SIROLIMUS - sirolimus solution
Novitium Pharma LLC
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use SIROLIMUS oral solution safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SIROLIMUS oral solution.
SIROLIMUS Oral Solution Initial U.S. Approval;: 1999
WARNING: IMMUNOSUPPRESSION, USE IS NOT RECOMMENDED IN
|
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: IMMUNOSUPPRESSION, USE IS NOT RECOMMENDED IN LIVER OR LUNG TRANSPLANT PATIENTS
WARNING: IMMUNOSUPPRESSION, USE IS NOT RECOMMENDED IN LIVER OR LUNG TRANSPLANT PATIENTS
· Increased susceptibility to infection and the possible development of lymphoma and other malignancies may result from immunosuppression
Increased susceptibility to infection and the possible development of lymphoma may result from immunosuppression. Only physicians experienced in immunosuppressive therapy and management of renal transplant patients should use sirolimus for prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving renal transplants. Patients receiving the drug should be managed in facilities equipped and staffed with adequate laboratory and supportive medical resources. The physician responsible for maintenance therapy should have complete information requisite for the follow-up of the patient [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
· The safety and efficacy of sirolimus as immunosuppressive therapy have not been established in liver or lung transplant patients, and therefore, such use is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3) ] .
· Liver Transplantation – Excess Mortality, Graft Loss, and Hepatic Artery Thrombosis (HAT)
The use of sirolimus in combination with tacrolimus was associated with excess mortality and graft loss in a study in de novo liver transplant patients. Many of these patients had evidence of infection at or near the time of death.
In this and another study in de novo liver transplant patients, the use of sirolimus in combination with cyclosporine or tacrolimus was associated with an increase in HAT; most cases of HAT occurred within 30 days post-transplantation and most led to graft loss or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
· Lung Transplantation – Bronchial Anastomotic Dehiscence
Cases of bronchial anastomotic dehiscence, most fatal, have been reported in de novo lung transplant patients when sirolimus has been used as part of an immunosuppressive regimen [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
1 INDICATIONS & USAGE
1.1 Prophylaxis of Organ Rejection in Renal Transplantation
Sirolimus Oral Solution is indicated for the prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients aged 13 years or older receiving renal transplants.
In patients at low-to moderate-immunologic risk, it is recommended that Sirolimus Oral Solution be used initially in a regimen with cyclosporine and corticosteroids; cyclosporine should be withdrawn 2 to 4 months after transplantation [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
In patients at high-immunologic risk (defined as Black recipients and/or repeat renal transplant recipients who lost a previous allograft for immunologic reason and/or patients with high panel-reactive antibodies [PRA; peak PRA level > 80%]), it is recommended that Sirolimus Oral Solution be used in combination with cyclosporine and corticosteroids for the first year following transplantation [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Clinical Studies (14.3)].
1.2 Limitations of Use in Renal Transplantation
Cyclosporine withdrawal has not been studied in patients with Banff Grade 3 acute rejection or vascular rejection prior to cyclosporine withdrawal, those who are dialysis-dependent, those with serum creatinine > 4.5 mg/dL, Black patients, patients of multi-organ transplants, secondary transplants, or those with high levels of panel-reactive antibodies [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ].
In patients at high-immunologic risk , the safety and efficacy of Sirolimus Oral Solution used in combination with cyclosporine and corticosteroids has not been studied beyond one year; therefore after the first 12 months following transplantation, any adjustments to the immunosuppressive regimen should be considered on the basis of the clinical status of the patient [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ].
In pediatric patients, the safety and efficacy of Sirolimus Oral Solution have not been established in patients < 13 years old, or in pediatric (< 18 years) renal transplant patients considered at high-immunologic risk [see Adverse Reactions (6.5), Clinical Studies (14.6) ].
The safety and efficacy of de novo use of Sirolimus Oral Solution without cyclosporine have not been established in renal transplant patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ].
The safety and efficacy of conversion from calcineurin inhibitors to Sirolimus Oral Solution in maintenance renal transplant patients have not been established [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ].
2 DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Sirolimus Oral Solution is to be administered orally once daily, consistently with or without food [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
2.1 General Dosing Guidance for Renal Transplant Patients
The initial dose of Sirolimus Oral Solution should be administered as soon as possible after transplantation. It is recommended that Sirolimus Oral Solution be taken 4 hours after administration of cyclosporine oral solution (MODIFIED) and/or cyclosporine capsules (MODIFIED) [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Frequent Sirolimus Oral Solution dose adjustments based on non-steady-state sirolimus concentrations can lead to over dosing or underdosing because sirolimus has a long half-life. Once Sirolimus Oral Solution maintenance dose is adjusted, patients should continue on the new maintenance dose for at least 7 to 14 days before further dosage adjustment with concentration monitoring. In most patients, dose adjustments can be based on simple proportion: new Sirolimus Oral Solution dose = current dose x (target concentration/current concentration). A loading dose should be considered in addition to a new maintenance dose when it is necessary to increase sirolimus trough concentrations: Sirolimus Oral Solution loading dose = 3 x (new maintenance dose - current maintenance dose). The maximum Sirolimus Oral Solution dose administered on any day should not exceed 40 mg. If an estimated daily dose exceeds 40 mg due to the addition of a loading dose, the loading dose should be administered over 2 days. Sirolimus trough concentrations should be monitored at least 3 to 4 days after a loading dose(s).
Two milligrams (2 mg) of Sirolimus Oral Solution have been demonstrated to be clinically equivalent to 2 mg Sirolimus Tablets; hence, at this dose these two formulations are interchangeable. However, it is not known if higher doses of Sirolimus Oral Solution are clinically equivalent to higher doses of Sirolimus Tablets on a mg-to-mg basis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Renal Transplant Patients at Low- to Moderate-Immunologic Risk
Sirolimus Oral Solution and Cyclosporine Combination Therapy
For de novo renal transplant patients, it is recommended that Sirolimus Oral Solution and Tablets be used initially in a regimen with cyclosporine and corticosteroids. A loading dose of sirolimus equivalent to 3 times the maintenance dose should be given, i.e. a daily maintenance dose of 2 mg should be preceded with a loading dose of 6 mg. Therapeutic drug monitoring should be used to maintain sirolimus drug concentrations within the target-range [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Sirolimus Oral Solution Following Cyclosporine Withdrawal
At 2 to 4 months following transplantation, cyclosporine should be progressively discontinued over 4 to 8 weeks, and the Sirolimus Oral Solution dose should be adjusted to obtain sirolimus whole blood trough concentrations within the target-range [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Because cyclosporine inhibits the metabolism and transport of sirolimus, sirolimus concentrations may decrease when cyclosporine is discontinued, unless the Sirolimus Oral Solution dose is increased [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Renal Transplant Patients at High-Immunologic Risk
In patients with high-immunologic risk, it is recommended that Sirolimus Oral Solution be used in combination with cyclosporine and corticosteroids for the first 12 months following transplantation [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. The safety and efficacy of this combination in high-immunologic risk patients has not been studied beyond the first 12 months. Therefore, after the first 12 months following transplantation, any adjustments to the immunosuppressive regimen should be considered on the basis of the clinical status of the patient.
For patients receiving Sirolimus Oral Solution with cyclosporine, Sirolimus Oral Solution therapy should be initiated with a loading dose of up to 15 mg on day 1 post-transplantation. Beginning on day 2, an initial maintenance dose of 5 mg/day should be given. A trough level should be obtained between days 5 and 7, and the daily dose of Sirolimus Oral Solution should thereafter be adjusted [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
The starting dose of cyclosporine should be up to 7 mg/kg/day in divided doses and the dose should subsequently be adjusted to achieve target whole blood trough concentrations [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Prednisone should be administered at a minimum of 5 mg/day.
Antibody induction therapy may be used.
2.5 Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
Monitoring of sirolimus trough concentrations is recommended for all patients, especially in those patients likely to have altered drug metabolism, in patients ≥ 13 years who weigh less than 40 kg, in patients with hepatic impairment, when a change in the sirolimus dosage form is made, and during concurrent administration of strong CYP3A4 inducers and inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Therapeutic drug monitoring should not be the sole basis for adjusting sirolimus therapy. Careful attention should be made to clinical signs/symptoms, tissue biopsy findings, and laboratory parameters.
When used in combination with cyclosporine, sirolimus trough concentrations should be maintained within the target-range [see Clinical Studies (14), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Following cyclosporine withdrawal in transplant patients at low- to moderate-immunologic risk, the target sirolimus trough concentrations should be 16 to 24 ng/mL for the first year following transplantation. Thereafter, the target sirolimus concentrations should be 12 to 20 ng/mL.
The above recommended 24-hour trough concentration ranges for sirolimus are based on chromatographic methods. Currently in clinical practice, sirolimus whole blood concentrations are being measured by both chromatographic and immunoassay methodologies. Because the measured sirolimus whole blood concentrations depend on the type of assay used, the concentrations obtained by these different methodologies are not interchangeable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Adjustments to the targeted range should be made according to the assay utilized to determine sirolimus trough concentrations. Since results are assay and laboratory dependent, and the results may change over time, adjustments to the targeted therapeutic range must be made with a detailed knowledge of the site-specific assay used. Therefore, communication should be maintained with the laboratory performing the assay. A discussion of different assay methods is contained in Clinical Therapeutics, Volume 22, Supplement B, April 2000 [see References (15)].
2.6 Patients with Low Body Weight
The initial dosage in patients ≥ 13 years who weigh less than 40 kg should be adjusted, based on body surface area, to 1 mg/m2/day. The loading dose should be 3 mg/m2.
2.7 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
It is recommended that the maintenance dose of Sirolimus Oral Solution be reduced by approximately one third in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment and by approximately one half in patients with severe hepatic impairment. It is not necessary to modify the Sirolimus Oral Solution loading dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.8 Patients with Renal Impairment
Dosage adjustment is not needed in patients with impaired renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ].
2.9 Instructions for Dilution and Administration of Sirolimus Oral Solution
The amber oral dose syringe should be used to withdraw the prescribed amount of Sirolimus Oral Solution from the bottle. Empty the correct amount of Sirolimus Oral Solution from the syringe into only a glass or plastic container holding at least two (2) ounces (1/4 cup, 60 mL) of water or orange juice. No other liquids, including grapefruit juice, should be used for dilution [see Drug Interactions (7.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Stir vigorously and drink at once. Refill the container with an additional volume [minimum of four (4) ounces (1/2 cup, 120 mL)] of water or orange juice, stir vigorously, and drink at once.
Sirolimus Oral Solution contains polysorbate 80, which is known to increase the rate of di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) extraction from polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This should be considered during the preparation and administration of Sirolimus Oral Solution. It is important that these recommendations be followed closely.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sirolimus Oral Solution is contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to sirolimus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Susceptibility to Infection and the Possible Development of Lymphoma
Increased susceptibility to infection and the possible development of lymphoma and other malignancies, particularly of the skin, may result from immunosuppression. The rates of lymphoma/lymphoproliferative disease observed in Studies 1 and 2 were 0.7-3.2% (for sirolimus-treated patients) versus 0.6-0.8% (azathioprine and placebo control) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and (6.2)]. Oversuppression of the immune system can also increase susceptibility to infection, including opportunistic infections such as tuberculosis, fatal infections, and sepsis. Only physicians experienced in immunosuppressive therapy and management of organ transplant patients should use sirolimus for prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving renal transplants. Patients receiving the drug should be managed in facilities equipped and staffed with adequate laboratory and supportive medical resources. The physician responsible for maintenance therapy should have complete information requisite for the follow-up of the patient.
5.2 Liver Transplantation – Excess Mortality, Graft Loss, and Hepatic Artery Thrombosis
The safety and efficacy of sirolimus as immunosuppressive therapy have not been established in liver transplant patients; therefore, such use is not recommended. The use of sirolimus has been associated with adverse outcomes in patients following liver transplantation, including excess mortality, graft loss and hepatic artery thrombosis (HAT).
In a study in de novo liver transplant patients, the use of sirolimus in combination with tacrolimus was associated with excess mortality and graft loss (22% in combination versus 9% on tacrolimus alone). Many of these patients had evidence of infection at or near the time of death.
In this and another study in de novo liver transplant patients, the use of sirolimus in combination with cyclosporine or tacrolimus was associated with an increase in HAT (7% in combination versus 2% in the control arm); most cases of HAT occurred within 30 days post-transplantation, and most led to graft loss or death.
In a clinical study in stable liver transplant patients 6-144 months post-liver transplantation and receiving a CNI-based regimen, an increased number of deaths was observed in the group converted to a sirolimus-based regimen compared to the group who was continued on a CNI-based regimen, although the difference was not statistically significant (3.8% versus 1.4%) [see Clinical Studies (14.5)].
5.3 Lung Transplantation – Bronchial Anastomotic Dehiscence
Cases of bronchial anastomotic dehiscence, most fatal, have been reported in de novo lung transplant patients when sirolimus has been used as part of an immunosuppressive regimen.
The safety and efficacy of sirolimus as immunosuppressive therapy have not been established in lung transplant patients; therefore, such use is not recommended.
5.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, angioedema, exfoliative dermatitis and hypersensitivity vasculitis, have been associated with the administration of sirolimus [see Adverse Reactions (6.7)].
5.5 Angioedema
Sirolimus has been associated with the development of angioedema. The concomitant use of sirolimus with other drugs known to cause angioedema, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, may increase the risk of developing angioedema. Elevated sirolimus levels (with/without concomitant ACE inhibitors) may also potentiate angioedema [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. In some cases, the angioedema has resolved upon discontinuation or dose reduction of sirolimus.
5.6 Fluid Accumulation and Impairment of Wound Healing
There have been reports of impaired or delayed wound healing in patients receiving sirolimus, including lymphocele and wound dehiscence [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors such as sirolimus have been shown in vitro to inhibit production of certain growth factors that may affect angiogenesis, fibroblast proliferation, and vascular permeability. Lymphocele, a known surgical complication of renal transplantation, occurred significantly more often in a dose-related fashion in patients treated with sirolimus [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Appropriate measures should be considered to minimize such complications. Patients with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2 may be at increased risk of abnormal wound healing based on data from the medical literature.
