IVERMECTIN- ivermectin lotion
Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use IVERMECTIN LOTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for IVERMECTIN LOTION.
IVERMECTIN lotion, for topical use Initial U.S. Approval: 1996 INDICATIONS AND USAGEIvermectin Lotion is a pediculicide indicated for the topical treatment of head lice infestations in patients 6 months of age and older. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONDOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSLotion: 0.5% (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSNone. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSAccidental ingestion in pediatric patients may occur: Administer only under direct adult supervision. (5.1) ADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions (incidence <1%) are conjunctivitis, ocular hyperemia, eye irritation, dandruff, dry skin, and skin burning sensation. (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. at 1-866-923-4914 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSSafety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 6 months have not been established. (8.4) See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 12/2019 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Indication
Ivermectin Lotion is indicated for the topical treatment of head lice infestations in patients 6 months of age and older.
1.2 Adjunctive Measures
Ivermectin Lotion should be used in the context of an overall lice management program:
- Wash (in hot water) or dry-clean all recently worn clothing, hats, used bedding and towels.
- Wash personal care items such as combs, brushes and hair clips in hot water.
- A fine-tooth comb or special nit comb may be used to remove dead lice and nits.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For topical use only. Ivermectin Lotion is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
Apply Ivermectin Lotion to dry hair in an amount sufficient (up to 1 tube) to thoroughly coat the hair and scalp.
Leave Ivermectin Lotion on the hair and scalp for 10 minutes, and then rinse off with water. It is recommended to wait 24 hours before applying shampoo to hair and scalp.
The tube is intended for single use; discard any unused portion. Avoid contact with eyes.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Lotion: 0.5%; each gram of lotion contains 5 mg of ivermectin. Ivermectin Lotion is an off-white to tan lotion.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to a single 10 minute treatment of Ivermectin Lotion in 379 patients, ages 6 months and older, in placebo-controlled trials. Of these subjects, 47 subjects were age 6 months to 4 years, 179 subjects were age 4 to 12 years, 56 subjects were age 12 to 16 years and 97 subjects were age 16 or older. Adverse reactions, reported in less than 1% of subjects treated with Ivermectin Lotion, include conjunctivitis, ocular hyperemia, eye irritation, dandruff, dry skin, and skin burning sensation.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no studies with the use of Ivermectin Lotion in pregnant women. Epidemiologic studies with the use of oral ivermectin during pregnancy are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes, because either the timing of administration during gestation was not accurately ascertained or the administration occurred only during the second trimester (see Data). However, systemic exposure from topical use of ivermectin is much lower than that from oral use [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In animal reproduction studies, ivermectin induced adverse developmental outcomes when orally administered to pregnant mice, rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis only at or near doses that were maternally toxic to the pregnant females [see Data].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Four published epidemiology studies, all performed in rural Africa to treat soil-transmitted helminths, evaluated pregnancy outcomes in a total of 744 women exposed to oral ivermectin in various stages of pregnancy. In the largest of these studies, 397 women in their second trimester of pregnancy were treated open-label with single doses of oral ivermectin, or ivermectin plus albendazole, for soil-transmitted helminths and compared with a pregnant, non-treated population. No differences in pregnancy outcomes were observed between treated and untreated populations. These studies cannot definitively establish or exclude the absence of any drug-associated risk during pregnancy, because either the timing of administration during gestation was not accurately ascertained or the administration occurred only during the second trimester.
