ASTEPRO
-
azelastine hydrochloride spray, metered
MEDA Pharmaceuticals
----------
|
|||||||||||||||||||
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis
ASTEPRO Nasal Spray is indicated for the relief of the symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis in patients 12 years of age and older.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Administer ASTEPRO Nasal Spray by the intranasal route only.
2.1 Adults and Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older
The recommended dose of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray is 1 or 2 sprays per nostril twice daily.
2.2 Administration Information
Priming: Prime ASTEPRO Nasal Spray before initial use by releasing 6 sprays or until a fine mist appears. When ASTEPRO Nasal Spray has not been used for 3 or more days, reprime with 2 sprays or until a fine mist appears. Avoid spraying ASTEPRO Nasal Spray into the eyes.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ASTEPRO Nasal Spray is a nasal spray solution. Each spray delivers a volume of 0.137 mL solution containing 137 mcg of azelastine hydrochloride.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
In clinical trials, the occurrence of somnolence has been reported in some patients taking ASTEPRO Nasal Spray [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Patients should be cautioned against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness and motor coordination such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle after administration of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray. Concurrent use of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Use of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray has been associated with somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
The safety data described below reflect exposure to ASTEPRO Nasal Spray in 564 patients 12 years of age and older from 2 clinical trials of 2 weeks to 6 months duration. In a 2 week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, and active controlled (Astelin® Nasal Spray) clinical trial, 285 patients 12 years of age and older with seasonal allergic rhinitis were treated with ASTEPRO Nasal Spray one or two sprays per nostril daily. In the 6 month open-label, active controlled (Astelin Nasal Spray) clinical trial, 279 patients 12 years of age and older with perennial allergic rhinitis and/or nonallergic rhinitis were treated with ASTEPRO Nasal Spray two sprays per nostril twice daily. Of the 564 patients, 256 were male and 308 were female. The racial and ethnic distribution of the 564 patients was 86% white, 11% black, 6% Hispanic, < 2% Asian, and 1% other.
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect rates observed in practice.
Adults and Adolescents 12 years of Age and Older
In the two week clinical trial, 835 patients 12 years of age and older with seasonal allergic rhinitis were treated with one of six treatments: one spray per nostril of either ASTEPRO Nasal Spray, Astelin Nasal Spray or placebo twice daily; or 2 sprays per nostril of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray, Astelin Nasal Spray, or placebo twice daily. Overall, adverse reactions were more common on the ASTEPRO Nasal Spray treatment group (21-28%) than in the placebo group (16-20%). Overall, less than 1% of patients discontinued due to adverse reactions and withdrawal due to adverse reactions was similar among the treatment groups.
Table 1 contains adverse reactions reported with frequencies greater than 2% and more frequently than placebo in patients treated with ASTEPRO Nasal Spray in the controlled clinical trial described above.
| 1 spray twice daily | 2 sprays twice daily | |||||
| ASTEPRO Nasal Spray(N=139) | Astelin Nasal Spray(N=137) | Vehicle Placebo (N=137) | ASTEPRO Nasal Spray(N=146) | Astelin Nasal Spray(N=137) | Vehicle Placebo (N=138) |
|
| Bitter Taste | 8 (6%) | 13 (10%) | 2 (2%) | 10 (7%) | 11 (8%) | 3 (2%) |
| Epistaxis | 3 (2%) | 8 (6%) | 3 (2%) | 4 (3%) | 3 (2%) | 0 (0%) |
| Headache | 2 (1%) | 5 (4%) | 1 (<1%) | 4 (3%) | 3 (2%) | 1 (<1%) |
| Nasal Discomfort | 0 (0%) | 3 (2%) | 1 (<1%) | 2 (1%) | 6 (4%) | 0 (0%) |
| Fatigue | 0 (0%) | 1 (<1%) | 1 (<1%) | 3 (2%) | 3 (2%) | 1 (<1%) |
| Somnolence | 2 (1%) | 2 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (2%) | 2 (1%) | 0 (0%) |
Long-Term (6 Month)
Safety Trial:
In the 6 month,
open-label, active-controlled, long-term safety trial,
555 patients 12 years of age and older with perennial
allergic and/or nonallergic rhinitis were treated with ASTEPRO Nasal Spray two sprays per nostril twice daily
or Astelin Nasal Spray two sprays per nostril twice
daily. The most frequently reported adverse reactions
were headache, bitter taste, epistaxis, and
nasopharyngitis and were generally similar between
treatment groups. Focused nasal examinations were
performed and showed that the incidence of nasal mucosal
ulceration in each treatment group was approximately
1.5% at baseline and approximately 4%
throughout the 6 month treatment period. In each
treatment group, 3% - 5% of patients had
mild epistaxis. No patients had reports of nasal septal