There have also been reports of fluid accumulation, including peripheral edema, lymphedema, pleural effusion, ascites, and pericardial effusions (including hemodynamically significant effusions and tamponade requiring intervention in children and adults), in patients receiving sirolimus.
5.7 Hyperlipidemia
Increased serum cholesterol and triglycerides requiring treatment occurred more frequently in patients treated with sirolimus compared with azathioprine or placebo controls in Studies 1 and 2 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. There were increased incidences of hypercholesterolemia (43-46%) and/or hypertriglyceridemia (45-57%) in patients receiving sirolimus compared with placebo controls (each 23%). The risk/benefit should be carefully considered in patients with established hyperlipidemia before initiating an immunosuppressive regimen including sirolimus.
Any patient who is administered sirolimus should be monitored for hyperlipidemia. If detected, interventions such as diet, exercise, and lipid-lowering agents should be initiated as outlined by the National Cholesterol Education Program guidelines.
In clinical trials of patients receiving sirolimus plus cyclosporine or sirolimus after cyclosporine withdrawal, up to 90% of patients required treatment for hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterolemia with anti-lipid therapy (e.g., statins, fibrates). Despite anti-lipid management, up to 50% of patients had fasting serum cholesterol levels >240 mg/dL and triglycerides above recommended target levels. The concomitant administration of sirolimus and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors resulted in adverse reactions such as CPK elevations (3%), myalgia (6.7%) and rhabdomyolysis (<1%). In these trials, the number of patients was too small and duration of follow-up too short to evaluate the long-term impact of sirolimus on cardiovascular mortality.
During sirolimus therapy with or without cyclosporine, patients should be monitored for elevated lipids, and patients administered an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor and/or fibrate should be monitored for the possible development of rhabdomyolysis and other adverse effects, as described in the respective labeling for these agents.
5.8 Decline in Renal Function
Renal function should be closely monitored during the co-administration of sirolimus with cyclosporine, because long-term administration of the combination has been associated with deterioration of renal function. Patients treated with cyclosporine and sirolimus were noted to have higher serum creatinine levels and lower glomerular filtration rates compared with patients treated with cyclosporine and placebo or azathioprine controls (Studies 1 and 2). The rate of decline in renal function in these studies was greater in patients receiving sirolimus and cyclosporine compared with control therapies.
Appropriate adjustment of the immunosuppressive regimen, including discontinuation of sirolimus and/or cyclosporine, should be considered in patients with elevated or increasing serum creatinine levels. In patients at low- to moderate-immunologic risk, continuation of combination therapy with cyclosporine beyond 4 months following transplantation should only be considered when the benefits outweigh the risks of this combination for the individual patients. Caution should be exercised when using agents (e.g., aminoglycosides and amphotericin B) that are known to have a deleterious effect on renal function.
In patients with delayed graft function, sirolimus may delay recovery of renal function.
5.9 Proteinuria
Periodic quantitative monitoring of urinary protein excretion is recommended. In a study evaluating conversion from calcineurin inhibitors (CNI) to sirolimus in maintenance renal transplant patients 6-120 months post-transplant, increased urinary protein excretion was commonly observed from 6 through 24 months after conversion to sirolimus compared with CNI continuation [see Clinical Studies (14.4), Adverse Reactions (6.4)]. Patients with the greatest amount of urinary protein excretion prior to sirolimus conversion were those whose protein excretion increased the most after conversion. New onset nephrosis (nephrotic syndrome) was also reported as a treatment-emergent adverse reaction in 2.2% of the sirolimus conversion group patients in comparison to 0.4% in the CNI continuation group of patients. Nephrotic range proteinuria (defined as urinary protein to creatinine ratio > 3.5) was also reported in 9.2% in the sirolimus conversion group of patients in comparison to 3.7% in the CNI continuation group of patients. In some patients, reduction in the degree of urinary protein excretion was observed for individual patients following discontinuation of sirolimus. The safety and efficacy of conversion from calcineurin inhibitors to sirolimus in maintenance renal transplant patients have not been established.
5.10 Latent Viral Infections
Immunosuppressed patients are at increased risk for opportunistic infections, including activation of latent viral infections. These include BK virus-associated nephropathy, which has been observed in renal transplant patients receiving immunosuppressants, including sirolimus. This infection may be associated with serious outcomes, including deteriorating renal function and renal graft loss [see Adverse Reactions (6.7)]. Patient monitoring may help detect patients at risk for BK virus-associated nephropathy. Reduction in immunosuppression should be considered for patients who develop evidence of BK virus-associated nephropathy.
Cases of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), sometimes fatal have been reported in patients treated with immunosuppressants, including sirolimus. PML commonly presents with hemiparesis, apathy, confusion, cognitive deficiencies and ataxia. Risk factors for PML include treatment with immunosuppressant therapies and impairment of immune function. In immunosuppressed patients, physicians should consider PML in the differential diagnosis in patients reporting neurological symptoms and consultation with a neurologist should be considered as clinically indicated. Consideration should be given to reducing the amount of immunosuppression in patients who develop PML. In transplant patients, physicians should also consider the risk that reduced immunosuppression represents to the graft.
5.11 Interstitial Lung Disease/Non-Infectious Pneumonitis
Cases of interstitial lung disease [ILD] (including pneumonitis, bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia [BOOP], and pulmonary fibrosis), some fatal, with no identified infectious etiology have occurred in patients receiving immunosuppressive regimens including sirolimus. In some cases, the ILD was reported with pulmonary hypertension (including pulmonary arterial hypertension [PAH]) as a secondary event. In some cases, the ILD has resolved upon discontinuation or dose reduction of sirolimus. The risk may be increased as the trough sirolimus concentration increases [see Adverse Reactions (6.7)].
5.12 De Novo Use Without Cyclosporine
The safety and efficacy of de novo use of sirolimus without cyclosporine is not established in renal transplant patients. In a multicenter clinical study, de novo renal transplant patients treated with sirolimus, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), steroids, and an IL-2 receptor antagonist had significantly higher acute rejection rates and numerically higher death rates compared to patients treated with cyclosporine, MMF, steroids, and IL-2 receptor antagonist. A benefit, in terms of better renal function, was not apparent in the treatment arm with de novo use of sirolimus without cyclosporine. These findings were also observed in a similar treatment group of another clinical trial.
5.13 Increased Risk of Calcineurin Inhibitor-Induced Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome/ Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura/Thrombotic Microangiopathy
The concomitant use of sirolimus with a calcineurin inhibitor may increase the risk of calcineurin inhibitor-induced hemolytic uremic syndrome/thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/thrombotic microangiopathy (HUS/TTP/TMA) [see Adverse Reactions (6.7)].
5.14 Antimicrobial Prophylaxis
Cases of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia have been reported in transplant patients not receiving antimicrobial prophylaxis. Therefore, antimicrobial prophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia should be administered for 1 year following transplantation.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) prophylaxis is recommended for 3 months after transplantation, particularly for patients at increased risk for CMV disease.
5.15 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on animal studies and the mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], sirolimus may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal studies, mTOR inhibitors caused embryo-fetal toxicity when administered during the period of organogenesis at maternal exposures that were equal to or less than human exposures at the recommended lowest starting dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise women of childbearing potential to avoid becoming pregnant and to use effective contraception while using sirolimus and for 12 weeks after ending treatment. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
5.16 Different Sirolimus Trough Concentration Reported between Chromatographic and Immunoassay Methodologies
Currently in clinical practice, sirolimus whole blood concentrations are being measured by various chromatographic and immunoassay methodologies. Patient sample concentration values from different assays may not be interchangeable [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.17 Skin Cancer Events
Patients on immunosuppressive therapy are at increased risk for skin cancer. Exposure to sunlight and ultraviolet (UV) light should be limited by wearing protective clothing and using a sunscreen with a high protection factor [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2, 6.7)].
5.18 Interaction with Strong Inhibitors and Inducers of CYP3A4 and/or P-gp
Avoid concomitant use of sirolimus with strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 and/or P-gp (such as ketoconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole, erythromycin, telithromycin, or clarithromycin) or strong inducers of CYP3A4 and/or P-gp (such as rifampin or rifabutin) [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label.
· Increased susceptibility to infection, lymphoma, and malignancy [see Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
· Excess mortality, graft loss, and hepatic artery thrombosis in liver transplant patients [see Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
· Bronchial anastomotic dehiscence in lung transplant patients [see Boxed Warning , Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
· Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
· Exfoliative dermatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
· Angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
· Fluid Accumulation and Impairment of Wound Healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
· Hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
· Decline in renal function in long-term combination of cyclosporine with sirolimus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
· Proteinuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
· Interstitial lung disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ]
· Increased risk of calcineurin inhibitor-induced HUS/TTP/TMA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13) ].
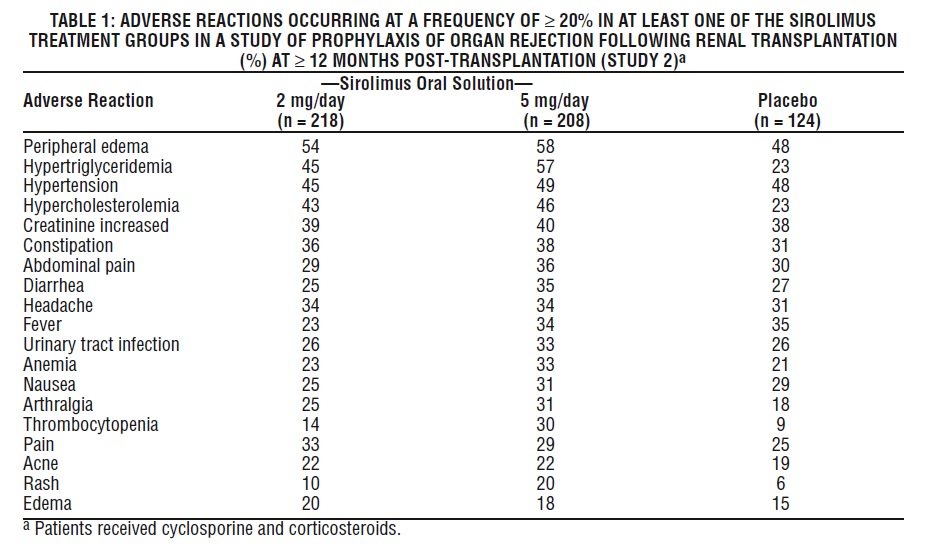
The most common (≥ 30%) adverse reactions observed with sirolimus in clinical studies for organ rejection prophylaxis in recipients of renal transplantation are: peripheral edema, hypertriglyceridemia, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, creatinine increased, constipation, abdominal pain, diarrhea, headache, fever, urinary tract infection, anemia, nausea, arthralgia, pain, and thrombocytopenia.
The following adverse reactions resulted in a rate of discontinuation of > 5% in clinical trials for renal transplant rejection prophylaxis: creatinine increased, hypertriglyceridemia, and TTP.
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience in Prophylaxis of Organ Rejection Following Renal Transplantation
The safety and efficacy of Sirolimus Oral Solution for the prevention of organ rejection following renal transplantation were assessed in two randomized, double-blind, multicenter, controlled trials [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ]. The safety profiles in the two studies were similar.
The incidence of adverse reactions in the randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial (Study 2) in which 219 renal transplant patients received Sirolimus Oral Solution 2 mg/day, 208 received Sirolimus Oral Solution 5 mg/day, and 124 received placebo is presented in Table 1 below. The study population had a mean age of 46 years (range 15 to 71 years), the distribution was 67% male, and the composition by race was: White (78%), Black (11%), Asian (3%), Hispanic (2%), and Other (5%). All patients were treated with cyclosporine and corticosteroids. Data (≥ 12 months post-transplant) presented in the following table show the adverse reactions that occurred in at least one of the sirolimus treatment groups with an incidence of ≥ 20%.
The safety profile of the tablet did not differ from that of the oral solution formulation [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ].
In general, adverse reactions related to the administration of sirolimus were dependent on dose/concentration. Although a daily maintenance dose of 5 mg, with a loading dose of 15 mg, was shown to be safe and effective, no efficacy advantage over the 2 mg dose could be established for renal transplant patients. Patients receiving 2 mg of Sirolimus Oral Solution per day demonstrated an overall better safety profile than did patients receiving 5 mg of Sirolimus Oral Solution per day.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in one clinical trial of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of the same or another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The following adverse reactions were reported less frequently (≥ 3%, but < 20%)
- Body as a Whole – Sepsis, lymphocele, herpes zoster, herpes simplex.
- Cardiovascular – Venous thromboembolism (including pulmonary embolism, deep venous thrombosis), tachycardia.
- Digestive System – Stomatitis.
- Hematologic and Lymphatic System – Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome (TTP/HUS), leukopenia.
- Metabolic/Nutritional – Abnormal healing, increased lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), hypokalemia, diabetes mellitus.
- Musculoskeletal System – Bone necrosis.
- Respiratory System – Pneumonia, epistaxis.
- Skin – Melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma.
- Urogenital System – Pyelonephritis, decline in renal function (creatinine increased) in long-term combination of cyclosporine with sirolimus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)], ovarian cysts, menstrual disorders (including amenorrhea and menorrhagia).
Less frequently (< 3%) occurring adverse reactions included: lymphoma/post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, mycobacterial infections (including M. tuberculosis), pancreatitis, cytomegalovirus (CMV), and Epstein-Barr virus.
Increased Serum Cholesterol and Triglycerides
The use of sirolimus in renal transplant patients was associated with increased serum cholesterol and triglycerides that may require treatment.
In Studies 1 and 2, in de novo renal transplant patients who began the study with fasting, total serum cholesterol < 200 mg/dL or fasting, total serum triglycerides < 200 mg/dL, there was an increased incidence of hypercholesterolemia (fasting serum cholesterol > 240 mg/dL) or hypertriglyceridemia (fasting serum triglycerides > 500 mg/dL), respectively, in patients receiving both sirolimus 2 mg and sirolimus 5 mg compared with azathioprine and placebo controls.