Animal Data
No comparisons of animal exposure with human exposure are made due to the low systemic exposure noted in the clinical pharmacokinetic study [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in mice, rats and rabbits. Oral doses of ivermectin at 0.1 mg/kg/day, 0.2 mg/kg/day, 0.4 mg/kg/day, 0.8 mg/kg/day, and 1.6 mg/kg/day were administered during the period of organogenesis to pregnant female mice. Maternal death occurred at 0.4 mg/kg/day and above. Cleft palate occurred in the fetuses from the 0.4 mg/kg/day, 0.8 mg/kg/day, and 1.6 mg/kg/day groups. Exencephaly was seen in the fetuses from the 0.8 mg/kg group. Oral doses of ivermectin at 2.5 mg/kg/day, 5 mg/kg/day, and 10 mg/kg/day were administered during the period of organogenesis to pregnant female rats. Maternal death and pre-implantation loss occurred at 10 mg/kg/day. Cleft palate and wavy ribs were seen in fetuses from the 10 mg/kg/day group. Oral doses of ivermectin at 1.5 mg/kg/day, 3 mg/kg/day, and 6 mg/kg/day were administered during the period of organogenesis to pregnant female rabbits. Maternal toxicity and abortion occurred at 6 mg/kg/day. Cleft palate and clubbed forepaws occurred in the fetuses from the 3 mg/kg and 6 mg/kg groups. These teratogenic effects were found only at or near doses that were maternally toxic to the pregnant female. Therefore, ivermectin does not appear to be selectively fetotoxic to the developing fetus.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is information available on the presence of ivermectin in human milk in 4 lactating women after a single 150 mcg/kg oral dose of ivermectin. However, there is insufficient information from this study to determine the effects of ivermectin on the breastfed infant or the effects of ivermectin on milk production.
Topical ivermectin systemic exposure is much lower than that for oral ivermectin [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Furthermore, the amount of ivermectin present in human milk after topical application of ivermectin to lactating women has not been studied.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Ivermectin Lotion and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Ivermectin Lotion or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Ivermectin Lotion have been established for pediatric patients 6 months of age and older [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14)].
The safety of Ivermectin Lotion has not been established in pediatric patients below the age of 6 months. Ivermectin Lotion is not recommended in pediatric patients under 6 months of age because of the potential increased systemic absorption due to a high ratio of skin surface area to body mass and the potential for an immature skin barrier and risk of ivermectin toxicity.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Ivermectin Lotion did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
10 OVERDOSAGE
In accidental or significant exposure to unknown quantities of veterinary formulations of ivermectin in humans, either by ingestion, inhalation, injection, or exposure to body surfaces, the following adverse effects have been reported most frequently: rash, edema, headache, dizziness, asthenia, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Other adverse effects that have been reported include: seizure, ataxia, dyspnea, abdominal pain, paresthesia, urticaria, and contact dermatitis.
In case of accidental poisoning, supportive therapy, if indicated, should include parenteral fluids and electrolytes, respiratory support (oxygen and mechanical ventilation if necessary) and pressor agents if clinically significant hypotension is present. Induction of emesis and/or gastric lavage as soon as possible, followed by purgatives and other routine anti-poison measures, may be indicated if needed to prevent absorption of ingested material.
11 DESCRIPTION
Ivermectin Lotion, for topical administration, is an off-white/tan lotion containing 0.5% ivermectin.
Ivermectin, the active ingredient, is a pediculicide, derived from the fermentation of a soil dwelling actinomycete, Streptomyces avermitilis.
Ivermectin is a mixture containing at least 90% 5-O-demethyl-22,23-dihydroavermectin A1a and less than 10% 5-O-demethyl-25-de(1-methylpropyl)-22,23-dihydro25-(1-methylethyl) avermectin A1a, generally referred to as 22,23-dihydroavermectin B1a and B1b, or H2B1a and H2B1b, respectively. The respective empirical formulas are C48H74O14 and C47H72O14, with molecular weights of 875.10 and 861.07, respectively. The structural formulas are:
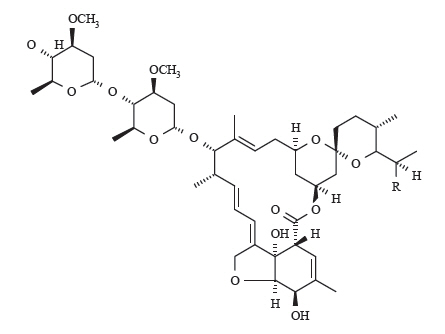 |
| Component H2B1a: R = CH2CH3 Component H2B1b: R = CH3 |