perforation or severe epistaxis.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during the post approval use of Astelin Nasal Spray. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Adverse reactions reported include the following: anaphylactoid reaction, application site irritation, atrial fibrillation, blurred vision, chest pain, confusion, dizziness, dyspnea, facial edema, hypertension, involuntary muscle contractions, nervousness, palpitations, paresthesia, parosmia, paroxysmal sneezing, pruritus, rash, disturbance or loss of sense of smell and/or taste, tachycardia, tolerance, urinary retention, and xerophthalmia.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Central Nervous System Depressants
Concurrent use of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because reductions in alertness and impairment of central nervous system performance may occur [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.2 Erythromycin and Ketoconazole
Interaction studies investigating the cardiac effects, as measured by the corrected QT interval (QTc), of concomitantly administered oral azelastine hydrochloride and erythromycin or ketoconazole were conducted. Oral erythromycin (500 mg three times daily for 7 days) had no effect on azelastine pharmacokinetics or QTc based on analyses of serial electrocardiograms. Ketoconazole (200 mg twice daily for 7 days) interfered with the measurement of azelastine plasma concentrations; however, no effects on QTc were observed [see Pharmacodynamics (12.2) Pharmacokinetics (12.3)].
7.3 Cimetidine
Cimetidine (400 mg twice daily) increased the mean Cmax and AUC of orally administered azelastine hydrochloride (4 mg twice daily) by approximately 65% [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: There are no adequate and well-controlled clinical studies in pregnant women. ASTEPRO Nasal Spray should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Teratogenic Effects: Azelastine hydrochloride has been shown to cause developmental toxicity in mice, rats, and rabbits. In mice, azelastine hydrochloride caused embryo-fetal death, malformations (cleft palate; short or absent tail; fused, absent or branched ribs), delayed ossification, and decreased fetal weight at an oral dose approximately 280 times the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose (MRDID) in adults on a mg/m2 basis. This dose also caused maternal toxicity as evidenced by decreased body weight. Neither fetal nor maternal effects occurred at a dose that was approximately 10 times the MRDID.
In rats, azelastine hydrochloride caused malformations (oligo- and brachydactylia), delayed ossification and skeletal variations, in the absence of maternal toxicity, at an oral dose approximately 240 times the MRDID in adults on a mg/m2 basis. At a dose approximately 560 times the MRDID, azelastine hydrochloride also caused embryo-fetal death and decreased fetal weight; however, this dose caused severe maternal toxicity. Neither fetal nor maternal effects occurred at a dose approximately 25 times the MRDID.
In rabbits, azelastine hydrochloride caused abortion, delayed ossification and decreased fetal weight at oral doses approximately 500 times or greater the MRDID in adults on a mg/m2 basis; however, these doses also resulted in severe maternal toxicity. Neither fetal nor maternal effects occurred at a dose approximately 5 times the MRDID.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether azelastine hydrochloride is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ASTEPRO Nasal Spray is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray in pediatric patients below the age of 12 years have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Asthmatic Patients
Oral azelastine has been safely administered to over 1400 asthmatic subjects, supporting the safety of administering azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray to allergic rhinitis patients with asthma.
10 OVERDOSAGE
There have been no reported overdosages with ASTEPRO Nasal Spray. Acute overdosage by adults with this dosage form is unlikely to result in clinically significant adverse events, other than increased somnolence, since one bottle of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray contains 30 mg of azelastine hydrochloride. Clinical studies in adults with single doses of the oral formulation of azelastine hydrochloride (up to 16 mg) have not resulted in increased incidence of serious adverse events. General supportive measures should be employed if overdosage occurs. There is no known antidote to ASTEPRO Nasal Spray. Oral ingestion of antihistamines has the potential to cause serious adverse effects in children. Accordingly, ASTEPRO Nasal Spray should be kept out of the reach of children. Oral doses of 120 mg/kg and greater (approximately 460 times the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose (MRDID) in adults and children on a mg/m2 basis) were lethal in mice. Responses seen prior to death were tremor, convulsions, decreased muscle tone, and salivation. In dogs, single oral doses as high as 10 mg/kg (approximately 260 times the MRDID in adults and children on a mg/m2 basis) were well tolerated, but single oral doses of 20 mg/kg were lethal.