Treatment of new-onset hypercholesterolemia with lipid-lowering agents was required in 42-52% of patients enrolled in the sirolimus arms of Studies 1 and 2 compared with 16% of patients in the placebo arm and 22% of patients in the azathioprine arm. In other sirolimus renal transplant studies, up to 90% of patients required treatment for hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterolemia with anti-lipid therapy (e.g., statins, fibrates). Despite anti-lipid management, up to 50% of patients had fasting serum cholesterol levels >240 mg/dL and triglycerides above recommended target levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Abnormal Healing
Abnormal healing events following transplant surgery include fascial dehiscence, incisional hernia, and anastomosis disruption (e.g., wound, vascular, airway, ureteral, biliary).
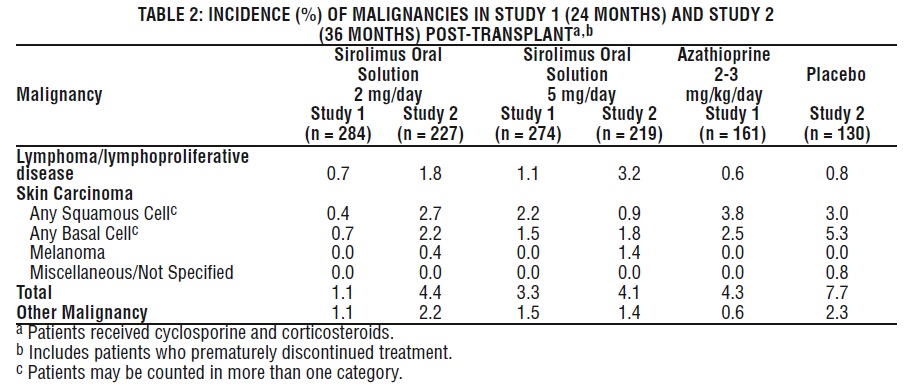
Malignancies
Table 2 below summarizes the incidence of malignancies in the two controlled trials (Studies 1 and 2) for the prevention of acute rejection [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
At 24 months (Study 1) and 36 months (Study 2) post-transplant, there were no significant differences among treatment groups.
6.2 Sirolimus Following Cyclosporine Withdrawal
The incidence of adverse reactions was determined through 36 months in a randomized, multicenter, controlled trial (Study 3) in which 215 renal transplant patients received sirolimus as a maintenance regimen following cyclosporine withdrawal, and 215 patients received sirolimus with cyclosporine therapy [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ]. All patients were treated with corticosteroids. The safety profile prior to randomization (start of cyclosporine withdrawal) was similar to that of the 2 mg sirolimus groups in Studies 1 and 2.
Following randomization (at 3 months), patients who had cyclosporine eliminated from their therapy experienced higher incidences of the following adverse reactions: abnormal liver function tests (including increased AST/SGOT and increased ALT/SGPT), hypokalemia, thrombocytopenia, and abnormal healing. Conversely, the incidence of the following adverse events was higher in patients who remained on cyclosporine than those who had cyclosporine withdrawn from therapy: hypertension, cyclosporine toxicity, increased creatinine, abnormal kidney function, toxic nephropathy, edema, hyperkalemia, hyperuricemia, and gum hyperplasia. Mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure improved significantly following cyclosporine withdrawal.
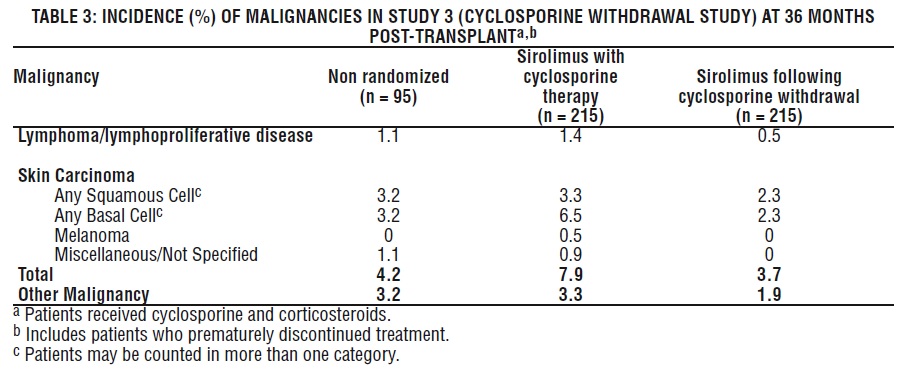
Malignancies
The incidence of malignancies in Study 3 [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] is presented in Table 3.
In Study 3, the incidence of lymphoma/lymphoproliferative disease was similar in all treatment groups. The overall incidence of malignancy was higher in patients receiving sirolimus plus cyclosporine compared with patients who had cyclosporine withdrawn. Conclusions regarding these differences in the incidence of malignancy could not be made because Study 3 was not designed to consider malignancy risk factors or systematically screen subjects for malignancy. In addition, more patients in the sirolimus with cyclosporine group had a pretransplantation history of skin carcinoma.
6.3 High-Immunologic Risk Renal Transplant Patients
Safety was assessed in 224 patients who received at least one dose of sirolimus with cyclosporine [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. Overall, the incidence and nature of adverse reactions was similar to those seen in previous combination studies with sirolimus. The incidence of malignancy was 1.3% at 12 months.
6.4 Conversion from Calcineurin Inhibitors to Sirolimus in Maintenance Renal Transplant Population
The safety and efficacy of conversion from calcineurin inhibitors to sirolimus in maintenance renal transplant population have not been established [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ]. In a study evaluating the safety and efficacy of conversion from calcineurin inhibitors to sirolimus (initial target sirolimus concentrations of 12-20 ng/mL, and then 8-20 ng/mL, by chromatographic assay) in maintenance renal transplant patients, enrollment was stopped in the subset of patients (n = 87) with a baseline glomerular filtration rate of less than 40 mL/min. There was a higher rate of serious adverse events, including pneumonia, acute rejection, graft loss and death, in this stratum of the sirolimus treatment arm.
The subset of patients with a baseline glomerular filtration rate of less than 40 mL/min had 2 years of follow-up after randomization. In this population, the rate of pneumonia was 25.9% (15/58) versus 13.8% (4/29), graft loss (excluding death with functioning graft loss) was 22.4% (13/58) versus 31.0% (9/29), and death was 15.5% (9/58) versus 3.4% (1/29) in the sirolimus conversion group and CNI continuation group, respectively.
In the subset of patients with a baseline glomerular filtration rate of greater than 40 mL/min, there was no benefit associated with conversion with regard to improvement in renal function and a greater incidence of proteinuria in the sirolimus conversion arm.
Overall in this study, a 5-fold increase in the reports of tuberculosis among sirolimus 2.0% (11/551) and comparator 0.4% (1/273) treatment groups was observed with 2:1 randomization scheme.
In a second study evaluating the safety and efficacy of conversion from tacrolimus to Sirolimus 3 to 5 months post kidney transplant, a higher rate of adverse events, discontinuations due to adverse events, acute rejection, and new onset diabetes mellitus was observed following conversion to Sirolimus. There was also no benefit with respect to renal function and a greater incidence of proteinuria was observed after conversion to sirolimus [(see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
6.5 Pediatric Renal Transplant Patients
Safety was assessed in a controlled clinical trial in pediatric (< 18 years of age) renal transplant patients considered at high-immunologic risk, defined as a history of one or more acute allograft rejection episodes and/or the presence of chronic allograft nephropathy on a renal biopsy [see Clinical Studies (14.6)]. The use of sirolimus in combination with calcineurin inhibitors and corticosteroids was associated with a higher incidence of deterioration of renal function (creatinine increased) compared to calcineurin inhibitor-based therapy, serum lipid abnormalities (including, but not limited to, increased serum triglycerides and cholesterol), and urinary tract infections.
6.7 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of sirolimus in transplant patients. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
•Body as a Whole – Lymphedema.
•Cardiovascular – Pericardial effusion (including hemodynamically significant effusions and tamponade requiring intervention in children and adults) and fluid accumulation.
•Digestive System – Ascites.
•Hematological/Lymphatic –Pancytopenia, neutropenia.
•Hepatobiliary Disorders – Hepatotoxicity, including fatal hepatic necrosis, with elevated sirolimus trough concentrations.
•Immune System – Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, angioedema, and hypersensitivity vasculitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
•Infections – Tuberculosis. BK virus associated nephropathy has been observed in patients receiving immunosuppressants, including sirolimus. This infection may be associated with serious outcomes, including deteriorating renal function and renal graft loss. Cases of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), sometimes fatal, have been reported in patients treated with immunosuppressants, including sirolimus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. Clostridium difficile enterocolitis.
•Metabolic/Nutritional – Liver function test abnormal, AST/SGOT increased, ALT/SGPT increased, hypophosphatemia, hyperglycemia, diabetes mellitus.
•Nervous system - Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome.
•Respiratory – Cases of interstitial lung disease (including pneumonitis, bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia [BOOP], and pulmonary fibrosis), some fatal, with no identified infectious etiology have occurred in patients receiving immunosuppressive regimens including sirolimus. In some cases, the interstitial lung disease has resolved upon discontinuation or dose reduction of sirolimus. The risk may be increased as the sirolimus trough concentration increases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]; pulmonary hemorrhage; pleural effusion; alveolar proteinosis.
•Skin – Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin (Merkel cell carcinoma) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17)], exfoliative dermatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
•Urogenital – Nephrotic syndrome, proteinuria, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, ovarian cysts, menstrual disorders (including amenorrhea and menorrhagia). Azoospermia has been reported with the use of sirolimus and has been reversible upon discontinuation of sirolimus in most cases.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Sirolimus is known to be a substrate for both cytochrome P-450 3A4 (CYP3A4) and p-glycoprotein (P-gp). Inducers of CYP3A4 and P-gp may decrease sirolimus concentrations whereas inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-gp may increase sirolimus concentrations.
7.1 Use with Cyclosporine
Cyclosporine, a substrate and inhibitor of CYP3A4 and P-gp, was demonstrated to increase sirolimus concentrations when co-administered with sirolimus. In order to diminish the effect of this interaction with cyclosporine, it is recommended that sirolimus be taken 4 hours after administration of cyclosporine oral solution (MODIFIED) and/or cyclosporine capsules (MODIFIED). If cyclosporine is withdrawn from combination therapy with sirolimus, higher doses of sirolimus are needed to maintain the recommended sirolimus trough concentration ranges [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Strong Inducers and Strong Inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-gp
Avoid concomitant use of sirolimus with strong inducers (e.g., rifampin, rifabutin) and strong inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole, erythromycin, telithromycin, clarithromycin) of CYP3A4 and P-gp. Alternative agents with lesser interaction potential with sirolimus should be considered [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Grapefruit Juice
Because grapefruit juice inhibits the CYP3A4-mediated metabolism of sirolimus, it must not be taken with or be used for dilution of sirolimus [see Dosage and Administration (2.9), Drug Interactions (7.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.4 Weak and Moderate Inducers or Inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-gp
Exercise caution when using sirolimus with drugs or agents that are modulators of CYP3A4 and P-gp. The dosage of sirolimus and/or the co-administered drug may need to be adjusted [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Drugs that could increase sirolimus blood concentrations:
Bromocriptine, cimetidine, cisapride, clotrimazole, danazol, diltiazem, fluconazole, protease inhibitors (e.g., HIV and hepatitis C that include drugs such as ritonavir, indinavir, boceprevir, and telaprevir), metoclopramide, nicardipine, troleandomycin, verapamil
- Drugs and other agents that could decrease sirolimus concentrations:
Carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifapentine, St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum)
- Drugs with concentrations that could increase when given with sirolimus:
Verapamil
7.5 Vaccination
Immunosuppressants may affect response to vaccination. Therefore, during treatment with sirolimus, vaccination may be less effective. The use of live vaccines should be avoided; live vaccines may include, but are not limited to, the following: measles, mumps, rubella, oral polio, BCG, yellow fever, varicella, and TY21a typhoid.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: Sirolimus was embryo/fetotoxic in rats when given in doses approximately 0.2 to 0.5 the human doses (adjusted for body surface area). Embryo/fetotoxicity was manifested as mortality and reduced fetal weights (with associated delays in skeletal ossification). However, no teratogenesis was evident. In combination with cyclosporine, rats had increased embryo/feto mortality compared with sirolimus alone. There were no effects on rabbit development at a maternally toxic dosage approximately 0.3 to 0.8 times the human doses (adjusted for body surface area). There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Effective contraception must be initiated before sirolimus therapy, during sirolimus therapy, and for 12 weeks after sirolimus therapy has been stopped.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Sirolimus is excreted in trace amounts in milk of lactating rats. It is not known whether sirolimus is excreted in human milk. The pharmacokinetic and safety profiles of sirolimus in infants are not known. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants from sirolimus, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Renal Transplant
The safety and efficacy of sirolimus in pediatric patients < 13 years have not been established.
The safety and efficacy of sirolimus oral solution have been established for prophylaxis of organ rejection in renal transplantation in children ≥ 13 years judged to be at low- to moderate-immunologic risk. Use of sirolimus oral solution in this subpopulation of children ≥ 13 years is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled trials of sirolimus oral solution in adults with additional pharmacokinetic data in pediatric renal transplantation patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Safety and efficacy information from a controlled clinical trial in pediatric and adolescent (< 18 years of age) renal transplant patients judged to be at high-immunologic risk, defined as a history of one or more acute rejection episodes and/or the presence of chronic allograft nephropathy, do not support the chronic use of sirolimus oral solution in combination with calcineurin inhibitors and corticosteroids, due to the higher incidence of lipid abnormalities and deterioration of renal function associated with these immunosuppressive regimens compared to calcineurin inhibitors, without increased benefit with respect to acute rejection, graft survival, or patient survival [see Clinical Studies (14.6)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of sirolimus oral solution did not include sufficient numbers of patients ≥ 65 years to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Data pertaining to sirolimus trough concentrations suggest that dose adjustments based upon age in geriatric renal patients are not necessary. Differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients have not been identified. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Reports of overdose with sirolimus have been received; however, experience has been limited. In general, the adverse effects of overdose are consistent with those listed in the adverse reactions section [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
General supportive measures should be followed in all cases of overdose. Based on the low aqueous solubility and high erythrocyte and plasma protein binding of sirolimus, it is anticipated that sirolimus is not dialyzable to any significant extent. In mice and rats, the acute oral LD50 was greater than 800 mg/kg.
