BROMFENAC - bromfenac solution/ drops
Apotex Corp
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution, 0.09% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution, 0.09%.
Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution, 0.09% Initial U.S. Approval: 1997 INDICATIONS AND USAGEBromfenac Ophthalmic Solution is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) indicated for the treatment of postoperative inflammation and reduction of ocular pain in patients who have undergone cataract extraction (1). DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONOne drop should be applied to the affected eye two times daily beginning 24 hours after cataract surgery and continued through the first 2 weeks of the post-operative period (2.1). DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSTopical ophthalmic solution: bromfenac 0.09% (3). CONTRAINDICATIONSNone (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSADVERSE REACTIONSThe most commonly reported adverse reactions in 2 to 7% of patients were abnormal sensation in eye, conjunctival hyperemia and eye irritation (including burning/stinging) (6.1). To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Apotex Corp. at 1-800-667-4708, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 2/2014 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution, 0.09% is indicated for the treatment of postoperative inflammation and reduction of ocular pain in patients who have undergone cataract surgery.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
One drop of bromfenac ophthalmic solution should be applied to the affected eye two times daily beginning 24 hours after cataract surgery and continuing through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period.
2.2 Use with Other Topical Ophthalmic Medications
Bromfenac ophthalmic solution may be administered in conjunction with other topical ophthalmic medications such as alpha-agonists, beta-blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, cycloplegics, and mydriatics. Drops should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Sulfite Allergic Reactions
Contains sodium sulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown and probably low. Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in asthmatic than in non-asthmatic people.
5.2 Slow or Delayed Healing
All topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may slow or delay healing. Topical corticosteroids are also known to slow or delay healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical steroids may increase the potential for healing problems
5.3 Potential for Cross-Sensitivity
There is the potential for cross-sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, phenylacetic acid derivatives, and other NSAIDs. Therefore, caution should be used when treating individuals who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs.
5.4 Increased Bleeding Time
With some NSAIDs, there exists the potential for increased bleeding time due to interference with platelet aggregation. There have been reports that ocularly applied NSAIDs may cause increased bleeding of ocular tissues (including hyphemas) in conjunction with ocular surgery.
It is recommended that bromfenac ophthalmic solution be used with caution in patients with known bleeding tendencies or who are receiving other medications which may prolong bleeding time.
5.5 Keratitis and Corneal Reactions
Use of topical NSAIDs may result in keratitis. In some susceptible patients, continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration or corneal perforation. These events may be sight threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Post-marketing experience with topical NSAIDs suggests that patients with complicated ocular surgeries, corneal denervation, corneal epithelial defects, diabetes mellitus, ocular surface diseases (e.g., dry eye syndrome), rheumatoid arthritis, or repeat ocular surgeries within a short period of time may be at increased risk for corneal adverse events which may become sight threatening. Topical NSAIDs should be used with caution in these patients.
Post-marketing experience with topical NSAIDs also suggests that use more than 24 hours prior to surgery or use beyond 14 days post surgery may increase patient risk for the occurrence and severity of corneal adverse events.
5.6 Contact Lens Wear
Bromfenac ophthalmic solution should not be administered while wearing contact lenses. Remove contact lenses prior to instillation of bromfenac ophthalmic solution. The preservative in bromfenac ophthalmic solution, benzalkonium chloride, may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Lenses may be reinserted after 10 minutes following administration of bromfenac ophthalmic solution.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions reported following use of bromfenac after cataract surgery include: abnormal sensation in eye, conjunctival hyperemia, eye irritation (including burning/stinging), eye pain, eye pruritus, eye redness, headache, and iritis. These events were reported in 2 to 7% of patients.
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
The following reactions have been identified during post-marketing use of bromfenac ophthalmic solution, 0.09% in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The reactions, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to topical bromfenac ophthalmic solution, 0.09% or a combination of these factors, include corneal erosion, corneal perforation, corneal thinning, and epithelial breakdown. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with bromfenac ophthalmic solution in pregnant women. No malformations were observed in reproduction studies in rats and rabbits with oral doses of bromfenac at exposures up to 150 times (rats) and 90 times (rabbits) the predicted human systemic exposure; however, both embryolethality and maternal toxicity were observed at the highest dose exposures. The systemic concentration of bromfenac is estimated to be below the limit of quantification (50 ng/mL) at steady-state in humans, following ocular administration [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Clinical Considerations
Premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus has occurred with third trimester use of oral and injectable NSAIDs. Measurable maternal and fetal plasma drug levels are available with oral and injectable routes of NSAID administration. The maternal plasma level of bromfenac following ocular administration is unknown [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Animal Data
Reproduction studies performed in rats at oral doses of bromfenac up to 0.9 mg/kg/day (systemic exposure 90 times the systemic exposure predicted from the recommended human ophthalmic dose [RHOD] assuming the human systemic concentration is at the limit of quantification) and rabbits at oral doses up to 7.5 mg/kg/day (150 times the predicted human systemic exposure) produced no drug-related malformations in reproduction studies. However, embryo-fetal lethality and maternal toxicity were produced in rats and rabbits at 0.9 mg/kg/day and 7.5 mg/kg/day, respectively. In rats, bromfenac treatment caused delayed parturition at 0.3 mg/kg/day (30 times the predicted human exposure), and caused dystocia, increased neonatal mortality, and reduced postnatal growth at 0.9 mg/kg/day.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known if bromfenac is present in human milk. The systemic concentration of bromfenac is estimated to be below the limit of quantification (50 ng/mL) at steady-state in humans, following ocular administration [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Based on the low level of systemic exposure, it is unlikely that bromfenac would be detected in human milk using available assays. Caution should be exercised when bromfenac ophthalmic solution is administered to a nursing woman.