11 DESCRIPTION
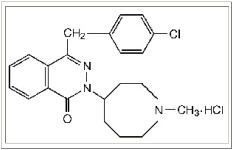
ASTEPRO (azelastine hydrochloride) Nasal Spray, 137 micrograms (mcg), is an antihistamine formulated as a metered-spray solution for intranasal administration. Azelastine hydrochloride occurs as a white, almost odorless, crystalline powder with a bitter taste. It has a molecular weight of 418.37. It is sparingly soluble in water, methanol, and propylene glycol and slightly soluble in ethanol, octanol, and glycerine. It has a melting point of about 225°C and the pH of a saturated solution is between 5.0 and 5.4. Its chemical name is (±)-1-(2H)-phthalazinone,4-[(4-chlorophenyl) methyl]-2-(hexahydro-1-methyl-1H-azepin-4-yl)-, monohydrochloride. Its molecular formula is C22H24ClN3O·HCl with the following chemical structure:
ASTEPRO Nasal Spray contains 0.1% azelastine hydrochloride in an isotonic aqueous solution containing sorbitol, sucralose, hypromellose, sodium citrate, edetate disodium, benzalkonium chloride (125 mcg/mL), and purified water (pH 6.4).
After priming [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.2)], each metered spray delivers a 0.137 mL mean volume containing 137 mcg of azelastine hydrochloride (equivalent to 125 mcg of azelastine base). The 30-mL (net weight 30 gm of solution) bottle provides 200 metered sprays.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Azelastine hydrochloride, a phthalazinone derivative, exhibits histamine H1 -receptor antagonist activity in isolated tissues, animal models, and humans. ASTEPRO Nasal Spray is administered as a racemic mixture with no difference in pharmacologic activity noted between the enantiomers in in vitro studies. The major metabolite, desmethylazelastine, also possesses H1 -receptor antagonist activity.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Effects:
In a placebo-controlled study (95 patients with allergic rhinitis), there was no evidence of an effect of azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray (2 sprays per nostril twice daily for 56 days) on cardiac repolarization as represented by the corrected QT interval (QTc) of the electrocardiogram. Following multiple dose oral administration of azelastine 4 mg or 8mg twice daily, the mean change in QTc was 7.2 msec and 3.6 msec, respectively.
Interaction studies investigating the cardiac repolarization effects of concomitantly administered oral azelastine hydrochloride and erythromycin or ketoconazole were conducted. Oral erythromycin had no effect on azelastine pharmacokinetics or QTc based on analysis of serial electrocardiograms. Ketoconazole interfered with the measurement of azelastine plasma levels; however, no effects on QTc were observed [see Drug Interactions (7)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: After intranasal administration of 2 sprays per nostril (548 mcg total dose) of ASTEPRO, the mean azelastine peak plasma concentration (Cmax) is 200 pg/mL, the mean extent of systemic exposure (AUC) is 5122 pg•hr/ml and the median time to reach Cmax (tmax) is 3 hours. Azelastine hydrochloride administered intranasally at doses above two sprays per nostril twice daily for 29 days resulted in greater than proportional increases in Cmax and AUC for azelastine. The systemic bioavailability of azelastine hydrochloride is approximately 40% after intranasal administration.
Distribution: Based on intravenous and oral administration, the steady-state volume of distribution of azelastine is 14.5 L/kg. In vitro studies with human plasma indicate that the plasma protein binding of azelastine and its metabolite, desmethylazelastine, are approximately 88% and 97%, respectively.
Metabolism: Azelastine is oxidatively metabolized to the principal active metabolite, desmethylazelastine, by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. The specific P450 isoforms responsible for the biotransformation of azelastine have not been identified. After a single-dose, intranasal administration of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray, the mean desmethylazelastine Cmax is 23 pg/mL, the AUC is 2131 pg•hr/mL and the median tmax is 24 hours. After intranasal dosing of azelastine to steady-state, plasma concentrations of desmethylazelastine range from 20-50% of azelastine concentrations.
