POTASSIUM CHLORIDE- potassium chloride injection, solution, concentrate
General Injectables & Vaccines, Inc.
----------
45767G/Revised: September 2018
POTASSIUM CHLORIDE FOR INJECTION CONCENTRATE, USP
DESCRIPTION
Potassium Chloride for Injection Concentrate, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic concentrated solution of Potassium Chloride, USP in Water for Injection to be administered by intravenous infusion only after dilution in a larger volume of fluid.
Each mL of Potassium Chloride for Injection Concentrate contains 2 mEq of K+ and Cl– equivalent to 149 mg of potassium chloride and has an osmolarity of 4000 mOsmol/L (calc). A more concentrated Potassium Chloride for Injection Concentrate is also available. Each mL of this injection contains 3 mEq of K+ and Cl– equivalent to 224 mg of potassium chloride and has an osmolarity of 6000 mOsmol/L(calc).
pH (4.0-8.0) may have been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and if necessary, potassium hydroxide.
Some packages are intended for multiple dose use and contain preservatives (0.05% methylparaben and 0.005% propylparaben). A summary of the available products is presented in the HOW SUPPLIED section.
Potassium Chloride for Injection Concentrate (appropriately diluted) is a parenteral fluid and electrolyte replenisher.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Potassium is the chief cation of body cells (160 mEq/L of intracellular water) and is concerned with the maintenance of body fluid composition and electrolyte balance. Potassium participates in carbohydrate utilization and protein synthesis, and is critical in the regulation of nerve conduction and muscle contraction, particularly in the heart. Chloride, the major extracellular anion, closely follows the metabolism of sodium, and changes in the acid-base balance of the body are reflected by changes in the chloride concentration.
Normally about 80 to 90% of the potassium intake is excreted in the urine, the remainder in the stools and to a small extent, in the perspiration. The kidney does not conserve potassium well, so that during fasting, or in patients on a potassium-free diet, potassium loss from the body continues resulting in potassium depletion. A deficiency of either potassium or chloride will lead to a deficit of the other.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Potassium Chloride for Injection Concentrate, USP is indicated in the treatment of potassium deficiency states when oral replacement is not feasible.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Potassium Chloride for Injection Concentrate is contraindicated in diseases where high potassium levels may be encountered, and in patients with hyperkalemia, renal failure and in conditions in which potassium retention is present.
WARNINGS
WARNING: This product contains aluminum that may be toxic. Aluminum may reach toxic levels with prolonged parenteral administration if kidney function is impaired. Premature neonates are particularly at risk because their kidneys are immature, and they require large amounts of calcium and phosphate solutions, which contain aluminum.
Research indicates that patients with impaired kidney function, including premature neonates, who receive parenteral levels of aluminum at greater than 4 to 5 mcg/kg/day accumulate aluminum at levels associated with central nervous system and bone toxicity. Tissue loading may occur at even lower rates of administration.
To avoid potassium intoxication, do not infuse these solutions rapidly. In patients with renal insufficiency, administration of potassium chloride may cause potassium intoxication and life-threatening hyperkalemia.
The administration of intravenous solutions can cause fluid and/or solute overload resulting in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations, overhydration, congested states or pulmonary edema. The risk of dilutional states is inversely proportional to the electrolyte concentration. The risk of solute overload causing congested states with peripheral and pulmonary edema is directly proportional to the electrolyte concentration.
PRECAUTIONS
GeneralClinical evaluation and periodic laboratory determinations are necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance during prolonged parenteral therapy or whenever the condition of the patient warrants such evaluation. Significant deviations from normal concentrations may require the use of additional electrolyte supplements, or the use of electrolyte-free dextrose solutions to which individualized electrolyte supplements may be added.
Potassium therapy should be guided primarily by serial electrocardiograms, especially in patients receiving digitalis. Serum potassium levels are not necessarily indicative of tissue potassium levels. Solutions containing potassium should be used with caution in the presence of cardiac disease, particularly in the presence of renal disease, and in such instances, cardiac monitoring is recommended.
Solutions containing dextrose should be used with caution in patients with overt or known subclinical diabetes mellitus, or carbohydrate intolerance for any reason.
If the administration is controlled by a pumping device, care must be taken to discontinue pumping action before the container runs dry or air embolism may result.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C — Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with potassium chloride. It is also not known whether potassium chloride can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Potassium chloride should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Reactions which may occur because of the solution or the technique of administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation, hypervolemia, and hyperkalemia.