11 DESCRIPTION
Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution, 0.09% is a sterile, topical, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) for ophthalmic use. Each mL of Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution contains 1.035 mg bromfenac sodium sesquihydrate (equivalent to 0.9 mg bromfenac free acid). Bromfenac sodium sesquihydrate is designated chemically as sodium 2-amino-3-(4-bromobenzoyl) phenylacetate sesquihydrate, with an empirical formula of C15H11BrNNaO3• 3/2 H2O. The structural structure for bromfenac sodium is:
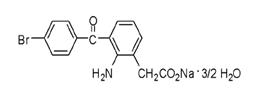
Bromfenac sodium sesquihydrate is a yellow or orange yellow crystalline powder. The molecular weight of bromfenac sodium sesquihydrate is 383.17. Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution is supplied as a sterile aqueous 0.09% solution, with a pH of 8.3. The osmolality of Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution is approximately 300 mOsmol/kg.
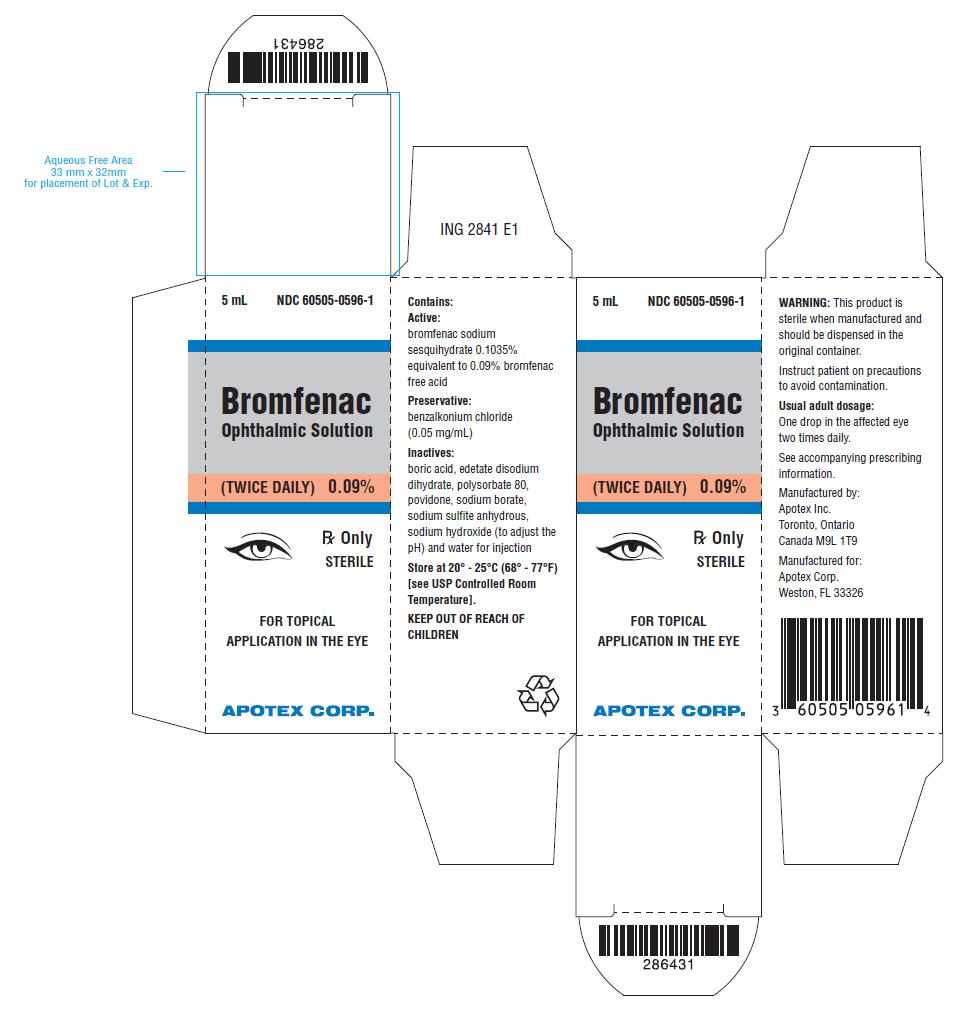
Each mL of Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution contains:
Active: bromfenac sodium sesquihydrate 0.1035% equivalent to 0.9 mg bromfenac free acid
Preservative: benzalkonium chloride (0.05 mg/mL)
Inactives: boric acid, edetate disodium dihydrate, polysorbate 80, povidone, sodium borate, sodium sulfite anhydrous, sodium hydroxide to adjust pH and water for injection.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Bromfenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that has anti-inflammatory activity. The mechanism of its action is thought to be due to its ability to block prostaglandin synthesis by inhibiting cyclooxygenase 1 and 2.