Elimination: Following intranasal administration of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray, the elimination half-life of azelastine is 22 hours while that of desmethylazelastine is 52 hours. Approximately 75% of an oral dose of radiolabeled azelastine hydrochloride was excreted in the feces with less than 10% as unchanged azelastine.
Special Populations:
Hepatic Impairment: Following oral administration, pharmacokinetic parameters were not influenced by hepatic impairment.
Renal Impairment: Based on oral, single-dose studies, renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance<50 mL/min) resulted in a 70-75% higher Cmax and AUC compared to healthy subjects. Time to maximum concentration was unchanged.
Age: Following oral administration, pharmacokinetic parameters were not influenced by age.
Gender: Following oral administration, pharmacokinetic parameters were not influenced by gender.
Race: The effect of race has not been evaluated.
Drug-Drug Interactions:
Erythromycin: Clinical interaction studies with a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor erythromycin failed to demonstrate a pharmacokinetic interaction.
Cimetidine and Ranitidine: In a multiple-dose, steady-state drug interaction study in healthy subjects, cimetidine (400 mg twice daily), a nonspecific P450 inhibitor, raised orally administered mean azelastine (4 mg twice daily) concentrations by approximately 65%. Ranitidine hydrochloride (150 mg twice daily) had no effects on azelastine pharmacokinetics.
Theophylline: No significant pharmacokinetic interaction was observed with the coadministration of an oral 4-mg dose of azelastine hydrochloride twice daily and theophylline 300 mg or 400 mg twice daily.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In 2-year carcinogenicity studies in rats and mice azelastine hydrochloride did not show evidence of carcinogenicity at oral doses up to 30 mg/kg and 25 mg/kg, respectively (approximately 240 and 100 times the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose (MRDID) in adults and children on a mg/m2 basis).
Azelastine hydrochloride showed no genotoxic effects in the Ames test, DNA repair test, mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay, mouse micronucleus test, or chromosomal aberration test in rat bone marrow.
Reproduction and fertility studies in rats showed no effects on male or female fertility at oral doses up to 30 mg/kg (approximately 240 times the MRDID in adults on a mg/m2 basis). At 68.6 mg/kg (approximately 560 times the MRDID in adults on a mg/m2 basis), the duration of estrous cycles was prolonged and copulatory activity and the number of pregnancies were decreased. The numbers of corpora lutea and implantations were decreased; however, pre-implantation loss was not increased.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Reproductive Toxicology Studies
Azelastine hydrochloride has been shown to cause developmental toxicity. Treatment of mice with an oral dose of 68.6 mg/kg (approximately 280 times the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose [MRDID] in adults on a mg/m2 basis) caused embryo-fetal death, malformations (cleft palate; short or absent tail; fused, absent or branched ribs), delayed ossification, and decreased fetal weight. This dose also caused maternal toxicity as evidenced by decreased body weight. Neither fetal nor maternal effects occurred at a dose of 3 mg/kg (approximately 10 times the MRDID in adults on a mg/m2 basis).
In rats, an oral dose of 30 mg/kg (approximately 240 times the MRDID in adults on a mg/m2 basis) caused malformations (oligo-and brachydactylia), delayed ossification and skeletal variations, in the absence of maternal toxicity. At 68.6 mg/kg (approximately 560 times the MRDID in adults on a mg/m2 basis) azelastine hydrochloride also caused embryo-fetal death and decreased fetal weight; however, the 68.6 mg/kg dose caused severe maternal toxicity. Neither fetal nor maternal effects occurred at a dose of 3 mg/kg (approximately 25 times the MRDID in adults on a mg/m2 basis).
In rabbits, oral doses of 30 mg/kg and greater (approximately 500 times the MRDID in adults on a mg/m2 basis) caused abortion, delayed ossification and decreased fetal weight; however, these doses also resulted in severe maternal toxicity. Neither fetal nor maternal effects occurred at a dose of 0.3 mg/kg (approximately 5 times the MRDID in adults on a mg/m2 basis).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis
The efficacy and safety of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray was evaluated in a 2 week, randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial including 834 adult and adolescent patients 12 years of age and older with symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis. The population was 12 to 83 years of age (60% female, 40% male; 69% white, 16% black, 12% Hispanic, 2% Asian, 1% other).
