HYDROXYPROGESTERONE CAPROATE- hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection
Prasco Laboratories
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use HYDROXYPROGESTERONE CAPROATE INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for HYDROXYPROGESTERONE CAPROATE INJECTION.
HYDROXYPROGESTERONE CAPROATE INJECTION for intramuscular use. Initial U.S. Approval: 1956 INDICATIONS AND USAGEHydroxyprogesterone caproate is a progestin indicated to reduce the risk of preterm birth in women with a singleton pregnancy who have a history of singleton spontaneous preterm birth. Limitation of use: Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is not intended for use in women with multiple gestations or other risk factors for preterm birth. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS1 mL single dose vial contains 250 mg of hydroxyprogesterone caproate. 5 mL multidose vial (250 mg/mL) contains 1250 mg hydroxyprogesterone caproate. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions reported in ≥ 2% of subjects and at a higher rate in the Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection group than in the control group are injection site reactions (pain [35%], swelling [17%], pruritus [6%], nodule [5%]), urticaria (12%), pruritus (8%), nausea (6%), and diarrhea (2%). (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AMAG Pharmaceuticals at 1-888-261-4762 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy: Controlled studies show no increase in
congenital anomalies, including genital abnormalities in male or
female infants, from exposure during pregnancy to
hydroxyprogesterone caproate. (8.1) See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 1/2023 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is a progestin indicated to reduce the risk of preterm birth in women with a singleton pregnancy who have a history of singleton spontaneous preterm birth. The effectiveness of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is based on improvement in the proportion of women who delivered < 37 weeks of gestation. There are no controlled trials demonstrating a direct clinical benefit, such as improvement in neonatal mortality and morbidity.
Limitation of use: While there are many risk factors for preterm birth, safety and efficacy of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection has been demonstrated only in women with a prior spontaneous singleton preterm birth. It is not intended for use in women with multiple gestations or other risk factors for preterm birth.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing
- Administer intramuscularly at a dose of 250 mg (1 mL) once weekly (every 7 days) by a healthcare provider
- Begin treatment between 16 weeks, 0 days and 20 weeks, 6 days of gestation
- Continue administration once weekly until week 37 (through 36 weeks, 6 days) of gestation or delivery, whichever occurs first
2.2 Preparation and Administration
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is a clear, yellow solution. Do not store for long periods of time at low temperatures as this may cause the solution to appear cloudy due to crystallization. The solution must be clear at the time of use, replace vial if visible particles are present. Do not refrigerate.
Instructions for administration:
- Clean the vial top with an alcohol swab before use.
- Draw up 1 mL of drug into a 3 mL syringe with an 18 gauge needle.
- Change the needle to a 21 gauge 1½ inch needle.
- After preparing the skin, inject in the upper outer quadrant of the gluteus maximus. The solution is viscous and oily. Slow injection (over one minute or longer) is recommended.
- Applying pressure to the injection site may minimize bruising and swelling.
If the 5 mL multidose vial is used, discard any unused product 5 weeks after first use.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection (250 mg/mL) is a sterile solution of hydroxyprogesterone caproate in castor oil for injection. Each 1 mL single dose vial contains 250 mg hydroxyprogesterone caproate. Each 5 mL multidose vial contains 1250 mg hydroxyprogesterone caproate.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Do not use Hydroxyprogesterone caproate in women with any of the following conditions:
- Current or history of thrombosis or thromboembolic disorders
- Known or suspected breast cancer, other hormone-sensitive cancer, or history of these conditions
- Undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding unrelated to pregnancy
- Cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy
- Liver tumors, benign or malignant, or active liver disease
- Uncontrolled hypertension
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thromboembolic Disorders
Discontinue Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection if an arterial or deep venous thrombotic or thromboembolic event occurs.
5.2 Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions, including urticaria, pruritus and angioedema, have been reported with use of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection or with other products containing castor oil. Consider discontinuing the drug if such reactions occur.
5.3 Decrease in Glucose Tolerance
A decrease in glucose tolerance has been observed in some patients on progestin treatment. The mechanism of this decrease is not known. Carefully monitor prediabetic and diabetic women while they are receiving Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection.
