verdeso (Desonide) aerosol, foam
[Connetics Corporation]
Description
Verdeso™ Foam is a petrolatum-based emulsion aerosol foam containing the active ingredient desonide, a low-potency topical corticosteroid.
Chemically, desonide is (11β,16α)-11,21-dihydroxy-16,17-[(1-methylethylidene)-bis(oxy)]-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione.
The structural formula of desonide is represented below:
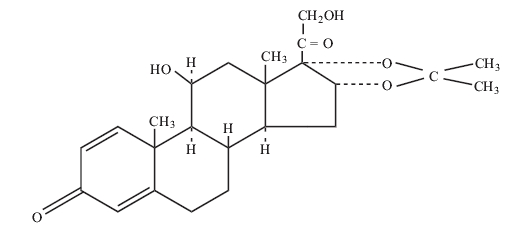
Desonide has a molecular formula of C24H32O6 and a molecular weight of 416.51. Desonide is a white powder or crystal that is practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol and in acetone, and soluble in chloroform. Each gram of Verdeso Foam contains 0.5 mg desonide. The foam also contains anhydrous citric acid USP, cetyl alcohol NF, cyclomethicone NF, isopropyl myristate NF, light mineral oil NF, white petrolatum USP, polyoxyl 20 cetostearyl ether NF, potassium citrate (monohydrate) USP, propylene glycol USP, purified water USP, sorbitan monolaurate NF, and phenoxyethanol NF as a preservative.
Verdeso Foam is dispensed from an aluminum can pressurized with a hydrocarbon (propane/butane) propellant.
Clinical Pharmacology
Topical corticosteroids share anti-inflammatory, anti-pruritic, and vasoconstrictive actions.
The mechanism of anti-inflammatory activity of the topical corticosteroids is unclear. However, corticosteroids are thought to act by the induction of phospholipase A2 inhibitory proteins, collectively called lipocortins. It is postulated that these proteins control the biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes by inhibiting the release of their common precursor arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2.
Pharmacokinetics: Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from intact healthy skin. The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors, including the product formulation and the integrity of the epidermal barrier. Occlusion, inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin may also increase percutaneous absorption. The use of pharmacodynamic endpoints for assessing the systemic exposure of topical corticosteroids may be necessary due to the fact that circulating levels are often below the level of detection. Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids. They are metabolized, primarily in the liver, and are then excreted by the kidneys. Some corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted in the bile.
In a controlled pharmacokinetic study, 3 of 75 (4%) pediatric patients with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis covering at least 25% body surface area, who applied Verdeso Foam twice daily, experienced reversible suppression of the adrenal glands following 4 weeks of therapy (see Pediatric use).
CLINICAL STUDIES:
In a double-blind, randomized study of 581 patients ages 3 months to 17 years old, with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis, Verdeso Foam was applied twice daily for 4 weeks. Success was defined as the proportion of patients who had all of the following: an Investigator’s Static Global Assessment (ISGA) score of clear or almost clear, a minimum improvement in the 5 point ISGA score of 2 grades from Baseline to Week 4, and a score of absent or minimal for both erythema and induration/papulation at Week 4. The results of this study are presented in the table below.
| Verdeso Foam | Vehicle Foam | |
| Number of Patients | 387 | 194 |
| Patients Achieving Success | 152 (39%) | 18 (9%) |
Indications and Usage
Verdeso Foam is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients 3 months of age and older.
Patients should be instructed to use Verdeso Foam for the minimum amount of time necessary to achieve the desired results because of the potential for Verdeso Foam to suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis (see Precautions). Treatment should not exceed 4 consecutive weeks.
Contraindications
The use of Verdeso Foam is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to desonide or to any ingredient in this preparation.
Warnings
FLAMMABLE. AVOID FIRE, FLAME OR SMOKING DURING AND IMMEDIATELY FOLLOWING APPLICATION.
Contents under pressure. Do not puncture or incinerate. Do not expose to heat or store at temperatures above 120°F (49°C).
Avoid contact with eyes or other mucous membranes.
Keep out of reach of children.
Precautions
General
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids has produced reversible HPA axis suppression, manifestations of Cushing’s syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria in some patients.