Ivermectin Lotion contains the following inactive ingredients: butylated hydroxyanisole, castor oil, cetyl alcohol, citric acid anhydrous, crodalan AWS, cyclomethicone, glycerin, imidurea, lanolin alcohols, methylparaben, oleyl alcohol, olive oil, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, shea butter, sodium citrate anhydrous, sorbitan tristearate and stearyl alcohol.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ivermectin, a member of the avermectin class, causes death of parasites, primarily through binding selectively and with high affinity to glutamate-gated chloride channels, which occur in invertebrate nerve and muscle cells. This leads to an increase in the permeability of the cell membrane to chloride ions with hyperpolarization of the nerve or muscle cell, resulting in paralysis and death of the parasite. Compounds of this class may also interact with other ligand-gated chloride channels, such as those gated by the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). The selective activity of compounds of this class is attributable to the fact that some mammals do not have glutamate-gated chloride channels, the avermectins have a low affinity for mammalian ligand-gated chloride channels, and ivermectin does not readily cross the blood-brain barrier in humans.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The absorption of ivermectin from Ivermectin Lotion was evaluated in a clinical study in subjects aged from 6 months to 3 years. This study evaluated pharmacokinetics in 20 lice infested subjects, and 13 of these subjects weighed 15 kg or less (overall weight range 8.5 to 23.9 kg). All enrolled subjects received a single treatment with Ivermectin Lotion. The systemic ivermectin exposure was evaluated using an assay with a lower limit of quantitation of 0.05 ng/mL. The mean (± standard deviation) plasma maximum concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve from 0 to time of last measurable concentration (AUC0-tlast) were 0.24 ± 0.23 ng/mL and 6.7 ± 11.2 hr∙ng/mL, respectively. These levels are much lower than those observed following oral administration of 165 mcg/kg dose of ivermectin.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Ivermectin Lotion or ivermectin.
Ivermectin was not genotoxic in vitro in the Ames test, the mouse lymphoma assay, or the unscheduled DNA synthesis assay in human fibroblasts.
Ivermectin had no adverse effects on fertility in rats at repeated oral doses of up to 3.6 mg/kg/day.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Two identical multi-center, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies were conducted in subjects 6 months of age and older with head lice infestation. All subjects received a single application of either Ivermectin Lotion or vehicle control with instructions not to use a nit comb. For the evaluation of efficacy, the youngest subject from each household was considered to be the index subject of the household (N=289). Other enrolled infested household members received the same treatment as the youngest subject and were evaluated for all safety parameters [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The primary efficacy was assessed as the proportion of index subjects who were free of live lice at day 2 and through day 8 to the final evaluation 14 (+2) days following a single application. Subjects with live lice present at any time up to the final evaluation were considered treatment failures. Table 1 contains the proportion of subjects who were free of live lice in each of the two trials.
| Study | Vehicle % (n/N) | Ivermectin Lotion % (n/N) |
|---|---|---|
| Study 1 | 16.2% (12/74) | 76.1% (54/71) |
| Study 2 | 18.9% (14/74) | 71.4% (50/70) |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Ivermectin Lotion, 0.5% is supplied in a 4 oz (117 g) white laminate tube (NDC 51672-4211-8).
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
"See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information)".
Inform the patient and caregiver of the following instructions:
- Use Ivermectin Lotion in the context of an overall lice management program.
- Apply Ivermectin Lotion to dry scalp and dry scalp hair.
- Wash hands after applying Ivermectin Lotion.
- Leave Ivermectin Lotion on the hair and scalp for 10 minutes, and then rinse off with water.
- For single use only; do not re-treat.
- It is recommended to wait 24 hours before applying shampoo to hair and scalp.
- Discard tube after use.
- Avoid contact with eyes.
- Do not swallow Ivermectin Lotion.
- Keep out of reach of children. Use on children should be under the direct supervision of an adult.
- Advise a lactating woman to avoid accidental transfer of Ivermectin Lotion directly to breast area where the infant might directly ingest the drug.
Manufactured by: Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Haifa Bay, Israel, 2624761
Dist. by: Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
Hawthorne, NY 10532
Issued: December, 2019
21180-1219-0
809
| Patient Information Ivermectin (eye'' ver mek' tin) Lotion, 0.5% |
| Important: For use on scalp hair and scalp only. Do not use Ivermectin Lotion in your eyes, mouth, or vagina. |
| What is Ivermectin Lotion?