5.4 Fluid Retention
Because progestational drugs may cause some degree of fluid retention, carefully monitor women with conditions that might be influenced by this effect (e.g., preeclampsia, epilepsy, migraine, asthma, cardiac or renal dysfunction).
5.5 Depression
Monitor women who have a history of clinical depression and discontinue Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection if clinical depression recurs.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
For the most serious adverse reactions to the use of progestins, see Warnings and Precautions (5).
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In a vehicle (placebo)-controlled clinical trial of 463 pregnant women at risk for spontaneous preterm delivery based on obstetrical history, 310 received 250 mg of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection and 153 received a vehicle formulation containing no drug by a weekly intramuscular injection beginning at 16 to 20 weeks of gestation and continuing until 37 weeks of gestation or delivery, whichever occurred first.1 [See Clinical Studies (14.1).]
Certain pregnancy-related fetal and maternal complications or events were numerically increased in the Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection-treated subjects as compared to control subjects, including miscarriage and stillbirth, admission for preterm labor, preeclampsia or gestational hypertension, gestational diabetes, and oligohydramnios (Tables 1 and 2).
| 1 N = Total number of subjects enrolled prior to 20 weeks 0 days 2 N = Total number of subjects at risk ≥ 20 weeks |
||
|
Pregnancy Complication |
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection |
Control |
|
n/N |
n/N |
|
|
Miscarriage (< 20 weeks)1 |
5/209 |
0/107 |
|
Stillbirth (≥ 20 weeks)2 |
6/305 |
2/153 |
| 1 Other than delivery admission. | |||||
|
Pregnancy Complication |
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection
|
Control
|
|||
|
Admission for preterm labor1 |
16.0 |
13.8 |
|||
|
Preeclampsia or gestational hypertension |
8.8 |
4.6 |
|||
|
Gestational diabetes |
5.6 |
4.6 |
|||
|
Oligohydramnios |
3.6 |
1.3 |
|||
Common Adverse Reactions:
The most common adverse reaction was injection site pain, which was reported after at least one injection by 34.8% of the Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection group and 32.7% of the control group. Table 3 lists adverse reactions that occurred in ≥ 2% of subjects and at a higher rate in the Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection group than in the control group.
|
Preferred Term |
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection
|
Control
|
|
Injection site pain |
34.8 |
32.7 |
|
Injection site swelling |
17.1 |
7.8 |
|
Urticaria |
12.3 |
11.1 |
|
Pruritus |
7.7 |
5.9 |
|
Injection site pruritus |
5.8 |
3.3 |
|
Nausea |
5.8 |
4.6 |
|
Injection site nodule |
4.5 |
2.0 |
|
Diarrhea |
2.3 |
0.7 |
In the clinical trial, 2.2% of subjects receiving Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection were reported as discontinuing therapy due to adverse reactions compared to 2.6% of control subjects. The most common adverse reactions that led to discontinuation in both groups were urticaria and injection site pain/swelling (1% each).
Pulmonary embolus in one subject and injection site cellulitis in another subject were reported as serious adverse reactions in Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection-treated subjects.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Body as a whole: Local injection site reactions (including erythema, urticaria, rash, irritation, hypersensitivity, warmth); fatigue; fever; hot flashes/flushes
- Digestive disorders: Vomiting
- Infections: Urinary tract infection
- Nervous system disorders: Headache, dizziness
- Pregnancy, puerperium and perinatal conditions: Cervical incompetence, premature rupture of membranes
- Reproductive system and breast disorders: Cervical dilation, shortened cervix
- Respiratory disorders: Dyspnea, chest discomfort
- Skin: Rash
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
In vitro drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection. [See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3).] No in vivo drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection use in women during the first trimester of pregnancy. Data from a vehicle (placebo)-controlled clinical trial of 310 pregnant women who received Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection at weekly doses of 250 mg by intramuscular injection in their second and third trimesters1, as well as long-term (2-5 years) follow-up safety data on 194 of their infants 2, did not demonstrate any teratogenic risks to infants from in utero exposure to Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection.
Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats at doses up to 95 and 5, respectively, times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection.