11 DESCRIPTION
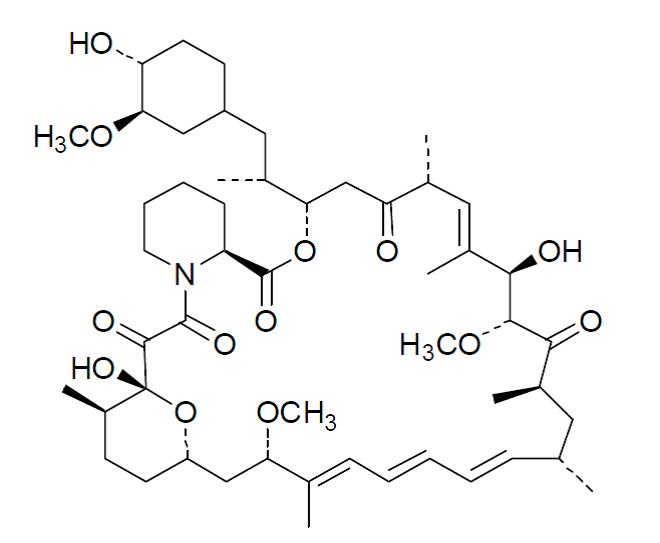
Sirolimus is an immunosuppressive agent. Sirolimus is a macrocyclic lactone produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. The chemical name of sirolimus (also known as rapamycin) is (3S,6R,7E,9R,10R,12R,14S,15E,17E,19E,21S,23S,26R,27R,34aS)- 9,10,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,32,33,34,34a-hexadecahydro-9,27-dihydroxy-3-[(1R)-2- [(1S,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylethyl)-10,21-dimethoxy- 6,8,12,14,20,26-hexamethyl-23,27-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4] oxaazacyclohentriacontine- 1,5,11,28,29 (4H,6H,31H)-pentone. Its molecular formula is C51H79NO13 and its molecular weight is 914.2. The structural formula of sirolimus is illustrated as follows
Sirolimus is a white to off-white powder and is practically insoluble in water, but freely soluble in acetone, dimethyl sulfoxide and methanol.
Sirolimus is available for administration as an oral solution containing 1 mg/mL sirolimus.
The inactive ingredients in Sirolimus Oral Solution are Phosal® 50 PG (alcohol, ascorbyl palmitate, phosphatidylcholine, propylene glycol, soy acid, soy lecithin, sunflower seed oil glyceride, and tocopherol) and polysorbate 80. Sirolimus Oral Solution contains 1.5% - 2.5% ethanol.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sirolimus inhibits T-lymphocyte activation and proliferation that occurs in response to antigenic and cytokine (Interleukin [IL]-2, IL-4, and IL-15) stimulation by a mechanism that is distinct from that of other immunosuppressants. Sirolimus also inhibits antibody production. In cells, sirolimus binds to the immunophilin, FK Binding Protein-12 (FKBP-12), to generate an immunosuppressive complex. The sirolimus: FKBP-12 complex has no effect on calcineurin activity. This complex binds to and inhibits the activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a key regulatory kinase. This inhibition suppresses cytokine-driven T-cell proliferation, inhibiting the progression from the G1 to the S phase of the cell cycle.
Studies in experimental models show that sirolimus prolongs allograft (kidney, heart, skin, islet, small bowel, pancreatico-duodenal, and bone marrow) survival in mice, rats, pigs, and/or primates. Sirolimus reverses acute rejection of heart and kidney allografts in rats and prolongs the graft survival in presensitized rats. In some studies, the immunosuppressive effect of sirolimus lasts up to 6 months after discontinuation of therapy. This tolerization effect is alloantigen-specific.
In rodent models of autoimmune disease, sirolimus suppresses immune-mediated events associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, collagen-induced arthritis, autoimmune type I diabetes, autoimmune myocarditis, experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, graft-versus-host disease, and autoimmune uveoretinitis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Orally-administered sirolimus, at doses of 2 mg/day and 5 mg/day, significantly reduced the incidence of organ rejection in low- to moderate-immunologic risk renal transplant patients at 6 months following transplantation compared with either azathioprine or placebo [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. There was no demonstrable efficacy advantage of a daily maintenance dose of 5 mg with a loading dose of 15 mg over a daily maintenance dose of 2 mg with a loading dose of 6 mg. Therapeutic drug monitoring should be used to maintain sirolimus drug levels within the target-range [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Sirolimus pharmacokinetics activity have been determined following oral administration in healthy subjects, pediatric patients, hepatically impaired patients, and renal transplant patients.
The pharmacokinetic parameters of sirolimus in low- to moderate-immunologic risk adult renal transplant patients following multiple dosing with sirolimus 2 mg daily, in combination with cyclosporine and corticosteroids, is summarized in Table 4.
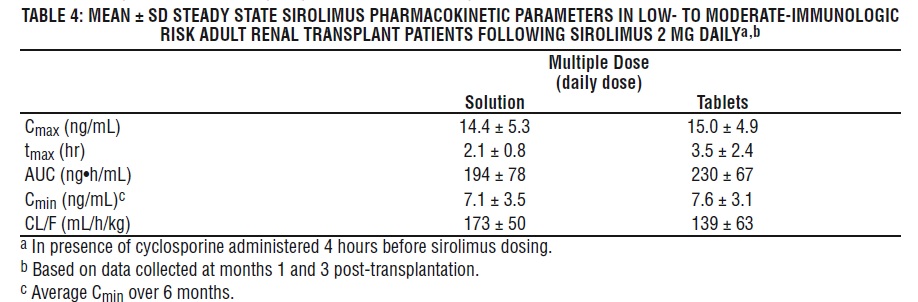
Whole blood trough sirolimus concentrations, as measured by LC/MS/MS in renal transplant patients, were significantly correlated with AUC τ, ss . Upon repeated, twice-daily administration without an initial loading dose in a multiple-dose study, the average trough concentration of sirolimus increases approximately 2- to 3-fold over the initial 6 days of therapy, at which time steady-state is reached. A loading dose of 3 times the maintenance dose will provide near steady-state concentrations within 1 day in most patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.5), Warning and Precautions (5.15) ].
Absorption
Following administration of sirolimus oral solution, the mean times to peak concentration (t max ) of sirolimus are approximately 1 hour and 2 hours in healthy subjects and renal transplant patients, respectively. The systemic availability of sirolimus is low, and was estimated to be approximately 14% after the administration of sirolimus oral solution. In healthy subjects, the mean bioavailability of sirolimus after administration of the tablet is approximately 27% higher relative to the solution. Sirolimus tablets are not bioequivalent to the solution; however, clinical equivalence has been demonstrated at the 2 mg dose level. Sirolimus concentrations, following the administration of sirolimus oral solution to stable renal transplant patients, are dose-proportional between 3 and 12 mg/m2 .
Food Effects
To minimize variability in sirolimus concentrations, sirolimus oral solution should be taken consistently with or without food [see Dosage and Administration (2) ]. In healthy subjects, a high-fat meal (861.8 kcal, 54.9% kcal from fat) increased the mean total exposure (AUC) of sirolimus by 23 to 35%, compared with fasting. The effect of food on the mean sirolimus C max was inconsistent depending on the sirolimus dosage form evaluated.
Distribution
The mean (± SD) blood-to-plasma ratio of sirolimus was 36 ± 18 in stable renal allograft patients, indicating that sirolimus is extensively partitioned into formed blood elements. The mean volume of distribution (Vss/F) of sirolimus is 12 ± 8 L/kg. Sirolimus is extensively bound (approximately 92%) to human plasma proteins, mainly serum albumin (97%), α1 -acid glycoprotein, and lipoproteins.
Metabolism
Sirolimus is a substrate for both CYP3A4 and P-gp. Sirolimus is extensively metabolized in the intestinal wall and liver and undergoes counter-transport from enterocytes of the small intestine into the gut lumen. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-gp increase sirolimus concentrations. Inducers of CYP3A4 and P-gp decrease sirolimus concentrations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18) and Drug Interactions (7) ]. Sirolimus is extensively metabolized by O-demethylation and/or hydroxylation. Seven (7) major metabolites, including hydroxy, demethyl, and hydroxydemethyl, are identifiable in whole blood. Some of these metabolites are also detectable in plasma, fecal, and urine samples. Sirolimus is the major component in human whole blood and contributes to more than 90% of the immunosuppressive activity.
Excretion
After a single dose of [14C] sirolimus oral solution in healthy volunteers, the majority (91%) of radioactivity was recovered from the feces, and only a minor amount (2.2%) was excreted in urine. The mean ± SD terminal elimination half life (t ½ ) of sirolimus after multiple dosing in stable renal transplant patients was estimated to be about 62 ± 16 hours.
Sirolimus Concentrations (Chromatographic Equivalent) Observed in Phase 3 Clinical Studies
The following sirolimus concentrations
(chromatographic equivalent) were observed in phase 3 clinical studies for prophylaxis of organ rejection in de novo renal transplant patients [see Clinical Studies (14)] .
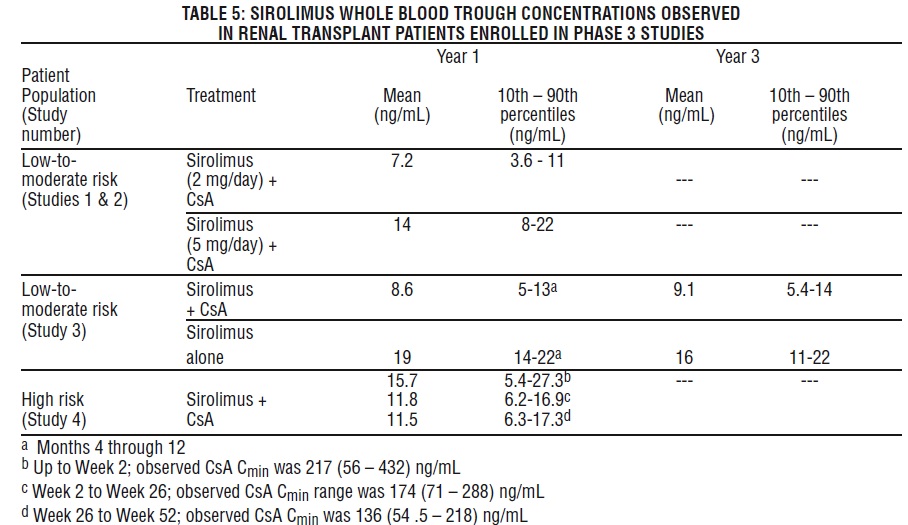
The withdrawal of cyclosporine andconcurrentincreases in sirolimustroughconcentrations to steady-state required approximately 6 weeks. Following cyclosporine withdrawal,larger Sirolimus doseswere required due to the absence of the inhibition of sirolimusmetabolism andtransportby cyclosporine and to achieve higher targetsirolimustrough concentrations during concentration-controlledadministration[see Dosage and Administration(2.1),Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Pharmacokinetics in Specific Populations
Hepatic Impairment
Sirolimus was administered as a single, oral dose to subjects with normal hepatic function and to patients with Child-Pugh classification A (mild), B (moderate), or C (severe) hepatic impairment. Compared with the values in the normal hepatic function group, the patients with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment had 43%, 94%, and 189% higher mean values for sirolimus AUC, respectively, with no statistically significant differences in mean Cmax. As the severity of hepatic impairment increased, there were steady increases in mean sirolimus t1/2, and decreases in the mean sirolimus clearance normalized for body weight (CL/F/kg).
The maintenance dose of sirolimus should be reduced by approximately one third in patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment and by approximately one half in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. It is not necessary to modify the sirolimus loading dose in patients with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment. Therapeutic drug monitoring is necessary in all patients with hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)].
Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of sirolimus is not known. However, there is minimal (2.2%) renal excretion of the drug or its metabolites in healthy volunteers. The loading and the maintenance doses of sirolimus need not be adjusted in patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
Pediatric Renal Transplant Patients
Sirolimus pharmacokinetic data were collected in concentration-controlled trials of pediatric renal transplant patients who were also receiving cyclosporine and corticosteroids. The target ranges for trough concentrations were either 10-20 ng/mL for the 21 children receiving tablets, or 5-15 ng/mL for the one child receiving oral solution. The children aged 6-11 years (n = 8) received mean ± SD doses of 1.75 ± 0.71 mg/day (0.064 ± 0.018 mg/kg, 1.65 ± 0.43 mg/m2). The children aged 12-18 years (n = 14) received mean ± SD doses of 2.79 ± 1.25 mg/day (0.053 ± 0.0150 mg/kg, 1.86 ± 0.61 mg/m2). At the time of sirolimus blood sampling for pharmacokinetic evaluation, the majority (80%) of these pediatric patients received the sirolimus dose at 16 hours after the once-daily cyclosporine dose. See Table 6 below.
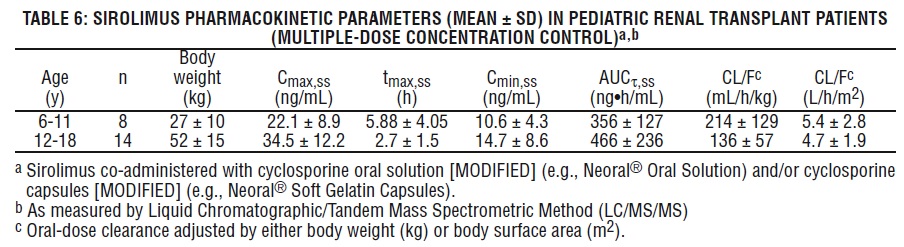
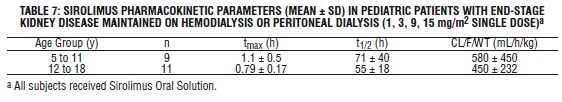
Table 7 below summarizes pharmacokinetic data obtained in pediatric dialysis patients with chronically impaired renal function.