Conditions which augment systemic absorption include the application of topical corticosteroids over large body surface areas, prolonged use, or the addition of occlusive dressings. Therefore, patients applying a topical corticosteroid to a large body surface area or to areas under occlusion should be evaluated periodically for evidence of HPA axis suppression (see Laboratory tests). If HPA axis suppression is noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or to substitute a less potent steroid.
Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt upon discontinuation of topical corticosteriods. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of glucocorticosteroid insufficiency may occur requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids. For information on systemic corticosteroid supplementation, see prescribing information for those products.
The effect of Verdeso Foam on HPA axis function was investigated in pediatric patients in one study. In this study, patients with atopic dermatitis covering at least 25% of their body applied Verdeso Foam twice daily for 4 weeks. Three out of 75 patients (4%) displayed adrenal suppression after 4 weeks of use based on the cosyntropin stimulation test. The laboratory suppression was transient; all subjects had returned to normal when tested 4 weeks post treatment.
Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity from equivalent doses because of their larger skin surface area to body mass ratios (See Pediatric use).
If irritation develops, Verdeso Foam should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Allergic contact dermatitis with corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by observing a failure to heal rather than noticing a clinical exacerbation, as with most products not containing corticosteroids. Such an observation should be corroborated with appropriate diagnostic patch testing.
If concomitant skin infections are present or develop, the use of an appropriate antifungal, antibacterial or antiviral agent should be instituted. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, use of Verdeso Foam should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled.
Information for patients
Patients using topical corticosteroids should receive the following information and instructions:
- This medication is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the eyes or other mucous membranes. The medication should not be dispensed directly onto the face. Dispense in hands and gently massage into affected areas of the face until the medication disappears. For areas other than the face, the medication may be dispensed directly on the affected area. Wash hands after use.
- This medication should not be used for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed.
- The treated skin area should not be bandaged, otherwise covered, or wrapped so as to be occlusive unless directed by the physician.
- Patients should report any signs of local or systemic adverse reactions to the physician.
- Patients should inform their physicians that they are using Verdeso Foam if surgery is contemplated.
- As with other corticosteriods, therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 4 weeks, contact the physician.
Laboratory tests
The cosyntropin (ACTH1-24) stimulation test may be helpful in evaluating patients for HPA axis suppression.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic or photoco-carcinogenic potential of Verdeso Foam or the effect on fertility of desonide.
Desonide revealed no evidence of mutagenic potential based on the results of two in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames assay, mouse lymphoma cell assay) and an in vivo genotoxicity test (mouse micronucleus assay).
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels. Some corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic after dermal application in laboratory animals.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Verdeso Foam in pregnant women. Therefore, Verdeso Foam should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
No long-term reproductive studies in animals have been performed with Verdeso Foam. Dermal embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits with a desonide cream, 0.05% formulation. Topical doses of 0.2, 0.6, and 2.0 g cream/kg/day of a desonide cream, 0.05% formulation or 2.0 g/kg of the cream base were administered topically to pregnant rats (gestational days 6–15) and pregnant rabbits (gestational days 6–18). Maternal body weight loss was noted at all dose levels of the desonide cream, 0.05% formulation in rats and rabbits. Teratogenic effects characteristic of corticosteroids were noted in both species. The desonide cream, 0.05% formulation was teratogenic in rats at topical doses of 0.6 and 2.0 g cream/kg/day and in rabbits at a topical dose of 2.0 g cream/kg/day. No teratogenic effects were noted for the desonide cream, 0.05% formulation at a topical dose of 0.2 g cream/kg/day in rats and at a topical dose of 0.6 g cream/kg/day in rabbits. These doses (0.2 g cream/kg/day in rats and 0.6 g cream/kg/day in rabbits) are similar to the maximum recommended human dose based on body surface area comparisons.
Labor and delivery
Nursing mothers
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. It is not known whether topical administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Verdeso Foam is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric use
Because of a higher ratio of skin surface area to body mass, pediatric patients are at a greater risk than adults of HPA axis suppression and Cushing’s syndrome when they are treated with topical corticosteroids. They are therefore also at greater risk of adrenal insufficiency during and/or after withdrawal of treatment. Adverse effects including striae have been reported with inappropriate use of topical corticosteroids in infants and children. HPA axis suppression, Cushing’s syndrome, linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain, and intracranial hypertension have been reported in children receiving topical corticosteroids. Manifestations of adrenal suppression in children include low plasma cortisol levels and an absence of response to ACTH stimulation. Manifestations of intracranial hypertension include bulging fontanelles, headaches, and bilateral papilledema. Administration of topical corticosteroids to children should be limited to the least amount compatible with an effective therapeutic regimen. Chronic corticosteroid therapy may interfere with the growth and development of children.