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection administration produced embryolethality in rhesus monkeys but not in cynomolgus monkeys exposed to 1 and 10 times the human dose equivalent every 7 days between days 20 and 146 of gestation. There were no teratogenic effects in either species.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is not intended for use to stop active preterm labor. The effect of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection in active labor is unknown.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Discontinue Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection at 37 weeks of gestation or upon delivery. Detectable amounts of progestins have been identified in the milk of mothers receiving progestin treatment. Many studies have found no adverse effects of progestins on breastfeeding performance, or on the health, growth, or development of the infant.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is not indicated for use in children. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients less than 16 years of age have not been established. A small number of women under age 18 years were studied; safety and efficacy are expected to be the same in women aged 16 years and above as for users 18 years and older. [See Clinical Studies (14).]
8.5 Geriatric Use
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is not intended for use in postmenopausal women. Safety and effectiveness in postmenopausal women have not been established.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No studies have been conducted to examine the pharmacokinetics of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection in patients with renal impairment.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No studies have been conducted to examine the pharmacokinetics of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection in patients with hepatic impairment. Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is extensively metabolized and hepatic impairment may reduce the elimination of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection.
10 OVERDOSAGE
There have been no reports of adverse events associated with overdosage of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection in clinical trials. In the case of overdosage, the patient should be treated symptomatically.
11 DESCRIPTION
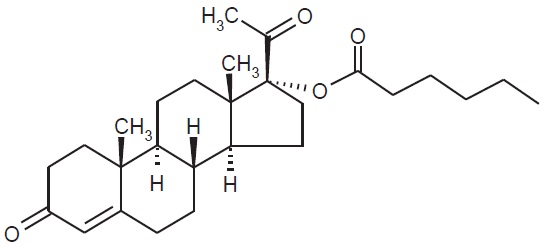
The active pharmaceutical ingredient in Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is hydroxyprogesterone caproate.
The chemical name for hydroxyprogesterone caproate is pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, 17[(1-oxohexyl)oxy]. It has an empirical formula of C27H40O4 and a molecular weight of 428.60. Hydroxyprogesterone caproate exists as white to practically white crystals or powder with a melting point of 120°-124°C.
The structural formula is:
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is a clear, yellow, sterile, non-pyrogenic solution for intramuscular injection. Each 1 mL single dose vial contains hydroxyprogesterone caproate USP, 250 mg/mL (25% w/v), in castor oil USP (30.6% v/v) and benzyl benzoate USP (46% v/v). Each 5 mL multidose vial contains hydroxyprogesterone caproate USP, 250 mg/mL (25% w/v), in castor oil USP (28.6% v/v) and benzyl benzoate USP (46% v/v) with the preservative benzyl alcohol NF (2% v/v).
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate is a synthetic progestin. The mechanism by which hydroxyprogesterone caproate reduces the risk of recurrent preterm birth is not known.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
No specific pharmacodynamic studies were conducted with Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: Female patients with a singleton pregnancy received intramuscular doses of 250 mg hydroxyprogesterone caproate for the reduction of preterm birth starting between 16 weeks 0 days and 20 weeks 6 days. All patients had blood drawn daily for 7 days to evaluate pharmacokinetics.
|
Blood was drawn daily for 7 days (1) starting 24 hours after the first dose between Weeks 16-20 (Group 1), (2) after a dose between Weeks 24-28 (Group 2), or (3) after a dose between Weeks 32-36 (Group 3) |
|||
|
a Reported as median (range) |
|||
|
b t = 7 days |
|||
| Group (N) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (days)a | AUC(1-t)b (ng·hr/mL) |
| Group 1 (N=6) | 5.0 (1.5) | 5.5 (2.0-7.0) | 571.4 (195.2) |
| Group 2 (N=8) | 12.5 (3.9) | 1.0 (0.9-1.9) | 1269.6 (285.0) |
| Group 3 (N=11) | 12.3 (4.9) | 2.0 (1.0-3.0) | 1268.0 (511.6) |
For all three groups, peak concentration (Cmax) and area under the curve (AUC(1-7 days)) of the mono-hydroxylated metabolites were approximately 3-8-fold lower than the respective parameters for the parent drug, hydroxyprogesterone caproate. While di-hydroxylated and tri-hydroxylated metabolites were also detected in human plasma to a lesser extent, no meaningful quantitative results could be derived due to the absence of reference standards for these multiple hydroxylated metabolites. The relative activity and significance of these metabolites are not known.