Geriatric
Clinical studies of sirolimus did not include a sufficient number of patients > 65 years of age to determine whether they will respond differently than younger patients. After the administration of sirolimus oral solution or tablets, sirolimus trough concentration data in renal transplant patients > 65 years of age were similar to those in the adult population 18 to 65 years of age.
Gender
Sirolimus clearance in males was 12% lower than that in females; male subjects had a significantly longer t1/2 than did female subjects (72.3 hours versus 61.3 hours). Dose adjustments based on gender are not recommended.
Race
In the phase 3 trials for the prophylaxis of organ rejection following renal transplantation using sirolimus solution or tablets and cyclosporine oral solution [MODIFIED] (e.g., Neoral® Oral Solution) and/or cyclosporine capsules [MODIFIED] (e.g., Neoral® Soft Gelatin Capsules) [see Clinical Studies (14)], there were no significant differences in mean trough sirolimus concentrations over time between Black (n = 190) and non-Black (n = 852) patients during the first 6 months after transplantation.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Sirolimus is known to be a substrate for both cytochrome CYP3A4 and P-gp. The pharmacokinetic interaction between sirolimus and concomitantly administered drugs is discussed below. Drug interaction studies have not been conducted with drugs other than those described below.
Cyclosporine: Cyclosporine is a substrate and inhibitor of CYP3A4 and P-gp. Sirolimus should be taken 4 hours after administration of cyclosporine oral solution (MODIFIED) and/or cyclosporine capsules (MODIFIED). Sirolimus concentrations may decrease when cyclosporine is discontinued, unless the sirolimus dose is increased [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
In a single-dose drug-drug interaction study, 24 healthy volunteers were administered 10 mg sirolimus tablets either simultaneously or 4 hours after a 300-mg dose of Neoral® Soft Gelatin Capsules (cyclosporine capsules [MODIFIED]). For simultaneous administration, mean Cmax and AUC were increased by 512% and 148%, respectively, relative to administration of sirolimus alone. However, when given 4 hours after cyclosporine administration, sirolimus Cmax and AUC were both increased by only 33% compared with administration of sirolimus alone.
In a single dose drug-drug interaction study, 24 healthy volunteers were administered 10 mg Sirolimus Oral Solution either simultaneously or 4 hours after a 300 mg dose of Neoral® Soft Gelatin Capsules (cyclosporine capsules [MODIFIED]). For simultaneous administration, the mean Cmax and AUC of sirolimus, following simultaneous administration were increased by 116% and 230%, respectively, relative to administration of sirolimus alone. However, when given 4 hours after Neoral® Soft Gelatin Capsules (cyclosporine capsules [MODIFIED]) administration, sirolimus Cmax and AUC were increased by only 37% and 80%, respectively, compared with administration of sirolimus alone.
In a single-dose cross-over drug-drug interaction study, 33 healthy volunteers received 5 mg sirolimus oral solution alone, 2 hours before, and 2 hours after a 300 mg dose of Neoral® Soft Gelatin Capsules (cyclosporine capsules [MODIFIED]). When given 2 hours before Neoral® Soft Gelatin Capsules (cyclosporine capsules [MODIFIED]) administration, sirolimus Cmax and AUC were comparable to those with administration of sirolimus alone. However, when given 2 hours after, the mean Cmax and AUC of sirolimus were increased by 126% and 141%, respectively, relative to administration of sirolimus alone.
Mean cyclosporine Cmax and AUC were not significantly affected when sirolimus oral solution was given simultaneously or when administered 4 hours after Neoral® Soft Gelatin Capsules (cyclosporine capsules [MODIFIED]). However, after multiple-dose administration of sirolimus given 4 hours after Neoral® in renal post-transplant patients over 6 months, cyclosporine oral-dose clearance was reduced, and lower doses of Neoral® Soft Gelatin Capsules (cyclosporine capsules [MODIFIED]) were needed to maintain target cyclosporine concentration.
In a multiple-dose study in 150 psoriasis patients, sirolimus 0.5, 1.5, and 3 mg/m2/day was administered simultaneously with Sandimmune® Oral Solution (cyclosporine Oral Solution) 1.25 mg/kg/day. The increase in average sirolimus trough concentrations ranged between 67% to 86% relative to when sirolimus was administered without cyclosporine. The intersubject variability (% CV) for sirolimus trough concentrations ranged from 39.7% to 68.7%. There was no significant effect of multiple-dose sirolimus on cyclosporine trough concentrations following dimmune® Oral Solution (cyclosporine oral solution) administration. However, the % CV was higher (range 85.9% - 165%) than those from previous studies.
Diltiazem: Diltiazem is a substrate and inhibitor of CYP3A4 and P-gp; sirolimus concentrations should be monitored and a dose adjustment may be necessary [see Drug Interactions (7.4)]. The simultaneous oral administration of 10 mg of sirolimus oral solution and 120 mg of diltiazem to 18 healthy volunteers significantly affected the bioavailability of sirolimus. Sirolimus Cmax, tmax, and AUC were increased 1.4-, 1.3-, and 1.6-fold, respectively. Sirolimus did not affect the pharmacokinetics of either diltiazem or its metabolites desacetyldiltiazem and desmethyldiltiazem.
Erythromycin: Erythromycin is a substrate and inhibitor of CYP3A4 and P-gp; co-administration of sirolimus oral solution or tablets and erythromycin is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18), Drug Interactions (7.2)]. The simultaneous oral administration of 2 mg daily of sirolimus oral solution and 800 mg q 8h of erythromycin as erythromycin ethylsuccinate tablets at steady state to 25 healthy volunteers significantly affected the bioavailability of sirolimus and erythromycin. sirolimus Cmax and AUC were increased 4.4- and 4.2-fold respectively and tmax was increased by 0.4 hr. Erythromycin Cmax and AUC were increased 1.6- and 1.7-fold, respectively, and tmax was increased by 0.3 hr.
Ketoconazole: Ketoconazole is a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4 and P-gp; co-administration of sirolimus oral solution or tablets and ketoconazole is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18), Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Multiple-dose ketoconazole administration significantly affected the rate and extent of absorption and sirolimus exposure after administration of sirolimus oral solution, as reflected by increases in sirolimus Cmax, tmax, and AUC of 4.3-fold, 38%, and 10.9-fold, respectively. However, the terminal t½ of sirolimus was not changed. Single-dose sirolimus did not affect steady-state 12-hour plasma ketoconazole concentrations.
Rifampin: Rifampin is a strong inducer of CYP3A4 and P-gp; co-administration of sirolimus oral solution or tablets and rifampin is not recommended. In patients where rifampin is indicated, alternative therapeutic agents with less enzyme induction potential should be considered [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18), Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Pretreatment of 14 healthy volunteers with multiple doses of rifampin, 600 mg daily for 14 days, followed by a single 20-mg dose of sirolimus oral solution, greatly decreased sirolimus AUC and Cmax by about 82% and 71%, respectively.
Verapamil: Verapamil is a substrate and inhibitor of CYP3A4 and P-gp; sirolimus concentrations should be monitored and a dose adjustment may be necessary; [see Drug Interactions (7.4)]. The simultaneous oral administration of 2 mg daily of sirolimus oral solution and 180 mg q 12h of verapamil at steady state to 25 healthy volunteers significantly affected the bioavailability of sirolimus and verapamil. Sirolimus Cmax and AUC were increased 2.3- and 2.2-fold, respectively, without substantial change in tmax. The Cmax and AUC of the pharmacologically active S(-) enantiomer of verapamil were both increased 1.5-fold and tmax was decreased by 1.2 hr.
Drugs Which May Be Co-administered Without Dose Adjustment
Clinically significant pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions were not observed in studies of drugs listed below. Sirolimus and these drugs may be co-administered without dose adjustments.
- Acyclovir
- Atorvastatin
- Digoxin
- Glyburide
- Nifedipine
- Norgestrel/ethinyl estradiol (Lo/Ovral®)
- Prednisolone
- Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim (Bactrim®)
Other Drug-Drug Interactions
Co-administration of sirolimus with other known strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 and/or P-gp (such as voriconazole, itraconazole, telithromycin, or clarithromycin) or other known strong inducers of CYP3A4 and/or P-gp (such as rifabutin) is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17), Drug Interactions (7.2)]. In patients in whom strong inhibitors or inducers of CYP3A4 are indicated, alternative therapeutic agents with less potential for inhibition or induction of CYP3A4 should be considered.
Care should be exercised when drugs or other substances that are substrates and/or inhibitors or inducers of CYP3A4 are administered concomitantly with sirolimus. Other drugs that have the potential to increase sirolimus blood concentrations include (but are not limited to):
• Calcium channel blockers: nicardipine.
• Antifungal agents: clotrimazole, fluconazole.
• Antibiotics: troleandomycin.
• Gastrointestinal prokinetic agents: cisapride, metoclopramide.
• Other drugs: bromocriptine, cimetidine, danazol, protease inhibitors (e.g., for HIV and hepatitis C that include drugs such as ritonavir, indinavir, boceprevir, and telaprevir).
Other drugs that have the potential to decrease sirolimus concentrations include (but are not limited to):
• Anticonvulsants: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin.
• Antibiotics: rifapentine.
Other Drug-Food Interactions
Grapefruit juice reduces CYP3A4-mediated drug metabolism. Grapefruit juice must not be taken with or used for dilution of sirolimus [see Dosage and Administration (2.9), Drug Interactions (7.3)].
Drug-Herb Interactions
St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum) induces CYP3A4 and P-gp. Since sirolimus is a substrate for both cytochrome CYP3A4 and P-gp, there is the potential that the use of St. John’s Wort in patients receiving sirolimus could result in reduced sirolimus concentrations [see Drug Interactions (7.4)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies were conducted in mice and rats. In an 86-week female mouse study at sirolimus doses 30 to 120 times higher than the 2 mg daily clinical dose (adjusted for body surface area), there was a statistically significant increase in malignant lymphoma at all dose levels compared with controls. In a second mouse study at dosages that were approximately 3 to 16 times the clinical dose (adjusted for body surface area), hepatocellular adenoma and carcinoma in males were considered sirolimus-related. In the 104-week rat study at dosages equal to or lower than the clinical dose of 2 mg daily (adjusted for body surface area), there were no significant findings.
Sirolimus was not genotoxic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay, the Chinese hamster ovary cell chromosomal aberration assay, the mouse lymphoma cell forward mutation assay, or the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
Fertility was diminished slightly in both male and female rats following oral administration of sirolimus at doses approximately 10 times or 2 times, respectively, the clinical dose of 2 mg daily (adjusted for body surface area). In male rats, atrophy of testes, epididymides, prostate, seminiferous tubules and/or reduction in sperm counts were observed. In female rats, reduced size of ovaries and uteri was observed. Reduction of sperm count in male rats was reversible upon cessation of dosing in one study. Testicular tubular degeneration was also seen in a 4- week intravenous study of sirolimus in monkeys at doses that were approximately equal to the clinical dose (adjusted for body surface area).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Prophylaxis of Organ Rejection in Renal Transplant Patients
Sirolimus Oral Solution
The safety and efficacy of sirolimus oral solution for the prevention of organ rejection following renal transplantation were assessed in two randomized, double-blind, multicenter, controlled trials. These studies compared two dose levels of sirolimus oral solution (2 mg and 5 mg, once daily) with azathioprine (Study 1) or placebo (Study 2) when administered in combination with cyclosporine and corticosteroids. Study 1 was conducted in the United States at 38 sites. Seven hundred nineteen (719) patients were enrolled in this trial and randomized following transplantation; 284 were randomized to receive sirolimus oral solution 2 mg/day; 274 were randomized to receive sirolimus oral solution 5 mg/day, and 161 to receive azathioprine 2-3 mg/kg/day. Study 2 was conducted in Australia, Canada, Europe, and the United States, at a total of 34 sites. Five hundred seventy-six (576) patients were enrolled in this trial and randomized before transplantation; 227 were randomized to receive sirolimus oral solution 2 mg/day; 219 were randomized to receive sirolimus oral solution 5 mg/day, and 130 to receive placebo. In both studies, the use of anti-lymphocyte antibody induction therapy was prohibited. In both studies, the primary efficacy endpoint was the rate of efficacy failure in the first 6 months after transplantation. Efficacy failure was defined as the first occurrence of an acute rejection episode (confirmed by biopsy), graft loss, or death.
The tables below summarize the results of the primary efficacy analyses from these trials. Sirolimus oral solution, at doses of 2 mg/day and 5 mg/day, significantly reduced the incidence of efficacy failure (statistically significant at the < 0.025 level; nominal significance level adjusted for multiple [2] dose comparisons) at 6 months following transplantation compared with both azathioprine and placebo.
