profenal (suprofen) solution
[Alcon Laboratories, Inc.]
DESCRIPTION
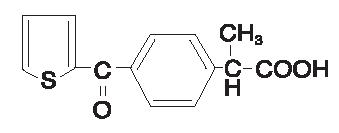
PROFENAL® (suprofen) 1% ophthalmic solution is a topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory product for ophthalmic use. Suprofen chemically is α -methyl-4-(2-thienylcarbonyl)benzeneacetic acid, with an empirical formula of C14H12O3S, and a molecular weight of 260.3. The chemical structure of suprofen is:
PROFENAL Sterile Ophthalmic Solution contains suprofen 1.0% (10 mg/mL), thimerosal 0.005% (0.05 mg/mL), caffeine 2% (20 mg/mL), edetate disodium, dibasic sodium phosphate, monobasic sodium phosphate, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH to 7.4) and purified water.
DM-00
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Suprofen is one of a series of phenylalkanoic acids that have shown analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory activity in animal inflammatory diseases. Its mechanism of action is believed to be through inhibition of the cyclooxygenase enzyme that is essential in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins.
Prostaglandins have been shown in many animal models to be mediators of certain kinds of intraocular inflammation. In studies performed on animal eyes, prostaglandins have been shown to produce disruption of the blood-aqueous humor barrier, vasodilatation, increased vascular permeability, leukocytosis, and increased intraocular pressure.
Prostaglandins appear to play a role in the miotic response produced during ocular surgery by constricting the iris sphincter independently of cholinergic mechanisms. In clinical studies, PROFENAL has been shown to inhibit the miosis induced during the course of cataract surgery. PROFENAL could possibly interfere with the miotic effect of intraoperatively administered acetylcholine chloride.
Results from clinical studies indicate that PROFENAL Ophthalmic Solution has no significant effect on intraocular pressure.
There are no data available on the systemic absorption of ocularly applied suprofen. The oral dose of suprofen is 200 mg every four to six hours. If PROFENAL 1% Ophthalmic Solution is applied as two drops (1 mg suprofen) to one eye five times on the day prior to surgery and three times on the day of surgery, the total applied dose over the two days would be about 25 times less than a single 200 mg oral dose.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PROFENAL Ophthalmic Solution is indicated for inhibition of intraoperative miosis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
PROFENAL is contraindicated in epithelial herpes simplex keratitis (dendritic keratitis) and in individuals hypersensitive to any component of the medication.
WARNINGS
The potential exists for cross sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Therefore, caution should be used when treating individuals who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs.
With nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the potential exists for increased bleeding time due to interference with thrombocyte aggregation. There have been reports that ocularly applied nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may cause increased bleeding tendency of ocular tissues in conjunction with ocular surgery.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Use of oral suprofen has been associated with a syndrome of acute flank pain and generally reversible renal insufficiency, which may present as acute uric acid nephropathy. This syndrome occurs in approximately 1 in 3500 patients and has been reported with as few as one to two doses of a 200 mg capsule. If PROFENAL 1% Ophthalmic Solution is applied as two drops (1 mg suprofen) to one eye five times on the day prior to surgery and three times on the day of surgery, the total applied dose over the two days would be about 25 times less than a single 200 mg oral dose. Do not touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the solution.
Ocular
Patients with histories of herpes simplex keratitis should be monitored closely. PROFENAL is contraindicated in patients with active herpes simplex keratitis.
The possibility of increased ocular bleeding during surgery associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be considered.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In an 18-month study in mice, an increased incidence of benign hepatomas occurred in females at a dose of 40 mg/kg/day. Male mice, treated at doses of 2, 5, 10 and 40 mg/kg/day, also had an increased incidence of hepatomas when compared to control animals. No evidence of carcinogenicity was found in long term studies in doses as high as 40 mg/kg/day in the rat and mouse. Based on a battery of mutagenicity tests (Ames, micronucleus, and dominant lethal), suprofen does not appear to have mutagenic potential. Reproductive studies in rats at a dose of up to 40 mg/kg/day revealed no impairment of fertility and only slight reductions of fertility at doses of 80 mg/kg/day. However, testicular atrophy/hypoplasia was observed in a six-month dog study (at 80 mg/kg/day) and a 12-month rat study (at 40 mg/kg/day).
Pregnancy Category C
Reproductive studies have been performed in rabbits at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day and in rats at doses up to 80 mg/kg/day. In rats, doses of 40 mg/kg/day and above, and in rabbits, doses of 80 mg/kg/day and above, resulted in an increased incidence of fetal resorption associated with maternal toxicity. There was an increase in stillbirths and a decrease in postnatal survival in pregnant rats treated with suprofen at 2.5 mg/kg/day and above. An increased incidence of delayed parturition occurred in rats. As there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Because of the known effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of ductus arteriosus), use during late pregnancy should be avoided.
Nursing Mothers
Suprofen is excreted in human milk after a single oral dose. Based on measurements of plasma and milk levels in women taking oral suprofen, the milk concentration is about 1% of the plasma level. Because systemic absorption may occur from topical ocular administration, a decision should be considered to discontinue nursing while receiving PROFENAL®, since the safety of suprofen in human neonates has not been established.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Drug Interactions
Clinical studies with acetylcholine chloride revealed no interference, and there is no known pharmacological basis for such an interaction. However, with other topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory products, there have been reports that acetylcholine chloride and carbachol have been ineffective when used in patients treated with these agents.
Interaction of PROFENAL with other topical ophthalmic medications has not been fully investigated.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Ocular
The most frequent adverse reactions reported are burning and stinging of short duration. Instances of discomfort, itching and redness have been reported. Other reactions occurring in less than 0.5% of patients include allergy, iritis, pain, chemosis, photophobia, irritation, and punctate epithelial staining.
Systemic
Systemic reactions related to therapy were not reported in the clinical studies. It is known that some systemic absorption does occur with ocularly applied drugs, and that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have been shown to increase bleeding time by interference with thrombocyte aggregation. It is recommended that PROFENAL be used with caution in patients with bleeding tendencies and those taking anticoagulants.
OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage will not ordinarily cause acute problems. If accidentally ingested, drink fluids to dilute.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
On the day of surgery, instill two drops into the conjunctival sac at three, two and one hour prior to surgery. Two drops may be instilled into the conjunctival sac every four hours, while awake, the day preceding surgery.
HOW SUPPLIED
Sterile ophthalmic solution, 2.5 mL in plastic DROP-TAINER® dispensers.
2.5 mL NDC 0065-0348-25
STORAGE: Store at room temperature.
Rx Only
U.S. Patents Nos. 4,035,376; 4,559,343

Alcon Laboratories, Inc.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134 USA
Printed in USA
343005-0798 Revised: July 1998
| Profenal (suprofen) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revised: 06/2007Alcon Laboratories, Inc.