The elimination half-life of hydroxyprogesterone caproate, as evaluated from 4 patients in the study who reached full-term in their pregnancies, was 16.4 (±3.6) days. The elimination half-life of the mono-hydroxylated metabolites was 19.7 (±6.2) days.
Distribution: Hydroxyprogesterone caproate binds extensively to plasma proteins including albumin and corticosteroid binding globulins.
Metabolism: In vitro studies have shown that hydroxyprogesterone caproate can be metabolized by human hepatocytes, both by phase I and phase II reactions. Hydroxyprogesterone caproate undergoes extensive reduction, hydroxylation and conjugation. The conjugated metabolites include sulfated, glucuronidated and acetylated products. In vitro data indicate that the metabolism of hydroxyprogesterone caproate is predominantly mediated by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. The in vitro data indicate that the caproate group is retained during metabolism of hydroxyprogesterone caproate.
Excretion: Both conjugated metabolites and free steroids are excreted in the urine and feces, with the conjugated metabolites being prominent. Following intramuscular administration to pregnant women at 10-12 weeks gestation, approximately 50% of a dose was recovered in the feces and approximately 30% recovered in the urine.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment: The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection has not been evaluated.
Hepatic Impairment: The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection has not been evaluated.
Drug Interactions
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes: An in vitro inhibition study using human liver microsomes and CYP isoform-selective substrates indicated that hydroxyprogesterone caproate increased the metabolic rate of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, and CYP2B6 by approximately 80%, 150%, and 80%, respectively. However, in another in vitro study using human hepatocytes under conditions where the prototypical inducers or inhibitors caused the anticipated increases or decreases in CYP enzyme activities, hydroxyprogesterone caproate did not induce or inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, or CYP2B6 activity. Overall, the findings indicate that hydroxyprogesterone caproate has minimal potential for CYP1A2, CYP2A6, and CYP2B6 related drug-drug interactions at the clinically relevant concentrations.
In vitro data indicated that therapeutic concentration of hydroxyprogesterone caproate is not likely to inhibit the activity of CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate has not been adequately evaluated for carcinogenicity.
No reproductive or developmental toxicity or impaired fertility was observed in a multigenerational study in rats. Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection administered intramuscularly, at gestational exposures up to 5 times the recommended human dose, had no adverse effects on the parental (F0) dams, their developing offspring (F1), or the latter offspring's ability to produce a viable, normal second (F2) generation.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Trial to Evaluate Reduction of Risk of Preterm Birth
In a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle (placebo)-controlled clinical trial, the safety and effectiveness of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection for the reduction of the risk of spontaneous preterm birth was studied in women with a singleton pregnancy (age 16 to 43 years) who had a documented history of singleton spontaneous preterm birth (defined as delivery at less than 37 weeks of gestation following spontaneous preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes).1 At the time of randomization (between 16 weeks, 0 days and 20 weeks, 6 days of gestation), an ultrasound examination had confirmed gestational age and no known fetal anomaly. Women were excluded for prior progesterone treatment or heparin therapy during the current pregnancy, a history of thromboembolic disease, or maternal/obstetrical complications (such as current or planned cerclage, hypertension requiring medication, or a seizure disorder).
A total of 463 pregnant women were randomized to receive either Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection (N=310) or vehicle (N=153) at a dose of 250 mg administered weekly by intramuscular injection starting between 16 weeks, 0 days and 20 weeks, 6 days of gestation, and continuing until 37 weeks of gestation or delivery. Demographics of the Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection-treated women were similar to those in the control group, and included: 59.0% Black, 25.5% Caucasian, 13.9% Hispanic and 0.6% Asian. The mean body mass index was 26.9 kg/m2.