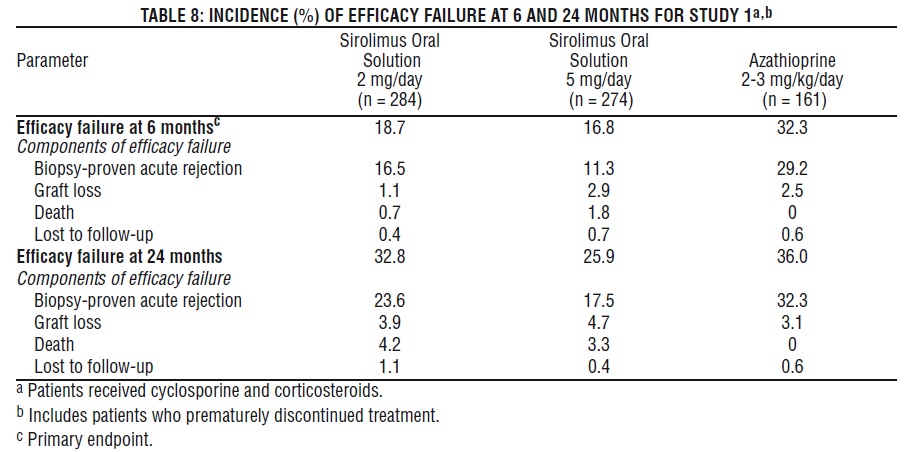
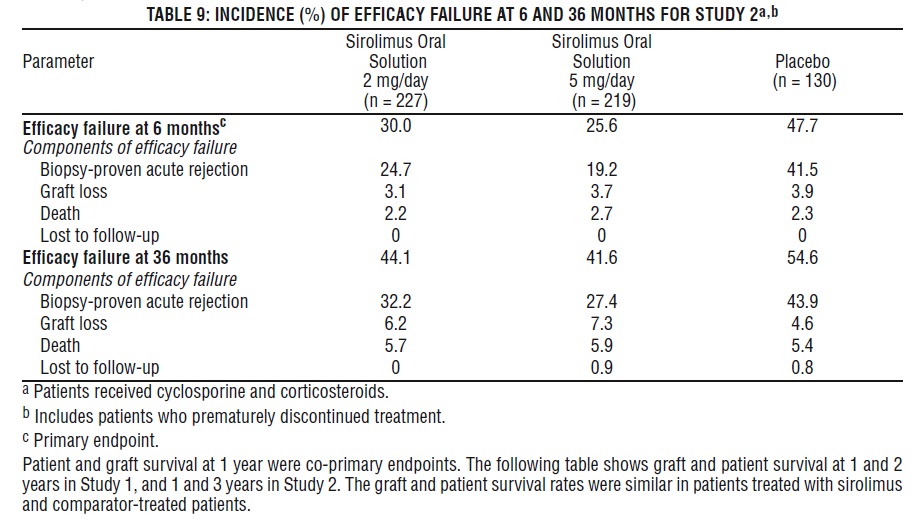
Patient and graft survival at 1 year were co-primary endpoints. The following table shows graft and patient survival at 1 and 2 years in Study 1, and 1 and 3 years in Study 2. The graft and patient survival rates were similar in patients treated with sirolimus and comparator-treated patients.
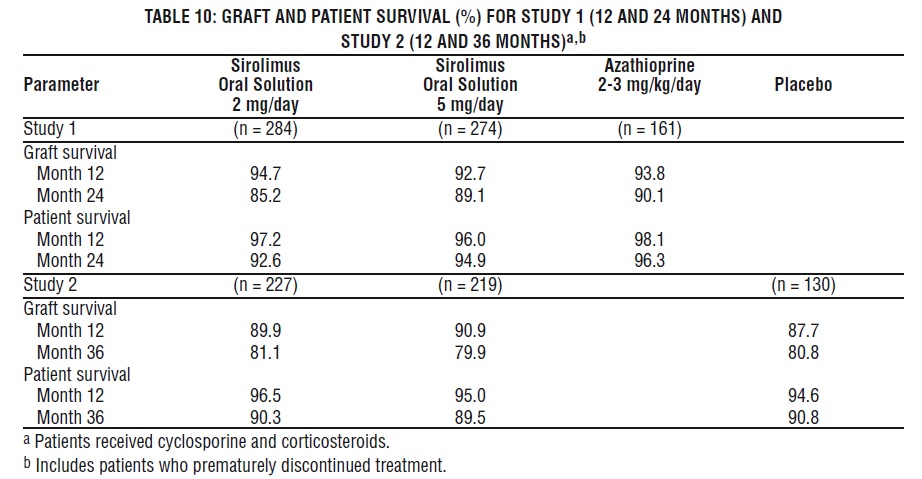
The reduction in the incidence of first biopsy-confirmed acute rejection episodes in patients treated with sirolimus compared with the control groups included a reduction in all grades of rejection.
In Study 1, which was prospectively stratified by race within center, efficacy failure was similar for sirolimus oral solution 2 mg/day and lower for sirolimus oral solution 5 mg/day compared with azathioprine in Black patients. In Study 2, which was not prospectively stratified by race, efficacy failure was similar for both sirolimus oral solution doses compared with placebo in Black patients. The decision to use the higher dose of sirolimus oral solution in Black patients must be weighed against the increased risk of dose-dependent adverse events that were observed with the sirolimus oral solution 5-mg dose [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
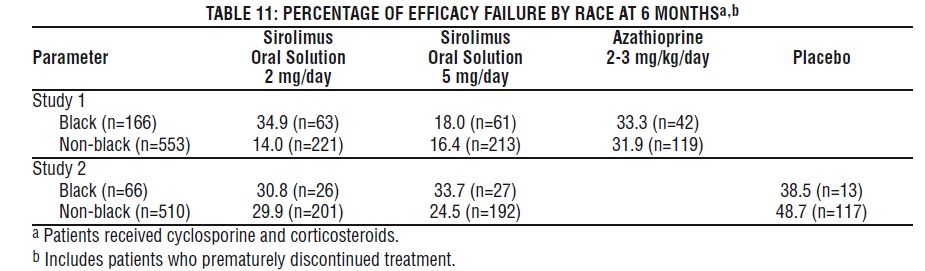
Mean glomerular filtration rates (GFR) post-transplant were calculated by using the Nankivell equation at 12 and 24 months for Study 1, and 12 and 36 months for Study 2. Mean GFR was lower in patients treated with cyclosporine and sirolimus oral solution compared with those treated with cyclosporine and the respective azathioprine or placebo control.
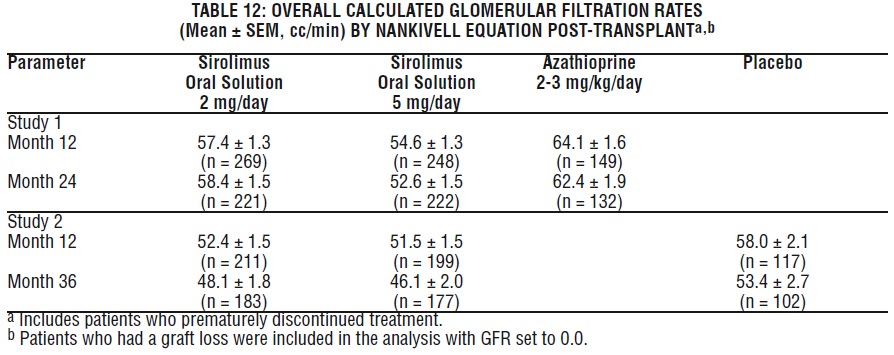
Within each treatment group in Studies 1 and 2, mean GFR at one-year post-transplant was lower in patients who experienced at least one episode of biopsy-proven acute rejection, compared with those who did not.
Renal function should be monitored, and appropriate adjustment of the immunosuppressive regimen should be considered in patients with elevated or increasing serum creatinine levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Sirolimus Tablets
The safety and efficacy of sirolimus oral solution and sirolimus tablets for the prevention of organ rejection following renal transplantation were demonstrated to be clinically equivalent in a randomized, multicenter, controlled trial [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
14.2 Cyclosporine Withdrawal Study in Renal Transplant Patients
The safety and efficacy of sirolimus as a maintenance regimen were assessed following cyclosporine withdrawal at 3 to 4 months after renal transplantation. Study 3 was a randomized, multicenter, controlled trial conducted at 57 centers in Australia, Canada, and Europe. Five hundred twenty-five (525) patients were enrolled. All patients in this study received the tablet formulation. This study compared patients who were administered sirolimus, cyclosporine, and corticosteroids continuously with patients who received this same standardized therapy for the first 3 months after transplantation (pre-randomization period) followed by the withdrawal of cyclosporine. During cyclosporine withdrawal, the sirolimus dosages were adjusted to achieve targeted sirolimus whole blood trough concentration ranges (16 to 24 ng/mL until month 12, then 12 to 20 ng/mL thereafter, expressed as chromatographic assay values). At 3 months, 430 patients were equally randomized to either continue sirolimus with cyclosporine therapy or to receive sirolimus as a maintenance regimen following cyclosporine withdrawal.
Eligibility for randomization included no Banff Grade 3 acute rejection or vascular rejection episode in the 4 weeks before random assignment, serum creatinine ≤ 4.5 mg/dL, and adequate renal function to support cyclosporine withdrawal (in the opinion of the investigator). The primary efficacy endpoint was graft survival at 12 months after transplantation. Secondary efficacy endpoints were the rate of biopsy-confirmed acute rejection, patient survival, incidence of efficacy failure (defined as the first occurrence of either biopsy-proven acute rejection, graft loss, or death), and treatment failure (defined as the first occurrence of either discontinuation, acute rejection, graft loss, or death).
The following table summarizes the resulting graft and patient survival at 12, 24, and 36 months for this trial. At 12, 24, and 36 months, graft and patient survival were similar for both groups
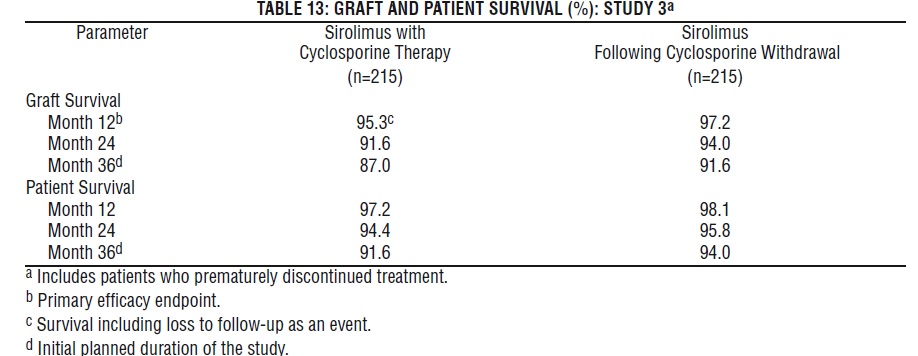
The following table summarizes the results of first biopsy-proven acute rejection at 12 and 36 months. There was a significant difference in first biopsy-proven rejection rates between the two groups after randomization and through 12 months. Most of the post-randomization acute rejections occurred in the first 3 months following randomization.
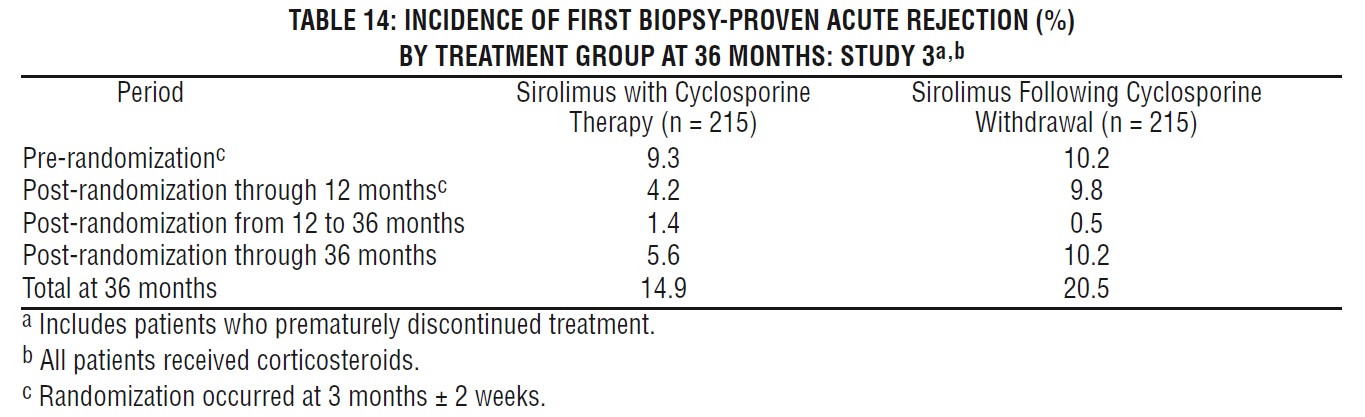
Patients receiving renal allografts with ≥ 4 HLA mismatches experienced significantly higher rates of acute rejection following randomization to the cyclosporine withdrawal group, compared with patients who continued cyclosporine (15.3% versus 3.0%). Patients receiving renal allografts with ≤ 3 HLA mismatches demonstrated similar rates of acute rejection between treatment groups (6.8% versus 7.7%) following randomization.
The following table summarizes the mean calculated GFR in Study 3 (cyclosporine withdrawal study).
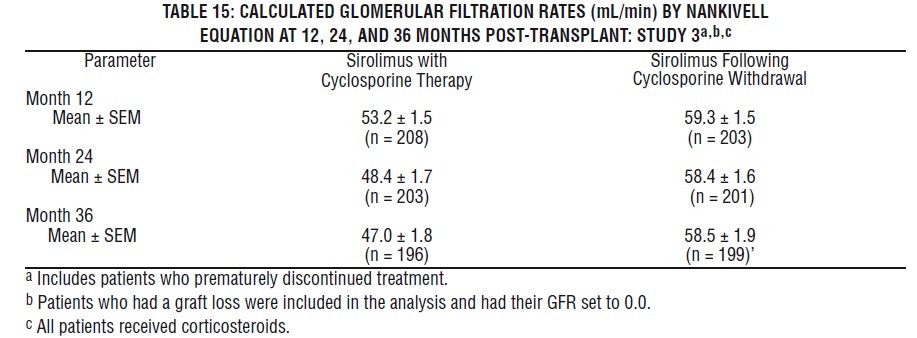
The mean GFR at 12, 24, and 36 months, calculated by the Nankivell equation, was significantly higher for patients receiving sirolimus as a maintenance regimen following cyclosporine withdrawal than for those in the sirolimus with cyclosporine therapy group. Patients who had an acute rejection prior to randomization had a significantly higher GFR following cyclosporine withdrawal compared to those in the sirolimus with cyclosporine group. There was no significant difference in GFR between groups for patients who experienced acute rejection post-randomization.
Although the initial protocol was designed for 36 months, there was a subsequent amendment to extend this study. The results for the cyclosporine withdrawal group at months 48 and 60 were consistent with the results at month 36. Fifty-two percent (112/215) of the patients in the sirolimus with cyclosporine withdrawal group remained on therapy to month 60 and showed sustained GFR.