Patients were randomized to one of six treatment groups: 1 spray per nostril of either ASTEPRO Nasal Spray, Astelin Nasal Spray or placebo twice daily; or 2 sprays per nostril of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray, Astelin Nasal Spray or placebo twice daily.
Assessment of efficacy was based on the 12-hour reflective total nasal symptom score (rTNSS) assessed daily in the morning and evening. TNSS is calculated as the sum of the patients’ scoring of the four individual nasal symptoms (rhinorrhea, nasal congestion, sneezing, and nasal itching) on a 0 to 3 categorical severity scale (0 = absent, 1 = mild, 2 = moderate, 3 = severe). The rTNSS required patients to record symptom severity over the previous 12 hours. For the primary efficacy endpoint, morning (AM) and evening (PM) rTNSS scores were summed for each day (maximum score of 24) and then averaged over the 14–day treatment period. (Table 2)
| Treatment (sprays per nostril twice daily) | n | Baseline LS Mean | Change from Baseline | Difference From Placebo | ||
| LS Mean | 95% CI | P value | ||||
| ASTEPRO Nasal Spray- two sprays | 146 | 18.0 | -5.0 | -2.2 | -3.2,-1.2 | <0.001 |
| Astelin Nasal Spray- two sprays | 137 | 18.1 | -4.2 | -1.4 | -2.4,-0.4 | 0.008 |
| Placebo Vehicle- two sprays | 138 | 18.1 | -2.8 | |||
| ASTEPRO Nasal Spray- one spray | 139 | 18.1 | -4.2 | -0.7 | -1.7,0.3 | 0.181 |
| Astelin Nasal Spray- one spray | 137 | 18.1 | -3.9 | -0.4 | -1.5,0.6 | 0.405 |
| Placebo Vehicle- one spray | 137 | 17.9 | -3.5 | |||
| *Sum of AM and PM rTNSS for each day (Maximum score=24) and averaged over the 14 day treatment period | ||||||
The efficacy of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray one spray per nostril twice daily is supported by two, 2-week, placebo controlled clinical trials with Astelin Nasal Spray in 413 patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. In these trials, efficacy was assessed using the TNSS (described above). Astelin Nasal Spray demonstrated a greater decrease from baseline in the summed AM and PM rTNSS compared with placebo and the difference was statistically significant.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
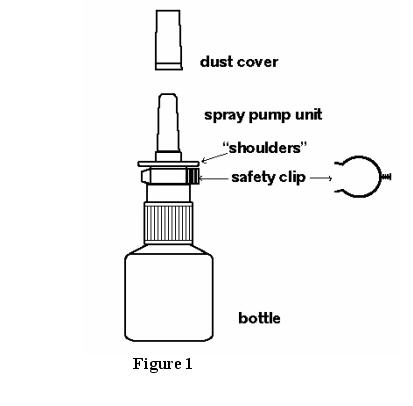
ASTEPRO (azelastine hydrochloride) Nasal Spray, 137 mcg, (NDC 0037-0242-30) is supplied as a package delivering 200 metered sprays in a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle fitted with a metered-dose spray pump unit. FDA-approved patient labeling is also provided. The spray pump unit consists of a nasal spray pump fitted with a blue safety clip and a blue plastic dust cover. Net contents of the bottle is 30 mL (net weight 30 gm of solution).
The ASTEPRO (azelastine hydrochloride) Nasal Spray, 137 mcg, bottle contains 30 mg (1 mg/mL) of azelastine hydrochloride. After priming [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)], each spray delivers a fine mist containing a mean volume of 0.137 mL solution containing 137 mcg of azelastine hydrochloride. The correct amount of medication in each spray cannot be assured before the initial priming and after 200 sprays have been used, even though the bottle is not completely empty. The bottle should be discarded after 200 sprays have been used.
Storage:
Store upright at controlled room temperature 20° -
25°C (68° - 77°F). Protect from
freezing.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Patients should be instructed to use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray only as prescribed. For the proper use of the nasal spray and to attain maximum improvement, the patient should read and follow carefully the accompanying FDA-Approved Patient Labeling.