The proportions of women in each treatment arm who delivered at < 37 (the primary study endpoint), < 35, and < 32 weeks of gestation are displayed in Table 5.
| 1 Four Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection-treated subjects were lost to follow-up. They were counted as deliveries at their gestational ages at time of last contact (184, 220, 343 and364 weeks). 2 Adjusted for interim analysis. |
|||
|
Delivery Outcome |
Hydroxyprogesterone % |
Control
% |
Treatment difference and
|
|
<37 weeks |
37.1 |
54.9 |
-17.8% [-28.0%, -7.4%] |
|
<35 weeks |
21.3 |
30.7 |
-9.4% [-19.0%, -0.4%] |
|
<32 weeks |
11.9 |
19.6 |
-7.7% [-16.1%, -0.3%] |
Compared to controls, treatment with Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection reduced the proportion of women who delivered preterm at < 37 weeks. The proportions of women delivering at < 35 and < 32 weeks also were lower among women treated with Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection. The upper bounds of the confidence intervals for the treatment difference at < 35 and < 32 weeks were close to zero. Inclusion of zero in a confidence interval would indicate the treatment difference is not statistically significant. Compared to the other gestational ages evaluated, the number of preterm births at < 32 weeks was limited.
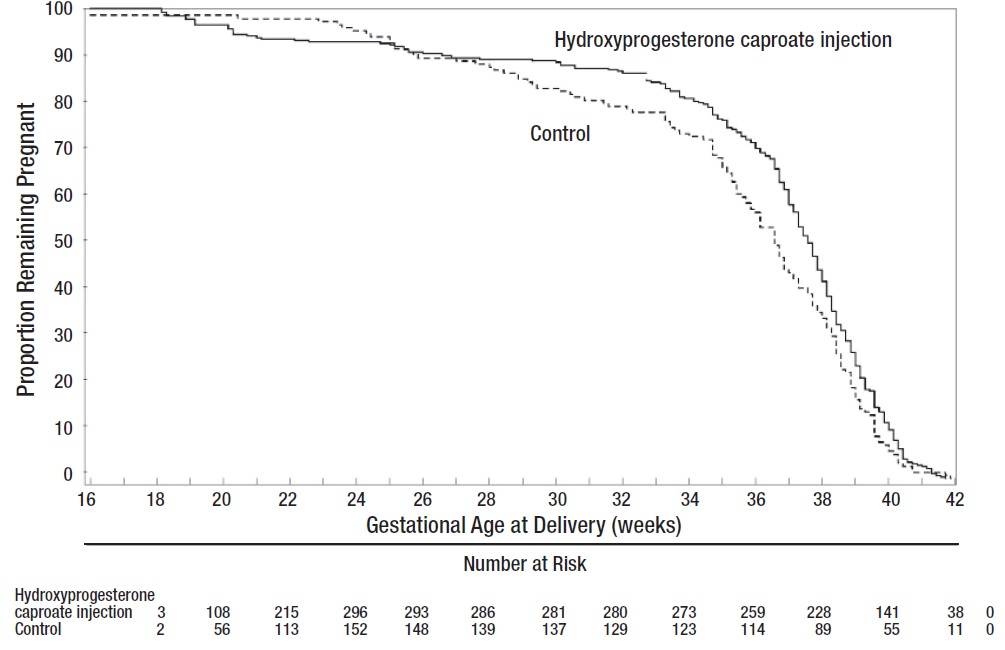
After adjusting for time in the study, 7.5% of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection-treated subjects delivered prior to 25 weeks compared to 4.7% of control subjects; see Figure 1.
Figure 1 Proportion of Women Remaining Pregnant as a Function of Gestational Age
The rates of fetal losses and neonatal deaths in each treatment arm are displayed in Table 6. Due to the higher rate of miscarriages and stillbirths in the Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection arm, there was no overall survival difference demonstrated in this clinical trial.