14.3 High-Immunologic Risk Renal Transplant Patients
Sirolimus was studied in a one-year, clinical trial in high risk patients (Study 4) who were defined as Black transplant recipients and/or repeat renal transplant recipients who lost a previous allograft for immunologic reasons and/or patients with high panel-reactive antibodies (PRA; peak PRA level > 80%). Patients received concentration-controlled sirolimus and cyclosporine (MODIFIED), and corticosteroids per local practice. The sirolimus dose was adjusted to achieve target whole blood trough sirolimus concentrations of 10-15 ng/mL (chromatographic method) throughout the 12-month study period. The cyclosporine dose was adjusted to achieve target whole blood trough concentrations of 200-300 ng/mL through week 2, 150-200 ng/mL from week 2 to week 26, and 100-150 ng/mL from week 26 to week 52 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] for the observed trough concentrations ranges. Antibody induction was allowed per protocol as prospectively defined at each transplant center, and was used in 88.4% of patients. The study was conducted at 35 centers in the United States. A total of 224 patients received a transplant and at least one dose of sirolimus and cyclosporine and was comprised of 77.2% Black patients, 24.1% repeat renal transplant recipients, and 13.5% patients with high PRA. Efficacy was assessed with the following endpoints, measured at 12 months: efficacy failure (defined as the first occurrence of biopsy-confirmed acute rejection, graft loss, or death), first occurrence of graft loss or death, and renal function as measured by the calculated GFR using the Nankivell formula. The table below summarizes the result of these endpoints.
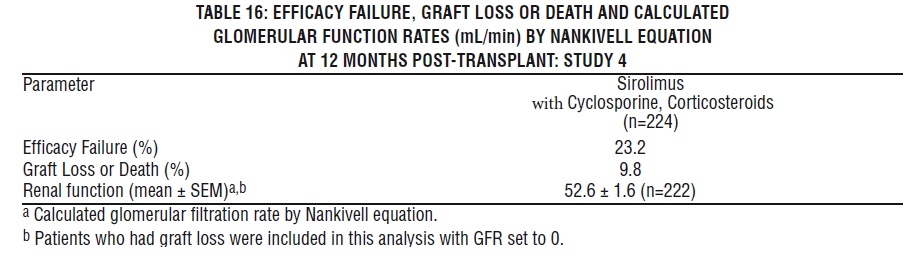
Patient survival at 12 months was 94.6%. The incidence of biopsy-confirmed acute rejection was 17.4% and the majority of the episodes of acute rejection were mild in severity.
14.4 Conversion from Calcineurin Inhibitors to Sirolimus in Maintenance Renal Transplant Patients
Conversion from calcineurin inhibitors (CNI) to sirolimus was assessed in maintenance renal transplant patients 6 months to 10 years post-transplant (Study 5). This study was a randomized, multicenter, controlled trial conducted at 111 centers globally, including US and Europe, and was intended to show that renal function was improved by conversion from CNI to s irolimus. Eight hundred thirty (830) patients were enrolled and stratified by baseline calculated glomerular filtration rate (GFR, 20-40 mL/min versus greater than 40 mL/min). In this trial there was no benefit associated with conversion with regard to improvement in renal function and a greater incidence of proteinuria in the sirolimus conversion arm. In addition, enrollment of patients with baseline calculated GFR less than 40 mL/min was discontinued due to a higher rate of serious adverse events, including pneumonia, acute rejection, graft loss and death [see Adverse Reactions (6.4) ].
This study compared renal transplant patients (6-120 months after transplantation) who were converted from calcineurin inhibitors to sirolimus , with patients who continued to receive calcineurin inhibitors. Concomitant immunosuppressive medications included mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), azathioprine (AZA), and corticosteroids. Sirolimus was initiated with a single loading dose of 12-20 mg, after which dosing was adjusted to achieve a target sirolimus whole blood trough concentration of 8-20 ng/mL (chromatographic method). The efficacy endpoint was calculated GFR at 12 months post-randomization. Additional endpoints included biopsy-confirmed acute rejection, graft loss, and death. Findings in the patient stratum with baseline calculated GFR greater than 40 mL/min (sirolimus conversion, n = 497; CNI continuation, n = 246) are summarized below: There was no clinically or statistically significant improvement in Nankivell GFR compared to baseline.
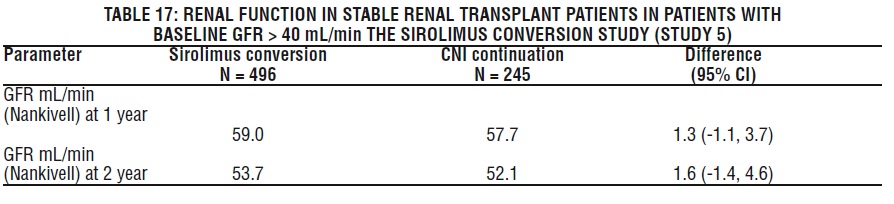
The rates of acute rejection, graft loss, and death were similar at 1 and 2 years. Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred more frequently during the first 6 months after sirolimus conversion. The rates of pneumonia were significantly higher for the sirolimus conversion group.
While the mean and median values for urinary protein to creatinine ratio were similar between treatment groups at baseline, significantly higher mean and median levels of urinary protein excretion were seen in the sirolimus conversion arm at 1 year and at 2 years, as shown in the table below [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]. In addition, when compared to patients who continued to receive calcineurin inhibitors, a higher percentage of patients had urinary protein to creatinine ratios > 1 at 1 and 2 years after sirolimus conversion. This difference was seen in both patients who had a urinary protein to creatinine ratio ≤ 1 and those who had a protein to creatinine ratio > 1 at baseline. More patients in the sirolimus conversion group developed nephrotic range proteinuria, as defined by a urinary protein to creatinine ratio > 3.5 (46/482 [9.5%] versus 9/239 [3.8%]), even when the patients with baseline nephrotic range proteinuria were excluded. The rate of nephrotic range proteinuria was significantly higher in the sirolimus conversion group compared to the calcineurin inhibitor continuation group with baseline urinary protein to creatinine ratio > 1 (13/29 versus 1/14), excluding patients with baseline nephrotic range proteinuria.
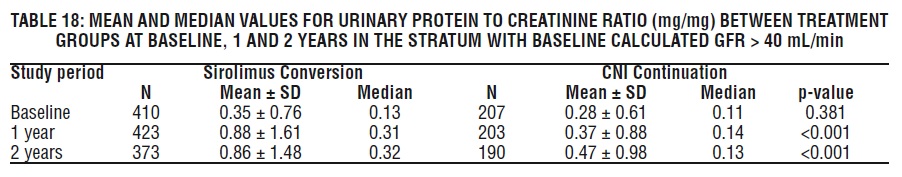
The above information should be taken into account when considering conversion from calcineurin inhibitors to sirolimus in stable renal transplant patients due to the lack of evidence showing that renal function improves following conversion, and the finding of a greater increment in urinary protein excretion, and an increased incidence of treatment-emergent nephrotic range proteinuria following conversion to sirolimus. This was particularly true among patients with existing abnormal urinary protein excretion prior to conversion.
In an open-label, randomized, comparative, multicenter study where kidney transplant patients were either converted from tacrolimus to sirolimus 3 to 5 months post-transplant (sirolimus group) or remained on tacrolimus, there was no significant difference in renal function at 2 years post-transplant. Overall, 44/131 33.6%) discontinued treatment in the sirolimus group versus 12/123 (9.8%) in the tacrolimus group. More patients reported adverse events 130/131 (99.2%) versus 112/123 (91.1%) and more patients reported discontinuations from the treatment due to adverse events 28/131 (21.4%) versus 4/123 (3.3%) in the sirolimus group compared to the tacrolimus group.
The incidence of biopsy-confirmed acute rejection was higher for patients in the sirolimus group 11/131 (8.4%) compared to the tacrolimus group 2/123 (1.6%) through 2 years post-transplant. The rate of new-onset diabetes mellitus post-randomization, defined as 30 days or longer of continuous or at least 25 days non-stop (without gap) use of any diabetic treatment after randomization, a fasting glucose ≥126 mg/dL or a non-fasting glucose ≥200 mg/dL, was higher in the sirolimus group 15/82 (18.3%) compared to the tacrolimus group 4/72 (5.6%). A greater incidence of proteinuria, was seen in the sirolimus group 19/131 (14.5%) versus 2/123 (1.6%) in the tacrolimus group.
14.5 Conversion from a CNI-based Regimen to a Sirolimus-based Regimen in Liver Transplant Patients
Conversion from a CNI-based regimen to a sirolimus-based regimen was assessed in stable liver transplant patients 6-144 months post-transplant. The clinical study was a 2:1 randomized, multi-center, controlled trial conducted at 82 centers globally, including the US and Europe, and was intended to show that renal function was improved by conversion from a CNI to sirolimus without adversely impacting efficacy or safety. A total of 607 patients were enrolled.
The study failed to demonstrate superiority of conversion to a sirolimus-based regimen compared to continuation of a CNI-based regimen in baseline-adjusted GFR, as estimated by Cockcroft-Gault, at 12 months (62 mL/min in the sirolimus conversion group and 63 mL/min in the CNI continuation group). The study also failed to demonstrate non-inferiority, with respect to the composite endpoint consisting of graft loss and death (including patients with missing survival data) in the sirolimus conversion group compared to the CNI continuation group (6.6% versus 5.6%). The number of deaths in the sirolimus conversion group (15/393, 3.8%) was higher than in the CNI continuation group (3/214, 1.4%), although the difference was not statistically significant. The rates of premature study discontinuation (primarily due to adverse events or lack of efficacy), adverse events overall (infections, specifically), and biopsy-proven acute liver graft rejection at 12 months were all significantly greater in the sirolimus conversion group compared to the CNI continuation group.
14.6 Pediatric Renal Transplant Patients
Sirolimus was evaluated in a 36-month, open-label, randomized, controlled clinical trial at 14 North American centers in pediatric (aged 3 to < 18 years) renal transplant patients considered to be at high-immunologic risk for developing chronic allograft nephropathy, defined as a history of one or more acute allograft rejection episodes and/or the presence of chronic allograft nephropathy on a renal biopsy. Seventy-eight (78) subjects were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to sirolimus (sirolimus target concentrations of 5 to 15 ng/mL, by chromatographic assay, n = 53) in combination with a calcineurin inhibitor and corticosteroids or to continue calcineurin-inhibitor-based immunosuppressive therapy (n = 25). The primary endpoint of the study was efficacy failure as defined by the first occurrence of biopsy-confirmed acute rejection, graft loss, or death, and the trial was designed to show superiority of sirolimus added to a calcineurin-inhibitor-based immunosuppressive regimen compared to a calcineurin-inhibitor- based regimen. The cumulative incidence of efficacy failure up to 36 months was 45.3% in the sirolimus group compared to 44.0% in the control group, and did not demonstrate superiority. There was one death in each group. The use of sirolimus in combination with calcineurin inhibitors and corticosteroids was associated with an increased risk of deterioration of renal function, serum lipid abnormalities (including, but not limited to, increased serum triglycerides and cholesterol), and urinary tract infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]. This study does not support the addition of sirolimus to calcineurin-inhibitor-based immunosuppressive therapy in this subpopulation of pediatric renal transplant patients.
15 REFERENCES
Clinical Therapeutics, Volume 22, Supplement B, April 2000 [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Since sirolimus is not absorbed through the skin, there are no special precautions. However, if direct contact of the oral solution occurs with the skin or eyes, wash skin thoroughly with soap and water; rinse eyes with plain water.
Do not use Sirolimus Oral Solution after the expiration date that is located on the carton. The expiration date refers to the last day of that month.
16.1 Sirolimus Oral Solution
Sirolimus Oral Solution is a yellow colored solution.
Each Sirolimus Oral Solution carton, NDC 70954-075-10, contains one 2 oz (60 mL fill) amber glass bottle of sirolimus (concentration of 1 mg/mL), one oral syringe adapter for fitting into the neck of the bottle, sufficient disposable amber oral syringes and caps for daily dosing, and a carrying case.
Sirolimus Oral Solution bottles should be stored protected from light and refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Once the bottle is opened, the contents should be used within one month. If necessary, the patient may store the bottles at room temperatures up to 25°C (77°F) for a short period of time (e.g., not more than 15 days for the bottles).
An amber syringe and cap are provided for dosing, and the product may be kept in the syringe for a maximum of 24 hours at room temperatures up to 25°C (77°F) or refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). The syringe should be discarded after one use. After dilution, the preparation should be used immediately.
Sirolimus Oral Solution provided in bottles may develop a slight haze when refrigerated. If such a haze occurs, allow the product to stand at room temperature and shake gently until the haze disappears. The presence of this haze does not affect the quality of the product.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and the FDA-approved Medication Guide
Advise patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide and assist them in understanding its contents. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of the document.
See FDA-Approved Medication Guide.
17.1 Dosage
Patients should be given complete dosage instructions [see FDA-Approved Medication Guide].
17.2 Skin Cancer Events
Patients should be told that exposure to sunlight and ultraviolet (UV) light should be limited by wearing protective clothing and using a sunscreen with a high protection factor because of the increased risk for skin cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17)].
17.3 Pregnancy Risks
Women of childbearing potential should be informed of the potential risks during pregnancy and told that they should use effective contraception prior to initiation of sirolimus therapy, during sirolimus therapy, and for 12 weeks after sirolimus therapy has been stopped [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
MEDICATION GUIDE
Sirolimus (sir-OH-li-mus) Oral Solution
What is the most important information I should know about sirolimus?
Sirolimus can cause serious side effects, including:
1. Increased risk of getting infections. Serious infections can happen including infections caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi (yeast). Your doctor may put you on medicine to help prevent some of these infections.
Call your doctor right away if you have symptoms of infection including fever or chills while taking sirolimus.
2. Increased risk of getting certain cancers. People who take sirolimus have a higher risk of getting lymphoma, and other cancers, especially skin cancer. Talk with your doctor about your risk for cancer.
