134) | (74.4, 88.3) |
| Trial 2
| 80.8 (125) | (73.5, 88.1) |
The median time to resolution of diarrhea was 5 days and 4 days in Trial 1 and Trial 2, respectively. For subjects older than 65 years of age, the median time to resolution was 6 days and 4 days in Trial 1 and Trial 2, respectively. In subjects with diarrhea resolution at end-of-treatment with vancomycin hydrochloride, recurrence of CDAD during the following four weeks occurred in 25 of 107 (23%) and 18 of 102 (18%) in Trial 1 and Trial 2, respectively.
Restriction Endonuclease Analysis (REA) was used to identify C. difficile baseline isolates in the BI group. In Trial 1, the vancomycin hydrochloride-treated subjects were classified at baseline as follows 31 (23%) with BI strain, 69 (52%) with non-BI strain, and 34 (25%) with unknown strain. Clinical success rates were 87% for BI strain, 81% for non-BI strain, and 76% for unknown strain. In subjects with diarrhea resolution at end-of treatment with vancomycin hydrochloride, recurrence of CDAD during the following four weeks occurred in 7 of 26 subjects with BI strain, 12 of 56 subjects with non-BI strain, and 6 of 25 subjects with unknown strain.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Vancomycin Hydrochloride Capsules, USP are available in a carton containing 2 blister cards of 10 capsules each, for a total of 20 capsules.
| Product
No. | NDC
No. | Strength | Description
|
| NP313820 | 63323-338-22 | 125 mg* | Capsules have a grey cap and opaque light-grey body imprinted with “VANCO” on the cap and “125 mg” on the body in black ink. |
| NP313920 | 63323-339-22 | 250 mg* | Capsules have a green cap and turquoise body imprinted with “VANCO” on the cap and “250 mg” on the body in white ink. |
*Equivalent to vancomycin.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including vancomycin hydrochloride should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When vancomycin hydrochloride is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by vancomycin hydrochloride or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Novation and NOVAPLUS are registered trademarks of Novation, LLC
Manufactured for: Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC
Schaumburg IL 60173
Made in Scotland
451305
Issued: October 2012

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Vancomycin Hydrochloride 125 mg Capsule Lidding Label
Vancomycin Hydrochloride Capsules, USP
Equiv. to 125 mg Vancomycin

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Vancomycin Hydrochloride 125 mg Capsule Carton Panel
NDC 63323-338-22
NP313820
Vancomycin Hydrochloride Capsules, USP
Equivalent to 125 mg* Vancomycin
Not a Child Resistant Container
20 Capsules
(2 x 10 unit dose capsules)
Rx only

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Vancomycin Hydrochloride 250 mg Capsule Lidding Label
Vancomycin Hydrochloride Capsules, USP
Equiv. to 250 mg Vancomycin

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Vancomcin Hydrochloride 250 mg Capsule Carton Panel
NDC 63323-339-22
NP313920
Vancomycin Hydrochloride Capsules, USP
Equivalent to 250 mg* Vancomycin
Not a Child Resistant Container
20 Capsules
(2 x 10 unit dose capsules)
Rx only

| VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
vancomycin hydrochloride capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
vancomycin hydrochloride capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC (608775388) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encap Drug Delivery | 578075491 | MANUFACTURE(63323-338, 63323-339) | |