17.1 Common Adverse Reactions
Patients should be informed that treatment with ASTEPRO Nasal Spray may lead to adverse reactions, which include bitter taste, epistaxis, headache, and somnolence [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
17.2 Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
Somnolence has been reported in some patients taking ASTEPRO Nasal Spray. Patients should be cautioned against engaging in hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness and motor coordination such as driving or operating machinery after administration of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
17.3 Concurrent Use of Alcohol and other Central Nervous System Depressants
Concurrent use of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of central nervous system performance may occur [See Warnings and Precautions(5.1)].
17.4 Priming
Patients should be instructed to prime the pump before initial use and when ASTEPRO Nasal Spray has not been used for 3 or more days. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
17.5 Keep Spray Out of Eyes
Patients should be instructed to avoid spraying ASTEPRO Nasal Spray into their eyes.
MEDA Pharmaceuticals
MEDA Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Somerset, NJ 08873
Astelin, ASTEPRO and MEDA Pharmaceuticals are trademarks or registered trademarks of MEDA Pharmaceuticals Inc.
PATIENT INFORMATION
ASTEPRO™ [AS-ta-PRO] (azelastine hydrochloride)
Nasal Spray
Important: For use in the nose only
Read this information carefully before you start using ASTEPRO Nasal Spray and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is ASTEPRO Nasal Spray?
- ASTEPRO Nasal Spray is a prescription medicine used to relieve symptoms of seasonal allergies in people age 12 and older.
- ASTEPRO Nasal Spray contains an antihistamine that may help reduce the nasal symptoms of rhinitis (inflammation of the lining of the nose): stuffy nose, runny nose, itching and sneezing.
It is not known if ASTEPRO Nasal Spray works and is safe in children under age 12.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using ASTEPRO Nasal Spray?
Before using ASTEPRO Nasal Spray tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you are:
- Allergic to any of the ingredients in ASTEPRO Nasal Spray. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in ASTEPRO Nasal Spray.
- Pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if ASTEPRO Nasal Spray will harm your unborn baby.
- Breastfeeding. It is not known if ASTEPRO Nasal Spray passes into your breast milk.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. ASTEPRO Nasal Spray and other medicines may affect each other, causing side effects.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider when you get a new medicine.
How should I use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray?
- ASTEPRO Nasal Spray is for use in your nose only. Do not spray it into your eyes or mouth.
- Use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Do not use more than your healthcare provider tells you.
- The usual dose of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray is 1 or 2 sprays in each nostril two times a day. Your healthcare provider will prescribe the dose that is right for you.
- Before you use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray for the first time, you will need to prime the bottle. See priming instructions at the end of this leaflet.
- Do not use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray if a fine mist is not seen after the initial priming sprays (6 sprays or less).
- Throw away your ASTEPRO Nasal Spray bottle after using 200 sprays. Even though the bottle may not be completely empty, you may not get the correct dose of medicine.
- If a child accidentally swallows ASTEPRO Nasal Spray, get medical help or call a poison control center right away.
What should I avoid while using ASTEPRO Nasal Spray?
ASTEPRO Nasal Spray can cause sleepiness:
- Do not drive a car, operate machinery or do dangerous activities after you use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray.
- Avoid drinking alcohol or taking other medicines that may also cause sleepiness while using ASTEPRO Nasal Spray.
What are the possible side effects of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray?
Side effects of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray include:
- unusual taste (bitter or sweet)
- nosebleeds
- headache
- fatigue
- sleepiness
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of ASTEPRO Nasal Spray. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store ASTEPRO Nasal Spray?
- Keep ASTEPRO Nasal Spray upright at 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Do not freeze ASTEPRO Nasal Spray.
Keep ASTEPRO Nasal Spray and all medicines out of reach of children.
General information about ASTEPRO Nasal Spray.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ASTEPRO Nasal Spray to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about ASTEPRO Nasal Spray. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ASTEPRO Nasal Spray that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.Astepro.com or call 1-800-598-4856.
What are the ingredients in ASTEPRO Nasal Spray?
Active ingredient: azelastine hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: sorbitol, sucralose, hypromellose, sodium citrate, edetate disodium, benzalkonium chloride and purified water.
Patient Instructions for Use
For use in your nose only
It is important that you read and follow these Patient Instructions for Use carefully to be sure you use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray the right way.