Sirolimus has not been shown to be safe and effective in people who have had liver or lung transplants. Serious complications and death may happen in people who take sirolimus after a liver or lung transplant. You should not take sirolimus if you have had a liver or lung transplant without talking with your doctor.
See the section “What are the possible side effects of sirolimus?” for information about other side effects of sirolimus.
What is sirolimus?
Sirolimus is a prescription medicine used to prevent rejection (anti-rejection medicine) in people 13 years of age and older who have received a kidney transplant. Rejection is when your body’s immune system recognizes the new organ as a “foreign” threat and attacks it.
Sirolimus is used with other medicines called cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune), and corticosteroids. Your doctor will decide:
· if sirolimus is right for you, and
· how to best use it with cyclosporine and corticosteroids after your transplant.
It is not known if sirolimus is safe and effective in children under 13 years of age.
Who should not take sirolimus?
Do not take Sirolimus Oral Solution if you are allergic to sirolimus or any of the other ingredients in Sirolimus Oral Solution. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Sirolimus Oral Solution.
What should I tell my doctor before taking sirolimus?
Before taking sirolimus, tell your doctor if you:
· have liver problems
· have skin cancer or it runs in your family
· have high cholesterol or triglycerides (fat in your blood)
· are pregnant or are a female who can become pregnant. Sirolimus may harm your unborn baby. You should not become pregnant during treatment with sirolimus and for 12 weeks after ending treatment with sirolimus. In order to avoid pregnancy, a female who can get pregnant should use effective birth control during treatment and for 12 weeks after your final dose of sirolimus. Talk with your doctor about what birth control method is right for you during this time. Tell your doctor right away if you become pregnant or think you are pregnant during treatment with sirolimus or within 12 weeks after your final dose of sirolimus.
· It is not known whether sirolimus passes into breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take sirolimus or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Using sirolimus with certain medicines may affect each other causing serious side effects.
Sirolimus may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how sirolimus works.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
· a medicine to lower your cholesterol or triglycerides
· cyclosporine (including Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune) or tacrolimus (Prograf) or other medicines that suppress the immune system
· an antibiotic
· an antifungal medicine
· a medicine for high blood pressure or heart problems
· an anti-seizure medicine
· medicines used to treat stomach acid, ulcers, or other gastrointestinal problems
· bromocriptine mesylate (Parlodel, Cycloset)
· danazol
· medicines to treat HIV or hepatitis C
· St. John’s Wort
How should I take sirolimus?
· Read the Instructions for Use that comes with your Sirolimus Oral Solution for information about the right way to take Sirolimus Oral Solution.
· Take sirolimus exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
· Your doctor will tell you how much sirolimus to take and when to take it. Do not change your dose of sirolimus unless your doctor tells you to.
· If you also take cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune), you should take your sirolimus and cyclosporine about 4 hours apart.
· Do not stop taking sirolimus or your other anti-rejection medicines unless your doctor tells you to.
· Your doctor will check the levels of sirolimus in your blood. Your doctor may change your dose of sirolimus depending on your blood test results.
· Sirolimus is taken by mouth 1 time each day.
· Take each dose of sirolimus the same way, either with or without food. Food can affect the amount of medicine that gets into your bloodstream. Taking each dose of sirolimus the same way helps keep your blood levels of sirolimus more stable. Do not take sirolimus with grapefruit juice.
· Sirolimus Oral Solution can develop a slight haze when it is refrigerated. If this happens, bring the Sirolimus Oral Solution to room temperature and then gently shake the bottle until the haze goes away.
· If you get Sirolimus Oral Solution on your skin, wash the area with soap and water.
· If you get Sirolimus Oral Solution in your eyes, rinse your eyes with water.
· If you have taken more medicine than you were told, contact a doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency department right away.
What should I avoid while taking Sirolimus Oral Solution?
· Avoid receiving live vaccines while taking sirolimus. Some vaccines may not work as well while you are taking sirolimus.
· Limit your time in sunlight and UV light. Cover your skin with clothing and use a sunscreen with a high protection factor because of the increased risk for skin cancer with sirolimus.
What are the possible side effects of sirolimus?
Sirolimus may cause serious side effects, including:
· See “What is the most important information I should know about sirolimus?”
· Serious allergic reactions. Tell your doctor or get medical help right away if you get any of following symptoms of an allergic reaction:
· swelling of your face, eyes, or mouth
· trouble breathing or wheezing
· throat tightness
· chest pain or tightness
· feeling dizzy or faint
· rash or peeling of your skin
· Swelling (edema). Fluid may collect in your hands and feet and in various tissues of your body, including in the sac around your heart or lungs. Call your doctor if you have trouble breathing.
· Poor wound healing. Sirolimus may cause your wounds to heal slowly or not heal well. Tell your doctor ifyou have any redness or drainage, your wound does not heal, or the wound opens up.
· Increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides (lipids or fat) in your blood. Your doctor should do blood tests to check your lipids during treatment with sirolimus. Your doctor may prescribe treatment with diet, exercise, or medicine if your lipid levels are too high. During treatment with sirolimus, your blood levels of cholesterol and triglycerides may remain high even if you follow your prescribed treatment plan.
· Effects on kidney function. When sirolimus is taken with cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune), the function of your transplanted kidney may be affected. Your doctor should regularly do tests to check your kidney function while you are taking sirolimus with cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune).
· Increased protein in your urine. Your doctor may regularly test your urine protein.
· Increased risk for viral infections.
· Certain viruses can live in your body and cause active infections when your immune system is weak. BK virus can affect how your kidney works and cause your transplanted kidney to fail.
· A certain virus can cause a rare serious brain infection called Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML). PML usually causes death or severe disability. Call your doctor right away if you notice any new or worsening medical problems such as:
· confusion
· sudden change in thinking, walking, strength on one side of your body
· other problems that have lasted over several days.
· Lung or breathing problems. This can sometimes lead to death. Tell your doctor if you have a new or worsening cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing or any new breathing problems. Your doctor may need to stop sirolimus or lower your dose.
· Blood clotting problems. When sirolimus is taken with cyclosporine or tacrolimus, you may develop a blood clotting problem. Tell your doctor if you get any unexplained bleeding or bruising.
The most common side effects of sirolimus in people with renal transplant include:
· high blood pressure
· pain (including stomach and joint pain)
· diarrhea
· headache
· fever
· urinary tract infection
· low red blood cell count (anemia)
· nausea
· low platelet count (cells that help blood to clot)
· high blood sugar (diabetes)
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of sirolimus. For more information ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Sirolimus Oral Solution?
· Store bottles of Sirolimus Oral Solution in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
· Protect from light.
· If necessary, bottles of Sirolimus Oral Solution can be stored at room temperature up to 77°F (25°C) for up to 15 days.
· When a bottle of Sirolimus Oral Solution is opened, it should be used within 1 month.
· Use any diluted Sirolimus Oral Solution right away.
Do not use Sirolimus Oral Solution after the expiration date, which is located on the carton. The expiration date refers to the last day of that month.
Safely throw away medicine that is out of date or no longer needed.
Keep Sirolimus Oral Solution and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about the safe and effective use of Sirolimus Oral Solution
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Sirolimus Oral Solution for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Sirolimus Oral Solution to other people even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Sirolimus Oral Solution. If you would like more information talk to your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about Sirolimus Oral Solution that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in Sirolimus Oral Solution?
Active ingredients: Sirolimus
Inactive ingredients: Phosal® 50 PG (alcohol, ascorbyl palmitate, phosphatidylcholine, propylene glycol, soy acid, soy lecithin, sunflower seed oil glyceride, and tocopherol) and polysorbate 80. Sirolimus Oral Solution contains 1.5% - 2.5% ethanol.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Sirolimus (sir-OH-li-mus) Oral Solution
Be sure that you read and understand the following instructions for the correct way to dilute and take Sirolimus Oral Solution. Ask your pharmacist or doctor if you are not sure.
Important:
•Always keep the bottle in an upright position.
•You may store Sirolimus Oral Solution that is in a syringe at room temperature up to 77°F (25°C) or in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) for up to 24 hours. See How should I store Sirolimus Oral Solution? at the end of these Instructions for Use.
•Sirolimus Oral Solution can develop a slight haze when it is refrigerated. If this happens, bring the Sirolimus Oral Solution to room temperature and then gently shake the bottle until the haze goes away.
•Only use a glass or plastic cup to dilute Sirolimus Oral Solution.
•If you are a caregiver, do not let Sirolimus Oral Solution come in contact with your skin or eyes. If you get the oral solution on your skin, wash the area well with soap and water. If you get the oral solution in your eyes, rinse with plain water.
•If you spill Sirolimus Oral Solution, dry the area with a dry paper towel and then wipe the area with a wet paper towel. Throw away the paper towels in the trash and wash your hands well with soap and water.
Each Sirolimus Oral Solution carton contains:
•a) a 2 oz. (60 mL fill) amber glass bottle of sirolimus (concentration of 1 mg/mL)
•b) 1 oral syringe adapter for fitting into the neck of the bottle
•c) enough disposable amber oral syringes and caps for daily dosing
•d) 1 carrying case
You will also need:
•glass or plastic cup
•6 oz. of water or orange juice only.
Figure 1:
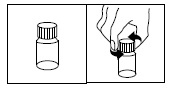
1. Opening the solution bottle
Remove the safety cap by pushing down and turning counterclockwise (Figure 1)
FIGURE 2
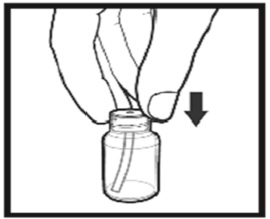
Figure 2: Inserting adapter
2. The first time you use a bottle of Sirolimus Oral Solution:
· Insert the oral syringe adapter (plastic tube with stopper) tightly into the bottle until it is even with the top of the bottle.(Figure 2)
· Do not remove the oral syringe adapter from the bottle once inserted
FIGURE 3
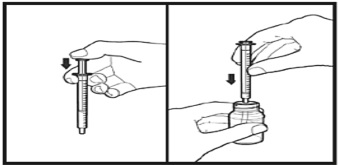
Figure 3: Inserting syringe
3. Use a new disposable amber oral syringe for each dose of Sirolimus Oral Solution.
· Fully push down (depress) on the plunger of the disposable amber oral syringe.
· Then, tightly insert the oral syringe into the opening in the adapter (Figure 3).
FIGURE 4
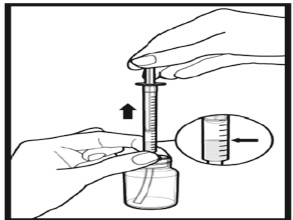
Figure 4: Withdrawing solution
4. Withdraw the prescribed amount of Sirolimus Oral Solution:
•Gently pull back the plunger of the syringe until the level of the oral solution is even with the marking of the syringe for your prescribed dose.
•Always keep the bottle in an upright position.
•If bubbles form within the oral solution in the syringe, empty the syringe into the bottle and repeat steps 4 (Figure 4).
•You may need to repeat step 4 more than once to draw up your prescribed dose.
FIGURE 5
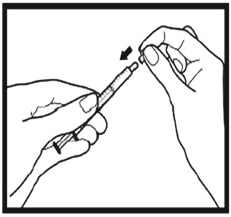
Figure 5: Capping syringe
5. If your doctor tells you to carry your medicine with you:
· If you need to carry your Sirolimus Oral Solution in a filled syringe, place a cap securely on each syringe. The cap should snap into place (Figure 5).
FIGURE 6
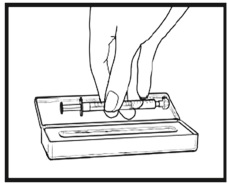
Figure 6: Placing syringe in carrying case
Place the capped syringe in the enclosed carrying case (Figure 6). If you need more than 1 carrying case, talk with your doctor or pharmacist.
FIGURE 7
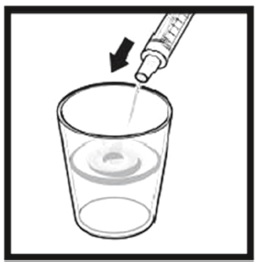
Figure 7: Emptying syringe into glass
6. Taking a dose of Sirolimus Oral Solution:
· Choose a clean flat work surface. Place a clean paper towel on the work surface. Wash and dry your hands.
· Empty the syringe into a glass or plastic cup containing at least 2 ounces (1/4 cup, 60 mL) of water or orange juice, stir vigorously for 1 minute and drink right away. (Figure 7).
· If more than 1 syringe is needed for your prescribed dose, empty the oral solution from each syringe into the same glass or plastic cup of water or orange juice.
· Refill the container with at least 4 ounces (1/2 cup, 120 mL) of water or orange juice, stir vigorously again and drink the rinse solution. Do not mix Sirolimus Oral Solution with apple juice, grapefruit juice, or other liquids. Only glass or plastic cups should be used to mix Sirolimus Oral Solution.
· The syringe and cap should be used only one time and then thrown away
Throw away the paper towel and clean the work surface. Wash your hands.
7. Always store the bottles of medication in the refrigerator
How should I store Sirolimus Oral Solution?
· Store bottles of Sirolimus Oral Solution in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C)
· Protect from light
· Store Sirolimus Oral Solution that is in a syringe at room temperature up to 77°F (25°C) or in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) for up to 24 hours
· If necessary, bottles of Sirolimus Oral Solution can be stored at room temperature up to 77°F (25°C) for up to 15 days
· When a bottle of Sirolimus Oral Solution is opened, it should be used within 1 month
· Use any diluted Sirolimus Oral Solution right away
Keep Sirolimus oral Solution and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instruction for Use has been approved by the U.S Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Novitium Pharma LLC
70 Lake Drive, East Windsor
New Jersey 08520
Distributed By
Vista Pharm Inc.
Largo, FL 33771
Trademarks are the property of their respective owners
Revised: April, 2019
LB4062-02
| SIROLIMUS
sirolimus solution |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novitium Pharma LLC (080301870) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Novitium Pharma LLC | 080301870 | MANUFACTURE(70954-075) , PACK(70954-075) | |