The effect of Verdeso Foam on HPA axis function was investigated in pediatric patients, ages 6 months to 17 years, in one study. In this study, patients with atopic dermatitis covering at least 25% of their body applied Verdeso Foam twice daily for 4 weeks. Three out of 75 patients (4%) displayed adrenal suppression after 4 weeks of use based on the ACTH stimulation test. The suppression was transient; all subjects’ cortisol levels had returned to normal when tested 4 weeks post treatment. Safety of Verdeso Foam has not been evaluated in pediatric patients below the age of 3 months.
Geriatric use
Clinical studies of Verdeso Foam did not include any subjects aged 65 or over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Adverse Reactions
In a controlled clinical study of 581 patients 3 months to 17 years of age, adverse events occurred at the application site in 6% of subjects treated with Verdeso Foam and 14% of subjects treated with vehicle foam. Other commonly reported adverse events for Verdeso Foam and vehicle foam are noted in Table 1.
Table 1—Commonly Occurring Adverse Events
| Verdeso Foam | Vehicle Foam | |
| Adverse Event | (N=387) | (N=194) |
| System Organ Class | ||
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 32 (8%) | 31 (16%) |
| Application site burning | 11 (3%) | 15 (8%) |
| Application site atrophy | 5 (1%) | 0 (0%) |
| Application site dermatitis | 2 (1%) | 1 (1%) |
| Application site reaction | 3 (1%) | 6 (3%) |
| Infections and infestations | 79 (20%) | 38 (20%) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 37 (10%) | 12 (6%) |
| Pharyngitis | 2 (1%) | 0 (0%) |
| Pharyngitis streptococcal | 2 (1%) | 1 (1%) |
| Viral Infection | 6 (2%) | 0 (0%) |
| Nervous System Disorder | 7 (2%) | 1 (1%) |
| Headache | 7 (2%) | 1 (1%) |
| Psychiatric Disorder | 3 (1%) | 0 (0%) |
| Irritability | 2 (1%) | 0 (0%) |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | 27 (7%) | 7 (4%) |
| Asthma | 3 (1%) | 0 (0%) |
| Cough | 14 (4%) | 3 (2%) |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | 10 (3%) | 6 (3%) |
| Dermatitis contact | 3 (1%) | 2 (1%) |
| Telangiectasia | 3 (1%) | 0 (0%) |
Elevated blood pressure was observed in 6 (2%) subjects receiving Verdeso Foam and 1 (1%) subject receiving vehicle foam. Other local adverse events occurred at rates less than 1.0%. The majority of adverse reactions were transient and mild to moderate in severity, and they were not affected by age, race or gender. The following additional local adverse reactions have been reported with topical corticosteroids. They may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings and higher potency corticosteroids. These reactions are listed in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence: folliculitis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, secondary infection, striae and miliaria.
Drug Abuse and Dependence
Overdosage
Topically applied Verdeso Foam can be absorbed in sufficient amounts to produce systemic effects (see Precautions).
Dosage and Administration
A thin layer of Verdeso Foam should be applied to the affected area(s) twice daily. Shake the can before use. Verdeso Foam should be dispensed by inverting the can (upright actuation will cause loss of the propellant which may affect product delivery). Dispense the smallest amount of foam necessary to adequately cover the affected area(s) with a thin layer.
The medication should not be dispensed directly on the face. Dispense in hands and gently massage into affected areas of the face until the medication disappears. For areas other than the face, the medication may be dispensed directly onto the affected area. Take care to avoid contact with the eyes or other mucous membranes.
Therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 4 weeks, reassessment of diagnosis may be necessary. Treatment should not exceed 4 consecutive weeks.
Unless directed by a physician, Verdeso Foam should not be used with occlusive dressings.
How Supplied
Verdeso Foam is supplied in 100 g (NDC 63032-111-00) and 50 g (NDC 63032-111-50) aluminum cans.
Store at controlled room temperature 68–77°F (20–25°C).
Manufactured for:
Connetics Corporation
Palo Alto, CA 94304 USA
© 2006 Connetics Corporation
| Verdeso (Desonide) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revised: 10/2006