Ivermectin Lotion is a prescription medicine for topical use on the hair and scalp only. Ivermectin Lotion is used to treat head lice in people 6 months of age and older. It is not known if Ivermectin Lotion is safe and effective for children under 6 months of age. |
Before you use Ivermectin Lotion, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you or your child:
|
How should I use Ivermectin Lotion?
|
| What are the possible side effects of Ivermectin Lotion? The most common side effects of Ivermectin Lotion include:
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
How should I store Ivermectin Lotion?
|
| General information about the safe and effective use of Ivermectin Lotion.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Ivermectin Lotion for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Ivermectin Lotion to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can also ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Ivermectin Lotion that is written for health professionals. |
| What are the ingredients in Ivermectin Lotion?
Active: Ivermectin 0.5% Inactive ingredients: butylated hydroxyanisole, castor oil, cetyl alcohol, citric acid anhydrous, crodalan AWS, cyclomethicone, glycerin, imidurea, lanolin alcohols, methylparaben, oleyl alcohol, olive oil, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, shea butter, sodium citrate anhydrous, sorbitan tristearate and stearyl alcohol. Manufactured by: Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Haifa Bay, Israel, 2624761 Dist. by: Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. Hawthorne, NY 10532 Issued: December, 2019 21180-1219-0 809 |
Instructions for Use
Before you use Ivermectin Lotion, it is important that you read the Patient Information and these Instructions for Use. Be sure that you read, understand, and follow these Instructions for Use so that you use Ivermectin Lotion the right way. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have questions about the right way to use Ivermectin Lotion.
- Your hair and scalp must be dry before applying Ivermectin Lotion.
|
||
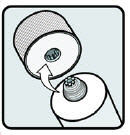
- Apply Ivermectin Lotion directly to dry hair and scalp (see Figure B).
- Completely cover your scalp and hair closest to the scalp first, and then apply outwards towards the ends of your hair (see Figure C).
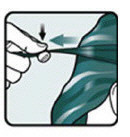
- Rub Ivermectin Lotion throughout your hair (see Figure D).
- It is important to completely cover your entire head so that all lice and eggs are exposed to the lotion. Be sure that each hair is coated from the scalp to the tip.
- Use up to 1 entire tube (4 oz) to completely cover hair and scalp.
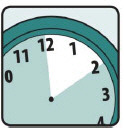
- Allow Ivermectin Lotion to stay on your hair and scalp for 10 minutes after it has been applied. Use a timer or clock. Start timing after you have completely covered your hair and scalp with Ivermectin Lotion (see Figure E).
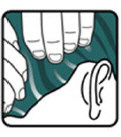
- After 10 minutes, completely rinse Ivermectin Lotion from your hair and scalp using only water (see Figure F).
- You or anyone who helps you apply Ivermectin Lotion should wash their hands after application.
- It is recommended to wait 24 hours before applying shampoo to hair and scalp.
- Do not use Ivermectin Lotion again without talking to your healthcare provider first.
- How do I stop the spread of lice?
To help prevent the spread of lice from one person to another, here are some steps you can take:
- Avoid direct head-to-head contact with anyone known to have live, crawling lice.
- Do not share combs, brushes, hats, scarves, bandannas, ribbons, barrettes, hair bands, towels, helmets, or other hair-related personal items with anyone else, whether they have lice or not.
- Avoid sleepovers and slumber parties during lice outbreaks. Lice can live in bedding, pillows, and carpets that have recently been used by someone with lice.
- After finishing treatment with lice medicine, check everyone in your family for lice after one week. Be sure to talk to your healthcare provider about treatments for those who have lice.
- Machine wash any bedding and clothing used by anyone having lice. Machine wash at high temperatures (150°F) and tumble in a hot dryer for 20 minutes.
This Patient Information and Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Issued: December 2019
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 117 g Tube Carton
Net wt.:
4 oz (117 g)
NDC 51672-4211-8
Ivermectin
Lotion 0.5%
FOR TOPICAL USE
ON THE SCALP HAIR
AND SCALP ONLY.
FOR SINGLE USE.
DISCARD THE TUBE
AFTER USE.
Warning:
Keep out of reach of children.
Use in children should be
under the direct supervision
of an adult.
Do not swallow.
Avoid eye contact.
Rx only
TARO

| IVERMECTIN
ivermectin lotion |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. (145186370) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taro Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | 600072078 | MANUFACTURE(51672-4211) | |