| A Four of the 310 Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection-treated subjects were lost to follow-up and stillbirth or neonatal status could not be determined B Percentages are based on the number of enrolled subjects and not adjusted for time on drug C Percentage adjusted for the number of at risk subjects (n=209 for Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection, n=107 for control) enrolled at <20 weeks gestation. |
||||||
|
Complication |
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection
|
Control
|
||||
|
Miscarriages <20 weeks gestation C |
5 (2.4) |
0 |
||||
|
Stillbirth |
6 (2.0) |
2 (1.3) |
||||
|
Antepartum stillbirth |
5 (1.6) |
1 (0.6) |
||||
|
Intrapartum stillbirth |
1 (0.3) |
1 (0.6) |
||||
|
Neonatal deaths |
8 (2.6) |
9 (5.9) |
||||
|
Total Deaths |
19 (6.2) |
11 (7.2) |
||||
A composite neonatal morbidity/mortality index evaluated adverse outcomes in livebirths. It was based on the number of neonates who died or experienced respiratory distress syndrome, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, grade 3 or 4 intraventricular hemorrhage, proven sepsis, or necrotizing enterocolitis. Although the proportion of neonates who experienced 1 or more events was numerically lower in the Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection arm (11.9% vs. 17.2%), the number of adverse outcomes was limited and thedifference between arms was not statistically significant.
14.2 Infant Follow-Up Safety Study
Infants born to women enrolled in this study, and who survived to be discharged from the nursery, were eligible for participation in a follow-up safety study. Of 348 eligible offspring, 79.9% enrolled: 194 children of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection-treated women and 84 children of control subjects. The primary endpoint was the score on the Ages & Stages Questionnaire (ASQ), which evaluates communication, gross motor, fine motor, problem solving, and personal/social parameters. The proportion of children whose scores met the screening threshold for developmental delay in each developmental domain was similar for each treatment group.2
15 REFERENCES
1Meis PJ, Klebanoff M, Thom E, et al. Prevention of recurrent preterm delivery by 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone caproate. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(24):2379-85.
2Northen A, Norman G, Anderson K, et al. Follow-up of children exposed in utero to 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone caproate. Obstet & Gynecol. 2007;110:865-872.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection (NDC 66993-038-83) is supplied as 1 mL of a sterile solution in a single dose glass vial.
Each 1 mL vial contains hydroxyprogesterone caproate USP, 250 mg/mL (25% w/v), in castor oil USP (30.6% v/v) and benzyl benzoate USP (46% v/v).
Single unit carton: Contains one 1 mL single dose vial of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection containing 250 mg of hydroxyprogesterone caproate.
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection (NDC 66993-039-01) is supplied as 5 mL of a sterile solution in a multidose glass vial.
Each 5 mL vial contains hydroxyprogesterone caproate USP, 250 mg/mL (25% w/v), in castor oil USP (28.6% v/v) and benzyl benzoate USP (46% v/v) with the preservative benzyl alcohol NF (2% v/v).
Single unit carton: Contains one 5 mL multidose vial of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection (250 mg/mL) containing 1250 mg of hydroxyprogesterone caproate.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). Excursions permitted to 15° – 30°C (59° – 86°F) [see USP controlled room temperature]. Do not refrigerate. Use multidose vials within 5 weeks after first use.
Caution: Protect vial from light. Store vial in its box. Store upright.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Counsel patients that Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection injections may cause pain, soreness, swelling, itching or bruising. Inform the patient to contact her physician if she notices increased discomfort over time, oozing of blood or fluid, or inflammatory reactions at the injection site [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Manufactured for: AMAG Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Waltham,
MA 02451
Distributed by: Prasco Laboratories, Inc.
Mason, OH 45040 USA
02/2018
Patient Information
Hydroxyprogesterone Caporate Injection 250 mg/mL
Read this Patient Information Leaflet before you receive Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
What is Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection?
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is a prescription hormone medicine (progestin) used in women who are pregnant and who have delivered a baby too early (preterm) in the past. Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is used in these women to help lower the risk of having a preterm baby again.
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is for women who:
- Are pregnant with one baby
- Have had a preterm delivery of one baby in the past
How well does Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection work?
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection was studied in women who were at risk for having a preterm baby because they had previously given birth to a preterm baby. In the main study, about 37 of 100 women who received Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection gave birth preterm (before 37 weeks of pregnancy), compared to about 55 of 100 women who did not receive Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection. Another study of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is going on to see whether Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection reduces the number of babies who have serious problems shortly after birth or who die.
It is not known whether Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is safe and effective in women who have other risk factors for preterm birth.