For the correct dose of medicine:
- Use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Keep your head tilted downward when spraying into your nostril.
- Change nostrils each time you use the spray.
- Breathe gently and do not tip your head back after using the spray. This will keep the medicine from running down into your throat. You may get a bitter taste in your mouth.
Follow the instructions below to use your ASTEPRO Nasal
Spray pump.
See Figure 1.
Before you use ASTEPRO for the first time, you will need to prime the bottle. To prime:
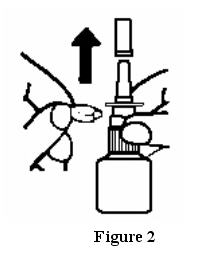
- Remove the blue dust cover over the tip of the bottle and the blue safety clip just under the “shoulders” of the bottle. See Figure 2.
- Hold the bottle upright with two fingers on the shoulders of the spray pump unit and
put your thumb on the bottom of the bottle. Press upward with your thumb and release for the pumping action. Repeat this until you see a fine mist (6 sprays or less). See Figure 3.
Now your pump is primed and ready to use.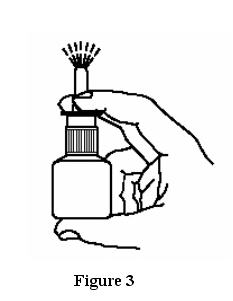
- To get a fine mist you must pump the spray fast and use firm pressure against the bottom of the bottle. If you see a stream of liquid, the spray will not work right and may cause nasal discomfort.
- If you do not use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray for 3 or more days, you will need to prime the pump with 2 sprays or until you see a fine mist. If you do not see a fine mist, clean the tip of the spray nozzle. See the cleaning section below.
To Use ASTEPRO Nasal Spray:
- Gently blow your nose to clear nostrils.
- Keep your head tilted downward toward your toes.
- Place the spray tip ¼ to ½ inch into one nostril. Hold
bottle upright and aim the spray tip toward the back of the nose. See Figure 4.
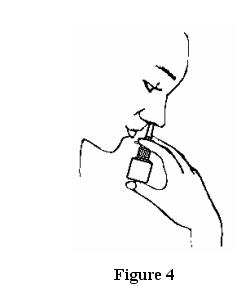
- Close your other nostril with a finger. Press the pump one time and sniff gently at the same time, keeping your head tilted forward and down.
- Repeat in other nostril.
- If your healthcare provider tells you to use 2 sprays in each nostril, repeat Steps 2 and 4 above for the second spray in each nostril.
- Breathe in gently, and do not tilt your head back after using ASTEPRO Nasal Spray. This will help to keep the medicine from going into your throat.
- When you finish using ASTEPRO Nasal Spray, wipe the spray tip with a clean tissue or cloth. Put the safety clip and dust cover back on the bottle.
To Clean the Spray Tip:
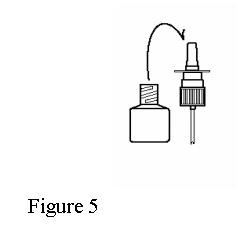
- If the spray tip opening is clogged, do not use a pin or pointed object to unclog the tip. Unscrew the spray pump unit from the bottle by turning it counter-clockwise (to the left). See Figure 5.
- Soak only the spray pump unit in warm water. Squirt several times while holding it under water. Use the pumping action to clear the opening in the tip. See Figure 6.
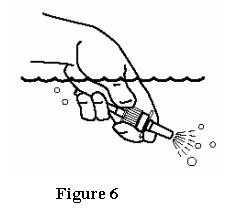
- Let the spray pump unit air dry. Make sure it is dry before you put it back onto the bottle.
- Put the spray pump unit back into the open bottle and tighten it by turning clockwise (to the right).
- To keep the medicine from leaking out, use firm pressure when you put the pump back onto the bottle.
- After cleaning, follow the instructions for priming.
Issued October 2008
Manufactured by
MEDA Pharmaceuticals
MEDA
Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Somerset, NJ 08873
©2008 MEDA Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Astelin, ASTEPRO and MEDA Pharmaceuticals are trademarks or registered trademarks of MEDA Pharmaceuticals Inc.
IN-023D6-03 Revised 10/08
| ASTEPRO
azelastine hydrochloride spray, metered |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revised: 11/2008MEDA Pharmaceuticals