Too rapid infusion of hypertonic solutions may cause local pain and, rarely, vein irritation. Rate of administration should be adjusted according to tolerance.
Reactions reported with the use of potassium-containing solutions include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea. The signs and symptoms of potassium intoxication include paresthesias of the extremities, areflexia, muscular or respiratory paralysis, mental confusion, weakness, hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias, heart block, electrocardiographic abnormalities and cardiac arrest. Potassium deficits result in disruption of neuromuscular function, and intestinal ileus and dilatation.
If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures and save the remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
OVERDOSAGE
In the event of fluid overload during parenteral therapy, reevaluate the patient's condition, and institute appropriate corrective treatment.
In the event of overdosage with potassium-containing solutions, discontinue the infusion immediately and institute corrective therapy to reduce serum potassium levels.
Treatment of hyperkalemia includes the following:
- Dextrose Injection, USP, 10% or 25%, containing 10 units of crystalline insulin per 20 grams of dextrose administered intravenously, 300 to 500 mL/hour.
- Absorption and exchange of potassium using sodium or ammonium cycle cation exchange resin, orally and as retention enema.
- Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. The use of potassium-containing foods or medications must be eliminated. However, in cases of digitalization, too rapid a lowering of plasma potassium concentration can cause digitalis toxicity.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Potassium Chloride for Injection Concentrate must be diluted before administration. Care must be taken to ensure there is complete mixing of the potassium chloride with the large volume fluid, particularly if soft or bag type containers are used.
The dose and rate of administration are dependent upon the specific condition of each patient.
If the serum potassium level is greater than 2.5 mEq/L, potassium can be given at a rate not to exceed 10 mEq/hour and in a concentration of up to 40 mEq/L. The 24 hour total dose should not exceed 200 mEq.
If urgent treatment is indicated (serum potassium level less than 2 mEq/L and electrocardiographic changes and/or muscle paralysis), potassium chloride may be infused very cautiously at a rate of up to 40 mEq/hour. In such cases, continuous cardiac monitoring is essential. As much as 400 mEq may be administered in a 24 hour period. In critical conditions, potassium chloride may be administered in saline (unless contraindicated) rather than in dextrose containing fluids, as dextrose may lower serum potassium levels.
Prior to entering a vial, cleanse the rubber closure with a suitable antiseptic agent.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
HOW SUPPLIED
The following are packaged in plastic vials.
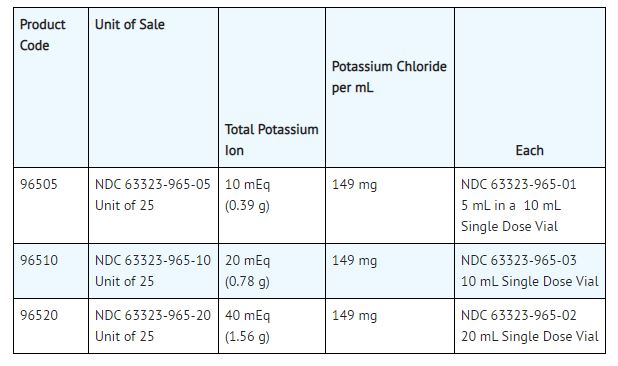
These are Single Dose Vials, no preservative added, packaged 25 vials per tray. Unused portion of vial should be discarded.
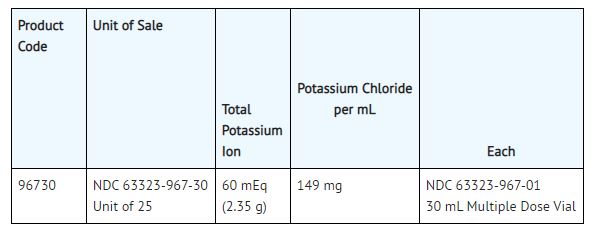
This is a Multiple Dose Vial, preserved with 0.05% methylparaben and 0.005% propylparaben, packaged 25 vials per tray.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Use only if solution is clear, seal intact and undamaged.
Vial stoppers do not contain natural rubber latex.

| POTASSIUM CHLORIDE
potassium chloride injection, solution, concentrate |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - General Injectables & Vaccines, Inc. (108250663) |