It is not known whether Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is safe and effective in women less than 16 years old.
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection is not intended for use to stop active preterm labor.
Who should not receive Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection?
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection should not be used if you:
- Have now or have had a history of blood clots or other blood clotting problems
- Have now or have had a history of breast cancer or other hormone-sensitive cancers
- Have unusual vaginal bleeding not related to your current pregnancy
- Have yellowing of your skin due to liver problems during your pregnancy
- Have liver problems, including liver tumors
- Have uncontrolled high blood pressure
What should I tell my healthcare provider before receiving Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection?
Before you receive Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection, tell your healthcare provider if you have:
- An allergy to hydroxyprogesterone caproate, castor oil, or any of the other ingredients in Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection. See the end of this patient leaflet for a complete list of the ingredients in Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection.
- Diabetes or prediabetes
- Epilepsy
- Migraine headaches
- Asthma
- Heart problems
- Kidney problems
- Depression
- High blood pressure
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection works.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medication.
How should I receive Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection?
- Do not give yourself Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection injections. A healthcare professional will give you the Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection injection into your hip area (upper outer area of the buttocks) once a week (every 7 days).
- You will start receiving Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection injections anytime from 16 weeks and 0 days of your pregnancy up to 20 weeks and 6 days of your pregnancy.
- You will continue to receive Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection injections once weekly until week 37 of your pregnancy or when your baby is delivered, whichever happens first.
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection comes in ready-to-use vials. There are either 1 or 5 doses of medicine in each vial. Your healthcare professional should give you only one dose (1 mL) of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection as prescribed each week.
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection supplied in multidose 5 mL vials should be used within 5 weeks after the first use.
It is very important that you do not miss a dose of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection and that you continue to receive the medicine once a week. If you miss a dose, talk to your healthcare provider for specific directions on how to get back on schedule.
What are the possible side effects of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection?
Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection may cause serious side effects, including:
-
Blood clots. Symptoms of a
blood clot may include:
- Leg swelling
- Redness in your leg
- A spot on your leg that is warm to touch
- Leg pain that worsens when you bend your foot
-
Allergic reactions. Symptoms
of an allergic reaction may include:
- Hives
- Itching
- Swelling of the face
Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the symptoms above.
- Depression
- Yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes
The most common side effects of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection include:
- Pain, swelling, itching, bruising or a hard bump at the injection site
- Hives
- Itching
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
Call your healthcare provider if you have the following at your injection site:
- Increased pain over time
- Oozing of blood or fluid
- Swelling
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
In a clinical study, certain complications or events associated with pregnancy occurred more often in women who received Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection compared to women who did not receive Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection, including:
- Miscarriage (pregnancy loss before 20 weeks of pregnancy)
- Stillbirth (fetal death occurring during or after the 20th week of pregnancy)
- Hospital admission for preterm labor
- Preeclampsia (high blood pressure and too much protein in your urine)
- Gestational hypertension (high blood pressure caused by pregnancy)
- Gestational diabetes
- Oligohydramnios (low amniotic fluid levels)
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects or pregnancy complications. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection?
- Store Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). Excursions permitted to 15° – 30°C (59° – 86°F)
- Do Not Refrigerate
- Store Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection in the original box to protect it from light
- Store the Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection box upright
- Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection 5 mL multidose vials should be used within 5 weeks after the first use
- Keep Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection out of the reach of children
General information about the safe and effective use of Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those mentioned in the Patient Information Leaflets. Do not take Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection for conditions for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection to other people, even if they have the same condition you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask for information about Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information, call AMAG Pharmaceuticals Customer Service at the toll free number 1-888-261-4762.
What are the ingredients in Hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection?
Active ingredient: hydroxyprogesterone caproate
Inactive ingredients: castor oil and benzyl benzoate. 5 mL multidose vials also contain benzyl alcohol (a preservative).
| HYDROXYPROGESTERONE CAPROATE
hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HYDROXYPROGESTERONE CAPROATE
hydroxyprogesterone caproate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Prasco Laboratories (065969375) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospira, Inc. | 030606222 | analysis(66993-038, 66993-039) , manufacture(66993-038, 66993-039) | |