Prostaglandins have been shown in many animal models to be mediators of certain kinds of intraocular inflammation. In studies performed in animal eyes, prostaglandins have been shown to produce disruption of the blood-aqueous humor barrier, vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, leukocytosis, and increased intraocular pressure.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The plasma concentration of bromfenac following ocular administration of 0.09% bromfenac ophthalmic solution in humans is unknown. Based on the maximum proposed dose of one drop to the eye (0.09 mg) twice a day and PK information from other routes of administration, the systemic concentration of bromfenac is estimated to be below the limit of quantification (50 ng/mL) at steady-state in humans.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in rats and mice given oral doses of bromfenac up to 0.6 mg/kg/day (systemic exposure 30 times the systemic exposure predicted from the recommended human ophthalmic dose [RHOD] assuming the human systemic concentration is at the limit of quantification) and 5 mg/kg/day (340 times the predicted human systemic exposure), respectively revealed no significant increases in tumor incidence. Bromfenac did not show mutagenic potential in various mutagenicity studies, including the reverse mutation, chromosomal aberration, and micronucleus tests.
Bromfenac did not impair fertility when administered orally to male and female rats at doses up to 0.9 mg/kg/day and 0.3 mg/kg/day, respectively (systemic exposure 90 and 30 times the predicted human exposure, respectively).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Ocular Inflammation and Pain
Clinical efficacy was evaluated in two randomized, double-masked, vehicle-controlled U.S. trials in which subjects with a summed ocular inflammation score ≥3 after cataract surgery were assigned to bromfenac ophthalmic solution or vehicle in a 2:1 ratio following surgery. One drop of bromfenac ophthalmic solution or vehicle was self-instilled in the study eye twice a day for 14 days, beginning the day after surgery. The primary endpoint was reduction of ocular inflammation (to trace inflammation or clearing) assessed 14 days post-surgery using a slit lamp binocular microscope. In the intent-to-treat analyses of both studies a significant effect of bromfenac ophthalmic solution on ocular inflammation after cataract surgery was demonstrated (62-66% vs. 40-48%).
An additional efficacy endpoint was the time required for resolution of ocular pain in subjects who reported pain. Overall, only 20% of the patients undergoing cataract surgery in these trials had pain on the first day after surgery. In these patients, the bromfenac ophthalmic solution group demonstrated a statistically significant difference in median time to resolution of ocular pain of 2 days compared to 4 days for patients receiving vehicle.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution, 0.09% is supplied in a white opaque LDPE ophthalmic bottle with white translucent LDPE ophthalmic dropper and grey opaque HDPE ophthalmic cap with sealing tape as follows: :
2.5 mL in 5 mL bottle - NDC 60505-0596-4
5 mL in 5 mL bottle - NDC 60505-0596-1
STORAGE
Store at 20° - 25°C (68° - 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Slowed or Delayed Healing
Advise patients of the possibility that slow or delayed healing may occur while using NSAIDs.
17.2 Sterility of Dropper Tip
Advise patients not to touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the contents.
Use of the same bottle for both eyes is not recommended with topical eye drops that are used in association with surgery.
17.3 Concomitant Use of Contact Lenses
Advise patients that contact lenses should not be worn during the use of this product. The preservative in bromfenac ophthalmic solution, benzalkonium chloride, may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Lenses may be reinserted after 10 minutes following administration of bromfenac ophthalmic solution.
17.4 Concomitant Topical Ocular Therapy
Advise patients that if more than one topical ophthalmic medication is being used, the medicines should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
| Manufactured by: | Manufactured for: |
| Apotex Inc. | Apotex Corp. |
| Toronto, Ontario | Weston, Florida |
| Canada M9L 1T9 | 33326 |
| 286446 | February 2014 |
| BROMFENAC
bromfenac solution/ drops |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Apotex Corp (845263701) |
| Registrant - Apotex Inc. (209429182) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apotex Inc. | 255092496 | analysis(60505-0596) , manufacture(60505-0596) | |